#vaccine preventable diseases surveillance
Explore tagged Tumblr posts
Text
How does one track and monitor vaccine coverage in a population?
Tracking and monitoring vaccine coverage in a population is essential for evaluating the success of immunization programs and identifying areas that require improvement. It allows public health authorities to assess the reach and impact of vaccination efforts, identify gaps in coverage, and make informed decisions to enhance immunization rates. This article explores the methods and considerations…

View On WordPress
#collaboration and partnerships#continuous quality improvement#data integration and analysis#immunization information systems#immunization rates#monitoring immunization rates#routine immunization surveys#sentinel surveillance#Tracking vaccine coverage#vaccination data#vaccination registries#vaccine preventable diseases surveillance
0 notes
Text
Also preserved in our archive
By Bill Shaw
The latest wastewater surveillance data show that the COVID-19 pandemic has entered its tenth wave in the United States. Last week’s spike in wastewater was the highest percentage increase in transmission in almost three years, though these figures could be revised downwards and the full severity of the wave will only become clear in the coming weeks. One reason for the rapid jump appears to be a later start for the “winter surge” than is typical, and thus the virus could be quickly rising to a level that has now become typical for this time of year.
The Pandemic Mitigation Collaborative (PMC) model estimates that 1.6 percent of Americans are presently infected and capable of transmitting the virus to others. That is 1 in 64 people and represents nearly 750,000 new COVID-19 cases per day. That means that on a flight of 100 people, there is an 80 percent chance that at least one person is infectious; on a flight of 300 people that rises to a 99 percent chance.
This level of transmission exceeds the levels for 73 percent of the duration of the pandemic to date. Given the known incidence of Long COVID, the current levels of transmission are generating an estimated 200,000 new cases of Long COVID per week.
Not a word about this latest COVID-19 wave has been uttered by the Biden administration or any major outlet in the corporate media. The entire political establishment is in agreement on the need to enforce the pro-corporate policy of “forever COVID,” in which the working class and broad layers of society as a whole are condemned to unending waves of mass infection, death and debilitation with Long COVID.
The PMC model projects that the current winter surge could peak between New Year’s Day and January 7. Because COVID-19 transmission followed a completely different pattern in 2024 than any other year of the pandemic, it is more difficult to forecast transmission during the current surge. This year’s summer surge was unusually late and sustained, while also declining abnormally rapidly, and the lull between the summer and winter surges was atypically long.
The latest data on test positivity and emergency department visits from the Centers for Disease Control and Prevention (CDC) show both these indicators on the increase. Hospitalizations and deaths are typically lagging indicators, and although they have not yet increased, they are likely to rise as well in the coming week or two.
The new XEC variant continues to increase as a percentage of COVID-19 infections, now estimated at 44 percent, compared to 33 percent a week ago. It is now the most common variant, having surpassed the KP3.1.1 variant per the most recent data.
Given the total absence of governmental support for the renovation of infrastructure to ensure that indoor air is purified in public spaces, the only defenses against COVID-19 continue to be vaccines and non-pharmaceutical measures, such as social distancing and masking. Vaccination additionally protects against the most adverse outcomes of COVID-19, including death and hospitalization, while providing moderate protection against Long COVID.
Unfortunately, misinformation coupled with the potential expense of paying for a costly vaccine have resulted in extremely low vaccination rates for COVID-19. Per the latest CDC data, only 21.0 percent of American adults reported that they have received the latest vaccine released at the beginning of the Fall. Coverage of children is even worse at 10.6 percent, or approximately half the rate of adults.
Dr. Alexander Sloboda, medical director of immunizations for the Chicago Department of Public Health, said:
There’s still a lot of misinformation, disinformation, particularly around the COVID vaccine, so just trying to overcome the misinformation, disinformation that’s out there with correct information is what we’re trying to do. Obviously, it’s a kind of an uphill battle.
In another development this week related to the science of COVID-19 treatment, a study from 2020 that purported to show that hydroxychloroquine was an effective treatment was finally retracted. According to the journal’s retraction notice, the paper was pulled because of ethical transgressions and major flaws in methodology.
Even though numerous scientists immediately spotted and exposed the flaws of the study, it took four years of campaigning before the journal editors finally relented and retracted the paper this month. In fact, a lead author on the study, Didier Raoult, at one point threatened legal action against the whistleblowers who challenged the study. One of the journal editors was a co-author of the study, likely a factor in the long time period between the paper being discredited and it being retracted.
The scientific discourse over the study included subsequent identification of additional serious methodological flaws in 2023. Recently, three of the study’s authors wrote a letter to the journal requesting a retraction, acknowledging that no confidence could be placed in the “results” and stating explicitly that they no longer wished to be associated with the paper.
Notably, Raoult has so far had 28 papers retracted, including this one. Raoult leads the French Hospital Institute of Marseille Mediterranean Infection (IHU). Overall, 32 papers authored by IHU members, including Raoult, have been retracted. Investigations are underway on at least 100 more papers by this group, mostly due to concerns that the studies violated ethical standards.
The discredited hydroxychloroquine study spawned massive misinformation promoting the drug as a treatment for COVID-19. The most infamous episodes involved then-President Donald Trump, who in a period of two months in 2020 made 11 tweets about unproven therapies for COVID-19 and mentioned them 65 times in White House briefings. Trump repeatedly referenced this now-retracted study, even after it had been discredited. During that time, purchases of hydroxychloroquine on Amazon surged by 200 percent.
With Trump returning to the presidency and having nominated a slate of anti-science quacks to every public health-related leadership position in the federal government—overseen by the notorious purveyor of anti-vaccine disinformation Robert F. Kennedy, Jr.—the working class must heighten its vigilance against medical misinformation and follow the advice of principled scientists. Any one of Trump’s nominees is damaging, but collectively it will be catastrophic when their pseudo-science becomes official policy.
Official policy under Biden already is criminally permitting the pandemic to continue to cause death and disability virtually unchecked. The constant emergence of new variants, including at least three major new variants this year alone, is a product of the dismantling of public health measures to contain the virus. Protecting the public’s health requires more than just vigilance. The working class must organize on its own political program to replace capitalism with socialism, a social system that prioritizes human health over private profit.
#mask up#public health#wear a mask#wear a respirator#pandemic#covid#still coviding#covid 19#coronavirus#sars cov 2#us politics
156 notes
·
View notes
Text
In the U.K., the Health Security Agency recently raised its threat level to 4 out of 6, the stage immediately before large-scale human outbreaks. In Europe, countries are proactively vaccinating dairy and poultry workers against infection, with 15 nations already securing a total of 40 million doses through the European Commission. In the United States, despite having a stockpile of those vaccines, we are not distributing them, instead focusing on standing up voluntary supplies of seasonal flu vaccines to frontline workers. (The hope is that this will prevent animal infections of human flu that might aid in the further mutation of H5N1.) The Centers for Disease Control and Prevention has cited the low number of cases to justify its inaction, but it has also moved remarkably slowly to promote the kind of widespread surveillance testing that could actually identify cases. Only recently has the agency begun to mobilize real funding for a testing push, after a period of months in which various federal groups batted around responsibility and ultimate authority like a hot potato. And as was the case early in the Covid-19 pandemic, the C.D.C.’s preferred test for bird flu “has issues.” Three months into the outbreak, only 45 people had even been tested; six weeks later, the total number of people tested had grown only to “230+.” [...] Most farms aren’t supplying N95 masks, goggles or aprons to protect workers, either, and when Amy Maxmen of KFF News surveyed farm workers to ask why they weren’t getting tested, “no one had heard of bird flu, never mind gotten P.P.E. or offers of tests,” she reported. “One said they don’t get much from their employers, not even water. If they call in sick, they worry about getting fired.” Last month, a crew was deployed to slow the spread of the disease by killing every last chicken of 1.78 million on a large Colorado farm where H5N1 had broken out and six of the workers contracted the virus, partly because the gear they’d been provided was hard to use in the punishing 104-degree heat. In June, Robert Redfield, former director of the C.D.C., echoed many epidemiologists in predicting that “it’s not a question of if, it’s more of a question of when we will have a bird flu pandemic.” In July, Brown’s Jennifer Nuzzo warned that the steady beat of new cases “screams at us that this virus is not going away.” Tulio de Oliveira, a bioinformatician who studies global disease surveillance, marveled that the American effort to track the spread of the disease was absolutely amateurish and the country’s apparent indifference “unbelievable.”
59 notes
·
View notes
Text
"Today, December 20, marks the official end of the Marburg Virus Disease outbreak in Rwanda. It has been 42 days – two full incubation periods – since the last confirmed case left the national Marburg treatment centre after testing negative.
In previous outbreaks, Marburg, which is caused by a virus related to Ebola, has killed up to 88 per cent of people infected. And Rwanda had never seen this disease within its borders before the current outbreak began in September. Despite Rwandan physicians having never encountered it before, the mortality rate observed in this outbreak is under 23 per cent – the lowest-ever death rate for a Marburg outbreak in Africa.
While the virus initially spread fiercely in two major hospitals in the capital Kigali and among family members of one of the initial cases, Rwanda’s rapid response, with implementation of strict infection prevention and control, isolation and containment of cases, prompt initiation of aggressive supportive care, delivery of investigational therapeutics and vaccines, and tracing and monitoring of contacts quickly brought the outbreak under control. The rate of new cases halved between the outbreak’s second and third weeks and dropped by around 90 per cent thereafter.
One of the most remarkable aspects of this response was an international effort, initiated and led by the Rwandan government, to administer thousands of doses of a promising experimental vaccine to front-line health workers under a clinical trial protocol, with the first subjects vaccinated in a remarkably short timeframe.
...
Rwanda, for its part, has invested heavily in its healthcare system and has incorporated epidemic preparedness into its national health policies. Rwanda has well-trained medical staff working in well-run hospitals and community-based health services. It has been investing in technology-based disease surveillance systems and its laboratories can handle fast, accurate diagnostic testing at scale.
In early September, after months of planning, Rwandan scientists and health officials joined CEPI and other private sector partners to walk through a “tabletop exercise” about the 100 Days Mission. It was through this in-person training exercise that key relationships between disease outbreak experts, Rwandan health authorities and researchers, vaccine developers and clinical trial specialists were cemented.
...
We also have no doubt that with the right focus and funding, such nationally-led, globally-supported, life-saving responses to novel disease outbreaks could be accomplished by any government in any region. By taking a proactive approach and using the 100 Days Mission as a game plan, all countries can get ahead of epidemic and pandemic threats and neutralise their catastrophic potential."
Read the full piece here: https://www.telegraph.co.uk/global-health/science-and-disease/partnerships-preparedness-halted-rwanda-marburg-outbreak/
https://www.telegraph.co.uk/global-health/science-and-disease/partnerships-preparedness-halted-rwanda-marburg-outbreak/
42 notes
·
View notes
Text
Have some COVID resources!! I recently started looking into the current state of COVID when I saw that cases were surging again and realized I was pretty uninformed about the current state of things, so I figure other people might be too.
So I‘m linking a few resources I‘ve bookmarked that has some good info about COVID and how to protect yourself and others.
Few things that stuck out to me:
1. We should all be masking at the very least indoors and in crowded outdoor settings (like concerts/festivals/etc)! PLEASE please mask if you are able to. N95/KN95 if you can! Surgical masks and cloth masks are better than nothing, but really try to get the respirator masks. You can reuse them as long as they don‘t get wet or crumpled.
2. The vaccine helps with severity but is actually not that great at preventing infection. Another good reason to be masking up - reducing the viral load you get exposed to helps the vaccine out.
3. Advocate for air purifiers in indoor spaces. We should be breathing clean air!
4. All COVID infections are severe or should be treated as such- ‚mild‘ cases included. Any infection is going to do damage to your body, and repeated infections increase your risk of Long COVID.
5. If you get COVID and you are able to, REST! Mind and body. This will go a long way to preventing long COVID. I know not everyone is in a position that they can do this, but take whatever time you can and let your body rest and heal.
And here are the resources I‘ve found:
This has a great PDF with a lot of good info and sources for all of it, as well as a small zine version you can hand out - https://linktr.ee/act_up_mask_up
This is a map with wastewater data, so you can see how things are trending nationwide (US only sorry!) and in various regions. Check and see if your state or city has its own tracker as well - I know Chicago does.
And here is a site that provides information to some questions/statements people say in attempts to get people to „move past“ COVID. This also has a lot of good information about the current state of COVID.
In conclusion (because this is a middle school paper now i guess)
MASK!
Get the boosters! There are new vaccines being developed that will hopefully help us stay ahead of these variants that keep evolving, but the best way to help those are to mask! Less infections mean less variants :)
AND ADVOCATE FOR BETTER COVID PROTECTIONS AND PROTOCOLS!!! We can only do so much as individuals, we have to lobby for governmental and systemic changes.
Also pls reblog this (and feel free to add your own resources! especially if you have resources for non-usamericans, mine are all pretty US focused unfortunately)
81 notes
·
View notes
Text
Even though a record number of kids died from the flu last year, the percentage of children getting flu shots continues to plummet. The Centers for Disease Control and Prevention reported Wednesday that as of Nov. 30, just over a third of U.S. kids — 37% — had gotten flu shots, down from 43% at the same time last year. The downward trend worries pediatricians who are starting to see an uptick in flu cases. “I always have a little bit of dread when flu season is around the corner,” said Dr. Kristina Bryant, a pediatric infectious disease doctor at Norton Children’s in Louisville, Kentucky, “because children experience illness and suffering during flu season, and much of that can be prevented through vaccination.” Just over half of kids, 55%, got the flu shot during the 2023-24 season, the lowest rate in 12 years, said Alicia Budd, head of the CDC’s domestic influenza surveillance team. “Flu coverage had been slowly increasing” before Covid hit, Budd said. “Flu vaccination levels have not rebounded to pre-pandemic levels.” This year’s flu shot covers the two main strains of the virus circulating so far, H1N1 and H3N2.
31 notes
·
View notes
Text
President Donald Trump signed an executive order Monday night withdrawing the U.S. from the World Health Organization.
The loss could hinder the WHO’s ability to swiftly and effectively respond to infectious disease outbreaks and other emergencies around the world.
In exchange, the U.S. is expected to lose access to the global network that sets the flu vaccine’s composition every year.
It will also weaken the Centers for Disease Control and Prevention’s ability to surveil and contain health threats abroad, according to global health experts.
And American drugmakers could lose the WHO’s help in selling their products worldwide since the WHO system endorsing drugs, vaccines and medical devices for global use that many developing countries rely on could be impaired by the loss of U.S. funding.
#infectious diseases#bird flu#us politics#us news#world health organization#donald trump#covid#covid 19#american politics
12 notes
·
View notes
Text
Think you’ve grasped the full extent of COVID’s ongoing impact? Think again. As Americans shrug off vaccines and forget indoor air quality, the virus stealthily continues its destructive path. This was pretty much inevitable without new guidance urging a change in strategy and nobody telling us the full truth. The danger is clear and present: COVID isn’t merely a respiratory illness; it’s a multi-dimensional threat impacting brain function, attacking almost all of the body’s organs, producing elevated risks of all kinds, and weakening our ability to fight off other diseases. Reinfections are thought to produce cumulative risks, and Long COVID is on the rise. Unfortunately, Long COVID is now being considered a long-term chronic illness — something many people will never fully recover from. Dr. Phillip Alvelda, a former program manager in DARPA’s Biological Technologies Office that pioneered the synthetic biology industry and the development of mRNA vaccine technology, is the founder of Medio Labs, a COVID diagnostic testing company. He has stepped forward as a strong critic of government COVID management, accusing health agencies of inadequacy and even deception. Alvelda is pushing for accountability and immediate action to tackle Long COVID and fend off future pandemics with stronger public health strategies. Contrary to public belief, he warns, COVID is not like the flu. New variants evolve much faster, making annual shots inadequate. He believes that if things continue as they are, with new COVID variants emerging and reinfections happening rapidly, the majority of Americans may eventually grapple with some form of Long COVID. Let’s repeat that: At the current rate of infection, most Americans may get Long COVID. In the following discussion with the Institute for New Economic Thinking, Alvelda discusses the wider social fallout from this ongoing health crisis, which could be avoided with the right mindset and action. He raises tough questions: Without robust surveillance and mitigation measures, how do we prevent future outbreaks from spiraling out of control? Is our pandemic readiness up to par for looming threats like bird flu? How do we cope with a population ravaged by the lasting impacts of Long COVID? The answers are a wake-up call.
continue reading
5 notes
·
View notes
Text
Avian flu is wreaking havoc in poultry farms and dairy cattle -- and public health experts are worried that the virus could mutate to spread among humans.1,2
Left unchecked, avian flu could result in the next deadly human pandemic. In order to prevent a public health catastrophe and reduce the impact on humans and animals, we need to take much more aggressive action.
Take action to help keep bird flu under control before it begins to pose a bigger threat to our health.
How can we reduce the risk of avian flu making the leap to humans and fueling another pandemic?
We're urging the Department of Health and Human Services (HHS) and the U.S. Department of Agriculture (USDA) to increase testing and monitoring, develop a vaccination program, and take prudent measures to protect the health of people working directly with impacted animals.
The first case of H5N1 bird flu in humans this year was confirmed in April. By November, the total number of confirmed human cases had grown to at least 52.3
Now is our chance to get this under control before it gets any worse -- but we need our public health agencies to take the right steps to make it possible.
Add your name to urge HHS and USDA to act now to reduce the spread of bird flu to humans.
These straightforward steps could make a huge difference for our health.
First, USDA and HHS should increase surveillance for bird flu in all food-producing animals. We can better track and control this disease if we have reliable data about where it is appearing and spreading in our food system. New federal rules requiring milk to be tested for bird flu on dairy farms are a great first step, but more testing and monitoring are needed.4
The agencies should also provide protective equipment and vaccines to workers who work directly with impacted animals. This will help form a shield that could stop the virus from making the leap to humans.
Developing and implementing a vaccination program for food-producing animals will also be an important way to control the spread of H5N1 bird flu.
And of course, supporting local pasture-based farms with high standards for animal welfare will make our entire food system healthier. Animals kept in clean, healthy environments are less likely to pass disease among each other, or to farm workers.
We can stop the next deadly pandemic before it starts -- but the solution has to start right now. Add your name to our petition to HHS and USDA today.
1. Susanne Rust, "As bird flu outbreaks rise, piles of dead cattle become shocking Central Valley tableau," Los Angeles Times, October 20, 2024. 2. Kai Kupferschmidt, "Many human infections with 'cow flu' are going undetected," Science, November 7, 2024. 3. "CDC A(H5N1) Bird Flu Response Update," U.S. Centers for Disease Control and Prevention, November 18, 2024. 4. Apoorva Mandavilli and Emily Anthes, "U.S. Milk to Be Tested for Bird Flu Virus," The New York Times, December 6, 2024.
@upontheshelfreviews
@greenwingspino
@one-time-i-dreamt
@tenaflyviper
@akron-squirrel
@ifihadaworldofmyown
@justice-for-jacob-marley
@voicetalentbrendan
@thebigdeepcheatsy
@what-is-my-aesthetic
@ravenlynclemens
@writerofweird
@bogleech
@anon-lephant
4 notes
·
View notes
Text
I think we all really need to sit with how devastating COVID was (while we were sort of acknowledging it) and is (now that we're pretending it's over). People saw mass death. It's a mass disabling event. We learned how deeply our infrastructure flaws go and how willing our government is to kill ALL of us who are not wealthy/do not have access to healthcare, which shifted a collective bias about that (AIDs is still thought of by many as a "gay" disease).
The way a system that prioritizes those who do well in traditional education, have money, want more money creates a system where doctors are NOT necessarily people called to help and heal others but instead people who want to be wealthy and have power/status. People who are often cruel, dismissive, and worse.
The way little access to healthcare creates confusion and fear around it. POC and some white poor RIGHTFULLY are mistrustful of "free" immunization/healthcare. Middle class weirdos with nothing better to do get away with pseudo science and anti vaxx bullshit BECAUSE many of us will do guerilla healthcare in our lifetime (for some of us, on a regular basis).
Repeated COVID infections are leaving people with weakened immune systems and a variety of cognitive delays and challenges. Those of us who lost loved ones and/or are disabled or immunocompromised have watched almost everyone else abandon any level of care for us. We've all seen the government wash its hands of responsibility and truly the vaccine roll out was the bare minimum and we've participated in no other preventative care or accessibility measures.
All of this to say that I think we are greatly underestimating how many people live in severe pain, with crippling illness, with grief forced into repression. I think we are greatly underestimating how many people are simply trying to NOT kill themselves every single day.
This is before you add in the rise in homelessness and poverty (many of us were there BEFORE COVID tbh). This is before you add in the U.S. funded and cosigned acceleration of human rights violations and genocide not just in Palestine. Before you look at the accelerating police and surveillance state. AT REST, suicidality and despair are touching places they never have before, are extending new invitations to people who were barely refusing them before this sequence of rising fascism.
You cannot approach the political or the personal in the same way you did in 2016, no matter who you were then. Whatever anyone was doing then has fuck all to do with who we all are now in 2024.
8 notes
·
View notes
Text
Also preserved in our archive
There are an increasing number of states across the U.S. where "very high" levels of the virus that causes COVID-19 are present in wastewater.
According to the U.S. Centers for Disease Control and Prevention (CDC), Idaho, New Mexico and South Dakota all had "very high" levels of the SARS-CoV-2 virus in their wastewater during the week between November 17 and November 23, 2024.
The week prior, between November 10 and November 16, only New Mexico's wastewater had this level of the virus present.
Arizona, Arkansas, Kentucky, Maine, Massachusetts and New Hampshire currently have "high" levels of COVID-19, while "moderate" levels were detected in Minnesota, Nebraska, Nevada, Oregon, Rhode Island, Utah and Wyoming.
(Follow link for interactive map!)
Nineteen states had "low" levels, while 14 states and D.C. had "minimal" levels of the SARS-CoV-2 virus present in wastewater.
Between November 10 and November 16, "high" levels were detected in Arizona, Kentucky, Minnesota, Oklahoma, Pennsylvania and South Dakota, with "moderate" levels of the virus detected in Colorado, Idaho, Maine, Maryland, Ohio, Oregon, Rhode Island, Utah and Wyoming.
The data from New Hampshire, Mississippi, Oklahoma, and South Dakota all have limited coverage for the most current data, which means it is "based on a small segment (less than 5 percent) of the population and may not be representative of the state/territory," the CDC explains. Additionally, North Dakota has no data for this period.
The CDC monitors COVID-19 levels in wastewater as part of its surveillance strategy to track the spread of the virus in communities. Infected individuals shed the virus in their feces, meaning that monitoring wastewater can reveal increases in infection rates earlier than clinical testing or hospitalizations.
"The wastewater viral activity level indicates whether the amount of virus in the wastewater is minimal, low, moderate, high or very high. The wastewater viral activity levels may indicate the risk of infection in an area," the CDC said.
Wastewater data helps public health officials allocate resources and make informed decisions about mask and vaccination policies.
In the week ending November 23, about 4.5 percent of COVID-19 tests around the country came back positive. This represents a 0.3 percent increase from the week prior. Some regions had rates of up to 6.3 percent, such as Arkansas, Louisiana, New Mexico, Oklahoma and Texas.
"SARS-CoV-2, the virus that causes COVID-19, is constantly changing and accumulating mutations in its genetic code over time. New variants of SARS-CoV-2 are expected to continue to emerge. Some variants will emerge and disappear, while others will emerge and continue to spread and may replace previous variants," the CDC said in a statement.
Subvariant KP.3.1.1 made up 37 percent of COVID-19 variants in U.S. wastewater over the two weeks before November 23. The new XEC variant made up 24 percent, KP.3 made up 17 percent, JN.1 made up 8 percent and "other" made up 14 percent.
For the same period, variants detected in positive test samples were slightly different, with KP.3.1.1 making up 44 percent of recorded COVID infections, XEC totaling 38 percent and MC.1 composing 6 percent.
#mask up#public health#wear a mask#pandemic#wear a respirator#covid#covid 19#still coviding#coronavirus#sars cov 2
94 notes
·
View notes
Text
Officials inside the CDC and global health specialists outside of the organization are trying to understand the ramifications of this order both for the U.S. and for the world.
"This is unprecedented," says Javier Guzman, the director of global health policy at the Center for Global Development.
CDC collaborates with WHO on a wide range of health efforts, including the ongoing efforts to quash a major mpox outbreak in parts of Africa and an outbreak of Marburg virus, which is Ebola's cousin, in Tanzania. The U.S. has donated more than a million vaccines to these efforts and sent expert teams to support the local response.
Asked to comment on the future of these collaborative efforts, a spokesperson for WHO wrote in an email to NPR, "we are analyzing developments and do not have further information at this time."
"There are a lot of people who are looking forward to further clarification and direction from the incoming administration," said a CDC official, who asked for anonymity because they are not authorized to speak to the press. They said they can't remember another presidential transition that included a directive similar to this. "I am not aware of any sort of communication that's gone out to CDC employees like this one."
A request for comment from CDC's media team was referred to the Health and Human Services media team, which has not responded.
How they've worked together
Among many other collaborations, the two agencies also work together on worldwide efforts to monitor and contain influenza. WHO runs the Global Influenza Surveillance Network. Josh Michaud, the associate director for global health policy at KFF, says that it may be challenging for the U.S. to develop flu vaccines each year tailored to the current strains of the virus that are circulating if scientists don't have access to the samples provided through the WHO system.
"There might be third parties which could create some communication channels and U.S. pharmaceutical companies on the private side could continue to have some kind of contact," he says. "But it definitely throws a wrench a little bit in the works of what had been a system which is really important – not just for global health security, but for U.S. health as well."
"It's absolutely vital that the CDC and WHO are talking to each other about what's happening. So a ban on that? I just can't see what benefit it has, but I see that it has a massive downside," say Dr. Chandy John, director of Indiana University School of Medicine's Ryan White Center for Infectious Diseases and Global Health.
Others agree. "It's very hard for me to see any U.S. national interest that's being advanced here. And quite the contrary, I just think it's making it very hazardous for Americans," says Lawrence Gostin, professor of global health law at Georgetown University and director of WHO's Center on Global Health Law.
For example, he says, WHO is convening an international meeting of experts who will discuss bird flu, among other things. Bird flu has been circulating widely in livestock and wildlife in the U.S. Without CDC representatives at the meeting, he says, CDC will be unable to examine the shared data from other countries where bird flu has been identified and understand how the virus is evolving and spreading across species. Gostin says this new clampdown on communications could hinder the country's ability to prevent humans from being infected as well as to develop medications and vaccines to combat bird flu.
"Not only is it reckless, but I think it's lawless," Gostin adds, explaining that even with the Trump administration's announcements, the U.S. is a party to the International Health Regulations and obliged to follow its guidelines. This is a legally-binding agreement managed by WHO that requires states to monitor health threats and report them to the WHO. However, there is not a strong enforcement mechanism for countries that don't comply.
"We criticize China relentlessly for failing to abide by [IHR] in rapid reporting and communicating of the Wuhan outbreak," says Gostin. "Why we would want to be in the company of China or Russia, that violates these international global health norms, certainly beats me."
In addition to withdrawing from WHO and halting communication between CDC and WHO, Trump has paused almost all foreign aid, including many health programs. Taken all together, KFF's Michaud calls the moment "incredibly precarious." And, he says, "for global health, it could mark a turning point" in how the U.S. contributes to the international effort to tackle diseases.
4 notes
·
View notes
Text
Toward the end of last year, US health authorities got a tip-off about an upcoming wave of respiratory syncytial virus, a seasonal virus that kills 160,000 people globally every year. Before hospitals reported an uptick in patients, they could see that RSV was more acute in the northeast of the country, with concentrations of the virus ultimately reaching levels more than five times greater than in the western United States. Their early warning system? Wastewater.
By regularly testing virus levels in public wastewater, health institutions are able to target treatments and interventions to the worst-affected areas before doctors on the ground realize something’s going on. “If you can get the information to hospitals or clinics weeks earlier, that gives the opportunity to start thinking about what treatments they might need,” says Marisa Donnelly, senior principal epidemiologist at Biobot Analytics, which helped develop a wastewater surveillance system for the US Centers for Disease Control.
RSV is very common: Every year, 64 million people worldwide get an RSV infection, according to the US National Institute for Allergy and Infectious Diseases—but it’s particularly problematic for the very old and very young. Preventative measures are available, including vaccines and monoclonal antibodies. But often, by the time a community recognizes it has an RSV outbreak, it’s too late to mount the most effective response. Getting hold of enough drugs can also be tricky. “Wastewater analysis gives you better situational awareness of what’s going on and how much it’s fluctuating over time, because we have [historically] very much underdetected RSV cases,” says Bill Hanage, associate director of the Center for Communicable Disease Dynamics at the Harvard T.H. Chan School of Public Health.
The concept of tracking a virus through wastewater came to prominence in the early days of the Covid-19 pandemic in 2020, says Tyson Graber, associate scientist at the Children's Hospital of Eastern Ontario Research Institute, who worked on wastewater analysis as part of Ontario’s Covid response. Initially, researchers weren’t too hopeful. “Nobody thought that you could actually detect bits and pieces of material from a respiratory virus,” says Graber. Yet it proved possible: The scientists were able to detect the presence of SARS-CoV-2, the virus behind Covid-19.
This near-real-time analysis of the virus’s spread helped improve responses to the pandemic not just in Ontario, but worldwide. In the US, the CDC launched its National Wastewater Surveillance System in September 2020.
While each pathogen has its own “predilections and eccentricities,” says Graber, it was possible to adapt the process to look for RSV. Regular RSV testing in wastewater now takes place in the US, Canada, Finland, and Switzerland.
A study of the Ontario experiment in RSV wastewater tracking found that it gives more than a month’s notice in identifying when RSV season begins, and nearly two weeks’ warning of a surge, compared to waiting for people to turn up sick. “We definitely see increases in [RSV in] wastewater starting before we see those same increases in clinical data like hospitalizations,” says Donnelly.
Jasmine Reed, a CDC spokesperson, says that wastewater analysis complements other surveillance systems. “It can capture asymptomatic cases and other cases independent from medical systems, and provides a broader population-level perspective on disease spread,” she says.
The CDC’s program is set up so that, if RSV levels are high in a particular community, local health departments can prioritize interventions, including testing, infection control, and vaccination efforts.
Donnelly envisions wastewater surveillance becoming like a public health “weather app” where communities can check virus activity in their area and make informed decisions on behaviors like masking or vaccination. “We want this system to be expanded across the United States so that everybody has access to wastewater information and add additional tools to keep themselves healthy,” she says. Hanage foresees wastewater analysis being used to track other communicable viruses, like mpox.
While there’s plenty of excitement about the technique, others are more cautious. “It’s one of those sciences that has got a lot of people really excited,” says Paul Hunter, a virologist and professor in medicine at the University of East Anglia. “You either think it’s brilliant or you think it’s pointless, and there’s very little in between.”
Hunter recognizes that wastewater analysis can pick up the spread of disease—and points to evidence that it did so in the Covid-19 pandemic—but questions whether the extra cost is worth the extra insights it provides. “Certainly in Covid, we didn’t think it was [necessary] in the UK, and I think that was the correct judgment,” he says.
But proponents say it’s worth it for RSV—especially given some of the challenges around drug shortages. Last year’s RSV season proved particularly vexing to the US health system, as shortages of nirsevimab, an antibody injection given to infants, were reported across the country.
There’s hope that things will be different when RSV season begins again in the coming weeks. “If you can get the information to hospitals or clinics weeks earlier, that gives the opportunity to start thinking about what treatments they might need,” says Donnelly.
3 notes
·
View notes
Text
'Social Media: The Unexpected Hero of the Pandemic?'
Social media? That cesspool of doomscrolling, misinformation, and endless arguments? But Hero of the pandemic? No way! Erdem, however argues the pandemic have enable social media to influence modern schooling of public health, essentially saving lives (Erdem 2021). Public health, as defined by Winslow, involves the science and practice of preventing disease, prolonging life, and promoting community health through organized efforts and informed choices made by various stakeholders (Winslow n.d.). These stakeholders include public and private entities, communities, individuals, and organizations. In contrast. Social media, on the other hand according to Gregersen, encompasses online platforms for mass communication, enabling users to connect and share content such as messages, ideas, and information(Gregersen 2024). In the modern era, public health and social media have increasingly intertwined. This interconnectedness prompts an important question: How effective is social media in disseminating information about COVID-19?

While pre-existing concerns about misinformation and echo chambers were amplified, the crisis also revealed the unprecedented power of these platforms for disease surveillance, information dissemination, community engagement, and health promotion. Social media became a virtual battleground where accurate information and dangerous falsehoods clashed, influencing public perception and behavior in ways never seen before.
Disease Surveillance and Public Health Monitoring
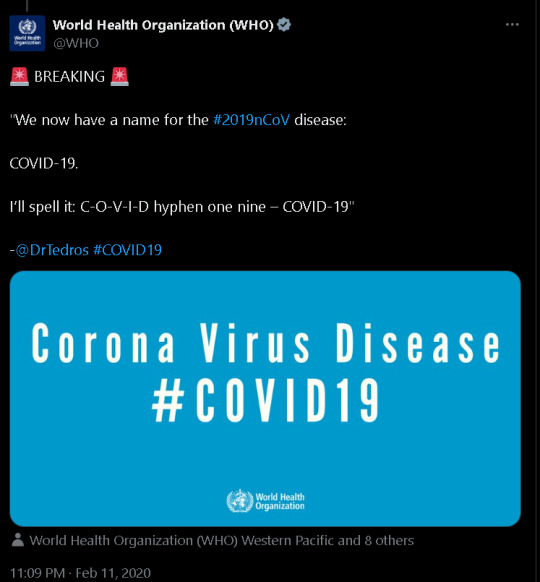
-First Alarm of Covid Emergence From Twitter (X)
The COVID-19 pandemic underscored the critical role of information in public health crises, with social media emerging as a dominant force. Platforms like Twitter and Facebook became primary sources for real-time updates, enabling organizations like the WHO and CDC to communicate directly with the public (Moorhead et al. as cited in Kanchan & Gaidhane 2023). This allowed for rapid dissemination of vital information about symptoms, prevention, and evolving public health recommendations, proving crucial in a dynamic situation with frequently changing guidelines (Kanchan & Gaidhane 2023).

-Snapshot of Facebook lives, providing updates in times of lockdown (Facebook-5.3 Million)
Furthermore, social media facilitated public health advocacy and policy shaping. Health professionals and advocacy groups utilized these platforms to engage with the public and decision-makers, promoting evidence-based policies like mask mandates and vaccination strategies (Kanchan & Gaidhane 2023). By amplifying diverse voices and marginalized perspectives, social media fostered a more inclusive and equitable public health response, ensuring a broader range of perspectives informed policy discussions and interventions.
Information Dissemination
However, this same speed and accessibility that made social media a valuable tool for public health communication also fueled the spread of misinformation, conspiracy theories, and unverified claims (Pool, Fatehi & Akhlaghpour 2021). The "infodemic" that accompanied the pandemic, as termed by the WHO (2020), hindered public health efforts, fueled distrust in authorities, and even led to harmful behaviors such as the rejection of vaccines or the promotion of unproven remedies (Pool, Fatehi & Akhlaghpour 2021). This effectively eluded the needs for effective strategies to combat misinformation and promote critical media literacy in the digital age.
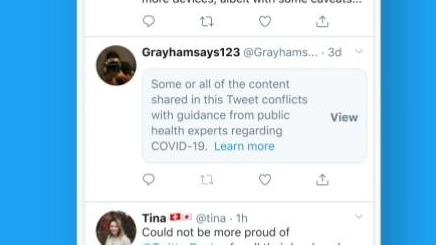
-Infodemic sources/Misinformation were censored and surveilled on Twitter (X)
Despite these challenges, social media also emerged as a powerful tool for combating misinformation. Experts and fact-checkers utilized these platforms to debunk false claims, provide evidence-based information, and promote adherence to public health guidelines (Sharma et al as cited in Kanchan & Gaidhane 2023). Social media also facilitated the rapid dissemination of research findings, clinical trial data, and treatment protocols, accelerating the global exchange of knowledge and helping healthcare professionals stay updated on the latest developments in COVID-19 management (Kanchan & Gaidhane 2023). This accelerated pace of information sharing proved crucial in a dynamic pandemic situation where scientific understanding and best practices were constantly evolving.
Community Engagement
youtube
-Solidarity among Malaysian Healthcare workers ticked up via social media, in times of Movement Control Order (MCO)
Beyond its role in information dissemination, social media played a crucial role in fostering a sense of community and providing support during a time of unprecedented isolation and anxiety. Online communities and forums became spaces for individuals to connect, share their experiences, and offer encouragement (Naslund et al. as cited in Kanchan & Gaidhane 2023). This virtual support network helped mitigate the mental health impacts of lockdowns and social distancing measures, reminding people that they were not alone in their struggles. Social media platforms also became hubs for organizing mutual aid initiatives, coordinating donation drives, and providing support to frontline healthcare workers, showcasing the potential of these platforms to galvanize collective action and foster resilience in the face of adversity (Kanchan & Gaidhane 2023).
Health promotion

-Facebook groups 'Caremongering' bring communities to our screens during MCO
Social media platforms also offer a opportunity to engage with individuals and communities in promoting healthy behaviors and facilitating positive change (Kanchan & Gaidhane 2023). Targeted campaigns and interventions can be delivered through social media, reaching specific demographics with tailored messages about disease prevention, healthy lifestyles, and mental well-being (Kanchan & Gaidhane 2023). Studies have shown the effectiveness of social media interventions in addressing issues such as risky drinking ,cannabis use among young adults and most importantly during Covid isolation (Kanchan & Gaidhane 2023).
Concluding, the COVID-19 pandemic served as a powerful demonstration of both the potential and the challenges of social media in public health. While the spread of misinformation and ethical concerns remain significant challenges, the pandemic also highlighted the unprecedented ability of these platforms to disseminate vital information, foster community support, empower individuals and communities to take action, and shape public health policies. As we move forward, it is crucial to learn from the experiences of the pandemic and harness the power of social media responsibly and ethically to build a more informed, connected, and resilient global community.

References
Erdem, B 2021, ‘The Role of Social Media in the Times of the Covid-19 Pandemic’, European Journal of Social Sciences, vol. 4, no. 2, p. 110.
Gregersen, E 2024, ‘Social Media’, Encyclopædia Britannica, viewed <https://www.britannica.com/topic/social-media>.
Kanchan, S & Gaidhane, A 2023, ‘Social Media Role and Its Impact on Public Health: a Narrative Review’, Cureus, vol. 15, no. 1, p. e33737, viewed <https://www.ncbi.nlm.nih.gov/pmc/articles/PMC9925030/>.
Pool, J, Fatehi, F & Akhlaghpour, S 2021, ‘Infodemic, Misinformation and Disinformation in Pandemics: Scientific Landscape and the Road Ahead for Public Health Informatics Research’, Studies in Health Technology and Informatics, vol. 281, pp. 764–768, viewed 31 August 2021, <https://pubmed.ncbi.nlm.nih.gov/34042681/>.
Winslow, C n.d., Public Health 101 Series Instructor name Title Organization, viewed <https://www.cdc.gov/training-publichealth101/media/pdfs/introduction-to-public-health.pdf>.
youtube
#MDA20009#Week7#SocialMedia#Covid19#Tumblr#StaySafe#Youtube#Malaysia#Current Events#Movement Control Order#Digital Communities
3 notes
·
View notes
Text
The Africa Center for Disease Control and Prevention and the World Health Organization launched on Friday a continent-wide response plan to the outbreak of mpox, three weeks after WHO declared outbreaks in 12 African countries a global emergency. The estimated budget for the six-month plan is almost $600 million, with 55% allocated to the response to mpox in 14 affected nations and boosting readiness in 15 others, Africa CDC director-general Dr. Jean Kaseya told reporters on Friday. The other 45% is directed towards operational and technical support through partners. The organization didn’t give an indication of who would be funding it. The plan focuses on surveillance, laboratory testing and community engagement, Kaseya said, underscoring the fact that vaccines aren’t enough to fight the spreading outbreak. The organization said that since the start of 2024, there have been 5,549 confirmed mpox cases across the continent, with 643 associated deaths, representing a sharp escalation in both infections and fatalities compared to previous years. The cases in Congo constituted 91% of the total number. Most mpox infections in Congo and Burundi, the second most affected country, are in children under age 15. The plan comes a day after the first batch of mpox vaccines arrived in the capital of Congo, the center of the outbreak. The 100,000 doses of the JYNNEOS vaccine, manufactured by the Danish company Bavarian Nordic, have been donated by the European Union through HERA, the bloc’s agency for health emergencies. Another 100,000 are expected to be delivered on Saturday, Congolese authorities said.
4 notes
·
View notes
Text


lorida’s surgeon general has warned healthcare providers against using Pfizer and Moderna’s COVID-19 mRNA vaccines due to concerns over genetic contamination.
Joseph Ladapo requested that providers prioritise other non-mRNA vaccines and treatments to ensure patient safety. He also called for the FDA to take greater regulatory responsibility in ensuring the integrity of the human genome.
Gov. Ron DeSantis has echoed concerns over mRNA vaccines and recently stated that Floridians would not be used as “guinea pigs” for unproven booster shots.
In November, Ladapo asked the Food and Drug Administration (FDA) and the Centers for Disease Control and Prevention (CDC) to investigate reports of foreign DNA material in Pfizer and Moderna’s vaccines. Ladapo argued that if mRNA vaccines were efficient delivery vehicles for mRNA, they may also be vehicles for delivering contaminant DNA, resulting in a process known as DNA integration. However, on Dec. 14, the FDA Director of the Center for Biologics Evaluation and Research, Peter Marks, wrote to Ladapo stating that animal studies over the past decade and global surveillance data showed no evidence of genotoxicity or genomic disruption.
Despite Ladapo’s concerns, the FDA stated that the practical risk of DNA integration was “quite implausible” and refuted the idea that mRNA vaccines presented a viable risk.
Ladapo contested the FDA’s claims, arguing that they had not performed adequate DNA integration assessments and that genotoxicity studies were an insufficient tool for assessing DNA integration risk. According to Ladapo, “If the risks of DNA integration have not been assessed for mRNA COVID-19 vaccines, these vaccines are not appropriate for use in human beings.”
The COVID vaccine destroyed my health. Since I had the vaccine I have not felt good two days in a row. It has caused me to have open heart surgery, ruptured my appendix, and left me with Stage Three Kidney disease. I am not the only one. My biggest fear is SDS. It's like my heart has become a living time bomb. Ironically I caught Covid two months AFTER the vaccine so.......so it didn't even work. --KD
--
9 notes
·
View notes