#urologist in jagatpura
Explore tagged Tumblr posts
Text
What are the latest treatments for overactive bladder?

Behavioral Therapies:
Bladder Training: This involves gradually increasing the intervals between urination to help control urges and increase bladder capacity.
Scheduled Toilet Trips: Establishing a fixed schedule for bathroom visits can help reduce the frequency of urges.
Fluid Management: Monitoring and adjusting fluid intake to avoid triggering symptoms.
Physical Therapy:
Pelvic Floor Muscle Exercises (Kegel exercises): Strengthening the pelvic floor muscles can improve bladder control and reduce urgency.
Medications:
Anticholinergics: These drugs help relax the bladder muscle and reduce urinary urgency and frequency. Newer formulations with improved side effect profiles are available.
Beta-3 Agonists: These medications work by relaxing the bladder muscle and increasing bladder capacity.
Neuromodulation:
Sacral Nerve Stimulation (InterStim): This involves implanting a device that sends electrical impulses to the nerves controlling the bladder, helping to reduce urgency and frequency.
Peripheral Tibial Nerve Stimulation (PTNS): Involves stimulating the nerves in the ankle, which in turn affects bladder function.
Botox Injections:
Botulinum toxin injections directly into the bladder muscle can help relax it and reduce urinary urgency and frequency. This treatment is typically reserved for those who do not respond to other therapies.
Surgical Interventions:
Augmentation Cystoplasty: This involves enlarging the bladder using a part of the bowel to increase its capacity.
Urinary Diversion: Redirecting urine away from the bladder to a surgically created stoma or pouch.
Emerging Therapies:
Gene Therapy: Research is ongoing into using gene therapy to modify the genes responsible for bladder function.
Stem Cell Therapy: Investigational studies are exploring the use of stem cells to repair damaged bladder tissue and improve function.
Advancements in understanding the underlying mechanisms of overactive bladder have led to more targeted and effective treatments. Personalized approaches, considering factors such as age, severity of symptoms, and underlying health conditions, are crucial in determining the most appropriate treatment plan. Regular consultation with healthcare providers and urologists is essential for monitoring progress and adjusting therapies as needed to achieve optimal outcomes and improve quality of life for individuals with overactive bladder.
0 notes
Text
Dr. Sandeep Nunia: The Best Urologist in Jaipur

The Expertise of Dr. Sandeep Nunia
Education and Training
Dr. Sandeep Nunia is a highly qualified urologist with a strong educational background. He completed his medical degree from a prestigious institution, followed by specialized training in urology. His dedication to staying abreast of the latest advancements in the field is evident in the quality of care he provides.
Specialization in Kidney Stone Treatment
One of Dr. Nunia’s key areas of expertise lies in the treatment of kidney stones. Kidney stones can be a painful and debilitating condition, requiring specialized care. Dr. Nunia employs a comprehensive approach to diagnose, treat, and prevent the recurrence of kidney stones. His success in this area has made him the go-to urologist for patients facing this challenge.
Commitment to Patient Care
Beyond his medical expertise, Dr. Sandeep Nunia is known for his compassionate and patient-centric approach. He understands the sensitive nature of urological issues and ensures that his patients feel comfortable discussing their concerns. His commitment to providing personalized care has endeared him to many in the community.
Services Offered by Dr. Nunia
Kidney Stone Treatment
Dr. Nunia employs state-of-the-art techniques for the diagnosis and treatment of kidney stones. From non-invasive procedures to surgical interventions, he tailors his approach to the unique needs of each patient.
Prostate Health
As a urologist, Dr. Nunia also specializes in addressing prostate-related issues. Regular check-ups and early detection are key aspects of his approach to maintaining prostate health.
General Urological Care
Apart from his specialized areas, Dr. Sandeep Nunia offers a wide range of general urological services. These include the management of urinary tract infections, bladder issues, and male reproductive health.
Patient Testimonials
The positive feedback from Dr. Nunia’s patients speaks volumes about his proficiency and compassionate care. Many express gratitude for his ability to explain complex medical conditions in a way that is easy to understand, fostering a sense of trust and confidence.
How to Contact Dr. Sandeep Nunia
If you are in Jaipur and seeking the expertise of the best urologist in the city, you can reach out to Dr. Sandeep Nunia. Here are the contact details:
Phone: +91–9119308400
Location: [EHCC Hospital, Jagatpura road, Malviya Nagar]
Conclusion
In conclusion, Dr. Sandeep Nunia is undeniably the best urologist in Jaipur, known for his extensive experience, specialized expertise in kidney stone treatment, and commitment to patient care. If you are dealing with urological issues, seeking his services is a step toward comprehensive and compassionate healthcare.
0 notes
Text
How is bladder cancer detected, and what are the treatment options?

Detection of Bladder Cancer
Symptoms and Initial Screening:
Blood in Urine (Hematuria): This is the most common symptom. Visible blood or blood detected under a microscope during a urinalysis may indicate bladder cancer.
Urinary Changes: Frequent urination, pain during urination, or urgency can also be signs, though these are less specific.
Diagnostic Tests:
Cystoscopy: A thin, flexible tube (cystoscope) is inserted into the bladder through the urethra to visually inspect the bladder lining for abnormalities.
Biopsy: If suspicious areas are found during cystoscopy, a small sample of tissue (biopsy) may be taken for examination under a microscope to confirm the presence of cancerous cells.
Imaging Tests:
CT Scan or MRI: These imaging tests help determine the extent of cancer spread (staging) beyond the bladder.
Treatment Options for Bladder Cancer
Treatment options for bladder cancer depend on several factors, including the stage of cancer, overall health, and personal preferences.
Non-Invasive or Early Stage Bladder Cancer:
Transurethral Resection of Bladder Tumor (TURBT): For tumors confined to the inner layers of the bladder, this procedure involves removing the tumor through a cystoscope.
Intravesical Therapy: After TURBT, medications (chemotherapy or immunotherapy) can be delivered directly into the bladder to destroy remaining cancer cells and reduce the risk of recurrence.
Muscle-Invasive or Advanced Bladder Cancer:
Surgery: Partial or radical cystectomy may be necessary to remove part or all of the bladder. In some cases, nearby lymph nodes may also be removed.
Chemotherapy: Used before or after surgery (neoadjuvant or adjuvant), or as the primary treatment for advanced cancer that has spread beyond the bladder.
Radiation Therapy: Sometimes used instead of surgery, or in combination with chemotherapy, especially for cancers that cannot be surgically removed.
Targeted Therapy and Immunotherapy:
Targeted Therapy: Drugs that specifically target cancer cells based on their genetic characteristics.
Immunotherapy: Drugs that help the immune system recognize and destroy cancer cells more effectively.
Follow-Up Care:
After treatment, regular follow-up visits are essential to monitor for recurrence and manage any side effects from treatment.
Conclusion
Early detection of bladder cancer is crucial for successful treatment outcomes. Advances in diagnostic techniques and treatment options continue to improve the prognosis for individuals diagnosed with bladder cancer. Tailored treatment plans, often involving a combination of surgery, chemotherapy, immunotherapy, and supportive care, aim to achieve the best possible outcomes while preserving bladder function and quality of life.
#best urologist in jaipur#urologist in jagatpura#urologist treatment in jaipur#best andrology treatment in jaipur#urologist in jaipur
0 notes
Text
Can you explain the process and benefits of a vasectomy?
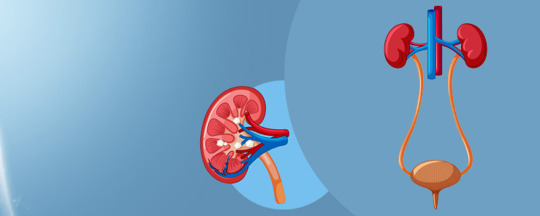
Maintaining urological health is crucial for overall well-being, and diet plays a significant role in achieving this. The urinary system, comprising the kidneys, bladder, ureters, and urethra, is responsible for filtering waste products from the blood, regulating electrolytes, and producing urine.

Process of Vasectomy:
Consultation and Preparation: Before the procedure, a consultation with a urologist or a healthcare provider is necessary. Medical history, risks, benefits, and alternatives are discussed. No-scalpel techniques are common, minimizing incisions and recovery time.
Anesthesia: Local anesthesia is typically administered to numb the scrotum, ensuring minimal discomfort during the procedure. Sedation may be offered to alleviate anxiety.
Accessing the Vas Deferens: Using a small puncture or incision, the urologist locates and accesses the vas deferens under the skin of the scrotum. The tubes are then isolated from the surrounding tissue.
Interruption of Vas Deferens: The vas deferens is either cut, tied off, or sealed using heat (cauterization) or clips. This prevents sperm from mixing with semen during ejaculation.
Closure and Recovery: The small puncture or incision is closed with dissolvable stitches or surgical glue. Recovery is generally quick, with minimal discomfort, though some swelling or bruising may occur.
Benefits of Vasectomy:
Highly Effective: Vasectomy is over 99% effective in preventing pregnancy. Once sperm-free semen is confirmed through follow-up tests, it provides a reliable long-term contraception method.
Permanent Contraception: Unlike temporary methods such as condoms or birth control pills, vasectomy is permanent. It eliminates the need for ongoing contraception management and is considered a one-time procedure.
Low Risk and Complications: Complications are rare, with the most common being minor discomfort, swelling, or bruising post-surgery. Serious complications like infection or chronic pain are extremely uncommon.
Cost-effective: Over time, vasectomy can be more cost-effective than other contraceptive methods that require ongoing purchases or prescriptions.
Non-hormonal: Unlike some forms of birth control for women, vasectomy does not involve hormones, making it suitable for individuals with hormone sensitivities or concerns about hormone-based contraception.
No Impact on Sexual Function: Vasectomy does not affect sexual desire, performance, or pleasure. It only prevents the release of sperm into semen during ejaculation.
Reversibility: While vasectomy is considered permanent, it can sometimes be reversed through surgical procedures such as vasectomy reversal or sperm retrieval. However, success rates for reversal decrease with time and are not guaranteed.
In conclusion, a vasectomy is a safe, effective, and permanent form of contraception that provides numerous benefits for individuals and couples seeking reliable family planning. It allows for sexual spontaneity without the worry of unintended pregnancy and offers a straightforward outpatient procedure with minimal recovery time. Prior to undergoing a vasectomy, thorough discussion with a healthcare provider ensures understanding of the procedure, its implications, and consideration of alternative options if desired.
#best urologist in jaipur#urologist in jagatpura#urologist treatment in jaipur#best urologist in jagatpura
0 notes
Text
What role does diet play in maintaining urological health?

A balanced diet can support these functions and prevent various urological issues such as kidney stones, urinary tract infections (UTIs), and bladder problems.
Hydration: Adequate hydration is fundamental for urological health. Water helps flush out toxins and prevents the concentration of minerals that can lead to kidney stones. Aim for at least 8 glasses (about 2 liters) of water per day, adjusting based on activity level and climate.
Controlled Sodium Intake: High sodium levels can contribute to hypertension and kidney damage over time. It’s essential to moderate salt intake to reduce the risk of kidney stones and maintain healthy blood pressure levels.
Balanced Diet: A diet rich in fruits, vegetables, whole grains, lean proteins, and healthy fats provides essential nutrients and antioxidants. These nutrients support kidney function and overall urinary tract health.
Limit Oxalate-rich Foods: Oxalates can contribute to the formation of kidney stones in susceptible individuals. Foods high in oxalates include spinach, rhubarb, nuts, and certain berries. While these foods are nutritious, moderation is key for those prone to kidney stones.
Healthy Weight Management: Obesity is linked to an increased risk of kidney stones and urinary tract infections. A balanced diet and regular exercise can help maintain a healthy weight and reduce these risks.
Protein Moderation: Diets excessively high in animal protein can stress the kidneys. Balancing protein sources with plant-based options like beans, lentils, and tofu can support kidney function without overloading it.
Limit Sugar and Refined Carbohydrates: Diets high in sugar and refined carbohydrates can contribute to obesity and diabetes, both of which increase the risk of kidney disease. Opt for whole grains and natural sweeteners like honey or maple syrup in moderation.
Moderate Caffeine and Alcohol: Both caffeine and alcohol can irritate the bladder and increase urine production. Moderation is key, especially if you are prone to bladder issues or urinary incontinence.
Vitamins and Minerals: Adequate intake of vitamins and minerals such as calcium, magnesium, and vitamin B6 is essential for preventing kidney stones and supporting overall urinary tract health. Consult with a healthcare provider to determine appropriate levels for your diet.
Special Considerations: Individuals with specific urological conditions such as interstitial cystitis may benefit from avoiding potential trigger foods like spicy dishes, acidic foods, and artificial sweeteners.
In conclusion, a balanced and varied diet plays a vital role in maintaining urological health by supporting kidney function, preventing urinary tract infections, and reducing the risk of kidney stones. Alongside diet, maintaining a healthy lifestyle that includes regular exercise, adequate sleep, and stress management further enhances overall urological well-being. Consulting with a healthcare professional or a registered dietitian can provide personalized guidance based on individual health needs and goals.
0 notes
Text
What are the potential side effects of prostate surgery?
Prostate surgery, a common treatment for conditions like benign prostatic hyperplasia (BPH) or prostate cancer, can bring relief and improve quality of life for many men. However, like any surgical procedure, it carries potential side effects that patients should be aware of.

Here are some of the common side effects associated with prostate surgery:
Erectile Dysfunction (ED):
One of the most concerning side effects of prostate surgery is erectile dysfunction. This can occur due to damage to nerves and blood vessels that are crucial for maintaining erections. The risk of ED varies depending on the type of surgery performed and the patient’s preoperative sexual function.
2. Urinary Incontinence:
Prostate surgery can lead to temporary or permanent urinary incontinence, which is the inability to control urine flow. This occurs because surgery may disrupt the sphincter muscles or nerves that control bladder function. Incontinence severity can range from mild leakage to complete loss of bladder control.
3. Urinary Symptoms:
Some men may experience persistent urinary symptoms following surgery, such as urgency, frequency, weak stream, or difficulty urinating. These symptoms can occur due to residual prostate tissue or bladder irritation.
4. Changes in Ejaculation:
Depending on the surgical technique used, men may experience changes in ejaculation. This can include retrograde ejaculation, where semen enters the bladder instead of exiting through the penis, or reduced semen volume.
5. Bleeding:
Bleeding is a common risk during and after prostate surgery. While most cases are minor and resolve on their own, excessive bleeding may require additional treatment or procedures.
6. Infection:
Like any surgery, prostate surgery carries a risk of infection. This can occur in the surgical site, urinary tract, or bloodstream. Antibiotics are typically given before and after surgery to reduce this risk.
7. Stricture Formation:
Scar tissue formation (strictures) can occur in the urethra following surgery, leading to difficulty urinating. This may require further treatment such as dilation or surgery to correct.
8. Chronic Pain:
Some men may experience chronic pain in the pelvic area or penis following surgery. This can be due to nerve damage, inflammation, or other factors.
9. Anesthesia Risks:
General anesthesia, which is often used during prostate surgery, carries its own set of risks including allergic reactions, respiratory problems, and cardiovascular complications.
10. Emotional and Psychological Effects:
Dealing with the physical changes and potential loss of sexual function can have emotional and psychological impacts on patients and their partners. Counseling and support groups may be helpful in managing these effects.
It’s important to note that not all men will experience these side effects, and the severity can vary widely. Factors such as age, overall health, the type of surgery performed, and the surgeon’s skill all play a role in determining the likelihood and extent of side effects. Before undergoing prostate surgery, patients should have a detailed discussion with their healthcare provider to understand the potential risks and benefits, as well as what to expect during recovery.
#best urologist in jaipur#urologist treatment in jaipur#urologist in jagatpura#best urologist in jagatpura
0 notes
Text
What are the signs and symptoms of an enlarged prostate (BPH)?
An enlarged prostate, medically known as benign prostatic hyperplasia (BPH), is a common condition among older men. It occurs when the prostate gland, which surrounds the urethra (the tube through which urine flows out of the bladder), grows larger than usual. This enlargement can cause various signs and symptoms that can affect urinary function and overall quality of life.

Here are the key signs and symptoms associated with BPH:
Frequent or Urgent Need to Urinate: Men with BPH often experience a sudden and urgent need to urinate, which may occur frequently throughout the day and night (nocturia). This can disrupt sleep patterns and lead to fatigue.
Difficulty Starting Urination: A common symptom of BPH is difficulty initiating the urinary stream. This may manifest as straining or pushing to begin urination.
Weak Urinary Stream: As the prostate gland enlarges, it can compress the urethra, leading to a weakened urinary stream. Men may notice that their urine stream is weaker than it used to be.
Incomplete Emptying of the Bladder: BPH can interfere with the complete emptying of the bladder, leaving some urine behind. This can cause a feeling of incomplete voiding and may increase the frequency of urination.
Dribbling at the End of Urination: After urination, some men with BPH may experience dribbling or leaking of urine, which can be bothersome and lead to damp undergarments.
Bladder Infections: In some cases, BPH can increase the risk of urinary tract infections (UTIs) due to incomplete bladder emptying.
Blood in Urine or Semen: While less common, some men with BPH may notice blood in their urine or semen. This requires medical evaluation to determine the cause.
Bladder Stones: Chronic urinary retention from severe BPH can sometimes lead to the formation of bladder stones, which may cause additional discomfort and complications.
Complications: Severe BPH can lead to more serious complications such as acute urinary retention (sudden inability to urinate), bladder damage, or kidney problems if left untreated.
It’s important to note that the severity and combination of symptoms can vary among individuals with BPH. Not all men with an enlarged prostate will experience all of these symptoms, and some may have mild symptoms that do not significantly impact their daily lives.
If you or someone you know is experiencing symptoms suggestive of BPH, it is advisable to seek medical evaluation and guidance. Effective treatments are available to manage BPH and improve symptoms, ranging from lifestyle changes and medications to surgical procedures in more severe cases. Early diagnosis and intervention can help mitigate symptoms and prevent complications associated with this common condition.
#best urologist in jaipur#urologist in jagatpura#urologist treatment in jaipur#best urologist in jagatpura
0 notes
Text
How is prostate cancer detected, and what are the treatment options?
Prostate cancer is one of the most common cancers affecting men, typically diagnosed through a combination of screening tests and further diagnostic procedures. Detecting prostate cancer early greatly increases the chances of successful treatment and cure.
Detection Methods:
Prostate-Specific Antigen (PSA) Test: This blood test measures the level of PSA, a protein produced by the prostate gland. Elevated PSA levels may indicate prostate cancer, although other conditions such as benign prostatic hyperplasia (BPH) or inflammation can also cause PSA levels to rise. A high PSA level usually prompts further investigation.
Digital Rectal Examination (DRE): During a DRE, a doctor inserts a gloved, lubricated finger into the rectum to feel the prostate gland for any abnormalities, such as lumps or hard areas that might suggest cancer.
Biopsy: If abnormalities are detected during a PSA test or DRE, a biopsy is performed. This involves taking small tissue samples from the prostate gland using a thin needle guided by ultrasound imaging. The tissue samples are then examined under a microscope to determine if cancer cells are present.
Diagnostic Imaging: In some cases, imaging tests such as MRI (Magnetic Resonance Imaging) or CT (Computed Tomography) scans may be used to further evaluate the extent of the cancer and whether it has spread beyond the prostate gland.
Grading and Staging: Once prostate cancer is diagnosed, it is graded based on the Gleason score, which assesses how aggressive the cancer cells appear under a microscope. Staging determines the extent and spread of cancer beyond the prostate, influencing treatment decisions.
Treatment Options:
Active Surveillance: For low-risk prostate cancer, where the cancer is slow-growing and unlikely to spread, active surveillance involves closely monitoring the cancer with regular PSA tests, DREs, and biopsies. Treatment is deferred unless the cancer shows signs of progression.
Surgery (Radical Prostatectomy): This involves surgical removal of the prostate gland and surrounding tissues. It is often recommended for younger men with localized prostate cancer and a longer life expectancy.
Radiation Therapy: This treatment uses high-energy beams to target and kill cancer cells. It can be delivered externally (external beam radiation therapy) or internally via radioactive implants (brachytherapy). Radiation therapy may be used as a primary treatment or after surgery to destroy any remaining cancer cells.
Hormone Therapy (Androgen Deprivation Therapy — ADT): Prostate cancer cells often rely on testosterone to grow. Hormone therapy aims to reduce testosterone levels or block its effects, slowing cancer growth or shrinking tumors. It is typically used in advanced or metastatic prostate cancer.
Chemotherapy: This treatment uses drugs to kill cancer cells or stop their growth. Chemotherapy may be recommended for advanced prostate cancer that has spread to other parts of the body.
Immunotherapy and Targeted Therapy: These newer treatment approaches use medications that target specific molecules involved in cancer growth or boost the body’s immune response against cancer cells. They are increasingly being studied and used in certain cases of advanced prostate cancer.
Treatment Decision: The choice of treatment depends on several factors, including the stage and grade of cancer, overall health and age of the patient, and preferences regarding potential side effects and quality of life. It is crucial for patients to discuss their options with a multidisciplinary team of healthcare providers to determine the most appropriate treatment plan tailored to their individual situation. Early detection and advances in treatment options have significantly improved outcomes for men diagnosed with prostate cancer, emphasizing the importance of regular screening and timely intervention.
0 notes
Text
Can you explain the typical symptoms of a urinary tract infection (UTI)?

Typical Symptoms
Frequent Urination: One of the hallmark symptoms of a UTI is a frequent and urgent need to urinate, even when the bladder is not full. This frequent urge can be accompanied by only small amounts of urine being passed.
Pain or Burning Sensation: A burning sensation or pain during urination, known as dysuria, is another common symptom of a UTI. This discomfort is caused by irritation and inflammation of the urinary tract lining due to the presence of bacteria.
Cloudy or Strong-Smelling Urine: Urine infected with bacteria may appear cloudy or have a strong, unpleasant odor. This change in urine color and smell is a result of the body’s immune response to the infection.
Blood in Urine: Hematuria, or the presence of blood in the urine, can occur with a UTI. The urine may appear pink, red, or cola-colored, indicating bleeding within the urinary tract.
Pelvic Pain:��Some individuals with UTIs may experience pelvic pain, discomfort in the lower abdomen, or pressure in the pelvic region. This discomfort may range from mild to severe and can persist even after urination.
Fatigue and Malaise: UTIs can cause systemic symptoms such as fatigue, malaise, and a general feeling of unwellness. These symptoms may accompany the localized urinary symptoms and can be indicative of a more severe infection.
Fever and Chills: In more severe cases of UTIs, particularly when the infection spreads to the kidneys (pyelonephritis), individuals may develop a fever, accompanied by chills and sweats. Fever is a sign that the infection has become more serious and requires prompt medical attention.
Seeking Medical Attention
It’s important to seek medical attention if you experience symptoms of a UTI, especially if they are severe or if you have a history of recurrent UTIs. Untreated UTIs can lead to complications such as kidney damage or bloodstream infections. Healthcare providers typically diagnose UTIs through a combination of symptoms assessment, urine analysis, and sometimes urine culture to identify the specific bacteria causing the infection.
Treatment
Treatment for UTIs usually involves a course of antibiotics prescribed by a healthcare provider. It’s essential to complete the full course of antibiotics as prescribed, even if symptoms improve before the medication is finished, to ensure that the infection is fully eradicated. In addition to antibiotics, drinking plenty of water and urinating frequently can help flush out bacteria from the urinary tract.
Prevention
Preventing UTIs often involves simple lifestyle changes, such as staying hydrated, practicing good hygiene, urinating after sexual intercourse, and avoiding irritating substances like harsh soaps or douches in the genital area. For individuals prone to recurrent UTIs, a healthcare provider may recommend additional preventive measures, such as low-dose antibiotics or cranberry supplements.
In conclusion, urinary tract infections are a common and often uncomfortable condition characterized by symptoms such as frequent urination, pain or burning during urination, cloudy or bloody urine, pelvic pain, and systemic symptoms like fever and fatigue. Seeking prompt medical attention and following prescribed treatment are essential for managing UTIs and preventing complications.
0 notes
Text
Understanding Timelines for Improvement with Urological Treatments
When it comes to seeking treatment for urological issues, such as urinary tract infections (UTIs), kidney stones, or prostate problems, patients often wonder how long it will take to experience improvement after starting treatment. While the timeline for improvement can vary depending on the specific condition, treatment approach, and individual factors, there are some general guidelines to consider.

Acute Conditions: For acute urological issues like UTIs or urinary retention, patients often experience relief relatively quickly after starting treatment. Antibiotics are commonly prescribed for UTIs, and many people notice an improvement in symptoms within a few days of beginning antibiotic therapy. Similarly, procedures to relieve urinary retention, such as catheterization or medication adjustments, can provide prompt relief.
Chronic Conditions: Chronic urological conditions, such as benign prostatic hyperplasia (BPH), interstitial cystitis, or overactive bladder, may require longer-term treatment and lifestyle modifications for significant improvement. Patients may not notice significant changes in symptoms immediately but may experience gradual improvement over weeks to months as treatment progresses.
Medication Therapies: Some urological conditions, such as erectile dysfunction or urinary incontinence, may be treated with medications. The timeline for improvement with medication therapy can vary depending on the specific medication, dosage, and individual response. While some patients may experience improvement within a few weeks of starting medication, others may require several months of treatment before noticing significant changes.
Surgical Interventions: In cases where urological conditions require surgical intervention, such as kidney stone removal or prostate surgery, the timeline for improvement can depend on the complexity of the procedure and individual healing factors. While some patients may experience immediate relief of symptoms following surgery, others may require a period of recovery before noticing significant improvement.
Follow-up Care: Regardless of the type of treatment received, regular follow-up care with a urologist is essential to monitor progress, adjust treatment as needed, and address any new concerns that arise. Patients should communicate openly with their healthcare providers about their symptoms, concerns, and treatment goals to ensure the best possible outcomes.
Individual Factors: It's important to recognize that individual factors, such as overall health, underlying medical conditions, lifestyle habits, and adherence to treatment recommendations, can influence the timeline for improvement with urological treatment. Patients who are proactive about following their treatment plan and making necessary lifestyle changes may experience faster and more significant improvement in their symptoms.
In summary, the timeline for improvement with urological treatment can vary widely depending on the specific condition, treatment approach, and individual factors. While some patients may experience prompt relief of symptoms, others may require longer-term treatment and follow-up care for optimal outcomes. Open communication with healthcare providers and adherence to treatment recommendations are key factors in achieving the best possible results.
#best urologist in jaipur#urologist in jagatpura#urologist treatment in jaipur#best urologist in jagatpura
0 notes
Text
What Conditions Do Urologists Treat?
When it comes to matters of the urinary tract and male reproductive system, urologists are the specialists to turn to. Their expertise encompasses a wide range of conditions, from common urinary issues to complex reproductive disorders. In this article, we'll delve into the diverse array of conditions that urologists treat, shedding light on the breadth of their specialty and the vital role they play in healthcare.

Urinary Tract Infections (UTIs):
Urinary tract infections are among the most common conditions treated by urologists. These infections can affect any part of the urinary system, including the bladder, kidneys, ureters, and urethra. Urologists diagnose UTIs through various tests and prescribe appropriate antibiotics to clear the infection.
Kidney Stones:
Kidney stones are solid deposits of minerals and salts that form inside the kidneys or urinary tract. Urologists specialize in diagnosing and treating kidney stones, employing techniques such as lithotripsy (shock wave therapy), ureteroscopy, and surgical removal to manage these painful stones.
Benign Prostatic Hyperplasia (BPH):
BPH is a common condition in older men characterized by an enlarged prostate gland. Urologists help manage BPH symptoms, which can include urinary frequency, urgency, weak urine flow, and difficulty urinating. Treatment options range from medications to minimally invasive procedures like transurethral resection of the prostate (TURP) or laser therapy.
Prostate Cancer:
Prostate cancer is one of the most prevalent cancers among men. Urologists play a central role in diagnosing and treating prostate cancer, utilizing techniques such as prostate-specific antigen (PSA) testing, biopsies, surgery, radiation therapy, and hormone therapy to manage the disease.
Erectile Dysfunction (ED):
Erectile dysfunction, or impotence, is a common condition characterized by the inability to achieve or maintain an erection sufficient for sexual activity. Urologists evaluate the underlying causes of ED, which can range from physical factors like vascular disease to psychological issues, and offer treatment options such as medications, vacuum erection devices, penile implants, or counseling.
Urinary Incontinence:
Urinary incontinence refers to the involuntary loss of urine, which can be a source of embarrassment and frustration for affected individuals. Urologists assess the underlying causes of urinary incontinence, which may include bladder dysfunction, pelvic floor weakness, or nerve damage, and provide tailored treatment plans, including medications, behavioral therapies, and surgical interventions.
Male Infertility:
Urologists specialize in diagnosing and treating male infertility, which can stem from various factors such as sperm production disorders, obstructive abnormalities, or hormonal imbalances. They offer fertility evaluations, semen analysis, and advanced reproductive techniques such as in vitro fertilization (IVF), intracytoplasmic sperm injection (ICSI), and sperm retrieval procedures.
Conclusion:
The scope of conditions treated by urologists is vast and encompasses a wide range of urinary and reproductive disorders affecting both men and women. From common ailments like UTIs and kidney stones to complex conditions such as prostate cancer and male infertility, urologists provide comprehensive care and innovative treatments to improve patients' quality of life. If you're experiencing any urological symptoms or concerns, don't hesitate to consult a urologist for expert evaluation and personalized care. Your urological health is too important to overlook.
0 notes
Text
A Guide to Maintaining Good Reproductive Health as a Male
Reproductive health is not just a concern for women; it's equally important for men. While discussions around men's reproductive health may not be as prevalent, taking care of your reproductive system is crucial for overall well-being and fertility. Whether you're planning to start a family or simply want to maintain optimal health, here's a comprehensive guide to help you ensure your reproductive health remains in top shape.

Healthy Lifestyle Choices:
Diet: A balanced diet rich in fruits, vegetables, whole grains, lean proteins, and healthy fats provides essential nutrients like antioxidants, vitamins, and minerals necessary for reproductive health.
Exercise: Regular physical activity not only helps in maintaining a healthy weight but also improves blood circulation, which is vital for reproductive function.
Avoid Smoking and Excessive Alcohol: Smoking and excessive alcohol consumption have been linked to decreased sperm quality and fertility issues. Quit smoking and limit alcohol intake to protect your reproductive health.
Manage Stress: Chronic stress can affect hormone levels and sperm production. Practice stress-reducing activities such as meditation, yoga, or hobbies you enjoy.
Practice Safe Sex:
Use Condoms: Consistently using condoms not only prevents unwanted pregnancies but also protects against sexually transmitted infections (STIs) that can damage reproductive organs and fertility.
Get Tested: Regular STI screenings are essential, even if you're in a monogamous relationship. Early detection and treatment of STIs can prevent complications and preserve reproductive health.
Maintain a Healthy Weight:
Obesity has been associated with hormonal imbalances, reduced sperm quality, and fertility issues. Maintain a healthy weight through a combination of diet and exercise to support optimal reproductive function.
Protect Yourself from Environmental Hazards:
Avoid Exposure to Toxins: Certain chemicals found in pesticides, plastics, and pollutants can disrupt hormone levels and impair fertility. Minimize exposure to these toxins by choosing organic produce, using BPA-free products, and avoiding environmental pollutants whenever possible.
Protect Your Groin Area: Activities or occupations that involve prolonged sitting, tight clothing, or exposure to extreme heat (such as hot tubs or saunas) can raise scrotal temperature, which may negatively impact sperm production. Take breaks, wear loose-fitting clothing, and avoid excessive heat to protect your reproductive organs.
Practice Good Hygiene:
Maintain Genital Hygiene: Keeping the genital area clean and dry can help prevent infections and discomfort. Practice good hygiene by washing the genital area with mild soap and water regularly.
Check for Abnormalities: Perform regular self-exams to check for any lumps, swelling, or other abnormalities in the testicles or surrounding areas. Early detection of issues like testicular cancer is key to successful treatment.
Schedule Regular Check-ups:
Visit a Healthcare Provider: Regular visits to a healthcare provider are essential for monitoring reproductive health, discussing concerns, and receiving necessary screenings or treatments. Be open and honest with your healthcare provider about any symptoms or issues you may be experiencing.
Conclusion:
Maintaining good reproductive health as a male requires a combination of healthy lifestyle choices, safe practices, and regular monitoring. By prioritizing your reproductive health and adopting preventive measures, you can safeguard your fertility and overall well-being for years to come. Remember, proactive care today can lead to a healthier tomorrow.
0 notes
Text
What to Expect After Urological Surgery
Undergoing urological surgery can be a significant step towards improving urinary tract health and addressing various conditions affecting the bladder, kidneys, prostate, or reproductive organs. Whether it's a minimally invasive procedure or a more complex surgical intervention, understanding the recovery process is essential for patients and their caregivers. Here, we explore what the recovery journey typically entails after urological surgery and provide insights to help individuals navigate this period with confidence.

Immediate Postoperative Period
Immediately after urological surgery, patients are usually taken to a recovery area where they are closely monitored by medical staff. Depending on the type of surgery and anesthesia used, patients may experience varying degrees of grogginess, discomfort, or pain. Pain management medications are often administered to alleviate discomfort and promote a smoother transition to the recovery phase.
Hospital Stay vs. Outpatient Recovery
The length of hospital stay following urological surgery depends on several factors, including the complexity of the procedure, the patient's overall health, and the presence of any postoperative complications. While some surgeries may require an overnight stay or longer hospitalization for observation and recovery, others may be performed on an outpatient basis, allowing patients to return home the same day.
Managing Pain and Discomfort
Pain management is a crucial aspect of the recovery process after urological surgery. Patients are typically prescribed pain medications to help alleviate discomfort during the initial days following surgery. It's important to take these medications as directed by your healthcare provider and to communicate any concerns or changes in pain levels promptly.
Activity and Mobility
During the early stages of recovery, patients are encouraged to gradually increase their activity level while avoiding strenuous activities or heavy lifting. Light walking and gentle movement can help promote circulation, prevent blood clots, and aid in the healing process. It's essential to follow any activity restrictions provided by your healthcare team and to listen to your body's signals to avoid overexertion.
Dietary Considerations
Following urological surgery, patients may receive dietary recommendations to support healing and prevent complications such as constipation or urinary issues. Depending on the type of surgery and individual needs, dietary restrictions or modifications may be advised, such as increasing fluid intake, consuming a soft or bland diet, or avoiding certain foods that may irritate the urinary tract.
Monitoring and Follow-Up Care
After discharge from the hospital or surgical center, patients typically have scheduled follow-up appointments with their urologist to monitor recovery progress, address any concerns, and remove any surgical drains or catheters if necessary. These follow-up visits are an opportunity to discuss postoperative care instructions, review pathology results, and develop a long-term management plan tailored to the individual's needs.
Emotional Support and Coping Strategies
The recovery period after urological surgery can be physically and emotionally challenging for patients and their loved ones. It's normal to experience a range of emotions, including anxiety, frustration, or fatigue, during this time. Seeking support from family, friends, or support groups can provide valuable emotional support and coping strategies to navigate the ups and downs of the recovery journey.
Conclusion: A Journey Towards Healing and Wellness
While the road to recovery after urological surgery may have its ups and downs, it's important to remember that healing takes time and patience. By following your healthcare provider's guidance, staying proactive in your recovery efforts, and seeking support when needed, you can embark on a journey towards improved urological health and overall well-being. Remember to prioritize self-care, listen to your body's needs, and celebrate each milestone along the way as you progress towards a brighter, healthier future.
0 notes
Text
Can Urological Conditions be Prevented?
Urological conditions encompass a wide range of issues affecting the urinary system, including the kidneys, bladder, ureters, and urethra. These conditions can range from urinary tract infections to more serious issues like kidney stones or prostate problems. While some urological conditions may be unavoidable, there are steps individuals can take to reduce their risk and promote overall urological health.

Maintaining a Healthy Lifestyle:
One of the key ways to prevent urological conditions is by maintaining a healthy lifestyle. This includes eating a balanced diet rich in fruits, vegetables, and whole grains, as well as staying hydrated by drinking an adequate amount of water each day. Regular exercise is also important, as it can help maintain a healthy weight and reduce the risk of conditions like kidney stones.
Practice Good Hygiene:
Practicing good hygiene is essential for preventing urological conditions, particularly those related to the urinary tract. This includes ensuring proper cleanliness when using the restroom, wiping from front to back to prevent bacteria from entering the urethra. For women, it's also important to urinate before and after sexual activity to help prevent urinary tract infections.
Avoiding Risky Behaviors:
Certain lifestyle choices can increase the risk of urological conditions. For example, smoking is not only harmful to overall health but can also contribute to bladder cancer. Limiting alcohol consumption and avoiding recreational drug use can also help prevent urological issues. Safe sex practices are important for preventing sexually transmitted infections that can affect the urinary system.
Regular Check-ups:
Routine visits to a healthcare provider can help catch urological conditions early or even prevent them altogether. Regular screenings for conditions like prostate cancer or bladder issues can help detect problems before they become serious. Individuals with a family history of urological conditions may benefit from earlier or more frequent screenings.
Conclusion:
While not all urological conditions can be prevented, there are steps individuals can take to reduce their risk and promote overall urological health. By maintaining a healthy lifestyle, practicing good hygiene, avoiding risky behaviors, and scheduling regular check-ups, individuals can take proactive steps towards preventing urological issues. Remember, early detection and prevention are key in maintaining good urological health.
0 notes
Text
Exploring Common Urological Procedures: Understanding Diagnosis and Treatment Options
Introduction:
Urological procedures encompass a wide array of diagnostic and treatment interventions aimed at addressing various conditions affecting the urinary tract and male reproductive system. From diagnostic tests to surgical interventions, these procedures play a crucial role in diagnosing, managing, and treating urological disorders. Let's delve into some of the most common urological procedures and their applications in clinical practice.
1. Cystoscopy:
Cystoscopy is a diagnostic procedure used to visualize the inside of the bladder and urethra using a thin, flexible instrument called a cystoscope. It is commonly performed to evaluate urinary symptoms such as hematuria (blood in the urine), urinary incontinence, or recurrent urinary tract infections. During cystoscopy, the urologist can identify abnormalities such as bladder stones, tumors, or structural abnormalities and, if necessary, perform biopsies or interventions such as the removal of bladder stones or small tumors.
2. Urodynamic Testing:
Urodynamic testing encompasses a series of diagnostic procedures used to assess the function and dynamics of the urinary system, particularly the bladder and urethra. These tests evaluate parameters such as bladder capacity, urinary flow rate, bladder pressure, and sphincter function to diagnose conditions such as urinary incontinence, overactive bladder, or neurogenic bladder dysfunction. Urodynamic testing can help guide treatment decisions and interventions tailored to the underlying urological condition.
3. Transrectal Ultrasound (TRUS) and Prostate Biopsy:
Transrectal ultrasound (TRUS) is a diagnostic imaging technique used to visualize the prostate gland and surrounding structures using high-frequency sound waves. TRUS is commonly performed in conjunction with prostate biopsy, a procedure used to sample tissue from the prostate gland for histopathological analysis. Prostate biopsy is indicated in cases of suspected prostate cancer based on abnormal findings on digital rectal exam (DRE) or elevated prostate-specific antigen (PSA) levels. Guided by TRUS imaging, urologists can obtain tissue samples from specific areas of the prostate gland to confirm or rule out the presence of prostate cancer.
4. Lithotripsy:
Lithotripsy is a minimally invasive procedure used to break down kidney stones or urinary calculi into smaller fragments that can be passed naturally through the urinary tract. Extracorporeal shock wave lithotripsy (ESWL) is the most common type of lithotripsy, involving the use of shock waves generated externally to fragment kidney stones. Alternatively, ureteroscopy with laser lithotripsy may be performed for stones located in the ureter or kidney that are not amenable to ESWL. Lithotripsy offers a non-surgical approach to the management of kidney stones, minimizing the need for invasive procedures and promoting faster recovery.
5. Transurethral Resection of the Prostate (TURP):
Transurethral resection of the prostate (TURP) is a surgical procedure used to treat benign prostatic hyperplasia (BPH), or enlarged prostate, by removing excess prostate tissue that obstructs the flow of urine. During TURP, a special instrument called a resectoscope is inserted through the urethra to remove obstructing prostate tissue using a cutting or cauterizing device. TURP is considered the gold standard surgical treatment for BPH and can provide significant relief of urinary symptoms such as hesitancy, weak stream, and urinary retention.
Conclusion:
Urological procedures encompass a diverse range of diagnostic and treatment interventions aimed at addressing conditions affecting the urinary tract and male reproductive system. From minimally invasive procedures like cystoscopy and lithotripsy to surgical interventions such as TURP and prostate biopsy, these procedures play a crucial role in diagnosing, managing, and treating urological disorders, ultimately improving patients' quality of life and urological health.
0 notes
Text
When to Consider Consulting a Urologist: Signs It's Time for Expert Care
Introduction:
Maintaining optimal urological health is crucial for overall well-being, yet many individuals may hesitate to seek assistance from a urologist until symptoms become severe. Knowing when to consult a urologist can help address concerns promptly, leading to timely diagnosis and effective treatment. In this blog, we'll explore common signs and symptoms that indicate it's time to schedule an appointment with a urologist.
1. Persistent Urinary Issues:
Frequent or urgent urination, difficulty initiating or maintaining urination, and pain or discomfort during urination are all signs of potential urological problems. Conditions such as urinary tract infections (UTIs), bladder infections, kidney stones, and benign prostatic hyperplasia (enlarged prostate) can manifest with these symptoms. If you experience persistent urinary issues, it's advisable to seek evaluation by a urologist to determine the underlying cause and receive appropriate treatment.
2. Blood in Urine:
Hematuria, or blood in the urine, should never be ignored, as it can indicate various urological conditions, including urinary tract infections, kidney stones, bladder cancer, and kidney cancer. Whether the blood is visible to the naked eye (gross hematuria) or detected through microscopic analysis (microscopic hematuria), it warrants prompt evaluation by a urologist to rule out serious underlying pathology.
3. Erectile Dysfunction:
Erectile dysfunction (ED) is a common condition that can significantly impact quality of life and intimate relationships. While occasional episodes of ED are normal, persistent difficulties achieving or maintaining an erection may indicate an underlying health issue, such as cardiovascular disease, diabetes, or hormonal imbalance. Consulting a urologist can help identify the cause of ED and explore appropriate treatment options, which may include medications, lifestyle modifications, or specialized therapies.
4. Testicular Abnormalities:
Changes in the size, shape, or consistency of the testicles should be evaluated by a urologist, as they can be indicative of conditions such as testicular cancer, epididymitis (inflammation of the epididymis), or hydrocele (fluid accumulation around the testicle). Prompt assessment and diagnosis are crucial for timely intervention and optimal outcomes, particularly in the case of testicular cancer, which has high cure rates when detected early.
5. Prostate Health Concerns:
Men over the age of 50, and those with a family history of prostate cancer, should consider regular prostate screenings, including digital rectal exams (DRE) and prostate-specific antigen (PSA) tests. Symptoms such as frequent urination, difficulty urinating, blood in the semen, or persistent pelvic pain may also warrant evaluation by a urologist to assess prostate health and rule out conditions such as prostatitis or prostate cancer.
6. Infertility Issues:
Couples experiencing difficulty conceiving may benefit from consultation with a urologist specializing in male infertility. Factors such as low sperm count, abnormal sperm morphology, or obstructive issues within the reproductive tract can contribute to infertility in men. A urologist can perform comprehensive evaluations, including semen analysis and hormonal testing, to identify potential causes of infertility and recommend appropriate interventions or assisted reproductive techniques.
Conclusion:
Knowing when to seek guidance from a urologist is essential for addressing urological concerns in a timely manner and optimizing health outcomes. Whether experiencing urinary symptoms, sexual dysfunction, testicular abnormalities, or fertility issues, consulting a urologist can provide valuable insights, diagnosis, and personalized treatment plans tailored to individual needs. Prioritizing urological health through proactive care empowers individuals to lead healthier, more fulfilling lives.
0 notes