#technology news aggregator
Explore tagged Tumblr posts
Text
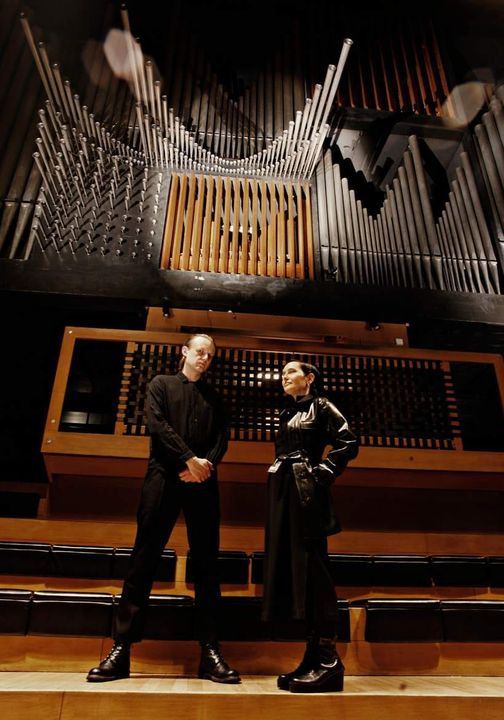

Dear Friends,
On November 29th-30th, the Aggregate, Electroacoustic Music Festival will take place in Berlin. This event merges tradition with electronic music, as through the use of MIDI, artists metaphorically awaken the spirit of the machine slumbering within the organ. Therefore, the festival features artists deeply connected to movements such as algorave—a type of event where the artist writes code in real-time, generating music—and electroacoustic traditions.
The festival’s approach to the relationship between musician and instrument is retro-futuristic, drawing from the ideas of electroacoustic avant-garde figures like Kotoński, Schaeffer, Varèse, Stockhausen, and many others. However, it raises new questions about how computer-controlled instrumental music, with its virtuosity, transcends the boundaries of perception in highly compressed musical events. It explores the intersections between electronic and acoustic music, objective interpretation, and the effects of mechanically precise performance.
Curators: gamut inc
Check the events: https://de.ra.co/events/1993705
#Electroacoustic#Music Festival#Berlin Events#Algorave#LiveCoding#MIDI#RetroFuturistic#AvantGarde Music#ElectroacousticTradition#Electronic Music#Organ Music#Sound Art#Virtual Virtuosity#Experimental Music#Music Technology#Aggregate Festival#GamutInc#RealTimeCoding#Musical Innovation#New Music#berlin
7 notes
·
View notes
Text
I'm flat out tired of seeing actual reputable news sources, real actual companies, and living, sentient people talking about investment in AI. Does nobody understand what this technology actually is.
my understanding is that large language models basically construct statistically likely combinations of words based upon enormous, sprawling aggregations of statistical data drawn from basically all written text on the entire internet. I've read a million articles explaining how AI works and I never learn anything new from them.
But I still feel like I'm constantly missing something because everybody seems to expect that in the near future chatGPT is going to like, transfigure into something other than a chatbot that aggregates an exceptionally large amount of information about how language tends to be constructed.
1K notes
·
View notes
Text
So, let me try and put everything together here, because I really do think it needs to be talked about.
Today, Unity announced that it intends to apply a fee to use its software. Then it got worse.
For those not in the know, Unity is the most popular free to use video game development tool, offering a basic version for individuals who want to learn how to create games or create independently alongside paid versions for corporations or people who want more features. It's decent enough at this job, has issues but for the price point I can't complain, and is the idea entry point into creating in this medium, it's a very important piece of software.
But speaking of tools, the CEO is a massive one. When he was the COO of EA, he advocated for using, what out and out sounds like emotional manipulation to coerce players into microtransactions.
"A consumer gets engaged in a property, they might spend 10, 20, 30, 50 hours on the game and then when they're deep into the game they're well invested in it. We're not gouging, but we're charging and at that point in time the commitment can be pretty high."
He also called game developers who don't discuss monetization early in the planning stages of development, quote, "fucking idiots".
So that sets the stage for what might be one of the most bald-faced greediest moves I've seen from a corporation in a minute. Most at least have the sense of self-preservation to hide it.
A few hours ago, Unity posted this announcement on the official blog.
Effective January 1, 2024, we will introduce a new Unity Runtime Fee that’s based on game installs. We will also add cloud-based asset storage, Unity DevOps tools, and AI at runtime at no extra cost to Unity subscription plans this November. We are introducing a Unity Runtime Fee that is based upon each time a qualifying game is downloaded by an end user. We chose this because each time a game is downloaded, the Unity Runtime is also installed. Also we believe that an initial install-based fee allows creators to keep the ongoing financial gains from player engagement, unlike a revenue share.
Now there are a few red flags to note in this pitch immediately.
Unity is planning on charging a fee on all games which use its engine.
This is a flat fee per number of installs.
They are using an always online runtime function to determine whether a game is downloaded.
There is just so many things wrong with this that it's hard to know where to start, not helped by this FAQ which doubled down on a lot of the major issues people had.
I guess let's start with what people noticed first. Because it's using a system baked into the software itself, Unity would not be differentiating between a "purchase" and a "download". If someone uninstalls and reinstalls a game, that's two downloads. If someone gets a new computer or a new console and downloads a game already purchased from their account, that's two download. If someone pirates the game, the studio will be asked to pay for that download.
Q: How are you going to collect installs? A: We leverage our own proprietary data model. We believe it gives an accurate determination of the number of times the runtime is distributed for a given project. Q: Is software made in unity going to be calling home to unity whenever it's ran, even for enterprice licenses? A: We use a composite model for counting runtime installs that collects data from numerous sources. The Unity Runtime Fee will use data in compliance with GDPR and CCPA. The data being requested is aggregated and is being used for billing purposes. Q: If a user reinstalls/redownloads a game / changes their hardware, will that count as multiple installs? A: Yes. The creator will need to pay for all future installs. The reason is that Unity doesn’t receive end-player information, just aggregate data. Q: What's going to stop us being charged for pirated copies of our games? A: We do already have fraud detection practices in our Ads technology which is solving a similar problem, so we will leverage that know-how as a starting point. We recognize that users will have concerns about this and we will make available a process for them to submit their concerns to our fraud compliance team.
This is potentially related to a new system that will require Unity Personal developers to go online at least once every three days.
Starting in November, Unity Personal users will get a new sign-in and online user experience. Users will need to be signed into the Hub with their Unity ID and connect to the internet to use Unity. If the internet connection is lost, users can continue using Unity for up to 3 days while offline. More details to come, when this change takes effect.
It's unclear whether this requirement will be attached to any and all Unity games, though it would explain how they're theoretically able to track "the number of installs", and why the methodology for tracking these installs is so shit, as we'll discuss later.
Unity claims that it will only leverage this fee to games which surpass a certain threshold of downloads and yearly revenue.
Only games that meet the following thresholds qualify for the Unity Runtime Fee: Unity Personal and Unity Plus: Those that have made $200,000 USD or more in the last 12 months AND have at least 200,000 lifetime game installs. Unity Pro and Unity Enterprise: Those that have made $1,000,000 USD or more in the last 12 months AND have at least 1,000,000 lifetime game installs.
They don't say how they're going to collect information on a game's revenue, likely this is just to say that they're only interested in squeezing larger products (games like Genshin Impact and Honkai: Star Rail, Fate Grand Order, Among Us, and Fall Guys) and not every 2 dollar puzzle platformer that drops on Steam. But also, these larger products have the easiest time porting off of Unity and the most incentives to, meaning realistically those heaviest impacted are going to be the ones who just barely meet this threshold, most of them indie developers.
Aggro Crab Games, one of the first to properly break this story, points out that systems like the Xbox Game Pass, which is already pretty predatory towards smaller developers, will quickly inflate their "lifetime game installs" meaning even skimming the threshold of that 200k revenue, will be asked to pay a fee per install, not a percentage on said revenue.

[IMAGE DESCRIPTION: Hey Gamers!
Today, Unity (the engine we use to make our games) announced that they'll soon be taking a fee from developers for every copy of the game installed over a certain threshold - regardless of how that copy was obtained.
Guess who has a somewhat highly anticipated game coming to Xbox Game Pass in 2024? That's right, it's us and a lot of other developers.
That means Another Crab's Treasure will be free to install for the 25 million Game Pass subscribers. If a fraction of those users download our game, Unity could take a fee that puts an enormous dent in our income and threatens the sustainability of our business.
And that's before we even think about sales on other platforms, or pirated installs of our game, or even multiple installs by the same user!!!
This decision puts us and countless other studios in a position where we might not be able to justify using Unity for our future titles. If these changes aren't rolled back, we'll be heavily considering abandoning our wealth of Unity expertise we've accumulated over the years and starting from scratch in a new engine. Which is really something we'd rather not do.
On behalf of the dev community, we're calling on Unity to reverse the latest in a string of shortsighted decisions that seem to prioritize shareholders over their product's actual users.
I fucking hate it here.
-Aggro Crab - END DESCRIPTION]
That fee, by the way, is a flat fee. Not a percentage, not a royalty. This means that any games made in Unity expecting any kind of success are heavily incentivized to cost as much as possible.

[IMAGE DESCRIPTION: A table listing the various fees by number of Installs over the Install Threshold vs. version of Unity used, ranging from $0.01 to $0.20 per install. END DESCRIPTION]
Basic elementary school math tells us that if a game comes out for $1.99, they will be paying, at maximum, 10% of their revenue to Unity, whereas jacking the price up to $59.99 lowers that percentage to something closer to 0.3%. Obviously any company, especially any company in financial desperation, which a sudden anchor on all your revenue is going to create, is going to choose the latter.
Furthermore, and following the trend of "fuck anyone who doesn't ask for money", Unity helpfully defines what an install is on their main site.
While I'm looking at this page as it exists now, it currently says
The installation and initialization of a game or app on an end user’s device as well as distribution via streaming is considered an “install.” Games or apps with substantially similar content may be counted as one project, with installs then aggregated to calculate the Unity Runtime Fee.
However, I saw a screenshot saying something different, and utilizing the Wayback Machine we can see that this phrasing was changed at some point in the few hours since this announcement went up. Instead, it reads:
The installation and initialization of a game or app on an end user’s device as well as distribution via streaming or web browser is considered an “install.” Games or apps with substantially similar content may be counted as one project, with installs then aggregated to calculate the Unity Runtime Fee.
Screenshot for posterity:
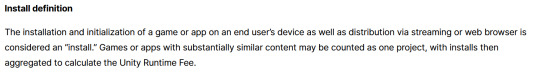
That would mean web browser games made in Unity would count towards this install threshold. You could legitimately drive the count up simply by continuously refreshing the page. The FAQ, again, doubles down.
Q: Does this affect WebGL and streamed games? A: Games on all platforms are eligible for the fee but will only incur costs if both the install and revenue thresholds are crossed. Installs - which involves initialization of the runtime on a client device - are counted on all platforms the same way (WebGL and streaming included).
And, what I personally consider to be the most suspect claim in this entire debacle, they claim that "lifetime installs" includes installs prior to this change going into effect.
Will this fee apply to games using Unity Runtime that are already on the market on January 1, 2024? Yes, the fee applies to eligible games currently in market that continue to distribute the runtime. We look at a game's lifetime installs to determine eligibility for the runtime fee. Then we bill the runtime fee based on all new installs that occur after January 1, 2024.
Again, again, doubled down in the FAQ.
Q: Are these fees going to apply to games which have been out for years already? If you met the threshold 2 years ago, you'll start owing for any installs monthly from January, no? (in theory). It says they'll use previous installs to determine threshold eligibility & then you'll start owing them for the new ones. A: Yes, assuming the game is eligible and distributing the Unity Runtime then runtime fees will apply. We look at a game's lifetime installs to determine eligibility for the runtime fee. Then we bill the runtime fee based on all new installs that occur after January 1, 2024.
That would involve billing companies for using their software before telling them of the existence of a bill. Holding their actions to a contract that they performed before the contract existed!
Okay. I think that's everything. So far.
There is one thing that I want to mention before ending this post, unfortunately it's a little conspiratorial, but it's so hard to believe that anyone genuinely thought this was a good idea that it's stuck in my brain as a significant possibility.
A few days ago it was reported that Unity's CEO sold 2,000 shares of his own company.
On September 6, 2023, John Riccitiello, President and CEO of Unity Software Inc (NYSE:U), sold 2,000 shares of the company. This move is part of a larger trend for the insider, who over the past year has sold a total of 50,610 shares and purchased none.
I would not be surprised if this decision gets reversed tomorrow, that it was literally only made for the CEO to short his own goddamn company, because I would sooner believe that this whole thing is some idiotic attempt at committing fraud than a real monetization strategy, even knowing how unfathomably greedy these people can be.
So, with all that said, what do we do now?
Well, in all likelihood you won't need to do anything. As I said, some of the biggest names in the industry would be directly affected by this change, and you can bet your bottom dollar that they're not just going to take it lying down. After all, the only way to stop a greedy CEO is with a greedier CEO, right?
(I fucking hate it here.)
And that's not mentioning the indie devs who are already talking about abandoning the engine.
[Links display tweets from the lead developer of Among Us saying it'd be less costly to hire people to move the game off of Unity and Cult of the Lamb's official twitter saying the game won't be available after January 1st in response to the news.]
That being said, I'm still shaken by all this. The fact that Unity is openly willing to go back and punish its developers for ever having used the engine in the past makes me question my relationship to it.
The news has given rise to the visibility of free, open source alternative Godot, which, if you're interested, is likely a better option than Unity at this point. Mostly, though, I just hope we can get out of this whole, fucking, environment where creatives are treated as an endless mill of free profits that's going to be continuously ratcheted up and up to drive unsustainable infinite corporate growth that our entire economy is based on for some fuckin reason.
Anyways, that's that, I find having these big posts that break everything down to be helpful.
#Unity#Unity3D#Video Games#Game Development#Game Developers#fuckshit#I don't know what to tag news like this
6K notes
·
View notes
Text
"Scientists have developed a way to dramatically reduce the cost of recycling certain electronic waste by using whey protein.
Their method allows for the easy recovery of gold from circuit boards at a cost of energy and materials amounting to 50 times less than the price of the gold they recover—these are the numbers that big business likes to see.
Indeed, the potential for scalability depends on this sort of cost savings, something traditional e-waste recycling methods just can’t achieve.
Professor Raffaele Mezzenga from ETH Zurich has found that whey protein, a byproduct of dairy manufacturing, can be used to make sponges that attract trace amounts of ionized gold.
Electronic waste contains a variety of valuable metals, including copper, cobalt, and gold. Despite gold’s public persona as being either money or jewelry, thousands of ounces of gold are used in electronics every year for its exceptional conductive properties.
Mezzenga’s colleague Mohammad Peydayesh first “denatured whey proteins under acidic conditions and high temperatures, so that they aggregated into protein nanofibrils in a gel,” writes the ETH Zurich press. “The scientists then dried the gel, creating a sponge out of these protein fibrils.”
The next step was extracting the gold: done by tossing 20 salvaged motherboards into an acid bath until the metals had dissolved into ionized compounds that the sponge began attracting.
Removing the sponge, a heat treatment caused the gold ions to aggregate into 22-carat gold flakes which could be easily removed.
“The fact I love the most is that we’re using a food industry byproduct to obtain gold from electronic waste,” Mezzenga says. In a very real sense, he observes, the method transforms two waste products into gold. “You can’t get much more sustainable than that!” ...
However the real dollar value comes from the bottom line—which was 50 times more than the cost of energy and source materials. Because of this, the scientists have every intention of bringing the technology to the market as quickly as possible while also desiring to see if the protein fibril sponge can be made of other food waste byproducts.
E-waste is a quickly growing burden in global landfills, and recycling it requires extremely energy-intensive machinery that many recycling facilities do not possess.
The environmental value of the minerals contained within most e-waste comes not only from preventing the hundreds of years it takes for them to break down in the soil, but also from the reduction in demand from new mining operations which can, though not always, significantly degrade the environments they are located in.
[Note: Absolutely massive understatement, mining is incredibly destructive to ecosystems. Mining is also incredibly toxic to human health and a major cause of conflict, displacement, and slavery globally.]
Other countries are trying to incentivize the recycling of e-waste, and are using gold to do so. In 2022, GNN reported that the British Royal Mint launched an electronically traded fund (ETF) with each share representing the value of gold recovered from e-waste as a way for investors to diversify into gold in a way that doesn’t support environmentally damaging mining.
The breakthrough is reminiscent of that old fairy tale of Rumpelstiltskin who can spin straw into gold. All that these modern-day, real-life alchemists are doing differently is using dairy and circuit boards rather than straw."
-via Good News Network, July 19, 2024
#ewaste#waste disposal#recycling#environment#e waste#e waste recycling#electronics#gold#mining#gold mining#wheyprotein#whey#chemistry#alchemy#good news#hope
497 notes
·
View notes
Text
Ending mass human deprivation and providing good lives for the whole world's population can be accomplished while at the same time achieving ecological objectives. This is demonstrated by a new study by the Institute of Environmental Science and Technology of the Universitat Autònoma de Barcelona (ICTA-UAB) and the London School of Economics and Political Science, recently published in World Development Perspectives. About 80% of humanity cannot access necessary goods and services and lives below the threshold for "decent living." Some narratives claim that addressing this problem will require massive economic growth on a global scale, multiplying existing output many times over, which would exacerbate climate change and ecological breakdown. The authors of the new study dispute this claim and argue that human development does not require such a dangerous approach. Reviewing recent empirical research, they find that ending mass deprivation and provisioning decent living standards for 8.5 billion people would require only 30% of current global resource and energy use, leaving a substantial surplus for additional consumption, public luxury, scientific advancement, and other social investments. This would ensure that everyone in the world has access to nutritious food, modern housing, high-quality health care, education, electricity, induction stoves, sanitation systems, clothing, washing machines, refrigerators, heating/cooling systems, computers, mobile phones, internet, and transport, and could also include universal access to recreational facilities, theaters, and other public goods. The authors argue that, to achieve such a future, strategies for development should not pursue capitalist growth and increased aggregate production as such but should rather increase the specific forms of production that are necessary to improve capabilities and meet human needs at a high standard, while ensuring universal access to key goods and services through public provisioning and decommodification. In the Global South, this requires using industrial policy to increase economic sovereignty, develop industrial capacity, and organize production around human well-being. At the same time, in high-income countries, less-necessary production (of things like mansions, SUVs, private jets and fast fashion) must be scaled down to enable faster decarbonization and to help bring resource use back within planetary boundaries, as degrowth scholarship holds.
July 25 2024
267 notes
·
View notes
Text
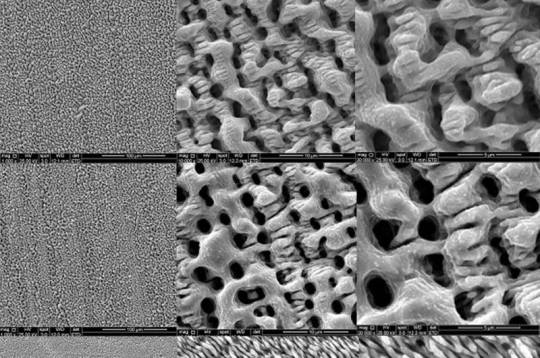
Laser-textured metal surfaces mimic shark skin to combat bacterial biofilms
Keeping work surfaces clean during meat processing is a challenge. Bacteria from meat can attach, grow, and build up to create a biofilm that is difficult to remove, even on stainless steel surfaces used in industrial facilities. It can also aggregate, clumping together into an invisible mass that is stronger than individual cells, making it harder to kill using food-grade antibacterial surface cleaners. In a paper published in the Journal of Laser Applications, researchers from the Hopkirk Research Institute, New Zealand Food Safety Science and Research Center, and Applied Technologies Group in New Zealand deliver key insights into a solution that could replace the current practice altogether: instead of constantly battling to prevent bacteria buildup, they created surfaces that stop bacteria from attaching in the first place. "Antimicrobial interventions currently approved and used commercially have a limited capacity to reduce well-established bacterial biofilms and spores, and complete decontamination is rarely achieved," author Sebastiampillai Raymond said.
Read more.
68 notes
·
View notes
Text
What, exactly, does a social network do? Is it a website that connects people with one another online, a digital gathering place where we can consume content posted by our friends? That’s certainly what it was in its heyday, in the two-thousands. Facebook was where you might find out that your friend was dating someone new, or that someone had thrown a party without inviting you. In the course of the past decade, though, social media has come to resemble something more like regular media. It’s where we find promotional videos created by celebrities, pundits shouting responses to the news, aggregated clips from pop culture, a rising tide of A.I.-generated slop, and other content designed to be broadcast to the largest number of viewers possible. The people we follow and the messages they post increasingly feel like needles in a digital haystack. Social media has become less social.
Facebook’s founder, Mark Zuckerberg, admitted as much during more than ten hours of testimony, over three days last week, in the opening phase of the Federal Trade Commission’s antitrust trial against Facebook’s parent company, Meta. The company, Zuckerberg said, has lately been involved in “the general idea of entertainment and learning about the world and discovering what’s going on.” This under-recognized shift away from interpersonal communication has been measured by the company itself. During the defense’s opening statement, Meta displayed a chart showing that the “percent of time spent viewing content posted by ‘friends’ ” has declined in the past two years, from twenty-two per cent to seventeen per cent on Facebook, and from eleven per cent to seven per cent on Instagram.
The F.T.C. is arguing that Meta maintained an illegal monopoly in the “personal social networking services” industry, in part by buying up Facebook’s competitors, such as Instagram, which the company acquired in 2012, and the messaging platform WhatsApp, which it acquired in 2014. But the F.T.C.’s definition of the social-media industry is hazy, and the antitrust case was already dismissed once, in 2021, partly because the “personal social networking services” market was too loosely defined. Meta’s counter-argument is, in a sense, that social media per se doesn’t exist now in the way that it did in the twenty-tens, and that what the company’s platforms are now known for—the digital consumption of all kinds of content—has become so widespread that no single company or platform can be said to monopolize it. In one of its slides at trial, Meta exhibited a graphic of a boxing ring showing the logos of Instagram, Facebook, and the various companies that Meta argues are competitors, including TikTok, YouTube, and Apple’s iMessage, though the F.T.C. doesn’t define any of those three as such. The company also used smartphone screenshots from the various apps to demonstrate how they’ve gravitated toward common formats: short video clips look similar on both Instagram and TikTok; messages look essentially the same in Instagram DMs as on Apple’s iMessage. Even as such similarities serve as helpful evidence for Meta’s defense, they also demonstrate how stultifying the entire online ecosystem has become. While in 2012 Facebook may have seemed singular and inescapable, now it looks like part of a crowded marketplace of apps competing to serve the same purpose.
The F.T.C.’s case, which originated during Donald Trump’s first term, entails reëvaluating business deals that it approved more than a decade ago, when the industry looked dramatically different. This makes the commission’s case less than airtight. Benedict Evans, an influential technology analyst, called the F.T.C.’s market definition of social networks “gerrymandering.” He told me, “By the F.T.C.’s definition, TikTok doesn’t compete with Facebook at all. Does that mean it would be O.K. for Facebook to buy TikTok?” Antitrust lawyers must prove that allegedly monopolistic practices cause consumer harm. In another antitrust case currently unfolding against Google, a court found that the company maintained a monopoly over parts of the online-advertising market by integrating its various automated advertising technologies, illegally privileging itself and harming its publishing customers by “reducing their revenue.” In the case of Meta, though, there is no price differential to point to—Meta’s platforms all allow users to access them for free—so the question of harm is less clear-cut.
The F.T.C. is arguing, instead, that Meta’s purported monopoly has led to a lack of innovation and to reduced consumer choice. But that, too, is difficult to prove in the case of Meta’s WhatsApp and Instagram acquisitions, because both sales occurred early in those companies’ life spans. In 2014, when WhatsApp was acquired, it had around half a billion users; now it has more than two billion. As Evans put it, the F.T.C. is arguing that “if Meta hadn’t bought WhatsApp, it would have become this voracious competitor.” He continued, “What we all actually know from following the history is that the founders of WhatsApp didn’t want to do any of the things that Meta did to fuel its runaway expansion. One of WhatsApp’s founders once compared the service’s goals to those of Craigslist, Zuckerberg recalled during his testimony. Meta, by contrast, aggressively pursued growth, loading WhatsApp with features such as social groups and video calls. The F.T.C. notes that market competition can result in “improved features, functionalities, integrity measures, and user experiences”; it’s hard to mount a persuasive argument that an independent WhatsApp would necessarily have provided more of those things than a Zuckerberg-owned one. (Many social networks fail; Path and Google+ were two other threats that Zuckerberg perceived, but neither grew into a viable competitor. He did at one point attempt to buy Snapchat, and though that company survived, it failed to become a major rival.)
One of the most surprising moments in Zuckerberg’s testimony came when the F.T.C. presented him with a memo that he sent to company executives, in 2018, suggesting that it might be better to spin Instagram into its own entity by choice. Zuckerberg wrote that Instagram was potentially undermining Facebook’s success, and that businesses that are independent often perform better than they would within a parent conglomerate. “Over time we may face antitrust regulation requiring us to spin off our other apps anyway,” he noted, with some prescience. Seven years ago, before the advent of TikTok and the diversification of content across digital platforms, that kind of split might have resulted in more varied products for users, more quickly—or it might not have. Either way, the social-media landscape today is arguably in the midst of a dramatic overhaul. TikTok may ultimately be banned; generative A.I. may supplant the existing model of an open, user-generated internet. On April 15th, the Verge broke the news that OpenAI is developing a social network of its own, to compete with the likes of Instagram and X. The F.T.C. may be chasing an old problem just as newer, bigger ones appear on the horizon.
This week, the European Union fined Apple and Meta for anticompetitive practices, but the penalties—five hundred million euros and two hundred million euros, respectively—are relatively modest. If the U.S. case prevails, the F.T.C. will have to decide whether to force a wholesale breakup of Meta or seek less dramatic “remedies.” One factor in this calculus might be the wishes of President Trump. In recent months, Zuckerberg has visited the White House repeatedly, and he’s ingratiated himself to the Administration with moves, at Meta, against D.E.I. and fact-checking. So far, despite a growing closeness with Silicon Valley, Trump has nevertheless continued to back the suit against Meta. As in the Administration’s ongoing trade war, Trump appreciates a pronounced threat as a tool to force a deal. Bytedance, the owner of TikTok, has all but capitulated to a mandated sale of a majority of the company. With regard to Trump, at least, Zuckerberg might be expected to capitulate one way or another.
33 notes
·
View notes
Text










Firebug - Pyrrhocoris apterus
Am I featuring this conspicuous insect too soon since the last post made in February? Perhaps I am. However, this post is a special one for a trifecta of reasons. Firstly, the finding of these Firebugs signifies the first find of the year and thusly the insect post photographed in 2025! I was out walking and to my surprise I found this cluster of individuals huddling against the base of a mallow tree. Nearby to them on other mallow trees, there were a few more small-sized aggregations. Likely they had all awoken from their overwintering among the dried leaves and the tree's hollows to enjoy the warm sun against their short-winged backs. They seemed slow and docile, and it's likely too early for them to form mating pairs, but such a gathering may help get things started as temperatures warm over the next few weeks. It's reassuring to see them active so early, but I hope that they aren't too early as we aren't truly safe from winter in Toronto until the beginning of May. Luckily these Bugs are resilient and can retreat under the protection of their tree until spring weather is stable. However, seeing them active and together among many trees gives me hope that spring has arrived a bit earlier. It also gives me incentive to leave the leaf coverage at our house alone a bit longer for all the insects dreaming beneath. Of course, I keep the leaves free of actual litter, and the Jolly Rancher wrapper seen in Picture 9 was removed afterwards.
As for the second reason, the timing of these pictures - literally 3 days ago - was perfect to welcome the first day of spring and the gradual return of warming weather. It's just something done on this blog every time the seasons change to honor the many insects seen throughout the year. With their crimson colors, these Red Bugs are perfect to get everyone excited for spring! Finally, today's post is a special one as it signifies a change in photography and videography equipment. Last month, I upgraded my phone and jumped from my Google Pixel 4 to a Google Pixel 8a. I hesitated a bit on this change, but the Pixel 4's battery and its ability to hold charges had recently deteriorated significantly. While I'm happy to have an upgraded phone, I'm deeply thankful for the Pixel 4's 5 years of loyal service and I'm especially thankful of how much it was able to capture and share here. Counting it up, the Pixel 4 has given the following in service to this blog:
24 gigabytes of insect pictures spread out over 7,008 pictures across 2020 to 2024
5.28 gigabytes of insect videos, spread out over 58 videos across 2020 to 2024
Countless more blurry pictures or small videos which were deleted during the insect observation process across 2020 to 2024
What a legacy to give, and a great technological companion for 5 years. If the 8a can achieve even half of that, I'd be satisfied. With the Pixel 8a, it works similarly to the 4 (with some refinements), and I've been learning the ins and outs while trimming most of the phone's bloat. These Firebugs represent the first step in relearning how to capture insects in a way that is natural but also clear, well-presented and artful to a degree. It immediate seems that it can better handle focusing and zooming in on insects, so hopefully this will carry into all future pictures (and videos too)! Image quality may change compared to what was shown previously, but hopefully it will be a positive change in the long run. Like the Pixel 4, I don’t intend to review the phone. I simply intend to continue to do my best and give these insects the showcasing they deserve. Lastly, thank you, dear reader, for taking the time to visit my blog, see the wonderful insects of Ontario (and other places), and read my writings and ramblings. You are appreciated, in every sense of the word.
Pictures were taken on March 18, 2025 with a Google Pixel 8a, the first showcase of many from a new phone. Happy First Day of Spring!

#jonny’s insect catalogue#ontario insect#firebug#common firebug#red bug#hemiptera#heteroptera#true bug#insect#blog announcement#toronto#march2025#2025#first day of spring#nature#entomology#invertebrates#arthropods#photography#animals
21 notes
·
View notes
Text
For a couple years, I worked in a video store in a small town. In many ways, this was the culmination of a childhood dream: routine, unchallenging labour. If you were a particularly annoying labour analyst, all I actually ever “did” was ring up rentals, restock returns in the morning, and clean the windows. Customer service has its own way of filling the space left by the actual work, though.
People who have worked retail are a sort of elite corps. For one thing, you’re never rude to another retail employee for the entire rest of your life. You’ve been in the trenches, too, and even if you somehow managed to escape, you’d still have had that shared trauma to know how bad that shift could get for that shelf-stocker at Maybe’s Drugs off I-40.
I have all the usual complaints, but there’s something else, too. My unique problem is this: I had this one customer who came in every Monday morning, asking for the same movie. We never had that movie, which is the crux of our conflict. He – and I can’t remember his name anymore, even if the electroshock therapy had been effective – never took “no” for an answer, and would come back the next week. He’d ask for the same thing, by title. No other details: no barcode, no publisher, no actors. Not even a description of the plot (he hadn’t seen it yet, obviously.) Now, this was before broadband internet was widely available, so I’d have to dial up after hours to America Online, and see if the movie had been added to their database. It never did, except one night I saw some folks talking about it in a video store chat room.
Their customers, too, were asking for this film. Insistently. After talking about it that night, we decided that we would form a bit of a trade union group. If any of us heard anything on this mysterious VHS, we would share the knowledge with the rest of the group. That retail-worker camaraderie at work again, you see. Nothing ever came of it, but I did end up becoming good friends with a manager at a Hobart’s Movies in Ames, Iowa, and we were even roommates for awhile before he got a new job at Seaworld. I moved on, too, making my slow, but inevitably in retrospect, drift towards the coast. Still, the whole thing bothered me. For years afterward, I would turn on my computer every Monday night, long after I had left the job, and search for any clue as to the existence of this film.
Once, on a day off, I called a librarian, who got pissy at me for even asking about it, and demanded to know who had put me up to calling her as a prank. I hung up in a panic, but she called back for hours. Obviously, she was also undergoing the same situation, and I felt shame at having brought a momentary pain to another proud Retail-American.
Now, video rental stores are a thing of the past. Even in small towns, they have been reduced to just a fond memory and an abandoned corner of a strip mall. Maybe my customer’s quest doesn’t matter anymore. The aggregation of the world’s knowledge into one hissing, unseen beast at the centre of our collective technological hallucination is complete. If they don’t have it, pick a different one. All I know is that, one day, someone will find a copy of this movie, and I’ll be able to go back to that town and shove it in the ground where the video store once stood. On that day, I can finally rest, freed from the slavedriver that is Mr. Magoo’s Christmas Carol.
328 notes
·
View notes
Text

LETTERS FROM AN AMERICAN
July 6, 2023
HEATHER COX RICHARDSON
JUL 7, 2023
The payroll processing firm ADP said today that private sector jobs jumped by 497,000 in June, far higher than the Dow Jones consensus estimate predicted. The big gains were in leisure and hospitality, which added 232,000 new hires; construction with 97,000; and trade, transportation and utilities with 90,000. Annual pay rose at a rate of 6.4%. Most of the jobs came from companies with fewer than 50 employees.
The Dow Jones Industrial Average, which is a way to measure the stock market by aggregating certain stocks, dropped 372 points as the strong labor market made traders afraid that the Fed would raise interest rates again to cool the economy. Higher interest rates make borrowing more expensive, slowing investment.
Today, as the Washington Post’s climate reporter Scott Dance warned that the sudden surge of broken heat records around the globe is raising alarm among scientists, Bloomberg’s Cailley LaPara reported that the incentives in the Inflation Reduction Act for emerging technologies to address climate change have long-term as well as short-term benefits.
Dance noted that temperatures in the North Atlantic are already close to their typical annual peak although we are early in the season, sea ice levels around Antarctica are terribly low, and Monday was the Earth’s hottest day in at least 125,000 years and Tuesday was hotter. LaPara noted that while much attention has been paid to the short-term solar, EV, and wind industries in the U.S., emerging technologies for industries that can’t be electrified—technologies like sustainable aviation fuel, clean hydrogen, and direct air capture, which pulls carbon dioxide out of the air—offer huge potential to reduce emissions by 2030.
This news was the backdrop today as President Biden was in South Carolina to talk about Bidenomics. After touting the huge investments of both public and private capital that are bringing new businesses and repaired infrastructure to that state, Biden noted that analysts have said that the new laws Democrats have passed will do more for Republican-dominated states than for Democratic ones. “Well, that’s okay with me,” Biden said, “because we’re all Americans. Because my view is: Wherever the need is most, that’s the place we should be helping. And that’s what we’re doing. Because the way I look at it, the progress we’re making is good for all Americans, all of America.”
On Air Force One on the way to the event, deputy press secretary Andrew Bates began his remarks to the press: “President Biden promised that he would be a president for all Americans, regardless of where they live and regardless of whether they voted for him or not. He also promised to rebuild the middle class. The fact that Bidenomics has now galvanized over $500 billion in job-creating private sector investment is the newest testament to how seriously he takes fulfilling those promises.”
Bates listed all the economic accomplishments of the administration and then added: “the most powerful endorsement of Bidenomics is this: Every signature economic law this President has signed, congressional Republicans who voted “no” and attacked it on Fox News then went home to their district and hailed its benefits.” He noted that “Senator Lindsey Graham called the Inflation Reduction Act ‘a nightmare for South Carolina,’” then, “[j]ust two months later, he called BMW’s electric vehicles announcement ‘one of the most consequential announcements in the history of the state of South Carolina.’” “Representative Joe Wilson blasted the Bipartisan Infrastructure Law but later announced, ‘I welcome Scout Motors’ plans to invest $2 billion and create up to 4,000 jobs in South Carolina.’ Nancy Mace called Bidenomics legislation a…‘disaster,’ then welcomed a RAISE grant to Charleston.”
“[W]hat could speak to the effectiveness of Bidenomics more than these conversions?” Bates asked.
While Biden is trying to sell Americans on an economic vision for the future, the Republican leadership is doubling down on dislike of President Biden and the Democrats. Early on the morning of July 2, Trump, who remains the presumptive 2024 Republican presidential nominee, shared a meme of President Biden that included a flag reading: “F*CK BIDEN AND F*CK YOU FOR VOTING FOR HIM!” The next morning, in all caps, he railed against what he called “massive prosecutorial conduct” and “the weaponization of law enforcement,” asking: “Do the people of this once great nation even have a choice but to protest the potential doom of the United States of America??? 2024!!!”
Prosecutors have told U.S. district judge Aileen Cannon that they want to begin Trump’s trial on 37 federal charges for keeping and hiding classified national security documents, and as his legal trouble heats up, Trump appears to be calling for violence against Democrats. On June 29 he posted what he claimed was the address of former president Barack Obama, inspiring a man who had been at the January 6 attack on the U.S. Capitol to repost the address and to warn, “We got these losers surrounded! See you in hell,…Obama’s [sic].” Taylor Tarranto then headed there with firearms and ammunition, as well as a machete, in his van. Secret Service agents arrested him.
Indeed, those crossing the law for the former president are not faring well. More than 1,000 people have been arrested for their participation in the events of January 6, and those higher up the ladder are starting to feel the heat as well. Trump lawyer Lin Wood, who pushed Trump’s 2020 election lies, was permitted to “retire” his law license on Tuesday rather than be disbarred. Trump lawyer John Eastman is facing disbarment in California for trying to overturn the 2020 election with his “fake elector” scheme, a ploy whose legitimacy the Supreme Court rejected last week. And today, Trump aide Walt Nauta pleaded not guilty to federal charges of withholding documents and conspiring to obstruct justice for allegedly helping Trump hide the classified documents he had at Mar-a-Lago.
Trump Republicans—MAGA Republicans—are cementing their identity by fanning fears based on cultural issues, but it is becoming clear those are no longer as powerful as they used to be as the reality of Republican extremism becomes clear.
Yesterday the man who raped and impregnated a then-9-year-old Ohio girl was sentenced to at least 25 years in prison. Last year, after the Supreme Court overturned the 1973 Roe v. Wade decision recognizing the constitutional right to abortion, President Biden used her case to argue for the need for abortion access. Republican lawmakers, who had criminalized all abortions after 6 weeks, before most people know they’re pregnant, publicly doubted that the case was real (Ohio Attorney General Dave Yost told the Fox News Channel there was “not a damn scintilla of evidence” to support the story). Unable to receive an abortion in Ohio, the girl, who had since turned 10, had to travel to Indiana, where Dr. Caitlin Bernard performed the procedure.
Republican Indiana attorney general Todd Rokita complained—inaccurately—that Bernard had not reported child abuse and that she had violated privacy laws by talking to a reporter, although she did not identify the patient and her employer said she acted properly. Bernard was nonetheless reprimanded for her handling of privacy issues and fined by the Indiana licensing board. Her employer disagreed.
As Republican-dominated states have dramatically restricted abortion, they have fueled such a backlash that party members are either trying to avoid talking about it or are now replacing the phrase “national ban” with “national consensus” or “national standard,” although as feminist writer Jessica Valenti, who studies this language, notes, they still mean strict antiabortion measures. In the House, some newly-elected and swing-district Republicans have blocked abortion measures from coming to a vote out of concern they will lose their seats in 2024.
But it is not at all clear the issue will go away. Yesterday, those committed to protecting abortion rights in Ohio turned in 70% more signatures than they needed to get a measure amending the constitution to protect that access on the ballot this November. In August, though, antiabortion forces will use a special election to try to change the threshold for constitutional amendments, requiring 60% of voters rather than a majority.
LETTERS FROM AN AMERICAN
HEATHER COX RICHARDSON
#Bidenomics#Joe Biden#economy#jobs#middle class#justice#Letters From an American#Heather Cox Richardson#infrastructure#climate change
256 notes
·
View notes
Text
The new technology, described in Nature Chemical Engineering and reported by Healio yesterday, was developed by researchers from MIT, Harvard Medical School, and the Broad Institute.
It delivers the long-acting contraceptive levonorgestrel through self-aggregating long-acting injectable microcrystals, or “SLIM,” that form an implant inside the recipient’s body after injection.
“Once injected, the drug microcrystals self-aggregate in the subcutaneous space to form a monolithic implant,” said Giovanni Traverso, MD, BChir, PhD, associate professor at MIT and physician at Harvard Medical School. In a press release, the researchers described the mechanism as “like tiny puzzle pieces that, once injected inside the body, undergo solvent exchange to assemble into a single solid implant that slowly releases the drug as the surface erodes.”
This solvent-exchange crystallization process, enabling administration with an ultra-thin 30-gauge needle, allows for “prolonged drug release” without requiring surgery.
It bypasses traditional medical oversight and dramatically increases the possibility of self-administration, which researchers claim would improve accessibility and “medication use.”
But this radical convenience comes at a cost.
9 notes
·
View notes
Note
Have you heard about what's happening on dreamwidth/FFA and volunteers talking about the dysfunction happening in the OTW and the CSEM incident?
I have! It's real fucked up!
(Blanket warning for discussion of CSAM/CSEM, as well as exposure to such in a volunteer context, in text and links below.)
For those who are unaware, failfandomanon (FFA) is an anonymous meme community on Dreamwidth for people to discuss all things fandom, serious or not. I think it tends towards kneejerk anti-purity wank, but it is one of the few places where people can talk openly about fandom things without it being traced back to a publicly identifiable handle. This context will become important later on.
You may remember last year AO3 got hit with emails containing CSAM and they had to lock everything down while they dealt with it.
A few days ago somebody on FFA asked about what happened re: the AO3 volunteers working through that period. Here is the tweet chain where I found out about it, with screencaps from FFA. Basically, said volunteers got a list of links to mental health hotlines and the names of people who volunteered themselves as resources for dealing with this stuff. Yeah. (As a tangent, the OTW has an estimated ~$2mm cash reserve. At no point did they decide to hire a counselor or any other sort of professional help to assist their volunteers in dealing with this.)
Impertinence has a good rundown of the timeline of events.
azarias, the person who became the defacto CSAM resource person (a truly horrifying statement), was traumatized dealing with this. The OTW used this opportunity to force her out because people on the Board didn't like her, realized they wouldn't have a defacto CSAM person, and reinstated her, expecting that she would go back to doing what she did previously. This goes beyond benign neglect into real actual harm inflicted upon volunteers.
Then! Then! THEN!! This message (FFA original) was sent out to everybody in the OTW volunteer Slack. Which basically says to volunteers "If we don't like you we'll come down on you like a ton of bricks if you talk about how we abused you."
I don't know who's keeping up on this on Twitter, but somebody started a Dreamwidth aggregating most of what you see above.
I know this is a lot of information to throw at people. I encourage you to read it and process at your own pace because this is important to understand. And while I believe this is trustworthy information (as far as I can tell), I'm not a substitute for your own personal judgment and brain.
It is clear to me the Organization of Transformative Works has abrogated its responsibility to its volunteers as people and as laborers on behalf of the organization. There is no formal mechanism for us as AO3 users or as people the organization claims to represent (members of fandom) to demand remediation on behalf of azarias or other volunteers who have been traumatized by this.
I expect there will be a lot more people than usual at the next board meeting (I do not see one scheduled currently), but they still don't really answer to us. If you donated at least $10 during the last pledge drive you're eligible to vote in the board elections, but that does not fix the current situation or the culture that lead to it.
As somebody who has been in fandom longer than some of you have been alive, and as somebody who's had an AO3 account since 2009, it grieves me to come to terms with the rot in the OTW culture, which is deeper than I could have imagined. It's one thing to see an organization drag its feet on things it promised to do years ago or misread the room regarding new technology. It is a whole other thing to have evidence it harmed people through active malice because they didn't like them and refused to make amends when confronted. That is not something I can support, regardless of what it may have done for fandom in the past.
#replies#Anonymous#otw#organization for transformative works#ao3#archive of our own#otw fuckery 2023
213 notes
·
View notes
Text
So you’ve written that our attention is getting fracked. What do you mean by that?
D. GRAHAM BURNETT: Fracking. I suspect most of your listeners have heard that term. Fracking is mostly associated with this idea of getting petroleum resources out of the earth. But it’s a new technology for doing that. In the old days, pre major exploitation of petroleum resources, there were these big, juicy zits of high-value crude oil just sitting there in the earth, waiting to geyser up if you tapped them. Drill a hole — whew, gusher.
We’ve tapped all that out. The only way you can get the remaining petroleum and natural gas resources out of the deep earth is to pump down in there high pressure, high volume detergent, which forces up to the surface this kind of slurry, mixture of natural gas, crude oil, leftover detergent, and juice and nasty stuff, which you then separate out, and you get your monetizable crude.
This is a precise analogy to what’s happening to us in our contemporary attention economy. We have a, depending on who you ask, $500 billion, $3 trillion, $7 trillion industry, which, to get the money value of our attention out of us, is continuously pumping into our faces high-pressure, high-value detergent in the form of social media and non-stop content that holds us on our devices. And that pumping brings to the surface that spume, that foam of our attention, which can be aggregated and sold off to the highest bidder.
— D. Graham Burnett, from “Ezra Klein Interviews D. Graham Burnett” (NY Times, May 31, 2024)
22 notes
·
View notes
Text
A small new trial published in the journal Nature Medicine describes what would be two firsts for Parkinson's disease, if they pan out: a diagnostic test and a potential immune-based treatment that works similarly to a vaccine. The research is still early, but researchers are excited by the prospect of advances for a disease that lacks good diagnostics and treatments.
The target of both innovations is alpha synuclein, a protein that takes an abnormal form in Parkinson's patients—aggregating in their brains and destroying nerve cells involved in motor and some cognitive functions. While researchers have long known that these proteins are involved in the disease, finding ways to measure and target them has not been easy.
The (potential) Parkinson's vaccine
The Florida-based biotech company Vaxxinity developed a vaccine, or what it calls an active immune medicine, to train the immune system to attack only abnormal versions of the protein—which are improperly folded—and not the regular forms. This would essentially help people's bodies treat themselves.
“The idea is that patients should recognize their own misfolded proteins, and it is personalized because their own immune systems are doing the work,” says Dr. Mark Frasier, chief scientific officer at the Michael J. Fox Foundation for Parkinson’s Research, which funded the testing part of the study.
The Parkinson's test
The new diagnostic test for Parkinson’s, which was developed by researchers at University of Texas and Vaxxinity, uses samples of cerebrospinal fluid to measure a person's levels of abnormal alpha synuclein. If the U.S. Food and Drug Administration (FDA) grants it full approval, it will become the first test for diagnosing Parkinson's. (The FDA classified it as a breakthrough device in 2019, a status that expedites access to innovative technologies where there is unmet need.) “Without [such a test], you’re kind of shooting in the dark,” says Mei Mei Hu, CEO and co-founder of Vaxxinity.
Alpha synuclein has been tricky to measure in the body for several reasons, says Frasier. While everyone has the protein, abnormal forms of it occur in relatively small amounts, so they're harder to detect via imaging. This type of alpha synuclein also tends to clump inside cells rather than outside of them, making it even harder to see. If clumps are large enough to become detectable, they can look structurally similar to amyloid or tau—the proteins implicated in Alzheimer’s disease—so imaging tests might misdiagnose people with Alzheimer’s rather than Parkinson’s.
Read More: Michael J. Fox: Chasing Parkinson's Treatments
The test overcomes those hurdles by cleverly exploiting normal forms of the protein. Parkinson’s experts believe that tiny amounts of abnormal alpha synuclein circulate in the spinal fluid of patients, but are too small to be detected through imaging. To run the new test in the study, researchers take normal forms of the protein in the lab and add them to samples of spinal fluid from patients; that prompts any misfolded protein that might be present in the samples to pull the normal proteins into misfolded aggregates, amplifying the signal for the abnormal form. Scientists then use a fluorescent probe to detect how much antibody to the misfolded protein patients generated, resulting in a biomarker, or stand-in for the treatment effect.
This test would be a critical advance because it makes it possible to identify patients with abnormal alpha synuclein at the earliest stages of the disease, when treatments might be more effective.
With more data from patients, researchers hope to further refine what different levels mean, so that the test will be able to tell not just if a person has Parkinson's but whether someone might be at a greater risk of developing it. Currently the test is only used in research studies, but more results like these—as well as data on whether the same process can be applied to blood samples—could speed the test to getting approved for wider use.
What the study found
The trial—conducted by researchers at the University of Texas, the Mayo Clinic, the Michael J. Fox Foundation for Parkinson’s Research, and Vaxxinity—included 20 people with Parkinson’s. It was just designed to test the safety of the approach, so the study only provided hints about the treatment's effectiveness. Everyone received three shots over nearly a year; some contained the treatment at different doses, and some contained a placebo.
Overall, people receiving the vaccine generated more antibodies against the abnormal alpha synuclein protein than those vaccinated with placebo, as measured by the Parkinson's test. Antibodies started to ramp up about four months after the vaccinations began.
“What is unique about our technology is that it can stimulate the immune system to produce very, very specific antibodies against toxic forms of alpha synuclein, and do it in a safe way, which is reassuring,” says Jean-Cosme Dodart, senior vice president of research at Vaxxinity and senior author of the paper.
According to the test results, about half of the patients in the trial showed high levels of antibodies against the misfolded alpha synuclein, and most of these patients received the highest dose of the vaccine. They also scored the highest on motor and cognitive tests. There were too few patients to adequately assess any changes of Parkinson’s symptoms, but the researchers believe that longer follow-up with those tests, and potentially more frequent or higher doses of the vaccine, could lead to improvements in those scores. “The results are very, very encouraging,” says Dodart.
“This paper demonstrates that in a small number of people, the vaccine is having an impact on misfolded alpha synuclein, which is really exciting,” says Frasier. “We are now in the biological era for Parkinson’s disease."
19 notes
·
View notes
Text
There's a lot of talk about Spotify "using AI in their latest wrapped," and jokes about how there's no way in hell anyone hand crafted previous years' wrapped, and while not wrong, I do think it is an oversimplification.
There's a difference between fine tuning an algorithm to aggregate a Wrapped vs using a GenAI out of the box. Spotify and YT already had automation running the show, but the difference is that genre categorization was probably originally done using graph theory and nodes—comparing which songs are often listened together, which artists often collaborate, and how people themselves classify the songs vs GenAI which opens ChatGPT or one of its competitors and types "Name a genre/vibe from these list of songs," and that's it.
It's not even an issue of neural networks. I'm certain you can use machine learning that analyzes the mp3/.wav files to classify songs for you, using songs everyone already knows the genres of as training data to calculate the unknowns. Van Halen is Metal, TSwift is Pop, Zedd is EDM, Kendrick Lamar is Hip-Hop and Rap (I listen to none of these people). Even lesser known but still sizeable indie artists with passionate fans can do some of the categorizing for your data.
To me, it's the difference between using a calculator vs. asking chatgpt to help you with math. They're both computers doing all the work, but one is actually tailor made for this purpose and the other is touted as a cyber cure all.
I'm a programmer myself. I've made and ran neural networks before, including LLMs, but I think there is a massive failure of communication regarding this shit. There's already a meme among programmers about how people boast "Their new AI service" and it's just an API to ChatGPT rather than actually taking what technologies run under the hood and deciding how and if it should be applied.
10 notes
·
View notes
Text
Unlocking the Power of Data: Essential Skills to Become a Data Scientist

In today's data-driven world, the demand for skilled data scientists is skyrocketing. These professionals are the key to transforming raw information into actionable insights, driving innovation and shaping business strategies. But what exactly does it take to become a data scientist? It's a multidisciplinary field, requiring a unique blend of technical prowess and analytical thinking. Let's break down the essential skills you'll need to embark on this exciting career path.
1. Strong Mathematical and Statistical Foundation:
At the heart of data science lies a deep understanding of mathematics and statistics. You'll need to grasp concepts like:
Linear Algebra and Calculus: Essential for understanding machine learning algorithms and optimizing models.
Probability and Statistics: Crucial for data analysis, hypothesis testing, and drawing meaningful conclusions from data.
2. Programming Proficiency (Python and/or R):
Data scientists are fluent in at least one, if not both, of the dominant programming languages in the field:
Python: Known for its readability and extensive libraries like Pandas, NumPy, Scikit-learn, and TensorFlow, making it ideal for data manipulation, analysis, and machine learning.
R: Specifically designed for statistical computing and graphics, R offers a rich ecosystem of packages for statistical modeling and visualization.
3. Data Wrangling and Preprocessing Skills:
Raw data is rarely clean and ready for analysis. A significant portion of a data scientist's time is spent on:
Data Cleaning: Handling missing values, outliers, and inconsistencies.
Data Transformation: Reshaping, merging, and aggregating data.
Feature Engineering: Creating new features from existing data to improve model performance.
4. Expertise in Databases and SQL:
Data often resides in databases. Proficiency in SQL (Structured Query Language) is essential for:
Extracting Data: Querying and retrieving data from various database systems.
Data Manipulation: Filtering, joining, and aggregating data within databases.
5. Machine Learning Mastery:
Machine learning is a core component of data science, enabling you to build models that learn from data and make predictions or classifications. Key areas include:
Supervised Learning: Regression, classification algorithms.
Unsupervised Learning: Clustering, dimensionality reduction.
Model Selection and Evaluation: Choosing the right algorithms and assessing their performance.
6. Data Visualization and Communication Skills:
Being able to effectively communicate your findings is just as important as the analysis itself. You'll need to:
Visualize Data: Create compelling charts and graphs to explore patterns and insights using libraries like Matplotlib, Seaborn (Python), or ggplot2 (R).
Tell Data Stories: Present your findings in a clear and concise manner that resonates with both technical and non-technical audiences.
7. Critical Thinking and Problem-Solving Abilities:
Data scientists are essentially problem solvers. You need to be able to:
Define Business Problems: Translate business challenges into data science questions.
Develop Analytical Frameworks: Structure your approach to solve complex problems.
Interpret Results: Draw meaningful conclusions and translate them into actionable recommendations.
8. Domain Knowledge (Optional but Highly Beneficial):
Having expertise in the specific industry or domain you're working in can give you a significant advantage. It helps you understand the context of the data and formulate more relevant questions.
9. Curiosity and a Growth Mindset:
The field of data science is constantly evolving. A genuine curiosity and a willingness to learn new technologies and techniques are crucial for long-term success.
10. Strong Communication and Collaboration Skills:
Data scientists often work in teams and need to collaborate effectively with engineers, business stakeholders, and other experts.
Kickstart Your Data Science Journey with Xaltius Academy's Data Science and AI Program:
Acquiring these skills can seem like a daunting task, but structured learning programs can provide a clear and effective path. Xaltius Academy's Data Science and AI Program is designed to equip you with the essential knowledge and practical experience to become a successful data scientist.
Key benefits of the program:
Comprehensive Curriculum: Covers all the core skills mentioned above, from foundational mathematics to advanced machine learning techniques.
Hands-on Projects: Provides practical experience working with real-world datasets and building a strong portfolio.
Expert Instructors: Learn from industry professionals with years of experience in data science and AI.
Career Support: Offers guidance and resources to help you launch your data science career.
Becoming a data scientist is a rewarding journey that blends technical expertise with analytical thinking. By focusing on developing these key skills and leveraging resources like Xaltius Academy's program, you can position yourself for a successful and impactful career in this in-demand field. The power of data is waiting to be unlocked – are you ready to take the challenge?
3 notes
·
View notes