#tech Solar
Explore tagged Tumblr posts
Text
I decided I need to draw more of my AUs 🤔
I’m motivating drawing the individually by putting the Solar’s in the AUs in the same room.
Techopolypse Au! Solar
[HR]Humanity’s restoration Au! Solar
Circus Au! Solar
And
[ICUA]Insanity consumes us all Au! Solar
Two of them are mentally unwell, one of them is mostly normal, and the other has been through over 3 years of a futuristic apocalypse.
This is going to be fun wiseman
#techopolypse au#tech Solar#tsams au#sams au#butcher Solar#icua Solar#Tragic Solar#icua au#circus au#HA au#chaos ensues
8 notes
·
View notes
Text

Setting Sail to Travel Through Space: 5 Things to Know about our New Mission
Our Advanced Composite Solar Sail System will launch aboard Rocket Lab’s Electron rocket from the company’s Launch Complex 1 in Māhia, New Zealand no earlier than April 23, at 6 p.m. EDT. This mission will demonstrate the use of innovative materials and structures to deploy a next-generation solar sail from a CubeSat in low Earth orbit.
Here are five things to know about this upcoming mission:
1. Sailing on Sunshine
Solar sails use the pressure of sunlight for propulsion much like sailboats harness the wind, eliminating the need for rocket fuel after the spacecraft has launched. If all goes according to plan, this technology demonstration will help us test how the solar sail shape and design work in different orbits.
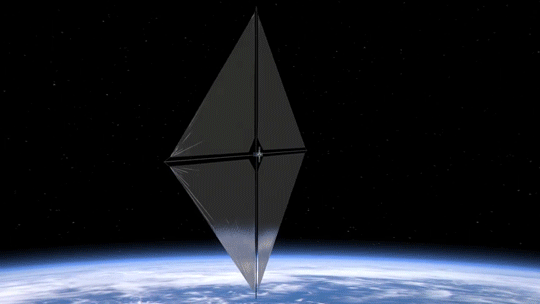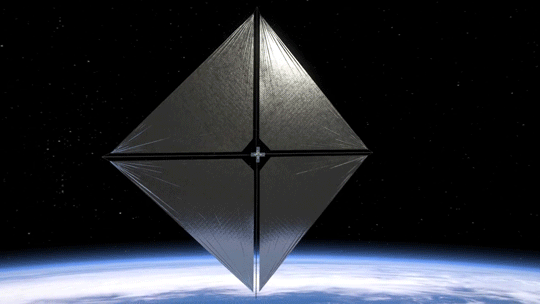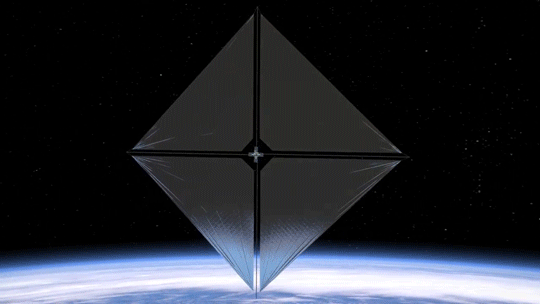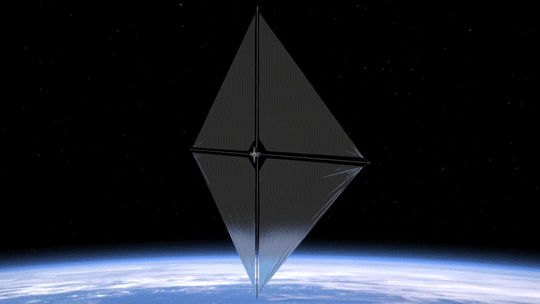
2. Small Package, Big Impact
The Advanced Composite Solar Sail System spacecraft is a CubeSat the size of a microwave, but when the package inside is fully unfurled, it will measure about 860 square feet (80 square meters) which is about the size of six parking spots. Once fully deployed, it will be the biggest, functional solar sail system – capable of controlled propulsion maneuvers – to be tested in space.

3. Second NASA Solar Sail in Space
If successful, the Advanced Composite Solar Sail System will be the second NASA solar sail to deploy in space, and not only will it be much larger, but this system will also test navigation capabilities to change the spacecraft’s orbit. This will help us gather data for future missions with even larger sails.

4. BOOM: Stronger, Lighter Booms
Just like a sailboat mast supports its cloth sails, a solar sail has support beams called booms that provide structure. The Advanced Composite Solar Sail System mission’s primary objective is to deploy a new type of boom. These booms are made from flexible polymer and carbon fiber materials that are stiffer and 75% lighter than previous boom designs. They can also be flattened and rolled like a tape measure. Two booms spanning the diagonal of the square (23 feet or about 7 meters in length) could be rolled up and fit into the palm of your hand!

5. It’s a bird...it’s a plane...it’s our solar sail!
About one to two months after launch, the Advanced Composite Solar Sail System spacecraft will deploy its booms and unfurl its solar sail. Because of its large size and reflective material, the spacecraft may be visible from Earth with the naked eye if the lighting conditions and orientation are just right!
To learn more about this mission that will inform future space travel and expand our understanding of our Sun and solar system, visit https://www.nasa.gov/mission/acs3/.
Make sure to follow us on Tumblr for your regular dose of space!
2K notes
·
View notes
Text
ECLIPSE :D!!!


#solar eclipse#ring of fire 2023#ecplise#the sun went bye bye#i don’t have the tech to photograph the sun just the ground#very very cool#there was visible cheering when it was fully ecplised#*audible#from the neighborhood#i got to see the whole ring of fire :)
2K notes
·
View notes
Text
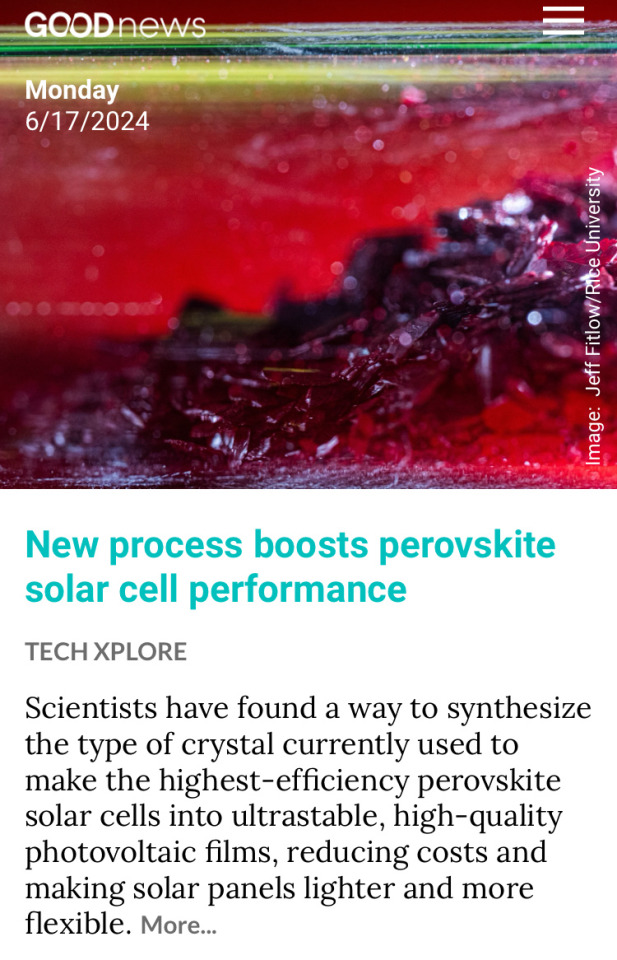
148 notes
·
View notes
Text

136 notes
·
View notes
Text

The Noor Power Plant in Ouarzazate, Morocco
source
#Morocco#marrakech#upload#solarpunk#solar field#solar power#solar plant#solar#tech#technology#reflection#light#energy#aerial view#earth from above#landscape#places#solar energy#Ouarzazate#noor power plant#Europe
515 notes
·
View notes
Text
totally love this: Solar panels that produce energy and water from the air.
The energy helps to extract the water which can be applied to the panels to help reduce temperatures, thereby improving energy output; or, the water can be dripped under the panels to grow crops (which also reduces temperature, in addition to providing food). OR, the water can be sent to a system for human use (needs minerals added to be safe for drinking; also may need some further decontamination to be safe to drink).
But basically the idea is that you can plop one of these down just about anywhere in the world, including extremely dry regions, and it will immediate help provide energy and drinking water. Put it over barren land, and you have an easy system for growing food.
I can envision large plots of formerly barren land, now providing electricity, food, and water. I can also see it being really helpful in developing areas, especially as the world's water crisis deepens. Really looking forward to seeing more and improved products like this.
p.s. pure water needs minerals added otherwise it messes up our cells. but minerals are just, like, bits of rock. So I'm curious if pure water can be made to drinking water more easily by putting it in the ground and letting it fill natural aquifers or wells or something like that. Maybe even a sort of specially dug "well" that aims to capture the water after it percolates through earth. I'm no expert on this. Thoughts?
30 notes
·
View notes
Text
Sara Benlafqih (photo) is a Moroccan industrial management engineer. She is also the CEO and one of the co-founders of agritech startup BMTA&C which develops innovative solutions to challenges like access to energy and food insecurity.
Through BMTA&C, she created a storage unit to help farmers extend the shelf life of their crops from 2 to 20 days. The unit uses a solar cooling system to help smallholder farmers in remote areas reduce crop losses in Morocco and the sub-region.
The said unit was inspired by a discovery Sara made during an academic internship. Indeed, she found out that farmers used to lose almost one-third of their harvest yearly just because they had no storage facility. The storage unit she created can now store up to six tons of fruit and vegetables without using coolants, which are harmful to the environment.
#solarpunk#solarpunk business#solarpunk business models#solar punk#startup#africa#farmers#solar power#morocco#women#women in tech
13 notes
·
View notes
Text
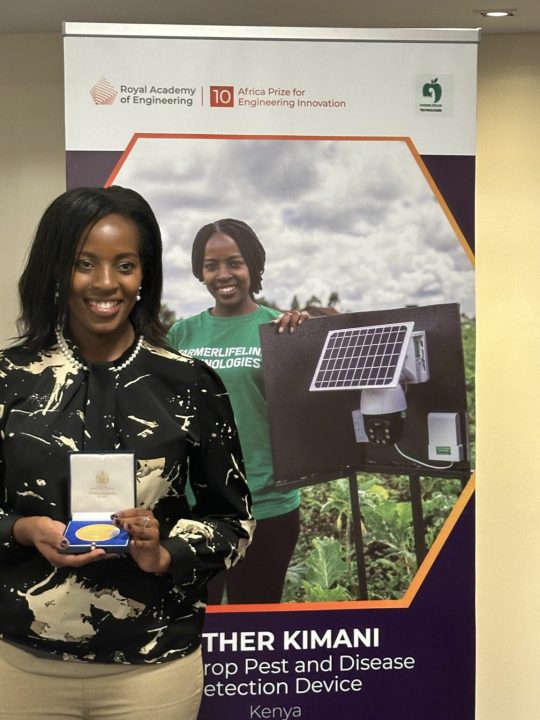

Esther Kimani, a computer programmer from Kenya, has won the UK’s Royal Academy of Engineering’s Africa Prize for Engineering Innovation. Her groundbreaking early crop pest and disease detection device wowed the judges, thanks to its remarkable ability to swiftly detect and identify agricultural pests and diseases. This innovative tool can reduce crop losses for smallholder farmers by up to 30% and boost yields by as much as 40%.
Harnessing the power of solar energy, the device employs computer vision algorithms and advanced machine learning to detect and identify crop pests, pathogens, or diseases, and the nature of the infection or infestation. Farmers receive notifications via SMS, making this an affordable alternative to traditional detection methods at just $3 per month—significantly cheaper than hiring drones or agricultural inspectors.
source
#solarpunk#solar punk#africa#ai#solarpower#agriculture#mobile tech#pest#solar power#solarpunk innovation#kenya#women#woman
17 notes
·
View notes
Photo

Paris Concept by Patrick Faulwetter
#fantasy art#fantasy#concept art#digital art#art#sci fi#science fiction#sci fi art#science fiction art#sf#sf art#cyberpunk#solar punk#street#paris#futuristic#high tech#balloon#hot air balloon#space craft#wind mill#street lamp#flying car#hover craft#patrick faulwetter
39 notes
·
View notes
Text
youtube
A lot has changed in the world of electric vehicles over the past five years. When we analyzed EV battery health (and published the original results in this blog post) in 2019, we found EV batteries degraded, on average, at 2.3% per year. Of course, some EVs performed better and others less well, but the average was surprisingly good. In 2024, we performed a new analysis and the results indicate that EV batteries have improved significantly, degrading at 1.8% per year on average. So how long do EV batteries last? Geotab research shows that EV batteries could last 20 years or more if they degrade at an average rate of 1.8% per year, as we have observed.
source
Whoa, that's really good news!
#youtube#youtube shorts#UFD Tech#geotab#electric vehicles#cars#batteries#good news#solar punk#electric dreams#electric cars
6 notes
·
View notes
Text

Let's Explore a Metal-Rich Asteroid 🤘
Between Mars and Jupiter, there lies a unique, metal-rich asteroid named Psyche. Psyche’s special because it looks like it is part or all of the metallic interior of a planetesimal—an early planetary building block of our solar system. For the first time, we have the chance to visit a planetary core and possibly learn more about the turbulent history that created terrestrial planets.
Here are six things to know about the mission that’s a journey into the past: Psyche.
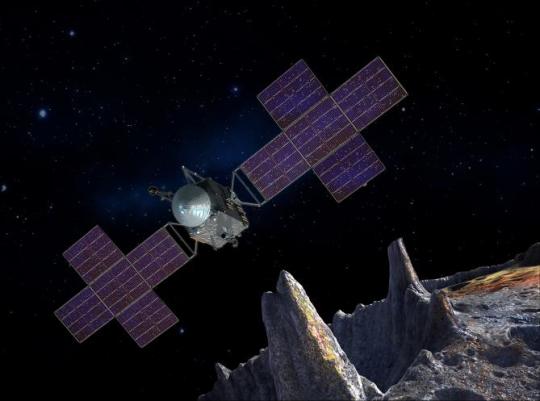

1. Psyche could help us learn more about the origins of our solar system.
After studying data from Earth-based radar and optical telescopes, scientists believe that Psyche collided with other large bodies in space and lost its outer rocky shell. This leads scientists to think that Psyche could have a metal-rich interior, which is a building block of a rocky planet. Since we can’t pierce the core of rocky planets like Mercury, Venus, Mars, and our home planet, Earth, Psyche offers us a window into how other planets are formed.

2. Psyche might be different than other objects in the solar system.
Rocks on Mars, Mercury, Venus, and Earth contain iron oxides. From afar, Psyche doesn’t seem to feature these chemical compounds, so it might have a different history of formation than other planets.
If the Psyche asteroid is leftover material from a planetary formation, scientists are excited to learn about the similarities and differences from other rocky planets. The asteroid might instead prove to be a never-before-seen solar system object. Either way, we’re prepared for the possibility of the unexpected!
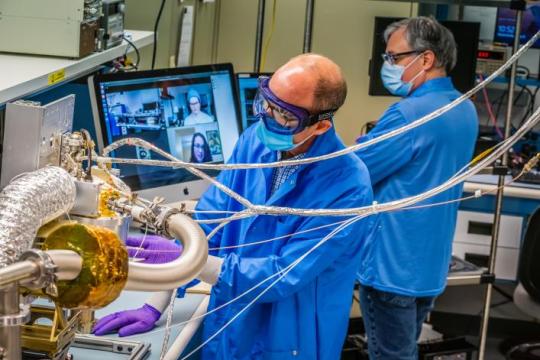
3. Three science instruments and a gravity science investigation will be aboard the spacecraft.
The three instruments aboard will be a magnetometer, a gamma-ray and neutron spectrometer, and a multispectral imager. Here’s what each of them will do:
Magnetometer: Detect evidence of a magnetic field, which will tell us whether the asteroid formed from a planetary body
Gamma-ray and neutron spectrometer: Help us figure out what chemical elements Psyche is made of, and how it was formed
Multispectral imager: Gather and share information about the topography and mineral composition of Psyche
The gravity science investigation will allow scientists to determine the asteroid’s rotation, mass, and gravity field and to gain insight into the interior by analyzing the radio waves it communicates with. Then, scientists can measure how Psyche affects the spacecraft’s orbit.
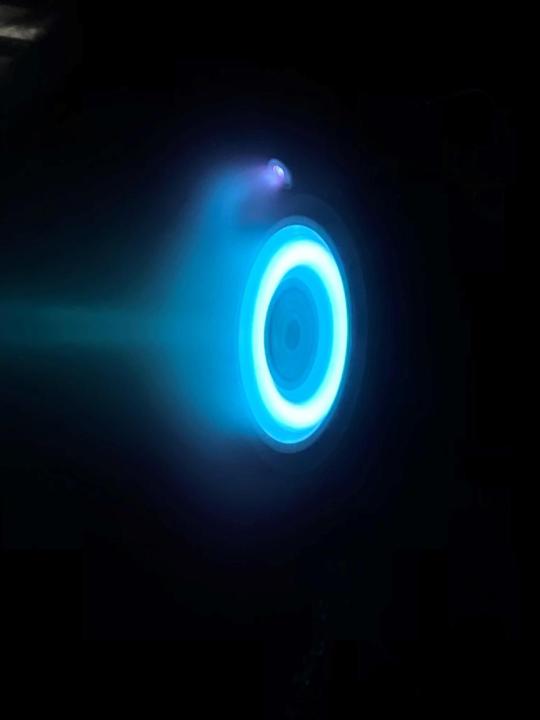

4. The Psyche spacecraft will use a super-efficient propulsion system.
Psyche’s solar electric propulsion system harnesses energy from large solar arrays that convert sunlight into electricity, creating thrust. For the first time ever, we will be using Hall-effect thrusters in deep space.

5. This mission runs on collaboration.
To make this mission happen, we work together with universities, and industry and NASA to draw in resources and expertise.
NASA’s Jet Propulsion Laboratory manages the mission and is responsible for system engineering, integration, and mission operations, while NASA’s Kennedy Space Center’s Launch Services Program manages launch operations and procured the SpaceX Falcon Heavy rocket.
Working with Arizona State University (ASU) offers opportunities for students to train as future instrument or mission leads. Mission leader and Principal Investigator Lindy Elkins-Tanton is also based at ASU.
Finally, Maxar Technologies is a key commercial participant and delivered the main body of the spacecraft, as well as most of its engineering hardware systems.

6. You can be a part of the journey.
Everyone can find activities to get involved on the mission’s webpage. There's an annual internship to interpret the mission, capstone courses for undergraduate projects, and age-appropriate lessons, craft projects, and videos.
You can join us for a virtual launch experience, and, of course, you can watch the launch with us on Oct. 12, 2023, at 10:16 a.m. EDT!
For official news on the mission, follow us on social media and check out NASA’s and ASU’s Psyche websites.
Make sure to follow us on Tumblr for your regular dose of space!
#Psyche#Mission to Psyche#asteroid#NASA#exploration#technology#tech#spaceblr#solar system#space#not exactly#metalcore#but close?
2K notes
·
View notes
Text
Making my own post because now capitalism is just revolving in my brain and I want to respond, but I've intruded more than enough. ^^"
I do think capitalism can be solved, and history actually gives me hope because it shows the fundamental need of society. Humans aren't inherently greedy or cruel. The greed and the cruelty are symptoms of a long-standing human need to make things better than they were before: to live comfortably, and without fear.
Capitalism is merely the current expression of this need that we live in.
Solving the need is absolutely possible by establishing a baseline standard of living and resource allotment. And that's comparable to an amount of 'work' that we deem acceptable in our daily lives. Because if you think about it, making coffee every morning with a Keurig gets you a similar product to making coffee every morning with a hand grinder and cold press: one just takes more resources and time than the other.
However, this needs to be flexible because humans are individuals with different needs, and the premise is also questionable because who's setting this baseline anyway?
I personally think it has more to do with government setting a cap on resource imports. (I think it should be stronger than tariffs, personally. Just a hard cap for the year.)
You can't really control demand. That's what most socialists do, and it always fails because humans fundamentally want to make their lives easier. But you can control resource management. If the government says we can only import 20 tons of cotton this year, and we produce 80 tons of cotton, so companies get 100 tons of cotton to do whatever with, and that's it. If we want more cotton, we have to axe some other import.
It 1) makes management visual. 2) gives citizens a personal reason to be invested in their government. 3) will not allocate resources fairly, but will show the true value of a product for the region it's in and prioritize local resources [i.e. if your country does not produce garnets, garnets will be more expensive than gold]. 4) increases jobs since there's far less incentive to outsource work, overall decreasing inequality. 5) encourages a circular economy.
In which case, I suppose I'm for some form of socialist autarky and I think that would solve a decent number of capitalist problems. Companies could no longer overrun workers and there's individual choice behind jobs, work, and some form of style of living.
It IS bad in like- fifty million other ways though. You can't just go from a country used to living in a capitalist society to imposing tariffs and screaming about autarky. Natural resources WILL be destroyed on your own soil and the biggest nation will have the highest quality of living. Imports have to be on a factor of population growth and this might only be possible with nations for a declining population rate. If at all. You also have to add a judicial angle for the people who will inevitably try to take over that system. And, most of all, you have to commit to not going to fucking war over state expansion for resources. Looking at you, Russia.
So I suppose we COULD solve capitalism, at the expense of a whole lot of other problems that are equally meh-to-bad.
Governments are fundamentally resource management machines though, and it's really stupid to pretend they aren't. With resource management, comes capping the fuck out of companies (specialists) that abuse the system (monopolies/oligarchies). When a government doesn't do that (whatever the method), it's failed its purpose as a government and also needs to be put down (revolution).
#Walking through this in my head and it's actually a bit bleaker than I thought. That is fundamentally the solution though. If you#had an autarky (with copious imports) you /can/ balance that budget but EVERYONE on the fucking planet has to be committed.#Otherwise you're just back to the Bronze Age. Rinse and repeat.#But I think there is hope because technology DOES upset that cycle. Tech DOES mean we can recycle resources more efficiently#than ever before and use nuclear/solar/wind power that doesn't necessitate human intervention. If we prioritize energy into regrowth#rather than production I think we could see substantial change into a circular economy that would shift the cycle of resource boom and bust#My dream is to run a hydrometallurgical plant on a fault line for the production of base and precious metals.#Low yield but not energy intensive and no damage to the environment.#ptxt#jesus christ alright I've thought enough about resources. xD Time to go write the Liztlie AU.#... I'm just kind of dwelling on all the problems with autarky now.
5 notes
·
View notes
Text
#good news#science#environmentalism#environment#climate change#climate crisis#green energy#wind turbines#solar energy#tech#technology#green technology
82 notes
·
View notes
Text
I cannot recommend this podcast interview with Cory Docotorow enough. It's about so much more than green tech and enshittification. anyone who uses the internet should listen.
#podcast#podcasts#Cory Docotorow#solar punk#green energy#climate change#climate crisis#enshittification#internet#tech bros#technology#canada#european union#monopoly#right to repair#capitalism is a scam#privacy#green technology#cars#computers#linux#social media#neoliberalism#economics#economy#fair trade#open source#union workers#labor vs capital#labor movement
5 notes
·
View notes
Video
Lava and debris brighten Mercury's surface by European Space Agency Via Flickr: This is one of a series of images taken by the ESA/JAXA BepiColombo mission on 8 January 2025 as the spacecraft sped by for its sixth and final gravity assist manoeuvre at the planet. Monitoring camera 2 (M-CAM 2) took this photo at 07:17 CET, when the spacecraft was about 2103 km from the planet’s surface. The spacecraft’s closest approach of 295 km took place on the planet's night side at 06:59 CET. The bright patch near the planet's upper edge in this image is the Nathair Facula, the aftermath of the largest volcanic explosion on Mercury. At its centre is a volcanic vent of around 40 km across that has been the site of at least three major eruptions. The explosive volcanic deposit is at least 300 km in diameter. Nathair Facula is a major target for several BepiColombo instruments, which will measure the composition of the erupted material. This will teach us about what Mercury is made of, and how the planet formed. Also visible is the relatively young Fonteyn crater, which formed a ‘mere’ 300 million years ago. Its youth is apparent from the brightness of the impact debris that radiates out from it. Older material on Mercury's surface has become much darker from weathering as it aged. Rustaveli, seen roughly in the centre of Mercury in this image, is about 200 km in diameter. Within its rim is a ring of peaks, making it a so-called peak ring basin. These peaks barely poke above smooth material on Rustaveli’s floor, which suggests the crater has been flooded by lava. Interestingly, NASA’s Messenger spacecraft detected a magnetic signal coming from Rustaveli. When molten rock such as lava or impact melt solidifies, magnetic carriers within it align with the direction of the planet's magnetic field. As the planetary magnetic field naturally changes over time, eventually the 'locked in' magnetic field in the planet's crust no longer agrees with the planetary magnetic field, something that can be detected from space. BepiColombo's two magnetometer instruments will investigate this further. In the foreground of the image, the Mercury Planetary Orbiter’s medium gain antenna (top centre) and magnetometer boom (right) are visible. [Technical details: This image of Mercury's surface was taken by M-CAM 2 onboard the Mercury Transfer Module (part of the BepiColombo spacecraft), using an exposure time of 4 millseconds. Taken from a distance of around 2103 km, the surface resolution in this photograph is around 2330 m/pixel. The image has been lightly processed; its brightness and contrast have been adjusted.] [Image description: Planet Mercury in the background with its grey, cratered, pockmarked surface. In the foreground are some spacecraft parts.] Credits: ESA/BepiColombo/MTM; CC BY-SA 3.0 IGO
#BepiColombo#Bepi#MPO#MTM#Mercury#Solar System#JAXA#Aerospace#宇宙航空研究開発機構#ISAS#MMO#水星探査計画BepiColombo#水星磁気圏探査機MMO#水星探査#ESA#European Space Agency#Space#Universe#Cosmos#Space Science#Science#Space Technology#Tech#Technology#flickr
5 notes
·
View notes
