#single inlet blower
Explore tagged Tumblr posts
Text
Revolutionizing Cement Transfer: The Air Chain Conveyor Solution
Introduction
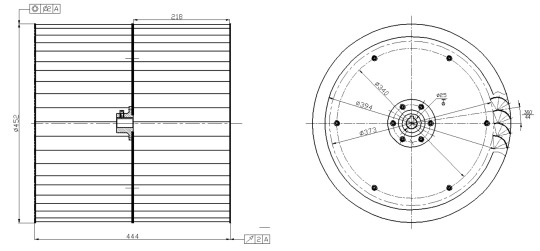
Company S operates six Φ18×35 cement silos. As shown in the diagram, there are air transport chutes under silos 1, 2, 3, and 4, 5, 6 to convey materials to the outside elevator. In August 2020, the company planned to increase its cement varieties. This required transferring cement from silo 4 to the chute under silos 1, 2, and 3. Due to the high transfer volume (300 m³/h) and the small height difference between the feed and discharge points, installing an air transport chute was not feasible. Other equipment options were either energy-intensive, prone to wear, or incompatible, making the selection and design process difficult.At this point, the storage and transportation department learned about Darko's air chain conveyor. They contacted Darko's technical team. After a site survey and extensive discussions, they finalized the technical plan to use the air chain conveyor. The order was placed at the end of 2020. Due to tight production schedules, installation only started in July 2021 and was completed within the month. The system performed exceptionally well and met all expectations. Here are the key technical features of the project:

1. Guaranteed Process Height
The air chain conveyor can transport materials horizontally. The design moves material from silo 4 to the chute under silo 2. This setup involves an approximately 135° bend. To save on height, we implemented two measures:
First, we changed the feed method at the inlet of the first air chain conveyor from the usual top feed to a side feed. This adjustment allows the material to drop directly from the silo's discharge valve to the side of the equipment, saving about 500 mm of space.
Second, at the junction of the two air chain conveyors, we switched from the typical vertical overlap to a horizontal overlap. The discharge from the first conveyor feeds into the side of the second conveyor. Due to the 135° angle, this horizontal overlap created a triangular area where material could accumulate, potentially hindering transport. To prevent material buildup, we installed an air cushion at the junction, supplied by a common Roots blower. This significantly reduced resistance, ensuring smooth material flow. As a result, this design saved about 1000 mm in process height, allowing material from silo 4 to enter the chute under silo 2 smoothly.

2. Rational Equipment Selection
For a transfer volume of 300 m³/h, a simple layout with a single device and minimal angles could typically use the FUK630 model. However, given the current process requirements, particularly the 135° junction and end discharge, we opted for the FUK800. After several months of operation, we found that this model met the 300 m³/h requirement and handled sudden increases in pressure within the silo without causing blockages.

3. Low Energy Consumption
The specifications for the two air chain conveyors are as follows: the first is FUK800×13.5 meters with a power of 5.5 kW, and the second is FUK800×31.7 meters with a power of 11 kW. Both conveyors share a single 18.5 kW Roots blower for air supply, resulting in a total transport distance of 45.2 meters and total power consumption of 35 kW. This is slightly higher than the FUK630 (30 kW) but significantly lower than traditional chain conveyors (75–90 kW), achieving over 50% energy savings. Additionally, the slightly lower chain speed enhances the lifespan of the conveyor while maintaining complete shell sealing, meeting all environmental standards.
Conclusion
While selecting high-performance equipment is essential, the design of the process based on equipment characteristics and site conditions is equally important. The success of the technical solutions depends on how well the equipment features align with the specific situation. Many users prioritize this aspect. Design experience is also invaluable in this process, so it is crucial to choose not only the right equipment but also an experienced manufacturer.
If you are interested in our technical solutions or need further information, please feel free to contact us. We are happy to help!
0 notes
Text
HOW TO CHOOSE INDUSTRIAL VACUUM CLEANER?
Today tons of wastes are generated by different industries on a daily basis. Most industries are facing challenges to get the waste cleaned. Roots Multiclean Ltd focuses to help industries solve their cleaning problem by providing the right Industrial Vacuum Cleaner (IVC) that is designed for continuous duty and reliable solutions for cleaning dusts, solids, and liquids.
Before choosing an industrial vacuum cleaner, let us know about two important things:- 1) What is IVC? 2) What are the things to be considered while choosing an IVC?
1. What is industrial vacuum cleaner?
Industrial Vacuum Cleaner is a machine used for the general cleaning in industrial environment, Industrial vacuum cleaners are designed to meet specific needs of users and particular tasks that are generally heavy to handle. It is provided with a side-channel blower that is powerful, silent, and suitable for performing round the clock.
The IVC ranges start from 1.8KW to 45KW suitable for various types of industries like Food, Pharmaceutical, Steel, Cement, Foundry, Textiles, Power plants, fertilizers, Bio labs, Engineering, and Automobile sectors available in a standalone, movable, fixed vacuum, online vacuuming, centralized vacuum system, and Truck mounted vacuum.
2. What are the things to be considered while choosing an IVC?
Once you get an idea about IVC you need to consider certain things before picking up the right industrial vacuum cleaner based on Power, Performance, Filtration, Quality & Durability, and Capacity.
2.1 Power:
In general, power is expressed in W (Watts) & kW (kiloWatt). Our product lineup is equipped with single-phase and three-phase motors, which ensures the efficient vacuuming of debris for long period.
2.2 Performance:
The performance of IVC is determined by the Vacuum pressure and Airflow.
Vacuum pressure represents the suction force to clean up the dusts, solids, and liquids. It is also called “Depression”. The top depression rate value is taken by mmH2O (millimeters of Water Column), mbars, or others pressure measures.
Air flow is measured by m3/h (cubic meters per hour), Liters/sec. It refers to the volume of air moved by the suction unit. The top airflow rate is measured with a suction inlet completely open.
2.3 Filtration:
The most important thing to consider is Filtration. Our Industrial Vacuum Cleaners are equipped with various types of primary filters and HEPA filters to accomplish high filtration efficiency which ensures the exhaust air is free from dust particles.
Primary filters generally have relatively low permeability. To achieve a reasonably low-pressure drop through the filter, the element area (surface area) must be increased. Quality of the filtration increases by large filter surface area to achieve better efficiency.
2.4 Collection tank:
It’s also an important thing to consider the capacity while choosing an Industrial Vacuum Cleaner. It depends on the size of the disposal tank. For continuous operations, you need a large collection unit to remove residuals and it is also easy to detach the collection container with rotatable castor wheels for easy transportation of dust collected.
2.5 Quality & durability:
Another element to be considered is Quality and Durability. All Industrial Vacuum Cleaners are provided with sturdy steels chassis to withstand for many years. When evaluating durability, the machine construction is designed and developed to work for the rugged nature of factories, where other industrial vacuum cleaners fail to do.
Conclusion:
On the market, there are many industrial vacuum cleaners available that differ by their performance, and applications. In the decision-making stage, it’s always better to hear from the professionals to guide you to choose the right Industrial Vacuum Cleaners. To know more about our Industrial Vacuum Cleaners visit our page
Read more posts: THE ROLE OF INDUSTRIAL VACUUM CLEANERS IN MANUFACTURING SECTORS VACUUM CLEANER BUYING GUIDE: FACTORS TO CONSIDER BEFORE PURCHASE
0 notes
Text
The Industrial dampers emerges as the silent main character amidst the intricate coordination of air movement within ducts, chimneys, and diverse air-handling systems. Have you ever contemplated the intricate variations in ventilation or the mechanisms by which your room sustains its optimal temperature in the face of external challenges? In pursuit of understanding their critical function in preserving stability and comfort, let’s delve into the realm of industrial dampers by removing their external sections.

Industrial Dampers
1. Understanding Dampers
Imagine oneself within a chamber, relishing in the finest convenience of temperature regulation. Unidentified to you, a damper is operating inconspicuously to regulate the airflow and preserve this comfortable environment. Therefore, what is a damper exactly? In essence, it comprises a valve or plate that is deliberately positioned within air-handling apparatus, ducts, chimneys, or ducts to regulate the airflow.
2. Types of Industrial Dampers
Dampers aren’t just simple valves; they’re adaptable tools, crafted to meet diverse requirements. Manual dampers offer a hands-on approach, allowing adjustments with a simple turn of a handle. However, the innovation doesn’t stop there. Enter automatic dampers, equipped with electric or pneumatic motors, ensuring continuous airflow regulation.
Automating Comfort: The Magic of Automatic Industrial Dampers
Imagine a world where your room’s temperature adjusts seamlessly, without any manual intervention. Automatic dampers make this a reality, effortlessly fine-tuning airflow to maintain ideal conditions. It’s a futuristic marvel that simplifies life and enhances comfort, showcasing the remarkable capabilities of modern technology in the realm of air control.
3. Applications of Industrial Dampers
Now, let’s talk applications. Ever noticed how chimneys have dampers to keep unwelcome guests like birds and pesky weather elements at bay? These dampers also play a crucial role in controlling the rate of combustion, ensuring your cozy fireplace experience doesn’t turn into a smoke-filled nightmare.
But it’s not just about fireplaces and chimneys. Dampers are the crucial part of centralized air conditioning systems too. They can isolate unused rooms to save energy or regulate airflow for room-by-room temperature control. It’s like having your own personal climate butler ensuring every corner of your space is just the way you like it.
Let’s Explore more types of Industrial dampers
Multi-Blade Control Dampers:
Multi-blade control dampers, also known as rectangular or multi-blade louver dampers, come in two varieties based on blade action.
-Parallel Blade Action: All blades open and close at the same angle and direction.
-Opposed Blade Action: Adjacent blades rotate in opposite directions.
Single Blade Dampers:
Single blade dampers, known as butterfly or wafer dampers, are versatile and can be round, square, or rectangular.
-They may feature single thickness blades or a double skin airfoil design.
-Often, they provide a cost-efficient alternative to pricier valves.
Commercial and Industrial Backdraft Dampers:
Also called gravity dampers, backdraft dampers are vital in light, medium, and heavy-duty industrial and HVAC applications.
-These Industrial dampers allow airflow in one direction while preventing reverse flow, crucial for maintaining system integrity.
-Commonly installed on fans to prevent backspin caused by back pressure.
Face and Bypass Dampers:
-Face and bypass dampers, also known as diverter or tee dampers, serve specialized functions.
-They redirect high-temperature gases, often from turbines, to recover heat efficiently.
-Typically part of a dual damper setup, these dampers are integral components in tee-pipe configurations.
Inlet Vane Dampers:
Inlet vane dampers, also referred to as inlet vane controls (IVC dampers) or variable inlet vanes (VIV dampers), control airflow and pressure from the inlet side of fans or blowers.
-Mounted directly to the fan inlet, they offer both shut-off and control capabilities by rotating to pre-spin the entering air.
-These round dampers ensure dependable operation and cost savings for fan or blower operations.
Bubble Tight and Guillotine Dampers:
Isolation dampers are categorized into bubble tight and guillotine dampers, purchasable for both round and rectangular duct systems.
-High-end bubble tight dampers provide the most reliable seals, preventing leakage when closed.
-Guillotine damper models, equipped with seal air fans, achieve zero leakage and minimal pressure drop, primarily used for ductwork isolation and shut-off during maintenance.
Industrial dampers, in their various forms, uphold system efficiency, reliability, and safety across a spectrum of applications, ensuring optimal performance and control in diverse industrial and HVAC environments.
Safety First
Safety is paramount and should never be taken lightly. Failing to open a damper before lighting a fireplace can lead to serious consequences, such as smoke-filled rooms or even a house fire. It’s crucial to always check the condition of dampers before starting any fire. Ensuring that dampers are properly open helps prevent potential hazards and ensures a safer environment for everyone. Always prioritize safety by double-checking the status of dampers before igniting flames, mitigating the risk of accidents or damage.
Conclusion
In the grand tapestry of HVAC systems and industrial setups, industrial dampers may seem like minor players, but their role is anything but insignificant. From maintaining comfort to ensuring safety, these unassuming valves silently orchestrate the airflow, making our lives a little more comfortable and a lot safer. So, the next time you adjust your room temperature or light up your fireplace, take a moment to appreciate the humble damper – the unsung hero of air control.
0 notes
Text
2024 - Top Quality Centrifugal Fans and Blowers Manufacturers in India
Centrifugal Fans and Blowers Manufacturers in India
Teral-Aerotech is a Top Centrifugal Fans and Blowers Manufacturers in India, offering a wide range of high-quality ventilation products. Their centrifugal blowers are engineered for high efficiency and low noise, making them suitable for various industrial and commercial applications. The company prides itself on its mission to develop, manufacture, and market top-notch ventilation products, with a focus on reliability, quality, and customer satisfaction.

Centrifugal Fans and Blowers
Centrifugal Fans and Blowers Manufacturers in India, Teral-Aerotech's centrifugal blower fans are precision designed to deliver efficient air movement and increase air or gas pressure. They offer a variety of fan types, including Double Inlet Double Width (DIDW) and Single Inlet fans, with features such as forward curved or backward curved impellers.
Teral
These fans are suitable for a wide range of applications, including general ventilation, pressurization, and various industrial processes, thanks to their high volume air displacement capabilities. The company's commitment to excellence is evident in its emphasis on trust, customer satisfaction, and continuous product development. They also prioritize timely delivery and aim to be the most reliable company for quality, availability, and delivery reliability.

Centrifugal Fans and Blowers
With a strong focus on customer relationships and community engagement, Teral-Aerotech is dedicated to providing the right products with the right performance characteristics, delivered at the right time. Their wide range of centrifugal blowers and fans, coupled with a commitment to quality and customer satisfaction, positions them as a leading manufacturer in the industry.
If you want to know more about our product how they are useful for your work , please contact us today . Our team is always here to help and find best solutions for your specific needs.
Visit:- https://www.blowers-fans.com/centrifugal-fan-blowers.html
Address : PLOT NO.188-89,ECOTECH EXTENSIONS-1, KASANA GREATER NOIDA-201301,(NEAR ASIAN PAINT) UTTAR PRADESH,INDIA
1 note
·
View note
Text
FORGINGS FOR POWER GENERATION AND ENERGY SECTORS
FORGINGS FOR POWER GENERATION AND ENERGY SECTORS
The Forge Power Generation Services should always remember to check the requirements of quality and specifications of the industry, providing faster, more reliable and accurate quotations. The open die forging includes simple rings to complex shapes with geometries. In this industry, on-time delivery is very crucial—the right steps to take to deliver your product on (or before) your quoted delivery date.
Power generation forged parts.
Forged shapes for turbines, generators, compressors, gearboxes, heat exchangers and blowers
Rings (Full/Segmented): Retainer, motor end, shear resistance, lock, seal, adapter or spherical seats, flanges, sleeves, Diaphragm, stator, spacer.
Shafts: Coupling, valve stem, fan,Rotor, generator, turbine, suction/discharge end stub,
Discs and Hubs: Adapters, impellers, tube sheets, nozzles,Covers, wheels, suction/discharge end caps,
Complex Shapes: Turbine blades,Bucket/fan blade stock
Additional Shapes: Bearing blocks, shells, transition cones,Casings, spacers, centrifuge bowls
Steam Valves
Bell seals, rings + disks
Inlet-sleeves
Valve seats, throttle valves
Interceptor valves
Mufflers, strainers
Nozzles + nozzle blocks
Bonnets
Spring guides & couplings for stream train
Generator
Rotating:
Blower parts
Rings
Couplings
Components shrunk on rotor
Stationary:
Lifting tools
Spacers
Gas Turbine
Compressor + turbine disks
Spacer rings
Rings + bushings
Exhaust cylinder supports
Lifting tools
Steam Valves
Exciters + Collectors:
Shafts
Rings + bushings
Couplings
Jackshafts
Diode wheels
Frame lifting tool
Reasons to choose Scot Forge
Emergency response
In times of unplanned critical situations, thousands or millions of dollars can be lost each and every day. To avoid this we have placed an emergency response program which will avoid the daily entry of breakdown and rush of orders for the production response which should be done immediately.
A vast inventory of materials
We maintain an extensive inventory of ferrous and non-ferrous materials. From vacuum degassed air melt to ESR or VAR cleanliness levels, parts are supplied using the highest-quality material available. Power generation-specific materials include carbon, alloy, stainless steel, copper base, nickel base and custom-melt alloys that meet OEM specifications.
Flexible sizes, shapes and quantities
No matter the shape of the material or rather the size of the part, We are designed to support both single-piece and high-volume manufacturing.
Value-added options
There is all value-added process which includes saw cutting, heat treating, contour torch cutting, destructive testing, metallurgical analysis, and Level III nondestructive testing. Combined with the advanced forging technology and the inherent advantages of the forging process, our capabilities provide a superior value solution.
1 note
·
View note
Text
HVAC Service Contractors Near by in Vancouver
HVAC Service Contractors Near by in Vancouver
Pioneer Plumbing has built a reputation of honesty with our long time returning customers. We’ve found that “doing the right thing” in all aspects of our company has brought us to where we are today, and will continue to guide us into the future. Don’t hesitate to call and ask us any plumbing, heating, ventilation, or gas related questions. Chances are if you have a tricky issue, we can solve it.
We have a few goals for our clients. One is to be available for you. It is very uncommon that when you call us we are unable to make it within the same day. We give our repeat customers priority service so if you’ve used us before and you have an emergency, we are going to do what we need to, to get someone there.
Two is to be upfront and honest. From our quotes to our service techs on site, we don’t like to beat around the bush. We will let you know our concerns, our recommendations, and our opinions on how we would handle each situation as if it were our own residence where the problem occurred. We won’t tell you the job is only a 2 hour repair when we have had situations where it turned into an all day repair.
Three is to stand behind our installations and repairs. With mechanical work, it is very common for jobs to get larger or go sideways as you get into them. If we give you a quote we will stand true to the price, if we complete a job for you and you are unhappy with the finished product, we will come back and make it right. In return, all we ask is that you communicate with our office respectfully and honestly so that we can make sure at the end of the day you are happy with our services!
So next time you have a plumbing, heating, cooling, or gas question, repair, or installation you would like quoted, give us a call! Were here to help.

HVAC in Vancouver
Just how do you feel with regards to Electric Furnace Repair?
Heating Repair And Regular Maintenance Tips
There are many ways to maintain your furnace system. Odds are, during wintertime months your heater is on throughout the day attempting to keep the house warm. In fact, it is usually on more than it needs to be because it is unable to maintain an operable climate. When troubleshooting and optimizing the heating portion of your furnace system, there are several things to consider.
Change The Air Filter
This subject is what gets talked about the most in talks about furnace maintenance, but is sometimes overlooked. When there is a blockage, you either run the risk of not circulating heat adequately or possibly starting a fire.When the air conditioner filter gets dirty air will not flow through either which suggests the furnace must work overtime and could also mean a likelihood of fire. When the system works overtime, it is more expensive to run. You want eliminate any likelihood of fire. Neither circumstance is good for the pocket book or your well-being..
Try The Blower
Check the blower blades and clean them. A messy fan will work overtime to blow air around and naturally use more energy to preserve the thermostat level you set it at. This implies strain in your furnace system and your wallet since more energy is required to constantly run the blower.
Fire Damper Function
Next, look at the fire damper to make sure it is running the right way. The fire damper is self-explanatory so take note of this aspect.
Look For Holes In The Flex Duct
It is feasible that your ducts have become damaged throughout the years for a variety of reasons. If there are obstructions or the duct has flattened anywhere the furnace system will think the correct temperature has been reached, which can be wrong. Ultimately your equipment will be straining to keep your home cool as you keep on lowering the thermostat to reach cozy settings.
Band Insulation
It is easy to overlook the insulation, but is one of the most common reason for a system malfunctioning. Be sure to check the insulation and validate it has never become unfastened and prompted gaps between the ductwork and the outside. If this happens, your system will not reach ideal temperatures and will work too much to try and accommodate.
Ductwork Needs To Be Connected
Make sure the ductwork is hooked up everywhere to all sections. Disconnected ductwork will allow warm air to escape and naturally add to the running costs.
Check For Leaks In The Return Air Inlets And Zone Dampers
Be sure to make sure return air intakes are dirt free and in good shape or your system will be unbalanced. Look at the zone dampers to check if they are in the right position. Throughout the year we may change the position of the damper for a lot of reasons (i.e. getting into a tight space or arranging for storage). Check to notice that the dampers are in the correct position too.
If that is a tad too much to handle yourself, we suggest you hire an area plumbing business certified for furnace and heating repair. There will be a number of heating companies around you who can care for this all quite competently. The most sage advice we can offer is to establish yearly upkeep for this appliance.
https://www.google.com/maps?cid=16109373416364653742 https://vancouver-plumber.business.site/
https://www.pioneerplumbing.com/
Pioneer Plumbing & Heating Inc
626 Kingsway, Vancouver BC, V5T 3K4 Phone: (604) 872-4946
Business Hours: Sunday Open 24 hours Monday Open 24 hours Tuesday Open 24 hours Wednesday Open 24 hours Thursday Open 24 hours Friday Open 24 hours Saturday Open 24 hours
Types of Heating Systems
Central Heat
Furnaces
The majority of North American households depend on a central furnace to provide heat. A furnace works by blowing heated air through ducts that deliver the warm air to rooms throughout the house via air registers or grills. This type of heating system is called a ducted warm-air or forced warm-air distribution system. It can be powered by electricity, natural gas, or fuel oil.
Inside a gas- or oil-fired furnace, the fuel is mixed with air and burned. The flames heat a metal heat exchanger where the heat is transferred to air. Air is pushed through the heat exchanger by the “air handler’s” furnace fan and then forced through the ductwork downstream of the heat exchanger. At the furnace, combustion products are vented out of the building through a flue pipe. Older “atmospheric” furnaces vented directly to the atmosphere, and wasted about 30% of the fuel energy just to keep the exhaust hot enough to safely rise through the chimney. Current minimum-efficiency furnaces reduce this waste substantially by using an “inducer” fan to pull the exhaust gases through the heat exchanger and induce draft in the chimney. “Condensing” furnaces are designed to reclaim much of this escaping heat by cooling exhaust gases well below 140°F, where water vapor in the exhaust condenses into water. This is the primary feature of a high-efficiency furnace (or boiler). These typically vent through a sidewall with a plastic pipe.
New furnace standards are currently under development by the U.S. Department of Energy, and are due to be finalized in the spring of 2016. The current furnace standards have not been updated since 1987.
Heating system controls regulate when the various components of the heating system turn on and off. The most important control from your standpoint is the thermostat, which turns the system — or at least the distribution system — on and off to keep you comfortable. A typical forced air system will have a single thermostat. But, there are other internal controls in a heating system, such as “high limit” switches that are part of an invisible but critical set of safety controls.
The best gas furnaces and boilers today have efficiencies over 90%
The efficiency of a fossil-fuel furnace or boiler is a measure of the amount of useful heat produced per unit of input energy (fuel). Combustion efficiency is the simplest measure; it is just the system’s efficiency while it is running. Combustion efficiency is like the miles per gallon your car gets cruising along at 55 miles per hour on the highway.
In the U.S., furnace efficiency is regulated by minimum AFUE (Annual Fuel Utilization Efficiency). AFUE estimates seasonal efficiency, averaging peak and part-load situations. AFUE accounts for start-up, cool-down, and other operating losses that occur in real operating conditions, and includes an estimate of electricity used by the air handler, inducer fan, and controls. AFUE is like your car mileage between fill-ups, including both highway driving and stop-and-go traffic. The higher the AFUE, the more efficient the furnace or boiler.
Boilers
Boilers are special-purpose water heaters. While furnaces carry heat in warm air, boiler systems distribute the heat in hot water, which gives up heat as it passes through radiators or other devices in rooms throughout the house. The cooler water then returns to the boiler to be reheated. Hot water systems are often called hydronic systems. Residential boilers generally use natural gas or heating oil for fuel.
In steam boilers, which are much less common in homes today, the water is boiled and steam carries heat through the house, condensing to water in the radiators as it cools. Oil and natural gas are commonly used.
Instead of a fan and duct system, a boiler uses a pump to circulate hot water through pipes to radiators. Some hot water systems circulate water through plastic tubing in the floor, a system called radiant floor heating (see “State of the Art Heating”). Important boiler controls include thermostats, aquastats, and valves that regulate circulation and water temperature. Although the cost is not trivial, it is generally much easier to install “zone” thermostats and controls for individual rooms with a hydronic system than with forced air. Some controls are standard features in new boilers, while others can be added on to save energy (see the “Modifications by Heating System Technicians” section on the heating maintenance page).
As with furnaces, condensing gas-fired boilers are relatively common, and significantly more efficient than non-condensing boilers (unless very sophisticated controls are employed). Oil-fired condensing boilers are uncommon in the U.S. for several reasons related to lower latent heat potential, and potential for greater fouling with conventional fuel oil.
Heat Pumps
Heat pumps are just two-way air conditioners (see detailed description in the cooling systems section). During the summer, an air conditioner works by moving heat from the relatively cool indoors to the relatively warm outside. In winter, the heat pump reverses this trick, scavenging heat from the cold outdoors with the help of an electrical system, and discharging that heat inside the house. Almost all heat pumps use forced warm-air delivery systems to move heated air throughout the house.
A ground-source heat pump heats and cools in any climate by exchanging heat with the ground, which has a more constant temperature.
There are two relatively common types of heat pumps. Air-source heat pumps use the outside air as the heat source in winter and heat sink in summer. Ground-source (also called geothermal, GeoExchange, or GX) heat pumps get their heat from underground, where temperatures are more constant year-round. Air-source heat pumps are far more common than ground-source heat pumps because they are cheaper and easier to install. Ground-source heat pumps, however, are much more efficient, and are frequently chosen by consumers who plan to remain in the same house for a long time, or have a strong desire to live more sustainably. How to determine whether a heat pump makes sense in your climate is discussed further under “Fuel Options.”
Whereas an air-source heat pump is installed much like a central air conditioner, ground-source heat pumps require that a “loop” be buried in the ground, usually in long, shallow (3–6' deep) trenches or in one or more vertical boreholes. The particular method used will depend on the experience of the installer, the size of your lot, the subsoil, and the landscape. Alternatively, some systems draw in groundwater and pass it through the heat exchanger instead of using a refrigerant. The groundwater is then returned to the aquifer.
Because electricity in a heat pump is used to move heat rather than to generate it, the heat pump can deliver more energy than it consumes. The ratio of delivered heating energy to consumed energy is called the coefficient of performance, or COP, with typical values ranging from 1.5 to 3.5. This is a “steady-state” measure and not directly comparable to the heating season performance factor (HSPF), a seasonal measure mandated for rating the heating efficiency of air-source heat pumps. Converting between the measures is not straightforward, but ground-source units are generally more efficient than air-source heat pumps.
Direct Heat
Gas-Fired Space Heaters
In some areas, gas-fired direct heating equipment is popular. This includes wall-mounted, free-standing, and floor furnaces, all characterized by their lack of ductwork and relatively small heat output. Because they lack ducts, they are most useful for warming a single room. If heating several rooms is required, either the doors between rooms must be left open or another heating method is necessary. Better models use “sealed combustion air” systems, with pipes installed through the wall to both provide combustion air and carry off the combustion products. These units can provide acceptable performance, particularly for cabins and other buildings where large temperature differences between bedrooms and main rooms are acceptable. The models can be fired with natural gas or propane, and some burn kerosene.
Unvented Gas-Fired Heaters: A Bad Idea
Gas or kerosene space heaters that do not have an exhaust vent have been sold for decades, but we strongly discourage their use for health and safety reasons. Known as “vent-free” gas heating appliances by manufacturers, they include wall-mounted and free-standing heaters as well as open-flame gas fireplaces with ceramic logs that are not actually connected to a chimney. Manufacturers claim that because the products’ combustion efficiency is very high, they are safe for building occupants. However, this claim is only valid if you keep a nearby window open for adequate fresh air— which defeats the purpose of supplemental heat. Dangers include exposure to combustion by-products, as discussed in Ventilation, and oxygen depletion (these heaters must be equipped with oxygen depletion sensors). Because of these hazards, at least five states (California, Minnesota, Massachusetts, Montana, and Alaska) prohibit their use in homes, and many cities in the United States and Canada have banned them as well.
Electric Space Heaters
Portable (plug-in) electric heaters are inexpensive to buy, but costly to use. These resistive heaters include “oil-filled” and “quartz-infrared” heaters. They convert electric current from the wall socket directly into heat, like a toaster or clothes iron. As explained further under “Selecting a New System,” it takes a lot of electricity to deliver the same amount of useful heat that natural gas or oil can provide onsite. A 1,500- watt plug-in heater will use almost the entire capacity of a 15-amp branch circuit; thus, adding much additional load will trip the circuit breaker or blow the fuse. The cost to operate a 1,500-watt unit for an hour is simple to compute: it is 1.5 times your electricity cost in cents per kilowatt-hour. At national average rates—12¢ kWh for electricity— that heater would cost 18¢ per hour to run—and quickly cost more than its purchase price. On the other hand, for intermittent use, it is the “least-bad” solution when alternatives would require major investments to improve ductwork for a specific area, for example. Just remember, electric resistance heat is usually the most expensive form of heat, and it is, therefore, seldom recommended.
“Electric baseboard heat” is yet another kind of resistive heating, similar to a plug-in space heater except that it is hard-wired. It has two principal virtues: the installation cost is low, and it is easy to install individual room thermostats so you can turn down the heat in rooms that aren’t being used. Operating costs, as for all resistive systems, are generally very high, unless the house is “super-insulated.”
Wood-Burning and Pellet Stoves
Wood heating can make a great deal of sense in rural areas if you enjoy stacking wood and stoking the stove or furnace. Wood prices are generally lower than gas, oil, or electricity. If you cut your own wood, the savings can be large. Pollutants from wood burning have been a problem in some parts of the country, causing the U.S. Environmental Protection Agency (EPA) to implement regulations that govern pollution emissions from wood stoves. As a result, new models are quite clean-burning. Pellet stoves offer a number of advantages over wood stoves. They are less polluting than wood stoves and offer users greater convenience, temperature control, and indoor air quality.
Fireplaces
Gas (and most wood) fireplaces are basically part of a room’s décor, providing a warm glow (and a way to dispose of secret documents), but typically not an effective heat source. With customary installations that rely on air drawn from the room into the fireplace for combustion and dilution, the fireplace will generally lose more heat than it provides, because so much warm air is drawn through the unit and must be replaced by cold outside air. On the other hand, if the fireplace is provided with a tight-sealing glass door, a source of outside air, and a good chimney damper, it can provide useful heat.
State of the Art Heating
Radiant floor heat generally refers to systems that circulate warm water in tubes under the floor. This warms the floor, which in turn warms people using the room. It is highly controllable, considered efficient by its advocates, and is expensive to install. It also requires a very experienced system designer and installer, and limits carpet choices and other floor finishes: you don’t want to “blanket” your heat source.
Contact the Radiant Panel Association(link is external)
Ductless, Mini-Split, Multi-Split. Residential ductwork is relatively rare outside North America. “Ductless” heat pumps, which distribute energy through refrigerant lines instead of water or air, are widely used. Large field trials in the Pacific Northwest suggest that they can have good cold weather performance, and be very cost-effective where replacing electric resistance heating. Like ground-source systems, relative immaturity of the market helps assure that whole-house multi-split systems carry premium prices.
Combined heat and power (CHP) or cogeneration for houses is being seriously studied in some countries. The basic premise is to use a small generator to meet some of the electric demand of the house, and recover the waste heat (typically more than 70% of the heating value of the fuel) to heat the house (hydronic or water-to-air systems) and make domestic hot water. These systems are not yet widely available. They are likely to have the best economics in houses with high heating bills because the house cannot be feasibly insulated, such as solid stone or brick homes.
https://smarterhouse.org/heating-systems/types-heating-systems
youtube
As a devoted person who reads on HVAC System Repair, I imagined sharing that excerpt was worthwhile. So long as you enjoyed our post please be sure to pass it around. I value reading our article about Home Furnace Replacement.
youtube
First Rate Heating Repair HVAC Replacement Furnace Repair Service Residential Ac Repair Home HVAC Repair
HVAC Service Contractors Near by in Vancouver
1 note
·
View note
Text
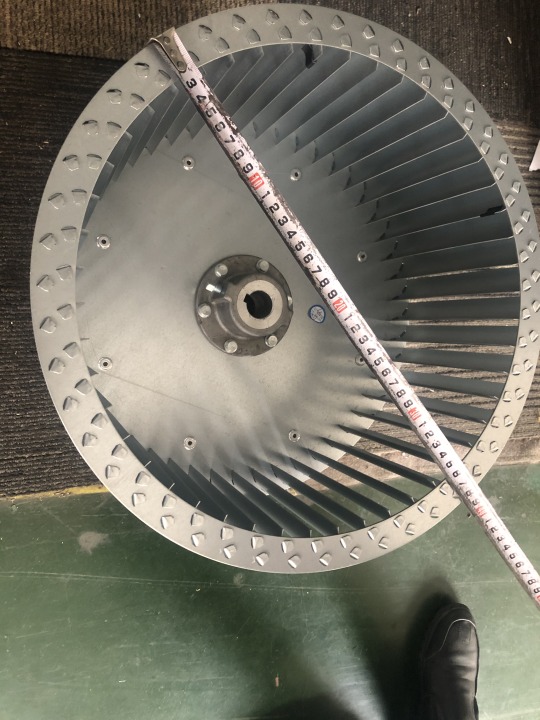
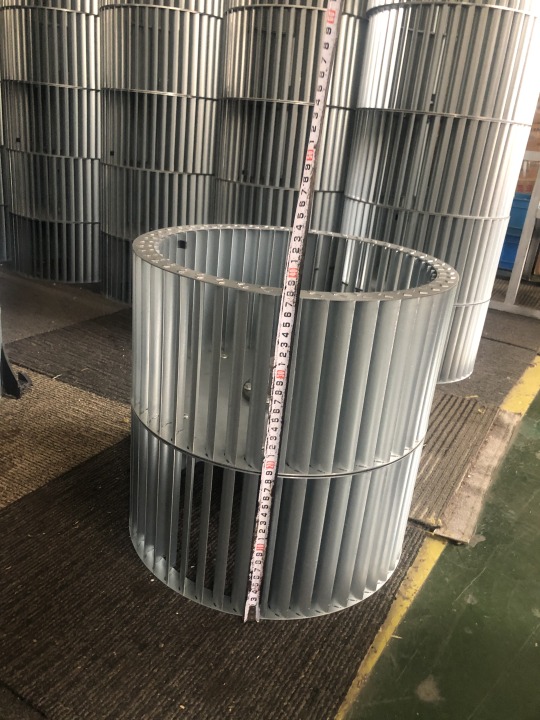
Galvanized Steel Centrifugal Fan Blades Multi-wing Impeller Double-Inlet Strip Type Blower Wheel
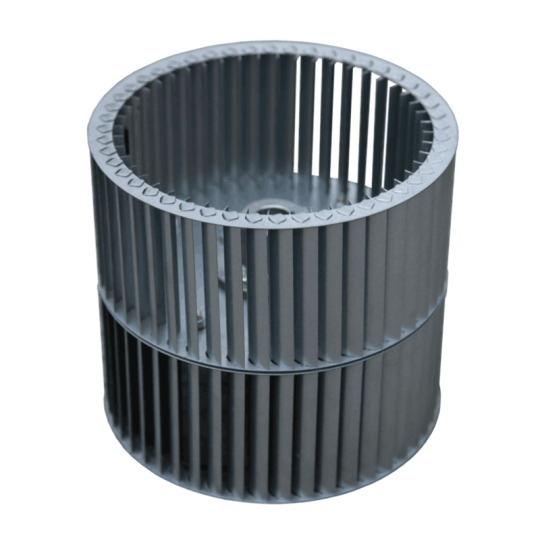


Centrifugal Fan Wheel — Fan Wheel / impeller. Centrifugal strip blower wheel · Centrifugal tablock blower wheel · strip dual wheel · tablock dual wheel · strong type · Centrifugal Strip Application: HVACR equipment, machinery, burner, oven, dryer, etc. Function: Ventilation, Cooling, heating, air conditioning, draft inducing, air refreshing, air circulation. Features: Configuration Type: Single inlet, Twin-inlet Order Information: Minimum Order: Negotiate OEM/ODM Product, Branded Product, Buyer's Label Offered FOB: China Ningbo /China Shanghai Customization Available If you don't find the products you want in our range , please contact us for customization services freely . our profesional engineer team will work out a satisfied stuff with you . Any dimensions of cross flow fans , perfromances of air flow ,air pressure ,noise level , installation positions or other functions are availble for your customizing




Read the full article
0 notes
Text
Fresh Technology For Mechanical Contractors
Commercial buildings are going green — and it’s not just new construction. Across the commercial market, demand for energy-efficient materials remains high as manufacturers work to develop products and processes that reduce a building’s overall energy consumption and stack up against stringent performance criteria.
Achrnews.com
This is just one of the four case studies included in the original full article, (link at bottom). To me this one is the coolest of the collection. The concept of using air curtains to block drafts from outdoors on huge trucking bays and saving thousands of dollars annually on energy costs at the same time is one of the neatest things to happen in the commercial HVAC space in a long time. Enjoy -
DODGING THE DRAFT
Royal Wine’s distribution center responded to employee wintertime requests for a warmer shipping area and received a bonus when six new air curtains significantly reduced operational energy costs.
ROYAL TREATMENT:In response to employee requests for a warmer shipping area in winter, Royal Wine installed Berner Industrial Direct Drive model IDC-12 air curtains with indirect gas-fired heat at the six roll-up door openings. The laminar air stream returns 70 to 80 percent of indoor energy back into the space while blocking drafts from outdoors.
Royal Wine, a global kosher winemaker, imports and produces more than 60 brands of wine, manufactures the Kedem fruit juice brand, and operates Herzog Wine Cellars with vineyards in Oxnard, California. During the winter, its distribution center in Bayonne, New Jersey, was losing thousands of dollars a year because of open shipping doors. Subfreezing temperatures near the open doors required workers to wear heavy clothing, which hampered their productivity, and caused cold air drafts regardless of portable truck and dock seals, according to Abraham Wechter, plant engineer.
Employees wanted a warmer shipping area. In response, Royal Wine decided to install air curtains on six shipping doorways.
The curtains were purchased from Berner International LLC, a U.S. manufacturer of air door/air curtain equipment. Berner is a member of the U.S. Green Building Council (USGBC), Green Building Alliance (GBA), Air Movement & Control Association (AMCA), and ASHRAE.
Royal Wine’s solution for the 8-by-10-foot roll-up door openings came in the form of six Berner Industrial Direct Drive model IDC-12 air curtains with indirect gas-fired heat. Each air curtain incorporates three ½-hp, single-speed, dual-shaft motors that drive blower wheel assemblies delivering 4,443 cfm. The resulting laminar air stream returns 70 to 80 percent of indoor energy back into the space while blocking drafts from outdoors.
Each air curtain has one 200-MBtuh indirect gas-fired unit heater, delivering a 32°F temperature rise to the air stream. Berner’s custom metal shop also attached a 14-gauge aluminized steel duct plenum transition to the air curtain inlet. Thus, the unit heater discharges heat toward the plenum, and each air curtain draws it through for uniform distribution. The heat option supplements Royal Wine’s existing unit heaters and high volume/low speed (HVLS) fans, which aid in pushing static heat down from the ceiling. The shipping area now remains at 70°, regardless of the outdoor temperature or how long the doors are open.
Each air curtain’s control package includes a factory-mounted and -wired UL listed motor control panel, complete with a rotary non-fused disconnect switch, time delay relay, a 24 V transformer, and a remote-mounted combination switch and thermostat. When the overhead roll-up doors are raised, the air curtains are activated through a 24 V floor-mounted magnetic reed switch.
Royal Wine plans to keep the air curtains activated year-round, as the plant uses several 20-ton rooftop HVAC units to maintain optimum temperatures for wine and juice storage. In addition to stable temperatures, summertime door protection will aid sanitation by keeping out dust and flying insects.
The air curtains, duct transition, and gas unit heaters were suspended from the 25-foot-high ceiling with threaded rod. Stabilization bars were used to maintain distance away from the wall, so the downward air stream isn’t obstructed by the roll-up door mechanism canister, and the air curtains were field-adjusted, so the air stream meets the floor just outside the threshold.
Consequently, employees now work in a warm, comfortable environment. Plus, per Berner’s calculations, each door reaps an annual energy savings of $3,500. Multiplying those savings by six doors totals an estimated savings of $21,000 per year.
The full article with all four case studies is here: https://www.achrnews.com/articles/139762-case-studies-show-how-green-technology-helps-commercial-buildings
from https://commercialhvaccontractors0.blogspot.com/2019/01/technology-for-mechanical-contractors.html
1 note
·
View note
Text
How To Choose Industrial Vacuum Cleaner?

Today tons of wastes are generated by different industries on a daily basis. Most industries are facing challenges to get the waste cleaned. Roots Multiclean Ltd focuses to help industries solve their cleaning problem by providing the right Industrial Vacuum Cleaner (IVC) that is designed for continuous duty and reliable solutions for cleaning dusts, solids, and liquids.
Before choosing an industrial vacuum cleaner, let us know about two important things:- 1) What is IVC? 2) What are the things to be considered while choosing an IVC?
1. What Is Industrial Vacuum Cleaner?
Industrial Vacuum Cleaner is a machine used for the general cleaning in industrial environment, Industrial vacuum cleaners are designed to meet specific needs of users and particular tasks that are generally heavy to handle. It is provided with a side-channel blower that is powerful, silent, and suitable for performing round the clock.
The IVC ranges start from 1.8KW to 45KW suitable for various types of industries like Food, Pharmaceutical, Steel, Cement, Foundry, Textiles, Power plants, fertilizers, Bio labs, Engineering, and Automobile sectors available in a standalone, movable, fixed vacuum, online vacuuming, centralized vacuum system, and Truck mounted vacuum.
2. What Are The Things To Be Considered While Choosing An IVC?
Once you get an idea about IVC you need to consider certain things before picking up the right industrial vacuum cleaner based on Power, Performance, Filtration, Quality & Durability, and Capacity.
2.1 Power:
In general, power is expressed in W (Watts) & kW (kiloWatt). Our product lineup is equipped with single-phase and three-phase motors, which ensures the efficient vacuuming of debris for long period.
2.2 Performance:
The performance of IVC is determined by the Vacuum pressure and Airflow.
Vacuum pressure represents the suction force to clean up the dusts, solids, and liquids. It is also called “Depression”. The top depression rate value is taken by mmH2O (millimeters of Water Column), mbars, or others pressure measures.
Air Flow is measured by m3/h (cubic meters per hour), Liters/sec. It refers to the volume of air moved by the suction unit. The top airflow rate is measured with a suction inlet completely open.
2.3 Filtration:
The most important thing to consider is Filtration. Our Industrial Vacuum Cleaners are equipped with various types of primary filters and HEPA filters to accomplish high filtration efficiency which ensures the exhaust air is free from dust particles.
Primary filters generally have relatively low permeability. To achieve a reasonably low-pressure drop through the filter, the element area (surface area) must be increased. Quality of the filtration increases by large filter surface area to achieve better efficiency.
2.4 Collection Tank:
It’s also an important thing to consider the capacity while choosing an Industrial Vacuum Cleaner. It depends on the size of the disposal tank. For continuous operations, you need a large collection unit to remove residuals and it is also easy to detach the collection container with rotatable castor wheels for easy transportation of dust collected.
2.5 Quality & Durability:
Another element to be considered is Quality and Durability. All Industrial Vacuum Cleaners are provided with sturdy steels chassis to withstand for many years. When evaluating durability, the machine construction is designed and developed to work for the rugged nature of factories, where other industrial vacuum cleaners fail to do.
Conclusion:
On the market, there are many industrial vacuum cleaners available that differ by their performance, and applications. In the decision-making stage, it’s always better to hear from the professionals to guide you to choose the right Industrial Vacuum Cleaners. To know more about our Industrial Vacuum Cleaners visit our page
www.rootsmulticlean.com
#cleaning machine#cleaning equipment#floor cleaning#industrial vacuum cleaner#floor scrubber#floor cleaners#floorcleaner#floorscrubbermachine#industrialcleaner#roots multiclean
0 notes
Text
On the other end of the spectrum are mega vacuum pumps
This demands to ensure the total differential pressure across the Booster must not exceed the rated limits. Various types of vacuum pumps are available such as diaphragm, rocking piston, reciprocating piston, liquid ring, rotary-screw, rotary vane and lobed-rotor ones. Many industrial and scientific processes require vacuum-pump applications such as for the production of electric lamps, vacuum tubes, semiconductor processes, lectron microscopy, and medical processes involving suction. This type of pump has a straight through design which ensures they are non-clogging and relatively maintenance free.The heart of any process in industry are the Industrial Fan. Boosters are the pumps which helps to dry that are installed to meet most of the ideal vacuum pump requirements. Because desirable characteristics which make these pumps the most cost effective and power efficient option. Boosters can be coupled with any one of the pumps, to overcome their limitations like to boost the performance of water ring, oil ring, rotating vane, piston pumps and steam or water ejectors.
A single mechanism or a series of mechanisms or parallel mechanisms are employed to achieve the best results according to specific requirements. Typically generating static pressures above 500 mmWG, these type of air movers are mainly used for blowing duties where low volume/ high pressure conditions are required. Large-sized vacuum pumps are meant for continuous pumping. However, smaller pumps have high efficiency; the only difficulty, however, is that they get overheated easily if used continuously. The final option manufacturers can consider is conveying pumps or air amplifiers. This type of vacuum pump provides a reliable and cost effective solution for in-line product transfer. Aero Foil Designs are available on request for extra high efficiencies. Reciprocating piston, diaphragm, rocking piston, and rotary vane pumps can go up to twenty-nine in Hg. These pumps are the largest compressed air driven option available.
Aerospace applications include the use of vacuum source to power gyroscopes in the various flight instruments. This makes it ideal for conveying systems which transfer bulk materials. These fans are mainly of many type like ID Fan, FD Fan, Industrial Blower, Industrial Air Blower, High Pressure Fan, Hot Air Circulation fan, Bag Filter Blower, Dust Collector Blower, Blower, boosters, and Pneumatic Conveying Fan. At the same time they are comparatively compact and lightweight.. Power Constraints restrict the total differential pressures across the vacuum boosters. Vacuum pumps have much lower power requirements than air compressors.
On the other end of the spectrum are mega vacuum pumps. These fans are employed for process air required for Combustion blowing or conveying duties. Rubber and plastic-sealed piston pumps, venture vacuum pump, and scroll pumps are also used. This type of pump is primarily used whenever a larger air volume must be evacuated or when a leakage flow must be compensated for. The impeller or wheel are typically radial or forward tipped, has comparatively China Ventilation Fans Manufacturers lower static efficiencies & have smaller inlet & outlets to allow for lower volume throughputs
0 notes
Text
Roots blower pressure and current problems
The reason why the current of the Compact integrated Roots blower is too large
Roots blower is a mechanical device used to transport air and various neutral gases. In the use of the Roots blower, there will also be an overcurrent situation. What is the reason for the excessive current of the Roots blower?
1. Is there any lubricating oil in all parts of the Roots blower? The Roots blower should be maintained regularly. When working in a state of oil shortage, the friction will increase, which will increase the motor load, resulting in excessive current.
2. Whether the air outlet of the Roots blower is smooth; if the wind cannot be beaten out, the pressure will rise, which will also increase the motor load, resulting in excessive current.
3. The quality of the Roots blower itself; the poor clearance of many parts and components will cause additional friction, and some parts may be damaged, which will increase the motor load and cause the fuse to blow.
4. Compared with the specified pressure, the pressure difference is large, that is, the back pressure or the inlet pressure is very high; compared with the flow rate required by the Roots fan, the flow rate of the fan is too large, so the pressure increases; the inlet filter is blocked, and the outlet pipe is blocked or blocked ; The rotating parts touch and rub; the oil level of the Roots fan is too high; the narrow V-belt is overheated, the vibration is too large, and the pulley is too small.
The Acoustic Enclosure for Roots Air blower providers pointed out that the failure of the Roots blower is inevitable. In order to effectively avoid the failure of the Roots blower, we must follow the correct use method and process during operation. and periodic size repairs and maintenance.
Reasons for pressure loss of roots blower
In the market, the pressure of the single-stage Roots blower is 9.8-98kpa, and the pressure of the double-stage Roots blower is 98-198kpa. No matter how high the pressure value is, other types of blowers can only be replaced. When using the Roots blower, the After a long time, the pressure of the Roots blower will become smaller and the flow rate will also become smaller. Next, I will explain the reasons for the pressure loss of the Roots blower:
1. Pipeline resistance: Pipeline resistance can reduce the pressure of the Roots blower, but it has been proved by experiments that the pressure loss caused by the pipe resistance is not the main factor, and can only affect the pressure of the Roots blower to a small extent.
2. Mechanical resistance: There are many kinds of mechanical resistance, such as: the resistance generated by the sealing ring, the resistance generated by the load of the display device, and the resistance of the impeller shaft. Generally speaking: the resistance depends on the pressure of the flow, and the loss caused by the mechanical resistance accounts for the Roots blower. a fraction of the pressure loss.
3. Turbulent flow: The impeller will generate turbulent flow when it rotates, and the pressure loss caused by the turbulent flow is proportional to the square of the flow.
4. Viscous resistance: There is a certain gap between the impeller and the impeller, the impeller and the wall of the Roots blower. During the flow of the gas, a part of the viscous resistance will be produced, which is the main factor affecting the pressure loss of the Roots blower, and the viscosity is high. more pressure loss.
The Roots blower is a constant flow fan. As long as the front resistance is stable, the Roots blower can provide a stable flow. Even if the front resistance fluctuates slightly, the Roots blower can also adapt to the change. If the front pressure changes greatly, it will affect the Roots. The fan is damaged to some extent.
Ming Ye Machinery has always been attentive to feel the needs of customers, providing customers with advanced technology, high-quality products, and sincere services, and has achieved common development with customers. In line with the tenet of variety, excellent quality and good service, the company continuously develops and innovates products to meet the growing market needs. The main products include: air suspension centrifugal blower, integrated roots blower, Fine Bubble aeration DISC Diffuser. The company has advanced horizontal machining centers, vertical machining centers, CNC machining equipment, and standard testing equipment. Can guarantee the stability and reliability of product quality.
0 notes
Text
Fan Types - Why choose a forward curved centrifugal fan
Forward Curved Motorised Impeller
When we have defined the volume flow rate that we require, whether this is to provide fresh air or process cooling, we need to combine this with the resistance to flow that the fan will encounter in the application. The volume flow rate, (in m3/hr) and the pressure (in Pascals - Pa), are combined to become the duty point against which the fan must operate. It is important that we select a fan whose performance characteristic meets the required duty point on or near the point of peak efficiency. Using the fan at its peak efficiency minimises the power consumption and noise emitted from the fan whilst delivering the required performance.
How does Forward Curved Centrifugal Fan work?
The name, ‘Centrifugal Fan’ is derived from the direction of flow and how the air enters the impeller in an axial direction and then propelled outwards from the outer circumference of the fan. The difference in flow direction between a forward and backward curved centrifugal fan is the direction that the air exits the impeller circumference. With a backward curved impeller, the air exits in a radial direction whereas with a forward curved the air exits tangentially from the circumference of the fan.
A forward curved centrifugal fan is characterised by its cylindrical shape and lots of small blades on the circumference of the impeller. In the example shown below, the fan rotates in a clockwise direction.
Unlike the backward curved impeller, the forward curved impeller requires a housing that converts high velocity air leaving the tips of the impeller blade into a lower velocity static force. The shape of the housing also directs the air flow to the outlet. This type of fan housing is commonly known as a scroll; however, it can also be referred to as a volute or a sirocco housing. By installing the forward curved impeller in a scroll housing, we usually refer to it as a forward curved blower.
There are two types of blowers that employ a forward curved motorised impeller as shown below…
The single inlet blower on the left, draws in air from one side of the housing through the round inlet and directs it to the square outlet, (seen here with a mounting flange). The double inlet blower has a wider scroll housing drawing air in from both sides of the scroll delivering it to the wider square outlet.
As with the backward curved centrifugal fan, the suction side of the impeller blade draws air from the centre of the cross flow fan which results in a directional change of the airflow between the inlet and the exhaust of 90o.
Fan Characteristic
The optimum operating area for a forward curved centrifugal fan is when it is operating at higher pressure. A forward curved centrifugal fan works best when high pressures against lower volume flows are required. The graph below illustrates the optimum working area…
The volume flow is plotted along the X-axis and the system pressure is plotted on the Y-axis. When there is no pressure in the system, (the fan is blowing freely), a forward or backward curved centrifugal fan will produce the greatest volume flow. As a resistance to flow is applied to the suction or exhaust side of the fan, the volume flow rate will drop.
Caution should be exercised when selecting a forward curved blower to operate at low pressures and highest volume flow. At this point, the impeller is operating in an aerodynamic stall in the same manner as an axial flow fan operating in the saddle point of its curve. At this point noise and power consumption will be at its peak due to turbulence.
The peak efficiency is at a point called the knee of the characteristic curve. At this point the ratio of the output power of the fan (Volume flow (m3/s) x Static Pressure development (Pa) and the electrical power input (W) is at its greatest and the sound pressure being produced by the fan will be at its quietest. Above and below the optimum range of operation the flow across the fan becomes noisier and the efficiency of the fan system decreases.
The benefit of using a single inlet forward curved motorised impeller is that it has a steep fan characteristic. This is particularly useful in systems that require consistent levels of filtration. As air passes through a particulate filter the filter arrests airborne dust and pollen, the finer the grade of filtration the smaller the particles arrested by the filter. Over time the filter will become increasingly clogged with dirt and debris which has the effect that more pressure is required to deliver the same air volume. Using an impeller with a steep characteristic curve in this case means that as the filter becomes increasingly clogged, the volume flow remains constant while the pressure across the filter is increasing.
The benefit of using a double inlet forward curved impeller is that from a relatively small size blower it can deliver a high-volume flow. The compromise with using a double inlet blower is that it has a lower pressure development meaning that it can only work with lower pressure systems.
Mounting options
As mentioned previously, the forward curved motorised impeller produces high velocity air at the tips of the blade that needs to be directed and slowed to convert dynamic pressure into static pressure. To facilitate this, we build a scroll around the impeller. The shape is created by a ratio of distances from the centre of the impeller to the fan outlet. As with the backward curved fan it is also recommended to have a small overlap between the inlet ring and the mouth of the impeller. Both mounting considerations are shown in the diagram below…
Summary – Why Choose a forward curved centrifugal fan?
When the required duty point falls in the area of higher system pressures versus lower volume flow on the fan characteristic a single inlet forward curved centrifugal fan should be considered. If the requirement for the application is for a high-volume flow in a restricted space envelope a double inlet forward curved centrifugal fan should be considered.
The fan should be selected within its optimum range which is at what is known as the knee of its characteristic curve. The point of peak efficiency is in the closer to the higher-pressure limit on the fan characteristic curve where it is also being operating at its quietest. Operating outside of the optimum range (at the extremes of high volume flow) should be avoided as the turbulence and the aerodynamic efficiency of the impeller blade at these points will create noise and the impeller will also be operating in an aerodynamic stall. At low pressures and high-volume flows consideration should be given to the operating temperature of the motor under load as there is a potential for a motor overheat to occur.
Air on the inlet side of the impeller should be kept as smooth and laminar as possible. To maximise the efficiency at least a clearance of 1/3rd of the impeller diameter should be allowed on the fan inlet. Using an inlet ring (Inlet nozzle) overlapping the impeller inlet will help to eliminate flow disturbances before the air is drawn through the fan, reduce turbulence induced noise, keep the power consumption at the duty point to a minimum and maximise efficiency.
0 notes
Text
Industrial Blower Services and Repair Texas
There are five main types of industrial blower with unique applications: Centrifugal Blowers, Positive Displacement Blowers, Helical Screw Blowers, High-Speed Blowers, and Regenerative Blowers.
Centrifugal blowers are gear-driven impeller that accelerates air. They are either Single or multi-stage blowers. These blowers operate at 0.35-0.70 kg/cm2 pressure. The airflow drops if system pressure rises.
In Positive Displacement blowers the rotors trap air and push it through the housing. There is a constant air volume regardless of system pressure and are suited for applications prone to clogging. They turn slower than centrifugal blowers and are belt-driven for speed changes.
Centrifugal blowers comprises of hosting, impeller and drive arrangement. The housing is of sheet iron with circular inlet and rectangular outlet. Centrifugal air blowers and helical screw blowers are designed and manufactured in different ranges. The impellers are precision balanced for smooth vibration less operation. The fans can be fabricated in M.S., Stainless Steel, Aluminium, etc., depending on the kind of application.
American Blower LLC provide services for any brand or manufacturer of pumps. Our services range from standard inspections and repairs to complete overhauls. A repair or overhaul of a pump generally consists of an inspection and repair/modification. Some of the key players operating in the global industrial blowers market are Gardner Denver Inc., Hoffman & Lamson, SPX and others. While in pumps Nash, Gardner Denver, Hoffman & Lamson, Sutorbilt, and Roots among others contribute to the major share in the market.
We rebuild all types of pumps and blowers to bring its operation back to OEM specifications. The technicians have been factory trained in the process of vacuum pump repair. After the repair or remanufacturing process is complete, each item is system tested to ensure proper operation, OEM specification verification, and extended operation under load and also with stocks of spares to support older or obsolete equipment which OEM no longer supports. We use only OEM parts for repairs to ensure the highest quality of work and extend the life of your equipment. You can repair, rebuild, or exchange your pump with our replace program.
Please contact us for all your requirements on blowers or pumps call us (713) 360 6995 or mail us at [email protected]. We are based in Houston, Texas and our skilled technicians will address all your queries.

0 notes
Text
How To Choose Industrial Vacuum Cleaner?
How To Choose Industrial Vacuum Cleaner?

Today tons of wastes are generated by different industries on a daily basis. Most industries are facing challenges to get the waste cleaned. Roots Multiclean Ltd focuses to help industries solve their cleaning problem by providing the right Industrial Vacuum Cleaner (IVC) that is designed for continuous duty and reliable solutions for cleaning dusts, solids, and liquids.
Before choosing an industrial vacuum cleaner, let us know about two important things:- 1) What is IVC? 2) What are the things to be considered while choosing an IVC?
1. What Is Industrial Vacuum Cleaner?
Industrial Vacuum Cleaner is a machine used for the general cleaning in industrial environment, Industrial vacuum cleaners are designed to meet specific needs of users and particular tasks that are generally heavy to handle. It is provided with a side-channel blower that is powerful, silent, and suitable for performing round the clock.
The IVC ranges start from 1.8KW to 45KW suitable for various types of industries like Food, Pharmaceutical, Steel, Cement, Foundry, Textiles, Power plants, fertilizers, Bio labs, Engineering, and Automobile sectors available in a standalone, movable, fixed vacuum, online vacuuming, centralized vacuum system, and Truck mounted vacuum.
2. What Are The Things To Be Considered While Choosing An IVC?
Once you get an idea about IVC you need to consider certain things before picking up the right industrial vacuum cleaner based on Power, Performance, Filtration, Quality & Durability, and Capacity.
2.1 Power:
In general, power is expressed in W (Watts) & kW (kiloWatt). Our product lineup is equipped with single-phase and three-phase motors, which ensures the efficient vacuuming of debris for long period.
2.2 Performance:
The performance of IVC is determined by the Vacuum pressure and Airflow.
Vacuum pressure represents the suction force to clean up the dusts, solids, and liquids. It is also called “Depression”. The top depression rate value is taken by mmH2O (millimeters of Water Column), mbars, or others pressure measures.
Air Flow is measured by m3/h (cubic meters per hour), Liters/sec. It refers to the volume of air moved by the suction unit. The top airflow rate is measured with a suction inlet completely open.
2.3 Filtration:
The most important thing to consider is Filtration. Our Industrial Vacuum Cleaners are equipped with various types of primary filters and HEPA filters to accomplish high filtration efficiency which ensures the exhaust air is free from dust particles.
Primary filters generally have relatively low permeability. To achieve a reasonably low-pressure drop through the filter, the element area (surface area) must be increased. Quality of the filtration increases by large filter surface area to achieve better efficiency.
2.4 Collection Tank:
It’s also an important thing to consider the capacity while choosing an Industrial Vacuum Cleaner. It depends on the size of the disposal tank. For continuous operations, you need a large collection unit to remove residuals and it is also easy to detach the collection container with rotatable castor wheels for easy transportation of dust collected.
2.5 Quality & Durability:
Another element to be considered is Quality and Durability. All Industrial Vacuum Cleaners are provided with sturdy steels chassis to withstand for many years. When evaluating durability, the machine construction is designed and developed to work for the rugged nature of factories, where other industrial vacuum cleaners fail to do.
Conclusion:
On the market, there are many industrial vacuum cleaners available that differ by their performance, and applications. In the decision-making stage, it’s always better to hear from the professionals to guide you to choose the right Industrial Vacuum Cleaners. To know more about our Industrial Vacuum Cleaners visit our page
www.rootsmulticlean.com
Roots Multiclean Ltd, the leading cleaning equipment manufacturer in India. We supply industrial and commercial cleaning equipment with high quality. Contact Info ROOTS MULTICLEAN LTD R.K.G. Industrial Estate, Ganapathy, Coimbatore – 641 006, Tamil Nadu, India.
Phone : +91 95978 12345 Phone : +91 422 4330330 Fax : +91 422 2332107
0 notes
Text
Wholesale İndüstrial Filter
Industrial fan, a huge industry has comprehensive strategies. This is achieved by way of hearting several blades linked to a hub and shaft and driven with the aid of a motor. The speeds of those fanatics vary with the applications.wholesale indüstrial filter A blower is some other name for a fan that operates in which the fan is downstream as the idea of improvement. Most commercial lovers are fanatics of general sorts: centrifugal and axial lovers.
Axial Fans
Sometimes additionally as propeller lovers, in big prunings, they flow large volumes of air at pressures in lovers. Air enters and exits the fan via the fan hub. Uses indicate protection, from small applications which includes electric cooling to plumbing homes and tunnels.
Axial layout, a hub is designed radially or radially to challenge the middle and outer round axially to recognise the motion of air gasoline. The fluid movements parallel to the shaft or loop of the fan wheel.wholesale indüstrial filter The axial fan wheel rotation is placed in a short segment of the canalic ducts where they could input from the inlet and outlet.
Axial lovers have fan wheels with pitches less than 3 meters) to toes (9 m) in-among diameters, however axial fan wheels can exceed eighty two toes ().
In preferred, axial lovers are used for the large insurance of the simple human profile and both the group and the wider design.
Axair elements axial lovers with frames, axial fanatics with plates, axial enthusiasts with frames and in EC excessive performance specifications.
Centrifugal Fans
The centrifugal layout makes use of centrifugal force to actuate centrifugal force by way of a rotating disk with blades directed toward the air gear or set up at right angles to the disk.
The creation of the hub and the blades is referred to as the fan wheel and includes one or the other that has standard dynamic or software functions. wholesale indüstrial filter The centrifugal fan wheel is typically in an association within the fan housing. From the out of doors of the rotating fan the air or fuel is exhausted to an outlet at the most important diameter of the enclosure. This simultaneously draws more air or gasoline from the important hole to the wheel.
It is a gadget used for business clear out systems. Filter systems, an e fan, a dust filter out bag, a clear out cleansing device and a dustbin to address masses of high dust weights.
It is used to take advantage of the terminations of filter structures. Dust collection is a process used for series to be taken as a supply from a text. The dirt collector may be a device in use due to situations wholesale indüstrial filter of the types having a single structure. Used as a climate control tool to shield or decorate climate.
Desiccant filters purify nice liquid droplets from the air. They are used for checking out steel operating fluids, coolant or oil. Dried collectors are used to apply or defend the air in the work surroundings.
Smoke collector structures are used to take away filters from the air in very small microns. Effectively or small measures the materials and gases of welding, rubber and plastic processing, bloodless and speedy paintings, annealing and comparable business processes.
Types of Filter Systems
There are five predominant styles of commercial filter out structures:
Separators and Cyclones
Bag Filters
Wet clear out Wet Scrubber
Unit collector filters
Electrostatic precipitating filters
What is "dust"?
Dust; consisting of very small cloth; very pleasant, powder-like substance on the ground, on, or in weaponry.
Why is “Dust” a Problem?
Canal or reasons
Causes health hassle for workers
Causes safety difficulty for equipment and facilities
Sanitation and hygiene control will become difficult
growth care
overseeing gadget
Making it tough to shop valuables.
Where is the Dust Problem Found?
Everywhere – product transfer Plant, plant drain, tunnel, tunnel, software, even in workplaces and houses.
The clear out baggage and the dirt cake at the media floor assist in filtration to split the debris from the incoming polluted air circulate, from the fresh air exiting the bag into the ecosystem.
Bag Cleaning Systems in Filter Systems:
Reverse-pulse (pulse-wave or Jet-Pulse)
High Pressure Low Volume
– Low volume of eighty to a hundred psig air
– Cleaning air supplied through the compressed air system
– Oil and moisture infection from the compressed air device is commonplace.
Medium Pressure
– 10-15 psig at medium to high air extent
– A effective displacement blower is used to deliver the air.
– Air supply nearby to the inlet of the PD blower; Oil and moisture infection are normally no longer a trouble.
Low Pressure – 30-one hundred “w.C.
– A fan is used to deliver excessive quantity air at low pressure.
Bag Filter Systems Air Inlet Configuration
A properly designed and carried out air intake gives many functionalities:
– Allows the air flow with the particles to enter the filter without detrimental the bag.
– Leaves enough room to enter the bag with out suffocating.
– Allows debris to fall from the air flow into the clear out decrease funnel.
High Air Intakes
– For medium to mild dirt loading.
-Deflectors are covered to lessen the damage of the bag so that incoming particles inside the air stream are filtered out.
– Used for popular dirt collection or for conveying air at the air outlets of cyclone creditors.
Cyclonic Material coping with inlets and outlets
– Ideal for heavy loading or material coping with.
– The inlet has a tangential inlet into the section beneath the filter bag segment.
– Heavy loaded negative raise
Low air intakes
– Air flows coming into the filter out beneath the luggage
– Not recommended due to the potential for air turbulence in the filter out at the grimy air inlet.
Baffle to deflect the airflow downwards can help lessen this capability.
Let's analyze a few fundamental concepts in filter out structures
Get airspeed
0 notes
Text
FSE Safe suppliers for Portable Fumes and Smoke Exhauster - Blower

Designed for continuous operation
One fume exhauster-blower does the job of two fans
By placing the hose on the inlet, fumes and smoke are drawn away from the operator at soldering, brazing and etching operations. Switch the same hose to the discharge to supply fresh air for workers inside tanks, manholes and other confined areas.
Available Models: Type 1 and Type 2
Features:
AMCA Type B spark resistant construction standard for all models
Totally Enclosed Fan Cooled (TEFC) motors are standard
Motors are continuous duty, full horsepower rated. NOT duty rated
Heavy-duty 14-gauge steel blower housing on all Type 1 models
All models available with 115/230 Volt, 1 Phase, 60 Cycle or 230/460 Volt, 3 Phase, 60 Cycle motors
575 Volt and 50 Cycle motors also available
Single Phase, TEFC motors (up to 1 HP) come with an 8-foot cord, 3 prong grounded plug and a switch pre-wired for 115 Volt, 60 Cycle
Inlet and discharge guards required by OSHA are standard
Safe, no exposed moving parts
We also supply axial fans – belt driven, axial fans – direct driven, Air Pneumatic Ventilation Fan 12” / 300mm (Blower + Extractor), mixed flow fans and tank vent fans.
For more information visit https://www.fsesafe.com/portable-fume-exhauster.php
For more information kindly visit us at www.fsesafe.com and for any enquiries email us at [email protected]
0 notes