#senolysis
Explore tagged Tumblr posts
Text
#ACCB #stemcell #SASO #PROTEIN STABILIZING TECHNOLOGY Modified Spherosome technology improves heat stability of protein molecules.Under the PATENT approval.#Cellularsenescence #Senotherapy #Senolysis #Aging
#Rejuvenation #Cosmeceutical #haircare #skincare #wwwaacblabcom

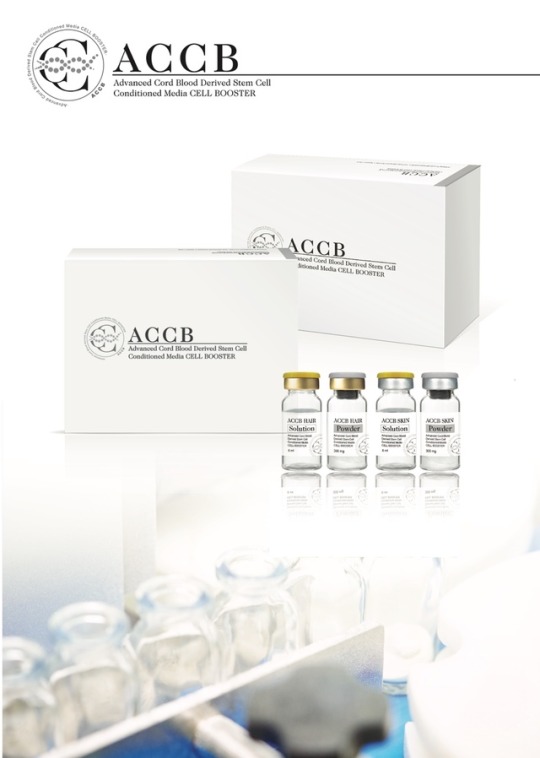

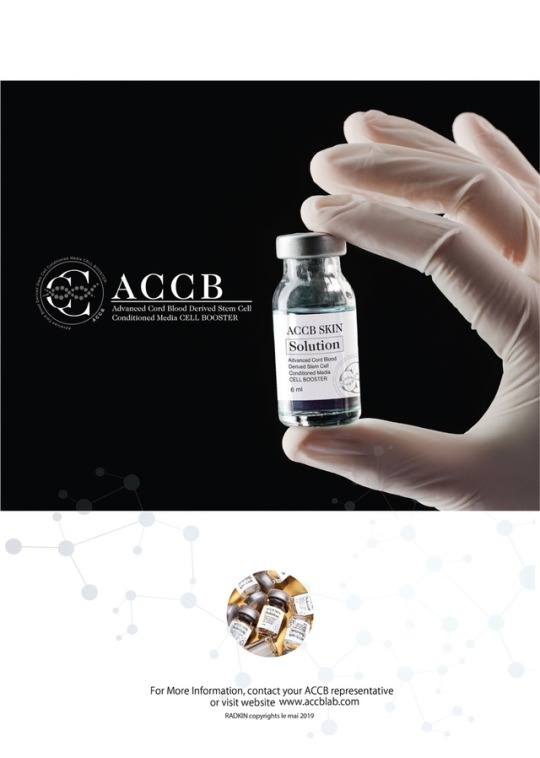

0 notes
Link
The estimated “natural” life span of humans is ∼30 years, but improvements in working conditions, housing, sanitation, and medicine have extended this to ∼80 years in most developed countries. However, much of the population now experiences aging-associated tissue deterioration. Healthy aging is limited by a lack of natural selection, which favors genetic programs that confer fitness early in life to maximize reproductive output. There is no selection for whether these alterations have detrimental effects later in life. One such program is cellular senescence, whereby cells become unable to divide. Cellular senescence enhances reproductive success by blocking cancer cell proliferation, but it decreases the health of the old by littering tissues with dysfunctional senescent cells (SNCs). In mice, the selective elimination of SNCs (senolysis) extends median life span and prevents or attenuates age-associated diseases (1, 2). This has inspired the development of targeted senolytic drugs to eliminate the SNCs that drive age-associated disease in humans.
8 notes
·
View notes
Text
Senolysis by glutaminolysis inhibition ameliorates various age-associated disorders
Senolysis by glutaminolysis inhibition ameliorates various age-associated disorders
Credit: ©NAKANISHI Makoto, The Institute of Medical Science, The University of Tokyo(IMSUT) Senescent cells accumulate in organs during aging, promote tissue dysfunction, and cause numerous aging-related diseases like cancer. The cells arise through a process called “cellular senescence,” a permanent cell cycle arrest resulting from multiple stresses. A collaborative research group led by…

View On WordPress
0 notes
Link

For the past quarter century, scientists battled Alzheimer’s disease under a single guiding principle: that protein clumps—beta-amyloid—deposited outside sensitive brain cells gradually damage neuronal functions and trigger memory loss. The solution seems simple: remove junk amyloid, protect the brain.
They could be completely wrong.
Last month, Alzheimer’s disease defeated another promising near-market drug that tried to prevent or remove amyloid deposits, adding to the disease’s therapeutic “graveyard of dreams.” Although the drug removed toxic amyloid, the patients didn’t get better. The failure is once again spurring scientists to confront an uncomfortable truth: targeting amyloid clumps when patients already show memory symptoms doesn’t work. Wiping out soluble amyloid—fragments of proteins before they aggregate into junk—also dead ends.
It’s time to think outside the box.
Last week in Nature Neuroscience, Dr. Mark Mattson’s team at the National Institute on Aging Intramural Research Program added substantial proof that senolytics, the golden child of anti-aging drugs, rescue memory loss in Alzheimer’s disease, at least in mice genetically engineered to accumulate amyloid clumps in their brains.
With age, the toxic proteins damaged a particular type of brain cell called OPCs, causing them to transform into cellular monsters that trigger inflammation in the brain. These zombie cells leak “toxic” molecules into their local environments, transforming essential parts of the brain into tiny inhospitable hellscapes that, like overheating CPUs, throttle efficient computation.
After weekly treatments with the drugs for barely three months, the team found fewer zombie OPC cells gathered around amyloid clumps in the mice’s brains. The treatment also disintegrated the clumps in memory-related regions, and—perhaps more importantly—the brains were no longer inflamed. In a series of memory tests, the treated mice regained their ability to learn and memorize complex mazes.
“Our findings pave the way for future preclinical and clinical studies that will test the hypothesis that senolytic therapies can … preserve brain function in [Alzheimer’s] and other age-related neurodegenerative disorders,” the authors concluded.
What Are Senolytics, Anyway?
Three years ago, in a lab at the Mayo clinic, Drs. Darren Baker and Jan van Deursen gaped at cages of spritely, healthy old mice roaming around their homes like zealous teenagers. At the time, the team had no idea they were about to spark an anti-aging revolution.
The mice had been dosed with powerful rejuvenating drugs called senolytics. Broadly, senolytics are a large drug family with multiple origins. Some were originally developed to destroy cancer cells. Others came from fruits and vegetables. Yet shockingly, when given to aging animals, senolytics efficiently hunted down stubborn zombie cells while sparing healthy ones.
Zombie cells are aging cells that can no longer efficiently perform their functions but refuse to retire. Rather than silently giving way to the younger generation, these senescent cells struggle to stay alive, leaking out molecules that increase inflammation into their environment. Aged tissues already suffer from long-term negative inflammation, which is akin to the body turning its molecular protective bazookas toward itself. Zombie cells pour gasoline onto that fire.
So far, senescent cells are linked to aging in the brain, muscles, hair, and heart. Their rap sheet makes them scientists’ favorite target for preventing tissue damage with age—or even prolonging lifespan.
If you’re thinking “duh, of course drugs that help aging also help Alzheimer’s,” that’s sadly rather uncommon. Normal aging and Alzheimer’s disease look completely different in the brain. For example, normal aging doesn’t kill neurons; Alzheimer’s does. This is why scientists don’t always equivocate stuff they learned from aging brains to those with Alzheimer’s.
But there are exceptions.
The Senolytics Connection
Mattson decided to take a leap of faith.
Because senolytics clearly help aging brains, his team decided to explore if these drugs also boost brain function with amyloid buildup. The team engineered mice carrying a genetic mutation that increased beta-amyloid deposits in their brains as they got older. Some mice also carried an additional mutation that made senescent cells glow neon green under fluorescent light, allowing the team to track these cells and uncover their identity.
Remarkably, it wasn’t neurons that turned into zombies. The brain’s immune cells, called microglia, also warded off the senescence curse. Rather, beta-amyloid worked their dark magic on OPCs, which gradually turned evil with age and “moved in” with amyloid clumps. Under the microscope, senescent OPCs gathered around these clumps like witches around a cauldron, and spewed out inflammatory molecules to injure their neighbors.
It’s a story of good cells gone bad. Normally, OPCs belong to a family of “guardian angel” cells that protect and support neuronal function. They activate in response to brain damage to repair the electrical insulation sheath that encapsulates neurons. Without OPCs, our brain’s wiring loses its insulating layer—and brain functions suffer.
Here’s where senolytics comes in. The DQ combo (alas, not Dairy Queen but the less intuitive dasatinib and quercetin duo) has previously been approved by the FDA as “senolytic” compounds due to its ability to wipe out senescent cells in aging or damaged tissues. The team squirted the drug cocktail into their Alzheimer’s mice once a week for 11 weeks.
Positive results came fast: the mice’s beta-amyloid levels dropped within three months. What’s more, the treated mice also had fewer senescent cells in their hippocampus, the brain’s main memory center, and navigated complex water mazes better than their peers.
Outside the Box
Given Alzheimer’s’ atrocious therapeutics record, Mattson’s study doesn’t prove much by itself—it’s one study, in one type of Alzheimer’s model that only captures part of the disease’s pathology.
But add a dose of previous evidence, and a trend is bubbling up. In 2018, Baker and van Deurson, the original senolytics-for-brain-health guys, found that these drugs also helped preserve memory in mice with another type of protein buildup—tau—that’s prevalent in Alzheimer’s brains in mice.
In their study, by cleverly killing off senescent cells (also not neurons, but star-shaped glia) using either genetic engineering or drugs, the team protected vulnerable neurons in the hippocampus and cortex and boosted memory. Around the same time, Dr. Miranda Orr at the University of Texas Health Science Center also found that senescent cells—this time, neurons—are linked to abnormal protein buildup in Alzheimer’s-like brains in mice.
Unlike these previous studies, Mattson’s team didn’t find any abnormalities in neurons or star-shaped glia. Confused? Yeah, that’s the mystery of Alzheimer’s: because animals don’t normally develop the disease, scientists have to rely on different genetic models to force symptoms on mice. The caveat is that DNA-level tinkering doesn’t completely recapitulate Alzheimer’s complexities, and we end up with conflicting—or sometimes complimentary—data.
“There is a lot that is unknown about the role of senescent cells in applications for most human diseases, including Alzheimer’s. We have not looked for long-term negative effects of senolysis in the brains of mice. The potential impact could be significant, but we should approach with caution,” said Baker to Singularity Hub.
Together, the three studies do clearly show that senolytics have a positive effect on Alzheimer’s brains in the short run—whatever cell type be damned.
At least in mice. Baker cautioned, “It is important to keep an open mind about what may happen when strategies are employed in people, as studies that are not properly designed or controlled could lead to issues with interpretation of the results of these studies.”
Nevertheless, branching out from the beta-amyloid tunnel vision is good: as other ideas gain steam, a long-awaited breakthrough could be in the future. For example, some scientists believe that blood components from young donors may be the answer. Some think that tinkering with brainwaves could be the cure. Others have their hopes on directly editing genetic links to the disorder.
In the end, it’s about helping roughly 50 million people worldwide suffering from Alzheimer’s, with numbers growing every day. Every. Lead. Counts. And senolytics is a promising one.
Image Credit: Sebastian Kaulitzki / Shutterstock.com
Shelly Fan Source: Singularity Hub
0 notes
Text
Inhibition of USP7 activity selectively eliminates senescent cells in part via restoration of p53 activity - He - - Aging Cell - Wiley Online Library
Inhibition of USP7 activity selectively eliminates senescent cells in part via restoration of p53 activity – He – – Aging Cell – Wiley Online Library
“The accumulation of senescent cells (SnCs) is a causal factor of various age‐related diseases as well as some of the side effects of chemotherapy. Pharmacological elimination of SnCs (senolysis) has the potential to be developed into novel therapeutic strategies to treat these diseases and pathological conditions. Here we show that ubiquitin‐specific peptidase 7 (USP7) is a novel target for…
View On WordPress
0 notes
Text





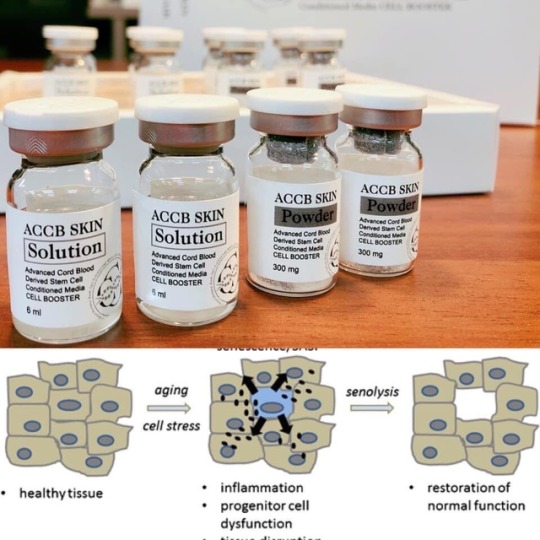
RADKIN是一家专注于科学的皮肤营养,健康和疾病治疗公司 乐德妍科技有限公司是一家专业从事健康美容抗老技术支持的科技型企业,采用精选的技术和经验丰富的治疗护肤方案。
我们可以根据您的需求进行产品的研发和市场营销,也可以为您提供产品贸易和注册服务。#Injectable #可注射的 #Mesotherapy #消脂减肥
Professional treatment cosmetics #专业护理护肤品
Professional therapy cosmetics #专业理疗护肤品
Home care cosmetics #家居护肤品 #radkin #Senescence #Cellularsenescence
#Senotherapy #Senolysis #Aging
#Rejuvenation #ACCB #Topical
#cellbooster #mesotherapy #plasticosmetic
#Demacosmetic #Cosmeceutical
#botoxcosmetics
www.theradkin.com 邮件地址:[email protected]
0 notes
Text

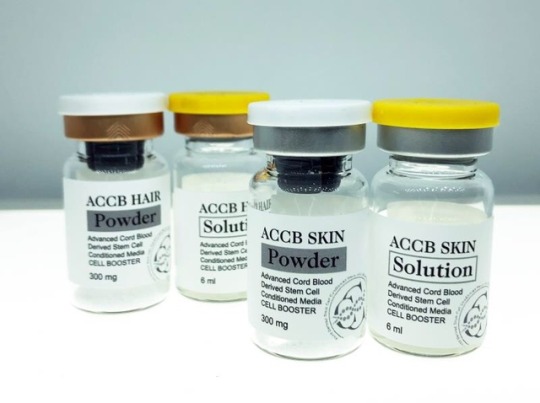


RADKIN是一家专注于科学的皮肤营养,健康和疾病治疗公司 乐德妍科技有限公司是一家专业从事健康美容抗老技术支持的科技型企业,采用精选的技术和经验丰富的治疗护肤方案。
我们可以根据您的需求进行产品的研发和市场营销,也可以为您提供产品贸易和注册服务。#Injectable #可注射的 #Mesotherapy #消脂减肥
Professional treatment cosmetics #专业护理护肤品
Professional therapy cosmetics #专业理疗护肤品
Home care cosmetics #家居护肤品 #radkin #Senescence #Cellularsenescence
#Senotherapy #Senolysis #Aging
#Rejuvenation #ACCB #Topical
#cellbooster #mesotherapy #plasticosmetic
#Demacosmetic #Cosmeceutical
#botoxcosmetics
www.theradkin.com 邮件地址:[email protected]
0 notes
Text




RADKIN是一家专注于科学的皮肤营养,健康和疾病治疗公司 乐德妍科技有限公司是一家专业从事健康美容抗老技术支持的科技型企业,采用精选的技术和经验丰富的治疗护肤方案。
我们可以根据您的需求进行产品的研发和市场营销,也可以为您提供产品贸易和注册服务。#Injectable #可注射的 #Mesotherapy #消脂减肥
Professional treatment cosmetics #专业护理护肤品
Professional therapy cosmetics #专业理疗护肤品
Home care cosmetics #家居护肤品 #radkin #Senescence #Cellularsenescence
#Senotherapy #Senolysis #Aging
#Rejuvenation #ACCB #Topical
#cellbooster #mesotherapy #plasticosmetic
#Demacosmetic #Cosmeceutical
#botoxcosmetics
www.theradkin.com 邮件地址:[email protected]
0 notes
Text






RADKIN是一家专注于科学的皮肤营养,健康和疾病治疗公司 乐德妍科技有限公司是一家专业从事健康美容抗老技术支持的科技型企业,采用精选的技术和经验丰富的治疗护肤方案。
我们可以根据您的需求进行产品的研发和市场营销,也可以为您提供产品贸易和注册服务。#Injectable #可注射的 #Mesotherapy #消脂减肥
Professional treatment cosmetics #专业护理护肤品
Professional therapy cosmetics #专业理疗护肤品
Home care cosmetics #家居护肤品 #radkin #Senescence #Cellularsenescence
#Senotherapy #Senolysis #Aging
#Rejuvenation #ACCB #Topical
#cellbooster #mesotherapy #plasticosmetic
#Demacosmetic #Cosmeceutical
#botoxcosmetics
www.theradkin.com 邮件地址:[email protected]
0 notes
Text







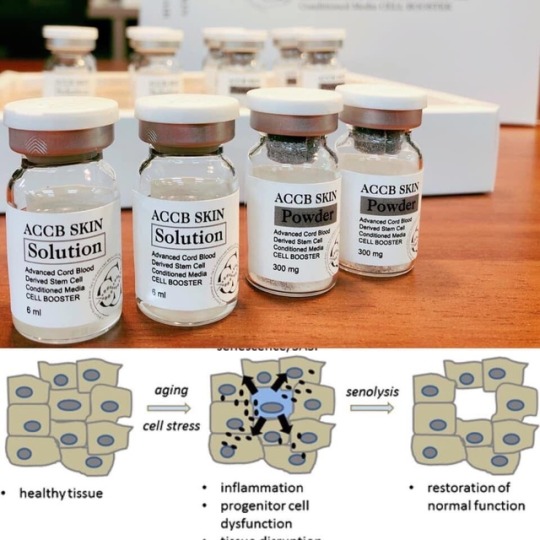
ACCB SKIN & HAIR Treatment program //PRODUCT INTRODUCTION
ACCB SKIN
ACCB HAIR
ACCB contains 5% of Human umbilical cord blood-derived mesenchymal stem cells (UCB-MSCs) conditioned media, biomaterials and plant derived anti-oxidant concoction for skin and scalp tissue regeneration. Advanced Cord Blood Derived Mesenchymal Stem Cell derived Cell Booster for Skin & Hair #radkin #Senescence #Cellularsenescence
#Senotherapy #Senolysis #Aging #exosome
#Rejuvenation #ACCB #Topical #stemcells
#cellbooster #mesotherapy #miRNA #Spherosome
#Demacosmetic #Cosmeceutical #protein #molecules
#botoxcosmetics #cellcommunication
0 notes
Text






ACCB SKIN & HAIR Treatment program //PRODUCT INTRODUCTION
ACCB SKIN
ACCB HAIR
ACCB contains 5% of Human umbilical cord blood-derived mesenchymal stem cells (UCB-MSCs) conditioned media, biomaterials and plant derived anti-oxidant concoction for skin and scalp tissue regeneration. Advanced Cord Blood Derived Mesenchymal Stem Cell derived Cell Booster for Skin & Hair #radkin #Senescence #Cellularsenescence
#Senotherapy #Senolysis #Aging #exosome
#Rejuvenation #ACCB #Topical #stemcells
#cellbooster #mesotherapy #miRNA #Spherosome
#Demacosmetic #Cosmeceutical #protein #molecules
#botoxcosmetics #cellcommunication
0 notes
Text








ACCB SKIN & HAIR Treatment program //PRODUCT INTRODUCTION
ACCB SKIN
ACCB HAIR
ACCB contains 5% of Human umbilical cord blood-derived mesenchymal stem cells (UCB-MSCs) conditioned media, biomaterials and plant derived anti-oxidant concoction for skin and scalp tissue regeneration. Advanced Cord Blood Derived Mesenchymal Stem Cell derived Cell Booster for Skin & Hair #radkin #Senescence #Cellularsenescence
#Senotherapy #Senolysis #Aging #exosome
#Rejuvenation #ACCB #Topical #stemcells
#cellbooster #mesotherapy #miRNA #Spherosome
#Demacosmetic #Cosmeceutical #protein #molecules
#botoxcosmetics #cellcommunication
#accb#cosmeceutical#rejuvenation#radkin#senotherapy#cellcommuication#miRNA#exsome#sphersome#demacosmetic
0 notes
Text

ACCB SKIN & HAIR Treatment program //PRODUCT INTRODUCTION
ACCB SKIN
ACCB HAIR
ACCB contains 5% of Human umbilical cord blood-derived mesenchymal stem cells (UCB-MSCs) conditioned media, biomaterials and plant derived anti-oxidant concoction for skin and scalp tissue regeneration. Advanced Cord Blood Derived Mesenchymal Stem Cell derived Cell Booster for Skin & Hair #radkin #Senescence #Cellularsenescence
#Senotherapy #Senolysis #Aging #exosome
#Rejuvenation #ACCB #Topical #stemcells
#cellbooster #mesotherapy #miRNA #Spherosome
#Demacosmetic #Cosmeceutical #protein #molecules
#botoxcosmetics #cellcommunication
#cosmeceutical#rejuvenation#accb#senotherapy#radkin#exsomes#cellbooster#cellcommunication#miRNA#spherosome#demacosmetic
0 notes
Text



Healthy and beautiful aging
Vieillissement sain et beau
健康美丽的衰老
Здоровое и красивое старение
健康で美しい老化
#radkin #Senescence #Cellularsenescence
#Senotherapy #Senolysis #Aging
#Rejuvenation #ACCB #Topical
#cellbooster #mesotherapy #plasticosmetic
#Demacosmetic #Cosmeceutical
#botoxcosmetics
www.theradkin.com
0 notes
Text

Healthy and beautiful aging
Vieillissement sain et beau
健康美丽的衰老
Здоровое и красивое старение
健康で美しい老化
#radkin #Senescence #Cellularsenescence
#Senotherapy #Senolysis #Aging
#Rejuvenation #ACCB #Topical
#cellbooster #mesotherapy #plasticosmetic
#Demacosmetic #Cosmeceutical
#botoxcosmetics
www.theradkin.com
0 notes
Text

Healthy and beautiful aging
Vieillissement sain et beau
健康美丽的衰老
Здоровое и красивое старение
健康で美しい老化
#radkin #Senescence #Cellularsenescence
#Senotherapy #Senolysis #Aging
#Rejuvenation #ACCB #Topical
#cellbooster #mesotherapy #plasticosmetic
#Demacosmetic #Cosmeceutical
#botoxcosmetics
www.theradkin.com
0 notes