#retinal haemorrhage
Explore tagged Tumblr posts
Text

RUBBER BULLETS? IT'S LIKE SHOOTING A NERF GUN AT SOMEONE!
The weapons have led to permanent disability in hundreds of cases and many deaths. There has been an alarming increase in eye injuries, including eyeball ruptures, retinal detachments and the complete loss of sight, as well as bone and skull fractures, brain injuries, the rupture of internal organs and haemorrhaging, punctured hearts and lungs from broken ribs, damage to genitalia, and psychological trauma

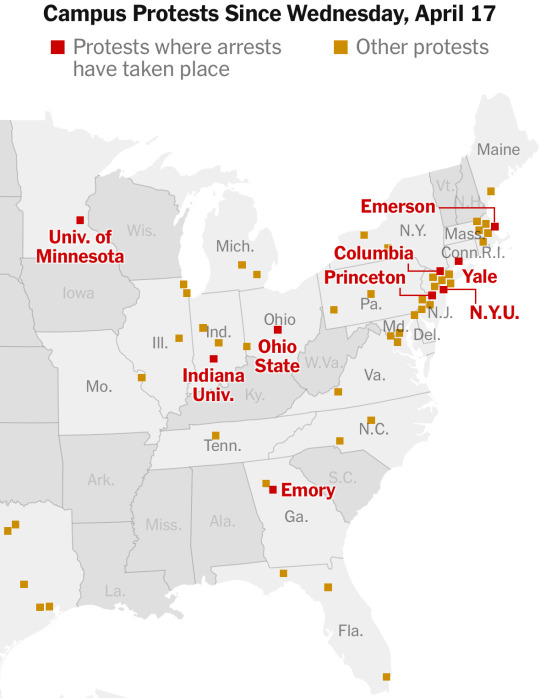
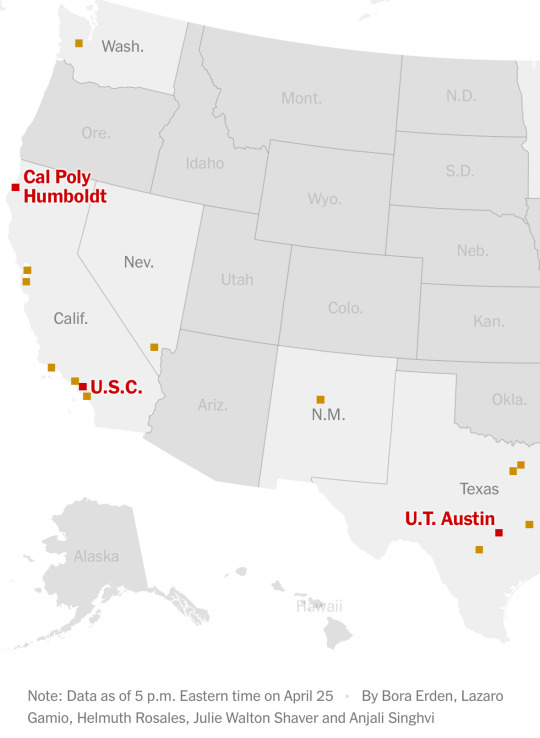
Source
Over 40 campuses and counting!
4K notes
·
View notes
Link
#market research future#vitrectomy devices market#vitrectomy devices market size#vitrectomy devices industry#vitrectomy devices
0 notes
Link
#market research future#vitrectomy devices market#vitrectomy devices market size#vitrectomy devices industry#vitrectomy devices
0 notes
Text
diabetesDiabetic Retinopathy — Ayurvedic Perspective & Treatment
Hyperglycemia is defined as elevated levels of sugar, or glucose, in the blood. Mellitus hyperglycemia is the starting point for the development of diabetic retinopathy in uncontrolled diabetes.
The following are the mechanisms through which hyperglycemia causes Microangiopathy:
Cellular damage: Hyperglycemia causes damage to retinal and endothelial cells. It also causes pericytes to be lost and the basement membrane of capillaries to thicken.
Changes in haematology and biochemistry: Hyperglycemia is a major factor in the development of Microangiopathy. It also involves an increase in platelet adhesiveness, blood viscosity, and distortion of red blood cells.
Microangiopathy, commonly known as tiny vessel disease, is a type of microvascular illness. Microangiopathy affects the pre-capillary arterioles, capillaries, and venules of the retina. It is the major pathology in diabetic retinopathy caused by hyperglycemia.
Microangiopathy’s effects on diabetic retinopathy include a breakdown of the blood-retinal barrier. A weakened capillary wall causes retinal edoema, haemorrhages, and lipid leaks.
Diabetic Retinopathy and Ayurveda
According to Ayurveda, there is no such condition that directly translates into diabetic retinopathy. Even in the Ashtanga Sangrah and Sushruta, where eye condition is covered in depth, there is no such mention. Few people translate it as Pramehajanya Timira from modern terminology. A name can be translated. However, pathological understanding is crucial. And due of the lack of this pathogenic manifestation, we are unable to help DR patients with Ayurveda.
Ayurveda allows a physician to make decisions regarding an illness based on the participation of the Doshas. Before we can make a choice concerning Dosha in the DR, we must first comprehend several other concepts.
In the case of diabetic retinopathy, we must comprehend the following facts, according to Ayurveda:
Low metabolism /Agni Mandya Blood vessel problems /Rakta Pitta and Vata Rakta
These are two significant points in the context of Diabetic Retinopathy. When we comprehend these, we will have a thorough understanding of the condition.
Agni Mandya / Low Metabolic Rate
According to Modern Biology, metabolism is the body’s ability to burn food for energy production. In Ayurveda, this is referred to as Agni. Diabetes is not the sole cause of retinal alterations.
Diabetes is a metabolic condition in and of itself. Diabetes primarily inhibits sugar metabolism, as well as other things (fats, etc.). However, when it is combined with dyslipidemia and other diseases, the situation worsens. And it is at this moment that diabetes problems become prevalent.
Blood vessel issues/Rakta Pitta and Vata Rakta
Ayurveda distinguishes two conditions: Vata Rakta and Rakta Pitta. These parameters are critical for comprehending the two fundamental features of DR. Infarct (no blood flow to an area) or bleeding from very tiny arteries are the two most serious issues.
Vata Rakta is all about blood supply loss, which could be caused by artery obstruction owing to cholesterol or even inflammation in the artery walls.
Rakta Pitta is concerned with bleeding. When blood heats up, it gathers extra water from the surrounding tissues, resulting in increased blood volume. As a result, blood vessel pressure rises, resulting in bleeding.
So we now have a name for the condition. The next step is to determine Doshas.
Diabetic Retinopathy Is Caused By Doshas
Diabetes is a classic Vata imbalance illness. However, this imbalance begins with the Kapha. But we’re talking about a secondary condition here. And the key issue in this case is the blood. Pitta is the Dosha associated with blood.
As a result, we must exercise caution with all of the Doshas, focusing primarily on the pitta dosha. In general, when all three doshas are present, one of them becomes imbalanced throughout treatment.
Diabetic Retinopathy Ayurvedic Treatment
Now that we have a comprehensive understanding of the issue, we can better differentiate the Ayurvedic treatment options. There are a few key aspects to consider:
Keeping blood sugar under control
Keeping the Agni in Check
Addressing the root cause- In the case of infarcts (Vata Rakta), when bleeding is prominent (Rakta Pitta).
With this three-dimensional approach, we can better deal with Diabetic Retinopathy.
Because the eye is only one of the organs affected by diabetic retinopathy. The eye is at the receiving end. As a result, it is critical to treat the illness on a systemic basis. The main advantage of treating this problem on a systemic level is that a patient can avoid subsequent diabetes complications such as diabetic nephropathy!
This is why, when we treat DR, we assure that we will work on the entire system to achieve complete recovery of your health. Not only the eye.
Ayurveda is the other side of the coin!
When we seek Ayurvedic treatment for an illness, the first question we ask is, “Is it curable through Ayurveda?” The same is true with Diabetic Retinopathy. And now for your question: How effective is Ayurveda in the treatment of diabetic retinopathy?
Ayurveda, without a doubt, can prevent “blindness.” Ayurvedic treatment can certainly halt the progression of your condition. You can also live a normal life. Patients’ vision improves over time.
However, in addition to treatment, we always advise patients to keep taking their diabetes medications. We just add certain Ayurvedic medicines that can assist in controlling blood sugar levels and avoiding illness complications.
Related-
Know more about Ayurveda Diabetes Reversal.
0 notes
Text
What is Intravitreal Injection therapy and why it is used?
An intravitreal (pronounced in tra VIT re al.) injection involves injecting a medicine directly into the vitreous cavity, the area behind the eye that is filled with a gel-like substance known as vitreous humour. In an office environment, the treatment is often carried out by a qualified retina specialist. In this post, we are going to discuss what exactly it is and why it is used.
Read it out carefully:
Why is intravitreal injection used?
Age-related macular degeneration (sometimes referred to as "wet" AMD), diabetic macular oedema (leakiness resulting from diabetic damage), retinal vein occlusion (blocked blood vessels in the retina causing leakiness), inflammation or abnormal blood vessel growth related to short-sightedness, or other uncommon issues with the blood supply to the retina are among the common diseases treated with this type of injection.
Your physician will have gone through other treatment choices with you and will have given you an explanation of the benefits and drawbacks of every option. The following factors will affect these therapy options:
The reason behind your vision issue
Where in your retina is the leakiness?
What additional treatments have you had in the past, such as laser surgery if necessary or other injectable therapies for the eyes, and how have those treatments affected your eyes?
If you have gone through cataract surgery in the past
Additional factors, such as the presence of glaucoma
The majority of patients benefit in some way from intravitreal medication injections, which are often quite successful therapies. In addition to our disease-specific information pamphlets, your doctor will go through the particular risks and advantages of the course of therapy that is advised for you.
Common Diseases Treated by Intravitreal Injections
Uveitis
CME (cystoid macular edema)
Neovascular AMD
RVO (retinal vein occlusions)
Geographic atrophy in AMD
Endophthalmitis
NPDR, DME, or PDR (non-proliferative diabetic retinopathy, diabetic macular edema, or proliferative diabetic retinopathy)
CNVM (choroidal neovascular membrane) as a result of certain disorders of the retina
Risks of Intravitreal Injection
Infection is the most dangerous side effect of intravitreal injections. There is around a 1 in 5,000 chance of infection. Serious infections can result in blindness and loss of eyesight. In 10% to 20% of cases, subconjunctival haemorrhage—or bleeding on the surface of the eye—occurs. Approximately 10% of treatments result in floaters. Ten percent or so of individuals get elevated intraocular pressure after receiving long-term therapy.
Conclusion
Hope this post is useful for you, and now you know what an intravitreal injection is and why it is used. If you are looking for a specialist for your eyes and facing any kind of eye-related issue, you can connect with a professional team. If you are looking for eye surgery in Devon, you can connect with us. Here, we have experienced surgeons to offer you the best services.
#eye#Eye surgery in Devon#Eye surgeon in Devon#Retinal disease in Devon#Holistic eye care in Devon#treatment of minor eye conditions in Devon#diabetic eye carein Devon#complex cataract surgery in Devon
0 notes
Text
Eales Disease Symptoms type Causes & Treatment
The mid-peripheral retina is affected by Eales' disease, an idiopathic occlusive vasculitis that is characterised by retinal venous inflammation (periphlebitis), vascular occlusion, and ensuing retinal neovascularization. Recurrent vitreous haemorrhage is a defining feature of Eales' illness.

What is Eales Disease?
Eales disease is an rare, idiopathic vascular condition primarily affecting the retina that results in inflammation and retinal vessel occlusions, first identified by British ophthalmologist Henry Eales in 1880. Primarily impacting young males from India and Pakistan as well as South Asia regions.
Although its exact cause remains unknown, vascular abnormalities and genetic predisposition are thought to play a part. Recognizing symptoms such as blurred vision, floaters and peripheral vision loss is essential for early diagnosis and treatment.
What are the symptoms of Eales Disease?
Eales disease symptoms vary between people, usually occurring gradually over time. Here are the more frequently seen indicators of Eales disease:
Blurred Vision: One of the main signs and symptoms of Eales disease is blurriness or reduced visual acuity, with affected individuals often finding difficulty in focusing and perceiving objects as blurry.
Floaters: Floaters are small specks or cobweb-like structures that appear to float across your visual field, often appearing dark or transparent, that interfere with clear vision and may obstruct clear sightlines. As eyes move they tend to shift accordingly causing these floaters to drift across.
Loss of Peripheral Vision: Eales disease may lead to the gradual deterioration of peripheral vision, commonly referred to as tunnel vision. Affected individuals may notice their field of view narrowing drastically and their ability to see objects through side vision diminished significantly.
Visual Field Defects: As disease progresses, certain areas of the visual field may become blank or distorted - this may present itself in form of dark spots or patches within vision.
Vitreous Hemorrhage: Eales disease may lead to bleeding in the vitreous gel that fills the center of your eye, potentially resulting in sudden and significant vision impairment, leading to a dark or shadowy appearance of vision.
Retinal Detachment: At advanced stages, Eales disease increases the risk of retinal detachment, in which the retina detaches from its supporting tissue and detaches completely from visual perception.
If left untreated promptly, retinal detachment can lead to permanent vision loss; symptoms include flashes of light or the perception of curtains or veil covering part of visual field or sudden increase in floaters. This condition requires medical intervention immediately as failure to do so could be fatal for permanent vision loss.
What are the causes of Eales Disease?
The exact cause Eales disease remains unknown, though it has been classified as an idiopathic disorder. Multiple factors are thought to contribute to its development, including:
Vascular Abnormalities: Eales disease is characterized by abnormal changes to retinal blood vessels. These changes include inflammation, narrowing of vessels (vasculitis), and formation of new fragile blood vessels (neovascularization). It is thought that these vascular abnormalities play a key role in its development; however, its cause remains elusive.
Genetics: No specific gene mutation has yet been linked with Eales disease; however, genetic predisposition may increase susceptibility. Studies indicate certain genetic factors could make certain individuals more prone to Eales. More research needs to be completed in order to establish definitive links.
Environmental Factors: Exposure to toxins or infections has been proposed as potential triggers for Eales disease. Some studies have reported an association between exposure to tuberculosis (TB) as well as other infectious agents and Eales disease; however, any direct relationship must first be explored further before any decisions on prevention are made.
#Eales Disease#health & fitness#sanjeevan netralaya#eye care#eyes#eye health#retina care center#retirement#ayurvedic treatment#ayurveda
0 notes
Text
TYPES OF SURGERY
I) IMMEDIATE
When life, limb or organ-saving intervention is required and resuscitation is performed simultaneous with intervention.
Normally it occurs within minutes of decision to operate.
Expected location: next available operating theatre, if required “break-in” to existing lists
E.g. Repair of ruptured aortic aneurysm; Laparotomy for control of haemorrhage.
🍁
II) URGENT
Intervention for acute onset or clinical deterioration of life, limb or organ survival; for fixation of multiple fractures; and for relief of pain or other distressing symptoms.
Normally it occurs within hours of decision to operate and once resuscitation is completed
Expected location: day time “emergency” list or Out-of-hours emergency theatre
E.g. Debridement plus fixation of fracture; Laparotomy for perforation
🍁
III) EXPEDITED
When a patient is stable but requires early intervention for a condition that is not an immediate threat to life, limb or organ survival.
Normally it occurs within days of decision to operate.
Expected Location: Elective list with “spare” capacity or Day time “emergency” list (except at night)
E.g. Retinal detachment; Excision of tumour with potential to bleed or obstruct
🍁
IV) ELECTIVE
Surgical procedure planned or booked in advance of routine admission to hospital.
It occurs within a planned time that suits patients, hospitals and staff.
Expected Location: Elective theatre list (after being booked and planned prior to admission)
E.g. all other conditions not classified as immediate, urgent, or expedited; example, Cystoscopy
🍁
THE IMPORTANCE OF SURGICAL CLASSIFICATION
Using this surgical classification, the urgency of patient intervention can be defined and data can be used by managers and clinicians to:
▪️Manage procedures lists and daily theatre allocations;
▪️Analyse patient experience by checking if they are being operated within the appropriate time frame;
▪️Verify that clinical governance is being adhered to and that medical staff are operating “out-of-hours” only when appropriate
▪️Organise and develop the department and internal services by taking appropriate corrective actions according to patient types and theatre session types.

0 notes
Text
Along with causing heart and kidney problems, untreated high blood pressure can also affect your eyesight and lead to eye disease.
Consult our eye specialist if are experiencing any of the following symptoms:
✅ Reduced Vision
✅ Eye swelling
✅ Double vision with Headache
✅ Optic disk oedema
✅ Retinal haemorrhages
𝗕𝗼𝗼𝗸 𝗬𝗼𝘂𝗿 𝗔𝗽𝗽𝗼𝗶𝗻𝘁𝗺𝗲𝗻𝘁!
084007 15572Best Eye Doctor in Lucknow | Best Eye care Clinic in Lucknow | Best Cataract Treatment Doctor in Lucknow
0 notes
Text
Journal of Ophthalmology Images and Case Reports
Vision is one of the most important senses we have. Vision care encompasses a number of medical, scientific, and social issues. It deals with the various studies related to different aspects of eye surgery such as post lasik conditions and care, surgically induced astigmatism, cataract surgery, corneal transplant success rate, paecilomyces infection, clear corneal incision, post-operative corneal melt, malyugin ring cataract surgery
Ophthalmology covers several issues such as ophthalmia neonatorum, pterygium histology, aphakic glaucoma, acute zonal occult outer retinopathy (AZOOR), hypertrophic pachymeningitis, phacomorphic glaucoma, pseudoexfoliation syndrome, binasal hemianopsia, bitemporal heteronymous hemianopsia, cycloplegic refraction, cycloplegic drugs, macular edema optical coherence tomography (OCT), juxta fovea retinal telangiectasis, central serous retinopathy treatment, involutional ectropion, impaired depth perception, lacrimal fistula, sagging eye syndrome, spontaneous periorbital ecchymosis, neonatal conjunctivitis, ocular pemphigoid, Non-Arteritic Anterior Ischemic Optic Neuropathy (NAION) and Arteritic Anterior Ischemic Optic Neuropathy (AAION) eye, macular pseudohole, scleromalacia perforans, and subperiosteal haemorrhage.
Primary eye care is the health care specialty which includes the nursing practice and eye care services related to eye disorders. The primary eye care practice deals with eye health and eye care needs. The conciliators of eye care include ophthalmic nurses, ophthalmic technicians, and eye care coordinators. Various processes in eye care include critical awareness, eye examinations, rehabilitation and long-term continuity of care which are carried out through health centers.

Journal of Ophthalmology Images and Case Reports publishes clinical images in Ophthalmology, case reports in clinical Ophthalmology, videos in clinical Ophthalmology etc. Ophthalmology is the specialty of medicine that deals with the anatomy, physiology of the eye in humans and animals. It also deals with the various disorders and diseases pertaining to eye in humans and in animals.
Manuscript Submission
Authors are requested to submit their manuscript by using Online Manuscript Submission Portal:
Journal of Ophthalmology Images and Case Reports publishes clinical images in Ophthalmology, case reports in clinical Ophthalmology, videos in clinical Ophthalmology etc. Ophthalmology is the specialty of medicine that deals with the anatomy, physiology of the eye in humans and animals. It also deals with the various disorders and diseases pertaining to eye in humans and in animals.
Manuscript Submission
Authors are requested to submit their manuscript by using Online Manuscript Submission Portal:
1 note
·
View note
Text
Hypertension Drugs Market to Observe Strong Growth to Generate Massive Revenue in Coming Years
Latest business intelligence report released on Global Hypertension Drugs Market, covers different industry elements and growth inclinations that helps in predicting market forecast. The report allows complete assessment of current and future scenario scaling top to bottom investigation about the market size, % share of key and emerging segment, major development, and technological advancements. Also, the statistical survey elaborates detailed commentary on changing market dynamics that includes market growth drivers, roadblocks and challenges, future opportunities, and influencing trends to better understand Hypertension Drugs market outlook. List of Key Players Profiled in the study includes market overview, business strategies, financials, Development activities, Market Share and SWOT analysis are:
Takeda Pharmaceutical Co. Ltd. (Japan)
Johnson & Johnson (United States)
Sun Pharmaceutical Industries (India)
Bausch Health Companies Inc. (Canada)
Pfizer Inc. (United States)
Novartis AG (Switzerland)
Daiichi Sankyo Co. Ltd. (Japan)
LG Life Sciences (South Korea)
Takeda Pharmaceuticals (Japan)
AstraZeneca plc (United Kingdom)
Hypertension is defined as a condition in which the arteries in the heart have continuously increased pressure. It is also known as high blood pressure (HBP). According to the 2017 American Heart Association, high blood pressure is a blood pressure condition greater than 130 and 80 millimetres of mercury (mmHg). The measurement of blood pressure is expressed as; systolic pressure and diastolic pressure. Hypertension is a serious health condition that increases the risk of coronary artery disease and ischemic heart disease, which are the leading causes of death worldwide. Hypertension also leads to various other health problems such as heart failure, kidney dysfunction, retinal haemorrhage, and visual impairment. The main purpose of high blood pressure drugs is to lower and control high blood pressure to protect organs like the brain, heart, and kidneys. Key Market Trends: Huge Funding In R&D and Various Initiatives by Government Opportunities: An Increase in Geriatric Population
Advancement in Technology, And Low Prices of the Drugs
Improved Awareness among People Regarding Hypertension and Its Available Treatment Options Market Growth Drivers: Rapid Urbanization and Globalization, Human Health Is Being Adversely Affected
Change In Lifestyle and Elevated Stress Levels
Challenges: Relative Side Effects by the Use of Hypertension Drug The Global Hypertension Drugs Market segments and Market Data Break Down by Type (Systemic Hypertension Drugs, Pulmonary Hypertension Drugs), Application (Hospital Use, Clinic Use, Others), Distribution Channel (Retail Pharmacies, Hospital Pharmacies, Online Pharmacies), Therapeutic Class (Diuretics, Angiotensin-Converting Enzyme Inhibitors, Angiotensin Receptor Blockers, Beta-blockers, Vasodilators, Calcium Channel Blockers, Renin Inhibitors, Alpha-blockers, Others), Illness Type (Primary Hypertension, Secondary Hypertension), Medication (Monotherapy, Combination Therapy, Fixed-Dose Combinations)
Presented By
AMA Research & Media LLP
0 notes
Text
MACULAR DEGENERATION
What is macular degeneration? AMD also called as(ARMD) occurs when cells in the macula – the central area of the retina – degenerate. Damage to the macula affects your central vision which is needed for reading, writing, driving, recognising people’s faces and doing other fine tasks. The damage occurs at the level of the layer of cells within the retina called the retinal pigment epithelium (RPE).

Who develops AMD?
AMD only develops in older people (there are other rare types of macular degeneration which occur in younger people). AMD is the most common cause of severe sight problems (visual impairment) in the developed world. It is more common with increasing age.
It usually begins in one eye. About 5 in 100 people aged over 65 and about 12 in 100 people aged over 80 have AMD severe enough to cause serious visual impairment. Women are more likely than men to develop AMD. People of Caucasian ethnicity are more likely to develop AMD than those of African or Asian ethnicity. It is also more common in those who smoke, those who are overweight and those with cardiovascular disease.

Wet macular degeneration
Wet AMD may also be called neovascular or exudative AMD. It occurs in about 1 in 10 cases. In wet AMD, in addition to the retinal pigment cells degenerating, fragile new blood vessels grow from the tiny blood vessels in the choroid into the macular part of the retina. These vessels tend to leak blood and fluid. This can damage the rods and cones and cause scarring in the macula, causing further vision loss. Wet AMD can cause distortion of your central vision, and causes severe visual loss over quite a short time – sometimes weeks or months. Very occasionally, if there is a bleed (haemorrhage), this visual loss can occur suddenly, within hours or days.
If you develop wet AMD (see below) in one eye the risk of developing wet AMD in the second eye is about 1 in 4.
Various systems exist to classify AMD. Both wet and dry AMD can be classified as early, intermediate or advanced, according to the degree of damage to the macula. 6 of every 10 cases of intermediate/advanced AMD are due to wet AMD. You may also see wet and dry AMD classified as early or late, and wet AMD as active or inactive.
Causes of macular degeneration:
In people with AMD the cells of the RPE stop working work so well with advancing age. They gradually fail to take enough nutrients to the rods and cones and do not clear waste materials and byproducts. As a result, tiny abnormal deposits called drusen develop under the retina. In time, the retinal pigment cells and their nearby rods and cones degenerate, stop working and die. This is the dry type of AMD.
In wet AMD, new blood vessels grow into the layers of the retina from the choroid. The reason why this happens in some cases of AMD is not known, although waste products or shortage of oxygen may be involved.
Certain risk factors increase the risk of developing AMD. These include:
Smoking tobacco. High blood pressure. A family history of AMD. (AMD is not a straightforward hereditary condition. However, your risk of developing AMD is increased if it occurs in other family members.) Sunlight. Laboratory studies suggest that the retina is damaged by sunlight rays (UVA and UVB rays). Being very overweight. Poor diet. AMD is more common in people from white (Caucasian) racial backgrounds than from other racial groups.
Symptoms of macular degeneration
Early symptoms AMD is painless. Symptoms of dry AMD tend to take 5-10 years to become severe. However, severe visual loss due to wet AMD can develop more quickly.
If macular degeneration develops in one eye only, you may not be aware of it until it’s quite advanced, as the other eye will still see the things you are looking at with your central vision. When both eyes are affected you are more likely to notice symptoms.
The main early symptom is worsening of central vision despite using your usual glasses. In the early stages of the condition you may notice that you need brighter light to read by. Words in a book or newspaper may become blurred. Colours may appear less bright and you may have difficulty recognising faces and facial expressions.
Later symptoms As the condition worsens, a ‘blind spot’ then develops in the middle of your visual field. This is not always initially noticeable. However, it tends to become larger over time as more and more rods and cones degenerate in the macula.
One early symptom of wet AMD is visual distortion. Typically, straight lines appear wavy or crooked. For example, the lines on a piece of graph paper, or the lines between tiles in a bathroom.
Visual hallucinations (also called Charles Bonnet syndrome) can occur if you have severe macular degeneration. People see different images, from simple patterns to more detailed pictures – often they see complicated images of children or animals. The experience can be upsetting but is less frightening if you are aware that it can happen in AMD. Importantly, it does not mean you are developing a serious mental illness. If you do develop visual hallucinations they typically improve by 18 months.
Peripheral vision is not affected with AMD and so it does not cause total loss of vision.
Always see a doctor or optometrist promptly if you develop visual loss or visual distortion.
Older people should in any case have regular eye checks to check each eye separately for early AMD (and to check for other eye conditions such as glaucoma).
Tests for macular degeneration If you develop symptoms suggestive of macular degeneration, your doctor or optician (optometrist) will refer you to an eye specialist (ophthalmologist). This should be done urgently, in case you have wet AMD (which can worsen rapidly but which can be treated).
The ophthalmologist may ask you to look at a special piece of paper with horizontal and vertical lines to check your visual fields. If you find that any section of the lines is missing or distorted then it is a possible cause of the visual problem. The ophthalmologist will examine the back of your eye with a slit-lamp microscope. Digital photographs can be taken of the retinae. The ophthalmologist will look for the typical changes that occur with dry and wet AMD.
Another test called ocular coherence tomography is becoming more commonly used. This is a non-invasive test that uses special light rays to scan the retina. It can give very detailed information about the macula and can show if it is abnormal. This test is useful when there is doubt about whether AMD is the wet or dry form, and to monitor treatment.
Diagnosis of wet AMD is further tested for fluorescein angiography. A dye is injected into a vein in your arm and then, by looking into your eyes with a magnifier the ophthalmologist can see where any dye leaks into the macula from the abnormal leaky blood vessels. This can give an indication of the severity of the condition.
Macular degeneration treatment:
Whether or not there is a treatment that can prevent progression, or even reverse your condition, it is important to maximise the sight you do have.
Stopping smoking and protecting the eyes from the sun’s rays by wearing sunglasses are important in slowing progression of the condition.
A healthy balanced diet rich in antioxidants can be beneficial, as may the addition of dietary supplements.
Homoeopathic Management and Treatment:AMD
The psychodynamics of eye complaints tells us certain vital things about the patients personality in a nutshell
we can see the patients non adaptibility to change and see new things.
It could also be related with disgust or anger towards certain person/people whom you dont want to see eye to eye.
Along with this a repulsive mood and irritability.I can still recall one of my patient who has her vision completely restored by Homoeopathy.you can refer to her testimonial in the related section.
0 notes
Link
#market research future#vitrectomy devices market#vitrectomy devices market size#vitrectomy devices industry#vitrectomy devices
0 notes
Text
Medical Applications, Importance & Adverse Effects of Sorbitol

Sorbitol is a sugar alcohol or polyol, which are water-soluble molecules found naturally in many fruits and vegetables. Sorbitol is also commercially synthesised from glucose for usage as a sweetener, texture, and moisture retainer in packaged foods and beverages.
Medical Applications:
● Laxative:
Sorbitol-containing meals, like other sugar alcohols, can cause gastrointestinal irritation. Sorbitol can be used as a laxative either orally or through an enema. Sorbitol acts as a laxative by attracting water to the large intestine and promoting bowel motions. Sorbitol has been found to be safe for elderly people to take, yet it is not recommended without the guidance of a doctor. Sorbitol is found in various dried fruits and may contribute to prunes' laxative properties. In 1872, sorbitol was identified in the fresh juice of mountain ash berries.
Palvi Chemicals is the distinguished Sorbitol exporter in Nigeria.
● Other medical applications:
Sorbitol is used in bacterial culture media to differentiate pathogenic Escherichia coli O157:H7 from most other E. coli strains because it is unable to ferment sorbitol, unlike 93 percent of known E. coli strains.
Sorbitol and the ion-exchange resin sodium polystyrene sulfonate are used to treat hyperkalaemia (high blood potassium) (tradename Kayexalate). In the bowel, the resin exchanges sodium ions for potassium ions, while sorbitol aids in elimination. The Food and Drug Administration of the United States issued a warning about the increased risk of gastrointestinal necrosis with this combination in 2010.
Sorbitol is also utilised in the production of softgel capsules, which are used to store single doses of liquid medications.
Palvi Chemicals is one of the most popular Sorbitol suppliers in Ghana.
Medical importance:
Aldose reductase is the first enzyme in the sorbitol-aldose reductase pathway, and it is responsible for converting glucose to sorbitol as well as galactose to galactitol. Long-term hyperglycemia with poorly controlled diabetes frequently results in too much sorbitol trapped in retinal cells, lens cells, and Schwann cells that myelinate peripheral nerves. This can harm these cells, resulting in retinopathy, cataracts, and peripheral neuropathy. Aldose reductase inhibitors, which are drugs that impede or decrease the action of aldose reductase, are now being studied as a means of preventing or delaying severe consequences.
If you are looking for one of the most recognized Sorbitol distributors in Ghana, Palvi Chemicals is the right place for you to fulfill all your chemical requirements.
Adverse medical effects:
As a result of small intestinal damage, people with untreated celiac disease frequently have sorbitol malabsorption. Sorbitol malabsorption is a common source of symptoms that persist in gluten-free people. Because of a strong link between the cut-off value and intestinal lesions, the sorbitol hydrogen breath test has been proposed as a diagnostic for detecting celiac disease. Nonetheless, while it may be useful for research, it is not yet suggested as a diagnostic tool in clinical practise.
Sorbitol added to sodium polystyrene sulfonate (SPS, used to treat hyperkalemia) has been linked to gastrointestinal problems such as haemorrhage, perforated colonic ulcers, ischemic colitis, and colonic necrosis, particularly in uremia patients. Immunosuppression, hypovolemia, the surgical context, hypotension after hemodialysis, and peripheral vascular disease are all risk factors for sorbitol-induced injury. As a result, SPS-sorbitol should be used with caution in the treatment of hyperkalemia.
2 notes
·
View notes
Text
Sudden Loss of Vision Associated with Use of Systemic Non-steroidal Anti-inflammatory Drugs | Chapter 08 | Emerging Research in Medical Sciences Vol. 1
Non-steroidal anti inflammatory agents have long been used in ocular therapeutics as a result of their effect on infllammation coupled with the undesirable side effects of steroids in Ophthalmology. Bleeding peptic ulcers have been strongly associated with use of oral non-steroidal anti inflammatory drugs. We present the case of a 51 year old male patient who presented with 4 days history of visual loss in his right eye following the use of 400 mg Ibuprofen three times a day for 3 days one week prior to presentation. Fundus examination revealed a pre-retinal hemorrhage. There may be need to be cautious with the use of these drugs.
Author(s) Details
Adeoti Caroline Olufunlayo Department of Ophthalmology, Ladoke Akintola University of Technology Teaching Hospital, Osogbo, Nigeria.
Olaopa Adedolapo Olufunke Department of Ophthalmology, Ladoke Akintola University of Technology Teaching Hospital, Osogbo, Nigeria.
Read full article: http://bp.bookpi.org/index.php/bpi/catalog/view/75/935/703-1
View Volume: https://doi.org/10.9734/bpi/erms/v1
0 notes
Text
Where can I find the best diabetic retinopathy treatment in India?
Diabetic Retinopathy is a common issue found among people who have diabetes. The disorder can damage the retina- the retina is the eye’s light-sensitive back lining. A significant problem caused due to diabetes; is diabetic Retinopathy can impair your eyesight to a great extent.
Diabetes can disrupt the body’s system responsible for storing and using sugar or glucose. The primary cause behind this disease is the availability of excess sugar within the blood- the presence of excess sugar can cause huge damage to several body parts, especially the eyes.
With the passage of time, diabetes can destroy the blood vessels present inside the retina. Blood leakage, along with the leakage of similar blood from the tiny blood vessels, gives rise to Diabetic Retinopathy.
This leakage can lead to swelling of the retinal tissue, which can lead to blurry or cloudy vision. The issue can have the worst impact on both eyes.
People who have diabetes are more likely to catch Diabetic Retinopathy. If the issue isn’t cured at the right time, it can lead to diabetes.
What are some of the signs of diabetic Retinopathy?
Blurry vision
The appearance of floaters or spots
Inability to view things properly in the dark
Viewing an empty spot or dark spot in the vision’s centre
What are the reasons behind diabetic Retinopathy?
One of the significant reasons behind diabetic Retinopathy is type 1 and type 2 diabetes. An increase in sugar levels can destroy the small blood vessels. These blood vessels are responsible for nourishing the retina; in a few cases, they can block them entirely.
The damaged blood vessels can fail to supply blood to the eye’s retina, affecting the vision. A lack in blood supply is more likely to give rise to factors that can contribute to macular oedema.
As a result, a person can suffer due to improper vision and proliferative diabetic Retinopathy. It will give rise to vision loss and retinal detachment.
To avoid vision loss or any other risks, you can go in for a diabetic retinopathy treatment in India. It helps restore your vision and take care of your eye. The treatment includes proper diagnosis, which can help detect the initial symptoms of diabetic Retinopathy inside the retina. It helps in preventing vision loss at the earliest.
Diabetic Retinopathy treatment helps to stop the neo-vascularization of the retina’s blood vessels- it helps to stop bleeding within the retina. Besides, the treatment aims to maintain as well as improve the overall condition of the blood vessels present in the retina.
It can help in the prevention of vitreous haemorrhage. It helps to stop the leakage of fluids coming out of damaged blood vessels. The damaged blood vessels can cause significant complexities within the eye.
However, one of the most critical parts of the treatment is to control diabetes or the fluctuation of blood sugar levels. During the treatment's initial phases, the issue's root cause is determined. Next, the aim is to control diabetes as it is responsible for causing diabetic Retinopathy.
0 notes
Text
Advanced Ayurveda For Treating Diabetic Retinopathy
When it comes to Ayurveda and eye diseases, the first thing that springs to mind is a calming eye drop. However, the real story is rather different. With its innovative Ayurvedic remedies for numerous retinal ailments such as Diabetic Retinopathy, Macular Degeneration, Retinitis Pigmentosa or Raycheekati, and Glaucoma problems, Sanjeevan Netralaya has broadened the scope of Ayurveda.
Let us talk about Diabetic Retinopathy. Diabetic Retinopathy develops when the blood vessels in the retina get damaged as a result of high blood sugar levels. This causes retinal haemorrhage, and new blood vessels may form, causing vision loss. Non-Proliferative Diabetic Retinopathy (NPDR) is a type of diabetic retinopathy that develops in the early stages of the disease. The retina swells as small blood vessels in the retina leak.

Macular edoema occurs when the macula, or central section of the retina, swells. This is one of the most common causes of eyesight loss. Blood vessels can close as a result of NPDR, a disease known as macular ischemia.
Blurred vision is common in those who have NPDR. PDR (Proliferative Diabetic Retinopathy) is a stage of Diabetic Retinopathy in which new blood vessels begin to form on the retina. This is referred to as neovascularization, and it occurs when these tiny, delicate blood vessels begin to bleed. When there is less bleeding in the retina, black floaters may appear when viewing objects.
If the bleeding is severe, your vision may be completely obstructed.
New blood vessels can also create scar tissue, resulting in macular damage and retinal detachment.
Diabetic Retinopathy is a disease that cannot be cured with traditional therapy.
There is increasing loss of peripheral vision, night vision, and colour vision as a result of repeated Laser operations and Laser burns.
Similarly, frequent eye injections include a number of risks, including glaucoma, optic nerve damage, and the risk of retinal detachment, all of which worsen eyesight.
Advanced Ayurvedic retina care involves healing the retina gradually. This treatment using best-in-class Ayurvedic medicines has benefitted many patients, giving them new hope.
As alternate medicine is gaining popularity across the globe, Ayurvedic treatment for Diabetic Retinopathy is a preferred choice for many patients. No wonder Sanjeevan Netralaya has treated more than 6,00,000 Retinal Cases across the globe!
#Sanjeevan Netralaya#health & fitness#peripheral neuropathy treatment#peripheral neuropathy#diabetic neuropathy#neuropathy#neuropathy treatment#diabetic neuropathy treatment#diabetic neuropathy treatment in ayurveda#ayurvedic treatment#treatment for neuropathy#treatments for peripheral neuropathy#peripheral neuropathy treatment in homeopathy#ayurveda
0 notes