#ra5c Vigilante
Explore tagged Tumblr posts
Text

I don’t know….parking accidents?
@CcibChris via X
#ra5c vigilante#north american aviation#reconnaissance#aircraft#navy#aviation#us navy#vietnam war aircraft#cold war aircraft#carrier aviation#military aviation#military aircraft#aviation military#aviation military pics
26 notes
·
View notes
Text

-An XA3J-1 at North American's factory during roll-out. Photo: North American Aviation
FLIGHTLINE: 152 - NORTH AMERICAN AVIATION A-5 VIGILANTE
Designed as a carrier-based supersonic bomber in the 1950s, the Vigilante saw service over Vietnam as a recon plane before being retired in 1979.
Development of what became the A-5 began in 1954 when North American Aviation started a internal program. Seeking to turn around the company's fortunes after the failed XA2J Super Savage, NAA began designing a Mach 2 capable bomber which would give the Navy a nuclear strike option. The initial design, known as the North American General Purpose Attack Weapon (NAGPAW) was evaluated by the US Navy, which replied with a series of needed changes and in July 1955 an initial design contract was awarded, which included a single mockup of the plane. NAA's engineers were able to successfully address the USN's concerns about the design, and in September 1956 a contract for two flying prototypes was signed.

-Orthograph of the A-5 Vigilante. | Illustration: aviastar
DESIGN
The plane, designated XA3J-1, was one of the largest and by far the most complex aircraft to be proposed to operate from a USN aircraft carrier. It had a high-mounted swept wing with a boundary-layer control system (blown flaps) to improve low-speed lift. There were no ailerons, roll control was provided by spoilers in conjunction with differential deflection of the all-moving tail surfaces. Power was provided by two widely spaced General Electric J79 turbojet engines (also used on the Convair B-58 and McDonnell Douglas F-4 Phantom II), fed by variable intake ramps. A single large all-moving vertical stabilizer was paired with the all-moving horizontal stabilizers. In order to save space, the wings, tail and radome were all folding. The XA3J had a crew of two seated in tandem, a pilot and a bombardier-navigator (BN) (reconnaissance/attack navigator (RAN) on later reconnaissance versions), who had some of the most advanced equipment of the time, including an early fly-by-wire system (with electromechanical backup), a primitive HUD system, a multi-mode, radar-equipped inertial navigation system, a TV camera in the nose, and a digital computer to run it all.
In order to make the bomber as streamlined as was possible, it was designed to carry additional fuel tanks and a single B27, B28 or B43 freefall nuclear bomb in internal weapons bay, which would be jettisoned over the target as a single "stores train". Provisions were also made to carry two B43 nukes or Mark 83 or Mark 84 conventional bombs on two external hardpoints, or drop tanks to increase range. Operationally however, these hardpoints were rarely used.
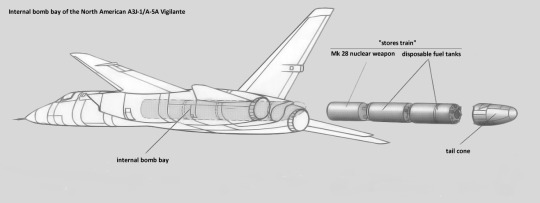
-Internal bomb bay and stores train of the North American A3J-1/A-5A Vigilante. | Illustration: Cobatfor
FLIGHT TESTING, INTRODUCTION, AND SERVICE
First flight of the XA3J was on 31 August 1958 from the same Columbus, OH plant that produced the F-86 and F-100s. Despite one of the prototypes crashing in 1959, the flight tests moved quickly, and by June 1961 the first A3J-1s entered service with Heavy Attack Squadron Three (VAH-3) at NAS Stanford, FL, replacing the Douglas A3D Skywarrior. The following year the plane was redesignated the A-5A under the new tri-service plan. The service life of the A-5A was fraught with issues, with numerous teething problems plaguing its advanced systems. These issues were tamed as maintenance crews became experienced with the Vig's high-tech gadgets, but the plane remained maintenance-intensive (a so-called "hangar-queen") throughout its life. A chronic issue was the stores train bomb release, which had a nasty habit of releasing during catapult shots, resulting in at least one crash. During tests, the train also tended to draft along in the aircraft's slipstream, making accurate bombing (for 1950s/60s definitions of "accurate") difficult.
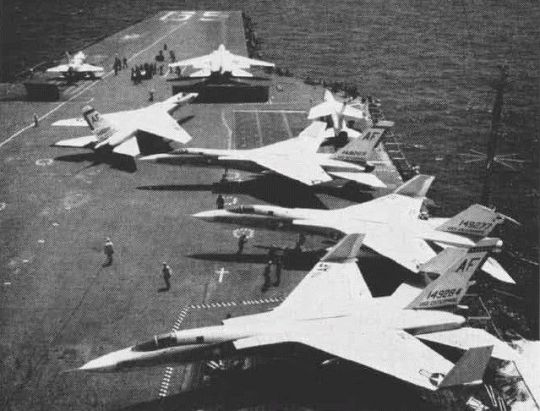

-Five A3J-1 Vigilantes of VAH-7 ("Peacemakers of the Fleet") on CVAN-65 USS Enterprise in 1962. | Photo: USN
Fifty-eight A-5A were completed (out of an order of 64 aircraft) when NAA switched to the upgraded A-5B model. The B model incorporated changes made in light of the Navy's requirement that the Vigilante be able to take off at max weight with zero wind over the carrier being rescinded. This change allowed North American to increase the bomber's weight, adding a dorsal hump to carry more fuel. Only 18 of the A-5B were completed before the US Navy, undergoing a shift in policy away from manned nuclear bombers, canceled the order.
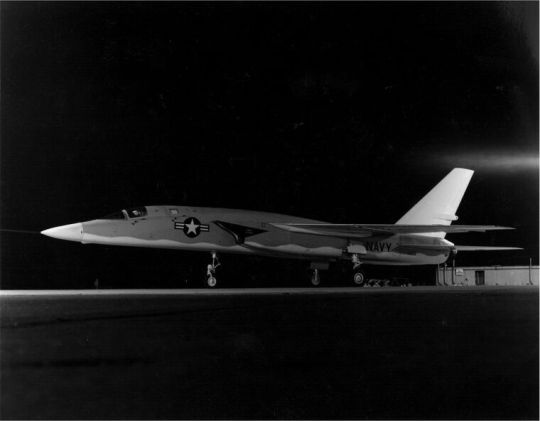

-North American A3J-2 Vigilante (BuNo 146699), circa 1960. This aircraft was the third production A3J-1 which was then modified to an A3J-2 (after 1962 A-5B and YA-5C) and finally to the A3J-3P (RA-5C). | Photo: US Navy
Developed from the A3J-2, the A3J-3P (later RA-5C) was a strike/reconnaissance variant of the Vigilante, incorporating the CCTV in the nose with a "canoe" fairing holding a full suite of gear including:
KA-51A/B forward-looking oblique angle film camera.
KA-50A, KA-51A, or KA-62A vertical film camera.
Passive electronics countermeasures (PECM) antenna for the AN/ALQ-61 Electronic Reconnaissance System. The AN/ALQ-61 was an "electronic intelligence (ELINT)" system that would pick up radar emissions and pin down their coordinates, frequency, and pulse pattern. The ELINT data was recorded on magnetic tape, with storage capacity for 112 minutes of continuous ELINT observations.
Various combinations of panoramic, vertical, or oblique film cameras. Camera fit included KA-58A panoramic camera for medium- to high-altitude work, or a KA-57A panoramic camera for low-altitude work. The cameras shot through prisms in the canoe that could be pivoted to permit shots straight down or from side to side.
AN/AAS-21 infrared sensor, which could provide a continuous film strip of thermal targets, such as hidden trucks, over a field of view 140 degrees wide.
Antenna for the Westinghouse AN/APD-7 "side looking airborne radar (SLAR)" system, which shot radar pulses out to the side of the aircraft and stored the return echo on a long film strip, permitting all-weather, day-night imaging.
Another PECM antenna for the AN/ALQ-21 system.
Additionally, a flash pod, powered by a ram-air turbine in its tail, could be carried under one wing to provide illumination for nighttime recon. The sensors were operated by the back-seater (also known as a "GIB": guy-in-back), formally called a "reconnaissance-attack navigator (RAN)". The bomb bay was filled with semi-permanent fuel tanks (though the plane apparently retained the ability to carry offensive weapons, this was never tested or confirmed). The remaining A-5A and A-5B aircraft were all converted to RA-5C standards, along with 33 new-build aircraft. Squadrons that had formerly flown the A-5 were transitioned to the RA-5 beginning with VAH-3 in July 1963, becoming Reconnaissance Attack Squadrons (RVAH) as they did so. Eventually ten squadrons of RA-5s were established, with the NAS Stanford RVAH-3 being joined by carrier-based RVAH-1, RVAH-5, RVAH-6, RVAH-7, RVAH-9, RVAH-11, RVAH-12, RVAH-13 and RVAH-14.

-RA-5C Vigilante of Reconnaissance Heavy Attack Squadron 3 (RVAH-3) "Sea Dragons" is parked on the flight line at Naval Air Station Sanford, Florida, on 27 March 1968. - | Photo: US Navy
Starting in July 1964, the RA-5Cs saw extensive service over Vietnam, carrying out dangerous post-strike damage assessment missions. Although fast and nimble, the Vig proved vulnerable to ground fire, with 14 RA-5s lost to AAA, 3 to SAMs and one shot down by a NVA MiG-21. Nine more were lost to accidents, and as a result three dozen additional aircraft were built between 1968 and 1970. Despite providing invaluable reconnaissance data, the RA-5 began to be phased out starting in 1968, with NAS Stanford being closed and the Vigilante's parent wing, Reconnaissance Attack Wing One, being transferred to Turner AFB in Georgia, which was turned over to the Navy and renamed NAS Albany. Barely six years later, NAS Albany was closed as a result of post-Vietnam drawdowns, and the remaining RA-5s were transferred again to NAS Key West. As newer and larger aircraft like the F-14 and S-3 were introduced in the mid-70s, the Navy began disestablishment of the RA-5 squadrons, with the last leaving Key West on 20 November 1979.
NASA, THE RAAF, AND THE USAF
At least one A3J-1 was bailed to NASA for a time while the Dryden FRC was participating in research for the US SST program. In 1962 Vigilante BuNo 147858 was given NASA tail number 858 and was flown by NASA pilot Bill Dana on 21 flights along airways around LAX to determine approach conditions for an SST landing patterns. After the conclusion of the program, the plane was returned to the Navy.
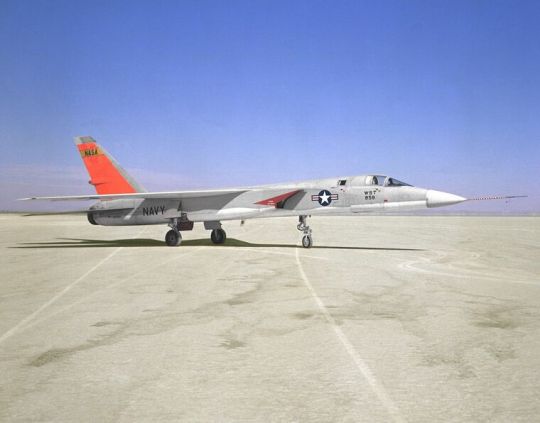

-NASA's A3J-1, wearing a day-glo orange tail flash, on 19 December 1962. | Photo: NASA DFRC
The RAAF was interested in the A-5 as a possible replacement for their aging Canberra bombers, considering the Vig alongside the F-4, Dassault Mirage IVA, BAC TSR-2 and F-111. Despite the A-5 being available without the delay anticipated for the F-111, the order for three dozen Vigilantes was not issued.
At some point in the Vigilante's development, North American advanced a proposal to the Air Force for the 'Retaliator', an A-5 with a liquid rocket added to the bomb bay, as an interceptor, but the USAF showed no interest. In 1972 NAA again proposed a modified A-5, known internally as the NR-349, to the USAF as an Improved Manned Interceptor. The internal bomb bay was modified to house a third jet, and six AIM-54 Phoenix missiles would be carried under the fuselage. Again the USAF was uninterested.

-Scale model of the Improved Manned Interceptor concept, in USAF markings. | Model: NAA/Rockwell
SURVIVORS
By 2004, all of the surviving RA-5s that had been retired to AMARG had been either scrapped or preserved as museum aircraft. A limited number of aircraft were still in storage at NAWS China Lake for eventual use in weapons tests. Around a dozen aircraft have been retained in museums around the US, with only one A-5A on display at NAS Pax River in Maryland, the balance being RA-5s.

-BuNo 146697, the sole remaining A-5A, on display at Pax River. | Photo: Richard Lane
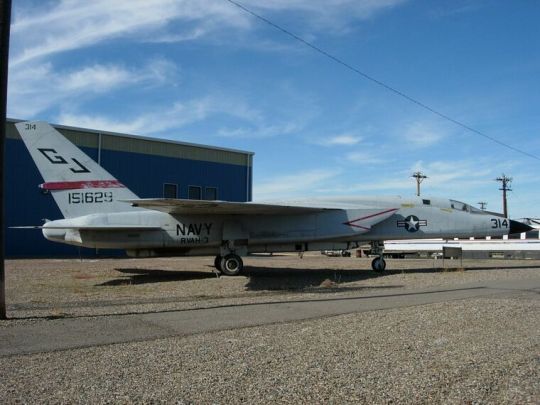

-RA-5C Vigilante (BuNo 151629) on display at the Pueblo Weisbrod Aircraft Museum. It wears the markings of the fleet replacement squadron RVAH-3 Sea Dragons. | Photo: Kristian Jones
#aircraft#aviation#avgeek#airplanes#cold war#airplane#cold war history#coldwar#aviation history#us navy#usn#north american aviation#north american a 5a#a3j-1 Vigilante#a-5a Vigilante#a5a Vigilante#a 5a Vigilante#ra5c Vigilante#ra5c
42 notes
·
View notes
Photo

Trumpeter RA5C Vigilante Aircraft - Plastic Model Airplane Kit 1 48 Scale
$62.73
BUY IT NOW
0 notes
Text

US Navy NATC North American RA-5C Vigilante 156643/643 displayed at NAS Patuxent River (2009)
aviationphotocompany.com/p934046062/ee9…
More A-5 images: aviationphotocompany.com/p651426092
Credit embedded
#ra5c vigilante#north american aviation#bomber reconnaissance#aircraft#navy#aviation#us navy#cold war aircraft#aviation military#aviation military pics#military aircraft#military aviation#mil
24 notes
·
View notes