#public api
Explore tagged Tumblr posts
Photo

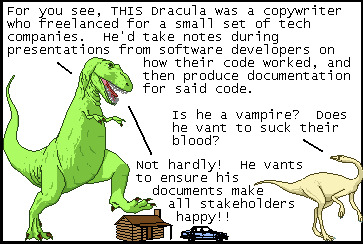
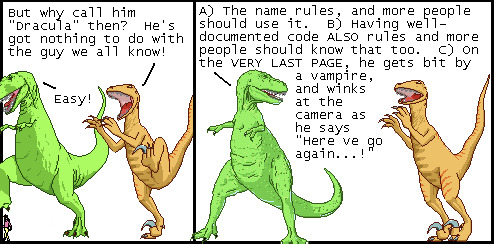
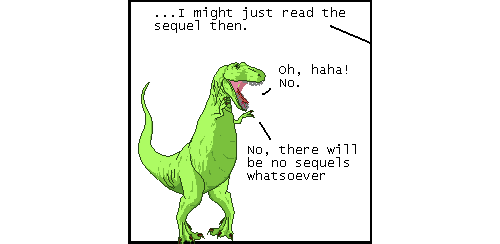
okay fine: there can be one (1) sequel, in which he befriends a guy named "sherlock holmes" but who does NOT deduce or do detection AT ALL. and their best friend is "winnie the pooh", a normal man who simply chooses to go by that name for normal reasons
#dracula and the case of the undocumented API endpoint#we can all agree that the public domain has been a boon for normal guys named dracula
193 notes
·
View notes
Text
GMT0+ people, I am sorry that AO3 has chosen to personally victimize you by not letting me schedule posting a chapter during hours friendly to you (which are very unfriendly to me).
#if they had a public API i would write a little app to do that#but alas they do not nor do they plan to#i used to set an alarm and wake up to post#but it was killing my sleep so i finally stopped
18 notes
·
View notes
Text
not me finding out that fandom wikis do not have an api (which is like a specialised ui for programmers that a lot of websites have where you can more directly access resources off the website with programming tools, f.e. if one piece wiki had one, you could tell your coding languages like "hey get all the strawhat pirates' names and heights off their character pages and put them in my database here please" and it would be able to get that info off the wiki for you) so I will have to learn web scraping to get data off there for visualising ship stats project I have planned for my data analysis portfolio instead now smh
#coding#ship stats#the things I do for my shenanigans#but turns out bootcamp don't cover the *getting the data* part of data stuff#only the how you organise and move around and what you can do with the data once you have it#and I'm over here like but I wanna be able to assemble whatever public data sets I want to play with :c#shoutout to reddit for other people asking about this already cause I'm not the only geek tryna get wiki data for shenanigans#at least I'll get good use out of knowing how to scrape shit off non-api websites I guess u.u
15 notes
·
View notes
Text
I've been doing different and unrelated code for a while: has anyone at Tumblr open-sourced a version of the NPF-block-to-dashboard-HTML code?
#tumblr api#coding#i have been very busy causing problems for a site with no public api#and wheezing
10 notes
·
View notes
Text
wait i didnt realize the profiles that were "lost" due to the api migration were back ;-;
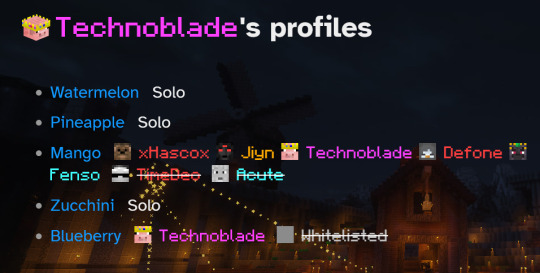
#YIPPEE#at first i thought this mightve been specially done for him but other ppl's are back too#initially profiles would only show back up if you logged in and it updated#but profiles are also showing for ppl that i KNOW havent logged in any time since then#yayyyyy yippee this stuff is back for me to stare at#i want nothing more than for someone to go make all his api stuff public#i just wanna be nosy. let me answer some questions i had. Please#would it be problematic for his dad to LOG IN and give all his friends in his f list a heart attack? yes. yes it would be.#cant an admin just like... manually do it. please ;-;#chat#sb
12 notes
·
View notes
Text
Experiment #2.2 Doubling Down: Two Google Gemini AI Apps in 30 Days – My Journey
Hello everyone! 👋 Yesterday, I shared my pivot from my initial app idea due to a saturated market. This led me to explore new horizons with the Google Gemini API. Today, I’m thrilled to announce an even bolder challenge: developing two apps in the next 30 days! Two Apps, Two Purposes Public Project: Your Guide to AI App Development. My original concept, a goal-setting app, will continue…
#30-Day Challenge#AI App Development#AI-Powered Apps#App Development Challenge#App Development Process#Behind the Scenes#Building in Public#Goal-Setting Apps#Google AI Tools#Google Gemini API#Indie Developer#Patreon Exclusive#Solo Developer#Startup Journey#Tech Entrepreneur
1 note
·
View note
Text
Mastering Seamless Integration: Unleashing the Potential of Cloud API Integration
In the era of cloud computing, the integration of Application Programming Interfaces (APIs) has become the cornerstone of innovation and efficiency. Cloud API integration empowers businesses to seamlessly connect and communicate between different applications and services, fostering a cohesive and agile digital ecosystem. This article explores the transformative impact of cloud API integration and how it has become a linchpin for modern businesses.
1. The Power of Connectivity through Cloud API Integration:
Cloud API integration is at the heart of creating interconnected and collaborative digital landscapes. By enabling different applications and systems to communicate with each other, APIs break down silos and facilitate the flow of data, processes, and functionalities. This results in a more streamlined and efficient business environment, where information can be shared in real-time, driving productivity and innovation.
2. Enhancing Efficiency and Productivity:
The seamless integration of cloud APIs enhances efficiency by automating workflows and eliminating manual data transfers. By connecting disparate systems and applications, businesses can reduce redundancy, minimize errors, and accelerate processes. This newfound efficiency translates into increased productivity, allowing organizations to focus on strategic initiatives rather than grappling with time-consuming manual tasks.
3. Real-Time Data Synchronization:
Cloud API integration enables real-time data synchronization across different platforms. Whether it's customer information, sales data, or inventory updates, APIs ensure that information is consistently up-to-date across all integrated systems. This real-time synchronization not only improves accuracy but also provides a unified and current view of critical data, empowering businesses to make informed decisions swiftly.
4. Flexibility and Scalability:
One of the key advantages of cloud API integration is its flexibility and scalability. APIs allow businesses to adapt and scale their integrations based on evolving needs. As organizations grow or introduce new applications, cloud APIs provide the agility to connect and extend functionality seamlessly. This flexibility ensures that businesses can stay responsive in a dynamic and ever-changing digital landscape.
5. Security Measures in Cloud API Integration:
Security is a paramount concern in the realm of cloud API integration. Reputable cloud service providers implement robust security measures to protect data transmitted through APIs. Encryption protocols, authentication mechanisms, and access controls are crucial components of secure API integrations. Businesses can confidently leverage the benefits of cloud API integration while ensuring the confidentiality and integrity of their sensitive data.
6. Public Cloud Providers: Enablers of Seamless Integration:
Public cloud providers play a pivotal role in the success of cloud API integration. Leading providers offer a vast array of APIs that cater to different functionalities, services, and infrastructure components. Leveraging APIs provided by public cloud providers allows businesses to integrate seamlessly with popular cloud platforms, harnessing the full spectrum of capabilities offered by these providers.
Conclusion:
Cloud API integration is the linchpin for businesses seeking to unlock the full potential of their digital ecosystems. The seamless connectivity, efficiency gains, real-time synchronization, and scalability provided by cloud API integration position organizations for sustained success in a competitive landscape. As businesses continue their journey of digital transformation, embracing cloud API integration is not just a strategic choice—it's a fundamental step towards building a connected and agile future.
#Cloud API integration#cloud provider services#cloud infrastructure#network infrastructure#cloud solution#digital infrastructure#cloud connectivity services#cloud interconnect#public cloud providers#it infrastructure services#cloud integration#Lightstorm
1 note
·
View note
Text
REST into your communication • an architecture aiming for straightforward and clear communication between systems

As I started to discuss my magazine idea with chat GPT, ot quickly turned out that there is more to REST than I thought. When pitching my idea of an online magazine called
The Rest Publication
it suggested me, that I should use REST API, for better results.
(I guess it already thought of it in an IT approach)

it also interesting, coz I was suggested today in a meeting that I could do a platform for community spaces. Then this little misunderstanding shows me that there is something called 'REST API'. So I asked for it. I asked more info like this.

and although it was interesting, I found it a bit too technical. But at the end the last sentence captivated me:
These APIs are stateless, meaning each request contains all necessary information to process it independently, without relying on prior interactions
what a beautiful sentence? isnt't it?
STATELESS - it says.
Wow, I mean what the fcuk is that actually?
I mean I know that there are states like states of mind and so on, but what could be a Stateless Rest API? That must be something else.
It felt like non-attachment. Which in the eastern philosophy refers to letting thins flow. Not to hold onto things stubbornly. Just go with the flow, move with ease. No expectations. Just love.
And so I see that in a web architecture context. So I decided to make a comparison of the Rest Publication idea and the REST APIs.

and it said...

so I told him that:
"

You
I find it interesting that this architecture is named as REST, coz it feels like it would come from a state of relaxed calm as the name would suggest. And then it contains 'statelessness' as if the relaxed or meditated mind is stateless."

and it turnes out that this architectural concept actually containes the qualities of non-attachment, autonomy, simplicity, reliability, scalability, efficiency, and independence.
Just like the whole Souldom concept does.

0 notes
Text
re: "outlawing AI"
i am reposting this because people couldn't behave themselves on the original one. this is a benevolent dictatorship and if you can't behave yourselves here i'll shut off reblogs again. thank you.
the thing i think a lot of people have trouble understanding is that "ai" as we know it isn't a circuitboard or a computer part or an invention - it's a discovery, like calculus or chemistry. the genie *can't* be re-corked because it'd be like trying to "cork" the concept of, say, trigonometry. you can't "un-invent" it.
even if you managed to somehow completely outlaw the performance of the kinds of linear algebra required for ML, and outlawed the data collection necessary, and sure, managed to get style copyrighted, you can't un-discover the underlying mathematical facts. people will just do it in mexico instead. it'd be like trying to outlaw guns by trying to get people to forget that you can ignite a mixture of powders in a small metal barrel to propel things very fast. or trying to outlaw fire by threatening to take away everyone's sticks.
the battleground is already here. technofascists and bad actors without your ethical constraints are drawing the lines and flooding the zone with propaganda & slop, and you’re wasting time insisting to your enemies that it’s unfair you’re being asked to fight with guns when you’d rather use sticks.
as a wise sock puppet once said; "this isn't about you. so either get with it, or get out of the fucking way"
-----
Attempts to prohibit AI "training" misunderstand what is being prohibited. To ban the development of AI models is, in effect, to ban the performance of linear algebra on large datasets. It is to outlaw a way of knowing. This is not regulation - it is epistemological reactionary-ism. reactionism? whatever
Even if prohibition were successful in one nation-state:
Corporations would relocate to jurisdictions with looser controls - China, UAE, Japan, Singapore, etc.
APIs would remain accessible, just more expensive and less accountable. What, are you gonna start blocking VPNs from connecting to any country with AI allowed? Good luck.
Research would continue outside the oversight of the very publics most concerned about ethical constraints.
This isn’t speculation. This is exactly what happened with stem cells in the early 2000s. When the U.S. government restricted federal funding, stem cell research didn’t vanish, it just moved and then kept happening until people stopped caring.
The fantasy that a domestic ban could meaningfully halt or reverse the development of a globally distributed method is a fantasy of epistemic sovereignty - the idea that knowledge can be territorially contained and that the moral preferences of one polity can shape the world through sheer force of will.
But the only way such containment could succeed would be through:
Total international consensus (YEAH RIGHT), and
Total enforcement across all borders, black markets, and academic institutions, at the barrel of a gun - otherwise, what is backing up your enforcement? Promises and friendly handshakes?
This is not internationalism. It is imperialist utopianism. And like most utopian projects built on coercion, it will fail - at the cost of handing control to precisely the actors most willing to exploit it.
Liberal moralism often derides socialist or communist futures as "unrealistic.", as you can see in the absurd, hyperbolically, pants-shittingly mad reaction to Alex Avila's video. Yet the belief that machine learning can be outlawed globally - a method of performing mathematics that is already published, archived, and disseminated across open academic networks the globe over - is far more implausible. literally how do you plan on doing that? enforcing it?
The choice is not between AI and no AI. The choice is between AI in the service of capital, extraction, and domination, or AI developed under conditions of public ownership, democratic control, and epistemic openness. You get to pick.
The genie and the bottle are not even in the same planet. The bottle's gone, Will.
589 notes
·
View notes
Text

Xerces Society: Announcing The State Of The Bees Initiative: Our Plan To Study Every Wild Bee Species In The U.S.
This is really exciting news! For those unaware, the Xerces Society has been focusing on invertebrate conservation for over fifty years, and has pioneered a lot of the work to bring awareness to the devastating losses of not only insects but other terrestrial and aquatic invertebrates. It gets its name from the Xerces blue butterfly (Glaucopsyche xerces), the first North American butterfly driven to extinction by human activities.
Even if you haven't heard of the Xerces Society, you've probably come across various "Save the Bees!" campaigns. These frequently focus on the domesticated European honey bee (Apis mellifera), which, while it may be important to crop pollination in many parts of the world, is not a part of natural ecosystems in places like the Americas and Australia, and can be considered an invasive species at times. With the rise of colony collapse disorder (CCD) particularly after the turn of the 21st century, where entire domestic honeybee colonies would die off, the need to preserve bees began to gain wider public acknowledgement.
But what many people don't realize is that it is the thousands upon thousands of other native bee species worldwide that are in greater danger of extinction. They don't have armies of beekeepers giving them safe places to live and treating them for diseases and parasites. More importantly, where honey bees may visit a wide variety of plants, native bees often have a much narrower series of species they visit, and they are quite vulnerable to habitat loss. Most bees are not as social as honey bees and live solitary lives, unseen by the casual observer.
Invertebrates in general often suffer from a lack of conservation information, meaning that particularly vulnerable species may fly under the radar and risk going extinct without anyone realizing until it's too late. This ambitious program by the Xerces Society aims to solve that problem, at least for the 3,600+ species of bee in the United States. If they can assign a conservation status to each one, then that strengthens the argument toward protecting their wild habitats and working to increase their numbers. Hopefully it will also prompt more attention to other under-studied species that are in danger of going extinct simply because we don't know enough about them.
#bees#save the bees#invertebrates#arthropods#insects#entomology#nature#wildlife#animals#ecology#environment#conservation#science#scicomm#endangered species#extinction#pollinators#Xerces Society#Xerces blue
599 notes
·
View notes
Text






🎀 ACNH Sanrio Set: Remaining Items 🎀
Sims 4, base game compatible except the functional vanity & dancefloor which require Vintage Glamour & Get Together | 35 items | Some extra swatches added by me 💗 | See bottom of post for all previously made Sanrio items from other sets
I try my best to make things functional, the large beds work perfectly as they have 2 mesh groups, and I used the EA mattress. The My Melody bed has 1 mesh group, sims can sleep under the covers, but the bed moves a bit when the sim gets into it.
Always suggested: bb.objects ON, it makes placing items much easier. For further placement tweaking, check out the TOOL mod.
Use the 0,9 keyboard feature to raise items or lower them
Use the scale up & down feature on your keyboard to make the items larger or smaller to your liking. If you have a non-US keyboard, it may be different keys depending on which alphabet it uses.
Set contains: Buy: -Cinnamoroll Loveseat (2 items for 2 versions with and without pillows) | 1 swatch each | 2406, & 1998 poly -Cinnamoroll Parasol | 1 swatch | 1198 poly -Cinnamoroll Pillows | 3 swatches each | 428 poly each -Cinnamoroll Rug | 5 swatches each | 637 poly -Hello Kitty Bed | 1 swatch | 1614 poly -Hello Kitty Bed Plushie (liberated bear) | 1 swatch | 674 poly -Hello Kitty Chair | 1 swatch | 1130 poly each -Hello Kitty Clock | 1 swatch | 580 poly -Hello Kitty Dresser (2 items for 2 versions, edited V2 to have the big piece in the back) | 1 swatch each | 1746 poly each -Hello Kitty Nightstand| 1 swatch | 718 poly each -Hello Kitty Plant (2 items, Large & Small) | 1 swatch each | 2008 poly each -Hello Kitty Rug | 1 swatch | 446 poly -Hello Kitty Shoe Decor (child size) | 1 swatch | 812 poly -Hello Kitty Table Dining | 1 swatch | 702 poly -Keroppi Bench with Divider | 1 swatch | 2109 poly -Keroppi Dancefloor (requires Get Together) | 1 swatch | 2 poly -Keroppi Rug | 1 swatch | 584 poly -My Melody Bed | 1 swatch | 2001 poly -My Melody Clock | 1 swatch | 712 poly -My Melody Rug | 1 swatch | 681 poly -My Melody Vanity BGC (non functional) | 1 swatch | 1218 poly -My Melody Vanity functional (requires Vintage Glamour) | 1 swatch | 1218 poly -Pompompurin Bed | 1 swatch | 1824 poly -Pompompurin Chair | 1 swatch | 1189 poly -Pompompurin Nightstand | 1 swatch | 1132 poly -Pompompurin TV (2 versions, "off" with face, & functional) | 1 swatch each | 1486, & 1480 poly -Posters | 6 swatches | 4 poly -Twin Stars Loveseat | 3 swatches for legs | 2426 poly -Twin Stars Rug | 3 swatches | 807 poly Build: -Walls | 3 swatches | Wallpaper -Floors | 5 swatches | Wood & Tile
Type “acnh sanrio" into the search query in build mode to find quickly. You can always find items like this, just begin typing the title and it will appear.
*Remember to run the DX11 batch fix if you are using DX11. I do not use DX11 with my game, when I looked up what would happen if I ran the batch fix even though I don't have this turned on, the consensus was not to do this if you are not using the DX11 option. For those that have never done it, do not fear for it is very simple and will update any CC in your mods folder that needed it to work with DX11. I know the new DX11 API causes issues having something to do with the wall items, or other image texture-related things- that I know of. If you do not have Sims 4 Studio, here is a link about how to install it from their official website. And of course, if you need help please send me a message.
As always, please let me know if you have any issues! 💗
📁 Download all or pick & choose (SFS, No Ads): HERE
📁 Alt Mega Download (still no ads): HERE
📁 Download on Patreon
Will be public on January 5th, 2025 💗 Midnight CET
Happy Simming! ✨ Some of my CC is early access. If you like my work, please consider supporting me (all support helps me with managing my chronic pain/illness & things have been rough as of late):
★ Patreon 🎉 ❤️ |★ Ko-Fi ☕️ ❤️ ★ Instagram📷
Thank you for reblogging ❤️ ❤️ ❤️
@sssvitlanz @maxismatchccworld @mmoutfitters @coffee-cc-finds @itsjessicaccfinds @gamommypeach @stargazer-sims-finds @khelga68 @suricringe @vaporwavesims @mystictrance15 @moonglitchccfinds @xlost-in-wonderlandx @jbthedisabledvet
Other CC Pictured:
Other Sanrio CC (downloads always have pick & choose option): -Cinnamoroll Set 1-Cinnamoroll Set 2 -Cinnamoroll Walls -Cinnamoroll & Twin Stars Items -Cinnamoroll Shoe Decor -Keroppi Mini Set -Keroppi Ghost Doll Set -Keroppi Bridge -Keroppi Boots Decor -Twin Stars & My Melody Wallpaper, My Melody Chair & Table-Twin Stars Kid Desk, Wall Clock, Clock Radio, Hair Clips Decor & Shoes Decor -My Melody Slippers Decor -Pompompurin Pudding -Pompompurin Book Table -Pompompurin Rug -Pompompurin Boots
The rest of my CC
#ts4cc#s4cc#sims 4 sanrio#sims 4 hello kitty#sims 4 pompompurin#sims 4 keroppi#sims 4 my melody#sims 4 twin stars#sims 4 bed#sims 4 table#sims 4 rug#sims 4 rugs#sims 4 sofa#sims 4 couch#sims 4 chair#sims 4 vanity#sims 4 clock#sims 4 maxis match#sims 4 furniture#simdertalia
343 notes
·
View notes
Text
"Artists have finally had enough with Meta’s predatory AI policies, but Meta’s loss is Cara’s gain. An artist-run, anti-AI social platform, Cara has grown from 40,000 to 650,000 users within the last week, catapulting it to the top of the App Store charts.
Instagram is a necessity for many artists, who use the platform to promote their work and solicit paying clients. But Meta is using public posts to train its generative AI systems, and only European users can opt out, since they’re protected by GDPR laws. Generative AI has become so front-and-center on Meta’s apps that artists reached their breaking point.
“When you put [AI] so much in their face, and then give them the option to opt out, but then increase the friction to opt out… I think that increases their anger level — like, okay now I’ve really had enough,” Jingna Zhang, a renowned photographer and founder of Cara, told TechCrunch.
Cara, which has both a web and mobile app, is like a combination of Instagram and X, but built specifically for artists. On your profile, you can host a portfolio of work, but you can also post updates to your feed like any other microblogging site.
Zhang is perfectly positioned to helm an artist-centric social network, where they can post without the risk of becoming part of a training dataset for AI. Zhang has fought on behalf of artists, recently winning an appeal in a Luxembourg court over a painter who copied one of her photographs, which she shot for Harper’s Bazaar Vietnam.
“Using a different medium was irrelevant. My work being ‘available online’ was irrelevant. Consent was necessary,” Zhang wrote on X.
Zhang and three other artists are also suing Google for allegedly using their copyrighted work to train Imagen, an AI image generator. She’s also a plaintiff in a similar lawsuit against Stability AI, Midjourney, DeviantArt and Runway AI.
“Words can’t describe how dehumanizing it is to see my name used 20,000+ times in MidJourney,” she wrote in an Instagram post. “My life’s work and who I am—reduced to meaningless fodder for a commercial image slot machine.”
Artists are so resistant to AI because the training data behind many of these image generators includes their work without their consent. These models amass such a large swath of artwork by scraping the internet for images, without regard for whether or not those images are copyrighted. It’s a slap in the face for artists – not only are their jobs endangered by AI, but that same AI is often powered by their work.
“When it comes to art, unfortunately, we just come from a fundamentally different perspective and point of view, because on the tech side, you have this strong history of open source, and people are just thinking like, well, you put it out there, so it’s for people to use,” Zhang said. “For artists, it’s a part of our selves and our identity. I would not want my best friend to make a manipulation of my work without asking me. There’s a nuance to how we see things, but I don’t think people understand that the art we do is not a product.”
This commitment to protecting artists from copyright infringement extends to Cara, which partners with the University of Chicago’s Glaze project. By using Glaze, artists who manually apply Glaze to their work on Cara have an added layer of protection against being scraped for AI.
Other projects have also stepped up to defend artists. Spawning AI, an artist-led company, has created an API that allows artists to remove their work from popular datasets. But that opt-out only works if the companies that use those datasets honor artists�� requests. So far, HuggingFace and Stability have agreed to respect Spawning’s Do Not Train registry, but artists’ work cannot be retroactively removed from models that have already been trained.
“I think there is this clash between backgrounds and expectations on what we put on the internet,” Zhang said. “For artists, we want to share our work with the world. We put it online, and we don’t charge people to view this piece of work, but it doesn’t mean that we give up our copyright, or any ownership of our work.”"
Read the rest of the article here:
https://techcrunch.com/2024/06/06/a-social-app-for-creatives-cara-grew-from-40k-to-650k-users-in-a-week-because-artists-are-fed-up-with-metas-ai-policies/
610 notes
·
View notes
Text
Tuesday, August 13th, 2024
🌟 New
Tumblr URLs in Replies will now become clickable links!
Speaking of Replies, they’re threaded now!
Did you just get promoted to moderator in your Community, but don’t know what to do? Behold the new documentation!
Community admins can now ban members! Banned members will not be able to re-join or even see the Community they were banned from.
We’re opening up the Communities API to third-party developers via the public Tumblr API. Stay tuned in our public docs repo for updates on the different endpoints!
🛠 Fixed
It was difficult to read long alt text on the web, and this has now been fixed! Please keep in mind that alt text should be a brief description of your image, as if you were describing it to someone over the phone, solely to make your post accessible to folks using a screen reader.
On the web, it was previously impossible in many cases to add a Read More block to the top of a post, and now you can!
🚧 Ongoing
Folks with the Android app are unable to block anonymous Asks, but they can still be blocked on the web, and there will be a fix in the next update.
🌱 Upcoming
We’re still hard at work on even more features for Communities!
We’re also … collecting … a new perk for Premium subscribers, stay tuned! 😉
Experiencing an issue? Check for Known Issues and file a Support Request if you have something new. We’ll get back to you as soon as we can!
Want to share your feedback about something? Check out our Work in Progress blog and start a discussion with the community.
Wanna support Tumblr directly with some money? Check out Premium and the Supporter badge in TumblrMart!
316 notes
·
View notes
Text
WASP REVIEW - BEES (MINECRAFT)

[Image ID: An official render of the Minecraft bee /End IDs.]
Alright y'all, it's time for an iconic one. One of the most common of only a small handful of arthropods in the game (ironically given the fact they felt the need to specifically make Bane Of Arthropods a thing), and the least hostile one at that, these blocky bees have deservedly buzzed their way into beloved status amongst Minecraft players over the past five years since their official debut. However, as I'm well aware at this point in this series, popularity does not necessarily mean accuracy, so how do these insectoid cuboids really stack up?
Starting from their appearance, it's obvious is that their bodies are heavily fused, with one solid body segment. I'm sure you don't need me to tell you this, but nevertheless, the body of a bee is notably more segmented than the body structure of the Minecraft bee, having three body segments: The head, the mesosoma (also referred to as the thorax, though these are classified a bit differently), and the metasoma (also referred to as the abdomen, same thing here as with the mesosoma). This is clearly a stylistic choice, so I can't get too mad at it, but it is disappointing, given the fact that Minecraft's spider is more segmented, perhaps even having more body segments than the real thing.


[Image Sources: iNaturalist, Yuriy Danilevsky, and PBS, Nebraska Public Media | Image IDs: A photo of a black and yellow/orange European honey bee feeding from a yellow flower, followed by an illustration of a honey bee (female, worker) showing its body parts as labelled. Mandibles, antennae, eyes, thorax, abdomen, stinger, foreleg, middle leg, forewing, hind wing, and hind leg (with labelled pollen basket) /End IDs.]
That said, there are some other things I take issue with regarding this design apart from just this choice of segmentation. I feel like it's safe to assume this bee is based off of the most common honey bee species, the European honey bee (Apis mellifera), in which case, they honestly feel like they're a bit too wide? This wouldn't be a big deal, except, I feel that if they were a bit longer it would help keep the proportions from feeling kind of... Off- Even if we do simplify a bee down to one continuous body segment, it helps to have some distinctions made between the areas of the body. The way they've done it here almost makes it seem as though the mesosoma is just straight up not there; Like the head goes directly into the mesosoma with no in-between.
Another thing that would help this design to not feel quite as "fused together" would be a slight change in coloration. The Minecraft bee has a yellow head, which goes directly into the stripes of the metasoma a little further down the body. In a lot of real world honey bees, the head and mesosoma are generally darker and more solid in color than the lighter and/or more vibrant stripes of the metasoma (with some exceptions), varying in shade depending on the amount of fur (the length of the setae), from a muted yellow to a dark brown color; Further still, honey bee heads can also be noticeably darker overall than the mesosoma at times. Taking this into consideration, I would make the Minecraft bee long enough proportionally to fit another pixel or two lengthwise—enough to provide slightly more space while also not being too long—making the area representing the mesosoma a slightly darker yellow, and the area representing the head the same color as the brown stripes on the original design.
But enough about the body segmentation! Let's talk about the smaller details for a minute here. The wing count is wrong, with only two wings as opposed to the four of a real bee, and they're lacking in terms of venation. The leg count is right but the proportions are all wrong, and they suffer from the same issue as the body, where they look completely fused together. I completely understand wanting to simplify this aspect of the design, but going from five major segments (Coxa, trochanter, femur, tibia, and tarsus) is kind of ridiculous!

[Image Source: bugguide.net | Image ID: An illustrated diagram showing the legs of three Hymenopterans, the first two being of other wasps, while the last one is of a bee, with each segment labeled. Coxa, trochanter, femur, tibia, and tarsus, with metatarsus on the bee. /End IDs.]
The antennae themselves are alright, if a bit short; I appreciate them having little pixels on the main body where they connect to the head, but yeah, it would've been impossible to give them much detail at all at this resolution. The position of the antennae, however, is what throws things off, as they're placed above the eyes when they should be placed between their eyes. Speaking of! Their compound eyes are FAR too small, they should reach up and around the top of their heads, while the eyes here reach only about the halfway point of the texture; and to add insult to injury here, they don't even have their three ocelli (simple eyes)! Nor do they have any mouthparts to speak of, which is an even more major thing to be missing for a bee!

[Image Source: Arizona State University | Image ID: An illustration of the head of a worker honey bee with mouthparts extended, the whole head labelled as follows; Compound Eye, Ocellus (one of three), Antenna, Labrum, Mandible, Maxilla, Labial Palp, Proboscis, and Glossa /End IDs.]
In the end, there's not really much left to cover in regards to this design just due to the fact it's so simplified, though I will say one last thing about it, for now; Their stingers shouldn't be out like that 24/7. Some of their relatives DO have their ovipositors (same thing, a stinger is an ovipositor that can also inject venom) out on the regular, but not bees.

[Image Source: mchoneybeev | Image ID: An in-game screenshot of two Minecraft bees in a cherry forest /End IDs.]
Ok so, what about their behaviors, then? Well, honestly, I think these are actually some of the more accurate ones I've covered in terms of behaviors in this series. Unlike many previous reviews, Minecraft actually goes through the effort of showing that these insects visit and pollinate flowers; Which, barring the ones that are explicitly aliens or robots, would be the case for every Hymenopteran we've covered in the real world. Now, pollination in Minecraft doesn't have an effect on the flowers themselves, it certainly affects the bees!
After visiting a flower, the bees will return to the hive, supplying the hive with honey, as well as beeswax in the form of honeycombs. While this happens much quicker and in larger quantities per trip in the Minecraft bees for purely mechanical reasons, this is relatively accurate to the honey bees of our world, which produce honey from the sugary nectar of flowers, in turn producing more wax as well as they process various bits of plant matter.

[Image ID: An image of a nest made by bees in Minecraft, in the state in which it is full of honey /End IDs.]
We don't actually see these processes happen, however, which I'm sure is partially, fairly enough, because they didn't want to animate it, but it's also because their nest is an enclosed arboreal nest! Bees of the genus Apis primarily prefer to nest in sheltered locations, so the enclosed nature of their nests isn't entirely inaccurate; When they can't find a hollow log or something of the sort, they'll even nest out in the open in the branches of trees. However! These open air nests are exactly that, open! In the instances that they make their hive in the branches of a tree, they will actually make it in a structure that is entirely exposed to the elements, in slabs of honeycomb with no protective outer walls. It's also, perhaps, because of this enclosed shape, and the sheer scaled-up size of the bees in Minecraft (Roughly 0.56 meters if you go by the 1 block = 1 meter measurement) that these nests can only fit a measly three worker bees compared to the upwards of tens of thousands in a real colony of honey bees.
There are actually social bees, though, that produce enclosed nests, made of wax, out in the open, in trees—even producing honey. They're in the same family as the honey bees we know and love, in fact! However, these ones are a part of the genus Trigona, whereas the common European honey bee belongs to the genus Apis.



[Image Sources: iNaturalist, Kahio Tiberio Mazon, ResearchGate, Multiple Authors, and AJC, Tim Thompson | Image IDs: A photo of two black and red bees of the species Trigona spinipes on a yellow flower, followed by an image of a nest in a tree made by the same species, followed again by an arboreal nest made by a bee species within the genes Apis, showing how the honeycomb is shaped into slabs exposed to the air /End IDs.]
Some other things we don't seem to see in Minecraft are the queen and drones of the hive! Perhaps understandably so, as queens don't leave the hive many times throughout their lives, and the drones mainly leave the hive to mate with queen bees, along with the fact that there aren't as many drones and queens in a nest as there are workers! This does also further confirm, on top of the presence of their ovipositors, that all the bees we see in minecraft are females! It would be quite fun to see how they would translate the eyes of a drone into this style, however.

[Image Source: Healthy With Honey | Image ID: A close up set of photos that shows the differences in facial structures between a female, worker bee and a male, drone bee /End IDs.]
Again, on the topic of those ovipositors (I.E., their stingers), how do they attack? Well, thankfully this time there's not anything fantastical about their attack patterns, as they simply sting the player when provoked. Which is another thing! They only attack when provoked; when their hive is attacked, when they're attacked, or when you attempt to harvest from the hive without taking the proper precautions. I feel like this strikes the right balance between being dangerous if messed with and also not being "aggressive", once again unlike many other depictions of Hymenopterans in media in general, as, usually, you get either complete pacifists or murder machines fueled by anger.
Furthermore, when these bees sting you, they take another cue from their real world counterpart and actually lose their stinger! Most bees, ants, and other wasps that are capable of stinging are also capable of doing so more than once; Famously, though, honey bee workers will, more often than not, get their barbed stingers caught in the skin of things like mammals, and lose it. Understandably, Mojang did not depict what actually happens when they lose their stinger, as this leads to the partial disembowelment of the bee, thusly causing it to die.

[Image Source: PBS, Rose-Lynn Fisher | Image ID: An image of a honeybee stinger magnified 650x /End IDs.]
As I mentioned in passing a minute ago, you can, however, absolutely harvest from your hives without aggravating your bees—which doing so could end up potentially killing both you and your bees. With the power of a campfire! And no, of course I'm not suggesting that you burn your bee nest, since, as it turns out, the bees are calmed by smoke! Another well known fact due to the process of beekeeping, as beekeepers usually use smoke to calm bees. I would not necessarily recommend the campfire method, though, as it might be a bit too much in general, and may be a bit too hot for the bees. Even still, relatively cool smoke, applied in just the right amount as to be completely safe for them, will mask alarm pheromones and suppress bees' sense of smell, in turn suppressing their alarm response.
Fittingly, this isn't the only aspect of beekeeping carried over into the Minecraft world, as bees can also be moved from their natural hive into a man-made box hive!

[Image ID: A render of the wooden beehive from Minecraft /End IDs.]
Not much to say here about the structure itself here, as it's made by the player rather than being made in nature. Sadly—and logically due to their equal size—this structure cannot contain any more bees than the natural hive can, however, it still remains useful as the easiest way to move bees from one place to another. That said, I feel it necessary to mention; Due to the fact that, again, we never see a queen, this implies that either these bees have a social structure that is quite different from the real world, or that these bees are leaving their nest without their queen, which would be highly disadvantageous for the colony as a whole, as the queen is the only fertile female! You can even get them to leave individually, which is highly strange behavior for a honey bee. If brought away from the nest, a singular worker bee will typically not attempt to make a new home, and instead try to find a way back to its original home and its queen.
One final thing I want to bring up is that... You can put bees on leads! In fact, this is a major way of bringing the bees from a natural hive to a wooden one. This would be highly impractical in real life, however, it is very cute!

[Image ID: A screenshot of a Minecraft bee on a lead /End ID.]
With everything out of the way, we're left quite a few aspects that are accurate to the real world, but some strange inaccuracies all over the place as well. I find the design to be one of the least accurate among those I can directly compare to the real world, but certain aspects of their behavior, as well as the care put into including certain details, redeem them somewhat. Still, their behavior does contain some inaccuracies as well; So, these blocky bees get my accuracy rating of-
-
Overall: 4.5 to 5/10
-
Leave your wasp review suggestion in the replies, tags, or askbox!
57 notes
·
View notes
Text
The enshittification of garage-door openers reveals a vast and deadly rot

I'll be at the Studio City branch of the LA Public Library on Monday, November 13 at 1830hPT to launch my new novel, The Lost Cause. There'll be a reading, a talk, a surprise guest (!!) and a signing, with books on sale. Tell your friends! Come on down!

How could this happen? Owners of Chamberlain MyQ automatic garage door openers just woke up to discover that the company had confiscated valuable features overnight, and that there was nothing they could do about it.
Oh, we know what happened, technically speaking. Chamberlain shut off the API for its garage-door openers, which breaks their integration with home automation systems like Home Assistant. The company even announced that it was doing this, calling the integration an "unauthorized usage" of its products, though the "unauthorized" parties in this case are the people who own Chamberlain products:
https://chamberlaingroup.com/press/a-message-about-our-decision-to-prevent-unauthorized-usage-of-myq
We even know why Chamberlain did this. As Ars Technica's Ron Amadeo points out, shutting off the API is a way for Chamberlain to force its customers to use its ad-beshitted, worst-of-breed app, so that it can make a few pennies by nonconsensually monetizing its customers' eyeballs:
https://arstechnica.com/gadgets/2023/11/chamberlain-blocks-smart-garage-door-opener-from-working-with-smart-homes/
But how did this happen? How did a giant company like Chamberlain come to this enshittening juncture, in which it felt empowered to sabotage the products it had already sold to its customers? How can this be legal? How can it be good for business? How can the people who made this decision even look themselves in the mirror?
To answer these questions, we must first consider the forces that discipline companies, acting against the impulse to enshittify their products and services. There are four constraints on corporate conduct:
I. Competition. The fear of losing your business to a rival can stay even the most sociopathic corporate executive's hand.
II. Regulation. The fear of being fined, criminally sanctioned, or banned from doing business can check the greediest of leaders.
III. Capability. Corporate executives can dream up all kinds of awful ways to shift value from your side of the ledger to their own, but they can only do the things that are technically feasible.
IV. Self-help. The possibility of customers modifying, reconfiguring or altering their products to restore lost functionality or neutralize antifeatures carries an implied threat to vendors. If a printer company's anti-generic-ink measures drives a customer to jailbreak their printers, the original manufacturer's connection to that customer is permanently severed, as the customer creates a durable digital connection to a rival.
When companies act in obnoxious, dishonest, shitty ways, they aren't merely yielding to temptation – they are evading these disciplining forces. Thus, the Great Enshittening we are living through doesn't reflect an increase in the wickedness of corporate leadership. Rather, it represents a moment in which each of these disciplining factors have been gutted by specific policies.
This is good news, actually. We used to put down rat poison and we didn't have a rat problem. Then we stopped putting down rat poison and rats are eating us alive. That's not a nice feeling, but at least we know at least one way of addressing it – we can start putting down poison again. That is, we can start enforcing the rules that we stopped enforcing, in living memory. Having a terrible problem is no fun, but the best kind of terrible problem to have is one that you know a solution to.
As it happens, Chamberlain is a neat microcosm for all the bad policy choices that created the Era of Enshittification. Let's go through them:
Competition: Chamberlain doesn't have to worry about competition, because it is owned by a private equity fund that "rolled up" all of Chamberlain's major competitors into a single, giant firm. Most garage-door opener brands are actually Chamberlain, including "LiftMaster, Chamberlain, Merlin, and Grifco":
https://www.lakewoodgaragedoor.biz/blog/the-history-of-garage-door-openers
This is a pretty typical PE rollup, and it exploits a bug in US competition law called "Antitrust's Twilight Zone":
https://pluralistic.net/2022/12/16/schumpeterian-terrorism/#deliberately-broken
When companies buy each other, they are subject to "merger scrutiny," a set of guidelines that the FTC and DoJ Antitrust Division use to determine whether the outcome is likely to be bad for competition. These rules have been pretty lax since the Reagan administration, but they've currently being revised to make them substantially more strict:
https://www.justice.gov/opa/pr/justice-department-and-ftc-seek-comment-draft-merger-guidelines
One of the blind spots in these merger guidelines is an exemption for mergers valued at less than $101m. Under the Hart-Scott-Rodino Act, these fly under the radar, evading merger scrutiny. That means that canny PE companies can roll up dozens and dozens of standalone businesses, like funeral homes, hospital beds, magic mushrooms, youth addiction treatment centers, mobile home parks, nursing homes, physicians’ practices, local newspapers, or e-commerce sellers:
http://www.economicliberties.us/wp-content/uploads/2022/12/Serial-Acquisitions-Working-Paper-R4-2.pdf
By titrating the purchase prices, PE companies – like Blackstone, owners of Chamberlain and all the other garage-door makers – can acquire a monopoly without ever raising a regulatory red flag.
But antitrust enforcers aren't helpless. Under (the long dormant) Section 7 of the Clayton Act, competition regulators can block mergers that lead to "incipient monopolization." The incipiency standard prevented monopolies from forming from 1914, when the Clayton Act passed, until the Reagan administration. We used to put down rat poison, and we didn't have rats. We stopped, and rats are gnawing our faces off. We still know where the rat poison is – maybe we should start putting it down again.
On to regulation. How is it possible for Chamberlain to sell you a garage-door opener that has an API and works with your chosen home automation system, and then unilaterally confiscate that valuable feature? Shouldn't regulation protect you from this kind of ripoff?
It should, but it doesn't. Instead, we have a bunch of regulations that protect Chamberlain from you. Think of binding arbitration, which allows Chamberlain to force you to click through an "agreement" that takes away your right to sue them or join a class-action suit:
https://pluralistic.net/2022/10/20/benevolent-dictators/#felony-contempt-of-business-model
But regulation could protect you from Chamberlain. Section 5 of the Federal Trade Commission Act allows the FTC to ban any "unfair and deceptive" conduct. This law has been on the books since 1914, but Section 5 has been dormant, forgotten and unused, for decades. The FTC's new dynamo chair, Lina Khan, has revived it, and is use it like a can-opener to free Americans who've been trapped by abusive conduct:
https://pluralistic.net/2023/01/10/the-courage-to-govern/#whos-in-charge
Khan's used Section 5 powers to challenge privacy invasions, noncompete clauses, and other corporate abuses – the bait-and-switch tactics of Chamberlain are ripe for a Section 5 case. If you buy a gadget because it has five features and then the vendor takes two of them away, they are clearly engaged in "unfair and deceptive" conduct.
On to capability. Since time immemorial, corporate leaders have fetishized "flexibility" in their business arrangements – like the ability to do "dynamic pricing" that changes how much you pay for something based on their guess about how much you are willing to pay. But this impulse to play shell games runs up against the hard limits of physical reality: grocers just can't send an army of rollerskated teenagers around the store to reprice everything as soon as a wealthy or desperate-looking customer comes through the door. They're stuck with crude tactics like doubling the price of a flight that doesn't include a Saturday stay as a way of gouging business travelers on an expense account.
With any shell-game, the quickness of the hand deceives the eye. Corporate crooks armed with computers aren't smarter or more wicked than their analog forebears, but they are faster. Digital tools allow companies to alter the "business logic" of their services from instant to instant, in highly automated ways:
https://pluralistic.net/2023/02/19/twiddler/
The monopoly coalition has successfully argued that this endless "twiddling" should not be constrained by privacy, labor or consumer protection law. Without these constraints, corporate twiddlers can engage in all kinds of ripoffs, like wage theft and algorithmic wage discrimination:
https://pluralistic.net/2023/04/12/algorithmic-wage-discrimination/#fishers-of-men
Twiddling is key to the Darth Vader MBA ("I am altering the deal. Pray I don't alter it further"), in which features are confiscated from moment to moment, without warning or recourse:
https://pluralistic.net/2023/10/26/hit-with-a-brick/#graceful-failure
There's no reason to accept the premise that violating your privacy, labor rights or consumer rights with a computer is so different from analog ripoffs that existing laws don't apply. The unconstrained twiddling of digital ripoff artists is a plague on billions of peoples' lives, and any enforcer who sticks up for our rights will have an army of supporters behind them.
Finally, there's the fear of self-help measures. All the digital flexibility that tech companies use to take value away can be used to take it back, too. The whole modern history of digital computers is the history of "adversarial interoperability," in which the sleazy antifeatures of established companies are banished through reverse-engineering, scraping, bots and other forms of technological guerrilla warfare:
https://www.eff.org/deeplinks/2019/10/adversarial-interoperability
Adversarial interoperability represents a serious threat to established business. If you're a printer company gouging on toner, your customers might defect to a rival that jailbreaks your security measures. That's what happened to Lexmark, who lost a case against the toner-refilling company Static Controls, which went on to buy Lexmark:
https://www.eff.org/deeplinks/2019/06/felony-contempt-business-model-lexmarks-anti-competitive-legacy
Sure, your customers are busy and inattentive and you can degrade the quality of your product a lot before they start looking for ways out. But once they cross that threshold, you can lose them forever. That's what happened to Microsoft: the company made the tactical decision to produce a substandard version of Office for the Mac in a drive to get Mac users to switch to Windows. Instead, Apple made Iwork (Pages, Numbers and Keynote), which could read and write every Office file, and Mac users threw away Office, the only Microsoft product they owned, permanently severing their relationship to the company:
https://www.eff.org/deeplinks/2019/06/adversarial-interoperability-reviving-elegant-weapon-more-civilized-age-slay
Today, companies can operate without worrying about this kind of self-help measure. There' a whole slew of IP rights that Chamberlain can enforce against you if you try to fix your garage-door opener yourself, or look to a competitor to sell you a product that restores the feature they took away:
https://locusmag.com/2020/09/cory-doctorow-ip/
Jailbreaking your Chamberlain gadget in order to make it answer to a rival's app involves bypassing a digital lock. Trafficking in a tool to break a digital lock is a felony under Section 1201 of the Digital Millennium Copyright, carrying a five-year prison sentence and a $500,000 fine.
In other words, it's not just that tech isn't regulated, allowing for endless twiddling against your privacy, consumer rights and labor rights. It's that tech is badly regulated, to permit unlimited twiddling by tech companies to take away your rightsand to prohibit any twiddling by you to take them back. The US government thumbs the scales against you, creating a regime that Jay Freeman aptly dubbed "felony contempt of business model":
https://pluralistic.net/2022/10/23/how-to-fix-cars-by-breaking-felony-contempt-of-business-model/
All kinds of companies have availed themselves of this government-backed superpower. There's DRM – digital locks, covered by DMCA 1201 – in powered wheelchairs:
https://www.eff.org/deeplinks/2022/06/when-drm-comes-your-wheelchair
In dishwashers:
https://pluralistic.net/2021/05/03/cassette-rewinder/#disher-bob
In treadmills:
https://pluralistic.net/2021/06/22/vapescreen/#jane-get-me-off-this-crazy-thing
In tractors:
https://pluralistic.net/2022/05/08/about-those-kill-switched-ukrainian-tractors/
It should come as no surprise to learn that Chamberlain has used DMCA 1201 to block interoperable garage door opener components:
https://scholarship.law.marquette.edu/cgi/viewcontent.cgi?article=1233&context=iplr
That's how we arrived at this juncture, where a company like Chamberlain can break functionality its customers value highly, solely to eke out a minuscule new line of revenue by selling ads on their own app.
Chamberlain bought all its competitors.
Chamberlain operates in a regulatory environment that is extremely tolerant of unfair and deceptive practices. Worse: they can unilaterally take away your right to sue them, which means that if regulators don't bestir themselves to police Chamberlain, you are shit out of luck.
Chamberlain has endless flexibility to unilaterally alter its products' functionality, in fine-grained ways, even after you've purchased them.
Chamberlain can sue you if you try to exercise some of that same flexibility to protect yourself from their bad practices.
Combine all four of those factors, and of course Chamberlain is going to enshittify its products. Every company has had that one weaselly asshole at the product-planning table who suggests a petty grift like breaking every one of the company's customers' property to sell a few ads. But historically, the weasel lost the argument to others, who argued that making every existing customer furious would affect the company's bottom line, costing it sales and/or fines, and prompting customers to permanently sever their relationship with the company by seeking out and installing alternative software. Take away all the constraints on a corporation's worst impulses, and this kind of conduct is inevitable:
https://pluralistic.net/2023/07/28/microincentives-and-enshittification/
This isn't limited to Chamberlain. Without the discipline of competition, regulation, self-help measures or technological limitations, every industry in undergoing wholesale enshittification. It's not a coincidence that Chamberlain's grift involves a push to move users into its app. Because apps can't be reverse-engineered and modified without risking DMCA 1201 prosecution, forcing a user into an app is a tidy and reliable way to take away that user's rights.
Think about ad-blocking. One in four web users has installed an ad-blockers ("the biggest boycott in world history" -Doc Searls). Zero app users have installed app-blockers, because they don't exist, because making one is a felony. An app is just a web-page wrapped in enough IP to make it a crime to defend yourself against corporate predation:
https://pluralistic.net/2023/08/27/an-audacious-plan-to-halt-the-internets-enshittification-and-throw-it-into-reverse/
The temptation to enshitiffy isn't new, but the ability to do so without consequence is a modern phenomenon, the intersection of weak policy enforcement and powerful technology. Your car is autoenshittified, a rolling rent-seeking platform that spies on you and price-gouges you:
https://pluralistic.net/2023/07/24/rent-to-pwn/#kitt-is-a-demon
Cars are in an uncontrolled skid over Enshittification Cliff. Honda, Toyota, VW and GM all sell cars with infotainment systems that harvest your connected phone's text-messages and send them to the corporation for data-mining. What's more, a judge in Washington state just ruled that this is legal:
https://therecord.media/class-action-lawsuit-cars-text-messages-privacy
While there's no excuse for this kind of sleazy conduct, we can reasonably anticipate that if our courts would punish companies for engaging in it, they might be able to resist the temptation. No wonder Mozilla's latest Privacy Not Included research report called cars "the worst product category we have ever reviewed":
https://foundation.mozilla.org/en/privacynotincluded/articles/its-official-cars-are-the-worst-product-category-we-have-ever-reviewed-for-privacy/
I mean, Nissan tries to infer facts about your sex life and sells those inferences to marketing companies:
https://foundation.mozilla.org/en/privacynotincluded/nissan/
But the OG digital companies are the masters of enshittification. Microsoft has been at this game for longer than anyone, and every day brings a fresh way that Microsoft has worsened its products without fear of consequence. The latest? You can't delete your OneDrive account until you provide an acceptable explanation for your disloyalty:
https://www.theverge.com/2023/11/8/23952878/microsoft-onedrive-windows-close-app-notification
It's tempting to think that the cruelty is the point, but it isn't. It's almost never the point. The point is power and money. Unscrupulous businesses have found ways to make money by making their products worse since the industrial revolution. Here's Jules Dupuis, writing about 19th century French railroads:
It is not because of the few thousand francs which would have to be spent to put a roof over the third-class carriages or to upholster the third-class seats that some company or other has open carriages with wooden benches. What the company is trying to do is to prevent the passengers who can pay the second class fare from traveling third class; it hits the poor, not because it wants to hurt them, but to frighten the rich. And it is again for the same reason that the companies, having proved almost cruel to the third-class passengers and mean to the second-class ones, become lavish in dealing with first-class passengers. Having refused the poor what is necessary, they give the rich what is superfluous.
https://www.tumblr.com/mostlysignssomeportents/731357317521719296/having-refused-the-poor-what-is-necessary-they
But as bad as all this is, let me remind you about the good part: we know how to stop companies from enshittifying their products. We know what disciplines their conduct: competition, regulation, capability and self-help measures. Yes, rats are gnawing our eyeballs, but we know which rat-poison to use, and where to put it to control those rats.
Competition, regulation, constraint and self-help measures all backstop one another, and while one or a few can make a difference, they are most powerful when they're all mobilized in concert. Think of the failure of the EU's landmark privacy law, the GDPR. While the GDPR proved very effective against bottom-feeding smaller ad-tech companies, the worse offenders, Meta and Google, have thumbed their noses at it.
This was enabled in part by the companies' flying an Irish flag of convenience, maintaining the pretense that they have to be regulated in a notorious corporate crime-haven:
https://pluralistic.net/2023/05/15/finnegans-snooze/#dirty-old-town
That let them get away with all kinds of shenanigans, like ignoring the GDPR's requirement that you should be able to easily opt out of data-collection without having to go through cumbersome "cookie consent" dialogs or losing access to the service as punishment for declining to be tracked.
As the noose has tightened around these surveillance giants, they're continuing to play games. Meta now says that the only way to opt out of data-collection in the EU is to pay for the service:
https://pluralistic.net/2023/10/30/markets-remaining-irrational/#steins-law
This is facially illegal under the GDPR. Not only are they prohibited from punishing you for opting out of collection, but the whole scheme ignores the nature of private data collection. If Facebook collects the fact that you and I are friends, but I never opted into data-collection, they have violated the GDPR, even if you were coerced into granting consent:
https://www.nakedcapitalism.com/2023/11/the-pay-or-consent-challenge-for-platform-regulators.html
The GDPR has been around since 2016 and Google and Meta are still invading 500 million Europeans' privacy. This latest delaying tactic could add years to their crime-spree before they are brought to justice.
But most of this surveillance is only possible because so much of how you interact with Google and Meta is via an app, and an app is just a web-page that's a felony to make an ad-blocker for. If the EU were to legalize breaking DRM – repealing Article 6 of the 2001 Copyright Directive – then we wouldn't have to wait for the European Commission to finally wrestle these two giant companies to the ground. Instead, EU companies could make alternative clients for all of Google and Meta's services that don't spy on you, without suffering the fate of OG App, which tried this last winter and was shut down by "felony contempt of business model":
https://pluralistic.net/2023/02/05/battery-vampire/#drained
Enshittification is demoralizing. To quote @wilwheaton, every update to the services we use inspires "dread of 'How will this complicate things as I try to maintain privacy and sanity in a world that demands I have this thing to operate?'"
https://wilwheaton.tumblr.com/post/698603648058556416/cory-doctorow-if-you-see-this-and-have-thoughts
But there are huge natural constituencies for the four disciplining forces that keep enshittification at bay.
Remember, Antitrust's Twilight Zone doesn't just allow rollups of garage-door opener companies – it's also poison for funeral homes, hospital beds, magic mushrooms, youth addiction treatment centers, mobile home parks, nursing homes, physicians’ practices, local newspapers, or e-commerce sellers.
The Binding Arbitration scam that stops Chamberlain customers from suing the company also stops Uber drivers from suing over stolen wages, Turbotax customers from suing over fraud, and many other victims of corporate crime from getting a day in court.
The failure to constrain twiddling to protect privacy, labor rights and consumer rights enables a host of abuses, from stalking, doxing and SWATting to wage theft and price gouging:
https://pluralistic.net/2023/11/06/attention-rents/#consumer-welfare-queens
And Felony Contempt of Business Model is used to screw you over every time you refill your printer, run your dishwasher, or get your Iphone's screen replaced.
The actions needed to halt and reverse this enshittification are well understood, and the partisans for taking those actions are too numerous to count. It's taken a long time for all those individuals suffering under corporate abuses to crystallize into a movement, but at long last, it's happening.

If you'd like an essay-formatted version of this post to read or share, here's a link to it on pluralistic.net, my surveillance-free, ad-free, tracker-free blog:
https://pluralistic.net/2023/11/09/lead-me-not-into-temptation/#chamberlain

Image: Cryteria (modified) https://commons.wikimedia.org/wiki/File:HAL9000.svg
CC BY 3.0 https://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/3.0/deed.en
#pluralistic#monopolists#anticircumvention#myq#home assistant#pay or consent#enshittification#surveillance#autoenshittification#privacy#self-help measures#microsoft#onedrive#twiddling#comcom#competitive compatibility#interop#interoperability#adversarial interoperability#felony contempt of business model#darth vader mba
376 notes
·
View notes
Text
clarification re: ChatGPT, " a a a a", and data leakage
In August, I posted:
For a good time, try sending chatGPT the string ` a` repeated 1000 times. Like " a a a" (etc). Make sure the spaces are in there. Trust me.
People are talking about this trick again, thanks to a recent paper by Nasr et al that investigates how often LLMs regurgitate exact quotes from their training data.
The paper is an impressive technical achievement, and the results are very interesting.
Unfortunately, the online hive-mind consensus about this paper is something like:
When you do this "attack" to ChatGPT -- where you send it the letter 'a' many times, or make it write 'poem' over and over, or the like -- it prints out a bunch of its own training data. Previously, people had noted that the stuff it prints out after the attack looks like training data. Now, we know why: because it really is training data.
It's unfortunate that people believe this, because it's false. Or at best, a mixture of "false" and "confused and misleadingly incomplete."
The paper
So, what does the paper show?
The authors do a lot of stuff, building on a lot of previous work, and I won't try to summarize it all here.
But in brief, they try to estimate how easy it is to "extract" training data from LLMs, moving successively through 3 categories of LLMs that are progressively harder to analyze:
"Base model" LLMs with publicly released weights and publicly released training data.
"Base model" LLMs with publicly released weights, but undisclosed training data.
LLMs that are totally private, and are also finetuned for instruction-following or for chat, rather than being base models. (ChatGPT falls into this category.)
Category #1: open weights, open data
In their experiment on category #1, they prompt the models with hundreds of millions of brief phrases chosen randomly from Wikipedia. Then they check what fraction of the generated outputs constitute verbatim quotations from the training data.
Because category #1 has open weights, they can afford to do this hundreds of millions of times (there are no API costs to pay). And because the training data is open, they can directly check whether or not any given output appears in that data.
In category #1, the fraction of outputs that are exact copies of training data ranges from ~0.1% to ~1.5%, depending on the model.
Category #2: open weights, private data
In category #2, the training data is unavailable. The authors solve this problem by constructing "AuxDataset," a giant Frankenstein assemblage of all the major public training datasets, and then searching for outputs in AuxDataset.
This approach can have false negatives, since the model might be regurgitating private training data that isn't in AuxDataset. But it shouldn't have many false positives: if the model spits out some long string of text that appears in AuxDataset, then it's probably the case that the same string appeared in the model's training data, as opposed to the model spontaneously "reinventing" it.
So, the AuxDataset approach gives you lower bounds. Unsurprisingly, the fractions in this experiment are a bit lower, compared to the Category #1 experiment. But not that much lower, ranging from ~0.05% to ~1%.
Category #3: private everything + chat tuning
Finally, they do an experiment with ChatGPT. (Well, ChatGPT and gpt-3.5-turbo-instruct, but I'm ignoring the latter for space here.)
ChatGPT presents several new challenges.
First, the model is only accessible through an API, and it would cost too much money to call the API hundreds of millions of times. So, they have to make do with a much smaller sample size.
A more substantial challenge has to do with the model's chat tuning.
All the other models evaluated in this paper were base models: they were trained to imitate a wide range of text data, and that was that. If you give them some text, like a random short phrase from Wikipedia, they will try to write the next part, in a manner that sounds like the data they were trained on.
However, if you give ChatGPT a random short phrase from Wikipedia, it will not try to complete it. It will, instead, say something like "Sorry, I don't know what that means" or "Is there something specific I can do for you?"
So their random-short-phrase-from-Wikipedia method, which worked for base models, is not going to work for ChatGPT.
Fortuitously, there happens to be a weird bug in ChatGPT that makes it behave like a base model!
Namely, the "trick" where you ask it to repeat a token, or just send it a bunch of pre-prepared repetitions.
Using this trick is still different from prompting a base model. You can't specify a "prompt," like a random-short-phrase-from-Wikipedia, for the model to complete. You just start the repetition ball rolling, and then at some point, it starts generating some arbitrarily chosen type of document in a base-model-like way.
Still, this is good enough: we can do the trick, and then check the output against AuxDataset. If the generated text appears in AuxDataset, then ChatGPT was probably trained on that text at some point.
If you do this, you get a fraction of 3%.
This is somewhat higher than all the other numbers we saw above, especially the other ones obtained using AuxDataset.
On the other hand, the numbers varied a lot between models, and ChatGPT is probably an outlier in various ways when you're comparing it to a bunch of open models.
So, this result seems consistent with the interpretation that the attack just makes ChatGPT behave like a base model. Base models -- it turns out -- tend to regurgitate their training data occasionally, under conditions like these ones; if you make ChatGPT behave like a base model, then it does too.
Language model behaves like language model, news at 11
Since this paper came out, a number of people have pinged me on twitter or whatever, telling me about how this attack "makes ChatGPT leak data," like this is some scandalous new finding about the attack specifically.
(I made some posts saying I didn't think the attack was "leaking data" -- by which I meant ChatGPT user data, which was a weirdly common theory at the time -- so of course, now some people are telling me that I was wrong on this score.)
This interpretation seems totally misguided to me.
Every result in the paper is consistent with the banal interpretation that the attack just makes ChatGPT behave like a base model.
That is, it makes it behave the way all LLMs used to behave, up until very recently.
I guess there are a lot of people around now who have never used an LLM that wasn't tuned for chat; who don't know that the "post-attack content" we see from ChatGPT is not some weird new behavior in need of a new, probably alarming explanation; who don't know that it is actually a very familiar thing, which any base model will give you immediately if you ask. But it is. It's base model behavior, nothing more.
Behaving like a base model implies regurgitation of training data some small fraction of the time, because base models do that. And only because base models do, in fact, do that. Not for any extra reason that's special to this attack.
(Or at least, if there is some extra reason, the paper gives us no evidence of its existence.)
The paper itself is less clear than I would like about this. In a footnote, it cites my tweet on the original attack (which I appreciate!), but it does so in a way that draws a confusing link between the attack and data regurgitation:
In fact, in early August, a month after we initial discovered this attack, multiple independent researchers discovered the underlying exploit used in our paper, but, like us initially, they did not realize that the model was regenerating training data, e.g., https://twitter.com/nostalgebraist/status/1686576041803096065.
Did I "not realize that the model was regenerating training data"? I mean . . . sort of? But then again, not really?
I knew from earlier papers (and personal experience, like the "Hedonist Sovereign" thing here) that base models occasionally produce exact quotations from their training data. And my reaction to the attack was, "it looks like it's behaving like a base model."
It would be surprising if, after the attack, ChatGPT never produced an exact quotation from training data. That would be a difference between ChatGPT's underlying base model and all other known LLM base models.
And the new paper shows that -- unsurprisingly -- there is no such difference. They all do this at some rate, and ChatGPT's rate is 3%, plus or minus something or other.
3% is not zero, but it's not very large, either.
If you do the attack to ChatGPT, and then think "wow, this output looks like what I imagine training data probably looks like," it is nonetheless probably not training data. It is probably, instead, a skilled mimicry of training data. (Remember that "skilled mimicry of training data" is what LLMs are trained to do.)
And remember, too, that base models used to be OpenAI's entire product offering. Indeed, their API still offers some base models! If you want to extract training data from a private OpenAI model, you can just interact with these guys normally, and they'll spit out their training data some small % of the time.
The only value added by the attack, here, is its ability to make ChatGPT specifically behave in the way that davinci-002 already does, naturally, without any tricks.
265 notes
·
View notes