#probably at least four feet long. very big giant toothless
Explore tagged Tumblr posts
Text
Okay so pocket sized Toothless would be a better demonstration of how I pick which design elements are necessary to make a plushie recognizably what I want it to be and how I work with the limitations of the medium, but I think the pattern I just made for the giant ant's head would work perfectly for a big cuddly Toothless’s head
Okay there's more interest in my "how I make patterns" post than I expected (I honestly did not expect any interest). Do y'all want to see me design a pattern from start to finish? If so, what should it be a pattern for? Send me ideas and I'll make a poll
#you see my dilemma. but also. big toothless will be Very Large#and I have to decide what I'd do with him#...maybe I'll make him out of fleece and he can live on my bed to hopefully stop me from running into the wall in my sleep?#that would mean I'd have to make him from black fabric from the prototype though#which is doable! but I would have to go buy some black fleece#not an insurmountable obstacle#surprisingly for someone who works so much with minky and faux fur I am not a fan of them touching me in my sleep#I don't like those faux fur blankets touching my legs at all idk why it's just Bad Texture for me#but only on my legs? hands are fine and I find plushies made with it very cuddly#if I were making it for someone else I'd get one of my fuzzy blankets I use for fabric#for maximum cuddly-ness but also if I make giant toothless it will be like#probably at least four feet long. very big giant toothless
51 notes
·
View notes
Text
Lisowicia bojani

By Scott Reid
Etymology: From Lisowice
First Described By: Sulej & Niedźwiedzki, 2019
Classification: Biota, Archaea, Proteoarchaeota, Asgardarchaeota, Eukaryota, Neokaryota, Scotokaryota Opimoda, Podiata, Amorphea, Obazoa, Opisthokonta, Holozoa, Filozoa, Choanozoa, Animalia, Eumetazoa, Parahoxozoa, Bilateria, Nephrozoa, Deuterostomia, Chordata, Olfactores, Vertebrata, Craniata, Gnathostomata, Eugnathostomata, Osteichthyes, Sarcopterygii, Rhipidistia, Tetrapodomorpha, Eotetrapodiformes, Elpistostegalia, Stegocephalia, Tetrapoda, Reptiliomorpha, Amniota, Synapsida, Eupelycosauria, Sphenacodontia, Sphenacodontoidea, Therapsida, Eutherapsida, Neotherapsida, Anomodontia, Chainosauria, Dicynodontia, Therochelonia, Bidentalia, Dicynodontoidea, Kannemeyeriiformes, Stahleckeriidae, Placeriinae
Status: Extinct
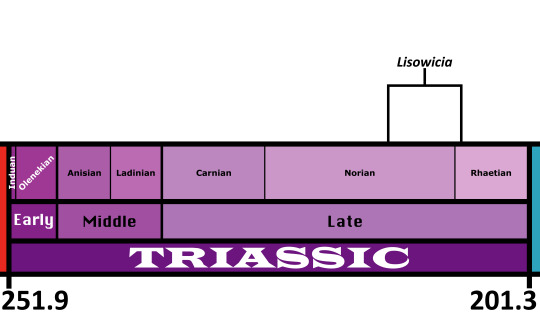
Time and Place: Approximately between 208 to 215 million years ago, in the late Norian to possibly the earliest Rhaetian of the Late Triassic
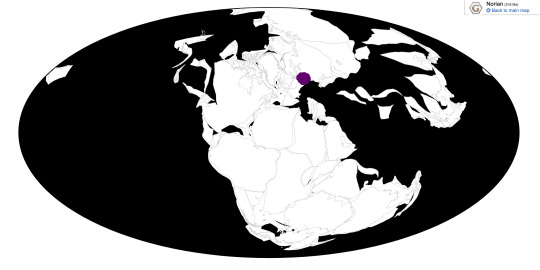
Lisowicia is known from the Lipie Śląskie clay−pit near Lisowice, Poland, as well as possibly other coeval sites in Poland
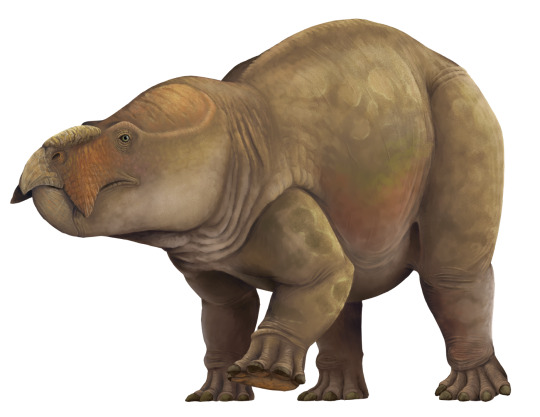
Physical Description: Lisowicia was a very large dicynodont. In fact, with an estimated length of more than 4 metres, a hip height over 2 metres, and an average body weight of 5.88 tons (and possibly up to 7 tons), it was the largest non-mammalian synapsid period, and would be the largest synapsids would ever grow to until the Eocene after the non-avian dinosaurs died out. By and large (ha!), Lisowicia resembles other closely related Triassic dicynodonts like Placerias; it was heavily built with a large barrel-shaped torso and short, stocky legs, a short stubby tail and a large head with a relatively long snout and a tortoise-like beak. Lisowicia was apparently tuskless, like some other Triassic dicynodonts, meaning that it was entirely toothless.
Lisowicia is not only distinctive for its massive size, but also for the design of its limbs. Most dicynodonts had either fully sprawled limbs, or upright hindlimbs and sprawling forelimbs as is the case for larger dicynodonts. Uniquely for dicynodonts, and for any stem-mammal for that matter, Lisowicia had an entirely upright stance with all four limbs being fully erect, holding them directly under its body and swinging them forwards and backwards when moving, like the legs of modern large mammals and dinosaurs. These column-like limbs are no doubt an adaptation for growing to such a massive size, as such limbs are necessary to support large body sizes in land animals, and in the Late Triassic only some sauropodomorph dinosaurs rivalled it in size. This involved not only changes to the orientation of the forelimb, but also changes to the shoulders, shortening of the forearm, and completely rearranging the musculature of the forelimbs in a way no other dicynodont is known to have done. Based on the footprints of other related dicynodonts, the feet of Lisowicia would have been very elephantine in appearance. Like elephants, they would have walked on the tips of the toes with a large fleshy pad underneath the heel to cushion the feet and support its weight. Basically, almost everything about Lisowicia was built to support a massive body size.
The outside appearance of Lisowicia is unknown, and the appearance of most stem-mammals in general is poorly understood. It’s possible it was covered in scales, had naked skin, or even hair, or maybe it had some other unknown structures. If it was anything like large herbivorous dinosaurs and mammals though, it may have been mostly naked anyways.
Diet: Lisowicia was a herbivore, browsing on low and mid-level vegetation using its long snout and toothless beak to crop and chew plants. Remarkably, coprolites attributed to Lisowicia can tell us what they were eating! Lisowicia appears to have mostly preferred eating softer vegetation, along with conifers, and in some cases they even supplemented it with pieces of wood! It’s possible this was a seasonal thing, feeding on tougher, fibrous vegetation during harder times.
Behavior: Like other large herbivores, Lisowicia may have been a herd animal based on fossil sites with multiple individuals preserved together, including adults and juveniles mixed together. Whether this means Lisowicia practised parental care is uncertain though, as it is with most other stem-mammals. Stem-mammal reproduction is poorly understood, but it’s at least probable that they laid eggs, and that includes Lisowicia. Other possible line of evidence for Lisowicia being social could be that they congregated in a specific place to defecate, called communal latrines. Hundreds of coprolites are known from where Lisowicia was first found, and other dicynodonts like Dinodontosaurus are known to have performed similar behaviour, so it’s possible Lisowicia did this too.
Ecosystem: The ecosystem in Late Triassic Poland is rather unusual, as it includes a mix of plants and animals that make it difficult to pin down just how old it really was. Some suggest an older Norian age, others seem more like they’re from younger Rhaetian ecosystems, and it’s still a bit of a mystery to what was going on in this environment compared to the rest of Europe at the time. In any case, the environment where Lisowicia was found was fairly wet and lush, an “everglades-like” swamp dominated by several types of conifers, alongside gingkos, cycads, seed ferns and liverworts. Lisowicia was one of the most common animals in this environment, but it coexisted with a wide variety of other animals. One of the most notable is the predatory archosaur Smok. Smok was the arch predator in this ecosystem, and is known to have directly fed upon Lisowicia, although whether they were actively hunted by it or just scavenged upon is unknown. Smok was certainly capable of crushing even the heavyset bones of Lisowicia, with not only bite marks on its bones attributed to Smok but even broken shards of its bones identified in Smok coprolites! Other reptiles that coexisted with Lisowicia included pterosaurs, dinosauromorphs and predatory theropods similar to Coelophysis or Liliensternus, a small predatory crocodylomorph, and small diapsids, including a sphenodont (a tuatara relative), a possible archosauromorph, and even a possible choristodere. The only other synapsid around was the little mammaliaform cynodont Hallautherium, which was many times smaller than the gigantic Lisowicia. There were also temnospondyl amphibians, including a large predatory capitosaur and a small plagiosaur (one of those very flat temnospondyls with the wide heads), as well as lungfish, coelacanths and even a hybodont shark. Notably, there are no sauropodomorphs known from this ecosystem, even though they were clearly already present in Europe at this time (e.g. Plateosaurus). It’s possible that Lisowicia occupied their role as a giant herbivore in their absence, although whether it had outcompeted them or just happened to live in a habitat without sauropodomorphs and got big is yet another mystery.
Other: In addition to achieving a size and stature amongst synapsids that wouldn’t be seen again until the mammals radiated during the Cenozoic, Lisowicia was also unique for how it grew. While some stem-mammals are known to have grown rapidly as young juveniles, Lisowicia is the only one known so far to never slow down its growth rate at all until adulthood. This type of continuous rapid growth is well known in dinosaurs and mammals, but is unique to Lisowicia amongst dicynodonts. Lisowicia is one of the most unique dicynodonts ever discovered, both as the largest and one of the most derived. It was also sadly one of the last. The cause of its—and all the other Late Triassic dicynodonts’—extinction is unknown, although it was probably a victim of the end-Triassic extinction event like so many other prominent Triassic animals. Late Triassic dicynodonts were once thought to be geographically restricted, left-over relicts from the past that eventually just fizzled away as “more advanced” animals pushed them out. But now we know that they were still globally widespread even in the latest Triassic, including in Europe with advanced forms like Lisowicia. Competition with sauropodomorphs was suspected, but the discovery of the related dicynodont Pentasaurus coexisting with sauropodomorphs in South Africa suggests they were capable of at least living together, and Lisowicia is proof dicynodonts could achieve similarly gigantic proportions. Ultimately, the extinction of the dicynodonts is a mystery, but Lisowicia shows that they were still getting bigger and better than ever, even at the end of their dynasty.
~ By Scott Reid
Sources under the Cut
Bajdek, P., Owocki, K. and Niedźwiedzki, G., 2014. Putative dicynodont coprolites from the Upper Triassic of Poland. Palaeogeography, Palaeoclimatology, Palaeoecology, 411, pp.1-17
Dzik, Jerzy; Sulej, Tomasz; Niedźwiedzki, Grzegorz (2008). "A Dicynodont-Theropod Association in the Latest Triassic of Poland". Acta Palaeontologica Polonica. 53 (4): 733–738
Fiorelli, L.E., Ezcurra, M.D., Hechenleitner, E.M., Argañaraz, E., Taborda, J.R., Trotteyn, M.J., Von Baczko, M.B. and Desojo, J.B., 2013. The oldest known communal latrines provide evidence of gregarism in Triassic megaherbivores. Scientific reports, 3, p.3348
Kowal-Linka, M., Krzemińska, E. and Czupyt, Z., 2019. The youngest detrital zircons from the Upper Triassic Lipie Śląskie (Lisowice) continental deposits (Poland): Implications for the maximum depositional age of the Lisowice bone-bearing horizon. Palaeogeography, palaeoclimatology, palaeoecology, 514, pp.487-501
NIEDŹWIEDZKI, G., GORZELAK, P. and Sulej, T., 2011. Bite traces on dicynodont bones and the early evolution of large terrestrial predators. Lethaia, 44(1), pp.87-92
Romano, Marco; Manucci, Fabio (14 June 2019). "Resizing Lisowicia bojani: volumetric body mass estimate and 3D reconstruction of the giant Late Triassic dicynodont". Historical Biology. 0: 1–6
Qvarnström, Martin; Ahlberg, Per E.; Niedźwiedzki, Grzegorz (2019). "Tyrannosaurid-like osteophagy by a Triassic archosaur". Scientific Reports. 9
Sulej, T., Bronowicz, R., Tałanda, M. and Niedźwiedzki, G., 2010. A new dicynodont–archosaur assemblage from the Late Triassic (Carnian) of Poland. Earth and Environmental Science Transactions of the Royal Society of Edinburgh, 101(3-4), pp.261-269
Sulej, T. and Niedźwiedzki, G., 2019. An elephant-sized Late Triassic synapsid with erect limbs. Science, 363(6422), pp.78-80
Świło, M., Niedźwiedzki, G. and Sulej, T., 2013. Mammal-like tooth from the Upper Triassic of Poland. Acta Palaeontologica Polonica, 59(4), pp.815-821
#Lisowicia#Dicynodont#Triassic March Madness#Palaeoblr#Synapsid#Lisowicia bojani#Triassic Madness#Prehistory#Paleontology#Prehistoric life#Mammal-like reptile#Stem mammal
218 notes
·
View notes