#polycotylidae
Explore tagged Tumblr posts
Text

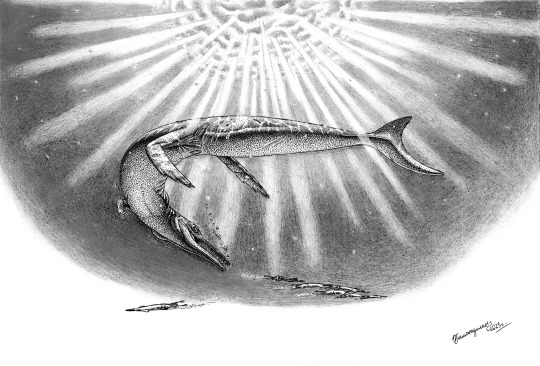
While the most iconic types of plesiosaur were long-necked with small heads and short blunt snouts, some of these marine reptiles actually developed the opposite sort of arrangement, with groups like the polycotylids and the pliosaurs independently evolving short necks, larger heads, and long snouts.
…Except some of them didn't keep it quite that simple.
Serpentisuchops pfisterae here lived during the late Cretaceous, about 70 million years ago, in the ancient Western Interior Seaway covering what is now Wyoming, USA. This 7m long (~23') plesiosaur was a member of the polycotylid lineage, but along with a long slender snout it also had an unusually long neck.
Some earlier polycotylids like Thililua had fairly long necks, too, but all of Serpentisuchops' closest relatives were short-necked species, so it seems to have actually re-evolved this condition rather than inheriting it from its ancestors. Since no other marine reptiles in its habitat had this particular body plan, it was probably occupying a very specific ecological niche – the presence of attachment points for powerful neck muscles suggest it was able to swing its head sideways to snap its jaws at prey at high speed, with its longer neck giving it more reach than other polycotylids.
———
NixIllustration.com | Tumblr | Twitter | Patreon
#science illustration#paleontology#paleoart#palaeoblr#serpentisuchops#polycotylidae#plesiosauria#plesiosaur#sauropterygia#pantestudines#marine reptile#art#long snout? or long neck?#both both is good
423 notes
·
View notes
Text
In the spring of last year, I made several color reconstructions of marine reptiles for a thesis and presentation (it was about the reconstruction of marine reptiles) for a conference that was held in Ulyanovsk in September. The drawings were done in ballpoint pen (lineart) and Paint Tool Sai 2.0 (shadows and colors).

The first is reconstruction of Mixosaurus cornalianus, a widespread small Triassic ichthyosaur. I had already drawn a Mixosaurus in water earlier and even wanted to use it in the article, but later changed my mind, deciding that lateral reconstruction would better convey the appearance of soft tissues. This earlier drawing can bee seen here:

Both pieces are based on the fin impressions described in 2020 from a specimen found in the Middle Triassic rocks of the Bezano formation, Italy (www.researchgate.net/publicati…). This specimen has preserved the tissues of the dorsal and caudal fins. Both prints have thin collagen filaments, and at the base of the caudal fin, it was possible to detect the remains of smooth, scaleless skin. The fins have a triangular shape, and the dorsal one is associated with 15-23 trunk vertebrae. In other words, its position turned out to be more
forward then in reconstructions done before his paper.

The second is lateral reconstruction of the metriorhynchid Cricosaurus albersdoerferi, belonging to a widespread genus that inhabited the shallow seas of future Europe, Central America and Argentina. It was not a particularly large animal, reaching from 2 to 3.2 meters in length. Like the first reconstruction of a Cricosaurus, which I performed in the spring, this drawing is based on a specimen that preserved a large volume of soft tissue on the tail (upload.wikimedia.org/wikipedia…). Also shown here is the salt gland in the antorbital fenestra, the presence of which was previously indicated in Cricosaurus araucanensis and Dakosaurus andiniensis. The spring work with C. albersdoerferi can be seen below:

Plesiosaurs are mentioned too. This is reconstruction of the polycotylid Mauriciosaurus fernandezi from the Late Cretaceous of Mexico. A complete reptile skeleton preserved in fine-grained rocks was described by a team of paleontologists in 2017: www.researchgate.net/publicati… There are five types of soft tissue imprints around the bones. Among them are dark material, probably left from the walls of the peritoneum, dark gray traces of blubber and impressions of possible small scales. The impressions show that the animal's belly was covered with rectangular scales, which were mixed with inclusions of small fragments closer to the limbs. The scales of the living reptile were almost indistinguishable, so that the skin looked smooth. This beautifully preserved specimen showed that plesiosaurs had much more soft tissue than previously thought. The tail was especially fleshy. Fat deposits created a smooth, streamlined shape, ideal for an agile swimmer.

The last thesis drawing is this reconstruction of the famous Early Jurassic ichthyosaur Stenopterygius quadriscissus. Many of its skeletons of amazing preservation were found in the fine-grained limestones of Holzmaden, Germany. Some of them were discovered back in the 19th century, which made it possible to quickly correct previous ideas about ichthyosaurs. The Stenopterygius specimens retained soft tissue prints in the form of a bacterial film, which made it clear that they were fish-like creatures with a dorsal fin and a crescent tail. They re still attract the attention of researchers. In 2018, the skin structure of one partial specimen was studied: www.researchgate.net/publicati… A fossilized blubber was described, similar in microstructure to that of marine mammals and leatherback turtles. This led to the conclusion that ichthyosaurs were reptiles with a high metabolism, which required fat insulation. Blubber allowed ichthyosaurs to travel across the oceans, swimming even into the cold polar waters. In addition, this Stenopterygius had pigment cells - melanophores. They were absent on the ventral side, which means that the Stenopterygius had a dark back and a light belly. This countershading coloring is typical of today's marine vertebrates and serves as a camouflage.
I did also three works in fully traditional style, with pens and pencils, but I'll show them in the separate post. :)
#mixosaurus#stenopterygius#ichthyosaurs#cricosaurus#metriorhynchidae#mauriciosaurus#polycotylidae#plesiosaur#mesozoic marine reptiles#paleoart
31 notes
·
View notes
Text

Unktaheela Specta breaching from the Western Interior Seaway on a sunny afternoon
#unktaheela specta#paleoart#dolichorhynchia#polycotylidae#plesiosauria#sauropterygia#reptilia#chordata#animalia#eukaryota
4 notes
·
View notes
Text
Serpentisuchops pfisterae, a polycotylid plesiosaur from late Cretaceous Wyoming.

With Hatsune Miku for scale:

14 notes
·
View notes
Photo

Mauriciosaurus fernandezi, a polycotylid plesiosaur from the Late Cretaceous of Mexico (~94-89 mya). About 1.9m long (6′3″) with a flipper-span of 1.5m (4′11″), it’s known from a near-complete skeleton with preserved soft tissue impressions. The fossil shows evidence of rows of very tiny scales, the skin outlines of the flippers, and also a thick layer of insulating blubbery fat.
Its body shape in life would have been similar to modern leatherback turtles, roughly teardrop-shaped and hydrodynamic -- much chubbier than most plesiosaur reconstructions had been previously depicting!
#science illustration#paleontology#paleoart#palaeoblr#mauriciosaurus#plesiosaur#polycotylidae#sauropterygia#marine reptiles#pantestudines#stem-turtle#blubber#art#soft tissue preservation#blubbery plesiosaurs confirmed#we need to go fatter#chub-blubs
360 notes
·
View notes
Link
Mauriciosaurus, a plesiosaur with extensive soft tissue preservation – revealing that these marine reptiles had a thick layer of insulating fat in life.
#paleontology#palaeoblr#plesiosaur#marine reptiles#mauriciosaurus#polycotylidae#sauropterygia#blubbery plesiosaurs confirmed#chub-blubs#i'm so happy
99 notes
·
View notes
Text
For no particular reason, I’ve decided that this animal is the cryptid inhabiting Lake Superior. Just cause it would be fun. Snapping at lake trout and sturgeon, chilling at the cold bottom of the lake.

While the most iconic types of plesiosaur were long-necked with small heads and short blunt snouts, some of these marine reptiles actually developed the opposite sort of arrangement, with groups like the polycotylids and the pliosaurs independently evolving short necks, larger heads, and long snouts.
…Except some of them didn't keep it quite that simple.
Serpentisuchops pfisterae here lived during the late Cretaceous, about 70 million years ago, in the ancient Western Interior Seaway covering what is now Wyoming, USA. This 7m long (~23') plesiosaur was a member of the polycotylid lineage, but along with a long slender snout it also had an unusually long neck.
Some earlier polycotylids like Thililua had fairly long necks, too, but all of Serpentisuchops' closest relatives were short-necked species, so it seems to have actually re-evolved this condition rather than inheriting it from its ancestors. Since no other marine reptiles in its habitat had this particular body plan, it was probably occupying a very specific ecological niche – the presence of attachment points for powerful neck muscles suggest it was able to swing its head sideways to snap its jaws at prey at high speed, with its longer neck giving it more reach than other polycotylids.
———
NixIllustration.com | Tumblr | Twitter | Patreon
#science illustration#paleontology#paleoart#palaeoblr#serpentisuchops#polycotylidae#plesiosauria#plesiosaur#cryptid#great lakes
423 notes
·
View notes