#pneumatic actuator Working Principle
Explore tagged Tumblr posts
Text
Pneumatic Cylinder: Types and Prices Guide
Pneumatic cylinders are the most important components used in industrial automation as they are used for linear motion in many modern applications. The machines are based on devices that extract mechanical force with compressed air, with pistons producing motion. Businesses can understand the different types of pneumatic cylinder they can buy and what their prices are. We at VS Enterprises offer a large number of pneumatic cylinders including double acting pneumatic cylinders and compact pneumatic cylinders that meet all the strict performance and quality standards.
In this guide, we will tell you what a pneumatic cylinder is, types of pneumatic cylinders and different pneumatic cylinder parts as well as give you a price overview to be able to make an informed decision.
What is a Pneumatic Cylinder?
So what is a pneumatic cylinder then? It is a mechanical device powered by compressed air, which provides linear or rotational motion. These cylinders are used very widely in industries where linear force is required to move objects, operate machines and perform automated tasks. There are many different types of pneumatic cylinders that can be configured for many different environments, load capacities and space requirements.
Pneumatic Cylinder Types

1. Single Acting Pneumatic Cylinder: These cylinders have a small volume of compressed air per wall space, and have a port to provide air to compress the piston in only one direction. An air centrifuge uses a built-in spring to return the piston to its original position once the air is exhausted. This type is excellent for situations involving simple unidirectional motion when carrying low loads.
2. Double Acting Pneumatic Cylinder: Because its two port design is suitable for allowing two-way motion, double acting pneumatic cylinders are widely used in a variety of industrial applications. One port admits compressed air and the other port draws compressed air to extend the piston and draws compressed air to retract the piston. The benefits of this design are more precise control, and it is perfect for applications that require constant motion in one direction or the other — for example conveyor belts or production lines.
3. Compact Pneumatic Cylinder: As per their name, these cylinders mean that they are small in size and fit in small spaces. Since they are very compact, they are good for use in applications where space is limited. Since they are somewhat inefficient but take up minimal installation space, they have become a major part of machinery that requires little installation space but requires efficient movement.
4. Rotary Pneumatic Cylinder: Unlike rotary cylinders, other pneumatic cylinder types produce linear motion. However, these types work best with parts that must be rotated or rotated, such as indexing tables and robotic arms.
5. Heavy-Duty Pneumatic Cylinder: Industrial cylinders have robust structure, making them reliable for high pressure and high temperature use in competitive mining, construction and heavy manufacturing applications. These are available in a wide range of sizes and can withstand extreme conditions.
6. Custom Pneumatic Cylinders: At VS Enterprise, we offer customized pneumatic cylinders that can be specialized for a particular application. Our options for different pneumatic cylinder parts include bore size, stroke length, and material, so our customers will find the solution they need for their specific needs.
Key Pneumatic Cylinder Parts
If you have never purchased a pneumatic cylinder before, you need to know what is included in the price of a pneumatic cylinder and what it amounts to overall. The following components are usually found in these devices:
Cylinder barrel: The part of the main body where the piston moves. The durability and price of a cylinder depends on what kind of material is being used, such as steel or aluminum.
Piston rod: This rod carries the motion down to the attached component and expands to connect with the piston. A major factor in price is the longevity provided by high-strength materials.
End caps: These plug the housing ports at the end of the cylinder for air ingress and egress.
Seals: High-quality seals prevent air from escaping and ensure efficiency. For high-temperature operation, high-temperature seals may be required.
Cushions: They increase cylinder life by reducing the impact on the piston when the piston reaches the end of its stroke.
When choosing a pneumatic cylinder model, you must understand the basic role of each part — performance, durability, or price of the pneumatic cylinder.
Pneumatic Cylinder Price Overview
The pneumatic cylinder goes at different prices based on the kind, dimension and the level of customization. Here’s a rough estimate to guide you:
Single Acting Cylinders: These are generally less expensive due to their single-port design, costing between 1000 to 3000, depending on size and material.
Double Acting Pneumatic Cylinder: Prices for these models can range from 3500 to 7000. Larger, heavy-duty models designed for intense applications may cost more due to the added durability and strength.
Compact Cylinders: Compact models, owing to their specialized design, typically range from 1000 to 15000. The price depends on stroke length and bore size, which are determined by space and load needs.
Rotary Cylinders: Rotary cylinders are slightly more complex and often come at a premium. Prices range from 1000 to 5000 depending on the required torque and rotational angle.
Heavy-Duty Cylinders: Designed for durability, heavy-duty models are priced higher, usually starting 15000 to 25000 and going upwards depending on customization needs, pressure ratings, and temperature resilience.
Custom Cylinders: Custom options at VS Enterprise can be tailored to meet specific needs, including size, stroke length, material, and additional features. Pricing varies based on specifications, but the added cost results in a more tailored and durable solution.
[Note :- The prices listed for our pneumatic cylinders are approximate, and may vary depending on specific configurations, customization options, and market fluctuations. All estimates, prices, and discussions about your specific needs should be sought from our sales team at VS Enterprise. That’s why we’re here to help you find the best solution for your needs!]
Why Choose VS Enterprise for Pneumatic Cylinders?
As a leading dealer of mercury pneumatic solutions from Noida, we ensure we provide the best quality pneumatic solutions that are ideal for various industrial needs. Here’s what sets us apart:
Wide Range of Types: We offer double acting pneumatic cylinders, custom heavy duty models, and virtually anything in between.
Customizable Options: Depending on your application needs, we can customize our cylinders to any bore size, stroke length, and material.
Strict Quality Assurance: We put each product through the ringer to ensure they perform and last.
Competitive Pricing: However, with us you can get a good punch out of pneumatic cylinders while paying competitive price points that are definitely good value for your business.
Conclusion
Determining the right pneumatic cylinder for any industrial enterprise is crucial. Knowing the different types, pricing, and various components of pneumatic cylinders will aid in your choice for your application. No matter what your needs are, from compact designs to heavy duty models with customization options, when it comes to cylinders at VS Enterprise, we have you covered. To learn more about reliable, high-performance pneumatic solutions at competitive prices, start a conversation with VS Enterprise.
Reach out to Us!
Determining the right pneumatic cylinder for any industrial enterprise is crucial. Knowing the different types, pricing, and various components of pneumatic cylinders will aid in your choice for your application. No matter what your needs are, from compact designs to heavy duty models with customization options, when it comes to cylinders at VS Enterprise, we have you covered. To learn more about reliable, high-performance pneumatic solutions at competitive prices, start a conversation with VS Enterprise.
#pneumatic actuator valve#pneumatic actuator#pneumatic actuator Diagram#pneumatic actuator Working Principle#What is pneumatic actuator#pneumatic actuator Example
0 notes
Text
Control valve supplier in Dubai

UAE Valves is one of the top Control Valve Supplier in Dubai. A control valve is a mechanical device used in various industrial processes to regulate the flow of fluids, such as gas, steam, or liquid, through a pipeline or duct. It achieves this regulation by adjusting the size of the flow passage according to signals received from a controller.
Control valves are crucial components in systems requiring precise control of flow rate, pressure, temperature, or liquid level. They are widely used in industries such as oil and gas, chemical processing, power generation, and water treatment.
Working Principle:
The working principle of a control valve is straightforward. In an industrial setting, a control valve adjusts the size of an opening to control the flow of fluid through a pipeline. When the valve is fully open, it allows maximum flow, and when fully closed, it stops the flow completely. Between these extremes, the valve can be precisely adjusted to allow a specific amount of fluid to pass through.
This adjustment is typically performed automatically based on signals from a controller, which monitors conditions such as pressure, temperature, or flow rate. Essentially, a control valve acts like a gatekeeper, regulating the flow of fluid to meet the system's requirements.
Parts of a Control Valve:
Valve Body: The main structure that contains the fluid and through which the fluid flows.
Actuator: A device that moves or controls the valve's mechanism, often powered by air, electricity, or hydraulic fluid.
Closure Element: The component that makes contact with the seat to restrict or allow flow.
Trim: Internal components such as the plug, seat, and stem that modulate the flow.
Seat: A surface against which the closure element seals to stop flow.
Positioner: A device that adjusts the valve actuator's position based on control signals.
Bonnet: The top part of the valve body that houses the stem and provides a seal.
Yoke: A support structure that holds the actuator in place and connects it to the valve body.
Stem: A rod that connects the actuator to the closure element and transmits motion.
Packing: Material that provides a seal around the stem to prevent fluid leakage.
Advantages:
Precisely controls the amount of fluid passing through a system.
Maintains the desired pressure levels within the system.
Helps maintain a stable temperature by regulating fluid flow.
Reduces energy consumption by optimizing fluid flow.
Enhances system performance by maintaining consistent operating conditions.
Prevents system overpressure and potential hazards.
Easily adjustable for various operating conditions.
Allows for control from a distance and integration into automated systems.
Designed for durability and ease of maintenance.
Ensures consistent production quality by maintaining optimal conditions.
Meets industry standards and regulatory requirements.
Industries Using Control Valves:
Control valves are used across numerous industries, including nuclear power, oil and gas, power generation, manufacturing and process industries, automotive, aerospace, mining and minerals processing, water treatment and distribution, pulp and paper, refining, marine, renewable energy, chemical and petrochemical, and steel and metal processing. These valves play a critical role in ensuring operational efficiency, safety, and compliance within these diverse sectors.
Types of Control Valves:
Three-way control valve
Cage type control valve
Double seat control valve
O type shutoff control valve
Single seat control valve
Water control valve
Globe control valve
Angle type control valve
We are a Control Valve Supplier in Dubai, supplying valves in the following descriptions:
Available Materials: Stainless Steel (SS316, SS304), Ductile Iron, Super Duplex (F51, F53, F55), Cast Iron (WCB, WCC, WC6), LCC, LCB
Class: 150 to 2500
Nominal Pressure: PN10 to PN450
Medium: Air, Water, Chemical, Steam, Oil
Operations: Electro Pneumatic Operated and Pneumatic Operated
Size: 1/2” – 24”
Ends: Butt Weld, Flanged, Threaded, Socket Weld
Electric Actuator Details:
Torque: 3 – 9 nm
Operating Pressure: 8 Bar
Port Connection: NPT 1.4”
Mounting Base: ISO 5211
Temperature: -20°C to +80°C
Configuration of a Pneumatic Actuator:
Torque: 3 – 9000 nm
Operating Pressure: 8 Bar
Port Connection: NPT 1.4”
Mounting Base: ISO 5211
Temperature: -20°C to +80°C
Temperature Ranges:
Standard: -4°F to 200°F (-20°C to 93°C)
Low: -40°F to 176°F (-40°C to 80°C)
High: 0°F to 300°F (-18°C to 149°C)
Visit us: https://www.uaevalves.com/product-category/control-valve/
3 notes
·
View notes
Text
Control Valve Manufacturer in USA
SVR Global is the most popular Control valve manufacturer in USA. A Control valve is a valve that is used in process control to regulate the flow, pressure, or temperature of a fluid such as gas, steam, or liquid. The actuator responds to a signal from the controller by shifting the valve position to maintain the desired process variable.
Control valves are used when there is a need to maintain process parameters at desirable levels. This set of valve controller points can be flow rate, pressure, and temperature. They also provide support to the seat surface, valve closing elements, fluid static pressure, and seat.
The working principle of a control valve is very simple. A control valve in an industrial setting works by adjusting the size of an opening to control the flow of fluid through a pipeline. When the valve is fully open, the passage allows maximum flow, and when it's fully closed, it stops the flow completely. In between, it can be set so that just a known quantity of fluid will pass through. In most cases, it is automatically controlled by signals from an associated controller, such as a pressure, temperature, or flow rate sensor.
As a Control Valve Manufacturer in USA, we offer these types of valves:
· Pneumatic Control Valve
· Pneumatic Angle Control Valve
· 3 Way pneumatic Diaphragm Control Valve
· 3 Way Converging and Diverging Control Valve
· Fluorine Lined Single Seat Control Valve
· Pneumatic Cage Control Valve
· Electric Actuated Control Valve
· Electric 3 Way Control Valve
· Electric Cage Type Control Valve
· Electric Double Seat Control Valve
Industries
· Oil & Gas Industry
· Pipeline Industry
· Marine Industry
· Power Industry
· Nuclear Industry
· Mining Industry
· Chemical Industry
· Petrochemical Industry
Applications:
Chemical Processing: Control valves in chemical processing plants control fluid and gas flow in chemical processing.
Oil and Gas Production: Control valves have become a ubiquitous part of the oil and gas production and process lines in their use for regulating the flow of fluids, gases, and other process variables within production.
Power Generation: It is used in power generation plants for the control of the steam and other fluids involved in the production of electricity.
Water Treatment: Control valves are used in water treatment plants to regulate the flow of chemicals and other substances used in the treatment process.
Advantages:
Control Accuracy: Control valves guarantee accurate control of the fluid flow or gas, or other process variable in a processing system so that such a system would function at optimum levels.
Energy efficiency: The fluids and gases will be controlled through control valves, so their flow will be reduced with the utilization of energy. This will reduce running costs and improve efficiency.
Safety: Applying control valves in regulating hazardous fluids or gases flow may make them safe and minimize the risk of accidents.
Low Maintenance: Control valves can be designed to serve for extended periods without failure, minimizing downtime and maintenance cost.
Flexibility: Control valves can be designed to serve the specific needs of a process, hence they can be very useful for a broad range of applications.
Description:
Available Materials: Ductile Iron Control Valve, Cast iron Control Valve(WCB, WCC, WC6) LCC, LCB, Stainless Steel (SS316, SS304), Super Duplex (F51, F53, F55)
Class: 150 to 2500
Nominal Pressure: PN10 to PN450
Medium: Air, Water, Chemical, Steam, Oil
Operations: Electric actuated and Pneumatic actuated
Size: 1/2”- 24”
Ends: Flanged, butt weld, socket weld, threaded
Electric actuator details:
· Torque – 3 – 9 nm
· Operating pressure- 8 Bar
· Port Connection- NPT1.4”
· Mounting Base-ISO5211
· Temperature--20°C - +80°C
Configuration of a Pneumatic Actuator:
· 4-20 amp
· Pneumatic single acting actuators
· Pneumatic double acting actuators
· Pneumatic rotary actuators
· Pneumatic Scotch and Yoke actuators
· Pressure: 228 bar
Temperature:
· Standard -4°F to 200°F (-20°C to 93°C)
· Low -40°F to 176°F (-40°C to 80°C)
· High 0°F to 300°F (-18°C to 149°C)
Visit our site for more information- https://www.svrglobal.net/product-category/control-valve/
Location : 80, Broad Street,Manhattan, New York – 10004

1 note
·
View note
Text
Design and Functionality of Pressure Reducing and Desuperheating Stations
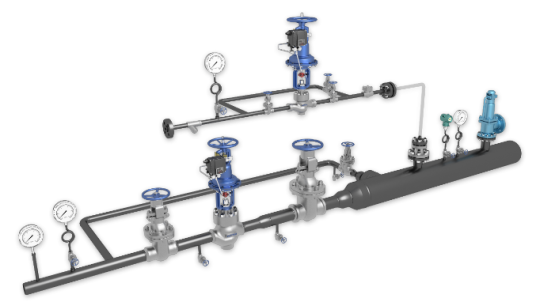
Superheating stations play a crucial role in processes that include the use of superheated steam. These heat exchangers help regulate the temperature and the phase of the steam through the injection of a specific quantity of cooling water into the stream.
Superheated steam, having high temperature and pressure, can be potentially hazardous for the downstream equipment, designed for saturated or slightly superheated steam. They are used in power generation, chemical processing, and other industries where maintaining a consistent temperature of the system is crucial for the quality of the end product and efficiency of the process.
A PRDS working principle represents a highly technical balance between many aspects, from safety and regulatory ones to purely technical and economical ones. Indeed, a PRDS is very important in applications where the steam has to be conditioned for use—specifically, to reduce its pressure and temperature to satisfy process requirements. This blog explains the necessary critical considerations in designing such a system.
Flow Requirements
The design of the system must be based on maximum and minimum flow rates of steam to be handled. Peak flow rates need to be ascertained that can ensure stable conditions in the PRDS even when the conditions vary concerning loads.
The number of the flow range that a system can handle without losing its efficiency or control is known as the turndown ratio. Proper design with adequate turndowns ensures smooth operation over a wide range of flow conditions.
What is required here is accounting for the variability of process demand so that the system can be designed as responsive to changes in immediate downstream pressure and temperature requirements.
Pressure and Temperature Ratings
Functionality of Pressure Reducing station should be done in such a manner so as to handle the peak upstream pressure with downstream pressure at the desired level. The pressure ratings of the valves, pipes and fittings shall be chosen in such a way so as to meet the operating conditions of the system.
This desuperheating section shall be capable of cooling steam down to rated levels. Materials and parts that will be at the different levels of temperature are rated for those same temperatures so thermal stresses don't damage the system. Since safety is optimized by maintaining the design pressure a little higher than that required at normal operating pressure, plus 10 to 20%, this buffer space takes up any unforeseen surge.
Material Selection
Materials such as stainless steel are selected due to their resistance properties, mainly when steam has various contaminants or condensate that could corrode the system. Materials chosen offer resistance against extremely high temperatures and pressure conditions without deformation and degradation with time. Some of these examples include some alloys applied in the high-temperature usage of chromium-molybdenum steel.
Desuperheating stations' valves erode due to high-velocity steam. Hard-facing alloys or materials, such as tungsten carbide, can be applied for extending valve life and minimizing maintenance.
Control Systems Design
The system has to use modulating control valves to regulate steam pressure according to the variations in process demand. Such valves are pneumatically or electrically operated. The minimum requirement for desuperheating is the precise injection of certain quantities of water to cool down the steam. Thus, such control systems have to be fitted with temperature sensors and actuators to monitor and regulate the flow of spray water so that the appropriate amount is mixed with the steam.
Advanced control systems employ PID (Proportional-Integral-Derivative) controllers to fine-tune the process of steam conditioning in such a way that energy use is reduced but efficiency is gained.
Safety Features
Pressure relief valves are an essential part of avoiding overpressure conditions. They open and allow steam to vent when pressures become so high that they exceed the safe limits, thereby avoiding damage to downstream equipment.
Automatic Shutdown Systems allow for the isolation of the PRDS in the event of failure, such as from main leak or malfunctioning equipment, in a way to prevent further damage and ensure safety. Safety interlocks can be fitted to prevent water injection when the temperature falls below a critical value and thus effectively avoid water hammer and/or condensate formation that can harm piping and equipment.
Regulatory Compliance
Safety is important in Pressure reducing design consideration. Most of the places require designs of PRDS to abide by the ASME requirement of the American Society of Mechanical Engineers on the pressure vessels and piping systems.
Most steam and pressure system codes vary from one country to another. You are therefore advised to reach out to the concerned office and find out their requirements in terms of the system and whether it meets those requirements. There must be adherence to the emission standards, particularly condensate release and steam venting, to ascertain control over environmental effects or avert litigation.
Energy Efficiency
Today, the most important goal is energy saving and reduction of energy usage and its impact on the environment. Energy conservation measures, when adopted in industries, provide numerous advantages, such as cutting down costs, enhanced productivity, and environmental sustainability.
Energy efficiency measures range from improving industrial practices to using clean energy; they enhance sustainable practices, lower the emission of greenhouse gases and create a basis for a sustainable world. Energy efficiency is not just an economic opportunity but rather a moral obligation and a responsibility that lies in the hands of every individual towards our planet and future generations.
Integration with Steam Systems
Desuperheating stations are designed to blend with steam systems and offer control of the superheat temperature as well as improve efficiency. By controlling the temperature of superheated steam, such special systems provide safeguards for the critical parts from thermal stress to guarantee the operation reliability and safety.
There are specific points in the steam cycle where desuperheating stations can be located to effectively control the enthalpy of steam and increase the efficiency of the system. With the integration of desuperheating technology and steam systems, the efficiency of the energy used, the durability of the equipment, and the control of the process improve, making it a crucial part of modern industrial applications that require high-temperature steam.
Conclusion
In the constantly changing industrial processes, pressure reducing and desuperheating stations appear as essential tools to address heat and temperature issues. This in turn means that industries need to tap the best of the manufacturers and the state-of-the-art technologies to get the best out of these systems. Desuperheating stations are instrumental in protecting equipment, enhancing procedures, and minimizing harm to the environment, which creates a solid foundation for progress and profitability.
By understanding the importance of energy saving and environmental protection in industries, the addition of desuperheating stations is not only the need for innovation, competition, and development of industries but also a responsibility to provide a better future for future generations.
0 notes
Text
Understanding the Role of a Pressure Transducer in Modern Industries
Introduction
A pressure transducer is a critical device used across various industries to measure and convert pressure into an electrical signal. These instruments play a vital role in ensuring system efficiency, safety, and accuracy in applications ranging from automotive to aerospace. This article explores the working principle, types, applications, and advantages of pressure transducers, providing a comprehensive understanding of their significance.
What Is a Pressure Transducer?
A pressure transducer, also known as a pressure sensor, is a device that detects pressure and converts it into an analog or digital electrical signal. The output signal can be used for monitoring, control, or data recording purposes. These devices are essential in environments where precise pressure measurement is crucial for operational success.
How Does a Pressure Transducer Work?
The working principle of a pressure transducer involves several key components:
Sensing Element: Detects the applied pressure (e.g., diaphragm, piezoelectric crystal).
Transduction Mechanism: Converts the mechanical pressure into an electrical signal (e.g., strain gauge, capacitive element).
Signal Conditioning Circuitry: Amplifies and processes the signal for accurate output.
Output Interface: Delivers the signal in a usable format (e.g., 4-20mA, 0-10V, digital protocols like I2C or SPI).
When pressure is applied, the sensing element deforms, causing a change in resistance, capacitance, or voltage, which is then converted into a measurable signal.
Types of Pressure Transducers
Different applications require specific types of pressure transducers, each designed for unique operational conditions.
1. Strain Gauge Pressure Transducers
Uses a strain-sensitive element bonded to a diaphragm.
Pressure causes deformation, altering electrical resistance.
Common in industrial and automotive applications.
2. Capacitive Pressure Transducers
Measures changes in capacitance due to diaphragm movement.
Highly accurate and suitable for low-pressure applications.
3. Piezoelectric Pressure Transducers
Utilizes piezoelectric materials that generate voltage under pressure.
Ideal for dynamic pressure measurements in aerospace and defense.
4. Optical Pressure Transducers
Uses fiber-optic technology to detect pressure-induced changes in light properties.
Immune to electromagnetic interference, making them useful in harsh environments.
Key Applications of Pressure Transducers
Pressure transducers are widely used across multiple industries due to their versatility and reliability.
1. Industrial Automation
Monitors hydraulic and pneumatic systems.
Ensures safe operation of machinery by detecting pressure anomalies.
2. Automotive Industry
Measures fuel, oil, and tire pressure for optimal vehicle performance.
Used in engine management and braking systems.
3. Medical Equipment
Critical in ventilators, blood pressure monitors, and dialysis machines.
Ensures patient safety by providing accurate pressure readings.
4. Aerospace & Defense
Monitors cabin pressure, fuel systems, and hydraulic actuators.
Essential for flight safety and performance optimization.
5. Oil & Gas Industry
Used in drilling, pipeline monitoring, and refinery processes.
Detects pressure changes to prevent leaks and equipment failure.
Advantages of Using Pressure Transducers
The adoption of pressure transducers offers numerous benefits, including:
High Accuracy: Provides precise measurements for critical applications.
Durability: Designed to withstand harsh environments (e.g., extreme temperatures, corrosive media).
Versatility: Available in various types to suit different industrial needs.
Real-Time Monitoring: Enables immediate detection of pressure fluctuations.
Compact Design: Fits into tight spaces without compromising performance.
Choosing the Right Pressure Transducer
Selecting the appropriate pressure transducer depends on several factors:
Pressure Range: Ensure the device covers the required measurement range.
Output Signal: Match the output (analog, digital) with the system requirements.
Environmental Conditions: Consider temperature, humidity, and exposure to chemicals.
Accuracy & Resolution: Higher precision is needed for critical applications.
Installation Requirements: Check compatibility with mounting and connection setups.
Maintenance and Calibration
To ensure long-term reliability, pressure transducers require regular maintenance:
Periodic Calibration: Ensures measurement accuracy over time.
Cleaning & Inspection: Prevents contamination and mechanical wear.
Signal Verification: Confirms the output remains consistent with expected values.
Future Trends in Pressure Transducer Technology
Advancements in sensor technology continue to enhance pressure transducer capabilities:
Miniaturization: Smaller, more efficient designs for portable and IoT applications.
Wireless Connectivity: Enables remote monitoring and data logging.
Smart Sensors: Integration with AI for predictive maintenance and diagnostics.
Improved Materials: Enhanced durability for extreme environments.
Conclusion
The pressure transducer is an indispensable tool in modern industries, providing accurate and reliable pressure measurements for diverse applications. Understanding its working principles, types, and selection criteria ensures optimal performance in any operational environment. As technology evolves, these devices will continue to play a pivotal role in automation, safety, and efficiency across multiple sectors.
By leveraging the right pressure transducer, industries can achieve greater precision, reduce downtime, and enhance overall system performance. Whether in manufacturing, healthcare, or aerospace, these sensors remain a cornerstone of pressure measurement technology.

1 note
·
View note
Text
Pilot Operated & Wafer Type NRV Valves – Udhhyog
💧 Industrial Flow Control with Pilot Operated and Wafer Type NRV Valves – Powered by Udhhyog
In the world of industrial piping and fluid systems, the demand for reliable, efficient, and compact valve solutions continues to rise. Whether it’s for controlling flow direction, managing pressure, or preventing backflow, non return valves (NRVs) are essential. Among these, two of the most in-demand designs are the pilot operated non return valve and the wafer type NRV valve.
At Udhhyog, we specialize in delivering advanced flow control solutions to industries across India. With a strong presence in Delhi, Punjab, Gujarat, Rajasthan, Jammu & Kashmir, Himachal Pradesh, Uttar Pradesh, and other key industrial states, our goal is to provide high-performance valves backed by engineering excellence and customer support.
In this article, we’ll explore both the pilot operated non return valve and the wafer type NRV valve, understand their working principles, advantages, applications, and how Udhhyog delivers the best in class products across sectors.
🔍 What is a Non Return Valve (NRV)?
A non return valve, also known as a check valve, allows fluid to flow in only one direction. Its primary role is to prevent reverse flow, which could otherwise damage pumps, contaminate clean lines, or disrupt system operation.
Unlike gate or globe valves, NRVs are automatic. They require no manual actuation or power supply, making them ideal for energy-efficient flow control.
🧠 Understanding the Pilot Operated Non Return Valve
The pilot operated non return valve is a smart evolution in NRV technology. Unlike conventional NRVs that depend purely on flow pressure to open or close, this type of valve includes a pilot mechanism—a control device that senses upstream or downstream conditions to trigger the valve operation.
✅ Key Features of Pilot Operated NRVs:
Precise Control: Opens only when system conditions meet specific pressure criteria.
No Slamming: Prevents sudden shut-off, reducing water hammer and shock.
Failsafe Mechanism: Designed to lock or unlock under set pilot pressures.
Remote Actuation: Some models allow manual or pneumatic overrides.
🔧 Applications:
High-pressure pumping stations
Water distribution networks
Oil and gas flow lines
Fire suppression systems
Marine and offshore platforms
These valves are especially valuable where flow reversal could damage critical equipment, or where automated safety control is required.
🧩 Wafer Type NRV Valve – Compact, Reliable, and Efficient
The wafer type NRV valve is one of the most space-efficient non return valves. It is designed to be sandwiched between two flanges in a piping system.
Instead of using a large body and bonnet like conventional valves, wafer NRVs consist of a flat disc or dual plates that open and close based on flow pressure.
✅ Benefits of Wafer Type NRV Valves:
Space Saving: Ideal for compact setups or where installation space is limited.
Lightweight Design: Reduces pipeline load and shipping cost.
Quick Installation: No need for special fittings—fits between existing flanges.
Low Pressure Drop: Disc design allows smooth, streamlined flow.
🔧 Typical Use Cases:
HVAC systems
Chemical dosing lines
Irrigation and agriculture
Cooling towers
Food and pharma processing units
At Udhhyog, our wafer type NRV valves are available in cast iron, stainless steel, bronze, and PTFE-lined variants to suit a wide range of fluids.
⚙️ Comparing Pilot Operated vs Wafer Type NRVs
FeaturePilot Operated NRVWafer Type NRVOperationControlled via pilot pressureAutomatic, spring/disk operatedInstallation SpaceRequires more spaceCompact and flange-mountedResponse TimeSlower but preciseFast closureApplicationsHigh-pressure, critical systemsStandard fluid flow systemsCostHigher due to control systemAffordable and widely used
🏭 Why Industries Prefer Udhhyog Valves
At Udhhyog, we are dedicated to delivering premium valve solutions to industries across India. Here’s why we’re the preferred partner for NRV systems:
✅ Wide Product Range:
Swing NRV
Lift NRV
Pilot operated non return valve
Wafer type NRV valve
Dual plate check valves
Foot valves and strainers
✅ Material Options:
Cast Iron (CI)
Ductile Iron (DI)
Carbon Steel (WCB)
Stainless Steel (SS 304, SS 316)
Bronze and Gunmetal
✅ Regional Expertise:
We are trusted suppliers in Delhi, Punjab, Gujarat, Rajasthan, Jammu & Kashmir, Himachal Pradesh, Uttar Pradesh, and NCR regions—ensuring rapid dispatch and strong service support.
✅ Services Offered:
Bulk order support
OEM manufacturing
Technical consultation
On-site valve sizing and selection
Credit facility for loyal buyers
Explore our complete catalog: 👉 https://udhhyog.com/valves
🧰 Installation Tips for Long Valve Life
Whether you’re using a wafer type NRV valve or a pilot operated valve, correct installation is key to performance and safety.
Always verify the flow direction arrow during installation.
Use correct gaskets and flange standards.
Make sure the pipeline is free from debris before installation.
Do not overtighten bolts—use torque values recommended by the manufacturer.
For pilot operated valves, test the pilot control line for leaks or blockages.
At Udhhyog, we offer free technical support to clients for pre-installation and commissioning.
🌍 Where Are These Valves Used?
Here’s where our NRV valves deliver unmatched performance:
🚰 Water treatment plants
🏭 Chemical & petrochemical industries
🚢 Marine systems and shipyards
🛢️ Refineries and oil storage terminals
🧪 Pharma and clean water systems
🌾 Agricultural irrigation networks
🔥 Fire hydrant and suppression systems
Wherever there is flow, there is the need to control and protect—and that’s where Udhhyog comes in.
💡 How to Select the Right NRV Valve?
Choosing between pilot operated non return valve and wafer type NRV valve depends on:
✔ System pressure and flow conditions
✔ Space constraints
✔ Fluid type (corrosive, clean, viscous)
✔ Requirement of automation or pilot control
✔ Budget and maintenance access
Our engineering team at Udhhyog helps clients identify the best fit by analyzing data sheets, pressure ratings, and real-time flow demands.
📦 Udhhyog Valve Solutions – Fast, Reliable, Affordable
From custom valve sourcing to bulk supply for EPC projects, we are equipped to support industrial demands at scale.
🔹 Available Sizes: 15mm to 600mm 🔹 Pressure Classes: PN10, PN16, PN25, ANSI 150# 🔹 Certifications: ISI, ISO, IBR-compliant products 🔹 MOQ: As per customer need 🔹 Delivery Time: 2–5 working days (based on location)
🔚 Conclusion
If you're setting up a critical pumping system or optimizing a process line, the pilot operated non return valve offers unmatched control and protection. On the other hand, the wafer type NRV valve gives you compact, cost-effective backflow prevention.
At Udhhyog, we bring you both—crafted to perfection, tested for performance, and delivered with service you can trust.
📞 Get in touch today to order, get specifications, or schedule a consultation. Let’s power your industrial pipelines with the best in flow control engineering.
#PilotOperatedNRV#WaferTypeNRVValve#NonReturnValve#CheckValvesIndia#FlowControlValves#UdhhyogValves#DelhiValveSupplier#IndustrialValvesIndia#BackflowPrevention#EngineeringSolutions
0 notes
Text
Pilot Operated & Wafer Type NRV Valves – Udhhyog
💧 Industrial Flow Control with Pilot Operated and Wafer Type NRV Valves – Powered by Udhhyog
In the world of industrial piping and fluid systems, the demand for reliable, efficient, and compact valve solutions continues to rise. Whether it’s for controlling flow direction, managing pressure, or preventing backflow, non return valves (NRVs) are essential. Among these, two of the most in-demand designs are the pilot operated non return valve and the wafer type NRV valve.
At Udhhyog, we specialize in delivering advanced flow control solutions to industries across India. With a strong presence in Delhi, Punjab, Gujarat, Rajasthan, Jammu & Kashmir, Himachal Pradesh, Uttar Pradesh, and other key industrial states, our goal is to provide high-performance valves backed by engineering excellence and customer support.
In this article, we’ll explore both the pilot operated non return valve and the wafer type NRV valve, understand their working principles, advantages, applications, and how Udhhyog delivers the best in class products across sectors.
🔍 What is a Non Return Valve (NRV)?
A non return valve, also known as a check valve, allows fluid to flow in only one direction. Its primary role is to prevent reverse flow, which could otherwise damage pumps, contaminate clean lines, or disrupt system operation.
Unlike gate or globe valves, NRVs are automatic. They require no manual actuation or power supply, making them ideal for energy-efficient flow control.
🧠 Understanding the Pilot Operated Non Return Valve
The pilot operated non return valve is a smart evolution in NRV technology. Unlike conventional NRVs that depend purely on flow pressure to open or close, this type of valve includes a pilot mechanism—a control device that senses upstream or downstream conditions to trigger the valve operation.
✅ Key Features of Pilot Operated NRVs:
Precise Control: Opens only when system conditions meet specific pressure criteria.
No Slamming: Prevents sudden shut-off, reducing water hammer and shock.
Failsafe Mechanism: Designed to lock or unlock under set pilot pressures.
Remote Actuation: Some models allow manual or pneumatic overrides.
🔧 Applications:
High-pressure pumping stations
Water distribution networks
Oil and gas flow lines
Fire suppression systems
Marine and offshore platforms
These valves are especially valuable where flow reversal could damage critical equipment, or where automated safety control is required.
🧩 Wafer Type NRV Valve – Compact, Reliable, and Efficient
The wafer type NRV valve is one of the most space-efficient non return valves. It is designed to be sandwiched between two flanges in a piping system.
Instead of using a large body and bonnet like conventional valves, wafer NRVs consist of a flat disc or dual plates that open and close based on flow pressure.
✅ Benefits of Wafer Type NRV Valves:
Space Saving: Ideal for compact setups or where installation space is limited.
Lightweight Design: Reduces pipeline load and shipping cost.
Quick Installation: No need for special fittings—fits between existing flanges.
Low Pressure Drop: Disc design allows smooth, streamlined flow.
🔧 Typical Use Cases:
HVAC systems
Chemical dosing lines
Irrigation and agriculture
Cooling towers
Food and pharma processing units
At Udhhyog, our wafer type NRV valves are available in cast iron, stainless steel, bronze, and PTFE-lined variants to suit a wide range of fluids.
⚙️ Comparing Pilot Operated vs Wafer Type NRVs
FeaturePilot Operated NRVWafer Type NRVOperationControlled via pilot pressureAutomatic, spring/disk operatedInstallation SpaceRequires more spaceCompact and flange-mountedResponse TimeSlower but preciseFast closureApplicationsHigh-pressure, critical systemsStandard fluid flow systemsCostHigher due to control systemAffordable and widely used
🏭 Why Industries Prefer Udhhyog Valves
At Udhhyog, we are dedicated to delivering premium valve solutions to industries across India. Here’s why we’re the preferred partner for NRV systems:
✅ Wide Product Range:
Swing NRV
Lift NRV
Pilot operated non return valve
Wafer type NRV valve
Dual plate check valves
Foot valves and strainers
✅ Material Options:
Cast Iron (CI)
Ductile Iron (DI)
Carbon Steel (WCB)
Stainless Steel (SS 304, SS 316)
Bronze and Gunmetal
✅ Regional Expertise:
We are trusted suppliers in Delhi, Punjab, Gujarat, Rajasthan, Jammu & Kashmir, Himachal Pradesh, Uttar Pradesh, and NCR regions—ensuring rapid dispatch and strong service support.
✅ Services Offered:
Bulk order support
OEM manufacturing
Technical consultation
On-site valve sizing and selection
Credit facility for loyal buyers
Explore our complete catalog: 👉 https://udhhyog.com/valves
🧰 Installation Tips for Long Valve Life
Whether you’re using a wafer type NRV valve or a pilot operated valve, correct installation is key to performance and safety.
Always verify the flow direction arrow during installation.
Use correct gaskets and flange standards.
Make sure the pipeline is free from debris before installation.
Do not overtighten bolts—use torque values recommended by the manufacturer.
For pilot operated valves, test the pilot control line for leaks or blockages.
At Udhhyog, we offer free technical support to clients for pre-installation and commissioning.
🌍 Where Are These Valves Used?
Here’s where our NRV valves deliver unmatched performance:
🚰 Water treatment plants
🏭 Chemical & petrochemical industries
🚢 Marine systems and shipyards
🛢️ Refineries and oil storage terminals
🧪 Pharma and clean water systems
🌾 Agricultural irrigation networks
🔥 Fire hydrant and suppression systems
Wherever there is flow, there is the need to control and protect—and that’s where Udhhyog comes in.
💡 How to Select the Right NRV Valve?
Choosing between pilot operated non return valve and wafer type NRV valve depends on:
✔ System pressure and flow conditions
✔ Space constraints
✔ Fluid type (corrosive, clean, viscous)
✔ Requirement of automation or pilot control
✔ Budget and maintenance access
Our engineering team at Udhhyog helps clients identify the best fit by analyzing data sheets, pressure ratings, and real-time flow demands.
📦 Udhhyog Valve Solutions – Fast, Reliable, Affordable
From custom valve sourcing to bulk supply for EPC projects, we are equipped to support industrial demands at scale.
🔹 Available Sizes: 15mm to 600mm 🔹 Pressure Classes: PN10, PN16, PN25, ANSI 150# 🔹 Certifications: ISI, ISO, IBR-compliant products 🔹 MOQ: As per customer need 🔹 Delivery Time: 2–5 working days (based on location)
🔚 Conclusion
If you're setting up a critical pumping system or optimizing a process line, the pilot operated non return valve offers unmatched control and protection. On the other hand, the wafer type NRV valve gives you compact, cost-effective backflow prevention.
At Udhhyog, we bring you both—crafted to perfection, tested for performance, and delivered with service you can trust.
📞 Get in touch today to order, get specifications, or schedule a consultation. Let’s power your industrial pipelines with the best in flow control engineering.
#PilotOperatedNRV#WaferTypeNRVValve#NonReturnValve#CheckValvesIndia#FlowControlValves#UdhhyogValves#DelhiValveSupplier#IndustrialValvesIndia#BackflowPrevention#EngineeringSolutions
0 notes
Text
Pilot Operated & Wafer Type NRV Valves – Udhhyog
💧 Industrial Flow Control with Pilot Operated and Wafer Type NRV Valves – Powered by Udhhyog
In the world of industrial piping and fluid systems, the demand for reliable, efficient, and compact valve solutions continues to rise. Whether it’s for controlling flow direction, managing pressure, or preventing backflow, non return valves (NRVs) are essential. Among these, two of the most in-demand designs are the pilot operated non return valve and the wafer type NRV valve.
At Udhhyog, we specialize in delivering advanced flow control solutions to industries across India. With a strong presence in Delhi, Punjab, Gujarat, Rajasthan, Jammu & Kashmir, Himachal Pradesh, Uttar Pradesh, and other key industrial states, our goal is to provide high-performance valves backed by engineering excellence and customer support.
In this article, we’ll explore both the pilot operated non return valve and the wafer type NRV valve, understand their working principles, advantages, applications, and how Udhhyog delivers the best in class products across sectors.
🔍 What is a Non Return Valve (NRV)?
A non return valve, also known as a check valve, allows fluid to flow in only one direction. Its primary role is to prevent reverse flow, which could otherwise damage pumps, contaminate clean lines, or disrupt system operation.
Unlike gate or globe valves, NRVs are automatic. They require no manual actuation or power supply, making them ideal for energy-efficient flow control.
🧠 Understanding the Pilot Operated Non Return Valve
The pilot operated non return valve is a smart evolution in NRV technology. Unlike conventional NRVs that depend purely on flow pressure to open or close, this type of valve includes a pilot mechanism—a control device that senses upstream or downstream conditions to trigger the valve operation.
✅ Key Features of Pilot Operated NRVs:
Precise Control: Opens only when system conditions meet specific pressure criteria.
No Slamming: Prevents sudden shut-off, reducing water hammer and shock.
Failsafe Mechanism: Designed to lock or unlock under set pilot pressures.
Remote Actuation: Some models allow manual or pneumatic overrides.
🔧 Applications:
High-pressure pumping stations
Water distribution networks
Oil and gas flow lines
Fire suppression systems
Marine and offshore platforms
These valves are especially valuable where flow reversal could damage critical equipment, or where automated safety control is required.
🧩 Wafer Type NRV Valve – Compact, Reliable, and Efficient
The wafer type NRV valve is one of the most space-efficient non return valves. It is designed to be sandwiched between two flanges in a piping system.
Instead of using a large body and bonnet like conventional valves, wafer NRVs consist of a flat disc or dual plates that open and close based on flow pressure.
✅ Benefits of Wafer Type NRV Valves:
Space Saving: Ideal for compact setups or where installation space is limited.
Lightweight Design: Reduces pipeline load and shipping cost.
Quick Installation: No need for special fittings—fits between existing flanges.
Low Pressure Drop: Disc design allows smooth, streamlined flow.
🔧 Typical Use Cases:
HVAC systems
Chemical dosing lines
Irrigation and agriculture
Cooling towers
Food and pharma processing units
At Udhhyog, our wafer type NRV valves are available in cast iron, stainless steel, bronze, and PTFE-lined variants to suit a wide range of fluids.
⚙️ Comparing Pilot Operated vs Wafer Type NRVs
FeaturePilot Operated NRVWafer Type NRVOperationControlled via pilot pressureAutomatic, spring/disk operatedInstallation SpaceRequires more spaceCompact and flange-mountedResponse TimeSlower but preciseFast closureApplicationsHigh-pressure, critical systemsStandard fluid flow systemsCostHigher due to control systemAffordable and widely used
🏭 Why Industries Prefer Udhhyog Valves
At Udhhyog, we are dedicated to delivering premium valve solutions to industries across India. Here’s why we’re the preferred partner for NRV systems:
✅ Wide Product Range:
Swing NRV
Lift NRV
Pilot operated non return valve
Wafer type NRV valve
Dual plate check valves
Foot valves and strainers
✅ Material Options:
Cast Iron (CI)
Ductile Iron (DI)
Carbon Steel (WCB)
Stainless Steel (SS 304, SS 316)
Bronze and Gunmetal
✅ Regional Expertise:
We are trusted suppliers in Delhi, Punjab, Gujarat, Rajasthan, Jammu & Kashmir, Himachal Pradesh, Uttar Pradesh, and NCR regions—ensuring rapid dispatch and strong service support.
✅ Services Offered:
Bulk order support
OEM manufacturing
Technical consultation
On-site valve sizing and selection
Credit facility for loyal buyers
Explore our complete catalog: 👉 https://udhhyog.com/valves
🧰 Installation Tips for Long Valve Life
Whether you’re using a wafer type NRV valve or a pilot operated valve, correct installation is key to performance and safety.
Always verify the flow direction arrow during installation.
Use correct gaskets and flange standards.
Make sure the pipeline is free from debris before installation.
Do not overtighten bolts—use torque values recommended by the manufacturer.
For pilot operated valves, test the pilot control line for leaks or blockages.
At Udhhyog, we offer free technical support to clients for pre-installation and commissioning.
🌍 Where Are These Valves Used?
Here’s where our NRV valves deliver unmatched performance:
🚰 Water treatment plants
🏭 Chemical & petrochemical industries
🚢 Marine systems and shipyards
🛢️ Refineries and oil storage terminals
🧪 Pharma and clean water systems
🌾 Agricultural irrigation networks
🔥 Fire hydrant and suppression systems
Wherever there is flow, there is the need to control and protect—and that’s where Udhhyog comes in.
💡 How to Select the Right NRV Valve?
Choosing between pilot operated non return valve and wafer type NRV valve depends on:
✔ System pressure and flow conditions
✔ Space constraints
✔ Fluid type (corrosive, clean, viscous)
✔ Requirement of automation or pilot control
✔ Budget and maintenance access
Our engineering team at Udhhyog helps clients identify the best fit by analyzing data sheets, pressure ratings, and real-time flow demands.
📦 Udhhyog Valve Solutions – Fast, Reliable, Affordable
From custom valve sourcing to bulk supply for EPC projects, we are equipped to support industrial demands at scale.
🔹 Available Sizes: 15mm to 600mm 🔹 Pressure Classes: PN10, PN16, PN25, ANSI 150# 🔹 Certifications: ISI, ISO, IBR-compliant products 🔹 MOQ: As per customer need 🔹 Delivery Time: 2–5 working days (based on location)
🔚 Conclusion
If you're setting up a critical pumping system or optimizing a process line, the pilot operated non return valve offers unmatched control and protection. On the other hand, the wafer type NRV valve gives you compact, cost-effective backflow prevention.
At Udhhyog, we bring you both—crafted to perfection, tested for performance, and delivered with service you can trust.
📞 Get in touch today to order, get specifications, or schedule a consultation. Let’s power your industrial pipelines with the best in flow control engineering.
#PilotOperatedNRV#WaferTypeNRVValve#NonReturnValve#CheckValvesIndia#FlowControlValves#UdhhyogValves#DelhiValveSupplier#IndustrialValvesIndia#BackflowPrevention#EngineeringSolutions
0 notes
Text
Understanding the Working Principle of Butterfly Valves
Introduction
When it comes to controlling the flow of fluids in pipelines, butterfly valves are one of the most efficient and widely used solutions. These valves offer a compact, lightweight design with quick and easy operation, making them suitable for various industries, including water treatment, oil & gas, pharmaceuticals, and food processing.
As a trusted butterfly valve manufacturer in Ahmedabad, Marck & Care Engineers Ltd specializes in designing high-quality butterfly valves that meet global industry standards. In this blog, we will explore the working principle of butterfly valves, their key components, types, advantages, and applications.

What is a Butterfly Valve?
A butterfly valve is a quarter-turn rotational valve used to start, stop, or regulate fluid flow. It gets its name from the disc inside the valve, which resembles a butterfly when rotated. When the disc is turned parallel to the flow, the valve is fully open, allowing unrestricted movement of fluids. When turned perpendicular, it blocks the flow, closing the pipeline.
These valves are widely used due to their cost-effectiveness, energy efficiency, and durability. Compared to other valve types like gate or ball valves, butterfly valves offer a lower pressure drop and require minimal space for installation.
Key Components of a Butterfly Valve
A butterfly valve consists of several essential components that ensure its efficient functioning:
Body – The outer casing that houses all internal components and provides structural integrity.
Disc – The rotating component responsible for regulating fluid flow.
Stem (Shaft) – The rod that connects the disc to the actuator or handle, enabling movement.
Seat – The sealing component that prevents leaks when the valve is in the closed position.
Actuator or Handle – The mechanism used to operate the valve, which can be manual, pneumatic, hydraulic, or electric.
Each of these components plays a crucial role in ensuring smooth and efficient fluid control in industrial applications.
Working Principle of Butterfly Valves
The working mechanism of a butterfly valve is simple yet highly effective. It operates on a quarter-turn rotational movement:
Closed Position: When the disc is perpendicular to the flow direction, it completely blocks the passage, stopping the fluid.
Open Position: A 90-degree turn of the actuator moves the disc parallel to the flow, allowing the liquid or gas to pass freely.
Partially Open Position: The valve can also be adjusted to a partially open position, regulating the flow as required.
Butterfly valves can be operated manually using a lever or automatically with actuators, which can be pneumatic, hydraulic, or electric. Automated valves are commonly used in large industrial plants where remote control is required.
Types of Butterfly Valves
Butterfly valves come in different types, depending on their design, sealing method, and application. The most common types include:
1. Concentric Butterfly Valve
The disc is positioned in the center, and the stem passes through the middle.
Used for low to medium-pressure applications.
Commonly found in water distribution and HVAC systems.
2. Double Offset Butterfly Valve
The stem is slightly offset from the center, reducing wear and tear.
Provides a better seal and is used in high-pressure applications.
Suitable for oil refineries, chemical plants, and steam systems.
3. Triple Offset Butterfly Valve
The disc and seat have a metal-to-metal contact, making it highly durable.
Designed for extreme conditions, such as high temperatures and high-pressure environments.
Used in power plants, shipbuilding, and the petrochemical industry.
Each type of butterfly valve is designed to cater to specific operational needs, ensuring maximum efficiency and reliability.
Advantages of Butterfly Valves
Butterfly valves are widely preferred over other valve types due to their numerous benefits, including:
Compact & Lightweight: Requires less space and is easier to install.
Cost-Effective: More affordable than gate or ball valves.
Quick Operation: A simple 90-degree turn opens or closes the valve instantly.
Low Maintenance: Minimal moving parts reduce wear and tear.
Energy-Efficient: Causes minimal pressure drop, ensuring smooth fluid flow.
High Durability: Available in different materials for corrosion and temperature resistance.
These advantages make butterfly valves the ideal choice for industries where fluid flow regulation is critical.
Applications of Butterfly Valves
Butterfly valves are used in a wide range of industries, including:
Water Supply & Wastewater Treatment: Managing water flow in treatment plants and municipal supply lines.
Oil & Gas Industry: Controlling the flow of crude oil, natural gas, and refined products.
Food & Beverage Industry: Maintaining hygienic and precise control over liquid products.
Pharmaceutical Industry: Ensuring precise dosing and fluid movement in medicine production.
Chemical & Petrochemical Industry: Handling corrosive and high-pressure chemicals safely.
HVAC Systems: Regulating air and water flow in heating and cooling systems.
Due to their versatility, butterfly valves play a critical role in ensuring efficiency, safety, and cost-effectiveness across different sectors.
Why Choose Marck & Care Engineers Ltd?
When selecting a butterfly valve manufacturer in Ahmedabad, choosing a reliable and experienced supplier is crucial. Marck & Care Engineers Ltd is a trusted name in the industry, known for producing high-quality, durable, and efficient butterfly valves.
What Sets Us Apart?
✔ ISO-Certified Manufacturing – Ensuring top-notch quality and safety standards. ✔ Advanced Engineering – Using cutting-edge technology for precision manufacturing. ✔ Wide Range of Valves – From concentric to triple offset butterfly valves. ✔ Customization Options – Tailored solutions for specific industrial applications. ✔ Global Clientele – Trusted by industries across India and beyond.
At Marck & Care Engineers Ltd, we focus on delivering superior valve solutions that enhance operational efficiency and safety.
Conclusion
Butterfly valves are essential components in various industries due to their compact design, efficiency, and cost-effectiveness. Their simple working principle and versatile applications make them a preferred choice for fluid control.
As a leading butterfly valve manufacturer in Ahmedabad, Marck & Care Engineers Ltd provides high-performance butterfly valves designed for long-lasting durability and optimal flow regulation. If you’re looking for reliable butterfly valves for your industrial needs, get in touch with us today!
0 notes
Text
Understanding Pneumatic Actuators: Working Principles, Types, And Key Components Explained
Pneumatic actuators are essential components in modern industrial automation and machinery. They convert compressed air energy into mechanical motion, enabling precise control of valves, grippers, and other mechanical systems. Widely used in manufacturing, robotics, and process industries, pneumatic actuators are valued for their reliability, simplicity, and cost-effectiveness. This article explores their working principles, common types, and key components.
1. Working Principles Of Pneumatic Actuators
Pneumatic actuators operate on the fundamental principle of pressure differential. When compressed air is introduced into the actuator, it creates a force that moves internal components, generating linear or rotary motion. Here’s a step-by-step breakdown:
Air Supply: Compressed air (typically 4–7 bar or 60–100 psi) is supplied from a pneumatic system or compressor.
Pressure Application: Air enters the actuator’s chamber, exerting pressure on a piston, diaphragm, or vane.
Motion Generation: The pressure differential across the piston/diaphragm creates linear or rotational movement.
Return Mechanism: In single-acting actuators, a spring returns the piston to its original position when air pressure is released. Double-acting actuators use compressed air to move in both directions.
Key advantages include rapid response times, high force-to-size ratios, and suitability for hazardous environments (no sparks or overheating).
2. Types Of Pneumatic Actuators
Pneumatic actuators are categorized based on their motion type and design:
A. Linear Actuators
Single-Acting: Compressed air moves the piston in one direction; a spring returns it. Ideal for simple on/off applications (e.g., clamping).
Double-Acting: Air pressure moves the piston in both directions, enabling precise bidirectional control. Common in industrial valves and automation.
B. Rotary Actuators
Rack-and-Pinion: A piston with a rack gear rotates a pinion gear, producing rotary motion. Used for quarter-turn valve control (e.g., ball valves).
Vane-Type: Compressed air pushes vanes in a circular chamber, generating torque. Suitable for continuous rotation applications.
Scotch Yoke: Converts linear piston motion into rotary motion via a slotted yoke mechanism. Offers high torque for heavy-duty valves.
C. Specialty Actuators
Diaphragm Actuators: Use a flexible diaphragm instead of a piston. Common in pressure control valves.
Rodless Actuators: Eliminate the piston rod, allowing for compact designs in confined spaces.
3. Key Components Of Pneumatic Actuators
Understanding the internal structure of pneumatic actuators is crucial for maintenance and selection:
Cylinder Body: Houses the piston and contains compressed air. Made of aluminum, stainless steel, or engineered plastics.
Piston: Converts air pressure into linear motion. Sealed with O-rings to prevent air leakage.
Piston Rod: Transmits motion to external mechanisms. Often chrome-plated for durability.
End Caps: Seal the cylinder and include ports for air inlet/outlet.
Seals and Gaskets: Ensure airtight operation. Common materials include nitrile rubber (NBR) or polytetrafluoroethylene (PTFE).
Spring (Single-Acting): Provides return force in single-acting designs.
Position Sensors (Optional): Detect piston position for feedback in automated systems.
4. Applications And Industry Use Cases
Pneumatic actuators are ubiquitous in industries requiring fast, reliable motion control:
Manufacturing: Operating conveyor belts, assembly line grippers.
Oil and Gas: Controlling pipeline valves in explosive environments.
Food and Beverage: Hygienic actuators for packaging and filling systems.
Automotive: Robotic welding and painting systems.
Conclusion
Pneumatic actuators remain a cornerstone of industrial automation due to their simplicity, safety, and adaptability. By leveraging compressed air, they provide efficient motion control for diverse applications. Engineers and technicians must consider factors like load requirements, operating environment, and cycle rates when selecting the right actuator type. As industries evolve, innovations in materials and smart pneumatics (e.g., IoT-enabled actuators) are enhancing their performance and integration with modern control systems.
This article provides a comprehensive overview of pneumatic actuators while maintaining readability for both technical and non-technical audiences.
If you want to learn more about low-priced products, please visit the following website: www.xm-valveactuator.com
0 notes
Text
Pneumatic Ball Valve: Working Principle and Guidelines
What is Pneumatic Ball Valve

How Does a Pneumatic Actuated Ball Valve Work
A Pneumatic Ball Valve operates through compressed air driving its actuator. Here’s a step-by-step breakdown:
1. Actuator Activation: Compressed air enters the actuator’s cylinder, forcing the piston to move forward or backward.
2. Mechanical Transfer: The piston’s motion is transmitted via a piston rod to the valve stem, which rotates the ball (valve core).
3. Ball Rotation: The ball, with a bore through its center, rotates 90 degrees. When aligned with the pipeline, fluid flows freely; when perpendicular, flow is blocked.
4. Control Integration: Solenoid valves or positioners regulate airflow to ensure precise control of the valve’s open/close positions.
Key Components of Pneumatic Ball Valves:
- Valve Body: Constructed from stainless steel, carbon steel, or alloy steel, it houses the ball and seats while connecting to pipelines.
- Ball: A spherical component (stainless steel, brass, etc.) with a bore that controls flow.
- Valve Seat: Made of PTFE or corrosion-resistant materials, it ensures leak-proof sealing.
- Pneumatic Actuator: Converts air pressure into rotary motion (single-acting or double-acting).
- Manual Override: Allows manual operation during power failures.
- Stem & Seals: Transmit motion and prevent leaks under high pressure/temperature.

Types of Pneumatic Ball Valves
Pneumatic ball valves are categorized by material and design:
- By Material: Stainless steel, carbon steel, plastic, and hygienic-grade valves.
- By Ports: 2-way, 3-way, or 4-way configurations for diverse flow control needs.
Advantages of Pneumatic Ball Valves
✅ Rapid Response: Achieves full operation in as little as 0.05 seconds.
✅ Low Fluid Resistance: Minimizes pressure loss with a straight-through design.
✅ Compact & Durable: Fewer parts for easy maintenance and long service life.
✅ Superior Sealing: Metal or soft seals ensure zero leakage.
✅ Versatility: Handles liquids, gases, and steam across extreme temperatures/pressures.
Applications
Pneumatic ball valves are essential in:
- Oil & Gas: Pipeline shutoff and safety systems.
- Chemical Plants: Corrosive fluid control.
- Power Generation: Steam and coolant regulation.
- Pharmaceuticals: Hygienic process automation.
Choosing a Reliable Pneumatic Ball Valve Manufacturer
NSW VALVE Manufacturer stands out as a trusted pneumatic ball valve factory and manufacturer, offering:
- In-house production of valves and actuators.
- High-performance valves with corrosion resistance, rapid response, and leak-proof designs.
- Custom solutions for industries like oil refining, chemicals, and power generation.
Whether you need standard or specialized valves, partnering with an experienced pneumatic ball valve manufacturer like NSW VALVE Manufacturer ensures quality, reliability, and technical support for your fluid control systems.
0 notes
Text
Direct-Acting vs Pilot-Operated Valves Key Differences
There are two types of pneumatic valves which are pilot and direct-acting valves used in hydraulic and pneumatic systems. Direct-acting valves are only used for low-flow applications as they are operated through mechanical force which makes them faster. On the other hand, pilot-operated valves use system pressure which helps them in valve movement to handle higher pressures and flow rates easily. As pilot-operated valves are energy-efficient and
better for high-load applications, direct-acting valves are suitable for quick responses. The selection depends on system requirements pressure and flow capacity.
Understanding Direct-Acting and Pilot-Operated Valves
What is a Direct Acting Valve?
A direct-acting valve is one that can differentiate itself from others because it operates without any additional pressure assistance. When the solenoid is activated, the valve is either opened or closed. This operating principle makes direct-acting valves exceptional in low-pressure systems. These types of valves are ideal for use in fast reacting situations such as emergency shut-offs and accurate fluid control.
Advantages of Direct-Acting Valves
Immediate response: Because no additional pressure is required, direct-acting valves respond quickly.
Reliable in low-pressure systems: They work efficiently even when system pressure is low.
Simple design:They contain fewer moving components which translates into a much lower maintenance requirement.
Versatile applications::Majorly employed in medical gadgets, food production, and laboratory tools.
What is a Pilot-Operated Valve?
A Pilot-Operated Valve systematically uses system pressure to open and close like a throttle. It employs a low capacity pilot valve to actuate a high capacity main valve to make it efficient in managing large flow quantities at high pressures. This design makes it appropriate for high-pressure systems due to reduced energy expenditure, while maintaining flow control.
Advantages of Pilot-Operated Valves
Energy-efficient operation: Suitable for industrial slow and heavy machines.
Handles high flow rates: Consumes less energy because it uses existing pressure.
Increased durability: Made with certain modifications to withstand repeated use fatigue.
Cost-effective for high-pressure applications: Optimal for HVAC, water treatment systems, and hydraulic circuits.
Key Differences Between Direct-Acting and Pilot-Operated Valves
Feature
Operation
Response Time
PressureRequirement
Application
Durability
Energy Efficiency
Direct-Acting Valve
Works without outside pressure
Faster
Works at low pressures
Small systems, emergency shutoffs
Less moving parts, less maintenance
Higher power consumption
Pilot-Operated Valve
Operates via system pressure assistance
We have a little delay because of the pilot mechanism
Need some pressure to work
High-flow, high-pressure systems
Complex, requires regular maintenance
Lower power consumption due
Importance of Choosing the Right Valve
The control valve is the regulating element in the system that controls the flow of air or gas. It guarantees that the critical parameters for manufacturing and industrial process is pressure and consistency in flow is maintained. Quality materials and good quality construction for durability is essential as the control valve works on the principle of a diaphragm, so the most well constructed diaphragm of the control valve is a key consideration for the effectiveness in changing flow.
The Role of a Pneumatic Control Valve
Regular maintenance must be done on valves to avoid getting clogged with debris which gives a lower quality efficiency.
Proper Valve Size: The pressure drop that occurs can be reduced by utilizing a valve with the proper size.
High quality components are durable and provide better overall performance this is the reason Quality Materials is important.
Enhancing System Efficiency with a Control Air Pressure Regulator
Guide to Utilizing Control Air Pressure Regulator For Enhancing System Efficiency .Well regulation permits the pressure of air to be ideal, enhancing the life and efficiency of the system and at the same time preserving energy. If the pressure regulators regulating the control air are maintained, it provides a potential 25% energy saving, indicating monitoring and calibration of control air also have a serious influence.
Benefits of Using a Control Air Pressure Regulator
Prevents overpressure damage: Shields delicate devices from severe harm.
Ensures consistent operation: Consistently move air for optimal performance.
Reduces energy costs:Air is consumed optimally which in turn lowers running costs.
Increases component lifespan: Lower risk of components burning out ahead of schedule.
Choosing the Right Solenoid Valve: Types and Benefits
In order to have optimum performance make sure, when selecting a solenoid valve, the following must be considered:
Response Time: Fast-acting solenoid valves can improve a system performance significantly.
Material Compatibility: Doing so will avoid corrosion and premature wear by ensuring compatibility with the system fluids.
Operational Pressure Range: acceptable pressures relative to avoid high-performance problems. OPR can avoid such issues.
The use of a high-quality solenoid valve reduces the maintenance effort and enhances system reliability that results in increased operational productivity.
Common Types of Solenoid Valves
Two-Way Solenoid Valves- Used for basic on off fluid control.
Three-Way Solenoid Valves- 3-way Solenoid Valve.
Four-Way Solenoid Valves- Used in complex hydraulic and pneumatic systems.
Proportional Solenoid Valves- provides variable flow control
Importance of Professional Solenoid Maintenance
With proper care, solenoid can extend the valve life and prevent costly system failure. The regular cleaning and inspection remove dirty deposits and debris and thus ensures smooth work. Well-maintained systems can run up to 50% longer than neglected systems.
Key Maintenance Tips for Solenoid Valves
Periodic Cleaning- Avoids agglomerating deposits on the valve or solenoid which cause a shut off or a solenoid failure..
Check for Wear and Tear- Inspect Seals and Diaphragms for any damage or cracking as they can become dried out and dissolved.
Monitor Electrical Connections- A loss of power can result in the valve chattering open and closed.
Lubricate- Avoids friction and prolongs Usage Life of the valve or solenoid.
Case Study: Efficiency Gains with Proper Valve Selection
A manufacturing plant recently decided to replace pilot operated valves to direct acting valves in the emergency shut off system. This resulted in:
30% decrease in response time leading to enhanced safety measures
Energy consumption is minimal, saving around 15% of costs.
Increased reliability reduces spontaneous failures and outages.
Similarly,One food process plant upgrad its control valve system with high precision control air pressure regulators. The results included:
A 20% reduction of wasted compressed air.
Stable pressure leads to more reliable product.
Prolonged lifetime of equipment that translates also on savings on maintenance costs.
Conclusion: Optimize Your System with the Right Valves
So proper selection of the valve whether direct acting . pilot operated valves has a significant effect on the system performance and life span. This means you will have better control of the pressure, which, when used with qualified solenoid repair. will help ensure maximum system efficiency.
Does your pneumatic powered system need optimizing? Consult an expert to guide you in selecting the most appropriate air pressure handle for your application. You have about 11 months from October 2023 to start. in order to optimize performance, lower costs, and provide sustainable reliability in the future.
#Direct Acting#pneumatic valves types#types of pneumatic valves#pneumatic valves#mercury pneumatics dealers in delhi#mercury pneumatics dealers#what is pneumatic valves#mercury pneumatic dealers in delhi#pneumatic dealers#pneumatic fittings suppliers in delhi
0 notes
Text
High-Pressure Valves in Oil and Gas: Ensuring Safety and Efficiency
High-pressure valves play a critical role in the oil and gas industry by regulating, controlling, and isolating the flow of liquids and gases under extreme conditions. These valves are designed to withstand intense pressure and temperature fluctuations, ensuring operational safety, system integrity, and process efficiency. Without high-pressure valves, oil rigs, refineries, and pipeline systems would be at significant risk of leaks, pressure surges, and catastrophic failures.
The selection of the right high-pressure valve is crucial for ensuring durability, compliance with industry standards (such as API and ASME), and seamless integration into complex industrial systems. Let’s explore their working principle, types, materials, challenges, and applications in the oil and gas sector.
Working Principle of High-Pressure Valves
High-pressure valves function by controlling fluid flow through a pressurized system, either by opening, closing, or regulating the passage of oil, gas, or steam. These valves are specifically designed to:
Withstand extreme pressures (up to 10,000+ PSI)
Prevent leaks with precision sealing mechanisms
Regulate flow rate to avoid pressure surges
Operate in high-temperature environments, often exceeding 400°C
The internal components, including valve seats, stems, and seals, are reinforced with high-strength alloys and corrosion-resistant coatings to ensure longevity. Advanced sealing technologies, such as metal-to-metal or polymer seals, further enhance their leak-proof performance.
Types of High-Pressure Valves
Different types of high-pressure valves are used in oil and gas operations, depending on their function and application:
1. Ball Valves
Ball valves use a rotating ball with a bore to control fluid flow. They provide tight sealing, quick operation, and are commonly used in high-pressure Ball Valve gas pipelines and offshore platforms.
2. Gate Valves
Gate valves feature a sliding gate mechanism that moves up and down to control flow. They are ideal for applications requiring full shut-off capability and minimal pressure drop.
3. Globe Valves
Globe valves regulate precise flow control and pressure modulation. Their spherical body design ensures excellent throttling capabilities in refining and processing units.
4. Check Valves
High Pressure Check valves in Oil and Gas Industry allow one-way flow to prevent backflow and potential contamination of pipelines. They are critical in oil transportation and offshore drilling applications.
5. Needle Valves
Needle valves provide fine flow control with a tapered needle-like stem. They are commonly used in high-pressure instrumentation and hydraulic systems.
Material Selection & Design Considerations
Given the harsh conditions of oil and gas extraction, refining, and distribution, high-pressure valves must be constructed using robust materials:
Stainless Steel (316, 304) – Corrosion-resistant, ideal for offshore applications
Alloy Steel (Inconel, Hastelloy) – High-temperature tolerance, excellent mechanical strength
Duplex & Super Duplex Steel – Superior strength and resistance to stress corrosion cracking
Tungsten Carbide Coatings – Enhances wear resistance and extends valve life
Design considerations such as pressure ratings (ANSI Class 1500–4500), end connections (flanged, threaded, or welded), and actuation methods (manual, electric, or pneumatic) also influence valve selection.
Challenges & Solutions in High-Pressure Environments
High-pressure valves in oil and gas Industry operations face several challenges, including:
Corrosion & Erosion – Exposure to saline environments, hydrocarbons, and chemicals leads to material degradation. Solution: Use corrosion-resistant alloys and coatings.
Pressure Surges & Water Hammer – Sudden pressure changes can damage pipelines and equipment. Solution: Install surge relief valves and use gradual valve actuation.
Seal Leakage & Valve Failure – Continuous exposure to high temperatures and pressures can degrade gaskets and seals. Solution: Implement advanced sealing technologies like graphite packing or polymer-based seals.
Applications of High-Pressure Valves in Oil & Gas Industry
High-pressure valves are indispensable in various oil and gas industry applications, including:
Drilling Operations – Controlling mud flow, well pressure, and blowout preventers (BOPs)
Refining & Processing – Regulating crude oil refining, gas separation, and chemical injections
Offshore Platforms – Ensuring seawater injection systems, safety shut-off, and subsea control valves
Pipeline Transportation – Preventing leaks and pressure drops in long-distance oil & gas pipelines
Storage & Distribution – Enhancing tank farm safety and LNG terminal operations
Future Trends & Technological Advancements
The oil and gas industry is evolving with technological innovations, leading to advancements in high-pressure valve design:
Smart Valves & IoT Integration – Remote monitoring, predictive maintenance, and automation for improved efficiency
Zero-Emission Valves – Reducing fugitive emissions to comply with environmental regulations
Advanced Materials – Development of self-lubricating polymers and composite materials for extended valve lifespan
With increasing emphasis on safety, reliability, and efficiency, high-pressure valve manufacturers continue to invest in cutting-edge technology to meet the industry’s growing demands.
Conclusion
High-pressure valves are the backbone of oil and gas operations, ensuring fluid control, system integrity, and operational safety. Their ability to withstand extreme conditions makes them indispensable in drilling, refining, offshore platforms, and pipeline systems.
Selecting the right high-pressure valve requires careful consideration of material compatibility, pressure ratings, sealing mechanisms, and compliance with API and ASME standards. With ongoing innovations like smart valve technology and zero-emission solutions, the future of high-pressure valves in the oil and gas sector is poised for significant advancements.
For businesses in the oil and gas industry, investing in high-quality, API-certified high-pressure valves is key to enhancing safety, efficiency, and long-term reliability.
#Oil and Gas Industry Valves Manufacturers#High pressure Check Vavles#High Pressure Ball Valve#High Pressure Needle Valve#freture techno#india
0 notes
Text
Exploring the Benefits of a Pneumatic Trainer Kit for Hands-On Learning | Niyo India
In today's fast-paced world of engineering and automation, understanding the principles of pneumatics is essential for students, technicians, and engineers. One effective way to gain practical knowledge in this field is through the use of a pneumatic trainer kit. These kits provide hands-on experience with pneumatic systems, allowing learners to explore the components, functions, and applications of pneumatic technologies.
What is a Pneumatic Trainer Kit?
A pneumatic trainer kit is an educational tool designed to teach the fundamentals of pneumatic systems. It typically includes a variety of components such as compressors, valves, cylinders, actuators, and pressure regulators, all arranged to simulate real-world pneumatic applications. These kits are ideal for training environments, where learners can physically interact with the components to better understand how compressed air is used to power machines and control movements in various industries.
Key Components of a Pneumatic Trainer Kit
Compressor: The heart of any pneumatic system, the compressor generates the compressed air that powers the entire system.
Air Valves: These control the direction, pressure, and flow of the air within the system, allowing for the precise operation of various actuators and cylinders.
Cylinders and Actuators: These components use the pressurized air to perform mechanical work, such as linear motion or lifting objects.
Pressure Regulators: These help control the air pressure to ensure that the system operates within safe and efficient limits.
Piping and Connectors: These link the components of the system and help guide the airflow between them.
Sensors and Indicators: Modern kits may also include sensors that allow learners to monitor variables like pressure, flow rate, or temperature in real-time.
Why Should You Use a Pneumatic Trainer Kit?
1. Hands-On Learning
A pneumatic trainer kit allows learners to apply theoretical knowledge in a practical, hands-on way. Instead of just reading about pneumatics or watching demonstrations, students can physically manipulate the components, see the results of their actions, and learn through trial and error.
2. Real-World Applications
Pneumatics plays a critical role in many industries, including manufacturing, automotive, and automation. A pneumatic trainer kit mimics real-world pneumatic systems, giving students insight into how these systems work in industrial environments. Understanding pneumatics is vital for careers in fields like robotics, automotive engineering, and industrial automation.
3. Develop Troubleshooting Skills
With a pneumatic trainer kit, learners can experiment with troubleshooting techniques, such as identifying leaks, diagnosing faulty valves, and adjusting pressures. These skills are highly valuable in professional settings, where the ability to identify and fix problems quickly can save time and money.
4. Versatile Training Tool
Whether you're a student in a vocational program or an engineer looking to brush up on your skills, a pneumatic trainer kit offers flexibility in its use. These kits can be used in classrooms, workshops, and labs, and they are suitable for learners at different levels of experience.
5. Interactive Learning Environment
Many pneumatic trainer kits come with interactive software or instructional manuals that guide learners through different experiments and projects. These tools help reinforce concepts like pressure regulation, air flow, and system design, enhancing the learning experience.
Applications of Pneumatic Systems
Pneumatic systems are used in a wide range of industries, from factory automation to medical devices. Some common applications include:
Robotics: Pneumatic actuators are often used in robots to provide movement for limbs and tools.
Packaging: Pneumatic systems power machines that handle, package, and label products.
Automotive: Pneumatics are used in car manufacturing, particularly in assembly lines for tasks like lifting, moving, and sorting parts.
Medical Equipment: In the medical field, pneumatics help power devices like ventilators, dental drills, and hospital beds.
Conclusion
A pneumatic trainer kit is a powerful tool for anyone looking to gain hands-on experience with pneumatic systems. Whether you're a student wanting to learn the basics, a technician looking to sharpen your skills, or an educator aiming to provide practical learning opportunities, these kits offer a tangible, engaging way to understand the theory and application of pneumatics.By using a pneumatic trainer kit, you’ll gain essential knowledge and skills that will be useful across various industries. From improving troubleshooting abilities to understanding the mechanics of air-powered systems, a pneumatic trainer kit is an invaluable resource for learning and growing in the field of pneumatics.
#pneumatictrainerkit#industry40centerofexcellence#mechatronicstrainingsystem#hydraulictrainerkit#cutsectionmodel
0 notes
Text
What is a multi turn electric actuator?
Multi turn electric actuators are sophisticated devices used to control the movement of valves and other mechanical systems that require rotation through multiple turns. Unlike their single-turn counterparts, which complete a full rotation in one turn, multi-turn actuators are designed to perform several revolutions, making them ideal for applications that involve more complex motion control. This article will explore the components, working principles, applications, advantages, and considerations associated with multi-turn electric actuators.
Components of Multi-Turn Electric Actuators
A typical multi-turn electric actuator consists of several key components:
Electric Motor: The core of the actuator, usually a DC or AC motor, converts electrical energy into mechanical energy. The choice of motor impacts the actuator's torque, speed, and efficiency.
Gearbox: Multi-turn actuators use gear mechanisms to multiply the torque generated by the motor while reducing the speed. The gearbox configuration determines the number of turns the actuator can make for each rotation of the motor.
Control System: This includes electronics that regulate the motor’s operation. It may involve simple on/off controls or advanced systems with feedback loops that adjust the actuator's position based on sensor input.
Output Shaft: This is the component that physically connects to the valve or mechanism being controlled. The output shaft rotates based on the actuator's motion.
Housing: The protective casing that encases the actuator's components, often designed to withstand environmental conditions such as moisture, dust, and temperature fluctuations.
Limit Switches: These are safety features that stop the actuator when it reaches its maximum or minimum position, preventing damage to the system.
Working Principle
The operation of a multi-turn electric actuator begins with the activation of the electric motor. The motor, controlled by an electrical signal, rotates the input shaft. This rotation is transmitted through a series of gears within the gearbox, which amplifies the torque and limits the speed. As the gears turn, they rotate the output shaft multiple times, allowing for precise positioning of the connected valve or device.
The control system plays a critical role in this process. Advanced multi-turn actuators can incorporate feedback mechanisms using position sensors. These sensors send real-time data about the shaft's position back to the control system, allowing for closed-loop control. This ensures that the actuator can make fine adjustments to reach the desired position accurately.
Applications
Multi-turn electric actuators are widely used in various industries due to their versatility and efficiency. Some common applications include:
Valves: They are often used in the oil and gas, water treatment, and chemical processing industries to control gate, globe, and butterfly valves.
Dampers: Multi-turn actuators can control dampers in HVAC systems, allowing for effective air flow regulation.
Robotics: In robotic systems, they provide precise movement for joints and grippers that require multiple turns for operation.
Industrial Automation: They are employed in conveyor systems, packaging machines, and other automated processes where precise control over movement is essential.
Hydraulic and Pneumatic Systems: Multi-turn actuators can control valves in hydraulic and pneumatic systems, ensuring optimal fluid or gas flow.
Advantages
The use of multi-turn electric actuators offers several benefits:
Precision: They provide high accuracy in positioning, crucial for applications where exact movements are necessary.
Energy Efficiency: Electric actuators are generally more energy-efficient compared to hydraulic or pneumatic systems.
Low Maintenance: With fewer moving parts and no need for hydraulic fluid, electric actuators typically require less maintenance.
Safety: Many models come with built-in safety features, such as limit switches, that prevent over-rotation and potential damage.
Versatility: They can be adapted for a wide range of applications, making them suitable for various industries.
Considerations
While multi-turn electric actuators have many advantages, there are some considerations to keep in mind:
Torque Requirements: It is essential to select an actuator that can provide sufficient torque for the application. Overloading can lead to failure.
Environmental Conditions: The actuator should be rated for the operating environment, including temperature extremes and exposure to corrosive substances.
Cost: Multi-turn actuators can be more expensive than simpler actuators, so budget considerations are crucial.
Complexity: The added complexity of these systems may require specialized knowledge for installation and maintenance.
Multi-turn electric actuators are vital components in modern automation and control systems. Their ability to provide precise, reliable movement across multiple turns makes them ideal for a wide array of applications, from industrial processes to robotics. By understanding their components, working principles, and advantages, users can make informed decisions when integrating these actuators into their systems.
0 notes
Text
Pneumatic Linear Actuators- An In-Depth Overview

Pneumatic linear actuators play a pivotal role in automation and control systems across various industries. They convert compressed air into linear motion, offering a reliable and efficient means of driving mechanical systems. In this article, we will explore the design, working principles, applications, advantages, and considerations of pneumatic linear actuators, highlighting their significance in modern engineering.
What is a Pneumatic Linear Actuator?
A pneumatic linear actuator is a device that uses compressed air to produce linear motion. Typically consisting of a cylinder and a piston, these actuators function by the expansion of air within the cylinder, pushing the piston to generate motion. The stroke length, or the distance the piston travels, can be customized based on the specific application requirements.
Working Principle
The operation of a pneumatic linear actuator is relatively straightforward:
Compressed Air Supply: The actuator is connected to a source of compressed air. When the system is activated, air enters the cylinder through an inlet valve.
Piston Movement: As compressed air fills the cylinder, it exerts pressure on the piston. This pressure pushes the piston in a linear direction, converting the energy from the compressed air into mechanical motion.
Exhaust: Once the desired stroke is achieved, the air can be released through an exhaust valve, allowing the piston to return to its original position. This can be controlled manually or automatically, depending on the actuator design.
Key Components
Pneumatic linear actuators consist of several key components:
Cylinder: The main body housing the piston and providing the chamber for air pressure.
Piston: A movable component within the cylinder that converts air pressure into linear motion.
Seals and Gaskets: Ensure that air does not leak out of the cylinder, maintaining pressure for effective operation.
Mounting Hardware: Allows for secure attachment to various machinery or systems.
Valves: Control the flow of compressed air into and out of the actuator, regulating its movement.
Applications
Pneumatic linear actuators are used in a wide range of applications, including:
Manufacturing: In assembly lines, these actuators automate tasks such as lifting, pushing, and moving products or components.
Material Handling: They are used in conveyor systems and robotic arms to transport materials efficiently.
Packaging: Pneumatic actuators control packaging machines, ensuring precise placement and sealing of products.
Automotive: Used in automated manufacturing processes, such as welding and painting, to enhance productivity.
Medical Equipment: In devices like hospital beds and surgical tables, pneumatic actuators provide adjustable height and positioning.
Advantages of Pneumatic Linear Actuators
High Speed: Pneumatic actuators can achieve rapid motion, making them ideal for applications requiring quick actuation.
Simplicity: Their simple design leads to lower maintenance requirements compared to electric or hydraulic actuators.
Cost-Effective: Pneumatic systems generally have a lower initial investment and operating costs, particularly in high-volume applications.
Force and Weight: Pneumatic actuators can produce significant force relative to their size and weight, making them suitable for compact designs.
Safety: Pneumatic systems are often safer than hydraulic systems, as they use air, which poses fewer risks in terms of leaks or spills.
Considerations When Choosing a Pneumatic Linear Actuator
While pneumatic linear actuators offer numerous advantages, there are several considerations to keep in mind when selecting one for your application:
Air Supply: Ensure you have a reliable source of compressed air, as insufficient pressure can lead to poor performance.
Stroke Length: Determine the required stroke length for your application, as this will influence the actuator's design.
Load Capacity: Calculate the force needed for the specific application to choose an actuator that can handle the load.
Environment: Consider the operating environment. Factors such as temperature, humidity, and potential exposure to contaminants can affect performance.
Control System: Choose compatible control systems and valves for the pneumatic actuator to ensure efficient operation.
Conclusion
Pneumatic linear actuators are vital components in many industrial applications, providing efficient and reliable motion control. With their simplicity, speed, and cost-effectiveness, they offer a compelling solution for automating various processes. Understanding their working principles, advantages, and considerations is essential for selecting the right pneumatic actuator for your specific needs. As industries continue to evolve towards automation, pneumatic linear actuators will undoubtedly remain a key player in driving innovation and efficiency.
Address
21225 FM 529 Rd Houston, TX 77433 Cypress Area
Phone: +1-713-934-0171 Fax: +1-713-934-9099 [email protected]
0 notes