#paramount famous studios
Explore tagged Tumblr posts
Text
Superman in The Mummy Strikes (Famous, 1943) dir. I. Sparber
Buy me a coffee!
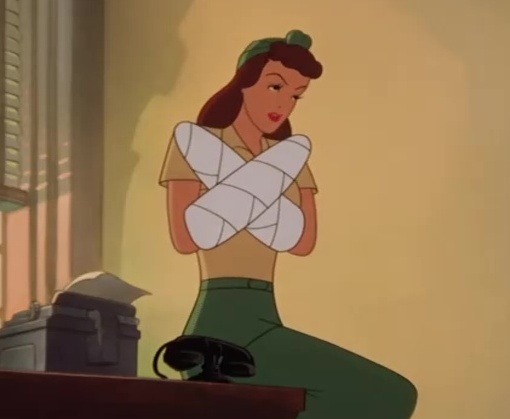




#classic cartoon#golden age animation#1940s#Paramount Famous Studios#Max fleischer#Superman#DC comics#Halloween cartoon
9 notes
·
View notes
Text

Famous Greetings (1950s)
#50s#paramount pictures#famous studios#happy holidays#merry christmas#happy new year#casper the friendly ghost#herman and katnip#baby huey#little audrey#buzzy crow#popeye#olive oyl
25 notes
·
View notes
Text

A Kartune Musical Short
38 notes
·
View notes
Text

Already have the Looney Tunes Golden Collection, Tom and Jerry Spotlight Collection, Walt Disney Treasures, and Woody Woodpecker Classic Cartoon Collection. Now it’s time to add Popeye to my classic animation DVD collection.
#they haven’t released any official sets for the 50s cartoons yet#i’ve seen most of them on old public domain videos as a kid#but it would be nice to see them restored#popeye#popeye the sailor#fleischer studios#famous studios#paramount#golden age of american animation#dvd collections#physical media
10 notes
·
View notes
Text

Went for a more obscure pull this time. It's Baby Hughes Duck, or Baby Huey for short. Most of the old Famous Studios / Harveytoons characters have gone the way of Mighty Mouse or Farmer Al Falfa in faded public consciousness but if a cartoon series' formula works, it works.
#KnoxRobbinsArt#fan art#Baby Huey#Harveytoons#Famous Studios#digital art#classic cartoons#classic animation#baby duck#dunce#1940s#Paramount Pictures#the baby huey show
9 notes
·
View notes
Text


Some storyboards from the 1947 Little Lulu cartoon. A Bout with a Trout. Attributed to Isadore Klein
Directed by Isadore Sparber (animation direction by Myron Waldman) for Famous Studios, Inc.
#animation#cartoons#classic cartoons#new york animation#golden age of animation#production art#storyboards#little lulu#paramount cartoon studios#famous studios#1940's
5 notes
·
View notes
Text
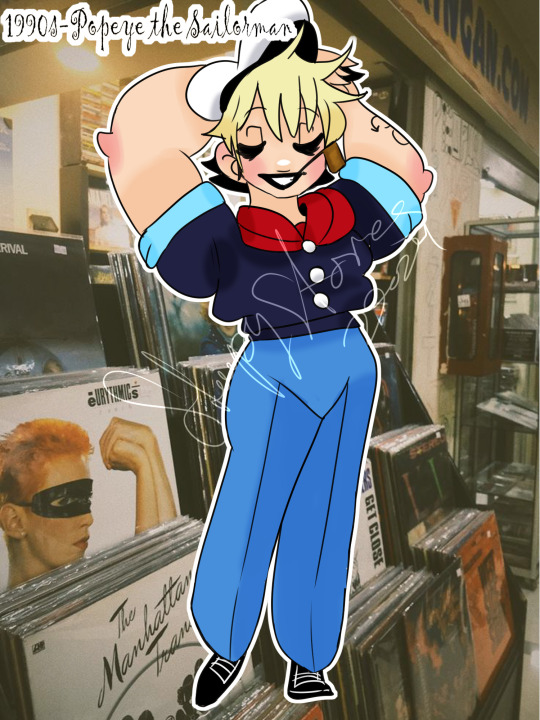

#1990s#art#original#genderbend#humanized#rule 63#youtube#speedpaint#picture day through time#popeye the sailor man#paramount pictures#paramount studios#famous studios
3 notes
·
View notes
Text
Casper #170, “The Littlest Trick-or-Treater”
In honor of Halloween, a fifty-year look back at Casper #170, “The Littlest Trick-or-Treater”
Looking for something Halloween themed while also looking to branch out into fresh genres and publishers, I figured there would be a ton of Halloween stories of Casper the Friendly Ghost out there, right? Continue reading Untitled

View On WordPress
#1970s#1980s#bronze age#Casper 170#casper the friendly ghost#comics#famous studios#ghostly trio#harvey comics#paramount#sid jacobson#unicef#warren kremer#“The Littlest Trick-or-Treater”
3 notes
·
View notes
Text
Star Crossing
On July 20, 1938, Sylvia Sidney sailed aboard the RMS Queen Mary for a month’s vacation in Europe. Upon her return to the States, she would begin filming, …One Third of a Nation…, in Astoria, New York, for Paramount Studios. Source: New York Times

View On WordPress
#astoria studios#cunard white star#famous passengers#one third of a nation#paramount studios#passenger list#RMS Queen Mary#sylvia sidney
0 notes
Text

Audrey Hepburn on her bike with her dog "Famous" at Paramount Studios. Los Angeles, CA. 1957
Photo: Sid Avery
600 notes
·
View notes
Text


Propaganda
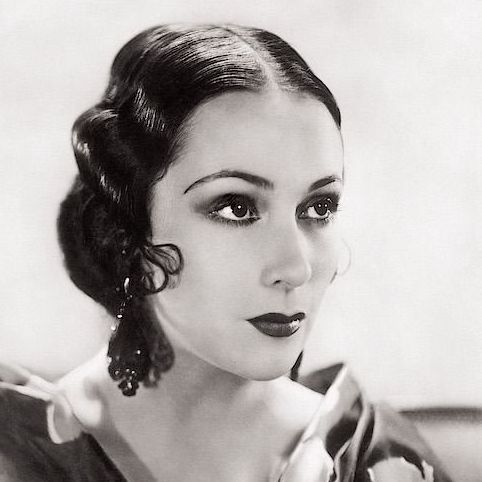
Dolores del Río (Flying Down to Rio, Flor silvestre)—to begin with, dolores is so RADIANTLY BEAUTIFUL, even more so in action then in images, its like she emits a literal glow. marlene dietrich (a close friend and rumored lover) considered her "the most beautiful woman who ever set foot in hollywood". she was the first mexican actress to become a major success in hollywood, rising to fame in the silent era and becoming an influential icon of beauty and glamor in the art deco age, though she was not thrilled with the exoticizing parts often pushed on her. in the mid 1940s having tired of the controlling hollywood studio system she returned to mexico, saying "I wish to choose my own stories, my own director and cameraman. I can accomplish this better in mexico", and proceeded to become a pivotal figure in the golden age of mexican cinema, making a string of masterpieces with directir emilio fernández and cinematographer gabriel figueroa. i love this anecdote about the insane art deco mansion she and her then-husband cedric gibbons lived in in the 30s, as related by david niven: "Dolores had a large sunny room on the first floor containing a huge and inviting bed. Gibbons lived in comparative squalor in a small room immediately below. The only connection between these rooms was by way of a stepladder, which could be lowered only when a trapdoor in the floor of Dolores room had been raised. There was a long stick with which, we conjectured, he signaled his intention or hopes by rapping out signals on the floor of his wife’s bedchamber." heres a pinterest album with a billion hot pictures of her
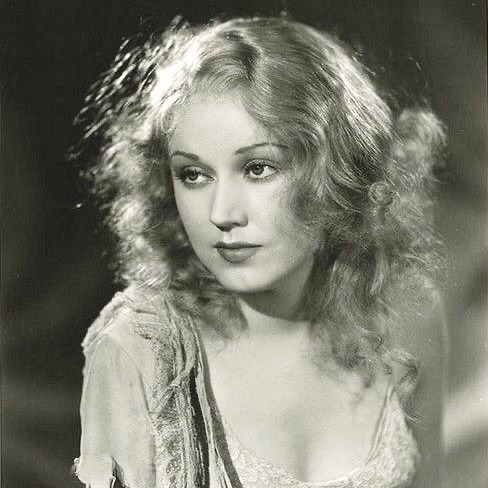
Fay Wray (King Kong)— the original scream queen!! she started acting in silent comedies as a teenager and got her first big break when erich von stroheim cast her as the lead in the wedding march. her career started to take off starring in silent movies at paramount, and she survived the transition to sound smoothly - josef von sternberg’s weird proto-noir thunderbolt was one of her first sound films. she began to make horror movies in the early 1930s, such as doctor x and mystery of the wax museum, both filmed in beautiful two-strip technicolor (which looked like this if you're curious. i just think it's neat!), as well as the vampire bat, the most dangerous game, and of course the boy himself, king kong. a little on how she worked with her most famous costar: “Although Kong appeared huge, the full figure was a model covered with rabbit hair, standing only 18 inches tall, that was filmed one frame at a time by stop-motion photography artist Willis O'Brien and his crew. The 5ft 3in Wray only knew one part of the ape's body when she was grasped in an articulated 8ft long hand. Hence the title of her 1989 autobiography, On The Other Hand. ‘I would stand on the floor,’ she recalled, ‘and they would bring this arm down and cinch it around my waist, then pull me up in the air. Every time I moved, one of the fingers would loosen, so it would look like I was trying to get away. Actually, I was trying not to slip through his hand.’” (link)
This is round 2 of the tournament. All other polls in this bracket can be found here. Please reblog with further support of your beloved hot sexy vintage woman.
[additional propaganda submitted under the cut.]
Dolores del Rio:
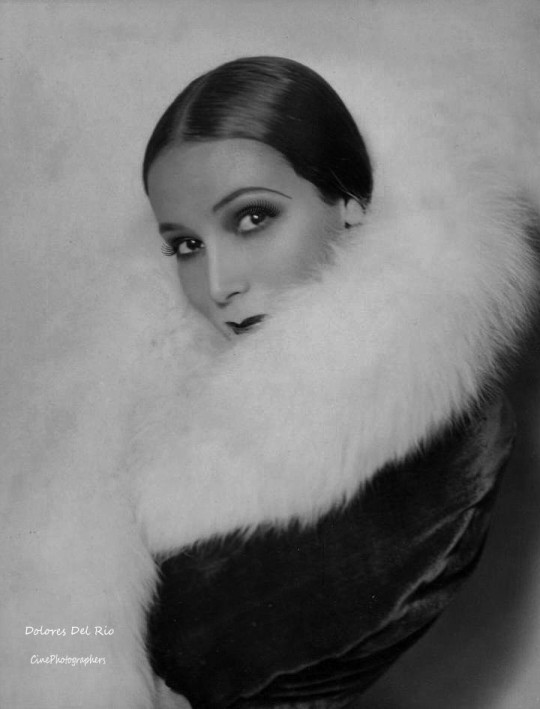

There's so much! She started in Silent films and successfully transitioned to sound, She is the first woman to wear a two piece swimsuit on screen & popularized the bikini!, She transitioned back to Mexican Cinema in the late 1940s and was a leading lady of the Golden Age of Mexican Cinema including staring in Maria Candelaria--the first Mexican film to win the palm d'Or at Cannes. She was literally studied for her beauty & was considered a beauty ideal in both the USA & Mexico--there's a whole section on her Wikipedia page about how beautiful everyone thinks she was. She never actually had a feud with any of the female stars she was rumored to feud with despite the fact that press & Hollywood culture attempted to pain them in competition... She remained a leader in Mexican theater & Cinema through her own production company. Mexican painter Diego Rivera: "The most beautiful, the most gorgeous of the west, east, north and south. I'm in love with her as 40 million Mexicans and 120 million Americans who can't be wrong" (quote source: Wikipedia)
*fan self* Leading actress in silents and early Hollywood. Lover of Orson Welles until she got fed up with him, friend of Diego Rivera and Frieda Kahlo. When she got tired of Hollywood executives typecasting her as a stereotypical spitfire (and trying to force her to feud with Lupe Velez as a publicity stunt), she ditched Hollywood and became a major star of Mexican cinema, where she got to play rounded characters
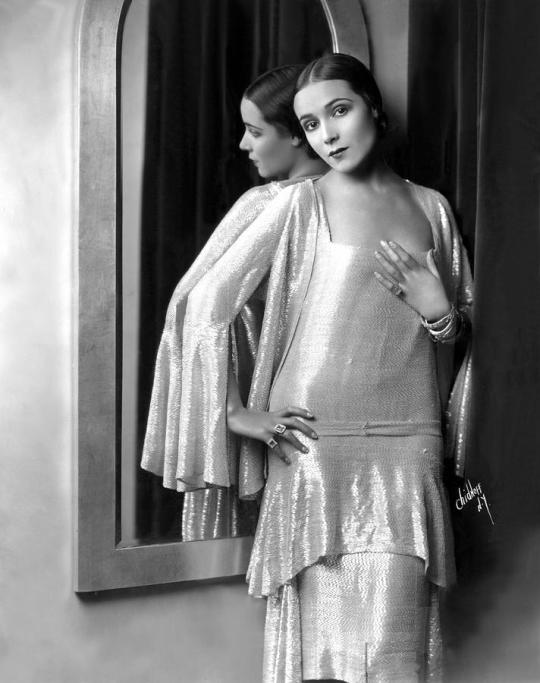

Had a career in American cinema in the 20s and 30s and considered one of the most important figures in the Golden Age of Mexican cinema (30s to 50s).
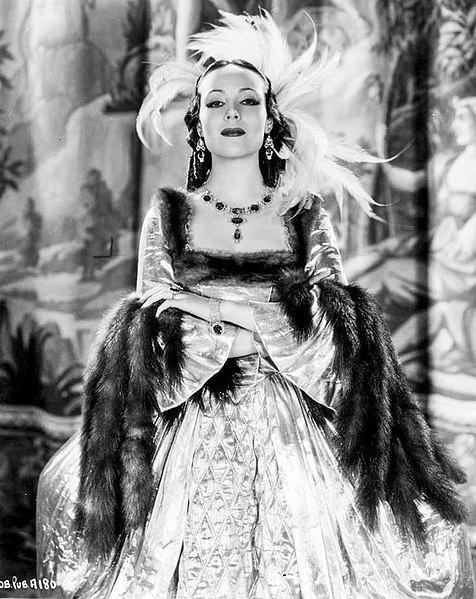

Marlene Dietrich said Dolores was the most beautiful woman to set foot in Hollywood
Joan Crawford: "Dolores became, and remains, as one of the most beautiful stars in the world."
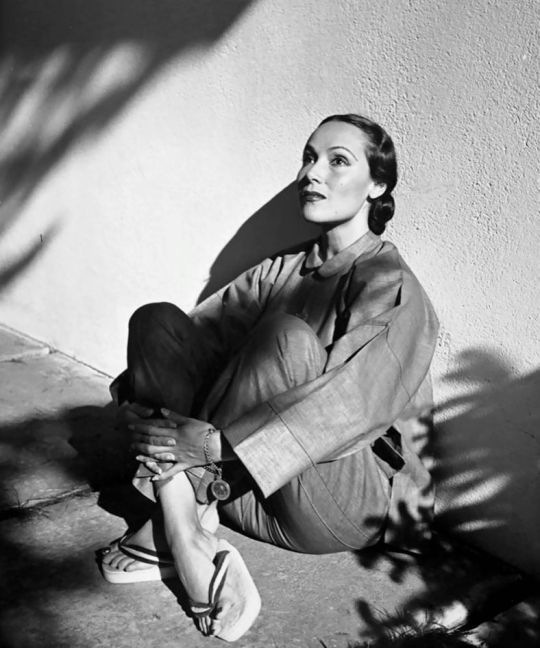

One of the few Latin American women working in the Hollywood industry to make it big not just in hre home country but internationally. In 1931, Photoplay magazine declared that Mexican film actress Dolores del Rio had the "best figure in Hollywood." (which I know not necessarily a good barometer) but! it shows that many people looked at her for her beauty and sought to emulate her. Famous for her years-long love affair with actor and director Orson Welles, who was 10 years her junior if that's anything.

We need more hispanic representation in this!! Del Río is one of the most important actresses of her time as she was one of the first Mexican movie stars to break through to Hollywood! She’s unbelievably sexy and an absolute icon. Thank you :)
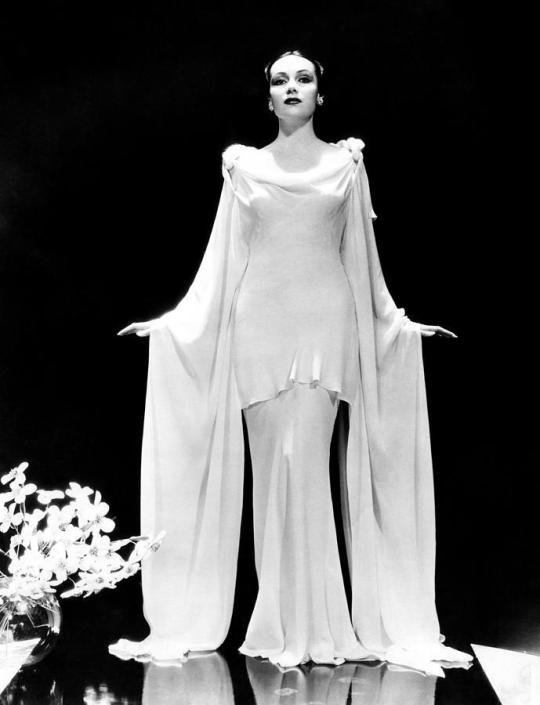

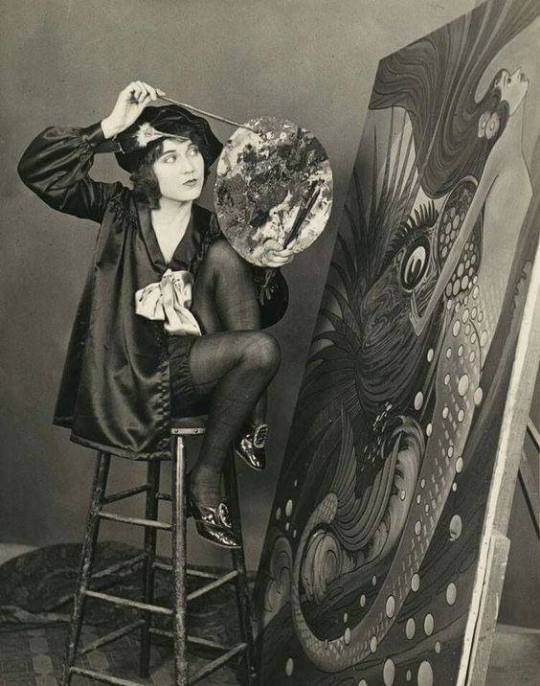
Fay Wray:
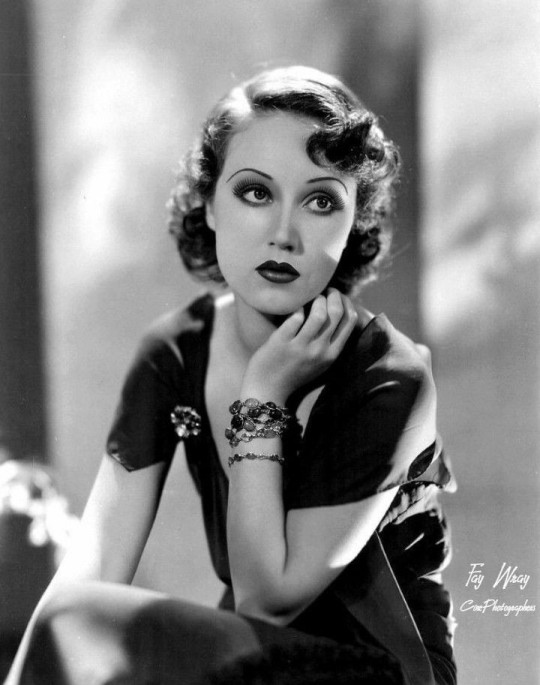


Actress prominently known for starring in horror, she was one of cinema's original "scream queens". She knocks it out of the park whenever she's with the horror genre, bringing a depth and likability to characters that would other be flat and boring characters.
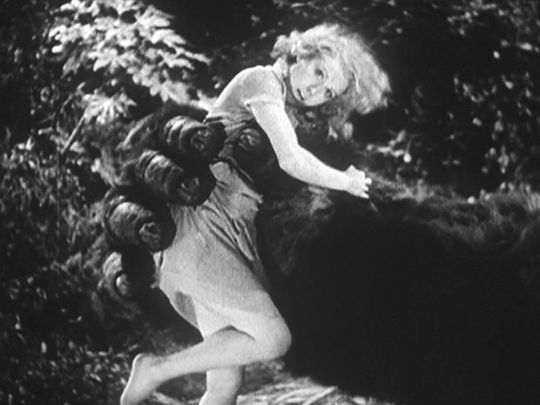

An early scream queen, name me another woman who could look so beautiful while so disheveled and scared for her life
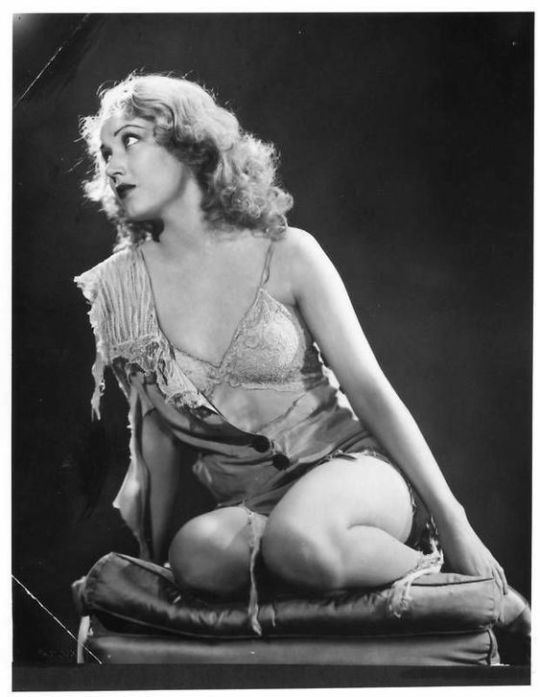
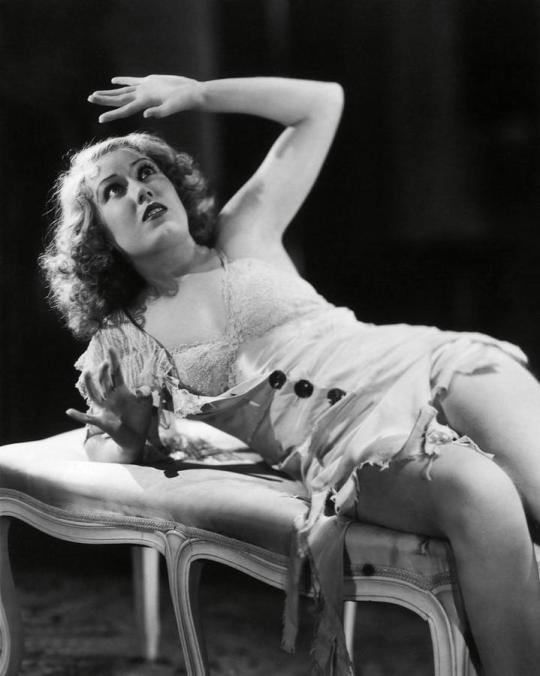


She was name-dropped not once but TWICE in the Rocky Horror Picture Show. She's arguably the original Scream Queen.

266 notes
·
View notes
Text
youtube
A Haunting We Will Go (Famous, 1949) ft. Casper the Friendly Ghost - dir. Seymour Kneitel
#Casper the Friendly Ghost#1940s#classic cartoon#golden age animation#seymour kneitel#Paramount famous studios#Youtube#Halloween cartoon
8 notes
·
View notes
Text

Gorilla Ghost Take “Casper Comes To Clown” (1951)
#50s#paramount pictures#famous studios#harvey comics#casper the friendly ghost#gif#gorilla#wild take#eye pop#Casper
44 notes
·
View notes
Text
"This looks like a job for SUPERMAN!"
From the Superman short Japoteurs, released September 18, 1942.
This was the first animated short produced by Famous Studios, the successor to Fleischer Studios, after Paramount Pictures took over the studio and removed the Fleischer brothers.
While the production teams and animation style remained essentially intact, there was a distinct change in story style. Five of the eight Famous Studios' shorts were focused on war propaganda stories and, like Japoteurs, depicted America's enemies with hideous racist caricatures.
43 notes
·
View notes
Text
Paper Hearts and Press Releases



Summary: Margaret Chen is a publicist secretly in love with her famous client, Elvis Presley. But his manager thinks she should cook up a story about him and his co-star to generate buzz for his upcoming movie. This involves arranging dates and photo ops for the two of them, but Margaret can't help but notice Elvis seems more interested in her.
Word count: ~2,500 words
Warnings: None. This is saccharine sweet!

If you asked Margaret Chen exactly when she fell in love with Elvis Presley, she probably couldn't tell you. Love's funny that way. It sneaks up on you like a summer cold, and by the time you notice the symptoms, it's already too late. But if really pressed - maybe after a couple glasses of wine, the kind she'd start allowing herself in the seventies - she might point to that Monday morning in 1965 when everything changed. Yes, that Monday. The Monday when Colonel Tom Parker walked into her office like he owned the place, which, in a way, he did.
The Hollywood publicity office was quiet enough to hear the whirring of the electric fan in the corner. Margaret straightened the papers on her desk for the third time that morning. The papers didn't need straightening, but hands need something to do when the heart's doing jumping jacks in your chest.
9:58 AM.
The Colonel had called yesterday, his voice like gravel in a garbage disposal. "Miss Chen, we need to generate some buzz for this picture. The studio's breathing down my neck. Set up a meeting, first thing Monday."
She'd known this was coming. Anyone with half a brain could see "Paradise, Hawaiian Style" was about as exciting as yesterday's meatloaf. Elvis's previous films had done well enough – they always did – but the formula was getting stale. The Colonel knew it. The studio knew it. And Margaret, who'd been handling publicity for Elvis's films for the past eighteen months, knew it better than anyone.
What the Colonel didn't know – what no one knew – was how Margaret's heart did a little skip every time her famous client walked into her office. How she'd memorized the way he absently ran his fingers through that famous hair when he was thinking (right to left, always right to left, like he was keeping time to some internal rhythm). How his "thank you very much" at the end of every meeting made her float around her apartment for hours afterward, until her roommate Susan would throw a pillow at her and tell her to "come back down to Earth, for Christ's sake."
The door burst open at exactly ten, making Margaret jump. Colonel Parker strode in first, his imposing frame filling the doorway like a bear in a business suit, followed by Elvis himself, who gave Margaret a warm smile that made her cheeks heat up.
"Morning, Miss Chen," Elvis said, settling into one of her visitor chairs with casual grace. He wore a perfectly tailored black suit that made his eyes look even bluer than usual.
"Good morning, Mr. Presley," she replied, and wasn't she proud of how steady she kept her voice? "Colonel."
The Colonel didn't waste time with pleasantries. The Colonel never wasted time with anything that couldn't be monetized. "Where's Victoria Sterling?"
"She's on her way, sir. Her meeting at Paramount ran late."
Victoria Sterling was their newest leading lady, brought in from the New York theater scene. At thirty-five, she was older than Elvis's usual co-stars, but she brought a sophistication that the studio hoped would elevate this picture above the typical beach movie fare.
As if on cue, Victoria swept into the office, bringing with her the scent of Shalimar and an air of Manhattan refinement. "So sorry I'm late, darlings. You wouldn't believe the traffic on Sunset."
Elvis stood politely, because his mama raised him right, and Victoria gave him an affectionate pat on the cheek like he was a particularly adorable puppy. "Hello, sweet boy." In the month since filming began, she'd taken to treating him like a younger brother, much to everyone's amusement.
The Colonel cleared his throat, the sound like rocks in a tumbler. "Now that we're all here, let's get down to business. The studio wants romance. They want passion. They want the public believing these two are madly in love."
Margaret's stomach clenched. She knew where this was going.
"Miss Chen, I want you to arrange a series of... let's call them 'chance encounters' between our stars. Romantic dinners, walks on the beach, maybe a little shopping on Rodeo Drive. The works."
Victoria arched one perfectly shaped eyebrow. "Darling, you can't be serious. Elvis is lovely, but he's practically a child."
"Hey now," Elvis protested good-naturedly.
"Besides," Victoria continued, examining her manicure, "Jean-Luc would be terribly jealous."
The Colonel's face reddened. "Who's Jean-Luc?"
"Jean-Luc Godard," Victoria said dreamily. "We met at Cannes last year. He's been sending me the most divine letters..."
"I don't care if he's the King of France! The public needs to believe you two are an item, at least until the picture releases."
Margaret watched Elvis during this exchange. He was fighting back a smile, clearly entertained by Victoria's dramatic flair. Their eyes met briefly, and he gave her a tiny wink that made her heart skip.
"Miss Chen will coordinate everything," the Colonel continued. "I want you two seen together at least twice a week. Make it look natural."
"I suppose I could cancel my lunch with Truman tomorrow," Victoria sighed, referring to Truman Capote as casually as if he were her neighbor.
The Colonel stood, and everyone else did too, because that's what you did when the Colonel stood. It was like a law of nature, like gravity or the way your heart speeds up when someone special walks into a room. "Good. Miss Chen, I want a full publicity schedule on my desk by Wednesday." He marched out, leaving behind the smell of cigars and authority.
Victoria rose gracefully. "Well, I'm off to my dialect coach. Elvis, darling, shall we say Musso & Frank's tomorrow at one? Margaret, you'll make the arrangements?"
Before Margaret could answer, Elvis spoke up. "Actually, Miss Chen, maybe you should join us? To, uh, coordinate the publicity angles in person?"
Victoria's eyes sparkled like she'd just been handed the juiciest piece of backstage gossip. "What a marvelous idea. Do join us, Margaret dear." With that, she glided out, leaving Margaret and Elvis alone in an office that suddenly felt about two sizes too small.
An awkward silence fell. Margaret shuffled some papers, very aware of Elvis still sitting there, watching her with those impossible blue eyes.
"So," he said finally, "you like Italian food?"
She looked up, surprised. "Yes, I do."
"Good." He stood, adjusting his cuffs. "Because the food at Musso & Frank's is terrible. Maybe we should get there early tomorrow, do a little research on better restaurants. Say, noon?"
Margaret knew she should say no. The Colonel would have her head if he found out. But Elvis was looking at her with such hopeful charm that she heard herself say, "I suppose that would be helpful. For publicity purposes."
His smile could have lit up all of Hollywood. "For publicity purposes," he agreed, heading for the door. At the threshold, he turned back. "Oh, and Miss Chen?"
"Yes?"
"Wear something pretty."
After he left, Margaret sat at her desk for a long time, trying to slow her racing heart. She had a feeling things were about to get complicated.
*
The next day found Margaret standing in front of her closet, surrounded by discarded dresses. She'd finally settled on a pale blue sundress that her roommate Susan swore brought out her eyes, but now she was having second thoughts.
"It's not a date," she told her reflection firmly. "It's work. Research for work."
Still, she found herself adding a pearl necklace and spending extra time on her hair.
She arrived at the restaurant at 11:55, determined to be professional. Elvis was already there, leaning against a sleek black convertible, looking like he'd stepped out of a magazine in pressed slacks and a light blue shirt that nearly matched her dress.
"Great minds think alike," he said, gesturing between their coordinating outfits.
Margaret blushed. "I should have worn something else. The photographers will have a field day if they catch us matching."
"What photographers?" Elvis looked around the empty street with exaggerated concern. "I don't see any photographers. Do you?"
She couldn't help but laugh. "Mr. Presley—"
"Elvis," he corrected. "Please."
"Elvis," she said softly, testing how it felt on her tongue. "We should probably go inside."
"Actually," he said, opening the car door, "I thought we might try this little place I know in Malibu. Best spaghetti this side of Memphis."
Every responsible bone in Margaret's body told her to decline. Instead, she found herself sliding into the butter-soft leather seat.
The drive up the coast was like something from a dream. Elvis handled the powerful car with casual confidence, one hand on the wheel as they talked about everything and nothing. He told her about growing up in Memphis, about his love of Southern cooking, about the first time he heard the blues on Beale Street. She found herself sharing stories about her childhood in San Francisco's Chinatown, her parents' hopes for her to become a doctor, how she fell in love with old Hollywood instead.
"So how does a nice girl like you end up working with the Colonel?" he asked as they cruised along the Pacific Coast Highway.
"I started as a secretary at William Morris," she explained. "Then I moved to the publicity department. The Colonel poached me after the 'Viva Las Vegas' campaign did well."
Elvis nodded. "I remember. You were the one who came up with that tagline – 'What happens in Vegas...'"
"Stays in Vegas," they finished together, laughing.
The restaurant turned out to be a tiny place tucked away from the tourist spots, with red-checkered tablecloths and candles stuck in wine bottles. The owner greeted Elvis like an old friend, leading them to a secluded corner table with an ocean view.
"The Colonel would hate this place," Elvis said, unfolding his napkin. "Too fancy for his taste."
"The Colonel would hate that we're here at all," Margaret pointed out.
Something flickered in Elvis's eyes. "The Colonel hates anything he can't control." He was quiet for a moment, then brightened. "But he's not here, is he?"
The afternoon stretched on like honey, sweet and golden. They shared plates of pasta and stories about the film industry. Elvis did spot-on impressions of various Hollywood personalities that had Margaret covering her mouth to keep from laughing too loud. She found herself relaxing, forgetting about publicity schedules and the Colonel's demands.
It wasn't until they were sharing a tiramisu that Elvis asked, "So, what's the real story with Victoria and this French fellow?"
Margaret hesitated. "I probably shouldn't..."
"Come on," he cajoled. "I promise not to tell. Besides, she calls me 'sweet boy' like I'm her kid brother. I think I deserve to know why."
Margaret glanced around conspiratorially. "Well... apparently, they had this torrid affair last summer. Very artistic, very passionate. But he's married."
"Ah." Elvis nodded sagely. "That explains the sighing whenever someone mentions Paris."
"She's actually been very understanding about this whole publicity stunt," Margaret said. "She knows it's just business."
"And what about you?" Elvis asked quietly. "Is this just business?"
Margaret's heart thundered in her chest. She looked down at her coffee cup, unable to meet his gaze. "Mr. Presley—"
"Elvis."
"Elvis." She took a deep breath. "We should probably head back. Victoria will be waiting."
He studied her for a long moment, then signaled for the check. The drive back was quieter, filled with a new awareness that made Margaret's skin tingle.
They arrived at Musso & Frank's at 1:05. Victoria was holding court at a corner table, regaling a group of admirers with what appeared to be a very dramatic story.
"Darlings, there you are!" she called out. "I was just telling everyone about the absolutely fascinating lunch meeting I've been having with Elvis. Such chemistry!" She winked at Margaret when no one else was looking.
As they took their seats, Victoria leaned over and whispered, "Your lipstick's smudged, dear. But don't worry – I've been covering for you both splendidly."
Margaret quickly dabbed at her lips with her napkin, mortified. She hadn't even realized...
Under the table, she felt Elvis's hand brush against hers. Just once, just briefly. But it was enough to make her forget to be embarrassed.
*
The next few weeks passed in a blur of arranged publicity dates and secret meetings. For every photographer-ready outing with Victoria, there seemed to be a quiet moment stolen with Elvis. A quick lunch here, a drive along Mulholland there. Nothing inappropriate, nothing that could cause a scandal, but enough to make Margaret's heart race every time she saw him.
Victoria proved to be an unexpected ally, providing cover stories and distractions whenever needed. She took to her role with theatrical flair, playing the smitten co-star for the cameras while secretly passing love notes from Jean-Luc between takes.
The Colonel, for his part, was thrilled with the publicity their "romance" was generating. "Keep it up," he'd growl during their weekly meetings. "The papers are eating it up."
But it couldn't last forever. As the film's release date approached, Margaret knew their time was running out. Whatever was happening between her and Elvis – this sweet, impossible thing – would have to end.
The last day of filming arrived too quickly. The wrap party was in full swing at some expensive Hollywood club, but Margaret had slipped away to the quiet of her office to finish some paperwork. Or at least, that's what she told herself she was doing.
A soft knock made her look up. Elvis stood in the doorway, still in his costume from the final scene.
"Shouldn't you be at the party?" she asked.
"Shouldn't you?" He came in, closing the door behind him. "Victoria's really selling it out there. She's telling anyone who'll listen about our tragic love affair and how she has to return to New York to nurse her broken heart."
Margaret smiled despite herself. "She's good at her job."
"So are you." He perched on the edge of her desk, something small glinting in his hand. "Too good, sometimes. Always so professional."
"Elvis..."
He held up the object – a delicate silver charm bracelet. "I got you something. To remember this by."
"I can't accept—"
"Please." He took her wrist gently, fastening the bracelet. "I want you to have it. Something to remember that not everything in Hollywood is fake."
Margaret blinked back sudden tears, touching the tiny charms – a heart, a musical note, a tiny palm tree. "It's beautiful."
"You know," he said softly, "we could tell the Colonel. About us. I know he'd be angry at first, but—"
She shook her head. "No. Elvis, you know we can't. Your career, your image... it's too important."
"Maybe it's not as important as—"
She stood quickly, cutting him off. "Don't. Please. Let's just... let's remember this summer exactly as it was. Something sweet."
He was quiet for a long moment, then nodded slowly. "Something sweet," he repeated. Then, with a sad smile, "Thank you very much, Miss Chen."
She laughed through her tears. "You're welcome, Mr. Presley."
He kissed her then, just once, very softly. A goodbye kiss. A thank you kiss. A what-might-have-been kiss.
Then he was gone, back to the party, back to his world of spotlight and spectacle.
Margaret touched the bracelet on her wrist, the silver warm against her skin. Tomorrow, she'd go back to being professional Miss Chen, efficient publicity manager. She'd watch Elvis's career from a respectable distance, maybe even handle publicity for his next film if the Colonel allowed it.
But for now, just for tonight, she let herself remember every stolen moment, every secret smile, every quiet conversation. She'd keep them locked away with the bracelet, a reminder that sometimes, even in Hollywood, the most real things happen when the cameras aren't watching.
*
Twenty years later, a package arrived at Margaret's San Francisco office, where she'd built her own successful publicity firm. Inside was a newspaper clipping about Elvis's death, and a note written in elegant, familiar handwriting:
"Darling –
Found this while clearing out my Malibu house. Thought you should have it.
You were the realest thing in his life that summer.
Love always,
Victoria"
Beneath the note was a photograph Margaret had never seen before. In it, she and Elvis sat at that little Italian restaurant in Malibu, both in pale blue, both laughing at something long forgotten. She was looking at the camera, but Elvis... Elvis was looking at her.
Margaret touched the silver bracelet she still wore, smiling at the memory of that golden California summer, when for just a moment, she'd known the real Elvis – not the star, not the legend, but the sweet boy from Memphis who matched his shirt to her dress and thought she looked pretty when she laughed.
#elvis presley#elvis#elvis fans#elvis fanfic#elvis presley fanfiction#elvis presley fic#elvis fanfiction#elvis presley fanfic#elvis fic#elvis x oc
16 notes
·
View notes
Text
How’d They Do That?
Special Effects & Stunts of Silent Cinema - Part 1
This is the first installment of an open-ended series where I try to highlight and illustrate the work of special effects and stunt artists of silent filmdom. Using articles from contemporary fan and trade magazines, I’ll make gifs or dig up images and/or video clips to accompany the descriptions of how the sequences were executed.
My notations will be bracketed and highlighted in a different color. Hope you all enjoy! Fair warning: this is a long read.


How They Do It!
[from Photoplay, April 1926]
by Cal York
Millions are asking how the motion pictures are accomplishing the marvelous new effects which have been developed in the past few years. It took months of investigation to give you the answer
DO you remember how you thrilled when the Red Sea parted to let Moses and the children of Israel pass through, only to close again and swallow up Pharaoh and his pursuing warriors in C.B. De Mille's stupendous "Ten Commandments" ?
How you gasped as T. Roy Barnes fled from the burning tenement with Claire Windsor in his arms as flames and smoke spurted about them and debris crashed on all sides in "Nellie, the Beautiful Cloak Model"?
The destruction of Pontius Pilate's palace with the crushing of hundreds underneath the ruins in "Ben Hur"?
The rescue of Doris Kenyon by Ronald Colman in Fitzmaurice's great picture, "A Thief in Paradise," as Miss Kenyon's runaway horse reared and stood poised on his hind legs on the very brink of a precipice?
Conway Tearle's hair-breadth escape from the mountain of rushing water in "The Great Divide"?
The stirring battle scenes in "The Big Parade" in which giant shells burst all around, tearing huge craters and spreading death as our boys marched on and on and on through No Man's Land.
How Blanche Sweet carried Ronald Colman to safety as the blazing roof fell and seemed certain to bury them. This in "His Supreme Moment."
I could go on and remind you of train wrecks which have brought you from your seats, of battles against storm and shipwrecks at sea—of thrills and hairbreadth escapes and terrific disasters.
How many times have you gone home from your motion picture theater and wondered how these things were accomplished, discussed with your family and friends what possible method could have been used to achieve the seemingly impossible?
AFTER months of investigation, I am able to give you an explanation of the thrills in the pictures I have mentioned and to explain to you the general method used in most other similar scenes.
First, I will tell you how they parted the Red Sea. This was done by a process of double printing, worked out by Roy Pomeroy, technical director at Lasky's. But that, marvelous as it seemed, was but a simple thing compared with the miracles now being wrought on celluloid by Frank Williams, the wizard of Hollywood, who has dreamed out and perfected the moving or traveling mat process of printing, which has made possible most of the recent marvels of the screen.
[Roy Pomeroy was head technical wizard for Famous Players-Lasky/Paramount (that is to say, he was their head special-effects engineer). We only know for certain about a handful of films that Pomeroy made specific contributions to, like The Ten Commandments (1923) and Wings (1927). As with many journeymen of the silent/studio era of Hollywood, the amount of films Pomeroy worked on was likely substantial, but many technical roles went uncredited at the time.]
To part the Red Sea, Pomeroy first built, on the Lasky lot, two wooden walls about the height of the ordinary room and backed them at one end with a scenic drop to represent the Red Sea country. These walls he covered with a jelly-like substance made from silicate of soda and sulphuric acid, which shimmered and shook and photographed like water. The floor space between these two walls was made to look like sand. He then photographed this set.

Then, with two cameras set up at the open end, he emptied thousands of gallons of water between the walls from huge water tanks behind them. One of the cameras was cranked backwards, and this showed the parting of the Red Sea. The other camera was cranked forward, and showed the waters joining together. Both were done in slow motion, which will be explained later.

The next step was taken out on the desert.
Wire fences were built a few inches further apart than were the jelly walls built on the stage. First Moses and his followers, with their live stock, were marched between these wire fences, which were just outside the camera lines, and therefore did not show in the picture. What the fences did do, however, was to keep the goats and donkeys from poking their noses outside the camera lines, which would never have done for in the double printing process the camera lines would become the walls of water. And it would never do for a donkey to shove his head through the Red Sea.
After Moses and his Children of Israel had passed through satisfactorily, under the grinding camera, they then photographed Pharaoh and his Egyptians madly pursuing in their chariots through the same fenced lane. And if the horses and chariots smashed out through the light wire fence, it was fine. for you will remember they were seen madly milling about before the walls of water finally obliterated them.
THEN when they put all together, by double printing, here is what they got:
First, a wall of water parted and left a lane of dry land in the Red Sea. (You remember the camera cranking backwards gave them the negative for this.)
Then Moses and his band were printed in passing along the space between the walls of water. After them, came Pharaoh and his warriors in full pursuit.
Right over these they printed the original negative of the waters rushing together, and this completely engulfed The Egyptians.


The only person to get wet in the closing of the Red Sea was Charles de Roche, who played Pharaoh. The blotting out of the King and his war chariot was not done by double printing but by trick photography, as it seemed necessary to the story of give this incident more personal drama.

The method used was this: DeRoche and his horses and chariot were placed on a treadmill. The camera was on a platform facing them. Over DeRoche's head and out of sight of the camera was a huge water tank, with a water chute projecting from it. This chute gave into a tank between DeRoche and the camera, but below the level of the camera line. While DeRoche whipped his horses like a madman on the treadmill and did all the acting necessary to being engulfed by water, the water in the tank was released and poured down in a torrent between him and the grinding camera, giving a perfect illusion. The only reason DeRoche got wet was because the water chute running above his head leaked badly.
Does this seem wonderful to you? It should. It is. And yet I tell you that it is simplicity itself compared with the moving mat.
Remember that in the "Ten Commandments" the double printing put the moving people into a vacancy on the film—the blank space left in the miniature between the walls of water. Also, that the double printing of the moving water over the Egyptians simply obliterated them.
READ ON BELOW the JUMP!
---

Photo caption: This great outdoor scene is made up of three parts and was made right in the studios of the Paramount Company at Astoria, L.I. It is composed of three parts: a miniature four feet high, six feet in front of the camera; the top part of the cliff, fifteen feet high, eighty feet in front of the camera; and a painted back drop, a few feet further away. In the long shots, or distant views, you see the whole in convincing reality. The close-up shots are shown in the white frame, the bottom of which indicates where the miniature ends and the larger set begins. This scene is from Gloria Swanson's new picture, "The Untamed Lady"
[The Untamed Lady (1926) is presumed lost, but luckily, a few images of this cliff-top sequence have survived.
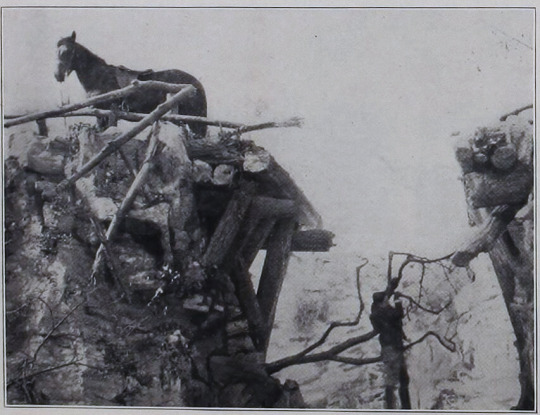


from Exhibitors Herald, 20 March 1926]
An amazing revelation of the latest discoveries of pictures which produce miracles before your eyes
---
But Frank Williams can put moving actors photographed in Hollywood into a moving background photographed anywhere in the world—put actual life and dramatic action into miniatures, which, during the previous years when they had worked with miniatures, seemed absolutely impossible.
[As you can gather from this article Frank Williams was a pioneer cinematographer and special effects artist. Williams was able to patent his moving matte process (and named it the Williams process) and it was an important effects technique used in film as as varied as Ben-Hur (1925), Sunrise: A Song of Two Humans (1926), The Lost World (1925), and The Invisible Man (1933). All of which are extant and easily accessible!
While it wasn’t in regular use for very long, the process was the basis for significant later developments in special effects photography, like green screening!]
Williams has made possible scenes that could never otherwise have been shot in motion pictures. It is not only that he has reduced the cost so that often he can give the producer scenes that would otherwise have been prohibitive because of building sets, etc. But he can give them scenes that couldn't be physically shot in any other way—such as a huge building crumbling and toppling in an earthquake and actually burying hundreds of people. It isn't only that he can make hairbreadth escapes without endangering the lives of actors and animals, as was sometimes done to get effects in the old days. He can make thrills that only the actual killing of animals and men would render possible—and this without the actor or animal being anywhere near the scene.
He can build a miniature town, put real, living people into it, and have them go through any necessary dramatic action, and then he can make a miniature torrent somewhere else altogether and have it sweep away the town with its laughing, singing, dancing population and make you believe when you see it on the screen that it actually happened.
THESE things he does by the patented process of the moving or traveling mat. It is a matter of printing, remember, more than of photography. Williams himself photographs nothing. The negatives from which he works are all shot for him, under his direction, and the miracles are performed in his laboratory.
It hasn't been easy for Williams to attain his title of the miracle man of films. He has given to the motion picture art one of its greatest discoveries. Like all great inventors, he has been scorned, laughed at, at times almost starved, forced to work under unspeakably difficult circumstances. But, none of these things moved him.
A big, quiet, simple fellow, only thirty-two years old. Shy, rather diffident of speech, he makes everything he does look easy. When he comes on a set, his quiet presence is scarcely noticed, and cameramen and technical experts go on spluttering and arguing, and when he is finally appealed to, he settles the problem so simply that everyone wonders why he didn't think of it himself.
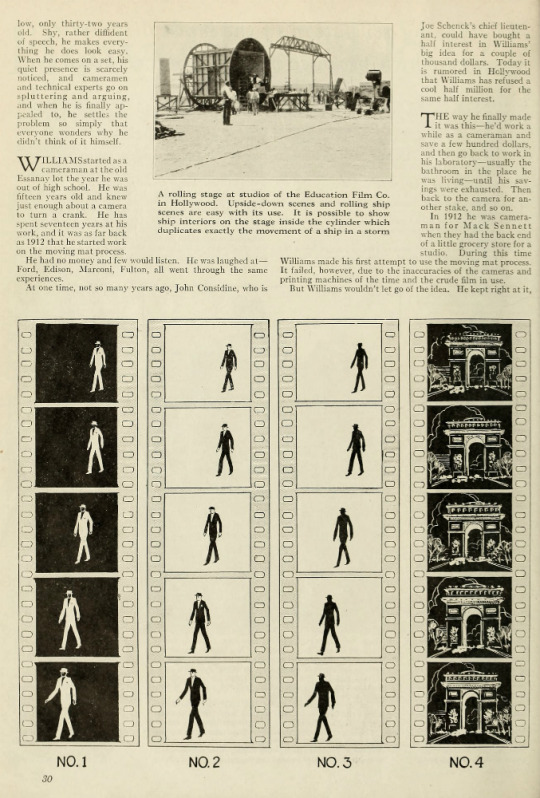

WILLIAMS started as a cameraman at the old Essanay lot the year he was out of high school. He was fifteen years old and knew just enough about a camera to turn a crank. He has spent seventeen years at his work, and it was as far back as 1912 that he started work on the moving mat process.
He had no money and few would listen. He was laughed at—Ford, Edison, Marconi, Fulton, all went through the same experiences.
At one time, not so many years ago, John Considine, who is Joe Schenck's chief lieutenant, could have bought a half interest in Williams' big idea for a couple of thousand dollars. Today it is rumored in Hollywood that Williams has refused a cool half million for the same half interest.
THE way he finally made it was this—he'd work a while as a cameraman and save a few hundred dollars, and then go back to work in his laboratory—usually the bathroom in the place he was living—until his savings were exhausted. Then back to the camera for another stake, and so on.
In 1912 he was cameraman for Mack Sennett when they had the back end of a little grocery store for a studio. During this time Williams made his first attempt to use the moving mat process. It failed, however, due to the inaccuracies of the cameras and printing machines of the time and the crude film in use.
But Williams wouldn’t let go of the idea. He kept right at it, and finally, in 1917, he again tried to perfect his process. working in a laboratory furnished by Adolph Zukor, of Paramount. But again he faced defeat, and for the same reasons—mechanical inaccuracies and improper film.
---
Photo caption: A rolling stage at studios of the Education Film Co. in Hollywood. Upside-down scenes and rolling ship scenes are easy with its use. It is possible to show ship interiors on the stage inside the cylinder which duplicates exactly the movement of a ship in a storm
[The rolling stage was used for lots of imaginative and comedic sequences in shorts and features. In the Lupino Lane short Movieland (1926), there’s a bit that shows the stage in action. Here’s a link to that specific scene, but the whole short is a lot of wacky fun and I recommend watching the full film!
Another illustration of how the rolling stage can be put to use is in When the Clouds Roll By (1919):


---
FINALLY, six years ago, his efforts were crowned with success. The Williams moving mat process was used in a Universal picture, "Wild Honey," and acknowledged commercially. Williams received a great deal of help and gives much credit for this to Elmer Sheeley, then a Universal art director, especially in the building of the miniatures.
Through the better grade of film, a motor-cranked camera set on a solid tripod, and through his own printing machine, built according to Williams' own drawings at a cost of $18,000, one whose accuracy is to within one ten-thousandth of an inch, all the obstacles which had frustrated him so long were overcome and Williams' moving mat process came to life, as perhaps the greatest single invention in motion pictures since that of the camera itself.
Once having demonstrated what he could do in "Wild Honey," in which he made a miniature stream appear a rushing torrent over a hundred feet high which pursued Priscilla Dean down a dry stream bed and finally engulfed her, Williams did not have much trouble getting producers to listen. This "Wild Honey" thrill was the forerunner of all big water spectacles, and when shown to C.B. DeMille gave him the idea for the parting of the Red Sea. DeMille admitted that this flood was the greatest spectacle he had ever seen up to that time.
[Unfortunately, Wild Honey (1922) is currently presumed lost and I was unable to find any depiction of Priscilla Dean fleeing from a torrent of water. As noted above however, there are quite a few extant films that also used Williams’ moving matte process.
In case you were wondering, I put $18,000 through an inflation calculator and it is equivalent to more than $315,000 in 2023 money!]
In trick photography miniatures have always been a very important part. It would hardly do to burn a huge building to have a woman carried from the blazing structure, and this the Williams process makes unnecessary.
TAKE the thrilling rescue front the burning tenement in "Nellie, the Beautiful Cloak Model." A replica of a New York tenement was built in miniature at the studio where the picture was made. We will say for illustration that the scale used in erecting the miniature was one and one-half inches to a foot, or one-ninth the actual size.
In working with miniatures there are two very important things to be considered, and these must be worked out with mathematical precision, if Williams is to be given a perfect negative on which to transpose living actors through his traveling mat. One is to make the miniature look the proper height. This is done by placing the camera the proper distance from the miniature (of course much closer than if it were a real building), and shooting from a lower level. The other is called timing. For example, if a miniature tree is to fall and the camera set-up is close enough and low enough to give the miniature the proper height when it is seen on the screen, then you must be careful of the speed with which it falls.
A little tree falls rapidly—a big tree slowly. And here is where the timing enters. Ultra speed cameras are used. The faster you crank the more pictures you get per second, and the slower the thing seems to move when you see it on the screen. You have all seen slow-motion pictures. These were made with slow-motion cameras, or what are more commonly termed ultra-speed cameras. And it is through this slow motion photography that the little tree is made to fall at the proper speed to be the big tree it represents, or the miniature stream is made to run at the proper speed for a giant river.
And so to get back to the fire which is still threatening "Our Nell." A torch is applied to the miniature tenement. At the proper count little invisible wires tied to window sashes are pulled and burning brands crash to the street below. And all the time the cameras, driven by motors at the proper speed, placed at the right distance from the conflagration and almost flat on the floor, are grinding away and recording this great fire.
[Nellie, the Beautiful Cloak Model (1924) is extant, with a print located at Gosfilmofond, but the film is not readily accessible. However, a depiction of the burning building sequence appears on an advertisement for the film:

from Film Daily, 28 February 1924]
OVER on some other part of the lot, and at any time which suits the director's convenience, T. Roy Barnes, with Miss Windsor in his arms, dashes through a black velvet door and down a street backed with more black velvet.
Two things must be remembered, however. The actors must come out of the velvet door at the right spot and at the right time or "count." This is necessary so that Williams can match up the fire negative, which is the background with action in it, with the negative of Miss Windsor and Barnes, which becomes the moving mat.
The remainder is simple, and is done by Williams and his printing process over at his laboratory.
On the screen you see Barnes dashing from a burning tenement with Miss Windsor in his arms while, in reality, neither of the actors has been close enough to a fire to singe a single eyelash.
Blanche Sweet's rescue of Colman in "The Supreme Moment" was worked out in the same manner as this, as have been most other burning building thrills in pictures made in the last few years.
[His Supreme Moment (1925) is presumed lost and unfortunately I was unable to locate a depiction of the burning building rescue mentioned here.]
Now for the destruction of Pontius Pilate's palace with the struggling mass crushed beneath, in "Ben Hur." Of course the palace was done in miniature, while the people did their acting out on the lot, where the street was built with a dead white backing. Again the timing had to correspond with that in the falling of the palace.
The throng of people was lined up and rehearsed. Two lines were drawn in the street a fixed distance apart—which represented the space where the ruins of the palace would fall, and the throng was sent dashing wildly down the street. At a fixed signal, all caught between the two marks fell flat on the ground. Those who had not reached the first line halted and registered terror. Those who had passed the second mark fled on, looking back and also registering terror. You see, those caught between the two marks were the people buried under the debris of Pilate's palace—those on either side had escaped.

Then came the trick printing with the two negatives, with considerable painting out of those who had fallen flat between the two lines, and you have the palace falling on the panic-stricken throng in the street. The accompanying drawings will help you to visualize this.
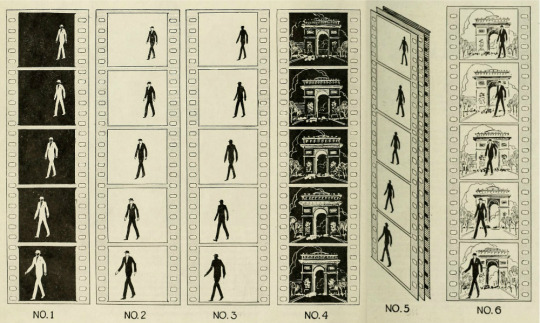
Never Before Told
This set of illustrations graphically explains for the first time the marvelous traveling mat process invented by Mr. Williams, which makes it possible for one cameraman to take a background in Europe, another to take the action of moving persons in Hollywood, and to combine them in one motion picture so that when it appears on the screen the action seems to take place against the background so perfectly that it cannot be detected by the human eye.
Follow this explanation carefully, and the method will be clearly demonstrated to you.
No. 1. This is the negative of the moving figure taken in front of a white background. In the negative, white appears black and black appears white. It is from this negative that the Williams traveling mat, which has revolutionized motion pictures, is made.
No. 2. This is a print made from the No. 1 negative and is printed on film of extreme contrast. In this the white and black values are given their true tones.
No. 3. This is the No. 2 film intensified in a silver nitrate solution so that it becomes a dead black silhouette, while the rest of the film is transparent.
No. 4. This is the background negative which can be taken any place in the world or made from still photographs or from miniatures. This background negative can have put in it any motion required.
No. 5. This shows the most important step in the Williams' moving mat process. In front you see the moving mat or drawing No. 3. In the middle is the background negative, drawing No. 4, and at the back is the unexposed film on which they are to be printed concurrently. By this double printing, you get a print of the background negative, which leaves an unexposed portion in each frame, corresponding exactly to the figure you see in drawing No. 1.
No. 6. The result of the double printing being made in No. 5, which leaves a silhouette blank space of the moving figure, is again double printed and into the blank space is printed the real photographic action taken in the original negative.
Thus you see that one double printing has left a blank silhouette space into which the real action is double printed in every detail.
---
The rescue of Doris Kenyon, which is also illustrated by the artist, was accomplished in this manner. One negative was shot of a very real and very steep precipice, the cameramen suspended on a platform far out over the edge to get the proper angle. Another negative was shot of Miss Kenyon's horse racing madly along what looked like a fence—but what was the inevitable white drop. Doris and the horse had to reach a certain mark at a certain count—for over at the precipice there had been rocks and dirt released at a certain count—the horse bad to rear, and Colman had to reach the frenzied beast, starting from outside the camera line, and he, too, must arrive on the right count. There could be no waiting for man or horse. They took it perhaps forty times before everything was exactly right, and then the two negatives (the precipice background and the moving mat) were ready for the printing wizard, and audiences got a great thrill.
[A Thief in Paradise (1925) is almost entirely lost. I profiled the film in my series Lost, but Not Forgotten in 2023.]
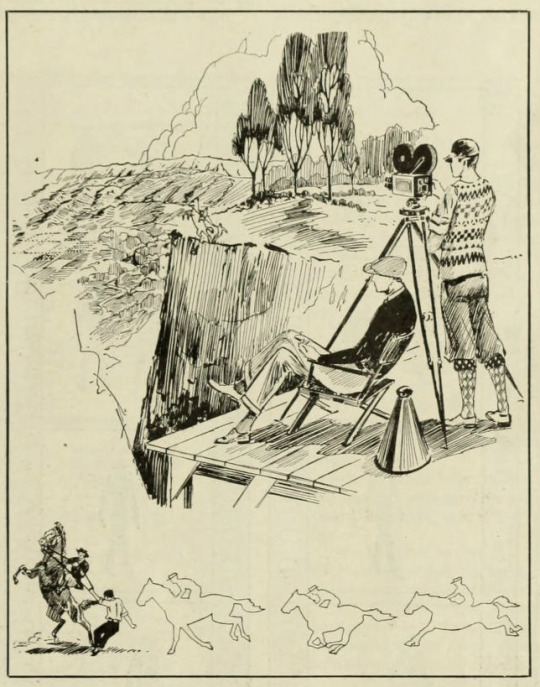

Photo caption: These two drawings explain how the runaway horse thrill in George Fitzmaurice's "A Thief in Paradise" was made. The upper drawing shows the cameraman getting his shots of a very steep and very real precipice. It also has the horse with its rider and the rescuer sketched in on the edge of the precipice where it actually appears in the picture.
The lower drawing shows the run that was made before the dead white background, with the horse rearing and Ronald Colman coming to Doris Kenyon's rescue.
The upper drawing was the background negative and the lower drawing the moving mat negative, and by the Williams' process the rearing horse, rider and Colman seemed to be actually placed on the brink of the precipice
---
You remember the mountain of water pursuing Conway Tearle in "The Great Divide." Of course they shot the torrent in miniature. Conway and his horse made their hairbreadth dash on a dark night and in an artificial rainstorm with nothing but a director threatening —then, although they did have quite a time making the steed climb a slippery and sloping wooden bridge, which was out on the back lot. Then up in Mr. Williams' laboratory, they finished one of the greatest thrills ever witnessed.
[While The Great Divide (1925) is thankfully extant at Cinemateket-Svenska Filminstitutet, it’s not easily accessible and I was unable to find a depiction of the effect.]
And the marvelous battle scenes in "The Big Parade." There were the big guns tearing huge craters in No Man's Land made on one negative, and the boys marched on and on and on in the other negative, and Mr. Williams brought them together in his printing laboratory. However, it was by no means as easy as it sounds, for this was one of the hardest pieces of moving mat printing ever accomplished.



SO critical is the public that the building, photographing and printing of these miniatures must be of the very highest type of workmanship obtainable. It might be interesting to know that this work in "The Big Parade" alone cost approximately $70,000 for the background negative and the moving mat negative. The miniature battlefield was about one hundred thirty-five feet long and more than seven thousand miniature shells were fired in a period of forty seconds.




On another picture—"The Barrier"—which shows a fierce storm at sea, icebergs, and a ship caught and crushed in an ice floe, more than $85,000 have been spent to create these illusions.
[The Barrier (1926) is unfortunately presumed lost and I wasn’t able to find a depiction of this effect.]
Mr. Waller, technical camera expert of the Famous Players Long Island Studio, had never seen a cyclone; yet he was instructed to produce one for D. W. Griffith's picture, "That Royle Girl." Mr. Waller did extensive research work on the subject, and then made one to experiment with. A scientific knowledge of the working of the law of gravity, by the way, is necessary to create this phenomenon of nature.
[That Royle Girl (1925) is also presumed lost, and without film footage of this sequence there’s not really a way to know how the cyclone looked in the film. However, I do think the image highlighted in the advertisement below is likely from the cyclone sequence.

from Motion Picture News, 21 November 1925]
In the basement of the studio Mr. Waller connected up three vacuum cleaners. With three suctions of air and some dust, he made a tiny cyclone. This was photographed in slow motion so that the camera and technical crew might study the formation and activity of the cone.
From his observations of the film, Mr. Waller was able to prepare the series of wash drawings which, photographed in animated cartoon fashion, represented the action of the cyclone's cone in this sequence of the picture.
Several hundred drawings had to be made, each one depicting gradually the advance of the cone toward the Inn, which it finally demolishes. These were photographed in rotation on motion picture negative, and this negative double exposed on the 180-foot miniature scene containing the houses and trees. Thus we got a very good illusion of the cone of a cyclone advancing over a village and sweeping houses and trees out of its path.
[I wonder if/hope that some of these drawings have survived!]
The animated cartoon idea was also used in "A Kiss for Cinderella," when the pumpkin and mice change into the coach and four. The first few feet of the sequence showed real mice and pumpkin; from then on 256 wash drawings of the gradual transformation were photographed in rotation and gave the impression of being animated.
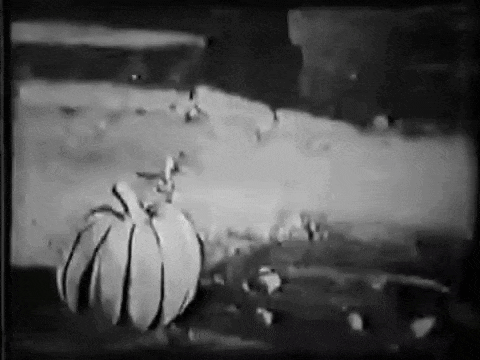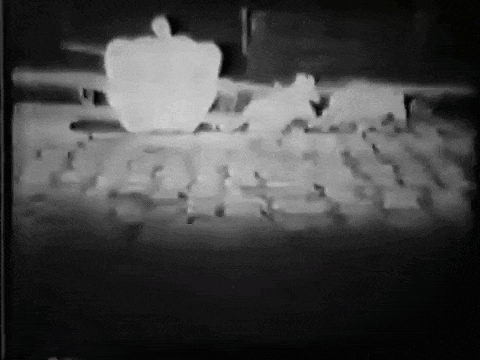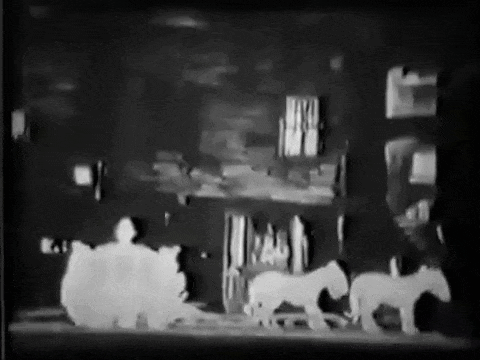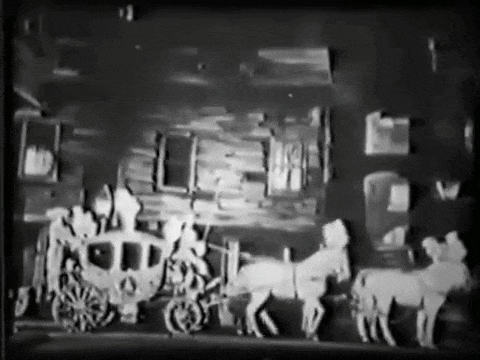
Double exposures of one actor playing two parts is the oldest and most familiar camera trick to the fans.
Just recently, however, has it been perfected to the point where the actor's two screen shadows can light each other's cigarettes and shake hands.
Tom Meighan, you recall, did this in Irish Luck."
AN invisible line from top to bottom divides each frame of the negative in half. One half at a time is exposed, photographing one half of the set.
Tom appears as Lord Fitzhugh on the left half, and as Tom Donohue on the right half. If you remember. Tom's two shadows are sitting side by side on a divan in the instance of the cigarette lighting. Fitzhugh leans over and gets a light from Donahue's cigarette. The illusion is perfect. But the cigarette from which his lordship really got the light was tacked onto a chair just outside the line, on the half of the set not being photographed at that moment. Only the lighted end of the cigarette projects into Fitzhugh's half of the picture.
[Irish Luck (1925) is extant at Eastman House, but it’s not currently easily accessible. I wasn’t able to find a depiction of this split-screen effect.]
Then when Donahue's half of the scene was being filmed, Tom leans forward and holds his cigarette in exactly the spot where the chair had been, the lighted end being outside his half of the picture. Think of the perfect matching this requires!
It is done this way. As Lord Fitzhugh performs on one side of the set, the director times his actions, counting the seconds out loud. He knows just where his lordship's right arm is, for instance, at the sixteenth second. When Donahue begins to perform on the other side of the set, his arm must be in a corresponding position at the sixteenth second. Tricky.
A thrilling moment in "Aloma of the South Seas," Gilda Grey's new picture, occurs when a shark eats a sailor. If you want this thrill, you naturally have to take it synthetic.
The shark cost $3,000. It was made of flexible rubber, and its insides consisted of a maze of electric wiring. Outside the body were several buttons which the actor could operate in his fight with the shark. It swims, wiggles its tail and bites electrically.
[Aloma of the South Seas (1926) is presumed lost and I wasn’t able to find images of the shark described here. However, as consolation, here is a photo from American Cinematographer of the film’s cinematographer Harry Fishbeck shooting on location in Puerto Rico:

from American Cinematographer, February 1926]
I guess most of the suffering for art is done by the actors who tie themselves into knots to create the illusion of paralysis, amputated legs and so on. John Gilbert is shown in the last reels of "The Big Parade" with an amputated leg. Jack Barrymore in "The Sea Beast," also does it. It is merely a painful process of strapping the foreleg back. In "The Street of Forgotten Men," with Percy Marmont, a very lucid expose of cripple fakes is shown. Marmont had his arm strapped to his back for hours at a stretch during the filming of this picture. It hurts the first fifteen minutes, Percy said. After that the arm becomes numb.
A vigorous massage is necessary to bring it back to life, but it doesn't feel normal for weeks, Percy says.
Lon Chaney has his tricks of deformity down so pat that they are almost painless to him now.
#1920s#1910s#1926#classic film#classic movies#film#american film#my edits#silent film#my gifs#silent movies#silent era#silent cinema#cinema#film history#history#Roy Pomeroy#Frank Williams#Film Art#How'd They Do It#photoplay#lantern
63 notes
·
View notes