#nivolumab/relatlimab
Explore tagged Tumblr posts
Text
Biologicals to have a lag-3 timelapse from spreading: the new strategy to prevent Parkinson onset
In studies with genetically engineered mice, Johns Hopkins Medicine researchers say they have identified a potentially new biological target involving APLP1, a cell surface protein that drives the spread of Parkinson’s disease-causing alpha-synuclein. The findings reveal how APLP1 connects with Lag3, another cell surface receptor, in a key part of a process that helps spread harmful…

View On WordPress
#alpha-synuclein#beta-amyloid#monoclonal antibody#neurodegeneration#nivolumab/relatlimab#Parkinson disease#tau protein
0 notes
Text
Exploring the Cancer Immunotherapy Market: Emerging Trends, Key Innovations, and Growth Opportunities - UnivDatos
Cancer immunotherapy has been considered the most revolutionary method in the field of oncology and has changed the cancer treatment paradigm. Companies have developed a promising type of treatment that recognizes the human body's immune system to identify and subsequently eliminate cancerous cells in patients with different types of cancer. As the understanding of cancer immunotherapy grows quickly, some of the recent trends and new developments in this area are following.
Access sample report (including graphs, charts, and figures): https://univdatos.com/get-a-free-sample-form-php/?product_id=5089&utm_source=LinkSJ&utm_medium=Snehal&utm_campaign=Snehal&utm_id=snehal
Advancements in Checkpoint Inhibitors
· August 2024 – Merck announced that PD-L1 expression thresholds for certain advanced gastric, gastroesophageal junction (GEJ) and esophageal cancer indications for immune checkpoint inhibitors, including KEYTRUDA (pembrolizumab), Merck’s anti-PD-1 therapy, will be discussed during an upcoming meeting of the U.S. Food and Drug Administration’s (FDA) Oncologic Drugs Advisory Committee (ODAC).
· August 2022 - Bristol Myers Squibb announced that OpdualagTM (nivolumab and relatlimab-rmbw), a new, first-in-class, fixed-dose combination of nivolumab and relatlimab, administered as a single intravenous infusion, was approved by the U.S. Food and Drug Administration (FDA) for the treatment of adult and pediatric patients 12 years of age or older with unresectable or metastatic melanoma.1 The approval is based on the Phase 2/3 RELATIVITY-047 trial, which compared Opdualag (n=355) to nivolumab alone (n=359).
Checkpoint inhibitors have been among the prominent immunotherapeutic agents since they allow treatment to block proteins that suppress the immune system’s attack on cancerous cells. More recent discoveries in this regard are increasing the applicability of these drugs in treatment. For example, new checkpoint inhibitors are emerging to target further proteins apart from the most common PD-1 and CTLA-4 pathways. To this end, drugs that target TIM-3, LAG-3, and other novel checkpoints are in initial clinical trials and may have better positive results on patients who do not benefit from current therapies.
The Building Blocks For Extension of CAR-T Cell Treatment
CAR-T therapy or Chimeric Antigen Receptor T-cell treatment has brought about a new era of cures for some blood malignancies. This form of treatment entails modifying a patient’s T-cells in a way that the cellular receptors will detect the cancer cells. New directions are therefore aimed at applying CAR-T in solid tumors which were previously difficult to manage through this process. The strategies including dual-target CAR-T cells and combined therapies make efforts to improve the therapeutic outcomes and minimize the side effects of CAR-T treatments for solid tumors.
Emergence of Bispecific Antibodies
Bispecific antibodies are a recently developed category of therapeutics with the capability to bind two different antigens at the same time. This approach targets two sites, and this can help in increasing the specificity of treatment. The results of the newest clinical trials have confirmed the opportunities offered by bispecific antibodies for the treatment of numerous cancers, including hematologic malignancies as well as solid cancers. For instance, bispecific T-cell engagers are getting effective in the process of stimulating T-cells to assassinate cancerous cells more proficiently.
Artificial intelligence in the advancement of drug development
The AI technology is steadily being utilized in the enhancement of the cancer immunotherapies. Self-learning algorithms are being utilized to mine big data sets from clinical studies, genetics, and pharmacology. The objective of this technology is to find out the possible therapeutic agents, evaluate patients’ outcomes, and select the most effective treatment regimen. AI-converted methods enable responsible findings for immunotherapies and the selection of possible therapies according to patients’ characteristics.
Advances in Combination Therapies
The use of immunotherapy in conjunction with other approaches forms a subtopic that is currently receiving much attention. The use of checkpoint inhibitors in conjunction with targeted therapy, chemotherapy, or radiation seems to possess profitability in boosting treatment outcomes. Recent has shown that such combination approaches can bypass resistance mechanisms and add value to patients’ enhanced survival. For instance, the administration of PD-1 inhibitors with other reagents has generated various success in diverse cancer varieties, such as melanoma and non-small cell lung cancer.
Focus on Overcoming Resistance
This is one of the main problems and pitfalls regarding immunotherapy at the moment. Scientists are studying the causes of resistance, and the ways to counteract it at present. Several of these strategies are based on the concept of avoiding immune suppression that can be occasioned by tumor microenvironments. Immunotherapy can be combined with agents changing the activity of immune cells within a tumor; the tumor microenvironment can be modified or the immunotherapy can be tried after which other agents can be used to change immune cell activity in tumors.
Improved Utilisation and Equality in Treatment
Thus, as the range of applications of cancer immunotherapies expands, there is a rising interest in the ways to increase its availability and inclusiveness. There are ongoing attempts to make these from-out wonderful promising treatments reachable to a larger number of patients including those living in remote areas or from low-income households. Efforts need to be made to keep costs down, prevent treatment from becoming more complex than it needs to be, and raise awareness to make immunotherapy available to all who might benefit from it.
Biomarkers and Personalized Medicine: Novel Findings.
One of the main objectives is the identification of biomarkers that could help to identify patients with responses to immunotherapy. These biomarkers allow physicians to know which patients are likely to benefit from the therapies, therefore improving patients’ treatment plans. New developments in biomarker identification and verification are opening new possibilities for better immunotherapy approaches to work by patient and tumor properties.
Regulatory and Policy Developments
That is why the regulatory bodies have responded to the dynamics of Immunotherapy by making changes in the guidelines and approval of the different techniques. Various strategies are being adopted including simplification of the regulatory process relating to the approval of new immunotherapy drugs and combinations. Besides, the policies used to enhance the clinical trial models and obtain experimental treatments are beneficial in delivering new treatments to patients faster.
Future Directions and Outlook
There are enormous prospects for cancer immunotherapy to grow in the future because of constant progression and advancements. New technologies, new classes of drugs, and more utilization of combination therapies are likely to provide better solutions to the current issues and improve the outcomes. As this progress goes on, the ideal has been to develop new more efficient, targeted, and available options to treat cancer thus translating to increased survival and improved patient quality of life.
Click here to view the Report Description & TOC: https://univdatos.com/get-a-free-sample-form-php/?product_id=5089&utm_source=LinkSJ&utm_medium=Snehal&utm_campaign=Snehal&utm_id=snehal
Conclusion
In conclusion, immunotherapy is at the forefront of new cancer treatments, many breakthroughs are going to be driving the future of cancer immunotherapy. From checkpoint inhibitors to CAR-T cells and from integration of Artificial Intelligence and combinations this area of cancer therapy is moving fast. With time and more developments in research and new inventions in medical fields the chances to transform the way cancer is treated and provide patients a fresh lease of life increases. According to the UnivDatos Market Insights analysis, the rising number of cancer cases globally, advancements in research and development, high efficacy of immunotherapy, increasing investment and funding, advancements in biomarker identification, and rising regulatory approvals and accelerated pathways drive the Cancer Immunotherapy market. As per their “Cancer Immunotherapy Market” report, the global market was valued at USD 120 Billion in 2023, growing at a CAGR of about 10% during the forecast period from 2024 - 2032.
0 notes
Text
Opdualag Approved for Advanced Melanoma Care

Understanding Opdualag: A Breakthrough in Cancer Treatment
In a significant medical advancement, the Medicines and Healthcare Products Regulatory Agency (MHRA) approved Opdualag (nivolumab-relatlimab) for treating patients with advanced melanoma, starting from the age of 12. Made on 27 December, this decision represents a critical step in combating a severe form of skin cancer known for its potential to spread to other body parts. The Threat of Melanoma and Opdualag's Role Melanoma, a skin cancer type largely attributed to ultraviolet light exposure from the sun and sunbeds, affects around 17,000 individuals annually in the UK. Not all cases are advanced melanoma, but for those that are, Opdualag offers a new ray of hope. This cancer medicine's approval is a testament to ongoing efforts to provide more effective treatment options for such severe conditions.
Global Collaboration through Project Orbis
Opdualag's authorization was facilitated by Project Orbis, a global initiative involving MHRA, the US FDA, and several other international health authorities. This program streamlines the review and approval of promising cancer drugs, thus accelerating patient access to critical treatments. Julian Beach, MHRA Interim Executive Director, underscores Project Orbis's commitment to opening access to innovative cancer treatments. Administration and Continued Monitoring Administered intravenously every four weeks, Opdualag's administration falls under the supervision of a doctor experienced in cancer treatment. Furthermore, the treatment duration varies depending on the clinical benefits observed by the doctor or the severity of side effects. Additionally, alongside its administration, MHRA commits to vigilantly monitoring Opdualag’s safety.
How Opdualag Works
Opdualag consists of two active ingredients, nivolumab and relatlimab, both monoclonal antibodies. These proteins specifically target and attach to substances in the body, enhancing the immune system's cancer-fighting ability. Nivolumab and relatlimab work by blocking proteins that could otherwise suppress T-cell activity, thereby enhancing the immune system's response against melanoma cells. Efficacy Proven in Clinical Trials A comprehensive phase 2/3 randomized, double-blind clinical trial involving 714 patients with previously untreated advanced melanoma backs the authorization of Opdualag. The trial demonstrated that the combined treatment of nivolumab and relatlimab significantly slowed disease progression compared to nivolumab alone, offering an extended period of disease stability for patients.
Managing Side Effects from this Advanced Melanoma Treatment
While Opdualag represents a major advancement, it does come with potential side effects, including fatigue, muscle and joint pain, skin rashes, decreased appetite, gastrointestinal symptoms, and respiratory issues. MHRA emphasizes the need to report any suspected side effects through the Yellow Card scheme, ensuring continuous monitoring of the drug's safety and effectiveness. Sources: THX News & Medicines and Healthcare products Regulatory Agency. Read the full article
#AdvancedMelanomaTreatment#CancerTreatmentSupervision#ClinicalTrialsforMelanoma#ManagingCancerSideEffects#MHRADrugApproval#MonoclonalAntibodiesTherapy#OpdualagNivolumab-Relatlimab#ProjectOrbisCollaboration#ReportingDrugSideEffects#SkinCancerMedication
0 notes
Text
RELATIVITY-047 Update: Nivolumab / Relatlimab Provides Progression Free Survival (PFS) Benefit in Previously Untreated Advanced Melanoma
Key Points: An updated analysis from RELATIVITY-047 trial: After a median follow-up of 25.3 months continues to show a significant PFS benefit for the nivolumab / relatlimab combination over nivolumab alone in the first-line treatment of patients with unresectable or metastatic melanoma: While no new safety findings were noted Although investigators observed improvements in melanoma-specific…

View On WordPress
0 notes
Text

Comparison between EMA and FDA positions. Different indications for OPDUALAG® in Europe and USA.
Cancer related news
Synopsis on decisions at September’s CHMP plenary for oncology products is now online.
ERON September 2022
----------------------------------------------------------------
Different indications for OPDUALAG ® in Europe and USA and the reason why:
On September 15th 2022, the European Commission (EC) authorised OPDUALAG® for the treatment of melanoma with tumour cell PD-L1 expression < 1%. Remarkably, the indication (SmPC 4.1) granted by the EC based on the positive CHMP opinion of July 2022 is different from the indication granted by the US FDA.
The exact indication wording in Europe is: Opdualag is indicated for the first line treatment of advanced (unresectable or metastatic) melanoma in adults and adolescents 12 years of age and older with tumour cell PD-L1 expression < 1%.
The indication wording in USA is: OPDUALAG is a combination of nivolumab, a programmed death receptor-1 (PD-1) blocking antibody, and relatlimab, a lymphocyte activation gene-3
(LAG-3) blocking antibody, indicated for the treatment of adult and pediatric patients 12 years of age or older with unresectable or metastatic melanoma.
Why this difference?
OPDUALAG® is a combination ->continue reading
#cancerimmunotherapy#health#melanoma#oncology#europe#medicine#science#immunotherapy#cancer#cancertreatment
0 notes
Text
Understanding differences between EMA and FDA positions - Different indications for OPDUALAG® in Europe and USA and the reason why:
On September 15 2022, the European Commission (EC) authorised OPDUALAG® for the treatment of melanoma with tumour cell PD-L1 expression < 1%. Remarkably, the indication (SmPC 4.1) granted by the EC based on the positive CHMP opinion of July 2022 is different from the indication granted by the US FDA.
The indication wording in Europe is: Opdualag is indicated for the first line treatment of advanced (unresectable or metastatic) melanoma in adults and adolescents 12 years and older with tumour cell PD-L1 expression <1%.
The indication wording in USA is: OPDUALAG is a combination of nivolumab, a programmed death receptor-1 (PD-1) blocking antibody, and relatlimab, a lymphocyte activation gene-3 (LAG-3) blocking antibody, indicated for the treatment of adult and pediatric patients 12 years of age or older with unresectable or metastatic melanoma.

Why this difference?
OPDUALAG® is a combination of the antibodies relatlimab and nivolumab. Nivolumab has previously been authorised for the treatment of melanoma (as OPDIVO®); relatlimab is authorised only in combination with nivolumab in OPDUALAG®. Both antibodies are checkpoint inhibitors and work as immunotherapy of cancer, with nivolumab directed against PD-1 (programmed death receptor-1) and relatlimab against LAG-3 (lymphocyte activation gene-3).
At variance with the European decision to restrict the indication to patients whose tumors have a low (<1%) PD-L1 expression, the FDA granted a broader indication without the need for a PD-L1 assay. Both indications can be justified:
Adding relatlimab to the treatment with nivolumab clearly and obviously increased PFS. In FDA’s prescribing information, the Kaplan-Meier curve clearly illustrate the superiority of OPDUALAG over nivolumab alone - obviously supporting the broader indication granted by FDA.
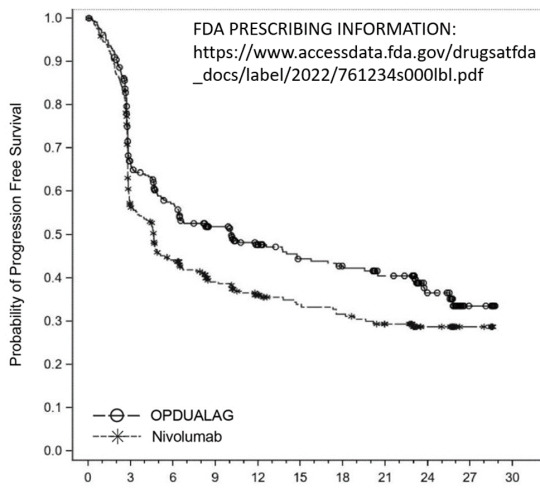
On the other hand, when CHMP looked at subgroups with a cut-off at 1% PD-L1, it seemed that the overall positive result is driven by the subgroup with tumour cell PD-L1 expression smaller than 1% - which is why EMA preferred the more restricted indication: OPDUALAG is indicated for the first line treatment of advanced (unresectable or metastatic) melanoma in adults and adolescents 12 years of age and older with tumour cell PD-L1 expression <1%. (https://www.ema.europa.eu/en/documents/smop-initial/chmp-summary-positive-opinion-opdualag_en.pdf)

Kaplan-Meier plot of PFS per BICR by baseline PD-L1 expression – All randomised subjects (28-Oct-2021 DBL)
Interestingly, this observation, that a second checkpoint inhibitor, which is added to nivolumab, works best in patients with low PD-L1 is not completely new. We have seen a similar subgroup effect for the combination of nivolumab (OPDIVO®) and ipilimumab (YERVOY®) we have seen a similar subgroup effect (https://www.ema.europa.eu/en/documents/product-information/opdivo-epar-product-information_en.pdf).
When the combination of nivolumab (OPDIVO®) and ipilimumab (YERVOY®) was approved for the treatment of melanoma, CHMP considered this subgroup difference important enough to justify the following addition to the indication (SmPC 4.1): Relative to nivolumab monotherapy, an increase in progression-free survival (PFS) and overall survival (OS) for the combination of nivolumab with ipilimumab is established only in patients with low tumour PD-L1 expression (see sections 4.4 and 5.1).


It looks like there’s a kind of ceiling effect for these checkpoint inhibitors, and if this ceiling has already been reached by nivolumab alone - in patients with high PD-L1 expression - another checkpoint inhibitor apparently will not add much benefit. With relatlimab, the second example after ipilimumab, for such a subgroup difference, it may seem reasonable to consider similar effects for future combinations of checkpoint inhibitors, at least with other anti-LAG-3 monoclonal antibodies, such as fianlimab. It might even be advisable to look for similar subgroup effects in trials combining other checkpoint inhibitors as well.
#melanoma#metastatic#nivolumab#Opdualag#relatimab#tumor#unresectable#europe#health#medicine#oncology#science
0 notes
Text
Update shows relatlimab + nivolumab slows advanced melanoma
For patients with previously untreated metastatic or unresectable melanoma, the combination of relatlimab + nivolumab continues to demonstrate a progression-free survival (PFS) benefit over nivolumab alone, according to updated study results presented March 14 as part of the American Society for Clinical Oncology Plenary Series. Source Link Update shows relatlimab + nivolumab slows advanced melanoma
0 notes
Text
Relatlimab With Nivolumab Improves Progression-free Survival in Melanoma
Relatlimab With Nivolumab Improves Progression-free Survival in Melanoma
The benefit of the combination therapy was observed across pre-specified subgroups. The Food and Drug Administration granted priority review to the combination in September 2021 based on the results of this study. “The results from this global effort advance the field of immunotherapy by establishing a third class of immune checkpoint inhibitors through the LAG-3 pathway and have the potential…

View On WordPress
0 notes
Text
LAG-3 drugs take centre stage at ASCO, showing potential as next-gen immunotherapies

LAG-3 drugs from arch-rivals Bristol-Myers Squibb and Merck & Co look set to become talking points at this year’s ASCO conference after trial results showed their potential as next-generation cancer immunotherapies.
Bristol-Myers Squibb made a splash ahead of the virtual conference early next month, with results showing a single infusion of its LAG-3 blocker relatlimab and its Opdivo immunotherapy improved progression-free survival in advanced melanoma compared with the PD-1 class Opdivo alone.
Not to be outdone, Merck & Co countered with results from its LAG-3 favezelimab, with phase 1 data showing a combination with rival PD-1 Keytruda could have potential in metastatic colorectal cancer.
BMS said that this is the first regimen showing a statistical benefit over PD-1 monotherapy such as Opdivo (nivolumab) in metastatic melanoma, which has become established as standard of care in the indication in the last decade or so.
Results come from the phase 2/3 RELATIVITY-047 trial in patients with metastatic or unresectable disease, which will be presented as an oral abstract at the American Society of Clinical Oncology (ASCO) on Sunday.
In those receiving the combination, the median progression-free survival (PFS) was significantly longer at 10.12 months compared with 4.63 months in those receiving Opdivo.
The PFS benefit of the fixed-dose combination was observed early, at the time of the first scan, and was consistent over time.
In exploratory, descriptive analyses, the combination of relatlimab and nivolumab extended PFS regardless of pre-specified subgroups and stratification factors, BMS said.
Safety-wise no new signals or types of clinically important events were identified with the fixed-dose combination therapy when compared with Opdivo monotherapy.
However there were more grade 3/4 drug-related adverse events were 18.9% in the combination arm compared to 9.7% in the Opdivo arm.
Discontinuation rates were higher in the combination arm (14.6%) compared with 6.7% seen in the Opdivo arm.
BMS, which snapped up a TIGIT class cancer drug from Agenus this week for up to $1.56 billion, said that results will be used as the basis for filings with the FDA and other regulators.
Favezelimab
Merck & Co’s data from favezelimab comes from a small group of patients with metastatic colorectal cancer, showing it shrank tumours in five patients (6.3%), with one seeing their tumours clear completely.
PFS was a median of 2.1 months and overall survival was around 8.3 months, according to the trial.
PD-1 inhibitors have a low response rate in this form of cancer, working in only around a fifth of patients as their tumours aren’t easily targeted by the immune system.
MacroGenics (tebotelimab) and Novartis (LAG525) are among around 20 companies that are researching LAG3 drugs.
Lymphocyte-activation gene 3 (LAG-3) and programmed death-1 (PD-1) are two distinct inhibitory immune checkpoints that are often co-expressed on tumour-infiltrating lymphocytes (TILs) – white blood cells that migrate to tumours attempting to kill them.
Tumours fight off the attack by stimulating LAG-3 and PD-1, causing the white blood cells to become exhausted.
The combination activates T-cells, beefing up the improved immune response and promoting tumour cell death.
The post LAG-3 drugs take centre stage at ASCO, showing potential as next-gen immunotherapies appeared first on .
from https://pharmaphorum.com/news/bms-lag3-combination-outperforms-opdivo-in-advanced-melanoma-trial/
0 notes
Photo

Bristol Myers Squibb Announces RELATIVITY-047, a Trial Evaluating Anti-LAG-3 Antibody Relatlimab and Opdivo (nivolumab) in Patients with Previously Untreated Metastatic or Unresectable Melanoma, Meets Primary Endpoint of Progression-Free Survival - Drugs.com MedNews
0 notes
Text
Lymphocyte Activation Gene - 3 Protein Market – Size, Growth, Outlook, and Analysis, 2018 - 2026
Immune checkpoint receptors such as lymphocyte activation gene - 3 (LAG-3) protein are found on cell surface of effector T cells and regulatory T cells (Tregs). T cells are a type of white blood cells that eliminate unhealthy or foreign cells that enter the immune system. Function of lymphocyte activation gene - 3 protein is to control T cell response, activation, and growth. Lymphocyte activation gene - 3 turns off the immune response when a T cell is activated to eliminate a target cell. This prevents the T cells from harming healthy cells. Moreover, lymphocyte activation gene - 3 protein is associated with T cell exhaustion in which the T cells become desensitized and lose their ability to function. LAG-3 is closely associated with regulation of cytotoxic T cells and regulatory T cells, which has attracted attention of researchers and manufacturers as a therapeutic target against cancer. In cancers, lymphocyte activation gene - 3 expressing exhausted cytotoxic t cells and regulatory T cells (Tregs) are found to be gathered at tumor locations.
Request Sample Copy Of This Report: https://www.coherentmarketinsights.com/insight/request-sample/2027
Lymphocyte Activation Gene - 3 Protein Market Drivers
Several drugs in clinical trials that target the LAG-3 protein, is expected to be a major factor contributing in global lymphocyte activation gene - 3 protein market growth over the forecast period. These drugs are still in the clinical trials in different phases. For instance, in 2017, BMS-986016 (Relatlimab)—developed by Bristol-Myers Squibb—in combination with Opdivo (nivolumab), effectively aided in treatment of advanced melanoma that was previously treated with anti-PD-1/PD-L1 therapy. The drug is in phase II clinical trial and its estimated study completion date is March 16, 2022.
Moreover, several other drugs such as MGD013 sponsored by MacroGenics (estimated study completion date - August 2022) and IMP321 (eftilagimod alpha) by Immutep (estimated study completion date is August 2019) that are in Phase 1 clinical trials, is expected to be a major factor contributing in global LAG-3 protein market growth over the forecast period.
Manufacturers and researchers are focused on development of novel therapies that aid in treatment of cancer. High prevalence of cancer is expected to boost growth of the market. According to National Cancer Institute, around 1,735,350 new cases of cancer are expected to be diagnosed in the U.S., in 2018. The most common types of cancer are lung cancer, breast cancer, prostate cancer, melanoma, bladder cancer, and others. According to Cancer Research UK, 2015, around 54,900 new cases of breast cancer are registered in the UK, which account for 15% of all new cancer cases, annually.
Download PDF Brochure @ https://www.coherentmarketinsights.com/insight/request-pdf/2027
Lymphocyte Activation Gene - 3 Protein Market Regional Insights
North America is expected to witness significant growth in the LAG -3 protein market over the forecast period. Robust pipeline of LAG-3 protein antibodies and the increasing demand for such drugs is expected to facilitate growth of the market, in the U.S. For instance, Bristol-Myers Squibb has Relatlimab in phase II clinical trials and Regeneron Pharmaceuticals Inc., in collaboration with Sanofi, has REGN3767 in phase I clinical trials, 2017.
Lymphocyte Activation Gene - 3 Protein Market Key Player
Key players operating in the global lymphocyte activation gene - 3 protein market include, Bristol-Myers Squibb, Icell Kealex Therapeutics, Incyte Corporation, MacroGenics, Inc., GlaxoSmithKline Plc, Crescendo Biologics Ltd, Regeneron Pharmaceuticals Inc., Sutro Biopharma Inc., Symphogen A/S, and Immutep Ltd.
Lymphocyte Activation Gene 3 Protein Market Taxonomy
The global lymphocyte activation gene - 3 protein market is segmented on the basis of drug, cancer type, and region. By Drug - BMS-986016 (Relatlimab), IMP321, IMP701, MGD013, Others,. By Cancer Type - Breast Cancer, Melanoma, Solid Tumors, Others,. By Region - North America, Europe, Asia Pacific, Latin America, Middle East, Africa,.
Click To Continue Reading On Lymphocyte Activation Gene 3 Protein Market
About Coherent Market Insights:
Coherent Market Insights is a prominent market research and consulting firm offering action-ready syndicated research reports, custom market analysis, consulting services, and competitive analysis through various recommendations related to emerging market trends, technologies, and potential absolute dollar opportunity.
Contact Us:
Mr. Shah Coherent Market Insights 1001 4th Ave, #3200 Seattle, WA 98154 Tel: +1-206-701-6702 Email: [email protected]
Visit our news Website: https://www.coherentwire.com/
#Lymphocyte Activation Gene - 3 Protein Market#Lymphocyte Activation Gene - 3 Protein Market size#Lymphocyte Activation Gene - 3 Protein Market growth
0 notes
Text
Novo imunoterápico para o melanoma avançado
Novo imunoterápico para o melanoma avançado
O acréscimo do novo inibidor do ponto de controle imunitário relatlimabe ao já comprovado nivolumabe no ensaio clínico de fase 3 RELATIVITY-047 aumentou significativamente a sobrevida livre de progressão da doença dos pacientes com melanoma avançado sem história de tratamento, em comparação à monoterapia com nivolumabe. Ambos os fármacos são da Bristol-Myers Squibb, que financiou o…

View On WordPress
0 notes
Text
Lymphocyte Activation Gene - 3 Protein Market Shows Expected Growth from 2018-2026
Immune checkpoint receptors such as lymphocyte activation gene - 3 (LAG-3) protein are found on cell surface of effector T cells and regulatory T cells (Tregs). T cells are a type of white blood cells that eliminate unhealthy or foreign cells that enter the immune system. Function of lymphocyte activation gene - 3 protein is to control T cell response, activation, and growth. Lymphocyte activation gene - 3 turns off the immune response when a T cell is activated to eliminate a target cell. This prevents the T cells from harming healthy cells. Moreover, lymphocyte activation gene - 3 protein is associated with T cell exhaustion in which the T cells become desensitized and lose their ability to function.
LAG-3 is closely associated with regulation of cytotoxic T cells and regulatory T cells, which has attracted attention of researchers and manufacturers as a therapeutic target against cancer. In cancers, lymphocyte activation gene - 3 expressing exhausted cytotoxic t cells and regulatory T cells (Tregs) are found to be gathered at tumor locations. Recent studies reported that inhibiting LAG-3 functions allows T cells to regain their cytotoxic function and affect tumor growth. There are several LAG-3 protein antibodies in the clinical trials, which are expected to further advance in clinical trials over the forecast period.
Lymphocyte Activation Gene - 3 Protein Market Drivers
Several drugs in clinical trials that target the LAG-3 protein, is expected to be a major factor contributing in global lymphocyte activation gene - 3 protein market growth over the forecast period. These drugs are still in the clinical trials in different phases. For instance, in 2017, BMS-986016 (Relatlimab)—developed by Bristol-Myers Squibb—in combination with Opdivo (nivolumab), effectively aided in treatment of advanced melanoma that was previously treated with anti-PD-1/PD-L1 therapy. The drug is in phase II clinical trial and its estimated study completion date is March 16, 2022.
Moreover, several other drugs such as MGD013 sponsored by MacroGenics (estimated study completion date - August 2022) and IMP321 (eftilagimod alpha) by Immutep (estimated study completion date is August 2019) that are in Phase 1 clinical trials, is expected to be a major factor contributing in global LAG-3 protein market growth over the forecast period.
Lymphocyte Activation Gene - 3 Protein Market Regional Insights
North America is expected to witness significant growth in the LAG -3 protein market over the forecast period. Robust pipeline of LAG-3 protein antibodies and the increasing demand for such drugs is expected to facilitate growth of the market, in the U.S. For instance, Bristol-Myers Squibb has Relatlimab in phase II clinical trials and Regeneron Pharmaceuticals Inc., in collaboration with Sanofi, has REGN3767 in phase I clinical trials, 2017.
High prevalence of various types of cancer in North America, Europe, and Asia Pacific region is expected to be a major factor contributing growth of the lymphocyte activation gene - 3 protein market over the forecast period. According to European Union (EU), in 2014, almost 1/3rd million people died from cancer in the EU-28. Moreover, manufacturers are focused on conducting clinical trials in these regions to expand their potential customer base.
Lymphocyte Activation Gene - 3 Protein Market Key Player
Key players operating in the global lymphocyte activation gene - 3 protein market include, Bristol-Myers Squibb, Icell Kealex Therapeutics, Incyte Corporation, MacroGenics, Inc., GlaxoSmithKline Plc, Crescendo Biologics Ltd, Regeneron Pharmaceuticals Inc., Sutro Biopharma Inc., Symphogen A/S, and Immutep Ltd.
Ask For Sample Copy Of This Business Research Report : https://www.coherentmarketinsights.com/insight/request-sample/2027
Lymphocyte Activation Gene 3 Protein Market Taxonomy
The global lymphocyte activation gene - 3 protein market is segmented on the basis of drug, cancer type, and region.
By Drug -
BMS-986016 (Relatlimab)
IMP321
IMP701
MGD013
Others
By Cancer Type -
Breast Cancer
Melanoma
Solid Tumors
Others
About Coherent Market Insights:
Coherent Market Insights is a prominent market research and consulting firm offering action-ready syndicated research reports, custom market analysis, consulting services, and competitive analysis through various recommendations related to emerging market trends, technologies, and potential absolute dollar opportunity.
Contact Us:
Mr. Shah Coherent Market Insights 1001 4th Ave, #3200 Seattle, WA 98154 Tel: +1-206-701-6702 Email: [email protected]
#Lymphocyte Activation Gene - 3 Protein Market Outlook#Lymphocyte Activation Gene - 3 Protein Market#Lymphocyte Activation Gene - 3 Protein Market Share#Lymphocyte Activation Gene - 3 Protein Market Size
0 notes
Text
Relatlimab plus nivolumab improves progression-free survival in metastatic melanoma
In patients with untreated, advanced melanoma, the combination of immune checkpoint inhibitors relatlimab and nivolumab doubled the progression-free survival benefit compared to nivolumab alone, with a manageable safety profile, according to the results of the Phase II/III RELATIVITY-047 clinical trial reported by The University of Texas MD Anderson Cancer Center today in the New England Journal of Medicine. Source Link Relatlimab plus nivolumab improves progression-free survival in metastatic melanoma
0 notes
Text
Mélanome au stade avancé : l'immunothérapie en premier améliore la chirurgie
Dans les mélanomes à haut risque de métastases, une association d’immunothérapies administrée avant la chirurgie est nettement plus efficace. Les protocoles thérapeutiques seront sans doute amenés à changer.
Aux stades avancés du mélanome, la chirurgie d’exérèse de la tumeur reste une option intéressante. Par contre, elle est souvent compliquée du fait de l’extension de la tumeur. Une chimiothérapie permet de réduire le volume tumoral pour faciliter la chirurgie : on appelle cela la chimiothérapie néoadjuvante. Dans le mélanome à un stade avancé, du fait du risque élevé de métastases et de la grande efficacité des immunothérapies, il était intéressant d’essayer une immunothérapie néoadjuvante. L’administration d’une association de 2 immunothérapies (anti-PD1 et anti-CTLA-4) avant la chirurgie donne un taux de réponse élevé chez les malades souffrant d’un mélanome de stade 3 à haut risque (3b, 3c) : près de la moitié des malades n’ont plus aucun signe de cancer au moment de la chirurgie, mais une incidence élevée d’effets secondaires a entraîné l’arrêt précoce de l’essai. Ces résultats sont publiés dans la revue Nature Medicine.
Une étude pilote innovante
L'étude de phase II a été menée par des chercheurs du MD Anderson Cancer Center, au Texas. Les malades ont reçu soit le nivolumab, un inhibiteur du PD-1 qui démasque les cellules cancéreuses vis-à-vis du système immunitaire, soit une association de nivolumab avec de l'ipilimumab, un inhibiteur du CTLA-4 qui stimule les cellules immunitaires T.
Chaque médicament ciblant un système de modulation immunitaire distinct sur les lymphocytes T, ils ont un effet additif, voire synergique, sur le système immunitaire pour stimuler la réponse lymphocytaire T vis-à-vis des cellules cancéreuses. Tous les patients ont reçu ensuite du nivolumab après la chirurgie.
Des résultats surprenants malgré le petit effectif de l’étude
Dans le groupe qui a reçu l’association, 8 patients sur 11 (73%) ont vu leur tumeur seéduire fortement et 5 (45%) n’avaient plus aucun signe de mélanome au moment de l'opération (réponse complète pathologique). Par contre, 73% des malades ont souffert d’effets indésirables de grade 3, entraînant un retard d'administration de la dose chez 64% d’entre eux et un retard de la chirurgie pour certains (pas d’effet secondaire de grade 4).
Dans le groupe qui n’a reçu que le nivolumab seul, 3 tumeurs sur 12 (25%) ont eu une diminution de volume de la tumeur ou une réponse pathologique complète. Par contre, seuls 8% des malades ont eu des effets indésirables de grade 3. Le problème est que 2 malades ont progressé vers un stade métastatique (stade 4) de la maladie avant de pouvoir se faire opérer.
Tous ceux qui ont obtenu une réponse complète pathologique dans l'un ou l'autre groupe demeurent indemnes de récidive de la maladie au terme de l’étude. La survie globale est de 100% à 24 mois dans le groupe association et de 75% dans le groupe nivolumab seul.
Identifier des biomarqueurs de réponse et de résistance
Dans cette étude, les chercheurs ont analysé des biopsies et des échantillons de sang prélevés à plusieurs moments au cours de l'essai. Ils ont ainsi confirmé les biomarqueurs connus de la réponse au traitement et observé de nouveaux biomarqueurs de la réponse thérapeutique. Les biopsies précoces au cours du traitement permettraient également d’identifier quels malades répondront à l’immunothérapie. L'infiltration initiale du tissu tumoral par les cellules lymphoïdes et l’importance des mutations dans les cellules du cancer (la charge mutationnelle totale) sont associées à la réponse à l’immunothérapie néoadjuvante.
En raison des résultats de cette étude, les chercheurs du MD Anderson Cancer Center ont repensé leur étude afin d’évaluer une autre association (nivolumab associé à relatlimab, un inhibiteur du point de contrôle immunitaire LAG3), une combinaison qui, selon eux, pourrait être plus efficace avec un meilleur profil d'effets secondaires. D’autre part, ils inscrivent désormais leur démarche dans un consortium international afin d’accélérer la recherche sur le mélanome de haut grade.
0 notes