#mosfet module mosfet explained
Explore tagged Tumblr posts
Text
https://www.futureelectronics.com/p/semiconductors--discretes--transistors--mosfets/dmg1012uw-7-diodes-incorporated-1004537
Transistor mosfet, High current mosfet , mosfet module mosfet explained
N-Channel 20 V 1 A 0.45 Ω Surface Mount Enhancement Mode Power MosFet - SOT-323
#Transistors#Mosfets#DMG1012UW-7#Diodes Incorporated#Mosfet Transistors#mosfet switch#mosfet model#Mosfet circuits#High current mosfet#mosfet module mosfet explained#mosfet applications#Power Mosfet#Mosfet vs transistor
1 note
·
View note
Text
https://www.futureelectronics.com/p/semiconductors--discretes--transistors--mosfets/irf4905strlpbf-infineon-8173863
Mosfet transistor, power mosfet, mosfet circuits, mosfet electronics
Single P-Channel 55 V 0.02 Ohm 180 nC HEXFET® Power Mosfet - D2PAK
#Infineon#IRF4905STRLPBF#Transistors#Mosfets#power mosfet#mosfet circuits#mosfet electronics#High voltage mosfet#high power mosfet#mosfet gate#mosfet power supply#High current mosfet#mosfet explained#mosfet module#audio mosfet
1 note
·
View note
Text
https://www.futureelectronics.com/p/semiconductors--discretes--transistors--mosfets/irfp4368pbf-infineon-9093816
Transistors, Mosfets, IRFP4368PBF, Infineon
Single N-Channel 75 V 1.85 mOhm 570 nC HEXFET® Power Mosfet - TO-247AC
#Transistors#Mosfets#IRFP4368PBF#Infineon#power supply#mosfet explained#power mosfet module#small signal mosfet#Power transistor#mosfet module#mosfet electronics#mosfet switch#Audio mosfet#mosfet gate#high voltage mosfet
1 note
·
View note
Text
Mosfet gate, mosfet model, power Mosfets, mosfet switch, mosfet module
1415898 RT1 Series SPST (1 Form A) 16 A 12 V PCB Mount General Purpose Power Relay
#TE Connectivity#1415898#Relays#Power Relays#Mosfet gate#mosfet model#power Mosfets#mosfet switch#mosfet module#Mosfet switch#high current mosfet#High current mosfet#mosfet explained#Mosfet transistor#Mosfet circuits
1 note
·
View note
Text
Transistor mosfet, mosfet driver, High current mosfet, mosfet explained
N-Channel 20 V 1 A 0.45 Ω Surface Mount Enhancement Mode Power MosFet - SOT-323
#Diodes Incorporated#DMG1012UW-7#Transistors#Mosfets#Transistor mosfet#mosfet driver#High current mosfet#mosfet explained#Mosfet transistor#Power MOSFET#Mosfet vs transistor#mosfet circuits#mosfet switch#how mosfet works#mosfet module
1 note
·
View note
Link
Exclusive selection of Metal Oxide Semiconductor Field Effect Transistor, shortly known as MOSFET available.
1 note
·
View note
Text
Mosfet power supply, mosfet explained, power mosfet module, small signal mosfet
Single N-Channel 30 V 80 mOhm 2.9 nC HEXFET® Power Mosfet - SOT-23
#Infineon#IRLML6346TRPBF#Transistors#Mosfets#Mosfet power supply#power mosfet module#small signal mosfet#Power transistor#mosfet uses#mosfet module#mosfet electronics#mosfet switch#Audio mosfet#mosfet gate#high voltage mosfet
1 note
·
View note
Text
Intelligent Power Module Market Size, Industry Growth, Sales Revenue, COVID-19 Market Scenario, Opportunity, and Industry Expansion Strategies to 2028
The report’s authors have offered necessary details on the latest Intelligent Power Module market trends and the crucial parameters impacting both short-term and long-term market growth. Its panoramic view of the Intelligent Power Module market entails useful insights into the estimated Intelligent Power Module market size, revenue share, and sales & distribution networks. Such helpful market insights are bound to help readers outline this industry’s key outcomes in the near future.
The global Intelligent power module market is expected to reach a market size of USD 3.78 Billion at a CAGR of 11.7% during the forecast period, according to the latest analysis by Emergen Research. This consistent growth in the revenue can be attributed to increasing adoption and research and development of electric and hybrid vehicles all around the world. The focus of major economies in the world to upgrade their power infrastructure is also a major factor in the growth of the market. Moreover, increased government funding in solar, wind and tidal projects further adds fuel to the market growth. Setting up of various new industries and expansion of already existing industries all around the world require electronic devices and equipment. This further adds to the development of the market.
Click the link to get info@ https://www.emergenresearch.com/industry-report/intelligent-power-module-market
The complete regional analysis covers:
North America (U.S., Canada, Mexico)
Europe (U.K., Italy, Germany, France, Rest of EU)
Asia Pacific (India, Japan, China, South Korea, Australia, Rest of APAC)
Latin America (Chile, Brazil, Argentina, Rest of Latin America)
Middle East & Africa (Saudi Arabia, U.A.E., South Africa, Rest of MEA)
Competitive Landscape:
The latest report encases an in-depth summary of the intensely competitive landscape of the global Synthetic Food market, with systematic profiling of the companies operating across this industry. In this section of the report, experts have listed down the strategic initiatives undertaken by these market rivals for proposed business expansion. Additionally, it highlights the key developments and financial positions of these companies to explain the overall market scenario. The company profiles of the established and new players have also been assessed in the report through effective analytical tools like SWOT analysis.
Major companies operating in Intelligent power module are Mitsubishi Electric Corporation, STMicroelectronics NV, ROHM Semiconductors, (Germany), Sanken Electric Co. Ltd, Texas Instruments Incorporated, ON Semiconductor, Fuji Electric Co. Ltd, Hon Hai Precision Industry Co., Ltd, Infineon Technologies, Central Semiconductor.
Key Highlights from the Report
In December 2020, the 1200V transfer molded silicon carbide (SIC) integrated power module was launched by Infineon Technologies AG. This has application in industrial motor drives and pump drives.
In April 2018, ACEPACK1 and ACEPACK 2 was launched by STMicroelectronics NV. These products were launched for the application in welding tools, solar panels and power management solutions.
In May 2017, CIPOS IPM was launched by Infineon Technologies AG. This provides a single switch boost by combining power factor correction and a 3-phase inverter.
For this report, Emergen Research has segmented the global intelligent power module market based on voltage rating, current rating, power devices, application and region.
Voltage Rating Outlook (Revenue, USD Billion; 2021–2028)
Current Rating Outlook (Revenue, USD Billion; 2021–2028)
Power Devices Outlook (Revenue, USD Billion; 2021–2028)
Application Outlook (Revenue, USD Billion; 2021–2028)
Up To 600V
601 V – 1200 V
Above 1200V
Up To 100 A
101 A – 600 A
Above 600 A
IGBT
MOSFET
Consumer Electronics
Industrial
ICT
Automotive
Aerospace & Defense
Thank you for reading our report. Customization of the report is available. To know more, please connect with us, and our team will ensure the report is customized as per your requirements.
Key takeaways of the Global Intelligent Power Module Market report:
Asia Pacific is expected to account for the largest revenue share during the forecast period. This growth can be attributed to the presense of major key players in the region.
The governments in the region are also adopting several policies to boost the projects related to the use of renewable energy source. Rising awareness about sustainable development in the region is also a driving factor in the growth of the market in the region.
In May 2017, CIPOS IPM was launched by Infineon Technologies AG. This provides a single switch boost by combining power factor correction and a 3-phase inverter.
Take a Look at our Related Reports:
smart building sensors market
https://www.google.com.br/url?q=https://www.emergenresearch.com/industry-report/smart-building-sensors-market
next generation ultrasound system market
https://www.google.com.br/url?q=https://www.emergenresearch.com/industry-report/next-generation-ultrasound-system-market
business intelligence and analytics platforms market
https://www.google.com.br/url?q=https://www.emergenresearch.com/industry-report/business-intelligence-and-analytics-platforms-market
cool roof coating market
https://www.google.com.br/url?q=https://www.emergenresearch.com/industry-report/cool-roof-coating-market
biobetters market
https://www.google.com.br/url?q=https://www.emergenresearch.com/industry-report/biobetters-market
smart oven market
https://www.google.com.br/url?q=https://www.emergenresearch.com/industry-report/smart-oven-market
UAS Traffic Management System Market
https://www.google.com.br/url?q=https://www.emergenresearch.com/industry-report/uas-traffic-management-system-market
Neoantigen Targeted Therapies Market
https://www.google.com.br/url?q=https://www.emergenresearch.com/industry-report/neoantigen-targeted-therapies-market
About Us:
At Emergen Research, we believe in advancing with technology. We are a growing market research and strategy consulting company with an exhaustive knowledge base of cutting-edge and potentially market-disrupting technologies that are predicted to become more prevalent in the coming decade.
Contact Us:
Eric Lee
Corporate Sales Specialist
Emergen Research | Web: www.emergenresearch.com
Direct Line: +1 (604) 757-9756
E-mail: [email protected]
Visit for More Insights: https://www.emergenresearch.com/insights
Explore Our Custom Intelligence services | Growth Consulting Services
0 notes
Text
Science and Chemistry Classes
Monolithic integration of GaN components boosts power integrated circuits
For decades, silicon-based power transistors (MOSFETs, field-effect transistors) formed the backbone of power conversion systems that convert alternating current (AC) into direct current (DC) and vice versa, or DC from low voltage to high voltage and vice versa. In the quest for alternatives that can drive up the switching speed, gallium nitride (GaN) quickly came forward as one of the leading candidate materials. The GaN/AlGaN materials system exhibits a higher electron mobility and higher critical electric field for breakdown. Combined with the high electron mobility transistor (HEMT) architecture, it results in devices and ICs that feature higher breakdown strength, faster switching speed, lower conductance losses and a smaller footprint than comparable silicon solutions.
Today, most GaN power systems are formed from multiple chips. GaN-based devices are assembled as discrete components before they are united on a printed circuit board. The downside of that approach is the presence of parasitic inductances that affects the performance of the devices. "Take a driver, for example. Discrete transistors with drivers on a separate chip suffer a lot from parasitic inductances between the output stages of the driver and the input of the transistor, and in the switching node of half bridges. GaN HEMTs have very high switching speed which leads to ringing, an unwanted oscillation of the signal, when the parasitic inductance is not suppressed. The best way to reduce the parasitics and exploit the superior switching speed of GaN is to integrate both driver and HEMT on the same chip," explains Stefaan Decoutere.
"At the same time, it reduces the dead-time control between two transistors in a half bridge, where one transistor has to switch off just as the other one switches on. During the time in between, there is a short-circuit between the power source and the ground, or dead time. Integrating all components on chip will address the ringing, reduce dead time, and ultimately improve the power efficiency of your converter."
Co-integration of d-mode HEMTs
Imec has already made tremendous progress monolithically integrating building blocks on a silicon-on-insulator (SOI) substrate such as drivers, half bridges, and control/protection circuits. Now, researchers have succeeded in adding two sought-after components to the portfolio: d-mode (depletion-mode) HEMTs and Schottky diodes.
One of the main hurdles to boost the full performance of GaN power ICs remains finding a suitable solution for the lack of p-channel devices in GaN with acceptable performance. CMOS technology uses complementary and more symmetrical pairs of p- and n-type FETs, based on the mobilities of holes and electrons for both types of FETs. However, in GaN, the mobility of holes is about 60 times worse than that of electrons; in silicon this is only a factor of 2. That means a p-channel device, where holes are the principal carriers, would be 60 times larger than the n-channel counterpart and highly inefficient. A widespread alternative is replacing the P-MOS with a resistor. Resistor-Transistor Logic (RTL) has been employed for GaN ICs but shows trade-offs between switching time and power consumption.

Schematic cross-section of IMEC 200V GaN-on-SOI Power IC technology and components. The process features monolithic co-integration of E/D mode HEMTs, Schottky diodes, resistors, capacitors, and includes advanced process modules.
"We have improved the performance of GaN ICs by co-integrating d-mode HEMTS on our functional e-mode HEMT platform on SOI. Enhancement and depletion mode refer to an ON (d-mode) or OFF (e-mode) state at zero source voltage, resulting in a current flow (or not) in the transistor. We expect that taking the step from RTL to direct-coupled FET logic will improve speed and reduce the power dissipation of the circuits," says Stefaan Decoutere.
Schottky diodes with low leak currents
The integration of a Schottky barrier diode further boosted the power efficiency of the GaN power ICs. In comparison with Si diodes, they can withstand higher voltages for the same ON-state resistance or lower ON-state resistance for the same breakdown voltage. "The challenge in making Schottky barrier diodes is to obtain low turn-on voltage and at the same time a low leakage level. Unfortunately, when you aim for lower turn-on voltages, you will end up with a small barrier to hold off the leakage current. And Schottky diodes are notorious for having high leak currents. Imec's proprietary Gate-Edge-Terminated Schottky Barrier Diode architecture (GET-SBD) results in a low turn-on voltage of about 0.8 Volt, while at the same time reduces the leakage current several orders of magnitude in comparison with conventional GaN Schottky barrier diodes," adds Stefaan Decoutere.

Process cross-sections of the high-voltage components fabricated on 200 mm GaN-on-SOI substrates (a) e-mode pGaN-HEMT (b) d-mode MIS-HEMT, (c) Schottky barrier diode. All devices include metal field plates based on front-end and interconnect metal layers and separated by dielectric layers
Fast switches and high voltages
GaN is the go-to material for high power applications because the critical voltage that induces breakdown of the transistor (breakdown voltage) lies 10 times higher than in silicon. But also for low-power applications GaN still has an edge over silicon because of its superior switching speed. "The GaN-based ICs we create, open the way towards smaller and more efficient DC/DC converters and Point-of-Load (PoL) converters. A smartphone, tablet or laptop for example, contain chips that work on different voltages, so they require AC/DC converters for charging the battery and PoL converters inside the devices for generating the different voltages. These components not only consist of a switch but also transformers, capacitors, and inductors. The faster the transistor can switch, the smaller these components become, ultimately resulting in a more compact and low-cost system for the same power."
Stefaan Decoutere: "Fast battery chargers form the largest market for GaN today, followed by power supplies for servers, automotive industry and renewable energy. It is expected that the power supplies using GaN are at the system level more reliable. They are smaller in form factor and weight, reducing the bill of materials and hence the cost."
Vertical devices under research

Characteristics of manufactured GET-SBDs showing (left) low turn-on voltage of 0.91V at 25°C in semi-log scale, and (right) low reverse leak currents (2 nA/mm for 25°C) for two different anode field plates configurations evaluated at 25 and 150°C.
"We will focus on improving the performance of the existing platform and perform further reliability tests. We currently offer a 200V and 650V platform for prototyping, soon to be followed by 100V. For GaN-ICs with integrated components, a 1200V high-power platform may not yield significant improvements. The higher the voltage, the slower the components become. Therefore, it may not be necessary to integrate the driver on chip; simulations will tell us."
"At the same time, we are looking into alternatives for discrete 1200V devices, enabling GaN technology for highest voltage power applications such as electric cars. Transistors with a lateral topology are the dominant GaN device architecture today. These devices have their three terminals (source, gate, and drain) at the surface in the same plane, so the electrical field is lateral, spanning the GaN buffer layers and partly the backend (metallization, oxide). In a vertical device, the source and gate are at the surface, while the drain is at the bottom of the epi stack. The electrical field in that case flows through the whole stack. It is the source-drain separation that determines the breakdown voltage of the device, and a larger separation safeguards the channel from breakdown. However, larger distances between a laterally-placed source and drain result in larger devices. Because the chips for 1200V devices would become too large, lateral architectures are usually advised up to 650V maximum. For a vertical device, on the contrary, going to higher voltages boils down to creating a thicker epi stack because source and drain are located on different ends of the stack. The chip's surface area doesn't increase," concludes Stefaan Decoutere.
0 notes
Text
Discrete Semiconductor Products
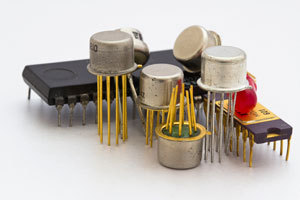
This week, we are talking about discrete semiconductor products!
What is a discrete semiconductor?
Various types of Semiconductors in the circuits make them different from other circuits. These circuits can perform several functions, and this feature differentiates them from discrete semiconductors. It has only a primary role. An integrated circuit can have different components on it, such as a diode, transistor, etc. They can either perform their functions in combination with other parts as a circuit or either on their own to perform several different functions. But it is not in the case of discrete semiconductors, which can only perform a single task (Dunion, 2018).
How is a discrete semiconductor made?
In the case of a semiconductor device, it is made up of silicon or various materials specially designed to exploit the distinctive features of electrons inside the crystal lattice. The electrons are not as far as the conductor, i.e., very much free to move, but they are more mobile than insulators. On the other hand, discrete devices contain their own packages that are not built on a semiconductor substrate and other components as in that of an integrated circuit. These circuits are made with individual parts connected on a terminal strip or a circuit board (Introduction to Discrete Semiconductor Circuits, n.d.).
What are different types of discrete semiconductors?
These are fundamental components in the field of electrical engineering and can be divided into various types. Some of its varieties are:
Bipolar Transistors:
These semiconductors, as explained by the term, carry both positive and negative charges, which means they have both holes and electrons involved in the operation. These are usually made a part of analog circuits. Bipolar transistors are generally sold as discrete units, but they are used quite frequently in integrated circuits.
Bridge Rectifiers:
It consists of diodes that are arranged in a configuration known as the namesake bridge. It performs a fundamental function, as per the electronic devices. It is designed to convert alternating current into direct current. They work having two-wire alternating current input. It is essential to combine them and other devices to perform the desired function since these are discrete devices. The semiconductors perform multiple functions that range from a switch to regulating power and a lot more. The discrete semiconductors are pretty inexpensive, due to which the production and prototyping become affordable.
Constant current diodes:
These perform differently from others as the design regulates current instead of voltage. The diode's current passing reaches up to a particular limit, and then it is leveled via a diode. These are available under various names such as CLD (Current limiting diodes), CRD (Current regulating diodes), and diode-connected transistors.
Darlington Transistors:
These amplify the current they are receiving and consist of a pair of transistors into a single one. The first transistor, when receiving the current, amplifies it. The second transistor amplifies it a bit more as per the requirement. These are primarily used for space optimization purposes as they take a lot less space on the board than two transistors connected discreetly.
DIACs:
These are mainly used for thyristors as triggers and are for TRIACs' triggering. The only difference between thyristors and the DIACs is the absence of gate electrodes in DIACs.
MOSFET transistors:
These are the most commonly used transistors that span digital and analog circuitry. These consist of four terminals. Out of those, three terminals are hooked up.
Unlike the types above, discrete semiconductors have different types: digital transistors, double triode valves, emitter-switched bipolar transistors, firing circuit commander modules, HEMT transistors, etc. (Dunion, 2018).
Where to buy discrete semiconductors?
For purchasing electronic components, the consumers are mainly dependent on the distribution networks apart from the manufacturers. In this concern, they require the best online service that caters to their requirements by supplying them with the best quality products at the appropriate time. To make sure that the customers are delivered the required electronic components BD electronics Ltd steps in. It is capable of providing the customers with components, including discrete semiconductors and various others. BD electronics Ltd has international networking with suppliers and manufacturers. We make sure that the customers are satisfied with the best possible service along with reasonable prices. These give us a competitive edge over our competitors due to fast and efficient delivery services and the maintenance of high standards in terms of our customers' functionality and satisfaction by ensuring their demands to meet within the shortest possible lead time.
For more info, visit our website!
#obsolete electronic components suppliers#bd electronics ltd#electronic components#semiconductor#electronics component
0 notes
Text
Mosfet 15a

Mosfet 15a 500v
Mosfet 100v 15a
Mosfet 60v 15a
Mosfet 15v
This post explains for the MOSFET PA110BDA.
Smart Filtering. As you select one or more parametric filters below, Smart Filtering will instantly disable any unselected values that would cause no results to be found. Applied Filters: Semiconductors Discrete Semiconductors Transistors MOSFET. Transistor Polarity = P-Channel Vds - Drain-Source Breakdown Voltage = 150 V.
The board is of high power MOS trigger switch driver module and control board with field-effect tube to adjust the electronic switch. It adopts imported double MOS parallel active output to show lower internal resistance,greater electric current and power. Besides it works at 15A,400W under common temperature which satisfies most devices usage. HAOYU Electronics High-power MOSFET Trigger Switch Drive Module MOSFET-Trigger-Switch-Module - Description The board is of high power MOS trigger switch driver module and control board with field-effect tube to adjust the electronic switch. It adopts imported double MOS parallel active output to show lower internal resistance,greater electric current and power. 2020 popular Mosfet 15a trends in Consumer Electronics, Electronic Components & Supplies, Home Improvement, Sports & Entertainment with Mosfet 15a and Mosfet 15a. Discover over 282 of our best selection of Mosfet 15a on AliExpress.com with top-selling Mosfet 15a brands. Shop the top 25 most popular Mosfet 15a at the best prices! MOSFET 150V, 15A, 40mΩ. A (1002kB) This N-Channel MOSFET is produced using an advanced PowerTrench ® process that has been tailored to minimize the on-state resistance while maintaining superior switching performance. R DS (on) = 31mΩ ( Typ.)@ V GS = 10V, I D = 15A. Low Gate Charge, Q G = 14.3nC ( Typ.) High Performance Trench.
The Part Number is PA110BDA.
The Package is TO-252 Type
The function of this transistor is Silicon N -hannel MOS Type Transistor.
Manufacturers : UNIKC Semiconductor
Image
Mosfet 15a 500v
Description : Silicon N Channel MOS Type Field Effect Transistor
Absolute Maximum Ratings (Tc = 25°C)
Microsoft office for mac os x 10.7 5 free download. Free switch download for mac. 1. Drain to source voltage : VDSS = 100 V 2. Gate to source voltage : VGSS = ± 20 V 3. Drain current : ID = 15 A 4. Drain power dissipation : PD =50 W 5. Single pulse avalanche energy : Eas = 14.8 mJ 6. Avalanche current : Iar = 5.4 A 7. Channel temperature : Tch = 150 °C 8. Storage temperature : Tstg = -55 to +150 °C

Mosfet 100v 15a
Pinout
PA110BDA PDF Datasheet
Mosfet 60v 15a
Posts related to ‘ MOSFET ‘
Part numberDescriptionCM2N65FCM2N65F – POWER MOSFETK10A60DR600V, N-Channel MOSFETJ377P-ch MOSFET, Vdss = -60V – ToshibaSUD50N06-36N-ch, 60V, MOSFET ( TO-252)85U03GHBVdss=30V, N-Ch MOSFET – APECIRF1730GIRF1730G – Power MOSFET(Vdss=400V/ Rds(on)=1.0ohm/ Id=3.7A)P9NK60ZN-Ch, 600V, 7A, Power MOSFET – STIRFZ24N55V, 17A, MOSFET (Transistor)P0603BDGP0603BDG – N-Channel Enhancement Mode MOSFETCS20N50CS20N50 – Silicon N-Channel Power MOSFET
Mosfet 15v
Related articles across the web

0 notes
Text
How to Transfer Data From One USB Hard Drive to Another USB
youtube
How to Transfer Data From One USB Hard Drive to Another USB |USB to USB data transfer cable (Unboxing + Review) | Transfer Files From USB Flash To Any Smartphone Without PC, ****************************************************************** If You Want To Purchase the Full Project or Software Code Mail Us: [email protected] Title Name Along With You-Tube Video Link Project Changes also Made according to Student Requirements http://svsembedded.com/ è https://www.svskits.in/ M1: +91 9491535690 è M2: +91 7842358459 ****************************************************************** 1. PEN DRIVE TO PEN DRIVE DATA TRANSFER USING RASPBERRY PI, 2. USB TO USB Data Transfer using Raspberry Pi, 3. Pendrive to pendrive data transfer without pc, 4. How to Transfer Data From One USB Hard Drive to Another, 5. How to Replace the Redmi Note 3/Redmi Note 3 Pro Screen, 6. USB TO USB Data Transfer using Raspberry Pi, 7. Micro USB Hub - Simultaneous Charging & OTG - works only on some Windows/Android devices, 8. DIY Very Easy and Simple to Make diy USB Speaker | Powerful Ultra Amplifier Circuit, 9. Portable Raspberry Pi 3 Project - Raspberry Pi Portable Computer, 10. Pen Drive Life Hack - How to Turn Usb Pendrive into OTG Pendrive, 11. USB to USB data transfer cable (Unboxing + Review), 12. Easy Transfer 3 in 1 OTG USB Flash Drive for Android, iPhone & Computer, 13. Water Cooled Raspberry Pi 3, 14. How to Replace the Xiaomi Mi Max Screen, 15. Creating rawprogram.xml and patch for flashing LG Qualacomm mobiles, 16. Transfer Files From USB Flash To Any Smartphone Without PC, 17. Arduino based women safety security system using gsm and gps modem, 18. Raspberry Pi Mount a USB Drive, 19. Mobile to Pen Drive Data Transfer in 5 Seconds, 20. Simple Basic audio Amplifier Circuit using 1 MOSFET Transistor, 21. How to Copy Data from Laptop to Pen drive, Computer to Pen Drive to Laptop, Computer, 22. Smart Garbage Collecting Truck Using Arduino, GSM, GPS and Internet of Things (IOT), 23. How to Assemble or Build a Computer - easy way, 24. program arduino with android smartphone, 25. Android Phone to Pen Drive Directly Transfer Images, Video, Music & All Date, 26. How to transfer files to Pendrive using OTG cable in Moto G4 Plus December 2020, 27. RJ45 Crimping Tutorial - Straight Cable Crimping - Network Cable Color Code, 28. HOW TO SEND FILES COMPUTER TO PENDRIVE, 29. How to Copy or Transfer Data from a USB Flash Drive to a Computer, 30. How to use a pen drive with android to transfer DSLR pics without a computer, 31. WiFi Home Door Lock| Blynk | iot project, 32. Don't buy a GSM module, use your old phone, 33. Computer Basics: Hardware, 34. Basic concept of Arduino in Hindi | Arduino tutorials for beginners part, 35. Control Your Room Lights With Your Mobile | Make Your Home "Smart" | Arduino Uno FULL Setup, 36. Raspberry Pi Reading Car Diagnostics – Data, 37. Hand Gesture Controlled Robot using Arduino | How to Make a Gesture Control Robot, 38. Top 10 IoT(Internet Of Things) Projects Of All Time | 2020, 39. What is Arduino? Arduino Projects? Arduino Vs Raspberry Pi3, 40. DHCP Explained - Dynamic Host Configuration Protocol, 41. Network Troubleshooting using PING, TRACERT, IPCONFIG, NSLOOKUP COMMANDS, 42. How to Format a Drive using Command Prompt, 43. How to configure a Shared Network Printer in Windows, 44. Four Distributed Systems Architectural Patterns by Tim Berglund, 45. LET`S BUILD - my first Raspberry Pi SMART MIRROR, 46. Arduino RFID Sensor (MFRC522) Tutorial, 47. Android Studio For Beginners Part
1 note
·
View note
Text
How to prepare the PCB before the industrialization
Nowadays technologies are driven by the development of both software and hardware. However, if software program writing is related to the programmers’ skills, hardware crafting requires more technical specifics to be optimized, especially concerning electronic hardware.
Thus, as the basis of electronic hardware, Printing Circuit Boards (PCBs) crafting necessitates particular processes to be efficiently performed.
The expert will explain the inner working of PCBs manufacturing :
In this article, I will be talking very much on the surface, covering all the important steps involved in the electronic development process in order to make it understandable for all.
“My perception and experiences with PCB suppliers and manufacturers led me to determine an approach to craft my own PCBs in 3 phases: prototyping, design, and industrialization.”
However, this article will be focused on the two first phases.
Prototyping:
The 1st phase of PCB manufacturing is the Prototyping which is the most important base of electronic development. Any development starts with an emergence of new idea or improvement of some existing solutions/products.
In any case, you need to validate your idea in real-time. The very first step is the choice of Electronic Development Board (EDB) and is followed by the associated components like sensors, actuators, power modules, and connectors, etc.
EDB
The choice of EDB usually depends upon the following parameters :
· Microcontroller or FPGA : this depends upon the choice of your architecture and also your comfort of working, price etc.
· IO Pins : The access to the outside peripherals, it depends on the number of peripherals you want to communicate with.
· Clock Speed : This is one of the factors which decides the processing speed.
· System on Chip (SoC) facilities (Eg. Bluetooth, Wifi etc).
· Kind of use/ application
· Availability of technical information and support
· Ease of embedded programming or Integrated Development Environment (IDE)
(Be more specific about the involvement of the parameters, you could draw up a list of questions the engineer must ask himself (e.g. In which case Microcontroller is better than FPGA? )
Components
Once the EDB choice is done, the next step is to choose your components. Thus this is important to :
· Read the datasheet very carefully; mainly supply voltage, communication protocol etc, so that you can easily interface the components with your EDB
· Be careful of the power consumption and/or operating current. For example, actuators often need more power than EDB capacity. In that case, you need to use separated power supply and some interfacing power transistors/ MOSFETs (e.g. TP120)
Electronic Prototyping mainly consists in the following two phases:
The Functional Validation phase
The Testing and Debugging phase
This simply means realizing in real-time the hardware of your idea and make it work. In most of the cases, electronic circuits won’t work because of one specific parameter.
For example, voltage supply changing, radio noise/ interferences, overheat, embedded software performances or power consumption problems are factors that work in interaction with the others, which means you have to configure each component taking into account all the other components.
In that case, you need to test and debug all these problems one by one and iterate the test methods until the final objective is reached.
Circuit Design
Circuit design mainly consists of
· Schematic Design
· Simulation (Either partial or for full circuit)
· PCB routing and design.
Schematic Design
Once your prototype is functional then it comes to circuit design. A basic electronic prototype includes :
· Bread Board
· Components
· Connecting wires
· EDB
· Power Modules
· Wireless Modules
· Antenna
· Antenna Circuitry
Now you need to transform all these into one single circuit. In order to do that we must start with the circuit of EDB and study in detail microcontroller or FPGA datasheet. Generally, in an EDB there are many electronic components that are not used for your circuit because these boards are designed for generic use.
0 notes
Link
0 notes
