#mcluhan lecture
Explore tagged Tumblr posts
Text
My McLuhan lecture on enshittification

IT'S THE LAST DAY for the Kickstarter for the audiobook of The Bezzle, the sequel to Red Team Blues, narrated by @wilwheaton! You can pre-order the audiobook and ebook, DRM free, as well as the hardcover, signed or unsigned. There's also bundles with Red Team Blues in ebook, audio or paperback.

youtube
Last night, I gave the annual Marshall McLuhan lecture at the Transmediale festival in Berlin. The event was sold out and while there's a video that'll be posted soon, they couldn't get a streaming setup installed in the Canadian embassy, where the talk was held:
https://transmediale.de/en/2024/event/mcluhan-2024
The talk went of fabulously, and was followed by commentary from Frederike Kaltheuner (Human Rights Watch) and a discussion moderated by Helen Starr. While you'll have to wait a bit for the video, I thought that I'd post my talk notes from last night for the impatient among you.
I want to thank the festival and the embassy staff for their hard work on an excellent event. And now, on to the talk!
Last year, I coined the term 'enshittification,' to describe the way that platforms decay. That obscene little word did big numbers, it really hit the zeitgeist. I mean, the American Dialect Society made it their Word of the Year for 2023 (which, I suppose, means that now I'm definitely getting a poop emoji on my tombstone).
So what's enshittification and why did it catch fire? It's my theory explaining how the internet was colonized by platforms, and why all those platforms are degrading so quickly and thoroughly, and why it matters – and what we can do about it.
We're all living through the enshittocene, a great enshittening, in which the services that matter to us, that we rely on, are turning into giant piles of shit.
It's frustrating. It's demoralizing. It's even terrifying.
I think that the enshittification framework goes a long way to explaining it, moving us out of the mysterious realm of the 'great forces of history,' and into the material world of specific decisions made by named people – decisions we can reverse and people whose addresses and pitchfork sizes we can learn.
Enshittification names the problem and proposes a solution. It's not just a way to say 'things are getting worse' (though of course, it's fine with me if you want to use it that way. It's an English word. We don't have der Rat für Englisch Rechtschreibung. English is a free for all. Go nuts, meine Kerle).
But in case you want to use enshittification in a more precise, technical way, let's examine how enshittification works.
It's a three stage process: First, platforms are good to their users; then they abuse their users to make things better for their business customers; finally, they abuse those business customers to claw back all the value for themselves. Then, they die.
Let's do a case study. What could be better than Facebook?
Facebook is a company that was founded to nonconsensually rate the fuckability of Harvard undergrads, and it only got worse after that.
When Facebook started off, it was only open to US college and high-school kids with .edu and k-12.us addresses. But in 2006, it opened up to the general public. It told them: “Yes, I know you’re all using Myspace. But Myspace is owned by Rupert Murdoch, an evil, crapulent senescent Australian billionaire, who spies on you with every hour that God sends.
“Sign up with Facebook and we will never spy on you. Come and tell us who matters to you in this world, and we will compose a personal feed consisting solely of what those people post for consumption by those who choose to follow them.”
That was stage one. Facebook had a surplus — its investors’ cash — and it allocated that surplus to its end-users. Those end-users proceeded to lock themselves into FB. FB — like most tech businesses — has network effects on its side. A product or service enjoys network effects when it improves as more people sign up to use it. You joined FB because your friends were there, and then others signed up because you were there.
But FB didn’t just have high network effects, it had high switching costs. Switching costs are everything you have to give up when you leave a product or service. In Facebook’s case, it was all the friends there that you followed and who followed you. In theory, you could have all just left for somewhere else; in practice, you were hamstrung by the collective action problem.
It’s hard to get lots of people to do the same thing at the same time. You and your six friends here are going to struggle to agree on where to get drinks after tonight's lecture. How were you and your 200 Facebook friends ever gonna agree on when it was time to leave Facebook, and where to go?
So FB’s end-users engaged in a mutual hostage-taking that kept them glued to the platform. Then FB exploited that hostage situation, withdrawing the surplus from end-users and allocating it to two groups of business customers: advertisers, and publishers.
To the advertisers, FB said, 'Remember when we told those rubes we wouldn’t spy on them? We lied. We spy on them from asshole to appetite. We will sell you access to that surveillance data in the form of fine-grained ad-targeting, and we will devote substantial engineering resources to thwarting ad-fraud. Your ads are dirt cheap to serve, and we’ll spare no expense to make sure that when you pay for an ad, a real human sees it.'
To the publishers, FB said, 'Remember when we told those rubes we would only show them the things they asked to see? We lied!Upload short excerpts from your website, append a link, and we will nonconsensually cram it into the eyeballs of users who never asked to see it. We are offering you a free traffic funnel that will drive millions of users to your website to monetize as you please, and those users will become stuck to you when they subscribe to your feed.' And so advertisers and publishers became stuck to the platform, too, dependent on those users.
The users held each other hostage, and those hostages took the publishers and advertisers hostage, too, so that everyone was locked in.
Which meant it was time for the third stage of enshittification: withdrawing surplus from everyone and handing it to Facebook’s shareholders.
For the users, that meant dialing down the share of content from accounts you followed to a homeopathic dose, and filling the resulting void with ads and pay-to-boost content from publishers.
For advertisers, that meant jacking up prices and drawing down anti-fraud enforcement, so advertisers paid much more for ads that were far less likely to be seen by a person.
For publishers, this meant algorithmically suppressing the reach of their posts unless they included an ever-larger share of their articles in the excerpt, until anything less than fulltext was likely to be be disqualified from being sent to your subscribers, let alone included in algorithmic suggestion feeds.
And then FB started to punish publishers for including a link back to their own sites, so they were corralled into posting fulltext feeds with no links, meaning they became commodity suppliers to Facebook, entirely dependent on the company both for reach and for monetization, via the increasingly crooked advertising service.
When any of these groups squawked, FB just repeated the lesson that every tech executive learned in the Darth Vader MBA: 'I have altered the deal. Pray I don’t alter it any further.'
Facebook now enters the most dangerous phase of enshittification. It wants to withdraw all available surplus, and leave just enough residual value in the service to keep end users stuck to each other, and business customers stuck to end users, without leaving anything extra on the table, so that every extractable penny is drawn out and returned to its shareholders.
But that’s a very brittle equilibrium, because the difference between “I hate this service but I can’t bring myself to quit it,” and “Jesus Christ, why did I wait so long to quit? Get me the hell out of here!” is razor thin
All it takes is one Cambridge Analytica scandal, one whistleblower, one livestreamed mass-shooting, and users bolt for the exits, and then FB discovers that network effects are a double-edged sword.
If users can’t leave because everyone else is staying, when when everyone starts to leave, there’s no reason not to go, too.
That’s terminal enshittification, the phase when a platform becomes a pile of shit. This phase is usually accompanied by panic, which tech bros euphemistically call 'pivoting.'
Which is how we get pivots like, 'In the future, all internet users will be transformed into legless, sexless, low-polygon, heavily surveilled cartoon characters in a virtual world called "metaverse," that we ripped off from a 25-year-old satirical cyberpunk novel.'
That's the procession of enshittification. If enshittification were a disease, we'd call that enshittification's "natural history." But that doesn't tell you how the enshittification works, nor why everything is enshittifying right now, and without those details, we can't know what to do about it.
What led to the enshittocene? What is it about this moment that led to the Great Enshittening? Was it the end of the Zero Interest Rate Policy? Was it a change in leadership at the tech giants? Is Mercury in retrograde?
None of the above.
The period of free fed money certainly led to tech companies having a lot of surplus to toss around. But Facebook started enshittifying long before ZIRP ended, so did Amazon, Microsoft and Google.
Some of the tech giants got new leaders. But Google's enshittification got worse when the founders came back to oversee the company's AI panic (excuse me, 'AI pivot').
And it can't be Mercury in retrograde, because I'm a cancer, and as everyone knows, cancers don't believe in astrology.
When a whole bunch of independent entities all change in the same way at once, that's a sign that the environment has changed, and that's what happened to tech.
Tech companies, like all companies, have conflicting imperatives. On the one hand, they want to make money. On the other hand, making money involves hiring and motivating competent staff, and making products that customers want to buy. The more value a company permits its employees and customers to carve off, the less value it can give to its shareholders.
The equilibrium in which companies produce things we like in honorable ways at a fair price is one in which charging more, worsening quality, and harming workers costs more than the company would make by playing dirty.
There are four forces that discipline companies, serving as constraints on their enshittificatory impulses.
First: competition. Companies that fear you will take your business elsewhere are cautious about worsening quality or raising prices.
Second: regulation. Companies that fear a regulator will fine them more than they expect to make from cheating, will cheat less.
These two forces affect all industries, but the next two are far more tech-specific.
Third: self-help. Computers are extremely flexible, and so are the digital products and services we make from them. The only computer we know how to make is the Turing-complete Von Neumann machine, a computer that can run every valid program.
That means that users can always avail themselves of programs that undo the anti-features that shift value from them to a company's shareholders. Think of a board-room table where someone says, 'I've calculated that making our ads 20% more invasive will net us 2% more revenue per user.'
In a digital world, someone else might well say 'Yes, but if we do that, 20% of our users will install ad-blockers, and our revenue from those users will drop to zero, forever.'
This means that digital companies are constrained by the fear that some enshittificatory maneuver will prompt their users to google, 'How do I disenshittify this?'
Fourth and finally: workers. Tech workers have very low union density, but that doesn't mean that tech workers don't have labor power. The historical "talent shortage" of the tech sector meant that workers enjoyed a lot of leverage over their bosses. Workers who disagreed with their bosses could quit and walk across the street and get another job – a better job.
They knew it, and their bosses knew it. Ironically, this made tech workers highly exploitable. Tech workers overwhelmingly saw themselves as founders in waiting, entrepreneurs who were temporarily drawing a salary, heroic figures of the tech mission.
That's why mottoes like Google's 'don't be evil' and Facebook's 'make the world more open and connected' mattered: they instilled a sense of mission in workers. It's what Fobazi Ettarh calls 'vocational awe, 'or Elon Musk calls being 'extremely hardcore.'
Tech workers had lots of bargaining power, but they didn't flex it when their bosses demanded that they sacrifice their health, their families, their sleep to meet arbitrary deadlines.
So long as their bosses transformed their workplaces into whimsical 'campuses,' with gyms, gourmet cafeterias, laundry service, massages and egg-freezing, workers could tell themselves that they were being pampered – rather than being made to work like government mules.
But for bosses, there's a downside to motivating your workers with appeals to a sense of mission, namely: your workers will feel a sense of mission. So when you ask them to enshittify the products they ruined their health to ship, workers will experience a sense of profound moral injury, respond with outrage, and threaten to quit.
Thus tech workers themselves were the final bulwark against enshittification,
The pre-enshittification era wasn't a time of better leadership. The executives weren't better. They were constrained. Their worst impulses were checked by competition, regulation, self-help and worker power.
So what happened?
One by one, each of these constraints was eroded until it dissolved, leaving the enshittificatory impulse unchecked, ushering in the enshittoscene.
It started with competition. From the Gilded Age until the Reagan years, the purpose of competition law was to promote competition. US antitrust law treated corporate power as dangerous and sought to blunt it. European antitrust laws were modeled on US ones, imported by the architects of the Marshall Plan.
But starting in the neoliberal era, competition authorities all over the world adopted a doctrine called 'consumer welfare,' which held that monopolies were evidence of quality. If everyone was shopping at the same store and buying the same product, that meant it was the best store, selling the best product – not that anyone was cheating.
And so all over the world, governments stopped enforcing their competition laws. They just ignored them as companies flouted them. Those companies merged with their major competitors, absorbed small companies before they could grow to be big threats. They held an orgy of consolidation that produced the most inbred industries imaginable, whole sectors grown so incestuous they developed Habsburg jaws, from eyeglasses to sea freight, glass bottles to payment processing, vitamin C to beer.
Most of our global economy is dominated by five or fewer global companies. If smaller companies refuse to sell themselves to these cartels, the giants have free rein to flout competition law further, with 'predatory pricing' that keeps an independent rival from gaining a foothold.
When Diapers.com refused Amazon's acquisition offer, Amazon lit $100m on fire, selling diapers way below cost for months, until diapers.com went bust, and Amazon bought them for pennies on the dollar, and shut them down.
Competition is a distant memory. As Tom Eastman says, the web has devolved into 'five giant websites filled with screenshots of text from the other four,' so these giant companies no longer fear losing our business.
Lily Tomlin used to do a character on the TV show Laugh In, an AT&T telephone operator who'd do commercials for the Bell system. Each one would end with her saying 'We don't care. We don't have to. We're the phone company.'
Today's giants are not constrained by competition.
They don't care. They don't have to. They're Google.
That's the first constraint gone, and as it slipped away, the second constraint – regulation – was also doomed.
When an industry consists of hundreds of small- and medium-sized enterprises, it is a mob, a rabble. Hundreds of companies can't agree on what to tell Parliament or Congress or the Commission. They can't even agree on how to cater a meeting where they'd discuss the matter.
But when a sector dwindles to a bare handful of dominant firms, it ceases to be a rabble and it becomes a cartel.
Five companies, or four, or three, or two, or just one company finds it easy to converge on a single message for their regulators, and without "wasteful competition" eroding their profits, they have plenty of cash to spread around.
Like Facebook, handing former UK deputy PM Nick Clegg millions every year to sleaze around Europe, telling his former colleagues that Facebook is the only thing standing between 'European Cyberspace' and the Chinese Communist Party.
Tech's regulatory capture allows it to flout the rules that constrain less concentrated sectors. They can pretend that violating labor, consumer and privacy laws is fine, because they violate them with an app.
This is why competition matters: it's not just because competition makes companies work harder and share value with customers and workers, it's because competition keeps companies from becoming too big to fail, and too big to jail.
Now, there's plenty of things we don't want improved through competition, like privacy invasions. After the EU passed its landmark privacy law, the GDPR, there was a mass-extinction event for small EU ad-tech companies. These companies disappeared en masse, and that's fine.
They were even more invasive and reckless than US-based Big Tech companies. After all, they had less to lose. We don't want competition in commercial surveillance. We don't want to produce increasing efficiency in violating our human rights.
But: Google and Facebook – who pretend they are called Alphabet and Meta – have been unscathed by European privacy law. That's not because they don't violate the GDPR (they do!). It's because they pretend they are headquartered in Ireland, one of the EU's most notorious corporate crime-havens.
And Ireland competes with the EU other crime havens – Malta, Luxembourg, Cyprus and sometimes the Netherlands – to see which country can offer the most hospitable environment for all sorts of crimes. Because the kind of company that can fly an Irish flag of convenience is mobile enough to change to a Maltese flag if the Irish start enforcing EU laws.
Which is how you get an Irish Data Protection Commission that processes fewer than 20 major cases per year, while Germany's data commissioner handles more than 500 major cases, even though Ireland is nominal home to the most privacy-invasive companies on the continent.
So Google and Facebook get to act as though they are immune to privacy law, because they violate the law with an app; just like Uber can violate labor law and claim it doesn't count because they do it with an app.
Uber's labor-pricing algorithm offers different drivers different payments for the same job, something Veena Dubal calls 'algorithmic wage discrimination.' If you're more selective about which jobs you'll take, Uber will pay you more for every ride.
But if you take those higher payouts and ditch whatever side-hustle let you cover your bills which being picky about your Uber drives, Uber will incrementally reduce the payment, toggling up and down as you grow more or less selective, playing you like a fish on a line until you eventually – inevitably – lose to the tireless pricing robot, and end up stuck with low wages and all your side-hustles gone.
Then there's Amazon, which violates consumer protection laws, but says it doesn't matter, because they do it with an app. Amazon makes $38b/year from its 'advertising' system. 'Advertising' in quotes because they're not selling ads, they're selling placements in search results.
The companies that spend the most on 'ads' go to the top, even if they're offering worse products at higher prices. If you click the first link in an Amazon search result, on average you will pay a 29% premium over the best price on the service. Click one of the first four items and you'll pay a 25% premium. On average you have to go seventeen items down to find the best deal on Amazon.
Any merchant that did this to you in a physical storefront would be fined into oblivion. But Amazon has captured its regulators, so it can violate your rights, and say, "it doesn't count, we did it with an app"
This is where that third constraint, self-help, would sure come in handy. If you don't want your privacy violated, you don't need to wait for the Irish privacy regulator to act, you can just install an ad-blocker.
More than half of all web users are blocking ads. But the web is an open platform, developed in the age when tech was hundreds of companies at each others' throats, unable to capture their regulators.
Today, the web is being devoured by apps, and apps are ripe for enshittification. Regulatory capture isn't just the ability to flout regulation, it's also the ability to co-opt regulation, to wield regulation against your adversaries.
Today's tech giants got big by exploiting self-help measures. When Facebook was telling Myspace users they needed to escape Rupert Murdoch’s evil crapulent Australian social media panopticon, it didn’t just say to those Myspacers, 'Screw your friends, come to Facebook and just hang out looking at the cool privacy policy until they get here'
It gave them a bot. You fed the bot your Myspace username and password, and it would login to Myspace and pretend to be you, and scrape everything waiting in your inbox, copying it to your FB inbox, and you could reply to it and it would autopilot your replies back to Myspace.
When Microsoft was choking off Apple's market oxygen by refusing to ship a functional version of Microsoft Office for the Mac – so that offices were throwing away their designers' Macs and giving them PCs with upgraded graphics cards and Windows versions of Photoshop and Illustrator – Steve Jobs didn't beg Bill Gates to update Mac Office.
He got his technologists to reverse-engineer Microsoft Office, and make a compatible suite, the iWork Suite, whose apps, Pages, Numbers and Keynote could perfectly read and write Microsoft's Word, Excel and Powerpoint files.
When Google entered the market, it sent its crawler to every web server on Earth, where it presented itself as a web-user: 'Hi! Hello! Do you have any web pages? Thanks! How about some more? How about more?'
But every pirate wants to be an admiral. When Facebook, Apple and Google were doing this adversarial interoperability, that was progress. If you try to do it to them, that's piracy.
Try to make an alternative client for Facebook and they'll say you violated US laws like the Digital Millennium Copyright Act and EU laws like Article 6 of the EUCD.
Try to make an Android program that can run iPhone apps and play back the data from Apple's media stores and they'd bomb you until the rubble bounced.
Try to scrape all of Google and they'll nuke you until you glowed.
Tech's regulatory capture is mind-boggling. Take that law I mentioned earlier, Section 1201 of the Digital Millennium Copyright Act or DMCA. Bill Clinton signed it in 1998, and the EU imported it as Article 6 of the EUCD in 2001
It is a blanket prohibition on removing any kind of encryption that restricts access to a copyrighted work – things like ripping DVDs or jailbreaking a phone – with penalties of a five-year prison sentence and a $500k fine for a first offense.
This law has been so broadened that it can be used to imprison creators for granting access to their own creations
Here's how that works: In 2008, Amazon bought Audible, an audiobook platform, in an anticompetitive acquisition. Today, Audible is a monopolist with more than 90% of the audiobook market. Audible requires that all creators on their platform sell with Amazon's "digital rights management," which locks it to Amazon's apps.
So say I write a book, then I read it into a mic, then I pay a director and an engineer thousands of dollars to turn that into an audiobook, and sell it to you on the monopoly platform, Audible, that controls more than 90% of the market.
If I later decide to leave Amazon and want to let you come with me to a rival platform, I am out of luck. If I supply you with a tool to remove Amazon's encryption from my audiobook, so you can play it in another app, I commit a felony, punishable by a 5-year sentence and a half-million-dollar fine, for a first offense.
That's a stiffer penalty than you would face if you simply pirated the audiobook from a torrent site. But it's also harsher than the punishment you'd get for shoplifting the audiobook on CD from a truck-stop. It's harsher than the sentence you'd get for hijacking the truck that delivered the CD.
So think of our ad-blockers again. 50% of web users are running ad-blockers. 0% of app users are running ad-blockers, because adding a blocker to an app requires that you first remove its encryption, and that's a felony (Jay Freeman calls this 'felony contempt of business-model').
So when someone in a board-room says, 'let's make our ads 20% more obnoxious and get a 2% revenue increase,' no one objects that this might prompt users to google, 'how do I block ads?' After all, the answer is, 'you can't.'
Indeed, it's more likely that someone in that board room will say, 'let's make our ads 100% more obnoxious and get a 10% revenue increase' (this is why every company wants you to install an app instead of using its website).
There's no reason that gig workers who are facing algorithmic wage discrimination couldn't install a counter-app that coordinated among all the Uber drivers to reject all jobs unless they reach a certain pay threshold.
No reason except felony contempt of business model, the threat that the toolsmiths who built that counter-app would go broke or land in prison, for violating DMCA 1201, the Computer Fraud and Abuse Act, trademark, copyright, patent, contract, trade secrecy, nondisclosure and noncompete, or in other words: 'IP law.'
'IP' is just a euphemism for 'a law that lets me reach beyond the walls of my company and control the conduct of my critics, competitors and customers.' And 'app' is just a euphemism for 'a web-page wrapped enough IP to make it a felony to mod it to protect the labor, consumer and privacy rights of its user.'
We don't care. We don't have to. We're the phone company.
But what about that fourth constraint: workers?
For decades, tech workers' high degrees of bargaining power and vocational awe put a ceiling on enshittification. Even after the tech sector shrank to a handful of giants. Even after they captured their regulators so they could violate our consumer, privacy and labor rights. Even after they created 'felony contempt of business model' and extinguished self-help for tech users. Tech was still constrained by their workers' sense of moral injury in the face of the imperative to enshittify.
Remember when tech workers dreamed of working for a big company for a few years, before striking out on their own to start their own company that would knock that tech giant over?
Then that dream shrank to: work for a giant for a few years, quit, do a fake startup, get acqui-hired by your old employer, as a complicated way of getting a bonus and a promotion.
Then the dream shrank further: work for a tech giant for your whole life, get free kombucha and massages on Wednesdays.
And now, the dream is over. All that’s left is: work for a tech giant until they fire your ass, like those 12,000 Googlers who got fired last year six months after a stock buyback that would have paid their salaries for the next 27 years.
Workers are no longer a check on their bosses' worst impulses
Today, the response to 'I refuse to make this product worse' is, 'turn in your badge and don't let the door hit you in the ass on the way out.'
I get that this is all a little depressing
OK, really depressing.
But hear me out! We've identified the disease. We've traced its natural history. We've identified its underlying mechanism. Now we can get to work on a cure.
There are four constraints that prevent enshittification: competition, regulation, self-help and labor.
To reverse enshittification and guard against its reemergence, we must restore and strengthen each of these.
On competition, it's actually looking pretty good. The EU, the UK, the US, Canada, Australia, Japan and China are all doing more on competition than they have in two generations. They're blocking mergers, unwinding existing ones, taking action on predatory pricing and other sleazy tactics.
Remember, in the US and Europe, we already have the laws to do this – we just stopped enforcing them in the Helmut Kohl era.
I've been fighting these fights with the Electronic Frontier Foundation for 22 years now, and I've never seen a more hopeful moment for sound, informed tech policy.
Now, the enshittifiers aren't taking this laying down. The business press can't stop talking about how stupid and old-fashioned all this stuff is. They call people like me 'hipster antitrust,' and they hate any regulator who actually does their job.
Take Lina Khan, the brilliant head of the US Federal Trade Commission, who has done more in three years on antitrust than the combined efforts of all her predecessors over the past 40 years. Rupert Murdoch's Wall Street Journal has run more than 80 editorials trashing Khan, insisting that she's an ineffectual ideologue who can't get anything done.
Sure, Rupert, that's why you ran 80 editorials about her.
Because she can't get anything done.
Even Canada is stepping up on competition. Canada! Land of the evil billionaire! From Ted Rogers, who owns the country's telecoms; to Galen Weston, who owns the country's grocery stores; to the Irvings, who basically own the entire province of New Brunswick.
Even Canada is doing something about this. Last autumn, Trudeau's government promised to update Canada's creaking competition law to finally ban 'abuse of dominance.'
I mean, wow. I guess when Galen Weston decided to engage in a criminal conspiracy to fix the price of bread – the most Les Miz-ass crime imaginable – it finally got someone's attention, eh?
Competition has a long way to go, but all over the world, competition law is seeing a massive revitalization. Ronald Reagan and Margaret Thatcher put antitrust law in a coma in the 80s – but it's awake, it's back, and it's pissed.
What about regulation? How will we get tech companies to stop doing that one weird trick of adding 'with an app' to their crimes and escaping enforcement?
Well, here in the EU, they're starting to figure it out. This year, the Digital Markets Act and the Digital Services Act went into effect, and they let people who get screwed by tech companies go straight to the federal European courts, bypassing the toothless watchdogs in Europe's notorious corporate crime havens like Ireland.
In America, they might finally get a digital privacy law. You people have no idea how backwards US privacy law is. The last time the US Congress enacted a broadly applicable privacy law was in 1988.
The Video Privacy Protection Act makes it a crime for video-store clerks to leak your video-rental history. It was passed after a right-wing judge who was up for the Supreme Court had his rentals published in a DC newspaper. The rentals weren't even all that embarrassing!
Sure, that judge, Robert Bork, wasn't confirmed for the Supreme Court, but that was because he was a virulently racist loudmouth and a crook who served as Nixon's Solicitor General.
But Congress got the idea that their video records might be next, freaked out, and passed the VPPA.
That was the last time Americans got a big, national privacy law. Nineteen. Eighty. Eight.
It's been a minute.
And the thing is, there's a lot of people who are angry about stuff that has some nexus with America's piss-poor privacy landscape. Worried that Facebook turned Grampy into a Qanon? That Insta made your teen anorexic? That TikTok is brainwashing millennials into quoting Osama Bin Laden?
Or that cops are rolling up the identities of everyone at a Black Lives Matter protest or the Jan 6 riots by getting location data from Google?
Or that Red State Attorneys General are tracking teen girls to out-of-state abortion clinics?
Or that Black people are being discriminated against by online lending or hiring platforms?
Or that someone is making AI deepfake porn of you?
Having a federal privacy law with a private right of action – which means that individuals can sue companies that violate their privacy – would go a long way to rectifying all of these problems. There's a big coalition for that kind of privacy law.
What about self-help? That's a lot farther away, alas.
The EU's DMA will force tech companies to open up their walled gardens for interoperation. You'll be able to use Whatsapp to message people on iMessage, or quit Facebook and move to Mastodon, but still send messages to the people left behind.
But if you want to reverse-engineer one of those Big Tech products and mod it to work for you, not them, the EU's got nothing for you.
This is an area ripe for improvement, and I think the US might be the first ones to open this up.
It's certainly on-brand for the EU to be forcing tech companies to do things a certain way, while the US simply takes away tech companies' abilities to prevent others from changing how their stuff works.
My big hope here is that Stein's Law will take hold: 'Anything that can't go on forever will eventually stop'
Letting companies decide how their customers must use their products is simply too tempting an invitation to mischief. HP has a whole building full of engineers thinking of new ways to lock your printer to its official ink cartridges, forcing you to spend $10,000/gallon on ink to print your boarding passes and shopping lists.
It's offensive. The only people who don't agree are the people running the monopolies in all the other industries, like the med-tech monopolists who are locking their insulin pumps to their glucose monitors, turning people with diabetes into walking inkjet printers.
Finally, there's labor. Here in Europe, there's much higher union density than in the US, which American tech barons are learning the hard way. There is nothing more satisfying in the daily news than the latest salvo by Nordic unions against that Tesla guy (Musk is the most Edison-ass Tesla guy imaginable).
But even in the USA, there's a massive surge in tech unions. Tech workers are realizing that they aren't founders in waiting. The days of free massages and facial piercings and getting to wear black tee shirts that say things your boss doesn't understand are coming to an end.
In Seattle, Amazon's tech workers walked out in sympathy with Amazon's warehouse workers, because they're all workers.
The only reason the tech workers aren't monitored by AI that notifies their managers if they visit the toilet during working hours is their rapidly dwindling bargaining power. The way things are going, Amazon programmers are going to be pissing in bottles next to their workstations (for a guy who built a penis-shaped rocket, Jeff Bezos really hates our kidneys).
We're seeing bold, muscular, global action on competition, regulation and labor, with self-help bringing up the rear. It's not a moment too soon, because the bad news is, enshittification is coming to every industry.
If it's got a networked computer in it, the people who made it can run the Darth Vader MBA playbook on it, changing the rules from moment to moment, violating your rights and then saying 'It's OK, we did it with an app.'
From Mercedes renting you your accelerator pedal by the month to Internet of Things dishwashers that lock you into proprietary dishsoap, enshittification is metastasizing into every corner of our lives.
Software doesn't eat the world, it enshittifies it
But there's a bright side to all this: if everyone is threatened by enshittification, then everyone has a stake in disenshittification.
Just as with privacy law in the US, the potential anti-enshittification coalition is massive, it's unstoppable.
The cynics among you might be skeptical that this will make a difference. After all, isn't "enshittification" the same as "capitalism"?
Well, no.
Look, I'm not going to cape for capitalism here. I'm hardly a true believer in markets as the most efficient allocators of resources and arbiters of policy – if there was ever any doubt, capitalism's total failure to grapple with the climate emergency surely erases it.
But the capitalism of 20 years ago made space for a wild and wooly internet, a space where people with disfavored views could find each other, offer mutual aid, and organize.
The capitalism of today has produced a global, digital ghost mall, filled with botshit, crapgadgets from companies with consonant-heavy brand-names, and cryptocurrency scams.
The internet isn't more important than the climate emergency, nor gender justice, racial justice, genocide, or inequality.
But the internet is the terrain we'll fight those fights on. Without a free, fair and open internet, the fight is lost before it's joined.
We can reverse the enshittification of the internet. We can halt the creeping enshittification of every digital device.
We can build a better, enshittification-resistant digital nervous system, one that is fit to coordinate the mass movements we will need to fight fascism, end genocide, and save our planet and our species.
Martin Luther King said 'It may be true that the law cannot make a man love me, but it can stop him from lynching me, and I think that's pretty important.'
And it may be true that the law can't force corporate sociopaths to conceive of you as a human being entitled to dignity and fair treatment, and not just an ambulatory wallet, a supply of gut-bacteria for the immortal colony organism that is a limited liability corporation.
But it can make that exec fear you enough to treat you fairly and afford you dignity, even if he doesn't think you deserve it.
And I think that's pretty important.

If you'd like an essay-formatted version of this post to read or share, here's a link to it on pluralistic.net, my surveillance-free, ad-free, tracker-free blog:
https://pluralistic.net/2024/01/30/go-nuts-meine-kerle#ich-bin-ein-bratapfel/a>


Back the Kickstarter for the audiobook of The Bezzle here!

Image: Drahtlos (modified) https://commons.wikimedia.org/wiki/File:Motherboard_Intel_386.jpg
CC BY-SA 4.0 https://creativecommons.org/licenses/by-sa/4.0/deed.en
-
cdessums (modified) https://commons.wikimedia.org/wiki/File:Monsoon_Season_Flagstaff_AZ_clouds_storm.jpg
CC BY-SA 2.0 https://creativecommons.org/licenses/by-sa/2.0/deed.en
404 notes
·
View notes
Text
This is an essay version of the 2024 McLuhan Lecture given by writer Cory Doctorow in Berlin. A vid of his lecture (and more) is included in the link below.
The inventor of the word "enshittification" outlines the process in detail. He describes this era as the "enshittocene". Before you despair, he does offer some remedies.
Pluralistic: My McLuhan lecture on enshittification (30 Jan 2024) – Pluralistic: Daily links from Cory Doctorow
An excerpt...
[T]he capitalism of 20 years ago made space for a wild and woolly internet, a space where people with disfavored views could find each other, offer mutual aid, and organize. The capitalism of today has produced a global, digital ghost mall, filled with botshit, crapgadgets from companies with consonant-heavy brand-names, and cryptocurrency scams. The internet isn't more important than the climate emergency, nor gender justice, racial justice, genocide, or inequality. But the internet is the terrain we'll fight those fights on. Without a free, fair and open internet, the fight is lost before it's joined.
If you'd like to see the internet de-enshittified, quit using platforms which contribute to the process. Not mentioning names, but they're run by multi-billionaires who could afford to buy entire countries.
While no platform is 100% perfect, Tumblr has been rather resistant to enshittification. Cory Docterow has an account here if you wish to follow him.
@mostlysignssomeportents
The tech oligarchs have turned the internet into a tool for extracting resources from us as if we were one large collective strip mine. Their only goals seem to be the preternatural accumulation of even more wealth and the ability to manipulate those in power. We need to become more aware of our own part in this and put distance between ourselves and the monopolies which we now help to prop up.
If you remember nothing else from this...
DON'T FEED THE OLIGARCHS.
#enshittification#oligarchs#monopolies#enshittocene#the internet#cory docterow#mcluhan lecture#tumblr
0 notes
Text
I was just going to ignore this because you sent it to the wrong blog and tumblr clowns and their clown followers are never worth the time. BUT ... I just love a teachable moment! Okay.
Take a look at these two definitions from Merriam-Webster. Can you spot the difference? Are these synonymous?
Publishing: the business or profession of the commercial production and issuance of literature, information, musical scores or sometimes recordings, or art
Printing: the act or product of one that prints; reproduction in printed form; the art, practice, or business of a printer
Now, why is this important, you ask? Because there is a difference between self-published, a defining characteristic of zines, and self-printed. Anyone can print their whole novel at a print shop if they're willing to pay, but they still have all the other work that goes with it to get it out to the world. They do not suddenly become professional authors, and these books do not become professionally published books, once printing has happened. Where is this "industry infrastructure," you speak of? The print-on-demand websites? The same services people use to print yearbooks and photo albums? Are these websites the ones big publishers are using to print their Colleen Hoovers? Are they sending their Sports Illustrateds there?
Zines are self-published, amateur magazines. In no definition of zine will you find the phrase "self-printed." You might find references to their roots in the humble photocopier, but being photocopied is not their defining feature, it is only one of a number of possible features, otherwise we'd be unnecessarily throwing out a whole host of zines from the club, from e-zines to screen-printing.
BUT, far more importantly, if you know anything about the history of art, you should know this: slapping arbitrary and restrictive definitions on art forms in a way that attempts to separate them into neat little boxes is not only impossible, but also detrimental to our understanding and our conversations about art as a whole.
But ya'll keep up with your binary thinking anyways. Surely that always ends well.
#I can't deal with the lack of media literacy on this website anymore ya'll havent gotten past “the medium is the message” yet have you#what am I talking about y'all havent even reached the marshall mcluhan#ya'll cant even do a basic search to define zine#weeeeee bye#thanks for giving me a chance to lecture about art
2 notes
·
View notes
Video
youtube
0 notes
Text
Dorelle Heisel Plumbed Brain Mysteries And Psychedelicized Cincinnati’s Social Circles
Dorelle Markley Heisel called Cincinnati her home for several decades, but her mind was in another dimension. She was known as “Cincinnati’s Brain Lady” and held college faculty positions in literature, psychology and fine art. She pioneered biofeedback techniques to control mental and bodily functions while introducing Cincinnati’s strait-laced society to the psychedelic subculture of the Sixties.
Virginia Dorelle Markley was born in 1917 in Danville, Illinois but spent her childhood shuttling between her father’s Palm Beach restaurant and her mother’s St. Louis hotel. At DePauw University in Greencastle, Indiana, she was student royalty – literally – voted May Queen in her senior year.
It was at DePauw that she met and became engaged to W. Donald Heisel, a Cincinnati native and Western Hills High School alumnus. At the time of his 1940 marriage to Dorelle, Heisel was assistant secretary to Cincinnati’s Civil Service Commission and was, according to the Cincinnati Enquirer [21 May 1940] “one of the city’s youngest executives.” The Heisels built a new house on a quiet cul de sac in Westwood, where they raised two daughters.
Don Heisel earned a reputation as the “godfather of public administration in the Tristate” [Cincinnati Enquirer 6 March 1988] because of the many governmental officials he mentored at the University of Cincinnati and at Xavier University. Dorelle, who had earned a degree in English from DePauw, added a bachelor’s (1952) and master’s (1965) in education from UC while also taking classes at the Cincinnati Art Academy.
Dorelle taught English for several years in Cincinnati high schools and at the Ohio Mechanics Institute. During the summers she was a fixture at Pogue’s Department Store. Hundreds of Queen City baby boomers likely display pastel portraits of themselves, sketched by Dorelle at her stand in the Pogue’s children’s department. She hated the drab institutional brown walls in her husband’s office, so one day she hauled her pastels over to City Hall and executed a large mural of the Cincinnati skyline, drawn from memory.
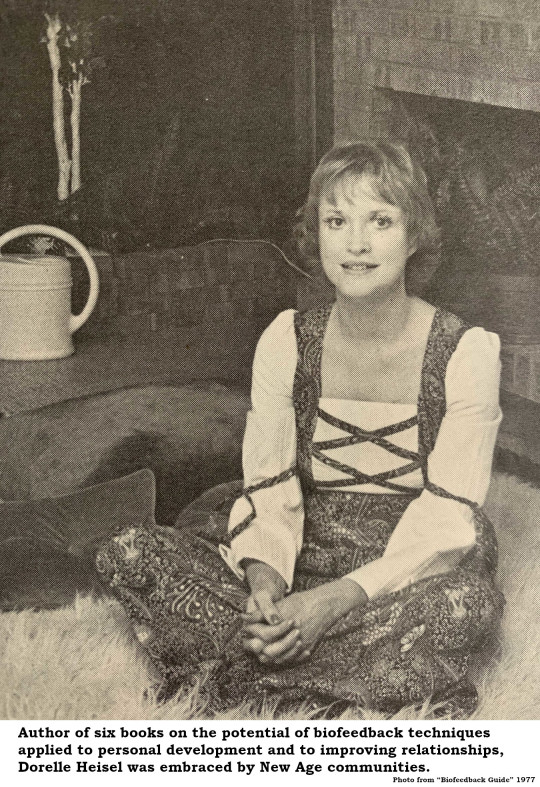

UC’s University College recruited Dorelle in the mid-1960s and she flourished there, teaching literature, art appreciation and psychology. With assistance from the Procter & Gamble company, she brought innovative technology into her classrooms with a push-button feedback device that allowed students to register immediate opinions regarding class content. She told the Cincinnati Post [14 March 1968]:
“When students become frustrated with a lecture or feel lost or just plain bored, they can indicate their anxiety by signaling me on the monitor.”
Dorelle’s interest in media and their effects on human communication led her to Canadian theorist Marshall McLuhan, known for his books “Understanding Media” and “The Medium Is The Massage.” Among the earliest mentions of McLuhan in Cincinnati newspapers is a reference to a 1966 Evening College class taught by Dorelle to introduce the Canadian theorist’s ideas to Cincinnati.
Simultaneously with her investigations of media and biofeedback, Dorelle dove into what was then known as the human potential movement. She presided over a multi-week UC Evening College class titled “Actualizing Your Potential: A Group Happening.” Enquirer reporter Jo Thomas sat in on the course and reported [21 August 1969] a most unusual classroom experience.
“I will not lecture,” Heisel said. “You will live out experiences, and I will ask you questions. Answer them in your head without verbalizing them. Writing is so slow and the mind works at such speed.”
Dorelle invited the students to form themselves into trains of about nine “cars,” kindergarten-style and take turns being the “engine” or the “caboose.”
“Elderly women hung on to 20-year-olds. Bald men chugged in front of bearded men. Around and around the room the trains went, gathering momentum and enthusiasm. One train burst out of the classroom door into the bright hall, chugging with gusto.”
The explosion of new ideas generated by the psychedelic Sixties energized Dorelle and she launched a series of public lectures to share her excitement. One wonders how her Cincinnati audiences, among such mainline organizations such as the Federation of Jewish Organizations and the Kiwanis Club, reacted to her exposition titled “Turn On, Tune In, Find Out!”
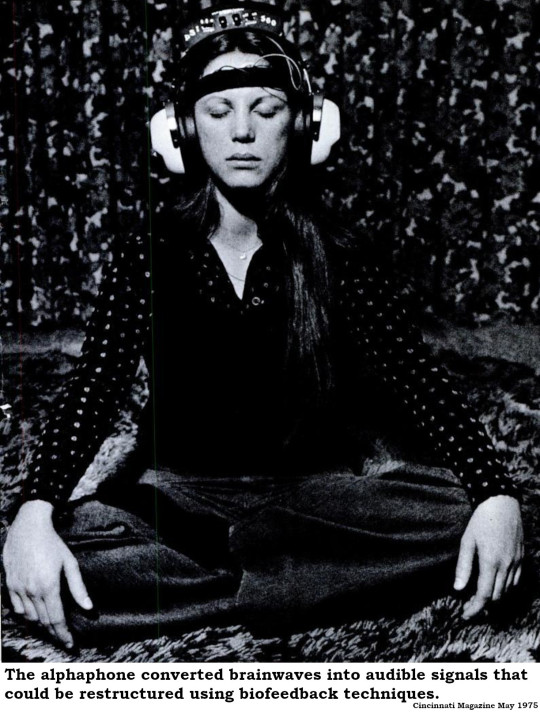

An early adopter of technology, Dorelle acquired a variety of devices to assist her research into altering thought patterns via biofeedback. Among these contraptions were the electromyograph and the alphaphone that made brainwaves audible or visual. She claimed that biofeedback, in addition to curing a variety of conditions from depression to migraines, transported users into a new state of being that she called the Kairos Dimension.
"The Kairos Dimension is nature taking its electronic course through you by providing strategies for amplifying your sensory range,” she announced in her 1974 book, “The Kairos Dimension.”
The titles of Dorelle’s non-credit classes and community lectures indicate the paths her biofeedback research led her down: “Brainfun: Steering Minds In New Directions,” “The Holographic Mind,” “How Biofeedback Opens Social Spaces,” and “How Biofeedback Supports Excitement And Growth.” Here is the course catalog description for one of these classes:
“Feelings of stress, tension and pressure take place only in muscles, never in the chemical-electrical brain that sends out orders. New research gives us a more accurate model of how we guide and control our range of ‘body sculptures.’ Small group exploration of the latest technologies.”
As the Human Potential movement evolved into various New Age philosophies, Dorelle’s biofeedback strategies caught on among that crowd. When the Montreal Star compiled a list of 50 important New Age books in 1975, Dorelle’s “Biofeedback Exercise Book” was featured along with books on transcendental meditation, herbal remedies, gestalt therapy and “The Joy of Sex.”
The nationally syndicated television show, P.M. Magazine, hosted Dorelle in November 1983 as “Cincinnati’s Brain Lady who enables you to see your brain on a television screen.” For a brief period, UC’s radio station WGUC aired a show devoted to Dorelle’s “Kairos Dimension.”
The Heisels divorced in 1977 and throughout the 1980s Dorelle’s public appearances waned. A Body/Mind/Spirit Festival at Avondale’s Unitarian Church in 1988 found her discussing biofeedback along with proponents of shamanism, tarot cards, crystals, chelation therapy and psychic powers.
Dorelle retired from UC and relocated to Plano, Texas where one of her daughters lived. In retirement, she played bridge and painted portraits. She died, aged 79, in November 1996.

10 notes
·
View notes
Text
"The pre-enshittification era wasn’t a time of better leadership. The executives weren’t better. They were constrained. Their worst impulses were checked by competition, regulation, self-help and worker power." – Corey Doctorow, McLuhan Lecture on 'Enshittification''
"Like Facebook, handing former UK deputy PM Nick Clegg millions every year to sleaze around Europe, telling his former colleagues that Facebook is the only thing standing between ‘European Cyberspace’ and the Chinese Communist Party." hmmm
3 notes
·
View notes
Text
Heres a speech about it, with full transcript
Sarcasm is dead
34K notes
·
View notes
Text
Captain Phil interviews Paul Levinson about Tom Cooper's Wisdom Weavers
I returned to Captain Phil's Planet on WUSB (Stony Brook University) Radio the other day to talk to Captain Phil about Tom Cooper's new book, Wisdom Weavers: The Lives and Thought of Harold Innis and Marshall McLuhan, to be pubished by Connected Editions (my publishing company) on May 1.
As we discussed in the interview, I'll be interviewing Tom about his book via Zoom on the evening of Wisdom Weavers' publication -- 8pm (New York time), May 1. If you'd like to attend, email me at [email protected] and I'll be happy to send the Zoom URL to you.
In the meantime, check out my Marshall McLuhan playlist on YouTube for 50 of my lectures, interviews, etc about McLuhan over the past 20 years. Here are my two books about McLuhan: Digital McLuhan and McLuhan in an Age of Social Media. You'll also find numerous essays about McLuhan on my Academia.edu page. And, if you're a fan of audio podcasts, just search on "McLuhan" on my Light On Light Through podcast page.
Check out this episode!
0 notes
Text

Over time, emerging technologies have enhanced communication by improving or creating new media channels. Today, Virtual Reality unites mediums to supply rich or hot user experiences. Let’s further examine the relationship between mediums, messages, and their temperature.

Marshall McLuhan proposed that the medium is the message, meaning how messages are presented and expressed has more significance and influence than its message. Further, mediums are extensions of a user, and the choice of medium is relevant to who the individual is or what they hope to be.

McLuhan organized media by their hot or coldness, defined by the richness of data, participation suggested, or interpretation needed. A hot medium provides rich information or high definition, requiring little involvement and interpretation of the message, and a cold medium presents the opposite.

For example, radio is hot because audiences cannot communicate directly with a host. Still, the content is high-definition, compared to cold conversations, where body language and visual cues must be interpreted for more understanding. Before claiming VR is hot, let's define what the medium is.

Virtual Reality is a computer-generated simulation allowing users to engage, explore, and experience immersive 3D environments. VR utilizes headsets and controllers to activate human senses to evoke authentic user experiences, effectively transporting people into new worlds.

VR is commonly used in gaming, but it is branching out as a learning tool in education and workforce training, with evidence supporting learning. For American armed forces, immersive combat training allows soldiers to practice special operations and test efficiency with emergency procedures.

VR is a hot medium because its rich information supports learning, with immersive environments contributing to user retention since distractions are limited. Further, lesson-based learning allows people to repeat exercises, giving them control over the rate and frequency of media.

Regarding retention, University of Maryland School of Medicine trauma surgeon Sarah Murthi shared, “If you’re on a computer, it’s hard to stay focused. Your phone is sitting right there. When you’re in VR, you’re in that reality. It’s more immersive and less distracting. Your attention is less fragmented.”

Engagement, learning, and retention are essential considerations in media, and McLuhuans touched on this with the hot medium of lectures, which is dense with data. However, while VR and lectures focus on contextual information, sensory information is another channel for communication.

VR also enables sensation with optics, headphones, and haptics to activate users' sight, hearing, and touch to “convince the brain that the virtual world is the physical world,” stated Coursera. High-definition experiences contribute to communicating concise messages to users by justifying information through their senses.
A University of Maryland article stated, “Studies show there is better recall and movement when you take off the headset after VR training. If you’re learning with your eyes, your ears, and even your hands and feet, you may be learning — and remembering — in a more complete way.”

Sensations prove a message has been delivered; consider how radio communicates to the ears or photography to the eyes and further prove McLuhan’s idea that mediums extend the human experience. With VR, users can maximize their sensory intake to increase the conceivability of experiences.

Lastly, reduced user interpretation supports hot media. VR accomplishes this by using storytelling to provide a narrative structure and guidance. By defining user flows and anticipated actions, a creator can use hints, lesson outlines, or complete storylines to offer enough support so users won't need to interpret information independently.

Shane Snow with Forbes explained, “Humans are wired for story. We tell ourselves stories to make sense of the world.” Through creating stories, users are given a roadmap that assists in navigating their immersive worlds and understanding their role and purpose.

Audience interpretation is valuable because it reflects how people internalize delivered messages and how they respond. If a message requires less interpretation from its audience, there is a greater chance of it not being shaped by personal preference or experience.

While VR may be a hot medium, its need for high user participation could suggest that it is cold instead. Cold mediums like cartoons, television, and the telephone require greater audience involvement to gain low-definition content that still needs to be interpreted. Cold media could be described as getting less bang for your buck.

Further, the retention, sensation, and interpretation previously covered may only happen while users actively participate in VR. Users must engage before accessing the messages it has to share. In this light, VR starts as a cold medium before heating up. While user engagement is a vital part of VR experiences, every medium requires a level of participation.

Whether passively viewing a painting or actively texting on the phone, mediums demand a reaction or response from their audience. An important consideration is that almost all mediums require a degree of participation, but not all access as many sensory points as VR.

I believe Virtual Reality is a hot medium because it immerses users with vivid information, engages human senses, and provides a clear context for users to navigate environments effectively and efficiently.

McLuhan proposed strong ideas highlighting how people consume media and how the messages we receive are recontextualized by the mediums it's presented in. Society should consider if the application of immersive technologies suggests that the medium is now the audience or user.
Work Cited
Images
https://en.wikipedia.org/wiki/Marshall_McLuhan
https://investingnews.com/daily/tech-investing/emerging-tech-investing/top-emerging-technologies/
https://www.flavorman.com/media/how-do-drink-temperatures-affect-us
https://www.pexels.com/photo/stack-of-vintage-radios-in-an-electronics-store-18449793/
https://www.techlearning.com/features/what-is-virtual-reality
https://ai.plainenglish.io/advancement-of-vr-ar-and-mr-in-the-military-sector-b6ff0a3784
https://blog.commlabindia.com/elearning-design/tips-to-overcome-poor-retention-of-learning
https://smarttek.solutions/blog/vr-training-for-healthcare-why-your-hospital-needs-it/
https://uwaterloo.ca/health/research/hallman-lecture-series
https://neurosciencenews.com/sensory-perception-noise-signals-28195/
https://dana.org/resources/how-do-the-senses-work-grades-3-5/
https://www.pexels.com/photo/selective-focus-photography-of-woman-holding-dslr-camera-1264210/
https://uxplanet.org/storytelling-elements-31b2a6a7e373
https://www.sharpn.co.uk/blog/clear-roadmaps
https://grahamjbaird.blogspot.com/2017/12/internalize-dont-memorize.html
https://factsandfigment.com/who-came-first-the-dawn-of-color-in-disney-cartoons/
https://www.thefield.co.uk/country-house/cold-houses-and-how-to-stay-warm-this-winter-48629
https://www.flickr.com/photos/tabor-roeder/4816444169
https://www.studiobinder.com/blog/what-is-virtual-reality/
https://www.druckerforum.org/articles/marshall-mcluhan/
0 notes
Text
Video Games: Hot or Cold Media?
Despite the amount of criticisms I hold of McLuhan's theory on hot and cold media, I think video games are one of the most clearly cold forms of media. By his definition, hot mediums require the least human interaction to be able to absorb information, and I think video games are the most interactive form of media out there. Before you can even play the game, you must learn how to use the controller. Once you learn the buttons, then you have to learn which buttons do what in whatever game you're playing. Every game has a different control scheme, so you must learn basically a new language with every new game you play. Once you've done that, you can finally start playing. Even if you disregard learning the controls as part of the theory, to get to the next part in the story, you must actively progress to the next part. Yes, you must sit and watch a movie to progress, or move your eyes between lines on a book, or pay attention to a lecture. But you must do all of this in a video game. You must pay attention to the story and where to go next, you must learn how to overcome its challenges. Oftentimes, the story is intertwined with whatever activities you're performing, and can contribute to the overall themes. This requires active thinking and consumption of the media in order to derive meaning. Some games are more forward with their story, acting as playable movies almost. However, oftentimes the stories are influenced by your actions, even leading to completely different endings/characters you meet. My biggest complaint about McLuhan's theory, that while he's so focused on the medium, some movies can require more deciphering to fully understand than certain tv shows or video games. He's so focused on categorizing everything, that it detracts from the human effort put into each individual piece of media, and I don't think anybody should subscribe to this way of thinking, especially with how media has evolved in all of its forms.
0 notes
Text
With Great Power Came No Responsibility

I'm on a 20+ city book tour for my new novel PICKS AND SHOVELS. Catch me in NYC TONIGHT (26 Feb) with JOHN HODGMAN and at PENN STATE TOMORROW (Feb 27). More tour dates here. Mail-order signed copies from LA's Diesel Books.

Last night, I traveled to Toronto to deliver the annual Ursula Franklin Lecture at the University of Toronto's Innis College:
The lecture was called "With Great Power Came No Responsibility: How Enshittification Conquered the 21st Century and How We Can Overthrow It." It's the latest major speech in my series of talks on the subject, which started with last year's McLuhan Lecture in Berlin:
https://pluralistic.net/2024/01/30/go-nuts-meine-kerle/#ich-bin-ein-bratapfel
And continued with a summer Defcon keynote:
https://pluralistic.net/2024/08/17/hack-the-planet/#how-about-a-nice-game-of-chess
This speech specifically addresses the unique opportunities for disenshittification created by Trump's rapid unscheduled midair disassembly of the international free trade system. The US used trade deals to force nearly every country in the world to adopt the IP laws that make enshittification possible, and maybe even inevitable. As Trump burns these trade deals to the ground, the rest of the world has an unprecedented opportunity to retaliate against American bullying by getting rid of these laws and producing the tools, devices and services that can protect every tech user (including Americans) from being ripped off by US Big Tech companies.
I'm so grateful for the chance to give this talk. I was hosted for the day by the Centre for Culture and Technology, which was founded by Marshall McLuhan, and is housed in the coach house he used for his office. The talk itself took place in Innis College, named for Harold Innis, who is definitely the thinking person's Marshall McLuhan. What's more, I was mentored by Innis's daughter, Anne Innis Dagg, a radical, brilliant feminist biologist who pretty much invented the field of giraffology:
https://pluralistic.net/2020/02/19/pluralist-19-feb-2020/#annedagg
But with all respect due to Anne and her dad, Ursula Franklin is the thinking person's Harold Innis. A brilliant scientist, activist and communicator who dedicated her life to the idea that the most important fact about a technology wasn't what it did, but who it did it for and who it did it to. Getting to work out of McLuhan's office to present a talk in Innis's theater that was named after Franklin? Swoon!
https://en.wikipedia.org/wiki/Ursula_Franklin
Here's the text of the talk, lightly edited:
I know tonight’s talk is supposed to be about decaying tech platforms, but I want to start by talking about nurses.
A January 2025 report from Groundwork Collective documents how increasingly nurses in the USA are hired through gig apps – "Uber for nurses” – so nurses never know from one day to the next whether they're going to work, or how much they'll get paid.
There's something high-tech going on here with those nurses' wages. These nursing apps – a cartel of three companies, Shiftkey, Shiftmed and Carerev – can play all kinds of games with labor pricing.
Before Shiftkey offers a nurse a shift, it purchases that worker's credit history from a data-broker. Specifically, it pays to find out how much credit-card debt the nurse is carrying, and whether it is overdue.
The more desperate the nurse's financial straits are, the lower the wage on offer. Because the more desperate you are, the less you'll accept to come and do the gruntwork of caring for the sick, the elderly, and the dying.
Now, there are lots of things going on here, and they're all terrible. What's more, they are emblematic of “enshittification,” the word I coined to describe the decay of online platforms.
When I first started writing about this, I focused on the external symptology of enshittification, a three stage process:
First, the platform is good to its end users, while finding a way to lock them in.
Like Google, which minimized ads and maximized spending on engineering for search results, even as they bought their way to dominance, bribing every service or product with a search box to make it a Google search box.
So no matter what browser you used, what mobile OS you used, what carrier you had, you would always be searching on Google by default. This got so batshit that by the early 2020s, Google was spending enough money to buy a whole-ass Twitter, every year or two, just to make sure that no one ever tried a search engine that wasn't Google.
That's stage one: be good to end users, lock in end users.
Stage two is when the platform starts to abuse end users to tempt in and enrich business customers. For Google, that’s advertisers and web publishers. An ever-larger fraction of a Google results page is given over to ads, which are marked with ever-subtler, ever smaller, ever grayer labels. Google uses its commercial surveillance data to target ads to us.
So that's stage two: things get worse for end users and get better for business customers.
But those business customers also get locked into the platform, dependent on those customers. Once businesses are getting as little as 10% of their revenue from Google, leaving Google becomes an existential risk. We talk a lot about Google's "monopoly" power, which is derived from its dominance as a seller. But Google is also a monopsony, a powerful buyer.
So now you have Google acting as a monopolist to its users (stage one), and a monoposonist for its business customers (stage two) and here comes stage three: where Google claws back all the value in the platform, save a homeopathic residue calculated to keep end users locked in, and business customers locked to those end users.
Google becomes enshittified.
In 2019, Google had a turning point. Search had grown as much as it possibly could. More than 90% of us used Google for search, and we searched for everything. Any thought or idle question that crossed our minds, we typed into Google.
How could Google grow? There were no more users left to switch to Google. We weren't going to search for more things. What could Google do?
Well, thanks to internal memos published during last year's monopoly trial against Google, we know what they did. They made search worse. They reduced the system's accuracy it so you had to search twice or more to get to the answer, thus doubling the number of queries, and doubling the number of ads.
Meanwhile, Google entered into a secret, illegal collusive arrangement with Facebook, codenamed Jedi Blue, to rig the ad market, fixing prices so advertisers paid more and publishers got less.
And that's how we get to the enshittified Google of today, where every query serves back a blob of AI slop, over five paid results tagged with the word AD in 8-point, 10% grey on white type, which is, in turn, over ten spammy links from SEO shovelware sites filled with more AI slop.
And yet, we still keep using Google, because we're locked into it. That's enshittification, from the outside. A company that's good to end users, while locking them in. Then it makes things worse for end users, to make things better for business customers, while locking them in. Then it takes all the value for itself and turns into a giant pile of shit.
Enshittification, a tragedy in three acts.
I started off focused on the outward signs of enshittification, but I think it's time we start thinking about what's going in inside the companies to make enshittification possible.
What is the technical mechanism for enshittification? I call it twiddling. Digital businesses have infinite flexibility, bequeathed to them by the marvellously flexible digital computers they run on. That means that firms can twiddle the knobs that control the fundamental aspects of their business. Every time you interact with a firm, everything is different: prices, costs, search rankings, recommendations.
Which takes me back to our nurses. This scam, where you look up the nurse's debt load and titer down the wage you offer based on it in realtime? That's twiddling. It's something you can only do with a computer. The bosses who are doing this aren't more evil than bosses of yore, they just have better tools.
Note that these aren't even tech bosses. These are health-care bosses, who happen to have tech.
Digitalization – weaving networked computers through a firm or a sector – enables this kind of twiddling that allows firms to shift value around, from end users to business customers, from business customers back to end users, and eventually, inevitably, to themselves.
And digitalization is coming to every sector – like nursing. Which means enshittification is coming to every sector – like nursing.
The legal scholar Veena Dubal coined a term to describe the twiddling that suppresses the wages of debt-burdened nurses. It's called "Algorithmic Wage Discrimination," and it follows the gig economy.
The gig economy is a major locus of enshittification, and it’s the largest tear in the membrane separating the virtual world from the real world. Gig work, where your shitty boss is a shitty app, and you aren't even allowed to call yourself an employee.
Uber invented this trick. Drivers who are picky about the jobs the app puts in front of them start to get higher wage offers. But if they yield to temptation and take some of those higher-waged option, then the wage starts to go down again, in random intervals, by small increments, designed to be below the threshold for human perception. Not so much boiling the frog as poaching it, until the Uber driver has gone into debt to buy a new car, and given up the side hustles that let them be picky about the rides they accepted. Then their wage goes down, and down, and down.
Twiddling is a crude trick done quickly. Any task that's simple but time consuming is a prime candidate for automation, and this kind of wage-theft would be unbearably tedious, labor-intensive and expensive to perform manually. No 19th century warehouse full of guys with green eyeshades slaving over ledgers could do this. You need digitalization.
Twiddling nurses' hourly wages is a perfect example of the role digitization pays in enshittification. Because this kind of thing isn't just bad for nurses – it's bad for patients, too. Do we really think that paying nurses based on how desperate they are, at a rate calculated to increase that desperation, and thus decrease the wage they are likely to work for, is going to result in nurses delivering the best care?
Do you want to your catheter inserted by a nurse on food stamps, who drove an Uber until midnight the night before, and skipped breakfast this morning in order to make rent?
This is why it’s so foolish to say "If you're not paying for the product, you're the product." “If you’re not paying for the product” ascribes a mystical power to advertising-driven services: the power to bypass our critical faculties by surveilling us, and data-mining the resulting dossiers to locate our mental bind-spots, and weaponize them to get us to buy anything an advertiser is selling.
In this formulation, we are complicit in our own exploitation. By choosing to use "free" services, we invite our own exploitation by surveillance capitalists who have perfected a mind-control ray powered by the surveillance data we're voluntarily handing over by choosing ad-driven services.
The moral is that if we only went back to paying for things, instead of unrealistically demanding that everything be free, we would restore capitalism to its functional, non-surveillant state, and companies would start treating us better, because we'd be the customers, not the products.
That's why the surveillance capitalism hypothesis elevates companies like Apple as virtuous alternatives. Because Apple charges us money, rather than attention, it can focus on giving us better service, rather than exploiting us.
There's a superficially plausible logic to this. After all, in 2022, Apple updated its iOS operating system, which runs on iPhones and other mobile devices, introducing a tick box that allowed you to opt out of third-party surveillance, most notably Facebook’s.
96% of Apple customers ticked that box. The other 4% were, presumably drunk, or Facebook employees, or Facebook employees who were drunk. Which makes sense, because if I worked for Facebook, I'd be drunk all the time.
So on the face of it, it seems like Apple isn't treating its customers like "the product." But simultaneously with this privacy measure, Apple was secretly turning on its own surveillance system for iPhone owners, which would spy on them in exactly the way Facebook had, for exactly the same purpose: to target ads to you based on the places you'd been, the things you'd searched for, the communications you'd had, the links you'd clicked.
Apple didn't ask its customers for permission to spy on them. It didn't let opt out of this spying. It didn’t even tell them about it, and when it was caught, Apple lied about it.
It goes without saying that the $1000 Apple distraction rectangle in your pocket is something you paid for. The fact that you've paid for it doesn't stop Apple from treating you as the product. Apple treats its business customers – app vendors – like the product, screwing them out of 30 cents on every dollar they bring in, with mandatory payment processing fees that are 1,000% higher than the already extortionate industry norm.
Apple treats its end users – people who shell out a grand for a phone – like the product, spying on them to help target ads to them.
Apple treats everyone like the product.
This is what's going on with our gig-app nurses: the nurses are the product. The patients are the product. The hospitals are the product. In enshittification, "the product" is anyone who can be productized.
Fair and dignified treatment is not something you get as a customer loyalty perk, in exchange for parting with your money, rather than your attention. How do you get fair and dignified treatment? Well, I'm gonna get to that, but let's stay with our nurses for a while first.
The nurses are the product, and they're being twiddled, because they've been conscripted into the tech industry, via the digitalization of their own industry.
It's tempting to blame digitalization for this. But tech companies were not born enshittified. They spent years – decades – making pleasing products. If you're old enough to remember the launch of Google, you'll recall that, at the outset, Google was magic.
You could Ask Jeeves questions for a million years, you could load up Altavista with ten trillion boolean search operators meant to screen out low-grade results, and never come up with answers as crisp, as useful, as helpful, as the ones you'd get from a few vaguely descriptive words in a Google search-bar.
There's a reason we all switched to Google. Why so many of us bought iPhones. Why we joined our friends on Facebook. All of these services were born digital. They could have enshittified at any time. But they didn't – until they did. And they did it all at once.
If you were a nurse, and every patient that staggered into the ER had the same dreadful symptoms, you'd call the public health department and report a suspected outbreak of a new and dangerous epidemic.
Ursula Franklin held that technology's outcomes were not preordained. They are the result of deliberate choices. I like that very much, it's a very science fictional way of thinking about technology. Good science fiction isn't merely about what the technology does, but who it does it for, and who it does it to.
Those social factors are far more important than the mere technical specifications of a gadget. They're the difference between a system that warns you when you're about to drift out of your lane, and a system that tells your insurer that you nearly drifted out of your lane, so they can add $10 to your monthly premium.
They’re the difference between a spell checker that lets you know you've made a typo, and bossware that lets your manager use the number of typos you made this quarter so he can deny your bonus.
They’re the difference between an app that remembers where you parked your car, and an app that uses the location of your car as a criteria for including you in a reverse warrant for the identities of everyone in the vicinity of an anti-government protest.
I believe that enshittification is caused by changes not to technology, but to the policy environment. These are changes to the rules of the game, undertaken in living memory, by named parties, who were warned at the time about the likely outcomes of their actions, who are today very rich and respected, and face no consequences or accountability for their role in ushering in the enshittocene. They venture out into polite society without ever once wondering if someone is sizing them up for a pitchfork.
In other words: I think we created a crimogenic environment, a perfect breeding pool for the most pathogenic practices in our society, that have therefore multiplied, dominating decision-making in our firms and states, leading to a vast enshittening of everything.
And I think there's good news there, because if enshittification isn't the result a new kind of evil person, or the great forces of history bearing down on the moment to turn everything to shit, but rather the result of specific policy choices, then we can reverse those policies, make better ones and emerge from the enshittocene, consigning the enshitternet to the scrapheap of history, a mere transitional state between the old, good internet, and a new, good internet.
I'm not going to talk about AI today, because oh my god is AI a boring, overhyped subject. But I will use a metaphor about AI, about the limited liability company, which is a kind of immortal, artificial colony organism in which human beings serve as a kind of gut flora. My colleague Charlie Stross calls corporations "slow AI.”
So you've got these slow AIs whose guts are teeming with people, and the AI's imperative, the paperclip it wants to maximize, is profit. To maximize profits, you charge as much as you can, you pay your workers and suppliers as little as you can, you spend as little as possible on safety and quality.
Every dollar you don't spend on suppliers, workers, quality or safety is a dollar that can go to executives and shareholders. So there's a simple model of the corporation that could maximize its profits by charging infinity dollars, while paying nothing to its workers or suppliers, and ignoring quality and safety.
But that corporation wouldn't make any money, for the obvious reasons that none of us would buy what it was selling, and no one would work for it or supply it with goods. These constraints act as disciplining forces that tamp down the AI's impulse to charge infinity and pay nothing.
In tech, we have four of these constraints, anti-enshittificatory sources of discipline that make products and services better, pay workers more, and keep executives’ and shareholders' wealth from growing at the expense of customers, suppliers and labor.
The first of these constraints is markets. All other things being equal, a business that charges more and delivers less will lose customers to firms that are more generous about sharing value with workers, customers and suppliers.
This is the bedrock of capitalist theory, and it's the ideological basis for competition law, what our American cousins call "antitrust law."
The first antitrust law was 1890's Sherman Act, whose sponsor, Senator John Sherman, stumped for it from the senate floor, saying:
If we will not endure a King as a political power we should not endure a King over the production, transportation, and sale of the necessaries of life. If we would not submit to an emperor we should not submit to an autocrat of trade with power to prevent competition and to fix the price of any commodity.
Senator Sherman was reflecting the outrage of the anitmonopolist movement of the day, when proprietors of monopolistic firms assumed the role of dictators, with the power to decide who would work, who would starve, what could be sold, and what it cost.
Lacking competitors, they were too big to fail, too big to jail, and too big to care. As Lily Tomlin used to put it in her spoof AT&T ads on SNL: "We don't care. We don't have to. We're the phone company.”
So what happened to the disciplining force of competition? We killed it. Starting 40-some years ago, the Reagaonomic views of the Chicago School economists transformed antitrust. They threw out John Sherman's idea that we need to keep companies competitive to prevent the emergence of "autocrats of trade,"and installed the idea that monopolies are efficient.
In other words, if Google has a 90% search market share, which it does, then we must infer that Google is the best search engine ever, and the best search engine possible. The only reason a better search engine hasn't stepped in is that Google is so skilled, so efficient, that there is no conceivable way to improve upon it.
We can tell that Google is the best because it has a monopoly, and we can tell that the monopoly is good because Google is the best.
So 40 years ago, the US – and its major trading partners – adopted an explicitly pro-monopoly competition policy.
Now, you'll be glad to hear that this isn't what happened to Canada. The US Trade Rep didn't come here and force us to neuter our competition laws. But don't get smug! The reason that didn't happen is that it didn't have to. Because Canada had no competition law to speak of, and never has.
In its entire history, the Competition Bureau has challenged three mergers, and it has halted precisely zero mergers, which is how we've ended up with a country that is beholden to the most mediocre plutocrats imaginable like the Irvings, the Westons, the Stronachs, the McCains and the Rogerses.
The only reason these chinless wonders were able to conquer this country Is that the Americans had been crushing their monopolists before they could conquer the US and move on to us. But 40 years ago, the rest of the world adopted the Chicago School's pro-monopoly "consumer welfare standard,” and we got…monopolies.
Monopolies in pharma, beer, glass bottles, vitamin C, athletic shoes, microchips, cars, mattresses, eyeglasses, and, of course, professional wrestling.
Remember: these are specific policies adopted in living memory, by named individuals, who were warned, and got rich, and never faced consequences. The economists who conceived of these policies are still around today, polishing their fake Nobel prizes, teaching at elite schools, making millions consulting for blue-chip firms.
When we confront them with the wreckage their policies created, they protest their innocence, maintaining – with a straight face – that there's no way to affirmatively connect pro-monopoly policies with the rise of monopolies.
It's like we used to put down rat poison and we didn't have a rat problem. Then these guys made us stop, and now rats are chewing our faces off, and they're making wide innocent eyes, saying, "How can you be sure that our anti-rat-poison policies are connected to global rat conquest? Maybe this is simply the Time of the Rat! Maybe sunspots caused rats to become more fecund than at any time in history! And if they bought the rat poison factories and shut them all down, well, so what of it? Shutting down rat poison factories after you've decided to stop putting down rat poison is an economically rational, Pareto-optimal decision."
Markets don't discipline tech companies because they don't compete with rivals, they buy them. That's a quote, from Mark Zuckerberg: “It is better to buy than to compete.”
Which is why Mark Zuckerberg bought Instagram for a billion dollars, even though it only had 12 employees and 25m users. As he wrote in a spectacularly ill-advised middle-of-the-night email to his CFO, he had to buy Instagram, because Facebook users were leaving Facebook for Instagram. By buying Instagram, Zuck ensured that anyone who left Facebook – the platform – would still be a prisoner of Facebook – the company.
Despite the fact that Zuckerberg put this confession in writing, the Obama administration let him go ahead with the merger, because every government, of every political stripe, for 40 years, adopted the posture that monopolies were efficient.
Now, think about our twiddled, immiserated nurses. Hospitals are among the most consolidated sectors in the US. First, we deregulated pharma mergers, and the pharma companies gobbled each other up at the rate of naughts, and they jacked up the price of drugs. So hospitals also merged to monopoly, a defensive maneuver that let a single hospital chain corner the majority of a region or city and say to the pharma companies, "either you make your products cheaper, or you can't sell them to any of our hospitals."
Of course, once this mission was accomplished, the hospitals started screwing the insurers, who staged their own incestuous orgy, buying and merging until most Americans have just three or two insurance options. This let the insurers fight back against the hospitals, but left patients and health care workers defenseless against the consolidated power of hospitals, pharma companies, pharmacy benefit managers, group purchasing organizations, and other health industry cartels, duopolies and monopolies.
Which is why nurses end up signing on to work for hospitals that use these ghastly apps. Remember, there's just three of these apps, replacing dozens of staffing agencies that once competed for nurses' labor.
Meanwhile, on the patient side, competition has never exercised discipline. No one ever shopped around for a cheaper ambulance or a better ER while they were having a heart attack. The price that people are willing to pay to not die is “everything they have.”
So you have this sector that has no business being a commercial enterprise in the first place, losing what little discipline they faced from competition, paving the way for enshittification.
But I said there are four forces that discipline companies. The second one of these forces is regulation, discipline imposed by states.
It’s a mistake to see market discipline and state discipline as two isolated realms. They are intimately connected. Because competition is a necessary condition for effective regulation.
Let me put this in terms that even the most ideological libertarians can understand. Say you think there should be precisely one regulation that governments should enforce: honoring contracts. For the government to serve as referee in that game, it must have the power to compel the players to honor their contracts. Which means that the smallest government you can have is determined by the largest corporation you're willing to permit.
So even if you're the kind of Musk-addled libertarian who can no longer open your copy of Atlas Shrugged because the pages are all stuck together, who pines for markets for human kidneys, and demands the right to sell yourself into slavery, you should still want a robust antitrust regime, so that these contracts can be enforced.
When a sector cartelizes, when it collapses into oligarchy, when the internet turns into "five giant websites, each filled with screenshots of the other four," then it captures its regulators.
After all, a sector with 100 competing companies is a rabble, at each others' throats. They can't agree on anything, especially how they're going to lobby.
While a sector of five companies – or four – or three – or two – or one – is a cartel, a racket, a conspiracy in waiting. A sector that has been boiled down to a mere handful of firms can agree on a common lobbying position.
What's more, they are so insulated from "wasteful competition" that they are aslosh in cash that they can mobilize to make their regulatory preferences into regulations. In other words, they can capture their regulators.
“Regulatory capture" may sound abstract and complicated, so let me put it in concrete terms. In the UK, the antitrust regulator is called the Competition and Markets Authority, run – until recently – by Marcus Bokkerink. The CMA has been one of the world's most effective investigators and regulators of Big Tech fuckery.
Last month, UK PM Keir Starmer fired Bokkerink and replaced him with Doug Gurr, the former head of Amazon UK. Hey, Starmer, the henhouse is on the line, they want their fox back.
But back to our nurses: there are plenty of examples of regulatory capture lurking in that example, but I'm going to pick the most egregious one, the fact that there are data brokers who will sell you information about the credit card debts of random Americans.
This is because the US Congress hasn't passed a new consumer privacy law since 1988, when Ronald Reagan signed a law called the Video Privacy Protection Act that bans video store clerks from telling newspapers which VHS cassettes you took home. The fact that Congress hasn't updated Americans' privacy protections since Die Hard was in theaters isn't a coincidence or an oversight. It is the expensively purchased inaction of a heavily concentrated – and thus wildly profitable – privacy-invasion industry that has monetized the abuse of human rights at unimaginable scale.
The coalition in favor of keeping privacy law frozen since the season finale of St Elsewhere keeps growing, because there is an unbounded set of way to transform the systematic invasion of our human rights into cash. There's a direct line from this phenomenon to nurses whose paychecks go down when they can't pay their credit-card bills.
So competition is dead, regulation is dead, and companies aren't disciplined by markets or by states.
But there are four forces that discipline firms, contributing to an inhospitable environment for the reproduction of sociopathic. enshittifying monsters.
So let's talk about those other two forces. The first is interoperability, the principle of two or more things working together. Like, you can put anyone's shoelaces in your shoes, anyone's gas in your gas tank, and anyone's lightbulbs in your light-socket. In the non-digital world, interop takes a lot of work, you have to agree on the direction, pitch, diameter, voltage, amperage and wattage for that light socket, or someone's gonna get their hand blown off.
But in the digital world, interop is built in, because there's only one kind of computer we know how to make, the Turing-complete, universal, von Neumann machine, a computing machine capable of executing every valid program.
Which means that for any enshittifying program, there's a counterenshittificatory program waiting to be run. When HP writes a program to ensure that its printers reject third-party ink, someone else can write a program to disable that checking.
For gig workers, antienshittificatory apps can do yeoman duty. For example, Indonesian gig drivers formed co-ops, that commission hackers to write modifications for their dispatch apps. For example, the taxi app won't book a driver to pick someone up at a train station, unless they're right outside, but when the big trains pull in that's a nightmare scene of total, lethal chaos.
So drivers have an app that lets them spoof their GPS, which lets them park up around the corner, but have the app tell their bosses that they're right out front of the station. When a fare arrives, they can zip around and pick them up, without contributing to the stationside mishegas.
In the USA, a company called Para shipped an app to help Doordash drivers get paid more. You see, Doordash drivers make most of their money on tips, and the Doordash driver app hides the tip amount until you accept a job, meaning you don't know whether you're accepting a job that pays $1.50 or $11.50 with tip, until you agree to take it. So Para made an app that extracted the tip amount and showed it to drivers before they clocked on.
But Doordash shut it down, because in America, apps like Para are illegal. In 1998, Bill Clinton signed a law called the Digital Millennium Copyright Act, and section 1201 of the DMCA makes is a felony to "bypass an access control for a copyrighted work," with penalties of $500k and a 5-year prison sentence for a first offense. So just the act of reverse-engineering an app like the Doordash app is a potential felony, which is why companies are so desperately horny to get you to use their apps rather than their websites.
The web is open, apps are closed. The majority of web users have installed an ad blocker (which is also a privacy blocker). But no one installs an ad blocker for an app, because it's a felony to distribute that tool, because you have to reverse-engineer the app to make it. An app is just a website wrapped in enough IP so that the company that made it can send you to prison if you dare to modify it so that it serves your interests rather than theirs.
Around the world, we have enacted a thicket of laws, we call “IP laws,” that make it illegal to modify services, products, and devices, so that they serve your interests, rather than the interests of the shareholders.
Like I said, these laws were enacted in living memory, by people who are among us, who were warned about the obvious, eminently foreseeable consequences of their reckless plans, who did it anyway.
Back in 2010, two ministers from Stephen Harper's government decided to copy-paste America's Digital Millennium Copyright Act into Canadian law. They consulted on the proposal to make it illegal to reverse engineer and modify services, products and devices, and they got an earful! 6,138 Canadians sent in negative comments on the consultation. They warned that making it illegal to bypass digital locks would interfere with repair of devices as diverse as tractors, cars, and medical equipment, from ventilators to insulin pumps.
These Canadians warned that laws banning tampering with digital locks would let American tech giants corner digital markets, forcing us to buy our apps and games from American app stores, that could cream off any commission they chose to levy. They warned that these laws were a gift to monopolists who wanted to jack up the price of ink; that these copyright laws, far from serving Canadian artists would lock us to American platforms. Because every time someone in our audience bought a book, a song, a game, a video, that was locked to an American app, it could never be unlocked.
So if we, the creative workers of Canada, tried to migrate to a Canadian store, our audience couldn't come with us. They couldn't move their purchases from the US app to a Canadian one.
6,138 Canadians told them this, while just 54 respondents sided with Heritage Minister James Moore and Industry Minister Tony Clement. Then, James Moore gave a speech, at the International Chamber of Commerce meeting here in Toronto, where he said he would only be listening to the 54 cranks who supported his terrible ideas, on the grounds that the 6,138 people who disagreed with him were "babyish…radical extremists."
So in 2012, we copied America's terrible digital locks law into the Canadian statute book, and now we live in James Moore and Tony Clement's world, where it is illegal to tamper with a digital lock. So if a company puts a digital lock on its product they can do anything behind that lock, and it's a crime to undo it.
For example, if HP puts a digital lock on its printers that verifies that you're not using third party ink cartridges, or refilling an HP cartridge, it's a crime to bypass that lock and use third party ink. Which is how HP has gotten away with ratcheting the price of ink up, and up, and up.
Printer ink is now the most expensive fluid that a civilian can purchase without a special permit. It's colored water that costs $10k/gallon, which means that you print out your grocery lists with liquid that costs more than the semen of a Kentucky Derby-winning stallion.
That's the world we got from Clement and Moore, in living memory, after they were warned, and did it anyway. The world where farmers can't fix their tractors, where independent mechanics can't fix your car, where hospitals during the pandemic lockdowns couldn't service their failing ventilators, where every time a Canadian iPhone user buys an app from a Canadian software author, every dollar they spend takes a round trip through Apple HQ in Cupertino, California and comes back 30 cents lighter.
Let me remind you this is the world where a nurse can't get a counter-app, a plug-in, for the “Uber for nurses” app they have to use to get work, that lets them coordinate with other nurses to refuse shifts until the wages on offer rise to a common level or to block surveillance of their movements and activity.
Interoperability was a major disciplining force on tech firms. After all, if you make the ads on your website sufficiently obnoxious, some fraction of your users will install an ad-blocker, and you will never earn another penny from them. Because no one in the history of ad-blockers has ever uninstalled an ad-blocker. But once it's illegal to make an ad-blocker, there's no reason not to make the ads as disgusting, invasive, obnoxious as you can, to shift all the value from the end user to shareholders and executives.
So we get monopolies and monopolies capture their regulators, and they can ignore the laws they don't like, and prevent laws that might interfere with their predatory conduct – like privacy laws – from being passed. They get new laws passed, laws that let them wield governmental power to prevent other companies from entering the market.
So three of the four forces are neutralized: competition, regulation, and interoperability. That left just one disciplining force holding enshittification at bay: labor.
Tech workers are a strange sort of workforce, because they have historically been very powerful, able to command high wages and respect, but they did it without joining unions. Union density in tech is abysmal, almost undetectable. Tech workers' power didn't come from solidarity, it came from scarcity. There weren't enough workers to fill the jobs going begging, and tech workers are unfathomnably productive. Even with the sky-high salaries tech workers commanded, every hour of labor they put in generated far more value for their employers.
Faced with a tight labor market, and the ability to turn every hour of tech worker overtime into gold, tech bosses pulled out all the stops to motivate that workforce. They appealed to workers' sense of mission, convinced them they were holy warriors, ushering in a new digital age. Google promised them they would "organize the world's information and make it useful.” Facebook promised them they would “make the world more open and connected."
There's a name for this tactic: the librarian Fobazi Ettarh calls it "vocational awe." That’s where an appeal to a sense of mission and pride is used to motivate workers to work for longer hours and worse pay.
There are all kinds of professions that run on vocational awe: teaching, daycares and eldercare, and, of course, nursing.
Techies are different from those other workers though, because they've historically been incredibly scarce, which meant that while bosses could motivate them to work on projects they believed in, for endless hours, the minute bosses ordered them to enshittify the projects they'd missed their mothers' funerals to ship on deadline these workers would tell their bosses to fuck off.
If their bosses persisted in these demands, the techies would walk off the job, cross the street, and get a better job the same day.
So for many years, tech workers were the fourth and final constraint, holding the line after the constraints of competition, regulation and interop slipped away. But then came the mass tech layoffs. 260,000 in 2023; 150,000 in 2024; tens of thousands this year, with Facebook planning a 5% headcount massacre while doubling its executive bonuses.
Tech workers can't tell their bosses to go fuck themselves anymore, because there's ten other workers waiting to take their jobs.
Now, I promised I wouldn't talk about AI, but I have to break that promise a little, just to point out that the reason tech bosses are so horny for AI Is because they think it'll let them fire tech workers and replace them with pliant chatbots who'll never tell them to fuck off.
So that's where enshittification comes from: multiple changes to the environment. The fourfold collapse of competition, regulation, interoperability and worker power creates an enshittogenic environment, where the greediest, most sociopathic elements in the body corporate thrive at the expense of those elements that act as moderators of their enshittificatory impulses.
We can try to cure these corporations. We can use antitrust law to break them up, fine them, force strictures upon them. But until we fix the environment, other the contagion will spread to other firms.
So let's talk about how we create a hostile environment for enshittifiers, so the population and importance of enshittifying agents in companies dwindles to 1990s levels. We won't get rid of these elements. So long as the profit motive is intact, there will be people whose pursuit of profit is pathological, unmoderated by shame or decency. But we can change the environment so that these don't dominate our lives.
Let's talk about antitrust. After 40 years of antitrust decline, this decade has seen a massive, global resurgence of antitrust vigor, one that comes in both left- and right-wing flavors.
Over the past four years, the Biden administration’s trustbusters at the Federal Trade Commission, Department of Justice and Consumer Finance Protection Bureau did more antitrust enforcement than all their predecessors for the past 40 years combined.
There's certainly factions of the Trump administration that are hostile to this agenda but Trump's antitrust enforcers at the DoJ and FTC now say that they'll preserve and enforce Biden's new merger guidelines, which stop companies from buying each other up, and they've already filed suit to block a giant tech merger.
Of course, last summer a judge found Google guilty of monopolization, and now they're facing a breakup, which explains why they've been so generous and friendly to the Trump administration.
Meanwhile, in Canada, our toothless Competition Bureau's got fitted for a set of titanium dentures last June, when Bill C59 passed Parliament, granting sweeping new powers to our antitrust regulator.
It's true that UK PM Keir Starmer just fired the head of the UK Competition and Markets Authority and replaced him with the ex-boss of Amazon UK boss.But the thing that makes that so tragic is that the UK CMA had been doing astonishingly great work under various conservative governments.
In the EU, they've passed the Digital Markets Act and the Digital Services Act, and they're going after Big Tech with both barrels. Other countries around the world – Australia, Germany, France, Japan, South Korea and China (yes, China!) – have passed new antitrust laws, and launched major antitrust enforcement actions, often collaborating with each other.
So you have the UK Competition and Markets Authority using its investigatory powers to research and publish a deep market study on Apple's abusive 30% app tax, and then the EU uses that report as a roadmap for fining Apple, and then banning Apple's payments monopoly under new regulations.Then South Korea and Japan trustbusters translate the EU's case and win nearly identical cases in their courts
What about regulatory capture? Well, we're starting to see regulators get smarter about reining in Big Tech. For example, the EU's Digital Markets Act and Digital Services Act were designed to bypass the national courts of EU member states, especially Ireland, the tax-haven where US tech companies pretend to have their EU headquarters.
The thing about tax havens is that they always turn into crime havens, because if Apple can pretend to be Irish this week, it can pretend to be Maltese or Cypriot or Luxembourgeois next week. So Ireland has to let US Big Tech companies ignore EU privacy laws and other regulations, or it'll lose them to sleazier, more biddable competitor nations.
So from now on, EU tech regulation is getting enforced in the EU's federal courts, not in national courts, treating the captured Irish courts as damage and routing around them.
Canada needs to strengthen its own tech regulation enforcement, unwinding monopolistic mergers from the likes of Bell and Rogers, but most of all, Canada needs to pursue an interoperability agenda.
Last year, Canada passed two very exciting bills: Bill C244, a national Right to Repair law; and Bill C294, an interoperability law. Nominally, both of these laws allow Canadians to fix everything from tractors to insulin pumps, and to modify the software in their devices from games consoles to printers, so they will work with third party app stores, consumables and add-ons.
However, these bills are essentially useless, because these bills don’t permit Canadians to acquire tools to break digital locks. So you can modify your printer to accept third party ink, or interpret a car's diagnostic codes so any mechanic can fix it, but only if there isn't a digital lock stopping you from doing so, because giving someone a tool to break a digital lock remains illegal thanks to the law that James Moore and Tony Clement shoved down the nation's throat in 2012.
And every single printer, smart speaker, car, tractor, appliance, medical implant and hospital medical device has a digital lock that stops you from fixing it, modifying it, or using third party parts, software, or consumables in it.
Which means that these two landmark laws on repair and interop are useless. So why not get rid of the 2012 law that bans breaking digital locks? Because these laws are part of our trade agreement with the USA. This is a law needed to maintain tariff-free access to US markets.
I don’t know if you've heard, but Donald Trump is going to impose a 25%, across-the-board tariff against Canadian exports. Trudeau's response is to impose retaliatory tariffs, which will make every American product that Canadians buy 25% more expensive. This is a very weird way to punish America!
You know what would be better? Abolish the Canadian laws that protect US Big Tech companies from Canadian competition. Make it legal to reverse-engineer, jailbreak and modify American technology products and services. Don't ask Facebook to pay a link tax to Canadian newspapers, make it legal to jailbreak all of Meta's apps and block all the ads in them, so Mark Zuckerberg doesn't make a dime off of us.
Make it legal for Canadian mechanics to jailbreak your Tesla and unlock every subscription feature, like autopilot and full access to your battery, for one price, forever. So you get more out of your car, and when you sell it, then next owner continues to enjoy those features, meaning they'll pay more for your used car.
That's how you hurt Elon Musk: not by being performatively appalled at his Nazi salutes. That doesn't cost him a dime. He loves the attention. No! Strike at the rent-extracting, insanely high-margin aftermarket subscriptions he relies on for his Swastikar business. Kick that guy right in the dongle!
Let Canadians stand up a Canadian app store for Apple devices, one that charges 3% to process transactions, not 30%. Then, every Canadian news outlet that sells subscriptions through an app, and every Canadian software author, musician and writer who sells through a mobile platform gets a 25% increase in revenues overnight, without signing up a single new customer.
But we can sign up new customers, by selling jailbreaking software and access to Canadian app stores, for every mobile device and games console to everyone in the world, and by pitching every games publisher and app maker on selling in the Canadian app store to customers anywhere without paying a 30% vig to American big tech companies.
We could sell every mechanic in the world a $100/month subscription to a universal diagnostic tool. Every farmer in the world could buy a kit that would let them fix their own John Deere tractors without paying a $200 callout charge for a Deere technician who inspects the repair the farmer is expected to perform.
They'd beat a path to our door. Canada could become a tech export powerhouse, while making everything cheaper for Canadian tech users, while making everything more profitable for anyone who sells media or software in an online store. And – this is the best part – it’s a frontal assault on the largest, most profitable US companies, the companies that are single-handedly keeping the S&P 500 in the black, striking directly at their most profitable lines of business, taking the revenues from those ripoff scams from hundreds of billions to zero, overnight, globally.
We don't have to stop at exporting reasonably priced pharmaceuticals to Americans! We could export the extremely lucrative tools of technological liberation to our American friends, too.
That's how you win a trade-war.
What about workers? Here we have good news and bad news.
The good news is that public approval for unions is at a high mark last seen in the early 1970s, and more workers want to join a union than at any time in generations, and unions themselves are sitting on record-breaking cash reserves they could be using to organize those workers.
But here's the bad news. The unions spent the Biden years, when they had the most favorable regulatory environment since the Carter administration, when public support for unions was at an all-time high, when more workers than ever wanted to join a union, when they had more money than ever to spend on unionizing those workers, doing fuck all. They allocatid mere pittances to union organizing efforts with the result that we finished the Biden years with fewer unionized workers than we started them with.
Then we got Trump, who illegally fired National Labor Relations Board member Gwynne Wilcox, leaving the NLRB without a quorum and thus unable to act on unfair labor practices or to certify union elections.
This is terrible. But it’s not game over. Trump fired the referees, and he thinks that this means the game has ended. But here's the thing: firing the referee doesn't end the game, it just means we're throwing out the rules. Trump thinks that labor law creates unions, but he's wrong. Unions are why we have labor law. Long before unions were legal, we had unions, who fought goons and ginks and company finks in` pitched battles in the streets.
That illegal solidarity resulted in the passage of labor law, which legalized unions. Labor law is passed because workers build power through solidarity. Law doesn't create that solidarity, it merely gives it a formal basis in law. Strip away that formal basis, and the worker power remains.
Worker power is the answer to vocational awe. After all, it's good for you and your fellow workers to feel a sense of mission about your jobs. If you feel that sense of mission, if you feel the duty to protect your users, your patients, your patrons, your students, a union lets you fulfill that duty.
We saw that in 2023 when Doug Ford promised to destroy the power of Ontario's public workers. Workers across the province rose up, promising a general strike, and Doug Ford folded like one of his cheap suits. Workers kicked the shit out of him, and we'll do it again. Promises made, promises kept.
The unscheduled midair disassembly of American labor law means that workers can have each others' backs again. Tech workers need other workers' help, because tech workers aren't scarce anymore, not after a half-million layoffs. Which means tech bosses aren't afraid of them anymore.
We know how tech bosses treat workers they aren't afraid of. Look at Jeff Bezos: the workers in his warehouses are injured on the job at 3 times the national rate, his delivery drivers have to pee in bottles, and they are monitored by AI cameras that snitch on them if their eyeballs aren't in the proscribed orientation or if their mouth is open too often while they drive, because policy forbids singing along to the radio.
By contrast, Amazon coders get to show up for work with pink mohawks, facial piercings, and black t-shirts that say things their bosses don't understand. They get to pee whenever they want. Jeff Bezos isn't sentimental about tech workers, nor does he harbor a particularized hatred of warehouse workers and delivery drivers. He treats his workers as terribly as he can get away with. That means that the pee bottles are coming for the coders, too.
It's not just Amazon, of course. Take Apple. Tim Cook was elevated to CEO in 2011. Apple's board chose him to succeed founder Steve Jobs because he is the guy who figured out how to shift Apple's production to contract manufacturers in China, without skimping on quality assurance, or suffering leaks of product specifications ahead of the company's legendary showy launches.
Today, Apple's products are made in a gigantic Foxconn factory in Zhengzhou nicknamed "iPhone City.” Indeed, these devices arrive in shipping containers at the Port of Los Angeles in a state of pristine perfection, manufactured to the finest tolerances, and free of any PR leaks.
To achieve this miraculous supply chain, all Tim Cook had to do was to make iPhone City a living hell, a place that is so horrific to work that they had to install suicide nets around the worker dorms to catch the plummeting bodies of workers who were so brutalized by Tim Cook's sweatshop that they attempted to take their own lives.
Tim Cook is also not sentimentally attached to tech workers, nor is he hostile to Chinese assembly line workers. He just treats his workers as badly as he can get away with, and with mass layoffs in the tech sector he can treat his coders much, much worse
How do tech workers get unions? Well, there are tech-specific organizations like Tech Solidarity and the Tech Workers Coalition. But tech workers will only get unions by having solidarity with other workers and receiving solidarity back from them. We all need to support every union. All workers need to have each other's backs.
We are entering a period of omnishambolic polycrisis.The ominous rumble of climate change, authoritarianism, genocide, xenophobia and transphobia has turned into an avalanche. The perpetrators of these crimes against humanity have weaponized the internet, colonizing the 21st century's digital nervous system, using it to attack its host, threatening civilization itself.
The enshitternet was purpose-built for this kind of apocalyptic co-option, organized around giant corporations who will trade a habitable planet and human rights for a three percent tax cut, who default us all into twiddle-friendly algorithmic feed, and block the interoperability that would let us escape their clutches with the backing of powerful governments whom they can call upon to "protect their IP rights."
It didn't have to be this way. The enshitternet was not inevitable. It was the product of specific policy choices, made in living memory, by named individuals.
No one came down off a mountain with two stone tablets, intoning Tony Clement, James Moore: Thou shalt make it a crime for Canadians to jailbreak their phones. Those guys chose enshittification, throwing away thousands of comments from Canadians who warned them what would come of it.
We don't have to be eternal prisoners of the catastrophic policy blunders of mediocre Tory ministers. As the omnicrisis polyshambles unfolds around us, we have the means, motive and opportunity to craft Canadian policies that bolster our sovereignty, protect our rights, and help us to set every technology user, in every country (including the USA) free.
The Trump presidency is an existential crisis but it also presents opportunities. When life gives you SARS, you make sarsaparilla. We once had an old, good internet, whose major defect was that it required too much technical expertise to use, so all our normie friends were excluded from that wondrous playground.
Web 2.0's online services had greased slides that made it easy for anyone to get online, but escaping from those Web 2.0 walled gardens meant was like climbing out of a greased pit. A new, good internet is possible, and necessary. We can build it, with all the technological self-determination of the old, good internet, and the ease of use of Web 2.0.
A place where we can find each other, coordinate and mobilize to resist and survive climate collapse, fascism, genocide and authoritarianism. We can build that new, good internet, and we must.

If you'd like an essay-formatted version of this post to read or share, here's a link to it on pluralistic.net, my surveillance-free, ad-free, tracker-free blog:
https://pluralistic.net/2025/02/26/ursula-franklin/#enshittification-eh

#pluralistic#bill c-11#canada#cdnpoli#Centre for Culture and Technology#enshittification#groundwork collective#innis college#jailbreak all the things#james moore#nurses#nursing#speeches#tariff wars#tariffs#technological self-determination#tony clement#toronto#u of t#university of toronto#ursula franklin#ursula franklin lecture
638 notes
·
View notes
Text
Blog #10
"Analyzing crime dollhouses using McLuhan Tetrad "
In one of the lectures, we were taught about extended reality and the many different types that exist within, with the types being augmented, mixed, and virtual reality. Virtual reality is perhpas the most well known and what most people think when hearing extended reality. Eaton defines virtual reality as "Technology leveraged to immerse oneself in a computer-generated 3D world through use of a head-mounted display, completely occluding the view of the physical world." (Eaton, 2024) Meaning, its practically a tool that allows the person to inmerse in a virtual and digital world as if its their new reality.
However, extended reality can also be applied to things outside of the virtual world, in the physical world, and that includes augmented reality, which Eaton claims to be "A digital overlay of 2D or 3D content onto the physical world, typically experienced with a smartphone, tablet, or wearable device."(Eaton, 2024) Extendend reality also does not neccesarily need advanced technology, and one such example that caught my attention where it might or might not be considered extended reality, is that of crime dollhouses,.

Fig.1: Crime dollhouse
These type of peculiar houses are often using with training purposes for forensics and police forces. The most famous artist behind them is Frances Glesner Lee. Glesner´s dollhouses represent real crimes that have occured and according to Burges, Glesner´s scenes were " perfectly scaled and intensely detailed—they are also highly functional. The locks on the doors and windows and even a tiny mousetrap all actually work. A tiny rocking chair moves when pushed. And, because the purpose of each one was to recreate the scene of a crime that had actually happened, each corpse—from clothing to blood stains to level of decomposition—had to be made precisely." Such amount of details then could be argued that dollhouses are able to create an alternate world, where investigators get absored into the the diorama trying to solve the complex mysteries and interpreting the detailed clues.
Thus, in my opinion, these type of houses should be considered part of the extended reality, perphaps falling into the augmented category, as the dolls and scenes do require some form of technology even if not extremely advanced like that of virtual.
To further analyze the effectiveness of these crime dollhouses, I will look at it through the McLuhan Tetrad. This tool was coined after Marshall McLuhan, famous for his research within media theory. Acoording to him, "all media are extensions of some human faculty,psychic or physical"(McLuhan, 1996) He then created this tetrad, as he claimed every type of medium followed the same "laws" in which they extend, retrieve, reverse and obsolesces.
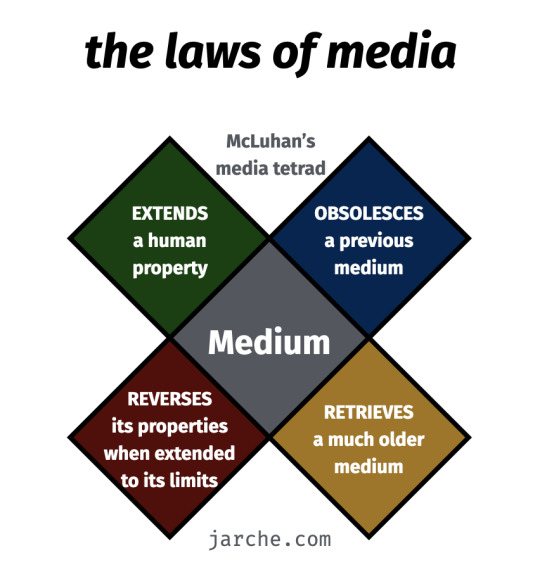
Fig.2: McLuhan Tetrad
The tetrad presents 4 main points and I will be applying it to the crime dollhouses:
-Extension: also sometimes called enhance, is what does the media extend from the human senses, or what does it enhance for humans. For the crime dollhouses, they extend the sight and observation, improving the analytical and interpretational skills as the person looks around the house.
-Obsoleces: it is the replacement of the older medium which is no longer neccesary or is an inferior choice to the new medium. In this case, perphaps it reduces the neccesity to visit real crime scenes for training, reducing costs and time, as well as sparing the person from a gruesome scene.
-Retrieves: is the recovery of older mediums, that this new media allows it to come back and have new uses. It could be argued that crime dollhouses obviously brings back dollmaking and its usage on more serious topics rather than just for entertainment purposes.
-Reverses: when the new medium is pushed to its limits, it might create new problems which make its initial purpose lost. For instance, if too many crimedoll houses are made, then perphaps the quality of detail will decrease as each scene is carefully crafted and takes time. The possible deterioation of quality will then make the dollhouses become unapt as a method of training.
In conclusion, I believe crimedoll houses are a good example of a media that is able to be inmersive, useful, and depsite being niche and not the most used tool, it can be seen with the McLuhan tetrad that they as of now have been to strive a good balance between the 4 quadrants. I have learnt more about extended reality beyond the virtual and has make me appreciate other type of realities and their utilities.
References
-----------------------------------------------------------------------
Eaton, A. (2024) The Extended Reality Blueprint: Demystifying the AR/VR Production Process. 1st edn. Newark: John Wiley & Sons
Burgess, A. (2017). The Grim Crime-Scene Dollhouses Made by the ‘Mother of Forensics’. [online] Atlas Obscura. Available at: https://www.atlasobscura.com/articles/frances-glessner-lee-crime-scence-forensics-investigation-dioramas.(Accessed 26/12/2024)
McLuhan, M. and Fiore, Q. (1996). The Medium is the Massage. Hardwired.
0 notes
Text
YouLearnt: Making the World a Global Village in Education

In the past few decades, the landscape of education has undergone a profound transformation. The evolution of technology, combined with innovative ideas in pedagogy, has reshaped the way knowledge is accessed and shared. One of the most striking examples of this evolution is platforms like YouLearnt, which exemplify the idea of making the world a "global village" in terms of education and learning.
The Global Village Concept in Education
The concept of the "global village," coined by Marshall McLuhan, refers to the idea of the world being interconnected through technology, where distances and barriers are virtually eliminated. In the context of education, this notion has become increasingly relevant. In the past, education was often limited to the boundaries of one's country or region. Access to quality learning resources was confined to certain geographical areas, and even within those areas, disparities existed in terms of access to education. However, platforms like YouLearnt have brought about a paradigm shift in this dynamic.
YouLearnt has played a pivotal role in breaking down geographical barriers to learning. By offering a wide range of educational materials, courses, and resources, it has allowed learners from all corners of the world to access knowledge previously unavailable to them. A student in a remote village can now learn from world-class instructors or gain exposure to a vast array of topics without ever leaving their home. This has brought us closer to the vision of a global village, where learning is not limited by borders, but rather, transcends them.
The Evolution of Education: From Traditional Classrooms to Online Learning
The journey of education from traditional classrooms to digital platforms has been nothing short of revolutionary. Education has always been considered the key to personal and societal progress, but its delivery mechanisms have evolved over time. In the early days, learning was conducted face-to-face, with knowledge passed from teacher to student in a physical classroom. Books and handwritten notes were the primary tools for learning, and information was often slow to circulate.
The industrial revolution brought about some changes with the advent of mass education. However, it wasn't until the digital age that education experienced truly groundbreaking developments. The internet revolutionized the way information is shared, and online platforms began to emerge as a powerful tool for education. Websites offering open courses, online degrees, and even entire curriculums have paved the way for a more accessible and flexible form of education.
This shift to online learning has been accelerated by platforms like YouLearnt, which combine the flexibility of the internet with the interactivity of modern educational tools. Learners now have access to a vast array of learning materials, including videos, quizzes, live lectures, and discussion forums. The ability to learn at one’s own pace, with resources tailored to different learning styles, is one of the key advantages of this new era in education.
Personalized Learning and the Role of YouLearnt
One of the greatest benefits of platforms like YouLearnt is the personalization of learning. Unlike traditional education systems, where students often have to follow a set curriculum with little room for customization, online platforms allow learners to choose their own path. Whether it's focusing on a particular subject of interest or moving at a pace that suits their individual needs, the opportunity to create a personalized learning experience has transformed the way people approach education.
YouLearnt, with its wide array of courses and learning materials, enables students to curate their own educational journey. Whether a learner is interested in mastering a new language, developing coding skills, or exploring new scientific theories, the platform offers a wealth of resources to help them achieve their goals. Moreover, it allows learners to set their own schedules, which has been especially beneficial for adults who need to balance work, family, and studies.
The Future of Education: Bridging the Gap
While platforms like YouLearnt have made significant strides in globalizing education, there are still challenges to overcome. Not all regions have equal access to the internet, and economic disparities often prevent individuals from taking full advantage of online education. However, as technology continues to advance, solutions to these problems are emerging. For instance, low-cost smartphones, internet infrastructure development in underserved areas, and the expansion of online education initiatives are gradually bridging the gap.
The future of education lies in the continued integration of technology with traditional teaching methods. YouLearnt, along with other platforms, is helping to shape that future by offering high-quality education that transcends geographical, cultural, and economic barriers. As access to technology improves and more people have the opportunity to engage with digital learning platforms, the dream of a truly interconnected global village for education will become a reality.
Conclusion
In conclusion, YouLearnt is a shining example of how education has evolved from a localized, often exclusive experience to a global, inclusive one. It embodies the idea that knowledge should be accessible to everyone, regardless of where they are in the world. Through its innovative platform, it has not only made education more accessible but has also fostered a sense of community among learners from diverse backgrounds. As education continues to evolve, platforms like YouLearnt will undoubtedly play a key role in ensuring that the world of learning remains interconnected and accessible to all.
0 notes
Text

Add. Join. React. Prompt. Lurk. Tip. Trade.
Digitale Plattformen und Systeme geben uns eine bestimmte Form der Kommunikation vor, die mit einer Performance von proximity einhergeht: Sie basieren auf einem choreografierten Algo-Rhythmus, der durch die reibungslose Benutzer:innenoberflächen unserer Geräte auf unsere Politiken, unsere Arbeit und unsere Beziehungen zueinander einwirkt.
Von ASMR Trash Talk Flüstern auf TikTok, über Kinder, die mit ihren Eltern sprechen als wären diese Alexa, bis hin zu e-girls, die ihr Badewasser verkaufen, oder Menschen, die Roboter cosplayen und auf einem Tesla-Event Getränke servieren – Algorithmen (ver)formen unser menschliches Bedürfnis nach Verbindung, indem sie trügerische Formen von Nähe (proximity) als Ersatz für tatsächliche Vertrautheit (closeness) vorantreiben.
(near) near but — far , die 38. Ausgabe von transmediale, erarbeitet ein Verständnis für das fragwürdige Verhältnis von dieser seltsamen, virtuell erzeugten Nähe und den damit einhergehenden neuen Formen der Vertrautheit, die uns durch automatisierte Transaktionen vorgeschlagen werden. Das Festival geht dabei über die bloße Gegenüberstellung des Begriffspaares von Nähe (proximity) und Vertrautheit (closeness) hinaus und nähert sich anhand einer Reihe von Affekten der Kernfrage der Thematik an: Wie können Technologien Beziehungen unterstützen, die angemessener auf die Komplexitäten unseres individuellen und kollektiven Unmuts reagieren können?
Ein umfassendes Diskurs- und Performanceprogramm wird am Freitag, Samstag und Sonntag im langjährigen Veranstaltungsort der transmediale, dem Haus der Kulturen der Welt (HKW), präsentiert. Konzipiert als Prolog gehen dem Festivalwochenende zwei Tage mit Workshops und Arbeitsgruppen im silent green Kulturquartier voraus, die eine separate Anmeldung erfordern. Das Festival wird am Abend des 30. Januar 2025 im silent green, der Berliner Basis von transmediale, eröffnet. Die jährliche Marshall McLuhan Lecture wird vor der Festivaleröffnung in der Botschaft von Kanada zu Berlin stattfinden.
transmediale 2025 folgt einer erneuerten kuratorischen Herangehensweise, die sowohl das Thema als auch die Programmatik und Methodologie des Festivals prägt. Zwei Kurator:innen, Ben Evans James and Elise Misao Hunchuck, entwickeln den thematischen Fokus der Festivalausgabe und leiten die kuratorische Forschung an. Ihre Schwerpunktsetzung bildet den Ausgangspunkt für ein erweitertes kuratorisches Team aus eingeladenen Programmakteur:innen und der engen inhaltlichen Zusammenarbeit mit langjährigen Partner:innen von transmediale. Weitere Details zum erweiterten Kurator:innenteam und den Mitwirkenden sowie dem Programm folgen in Kürze.
0 notes
Text
What is academic art? There are a lot of ways to define this. We all know what late-nineteenth-century French academic painting looks like. And we can see why Greenberg wouldn’t like that, but he defines academic art toward the end of his career in a way that would please McLuhan a great deal. Namely, Greenberg says, in a late lecture in Australia, that academic art is art that is unaware of its medium. So, one good example of academic art would be art that simply continues to paint three-dimensional objects arranged in three-dimensional space as if we’re looking out a window — and here is mainstream painting as we have had it since the Italian Renaissance. Graham Harman, “What Is an Object?” In Artful Objects: Graham Harman on Art and the Business of Speculative Realism, edited by Isak Nilson and Erik Wikberg, 11-41. Berlin: Sternberg Press, 2020.
1 note
·
View note