#kcl electronics
Explore tagged Tumblr posts
Text










y2k tech
looking for a cd player sadly the coolest ones are always sold for parts only ♡╭╮♡
#walkman#sony#sony walkman#y2k aesthetic#nostalgia#2000s#00s#retro tech#mary kate and ashley#kcl electronics#pink aesthetic#pinkcore#brat green#brat girls#im just a girl#girl blog aesthetic#portable cd player#cds#physical media#futuristic#pastel core#kawaii aesthetic
217 notes
·
View notes
Text
Mastering the Fundamentals: Key Concepts Every Electrical Engineering Student Should Understand

A solid grounding in the fundamentals is essential for every aspiring electrical engineer. Mastery of these core concepts not only enables effective problem-solving and innovation but also forms the basis for all advanced studies and professional success in the field.
Core Principles and Laws
Ohm’s Law: This fundamental law relates voltage, current, and resistance in a circuit. It states that the voltage across a conductor is directly proportional to the current flowing through it, provided the physical conditions remain constant (V = I × R).
Kirchhoff’s Laws:
Kirchhoff’s Current Law (KCL): The total current entering a junction equals the total current leaving it.
Kirchhoff’s Voltage Law (KVL): The algebraic sum of all voltages around any closed loop in a circuit is zero.
Network Theorems: Thevenin’s and Norton’s theorems are essential for simplifying complex circuits and analyzing their behavior.
Basic Electrical Quantities
Current (I): The flow of electric charge, measured in amperes. It is the movement of electrons through a conductor.
Voltage (V): The electrical potential difference that drives current through a circuit, measured in volts.
Resistance (R): The opposition to current flow, measured in ohms. It depends on the material, length, and cross-sectional area of the conductor.
Power (P): The rate of energy transfer in a circuit, calculated as P=IVP=IV, measured in watts.
Circuit Elements and Analysis
Passive Elements: Resistors, capacitors, and inductors, which absorb or store energy but do not generate it.
Active Elements: Voltage and current sources that supply energy to the circuit.
Series and Parallel Circuits: Understanding how components behave in series (same current, voltage divides) and parallel (same voltage, current divides) is crucial for circuit analysis.
Star-Delta Transformation: A technique for simplifying complex resistor networks.
Types of Circuits
DC Circuits: Circuits powered by a constant direct current source. Analysis involves the steady-state behavior of resistors, capacitors, and inductors.
AC Circuits: Circuits powered by alternating current sources. Analysis includes understanding reactance, impedance, and phase relationships.
Single-phase and Three-phase Systems: Essential for understanding power distribution and the operation of industrial equipment.
Electromagnetism and Machines
Electromagnetic Principles: Understanding magnetic fields, flux, and electromagnetic induction is foundational for working with motors, generators, and transformers.
Transformers: Devices that transfer electrical energy between circuits through electromagnetic induction. Key for voltage conversion and power distribution.
Motors and Generators: Machines that convert electrical energy to mechanical energy (motors) and vice versa (generators). Knowledge of their principles and operation is vital.
Measurement and Instrumentation
Measuring Instruments: Familiarity with devices like voltmeters, ammeters, and multimeters is essential for practical circuit analysis and troubleshooting.
Power Factor: Understanding and improving power factor is important for efficient energy use in AC systems.
Mathematics and Physics Foundations
Mathematics: Proficiency in calculus, trigonometry, and differential equations is necessary for modeling and analyzing electrical systems.
Physics: Concepts from electromagnetism and basic mechanics underpin much of electrical engineering theory and practice.
Digital and Analog Systems
Analog Circuits: Continuous signal processing; involves resistors, capacitors, inductors, and transistors.
Digital Circuits: Discrete signal processing; involves logic gates, memory systems, and microcontrollers.
Embedded Systems: Integration of hardware and software for intelligent electronic solutions.
Practical Skills and Lifelong Learning
Circuit Design and Simulation: The Ability to design, analyze, and simulate circuits using modern tools is crucial for both academic and professional success.
Project-Based Learning: Hands-on experience through projects enhances understanding and develops problem-solving skills.
Continuous Learning: The rapid evolution of technology in electrical engineering demands ongoing education and adaptability.
1. Concept/Area
Ohm’s Law, KCL, KVL
Why It’s Essential
Foundation for circuit analysis and design
2. Concept/Area
Circuit Elements
Why It’s Essential
Understanding the behavior and function of components
3. Concept/Area
AC/DC Circuits
Why It’s Essential
Basis for power systems, electronics, and signal processing
4. Concept/Area
Electromagnetism
Why It’s Essential
Underpins the operation of machines, transformers, and communication systems
5. Concept/Area
Measurement & Instrumentation
Why It’s Essential
Enables accurate analysis and troubleshooting
6.Concept/Area
Mathematics & Physics
Why It’s Essential
Provides tools for modeling and solving engineering problems
7. Concept/Area
Analog & Digital Systems
Why It’s Essential
Core to modern electronics and embedded systems
8. Concept/Area
Lifelong Learning
Why It’s Essential
Ensures relevance and adaptability in a fast-evolving field
Summary Table: Key Concepts and Their Importance
Conclusion
Mastering these fundamentals equips electrical engineering students to analyze, design, and maintain the systems that power modern society. Arya College of Engineering & I.T. is the best college of Jaipur which has a deep understanding of these core concepts fosters innovation, supports professional growth, and prepares students for the diverse challenges of an ever-evolving field.
Source: Click Here
#best btech college in jaipur#best engineering college in jaipur#best private engineering college in jaipur#top engineering college in jaipur#best engineering college in rajasthan
0 notes
Text
The Building Blocks of Electrical Engineering: What Every Student Should Master
A solid grounding in the fundamentals is essential for every aspiring electrical engineer. Mastery of these core concepts not only enables effective problem-solving and innovation but also forms the basis for all advanced studies and professional success in the field.
Core Principles and Laws
Ohm’s Law: This fundamental law relates voltage, current, and resistance in a circuit. It states that the voltage across a conductor is directly proportional to the current flowing through it, provided the physical conditions remain constant (V = I × R).
Kirchhoff’s Laws:
Kirchhoff’s Current Law (KCL): The total current entering a junction equals the total current leaving it.
Kirchhoff’s Voltage Law (KVL): The algebraic sum of all voltages around any closed loop in a circuit is zero.
Network Theorems: Thevenin’s and Norton’s theorems are essential for simplifying complex circuits and analyzing their behavior.
Basic Electrical Quantities
Current (I): The flow of electric charge, measured in amperes. It is the movement of electrons through a conductor.
Voltage (V): The electrical potential difference that drives current through a circuit, measured in volts.
Resistance (R): The opposition to current flow, measured in ohms. It depends on the material, length, and cross-sectional area of the conductor.
Power (P): The rate of energy transfer in a circuit, calculated as P=IVP=IV, measured in watts.
Circuit Elements and Analysis
Passive Elements: Resistors, capacitors, and inductors, which absorb or store energy but do not generate it.
Active Elements: Voltage and current sources that supply energy to the circuit.
Series and Parallel Circuits: Understanding how components behave in series (same current, voltage divides) and parallel (same voltage, current divides) is crucial for circuit analysis.
Star-Delta Transformation: A technique for simplifying complex resistor networks.
Types of Circuits
DC Circuits: Circuits powered by a constant direct current source. Analysis involves the steady-state behavior of resistors, capacitors, and inductors.
AC Circuits: Circuits powered by alternating current sources. Analysis includes understanding reactance, impedance, and phase relationships.
Single-phase and Three-phase Systems: Essential for understanding power distribution and the operation of industrial equipment.
Electromagnetism and Machines
Electromagnetic Principles: Understanding magnetic fields, flux, and electromagnetic induction is foundational for working with motors, generators, and transformers.
Transformers: Devices that transfer electrical energy between circuits through electromagnetic induction. Key for voltage conversion and power distribution.
Motors and Generators: Machines that convert electrical energy to mechanical energy (motors) and vice versa (generators). Knowledge of their principles and operation is vital.
Measurement and Instrumentation
Measuring Instruments: Familiarity with devices like voltmeters, ammeters, and multimeters is essential for practical circuit analysis and troubleshooting.
Power Factor: Understanding and improving power factor is important for efficient energy use in AC systems.
Mathematics and Physics Foundations
Mathematics: Proficiency in calculus, trigonometry, and differential equations is necessary for modeling and analyzing electrical systems.
Physics: Concepts from electromagnetism and basic mechanics underpin much of electrical engineering theory and practice.
Digital and Analog Systems
Analog Circuits: Continuous signal processing; involves resistors, capacitors, inductors, and transistors.
Digital Circuits: Discrete signal processing; involves logic gates, memory systems, and microcontrollers.
Embedded Systems: Integration of hardware and software for intelligent electronic solutions.
Practical Skills and Lifelong Learning
Circuit Design and Simulation: The Ability to design, analyze, and simulate circuits using modern tools is crucial for both academic and professional success.
Project-Based Learning: Hands-on experience through projects enhances understanding and develops problem-solving skills.
Continuous Learning: The rapid evolution of technology in electrical engineering demands ongoing education and adaptability.
Concept/Area
Why It’s Essential
Ohm’s Law, KCL, KVL
Foundation for circuit analysis and design
Circuit Elements
Understanding the behavior and function of components
AC/DC Circuits
Basis for power systems, electronics, and signal processing
Electromagnetism
Underpins the operation of machines, transformers, and communication systems
Measurement & Instrumentation
Enables accurate analysis and troubleshooting
Mathematics & Physics
Provides tools for modeling and solving engineering problems
Analog & Digital Systems
Core to modern electronics and embedded systems
Lifelong Learning
Ensures relevance and adaptability in a fast-evolving field
Summary Table: Key Concepts and Their Importance
Conclusion
Mastering these fundamentals equips electrical engineering students to analyze, design, and maintain the systems that power modern society. Arya College of Engineering & I.T. is the best college of Jaipur which has a deep understanding of these core concepts fosters innovation, supports professional growth, and prepares students for the diverse challenges of an ever-evolving field.
1 note
·
View note
Text
I realize that not everyone's education involved memorizing the Periodic Table of the Elements, but fer cryin' out loud, in this day of eavesdropping bots that can answer a question before one can finish asking it, check!
Here, this one's even color coded:

...which easily allows us to see that Potassium (K) is an alkali metal. Aside from the fact that potassium derives its symbol from the first letter of its Latin name, Kalium, it's placement on the Table in Group IA tells us that it is a lightweight, highly reactive metal. It has a single valence electron that happily pops off so that it can bond with the nearest negatively charged ion in its vicinity; not unlike a drunk frat boy on Homecoming weekend. This coupling, however, results in the formation of a salt. If we let it snog with Chlorine, it could go in the S shaker and be labled KCl and taste like table salt. The irony is, quite literally, delicious.
Meanwhile, phosphorus, a polyatomic nonmetal, has the proper symbol to be on the shaker. I'd like to say that it gives me no pleasure to dash (heh) OP's hopes yet again, but our friend phosphorus is also handsy with other elements and does not exist as elemental phosphorus. In nature it's found attached to several other atoms, thus its classification as polyatomic. Therefore, it would never have a shaker all to itself. Sorry, the Table has spoken.
Thank heaven OP didn't suggest sulfur for the S shaker. That would've stunk.

4K notes
·
View notes
Text
A810502010196 Right Door Assy for SANY machinery

A810502010196 Right Door Assy SANY spare parts Mail:[email protected] 160102040076A035 Valve Mechanism Module 160102030069B080 Dipstick Guide 920032400003A Reducer 10217855 SANY PARTS 160101100038A003 Screw 24902238 SANY PARTS 10024678 Flat plate QY26A-R-033.1-2 180103060163A Compound Drill 21039665 SANY PARTS 61014504 Reducer 160102080012A316 PUMP ASM; OIL 10446871 Pipe 22020006 CABLE TAB AWPSPHA-0836 10277949 SANY PARTS 61003485 sleeve bolt 10023995L 连接块料坯SYM5550J.3.6.3.1-2(L) 9181226000067 no name 160102050013A100 Idle Gear 894394-0923 160102110030A043 O-ring 10078899 - 10052648 Vertical Plate 160102100018B232 Breather Valve 919110700055A Full polish ratchet wrench 160604020042A Fuel Filter Element 10049474 Plate 10478891 Piston 10527565 槽钢WJX10JB.1.1-1 10448725 Beam, longitudinal 10277692 Board 160102150027A005 Generator 10507323 接头G1.5B.2-2 6735008730 End terminal SPEEA-0171 /EEA4558 922022400018A Centrifuge the filter paper 918060600036 soil layer apart drilling bucket φ0.75 22039364 Plate SPPCH006-A2032 10110519 Ground foot 10426413L SANY PARTS 10016272 Steel Sheet 532785 CABLE DRUM SUB-ASSEMBLY 21039770 SANY PARTS 160102080025B093 Plumbing, Exhaust 587844 SANY PARTS 160101100053A210 Lifting Lug Assy 10021931 Plate 1 160801010111A003 Water Cooler 10221701 SANY PARTS 10486170 Small car framework SRMG4530.5.13 A.1 10487743 SANY PARTS 10128239 - 160102030066A052 Rubber Hose [email protected] 59001455 SANY PARTS 21035112 Lock pin 180110990427B Full type Boring Tool 10067544 SANY PARTS 10166203 Handle 160899000068A Engines Lower Maintenance Package 523127 BASE 10034570 Wedge 10218643 Liner plate 61010858 Drive Shaft Assembly 24004576 Rubber Hose 21025970 SANY PARTS 521000 WING WELDMENT, LEFT 920031100042A 联轴器柱销牛筋圈IJ50-32-160PK 67300121 star knob M12X30_DIN6336 JB3717.22-85 /E 10268044 lateral riser 533316 EXT'N SHAFT KIT (AMSU3) 22029028 Spare part SPYS-0363 140x153x7x9.5 ÉÛÒº 160801010226A001 Cooling Module 180602990038A KCL-HCL 61030907 Wireless Data Acquisition Module 160102070174A028 CAN Line Basic Function Module 919050800001A SMHC35 type marking 10483795 钢管4SQ170.4.1.3-6 160101090060A127 Bolt M12×45 10177362 Side plate 59100370 元头鱼0 10405104 挡板SF808Ⅰ.26.7-2 160102050046A029 Exhaust Holder 160102040076A038 Cylinder Head Gasket 160102050080A075 Insert Element 180703990049A nylon brush 225400003 "支撑环D=56,7X61,0X1,23" 919122000015A Cable 10079390355 SCC500 Crawler Crane body 10606014 Platform Support 61016709 Dust ring 10079877 U-shaped protective cover Z2.1.1.2-2 10198115 Left arc shape plate 21028471 Front cover plate 10223499 torque converter tube clamp mount 24000918 Nut 9190314000296 电动阀门角行程DN20-WCB衬陶瓷 24905870 SANY PARTS 61005339 rubber hose 10261385 supporting frame2 10165501 Oil cylinder adaptor 160101160011A065 Crank Train 10133455 右墙板料坯QY50C.2.1.1-18AL 160102110019B008 Plug 180109990485A Carbide shank 61015167 Reducer 10621818 K953 Package for other small parts 67341650242 Deep groove ball bearings SPELW-0007 619 22025978 Valve assem SPKMG-00087A 10221878 车架YL1Z.6 10063614 Right Outer Panel 10165449B SANY PARTS 160102160037A203 Flange 10276333 spacer ring 61028322 WIRE HARNESS HVAC 22022391 Bending plate2 SPHA-0886 10053788 SANY PARTS 181604001214A Column Protective Sleeve 10250090 保险盒安装座SY200C3.1.5.4-3A 51003888 SANY PARTS 21018141 Board 10014850 板料坯QY50A.1.3-8(L) 160101070011B166 Pulley, Crankshaft 160101090029B135 WATER PUMP GASKET 59005781 SANY PARTS 10006814 Bolt 10260946 右梁PQ190Ⅱ.2.2.1B 21013587 Copper sleeve 24996741 Taper shank reamer for machining 10669833 Upper Flange 10526208 SANY PARTS 160102070164A089 Electronic Control Module Bracket 919080100001A 墙面除尘打磨机220V 22039898 Diagonal tube SPFP-0267 10014395 Group welding tooling of connecting fork 59010065 SANY PARTS 160501000009A SCR Catalyst Muffler 22039246 SPS8500HT Crane SP109-ST-M 53000297 Safety Helmet 922012600083A Thermostat 24912911 Bottom seat board 10122859MP SANY PARTS 160102110010A281 Flange screw 24909696 Small elbow 10260939 SANY PARTS 10690446 出料斗密封板SJ500.1.1.6-1 22029005 Spare part SPYS-0588 ¦Õ25.8¡Á2.65 ÓîÖÞ 10434860 SANY PARTS 61011307 Union 61028436 Cylinder Head Assembly 10213235 Right Sealing Board 51000729 SANY PARTS 10031127 truss 160507050062A High-Voltage Tube 160899000093A Alternator(24V 95A) 10638259 SANY PARTS 180605000104A Air spray gun 10451605 油箱右侧板LY226.3-2 10601163M 定位套锻坯(C9.1.5-4)- 61008244 车用三相永磁同步电机TZ208XFE00 10559777 thermal insulation plate 921081700010A MPGR 160101130096AJ1 Engine [email protected] 61024272 Fuel tank 160102090063A311 Fracture Resistant Screw [email protected] 21026105 Plate 10038536 Coupling bar 10057162 SANY PARTS 21085327 SANY PARTS 10125131 SANY PARTS 22023304 Extension boom 4 welding body SP105T04-A 10426297 SANY PARTS 61022085 Body, Cylinder 180103990218A indexable inserts drill bar 10111028 SANY PARTS 10010503B 平板SR200C.6.3.1.1-3(料坯) 920042100001A Active CompactLine module 10264846 SANY PARTS 532837 JOYSTICK SUB-ASSEMBLY 10096697 SANY PARTS 523885 SIDEPLATE, SUPPORT 10257361 SANY PARTS 10275816 SANY PARTS 10241753 SANY PARTS 21002078 SANY PARTS 10095290 Base Plate 160599000148A006 SCR Assembly 22032023 Steel tube assembly SPHLR-0872 21011573 SANY PARTS 10116687 Truck window frame RC1.4.2.4.2-1 10642496 oil tank outer plate 67336664070 Main control valve SPEV-0785A 5MSPCV140- Read the full article
0 notes
Text
Fwd: Workshop: KingsC_London.PythonForBiologists.Jan27-31
Begin forwarded message: > From: [email protected] > Subject: Workshop: KingsC_London.PythonForBiologists.Jan27-31 > Date: 14 January 2025 at 06:37:06 GMT > To: [email protected] > > > > > Python for Bioinformatics: 5-Day Course Overview > > Instructor: Dr. Martin Jones, in collaboration with the Hub for Applied > Bioinformatics (KCL). > > Audience: Biologists with no prior programming experience who want to > learn Python for bioinformatics. > > Course Highlights: > > Beginner-Friendly: No programming experience required; tailored for > complete beginners with a biology background. > > Practical Focus: Real-world bioinformatics examples and hands-on > exercises. > > Comprehensive Resources: Electronic copies of presentations, exercises, > data, and scripts provided. > > Goal-Oriented: Equip students to apply Python to their research and > continue learning independently. > > Who Should Attend? > > Designed for researchers and technical workers in biology who: > > Have a basic understanding of biological concepts (e.g., DNA, protein > sequences, translation, introns/exons). > > Want to learn programming from scratch. > > Requirements: A laptop with Python installed; no advanced computer > skills needed. > > Course Structure > > Session 1: Introduction and Basics > > Overview of Python and its benefits for research. > Fundamentals: terminals, variables, strings, and error handling. > Practical: Simple scripts for sequence manipulation. > > Session 2: File Handling and Slicing > > Reading/writing files and Python’s interaction with the OS. > Practical: File processing scripts using slice syntax. > > Session 3: Lists and Loops > > Handling large datasets with lists and loops. > Practical: Working with larger data files. > > Session 4: Conditions and Flow Control > > Decision-making with conditional tests and Boolean logic. > Practical: Filtering challenges with CSV files. > > Session 5: Structuring Code with Functions > > Writing reusable functions and introducing automated testing. > Practical: Creating functions for unit tests. > > Session 6: Standard Library and Regular Expressions > > Exploring Python’s standard library and regex for pattern matching. > Practical: Solving bioinformatics problems with regex. > > Session 7: Dictionaries > > Introduction to key-value data with dictionaries. > Practical: K-mer counting and DNA-to-protein translation. > > Session 8: File Management > > Automating file operations like renaming, moving, and organizing. > Practical: Managing DNA sequences by length. > > Sessions 9–10: Workshop Time > > Recap of key topics or applying Python to personal research. > > Contact Information > > For questions, email Dr. Martin Jones: [email protected]. > > For more information: > https://ift.tt/51VUqjz > > To sign up: > https://ift.tt/tZ0m4WG > > Jazmine Portch > Operations Assistant for Mathias Gautel > Administrator for Hub for Applied Bioinformatics > School of Basic and Medical Biosciences | Faculty of Life Sciences > and Medicine > > > Jazmine Portch
0 notes
Text
Harnessing the Power of Operational Amplifiers in Analog Design
Analog and signal circuit design is essential for countless electronic devices, ranging from smartphones and computers to medical instruments and automotive systems. Though digital technology often holds the utmost significance, analog circuits are necessary for processing and transmitting real-world signals with precision and efficiency. Please check out this post and understand the fundamentals of analog and signal circuit design, exploring their significance and applications.
Understanding Analog Circuit
Analog circuits are electronic circuits that process continuous signals like voltage or current whereas the binary values represent the discrete digital signals. These circuits manipulate analog signals in different ways, including amplification, filtering, modulation, and conversion. Analog circuits are specifically characterized by their ability to represent and manipulate real-world phenomena accurately. That’s why these circuits are essential for applications that require precise signal processing.
Important Principles of Analog Circuit Design
An analog circuit design requires a deep understanding of fundamental principles and components. Some important concepts include:
Ohm's Law – This law describes the relationship between voltage, current, and resistance in a circuit.
Kirchhoff's Laws – These laws administer the behavior of current and voltage in electrical circuits, including Kirchhoff's Current Law (KCL) and Kirchhoff's Voltage Law (KVL).
Component Characteristics – They allow you to understand the behavior of passive components like resistors, capacitors, and inductors, as well as active components like transistors and operational amplifiers (op-amps). These components are important for analog circuit design.
Frequency Response - Analog circuits work within certain frequency ranges and require the consideration of frequency-dependent effects like bandwidth, phase shift, and frequency response.
Understanding Signal Circuit Design
A signal circuit focuses on signal transmission and processing that can range from audio and video signals to sensor data and communication signals. These circuits are essential for various applications, including telecommunications, audio processing, instrumentation, and sensor interfacing. Signal circuit design covers different techniques and components tailored to specific signal processing needs.
Applications of Analog and Signal Circuit Design
There are so many applications of analog and signal circuit design in numerous industries and technologies:
Audio Amplification - Analog circuits are useful in audio amplifiers to enhance the amplitude of audio signals for speakers, headphones, and other audio devices.
Data Acquisition - Signal circuits are used in data acquisition systems to convert analog signals from sensors and transducers into digital data for processing and analysis.
Wireless Communication - Analog circuits are integral aspects of wireless communication systems, including radio frequency (RF) transmitters, receivers, and modulators/demodulators.
Medical Instrumentation - Analog circuits are applicable in medical devices like electrocardiographs (ECGs), ultrasound machines, and blood pressure monitors for processing and analyzing signals.
Automotive Electronics - Analog circuits are also used for automotive systems for applications like engine control, vehicle diagnostics, and entertainment systems.
Conclusion:
Analog and signal circuit design is the fundamental aspect of electrical engineering that enables the precise processing and transmission of real-world signals in a comprehensive range of applications. Using fundamental principles, components, and design techniques, Voler Systems engineers can provide analog circuit design services to accommodate the diverse demands of modern technology. Though digital systems continue to advance, the importance of analog and signal circuit design remains paramount, integrating the physical world into the digital counterpart smoothly and effortlessly.
1 note
·
View note
Text
Phản ứng hóa học là gì? Bản chất của phản ứng hóa học là gì?

Hóa học là bộ môn bắt buộc, bắt đầu từ chương trình học lớp 8. Trong hóa học chủ yếu nói về các phản ứng xảy ra giữa các chất với nhau. Vậy bạn hiểu phản ứng hóa học là gì? Có những loại nào? Bản chất? Vai trò của phản ứng hóa học là gì? Hãy cùng với muahangdambao.com tìm hiểu nhé!
Phản ứng hóa học là gì? Cho ví dụ
Khái niệm Phản ứng hóa học hiểu đơn giản là quá trình mà các chất tham gia (gọi là chất phản ứng) tương tác với nhau để tạo ra được các chất mới (gọi là chất sản phẩm). Trong phản ứng hóa học thì liên kết giữa các nguyên tử trong phản ứng bị phá vỡ và hình thành nên các liên kết mới để tạo ra các chất sản phẩm mới.

Phản ứng hóa học Phản ứng hóa học thường sẽ được biểu diễn bằng các phương trình hóa học. Trong đó các chất phản ứng được viết ở phía bên trái mũi tên và các chất sản phẩm được viết ở phía phải mũi tên. Phương trình hóa học được biểu thị cân bằng với số lượng nguyên tử, điện tích giữa các chất phản ứng và chất sản phẩm. Cụ thể: Tên các chất tham gia phản ứng → Tên chất sản phẩm. Ví dụ Phản ứng cháy của hidro và oxi được biểu diễn bằng phương trình hóa học như sau: 2H2 + O2 → 2H2O Cụ thể: Trong phản ứng này 2 phân tử hidro tương tác với 1 phân tử oxi để tạo thành 2 phần tử nước là chất sản phẩm. Các liên kết hidro và oxi có trong chất phản ứng sẽ bị phá vỡ và các liên kết giữa hidro và oxi trong nước sẽ được hình thành. Phản ứng hóa học có thể được diễn ra trong nhiều điều kiện khác nhau và nó được điều khiển bởi một yếu tố như: nhiệt độ áp suất, nồng độ chất phản ứng cũng như có sự có mặt của chất xúc tác. Phân loại Phản ứng hóa hợp Phản ứng hóa hợp là phản ứng hóa học trong đó chỉ có một chất mới được hình thành từ hai hay nhiều hợp chất ban đầu. Ví dụ: 4P + 5O2 → 2P2O5 3Fe + 2O2 → Fe3O4 Phản ứng phân hủy Phản ứng phân hủy là phản ứng hóa học trong đó thì một chất sẽ sinh ra hai hoặc là nhiều chất mới. Ví dụ: KMnO4 → K2MNO4 + MNO2 + O2 KClO3 → KCl + O2

Các loại phản ứng hóa học Phản ứng oxi hóa khử Phản ứng oxi hóa khử là phản ứng hóa học trong đó sẽ xảy ra đồng thời sự oxi hóa cũng như sự khử. Nói cách khác, phản ứng oxi hóa khử chính là phản ứng có sự dịch chuyển electron giữa các chất có trong phản ứng. Hay phản ứng có sự thay đổi của số oxi hóa của một số nguyên tố. Chất khử chính là chất nhường electron và chất oxi hóa chính là chất nhận electron. Phản ứng thế Phản ứng thế là phản ứng hóa học xảy ra giữa đơn chất và hợp chất, trong đó thì nguyên tử của đơn chất sẽ thay thế cho nguyên tử của một nguyên tố khác trong hợp chất. Ví dụ: Zn + 2HCl → ZnCl2 + H2 Fe + H2SO4 → FeSO4 + H2
Bản chất, đặc điểm của phản ứng hóa học là gì?
Các đặc điểm chính của phản ứng hóa học như sau: Tính chất đối tác: Phản ứng hóa học được xảy ra giữa các chất phản ứng còn gọi là đối tác. Các chất phản ứng này có thể làm các nguyên tố phân tử hoặc là ion. Tính chất sản phẩm: Phản ứng hóa học tạo ra các chất mới được gọi là chất sản phẩm. Các chất sản phẩm có thể là các nguyên tố phân tử hoặc là ion khác so với chất phản ứng ban đầu. Điều kiện phản ứng: Phản ứng hóa học thường phụ thuộc vào các điều kiện như nhiệt độ, áp suất, nồng độ, chất phản ứng, ánh sáng cũng như sự có mặt của chất xúc tác. Những điều kiện này có thể ảnh hưởng đến tốc độ cũng như hiệu suất của phản ứng.

Điều kiện xảy ra phản ứng Điện tích: Trong một số phản ứng hóa học có sự chuyển đổi điện tích. Xảy ra điều này có thể dẫn đến việc hình thành nên các ion hoặc thay đổi trạng thái oxi và khử của các nguyên tử trong phản ứng. Định luật bảo toàn khối lượng: Trong một phản ứng hóa học thì khối lượng không bị thay đổi. Điều này được biểu thị thông qua định luật bảo toàn khối lượng. Tức là tổng khối lượng của chất phản ứng sẽ bằng với tổng khối lượng của chất sản phẩm. Định luật bảo toàn nguyên tử: Trong một phản ứng hóa học thì số lượng nguyên tử của mỗi nguyên tố không bị thay đổi. Điều này được phản ánh thông qua định luật bảo toàn nguyên tử. Tức là tổng số nguyên tử của mỗi nguyên tố trong chất phản ứng sẽ bằng với số nguyên tử của mỗi nguyên tố trong chất sản phẩm.

Ví dụ định luật bảo toàn nguyên tử Tốc độ phản ứng: Tốc độ phản ứng hóa học sẽ thể hiện tốc độ cũng như các chất phản ứng tương tác với chế độ thành chất xúc tác. Tốc độ phản ứng có thể ảnh hưởng bởi nhiều yếu tố như: nhiệt độ, áp suất, nồng độ chất phản ứng và sự có mặt của chất xúc tác. Đổi màu và thay đổi nhiệt độ: Trong một số phản ứng hóa học thì có thể xảy ra sự thay đổi màu hoặc là thay đổi nhiệt độ. Điều này có thể làm cho phản ứng trở nên dễ nhìn thấy cũng như cảm nhận được sự thay đổi trong điều kiện vật lý.
Vai trò của phản ứng hóa học là gì?
Các phản ứng hóa học đóng vai trò quan trọng trong quá trình tự nhiên, công nghiệp và trong cuộc sống hàng ngày của chúng ta. Cụ thể một số vai trò của phản ứng hóa học: Sản xuất và chế biến hóa chất: Phản ứng hóa học được ứng dụng trong sản xuất cũng như chế biến các hợp chất quan trọng trong các ngành công nghiệp như: công nghiệp thực phẩm, công nghiệp hóa chất, công nghiệp luyện kim và nhiều ngành khác sử dụng phản ứng hóa học để sản xuất ra các sản phẩm và chất liệu cần thiết.

Phản ứng hóa học để sản xuất ra hóa chất Năng lượng: Phản ứng hóa học đóng vai trò quan trọng trong việc chuyển đổi cũng như sử dụng năng lượng. Các phản ứng hóa học như là phản ứng cháy, phản ứng điện hóa và phản ứng hạt nhân đều được sử dụng để tạo ra năng lượng điện nhiên liệu hay nguồn năng lượng tái tạo. Kiểm soát và xử lý ô nhiễm: Phản ứng hóa học được sử dụng để kiểm soát và xử lý ô nhiễm ở trong môi trường. Các quá trình xử lý nước, xử lý chất thải và khử trùng đều dựa trên các phản ứng hóa học để loại bỏ đi các chất ô nhiễm, tạo ra môi trường sống sạch hơn. Quá trình tự nhiên: Phản ứng hóa học xảy ra trong tự nhiên và nó đóng vai trò quan trọng trong các quá trình sinh học hay môi trường. Ví dụ như phản ứng quang hợp trong cây xanh sử dụng ánh sáng mặt trời để tạo ra năng lượng và tổng hợp nên các chất hữu cơ. Hay các phản ứng hóa học trong đất và nước cũng đóng vai trò quan trọng trong chu trình chuyển hóa các chất hóa học trong tự nhiên.

Phản ứng hóa học xảy ra trong tự nhiên Sản phẩm hàng ngày: Các phản ứng hóa học cũng đóng vai trò trong cuộc sống hàng ngày của con người. Ví dụ như việc nấu ăn, tiêu thụ thuốc, sử dụng xà phòng, chất tẩy rửa hay nhiều sản phẩm khác thì đều có liên quan đến các phản ứng hóa học. Nghiên cứu và phát triển: Phản ứng hóa học cung cấp cơ sở để nghiên cứu cũng như phát triển các phương pháp công nghệ, vật liệu mới… Có thể bạn quan tâm: Phản ứng thế là gì? Chia sẻ từ A – Z về phản ứng thế và ví dụ minh họa Kiến thức: Chất khử là gì? Ý nghĩa của phản ứng oxi hoá khử Phản ứng hóa học có nhiều ứng dụng quan trọng và rộng rãi trong đời sống hàng ngày cũng như trong các ngành công nghiệp. Hy vọng bài viết này sẽ giúp bạn có cái nhìn tổng quan hơn về phản ứng hóa học là gì và biết cách áp dụng trong học tập, nghiên cứu! Read the full article
0 notes
Text
A Glimpse into the Significance of Ag/AgCl Reference Electrodes and Pt Counter Electrodes in Electrochemistry
In the realm of electrochemistry, careful selection of electrodes is crucial for precise results. Two essential components in this field are the Ag/AgCl reference electrode and the Pt counter electrode. Let's delve into how these electrodes play a vital role in electrochemical experiments.
Ag/AgCl Reference Electrode:
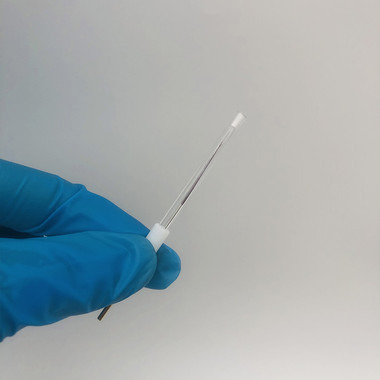
The Ag/AgCl reference electrode is a cornerstone of electrochemistry. Comprised of a silver wire coated with silver chloride (AgCl) submerged in a saturated KCl solution, this electrode is known for its stability, thanks to the reversible Ag/AgCl redox reaction.
One of its primary advantages is its consistent potential, which remains unchanged throughout experiments. This stable potential makes it ideal for measuring and controlling electrochemical reactions accurately.
Moreover, Ag/AgCl reference electrodes are non-toxic, making them suitable for various applications, including biological and environmental research. Their versatility and reliability make them a vital asset in the field of electrochemistry.
Pt Counter Electrode:
The platinum (Pt) counter electrode is a crucial component that complements the Ag/AgCl reference electrode. Its primary function is to ensure a continuous flow of current between the working and reference electrodes, facilitating desired electrochemical reactions.

Pt counter electrodes are favored for their excellent electrical conductivity, inertness, and resistance to corrosion. These properties promote efficient electron transfer and maintain a stable electrical connection during experiments.
Additionally, platinum counter electrodes are adaptable, accommodating a wide range of electrolytes and reaction conditions. This versatility allows researchers to work in various environments, from acidic to alkaline, with precision.
In summary, Ag/AgCl reference electrodes and Pt counter electrodes are indispensable in electrochemistry. They provide stability, accurate measurements, and efficient electrochemical reactions. Together, they contribute to a deeper understanding of chemical and biological processes, making significant contributions to scientific research.
0 notes
Text
Title:- What are ionic compounds?
Introduction:-
What are ionic compounds?is our main discussion today. I am just trying to focuss on the chemistry topic What are ionic compounds?which will be very helpful for class (ix) and class(x) school children, I think.
Explanation:-
To start this discussion, let us first know some basic definitions of chemistry,
what are elements?
Answer:- The matters which are composed of only one type of particles are known as elements.e.g; Sodium (Na), Magnesium(Mg), Carbon(C).....
How elements are classified?
Answer:-Elements are classified in three types:-(i) Metals (ii) Non metals. (iii) Metalloids. Metals:- Sodium(Na), Magnesium (Mg), Gold (Au)..... Non metals :-Carbon (C), Sulphur(S),Nitrogen (N).... Metalloids :- Boron(B), Silicon(Si), Arsenic(As)....
What are molecules?
Answer:- When two or more than two similar or different types of atoms combine together chemically they form molecules e.g; H + H —----> H₂ Hydrogen molecule(Diatomic molecule) Cl + Cl —-----> Cl₂
Chlorine molecule(Diatomic molecule) H₂ + S —------> H₂ S
Hydrogen sulphide(Triatomic molecule)
What are compounds?
Answer:- When two or more molecules or atoms chemically react themselves under some definite conditions and combines then they form compounds. e.g; C + ½ O₂ —---------> CO (atom) (molecule) (Carbon monoxide is a gas/compound) C + O₂ —--------> CO₂ (atom) (molecule) (Carbon dioxide is a gas/compound)
Finally I will discuss on todays topic
What are ionic compounds?
Answer:- The compounds which are formed by the transfer electrons from metal atom to non metal atom are known as ionic compounds. e,g; Potassium Chloride (Kcl), Aluminium oxide (Al₂O₃) Now we will learn a little more on ionic compounds .
How following ionic compounds are formed?
(a) Sodium Chloride (Nacl)
Answer:- Na is a metal, the electronic configuration of sodium (Na) = 2,8, 1 to complete octet and become stable sodium needs to collect 7 electrons from other element to full fill its outer most shell i.e its third shell or 'M' shell to get its nearest noble gas Argon (2,8,8) and to full fil octet and become stable or Na has to give up its only valence shell electron (1) to get 2,8 electronic configuration of Neon as sodium is a metal so according to metals chemical property , all metals give up electrons they do not accept electrons or they are unable to accept electrons due to strong inter molecular force, thats why sodium is also unable to accept 7 electrons.
Again, chlorine (Cl) is a non metal and its electronic configuration is 2,8,7 so to fulfil its octet chlorine needs to accept one(1)electron or must have to give up its valence shell's 7 electrons to get either its nearest noble 2,8,8(Argon) or 2,8 (Neon) gas configuration to become stable due to non metals chemical property non metals never give up electrons, so chlorin is also unable to give up electrons.So in chemical reaction between sodium(Na) and chlorine ,Sodium (Na) gives up its lone valence electron to get its nearest noble gas Neon's configuration(2,8) and become stable in the mean time chlorine accepts the lone electron which is given up by sodium(Na) to get its nearest noble gas Argon's (2,8,8)configuration and become stable and by the process of electrons transfer they form ionic compound (Nacl) The formation can be given by:-

(b) Magnesium Oxide (MgO)
Answer:- Magnesium is a metal,the electronic configuration magnesium(Mg) is 2,8,2 and these electrons occupies s,p,and d orbits. To become stable or get its nearest noble gas ,argon's(Ar) configuration(2,8,8) magnesium need 6 more electrons to fill up its d-orbit and to become stable but due to inter molecular force of electronic attraction magnesium is unable to take 6 more electrons from other atoms. On the other hand oxygen is a non metal and electronic configuration of oxygen is 2,6 ; which occupies its s and p orbits.To get its nearest noble gas, Neon's electronic configuration (2,8)oxygen need 2 more electrons to fill up its p-orbit and to get (2,8) neon gas configuration and to become stable. So in the chemical reaction between magnesium and oxygen one magnesium(Mg) atom gives up its lone pair(2) electrons to get neons configuration(2,8) and become stable also produces Mg⁺² ion ,in the same time one oxygen atom accepts 2 electrons which are given up by magnesium (Mg) aton also to get its nearest noble gas neon gas configuration (2,8) and become stable also produces o²⁻ion. Due to electro atomic force of attraction between Mg⁺² ion and o²⁻ion they combines themselves and produces magnesium oxide (MgO) The formation can be given by :- Mg - 2e —-------> Mg⁺² (Magnesium ion) (2,8,2) (2,8) neon gas O + 2e —-------> O²⁻(Oxygen ion) (2,6)�� (2,8) neon gas Now Mg⁺² + O²⁻ —------>Mg⁺²O²⁻ —->MgO
(magnesium oxide)
(c) Potassium Oxide (K₂O)
Answer:- Potassium is a metal,the electronic configuration magnesium(K) is 2,8,8,1 and these electrons occupies s,p, d and f orbit. To become stable or get its nearest noble gas ,krypton's(kr) configuration(2,8,8,18) potassium need 17 more electrons to fill up its f-orbit and to become stable but due to inter molecular force of electronic attraction magnesium is unable to take 17 more electrons from other atoms. On the other hand oxygen is a non metal and electronic configuration of oxygen is 2,6 ; which occupies its s and p orbits.To get its nearest noble gas, Neon's electronic configuration (2,8)oxygen need 2 more electrons to fill up its s-orbit and to get (2,8) neon gas configuration and to become stable. So in the chemical reaction between potassium and oxygen two potassium(K) atom gives up its lone (1) electron each to get argons configuration(2,8,8) and become stable also produces K⁺ ion ,in the same time one oxygen atom accepts 2 electrons which are given up by two potassium (K) aton also to get its nearest noble gas neon gas configuration (2,8) and become stable also produces o²⁻ion. Due to electro atomic force of attraction between 2K⁺ ion and o²⁻ion they combines themselves and produces potassium oxide (K₂O) The formation can be given by :-

Conclusion:-
Ionic compounds are formed by the transfer of electrons from metal atom to non metal atom......
To read more....
4 notes
·
View notes
Photo

Potassium chloride crystal
The crystal of potassium chloride is similar to that of sodium chloride and both salts adopt a face-centered cubic crystal structure. Each potassium atom loses one electron to form a unipositive potassium ion and the chlorine atom gains that electron to form a uni-negative chloride ion. The two oppositely charged ions are held together by the electrostatic force of attraction to form crystalline potassium chloride salt. for more about potassium chloride (KCl)
2 notes
·
View notes
Text
The first ionization potential of K is 4.34eV, the electron affinity of Cl is 3.82 eV and the equilibrium separation of KCl is 0.3 nm. The energy required to dissociate a KCl molecule into a K and a Cl atom is
1. 8.62 eV
2.8.16 eV
3. 4.28 eV
4. 4.14 eV
#ionisation#potential#potassium#electron#affinity#chlorine#equilibrium#molecule#dissociation#energy#atom#volt
1 note
·
View note
Text

Current Electricity
Introduction
Current electricity is a fundamental concept in physics and plays a crucial role in various fields, including medicine, engineering, and technology. For NEET (National Eligibility cum Entrance Test) aspirants, having a solid understanding of current electricity is essential as it forms a significant part of the physics syllabus. In this blog, we will delve into the world of current electricity, exploring its key principles, formulas, and real-world applications.
Understanding Current Electricity
Current electricity refers to the flow of electric charge through a conducting medium. The conductors, such as metals, allow the movement of charged particles, typically electrons, resulting in the flow of current. This flow occurs due to the presence of an electric potential difference or voltage across the conductor.
Ohm's Law
A cornerstone of current electricity is Ohm's Law, which establishes a relationship between current, voltage, and resistance. According to Ohm's Law, the current passing through a conductor is directly proportional to the voltage across it and inversely proportional to the resistance offered by the conductor. The Mathematical form of the expression for Ohm's Law is:
V = IR
Where: V represents the voltage (in volts) I represents the current (in amperes) R represents the resistance (in ohms)
This simple equation allows us to analyze and calculate various electrical quantities in a circuit.
Circuits and Components
Electric circuits consist of interconnected components that facilitate the flow of current. Key components include resistors, capacitors, inductors, and various types of power sources such as batteries or generators. Understanding the behavior of these components and their interactions within a circuit is crucial for solving problems related to current electricity.
Series and Parallel Circuits
The components in a series circuit are connected one after the other in a single path. The current flowing through each component remains the same, while the voltage is divided among them. The total resistance in a series circuit is the sum of individual resistances.
In parallel circuits, the components are connected across the same two points, creating multiple paths for the current. The voltage across each component remains the same, while the total current is divided among them.
Kirchhoff's Laws
Kirchhoff's laws are essential tools for analyzing complex circuits. They provide a systematic approach to determining the currents and voltages at various points within a circuit.
1. Kirchhoff's Current Law (KCL): The total current entering a junction is equal to the total current leaving that junction. In other words, the algebraic sum of currents at a node in a circuit is zero.
2. Kirchhoff's Voltage Law (KVL): The total sum of the voltage drops and rises in a closed loop within a circuit is zero. This law is based on the principle of conservation of energy.
Applications of Current Electricity
Current electricity finds application in various fields, and its understanding is crucial for aspiring medical professionals. Here are a few notable applications:
1. Medical Devices: Current electricity is extensively used in medical devices such as electrocardiograms (ECGs), electroencephalograms (EEGs), and defibrillators, which aid in the diagnosis and treatment of various medical conditions.
2. Bioelectrical Impedance Analysis (BIA): BIA is a technique that measures the body's composition by sending a small current through the body and analyzing its impedance. It helps determine parameters like body fat percentage and hydration levels.
3. Electrotherapy: Current electricity is used in electrotherapy for pain management, muscle stimulation, and tissue repair. Techniques like transcutaneous electrical nerve stimulation (TENS) and electrical muscle stimulation (EMS) rely on electrical currents for therapeutic purposes.
Conclusion
A comprehensive understanding of current electricity is indispensable for NEET aspirants pursuing a career in the medical field. Mastering the principles of current flow, Ohm's Law, circuit analysis, and Kirchhoff's laws will not only help in scoring well on the physics section of the NEET exam but also lay a strong foundation for future endeavors in the field of medicine. At DR Academy, we strive to provide you with the best NEET coaching in Bangalore and Hyderabad, equipping you with the knowledge and skills necessary to excel in your medical entrance exams. We, as the best institute for NEET preparation in Bangalore, encourage you to continue your exploration of physics and its applications, as it forms an integral part of the NEET syllabus.
0 notes
Text
The Importance of water testing

A raised complete broke up solids (TDS) fixation isn't a wellbeing danger. The TDS fixation is an optional drinking water standard and, thusly, is directed in light of the fact that it is a greater amount of a tasteful as water testing opposed to a wellbeing danger.The centralization of the disintegrated particles might make the water be destructive with a pungent or a harsh taste as well as result in scale development, diminishing the productivity of boiling water warmers.
It would likewise propose that there are numerous particles that are over the Essential or Auxiliary Drinking Water Guidelines, like a raised degree of nitrate, arsenic, aluminum, copper, lead, and so forth.The estimation of all out disintegrated solids doesn't show that there is explicit wellbeing hazard or danger, yet it tends to be utilized to give knowledge into the status or the water over the long run and as an advance notice indication of an expected issue.
Ordinarily, we prescribe water clients to get an extensive starting test that ought to incorporate various boundaries including the all out broke down solids of the water and the conductivity of the water. Conductivity and all out broke up solids are in a roundabout way related, however these are two devices to follow the difference in your water quality with time. As a general rule, a TDS of under 50 mg/L ought to raise a worry for a potential consumption issue, a TDS of more than 250 mg/L ought to raise a worry about the hardness, iron, manganese, alkalinity, chloride, sulfate, nitrate, and general salt substance, and north of 500 mg/L ought to raise a worry about different salts (bromide, lithium, aluminum, different metals, and the scale framing capability of the water). An all out broke up solids north of 1000 mg/L ought to raise a worry about the potential for a man-had direct effect or a saline water effect on the source.
For stylish reasons, the EPA has set an optional drinking water standard of < 500 mg/L (milligrams per liter) . A few states have laid out this as a drinking water standard.
Not at all like numerous impurities, there are advance notice signs that there might be an issue with your drinking water related or brought about by having to little or an excess of stuff in your water. Indeed Stuff-the all out broke up solids test doesn't let you know the stuff, however assuming that you connect your perceptions with some at-home water testing or screening, educational testing, or business confirmed testing you can distinguish this stuff, foster an arrangement to make a financially savvy arrangement, and execute an answer that safeguards yourself, your family, your home, and the frameworks in your home.
The all out disintegrated solids focus can be connected with the conductivity of the water, yet the relationship is definitely not a consistent. The connection between complete disintegrated solids and conductivity is a component of the sort and nature of the broke down cations and anions in the water and potentially the idea of any suspended materials. For instance, a NaCl arrangement and KCl arrangement with a conductivity of 10000 umhos/cm won't have similar convergence of NaCl or KCl and they will have an alternate complete broke up solids focus. Conductivity is estimated using a meter and is generally multiple times the complete cations or anions communicated as reciprocals and the all out broke down solids (TDS) in ppm as a rule goes from 0.5 to 1.0 times the electrical conductivity.
All out Broke down Solids can be estimated in the field utilizing an electronic pen. A considerable lot of these gadgets really measure the conductivity of the water, i.e., the capacity of the water to convey a charge, and not the genuine all out broke down solids. These gadgets then, at that point, compute the all out broke up solids expecting that the essential disintegrated minerals are either a mix of NaCl or KCl. In this manner, the estimation of absolute broken down solids by these gadgets are not a precise measure, but rather a guess. In the event that you are considering involving these gadgets for an undertaking, we would suggest buying a conductivity pen which estimates the conductivity of the water and finishing a lab test to KNOW the proportion of TDS to Conductivity that ought to be utilized as a remedy factor.
1 note
·
View note
Text
Electrical Engineering Questions and Answers for Competitive Exams
I can provide some information on electrical engineering topics that are commonly asked in competitive exams.
What is Ohm's law? Ohm's law states that the current through a conductor between two points is directly proportional to the voltage across the two points, and inversely proportional to the resistance between them.
What is Kirchhoff's laws? Kirchhoff's laws are two fundamental laws of circuit analysis that describe the conservation of charge and energy in an electrical circuit. The first law, Kirchhoff's current law (KCL), states that the total current entering a junction must equal the total current leaving the junction. The second law, Kirchhoff's voltage law (KVL), states that the sum of the voltages around a closed loop in a circuit must equal zero.
What is the purpose of a diode? A diode is a two-terminal electronic component that allows current to flow in only one direction, acting as a one-way valve for electric current. Diodes are commonly used in rectifier circuits to convert AC to DC, as voltage stabilizers, and to protect circuits from high-voltage transients.
What is the difference between AC and DC? AC (Alternating Current) changes direction periodically, while DC (Direct Current) flows in only one direction. AC is used in the electrical grid because it is more efficient to transmit over long distances, while DC is used in batteries and electronic devices.
What is a transistor and what is its function? A transistor is a three-terminal semiconductor device that can be used as an amplifier or switch. The transistor controls the flow of current between the input and output terminals by adjusting the voltage applied to the third terminal, the base. Transistors are widely used in electronic circuits for amplification, switching, and voltage regulation.
What is an inductor and how does it work? An inductor is a passive electrical component that stores energy in a magnetic field when electric current flows through it. Inductors oppose changes in current and can be used to filter, store, or regulate energy in an electrical circuit.
What is a capacitor and how does it work? A capacitor is a passive electrical component that stores energy in an electric field when a voltage difference exists between its plates. Capacitors can be used to store energy, filter signals, and regulate voltages in an electrical circuit.
What is a microcontroller?
0 notes
Text
Price: [price_with_discount] (as of [price_update_date] - Details) [ad_1] Product Description Storite 3 in 1 Screen Cleaning Kit with Microfiber Cloth and Brush for Electronic Screens (100 ml) Brand: Storite Microfiber cloth Size - 13cm x 13cm. Storite KCL-1005 dust free screen cleaning kit has the ultimate essentials for your electronic cleaning needs and provides an effective and safe way to clean your electronic devices. Conventional screen cleaners use alcohol and other chemicals which can resonate into electronic screens causing fading and depreciation. Our non-streak cleaner boasts an odorless, non-toxic solution.Our solution has been tested and is non-static, non-streak and free of alcohol and other toxic substances. Just spray the cleaner onto the included microfiber cleaning cloth, and say goodbye to dust, stains and fingerprints.Screen cleaner can not only removes fingerprints, oil and smudges, but also leaves a layer of ultra-thin coating on your screen. It resists fingerprint and being scratched, easier to clean and looks great Product Specification: 1. Could Clean The Dust Most Effectively and Completely, Without any Water Track, no cauterization, Cleaner Can Keep the LCD Screen Bright and Clean Like new one, There will be s film on the surface of LCD screen after use this Cleaner, to Keep Screen anti-static and dustproof. 2. The Superfine fiber cloth was made of special high-technology, can clean the oleic dust out. As the fibers are so thin to increase the surface area, can absorb more water and stubborn dust. dust together with special cleaner can clean up stubborn dust better. Easy To Use: Can be used to clean the TFT display, screen, notebook screen, PDA Screen, Printer Screen and CD safely. Will be no scratch and track left and won’ t hurt the screen coat. Remove Germs, Bacteria, Fingerprints: This Screen Cleaning kit includes a variety of cleaning tools to make sure that your DSLR, compact camera or action camera is always spotless and ready to use. MULTI-PURPOSE. Ideal for touchscreen mobiles, mac, android tablets, and PC monitors, even your spectacles! MMicrofiber cleaning cloths and lens tissues: Both of these items can be used to gently remove dust and dirt from your lens. Microfiber cloth Size - 14.
5cm x 14.5cm. Can Clean all kinds of cd,fold the Cloth and Clean the CD With The Center Of cloth, Clean The CD from the Center to the edge, Without any scratch and dust left. Liquid Volume 120 ML 100 ML 200 ML 100 ML Micro Fiber Cloth ✓ ✓ ✓ ✓ Dust Blower ✓ NO NO NO Pack 1 1 2 2 Solution Bottle Capacity: 100 ml Compatible Devices: LCD, LED TV, Laptops and All Electronic Screens This LCD Cleaning Kit cleans Messy Finger Prints, Dirt and Dust, Stains. Gives a good clean finish afterwards The Kit contains special liquid, special cloth and soft brush to clean corners and sides of the screen [ad_2]
0 notes