#internet services and social networking netiquette
Explore tagged Tumblr posts
Text
How to be socially responsible in Social Media
When one aims to be socially responsible through social media, one must practice netiquette. Netiquette is a portmanteau of “network” and “etiquette” In a nutshell, netiquette is socially accepted and expected behavior in an online space. Just like how one must be mindful of the things they do in a real life social space, being mindful of one’s actions in an online space is considered netiquette.

Here are a few ways to practice netiquette to be socially responsible online:
Use respectful language
Fact checking before posting or reposting
Use tone indicators or emoticons if necessary
Include trigger warnings on content if necessary
Respond to messages or emails promptly
Follow respective guidelines and terms of service
Be mindful of internet jargons and slangs
Avoid spamming
Respect fellow users’ privacy
Update online information
The emergence of social media has certainly pushed society towards a more progressive state of socializing and building connections with one another. As they say, with great power comes with great responsibility. Therefore, one must be socially responsible in an online space.
0 notes
Text
Internet Services | Class - 5 Computer | EXERCISES | Question and Answers | CAIE / CBSE
Internet Services | Class – 5 Computer | EXERCISES | Question and Answers | CAIE / CBSE
youtube
View On WordPress
#Cambridge ICT#ch 2 internet services class 10#chapter 2 internet services#class 5 computer#internet and services#internet based services#internet service provider#internet services and social networking netiquette#internet services class 10#internet services class 5#internet services class 5 cbse#internet services class 6#internet services mcq#internet services mcq class 10#Internet services notes#internet services notes class 10#Youtube
0 notes
Text
Empower ment
EMPOWERMENT TECHNOLOGIE (PORTFOLIO)
Chapter 1-INFORMATION AND COMMUNICATIONS TECHNOLOGY
ICT- Can impact student learning when teachers are digitally literate and understand how to integrate it into curriculum. Schools use a diverse set of ICT tools to communicate, create, disseminate, store, and manage information
This link will show you what ICT is?
https://icttechtips.wordpress.com/2018/02/23/what-is-ict-empowerment-technologies-k-to-12/

Here are the examples of ICT
ICT includes products that store, process, transmit, convert, duplicate, or receive electronic information. Electronic textbooks, instructional software, email, chat, and distance learning programs
Communication is an act of transmitting messages. It is a process whereby information is exchanged between individuals using symbols, signs or verbal interactions. Communication is important in order to gain knowledge. Technology is the use of scientific knowledge, experience and resources to create processes products that fulfill human needs. Technology is vital in communication.
ICT nowadays has also widened the horizon in developing new tools or emerging technologies. Mobile devices can communicate through wireless fidelity (WIFI), Bluetooth, third generation 3g & 4g, data services and dial up services and virtual private networks.
Emerging Technologies
Emerging technologies are characterized by radical novelty (in application even if not in origins), relatively fast growth, coherence, prominent impact, and uncertainty and ambiguity. In other words, an emerging technology can be defined as "a radically novel and relatively fast growing technology Characterized by a certain degree of coherence persisting over time and with the potential to exert a considerable impact on the socio-economic domain(s) which is observed in terms of the composition of actors, institutions and patterns of interactions among those, along with the associated knowledge production processes. Its most prominent impact, however, lies in the future and so in the emergence phase is still somewhat uncertain and ambiguous.

Artificial intelligence
Is the ability of a
digital computer or computer-controlled robot
to perform tasks commonly associated with intelligent
beings. The term is frequently applied to the project
of developing systems endowed with the intellectual processes characteristic of humans, such as the ability to reason, discover meaning, generalize, or learn from past experience.
Robotics
Is a branch of engineering that involves the conception, design, manufacture, and operation of robots. This field overlaps with electronics, computer science, artificial intelligence, mechatronics, nanotechnology and bioengineering.
Biometrics
Is the measurement and statistical analysis of people's unique physical and behavioral characteristics. The technology is mainly used for identification and access control or for identifying individuals who are under surveillance
Quantum cryptography
Science of exploiting quantum mechanical properties to perform cryptographic tasks. The best known example of quantum cryptography is quantum key distribution which offers an information-theoretically secure solution to the key exchange problem.
Online learning platform
is an integrated set of interactive online services
that provide trainers, learners, and others involved
in education with information, tools and resources
to support and enhance education delivery and management.
Computer assisted translation
CAT tools are typically understood to mean programs that specifically facilitate the actual translation process. Most CAT tools have the ability to translate a variety of source file formats in a single editing environment without needing to use the file format's associated software for most or all of the translation process, translation memory, and integration of various utilities or processes that increase productivity and consistency in translation.
3d imaging and holography
Holography is the next stage of photography and conventional film and its three-dimensionality creates completely new possibilities for use, such as for product presentation. A 3D hologram displays products, objects, and animated sequences three-dimensionally and enables seemingly real objects or animations to appear to float completely freely in space. Unlike a conventional film on a standard screen, a 3D hologram is visible from all sides, which means the observer can walk around the hologram, enabling an absolutely realistic-looking image to form.
Virtual Reality
(VR) refers to a computer-generated simulation in which a person can interact within an artificial three-dimensional environment using electronic devices, such as special goggles with a screen or gloves fitted with sensors.
Lesson-2 ONLINE SYSTEMS, FUNCTIONS, AND PLATFORMS
Online systems– are online versions of information systems, which is “the process of and tools for storing, managing, using, and gathering of data and communications in an organization.
An example of information systems are tools for sending out communications and storing files in a business.”
Common Online Platforms
Social Media Platform means a mobile and/or internet-based platform used and controlled by a Seller or any of its Affiliates for the exclusive purpose of promoting the Business, including any profiles or accounts on Facebook, Google+, Instagram, Pinterest, Tumblr, Twitter, Snapchat, and YouTube, in each case, to the extent exclusively related to the Business.
Online Video Platform
Provided by a video hosting service, enables users to upload, convert, store and play back video content on the Internet, often via a structured, large-scale system that may generate revenue.
Lesson-3 Online Safety, Security, Ethics and Etiquette
Issues and crimes on the internet are the following
1. Cyber bullying

2. Hacking

3. Identity theft

4. Plagiarism

5. Intellectual property rights and copyright issues

These issues caused the formulation of the rules and regulations to be followed when using the internet. Online safety and security defines how you are going to keep yourself safe while surfing the web.
Online Ethics and Netiquette
Online Ethics focuses on the acceptable use of online resources in an online environment.
Netiquette focuses on the acceptable behavior of the person while using the internet resource.
Netiquette is a combination of the words “net” (from internet) and “etiquette” (netiquette).
Lesson-4 Online Search and Research skills
Looking forward E- Commerce
The Philippines is now considered as
one of the countries in Asia Pacific that
consumes more than 3 hours on the
web. Users are mostly the younger
generation and social media is the most
popular platform being visited.
An article features the positive responses of the young Filipinos towards E- commerce. It was mentioned in the article that netizens (79) mostly discuss products and services while staying online. Even though most netizens are knowledgeable of the different online stores, many are still afraid to make purchases due to credibility issue.
CHAPTER 2: APPLIED PRODUCTIVITY TOOLS
Productivity tools can be a freeware or shareware., A freeware is copyrighted, which can be used for free and for an unlimited time while shareware is commercial software that is copyrighted, which can be copied for trial but needs to be purchased for continued use.
One of the most popular productivity suites is the Microsoft Office developed by Microsoft. This includes word processing software, electronic spreadsheet, and presentation software, not all Microsoft applications includes Access and Publisher. You can tell the some version of office contains a desktop publishing program. These tools will help you create, organize and present information to an audience for a more effective communication.
Reports, nowadays demand to be well-presented and dynamic. Away from the usual ways of [resenting information. A lot of presentation software are available whether online or offline. Similarly, financial reports are calculated and tabulated using electronic spreadsheets because of the automatic formulas and functions available.
2 notes
·
View notes
Text
What is Empowerment Technologies?
This blog, Empowerment Technologies, is an insight into what I have learned on our lessons about Empowerment Technologies: ICT for Professional Tracks, for 11th grade, under the teaching of Miss Shaira Denise Dela Cruz. The goal of this blog is to promote ICT and give you some insight into ICT

The first lesson that was discussed was, what is ICT? ICT is the abbreviation for Information and Communication Technologies. It refers to technologies that provide access to information through telecommunications such as mobile phones, wireless networks, telephones, and other communication mediums. The current state of ICT is WWW or World Wide Web.
The World Wide Web(WWW), commonly known as the Web, is an information system where documents and other web resources are identified by Uniform Resource Locators, which may be interlinked by hypertext, and are accessible over the Internet. It has three versions which are Web 1.0, Web 2.0, and Web 3.0. Web 1.0 is the first version and most web pages were static or “read-only web.”
The second and most used is Web 2.0, which allows users to interact and contribute with the page instead of just reading a page, the users are able to create a user account. Web 2.0 offers us five features: Folksonomy, Rich User Experience, Long Tail, User Participation, and software as a service.
The last is Web 3.0. Its aim is to have machines understand the user’s preference to be able to deliver web content specifically targeting the user. Web 3.0 hasn’t released yet as it still has some problems. Those problems are compatibility, security, vastness, vagueness, and logic.

Moving on to the next lesson which is all about ‘Online Saftey, security, ethics, and etiquette.’
The Internet consists of tens of thousands of interconnected networks run by service providers, individual companies, universities, and governments. It is defined as an information highway, which means anyone can access any information through the internet. That is why the internet is one of the most dangerous places, the reason why it is important how to keep yourself and your personal information safe. Some of the information that is in rick when spoiled on the internet are names of your immediate family, address, phone or home number, birthday, email address, your full name, and your previous and current school. It is important to keep this information top secret as cyber-creeps can use these to find you.
To keep yourself safe:
Be mindful of what you share online.
Do not just accept terms and conditions, read it.
Keep your passwords to yourself, and make sure your password is long, strong, and unique.
Do not talk or meet up with someone you don’t know.
Never post anything about a future vacation. This can signal some robbers about which date they can come and rob your house. It is better to post about your vacation when you got home already.
Add friends you know in real life, don’t accept someone you barely know or met.
Avoid visiting or downloading anything from an untrusted website, make sure to check the icon beside the search box. *picture* According to DigiCert Blog, “How to Know if a Website is Secure?”, Look at the URL of the website. If it begins with “https” instead of “http” it means the site is secured using an SSL certificate (the s stands for secure). SSL certificates secure all of your data as it is passed from your browser to the website’s server.
Make your home wifi private by adding a password.
Make sure to install and update antivirus software on your computer.
Do not reply or check links from suspicious emails as it can lead you to an untrusted site and can hack your laptop or social media.

To give you more information, here are some of the internet threats that we need to be aware of and try to avoid:
The Malware, stands for malicious software. It includes virus, worm, trojan, spyware, adware, and ransomware. The virus is the most common malware. It is a malicious program designed to replicate itself and transfer from one computer to another (internet, local networks, FDs, CDs,etc.). Worms is a standalone piece of malicious software that reproduces itself and spreads from computer to computer. The trojan is a malicious program that disguises as a useful program but once downloaded or installed, leaves your PC unprotected and allows hackers to get your information. Spyware is defined by Webroot Cybersecurity as "malware used for the purpose of secretly gathering data on an unsuspecting user." It is a program that runs in the background and spies your behavior as you are on your computer. Adware is malware that forces your browser to redirect to web advertisements, which often themselves seek to download further, even more, malicious software. Lastly, Ransomware, also known as scareware. This is a type of malicious software from cryptovirology that threatens to publish the victim’s data or perpetually block access to it unless a ransom is paid.
The Spam, this is any kind of unwanted, unsolicited digital communication, often an email, that gets sent out in bulk.
The Phishing, is a cybercrime in which a target/s are contacted by someone posing as a legitimate institution to lure individuals into providing sensitive data such as personally identifiable information, banking and credit card details, and passwords.

Lastly, before we move to the next lesson it is important to know ‘The Core Rules of Netiquette’ are excerpted from the book Netiquette by Virginia Shea.
First, Remember the Human.When communicating online, practice the Golden rule: Do unto others as you would have others do unto you. Remember that your written works or messages are read by real people, therefore you should ask yourself, "Would I be okay with this if someone else had written it?" before sending it.
Second, Adhere to the same standards of behavior online that you follow in real life. It is a must that your best to act within the laws and ethical manners of society whenever you inhabit "cyberspace." Standards of behavior may be different in some areas of cyberspace, but they are not lower than in real life. Be ethical. Don't believe anyone who says, "The only ethics out there are what you can get away with."
Third, Know where you are in cyberspace. What's perfectly acceptable in one area may be dreadfully rude in another. And because Netiquette is different in different places, it's important to know where you are. Thus the next corollary: Lurk before you leap.
Fourth, Respect other people’s time and bandwidth. Online communication takes time: time to read and time in which to respond. Most people today lead busy lives, just like you do, and don't have time to read or respond to frivolous emails or discussion posts. It's your responsibility to ensure that the time they spend reading your posting isn't wasted.
Fifth, Make yourself look good online. One of the best things about the virtual world is the lack of judgment associated with your physical appearance, the sound of your voice, or the clothes you wear. However, you will be judged by the quality of your writing so keep in mind the following tips: (1)Always check for spelling and grammar errors, (2) Know what you're talking about and state it clearly
Sixth, Share expert knowledge. The reason for asking questions online works is that a lot of knowledgeable people are reading the questions. And if even a few of them offer intelligent answers, the sum total of world knowledge increases. The Internet itself was founded and grew because scientists wanted to share information. Gradually, the rest of us got in on the act. So do your part. Despite the long lists of no-no's in this book, you do have something to offer. Don't be afraid to share what you know.
Seventh, Help keep flame wars under control. "Flaming" is what people do when they express a strongly held opinion without holding back any emotion.g. While "flaming" is not necessarily forbidden in virtual communication, "flame wars," when two or three people exchange angry posts between one another, must be controlled or the camaraderie of the group could be compromised. Don't feed the flames; extinguish them by guiding the discussion back to a more productive direction.
Eighth, Respect other people’s privacy. Depending on what you are reading in the virtual world, be it an online class discussion forum, Facebook page, or an email, you may be exposed to some private or personal information that needs to be handled with care. Thus, Just as you expect others to respect your privacy, so should you respect the privacy of others. Be sure to err on the side of caution when deciding to discuss or not to discuss virtual communication.
Ninth, Don’t abuse your power. Some people in cyberspace have more power than others. There are wizards in MUDs (multi-user dungeons), experts in every office, and system administrators in every system. Knowing more than others, or having more power than they do, does not give you the right to take advantage of them. For example, sysadmins should never read private emails.
Tenth, Be forgiving of other people’s mistakes. Everyone was a network newbie once. So when someone makes a mistake, whether it's a spelling error or a spelling flame, a stupid question or an unnecessarily long answer, be kind about it. If you do decide to inform someone of a mistake, point it out politely, and preferably by private email rather than in public. Give people the benefit of the doubt; assume they just don't know any better.

The last lesson that was taught to us is ‘Advanced Word Processing Skill’. This lesson focuses on the software word processor the ‘Microsoft Word.’
A Word Processor is an electronic device or computer software application that performs the task of composing, editing, formatting, and printing of documents.
Microsoft Word is a word processor developed by Microsoft and the first released on October 25, 1983. Microsoft Word has features and functions which are not mostly known by others. These are the Auto-Correct, Grammar Checker, Read Aloud, Template, Thesaurus, Mail Merge, and Text Wrap.
Advance Features of Microsoft Word are discussed. Beginning with the kinds of Materials we can have in Microsoft Word.
The first is Pictures. Generally, these are electronic or digital pictures or photographs you have saved on any local storage device. There are three file formats that pictures have which are JPEG or Joint Photographic Expert Group, this can support 16.7 million colors so that it is suitable for use when working with full-color photographic images, GIF or Graphics Interchange Format, this is used for computer-generated images that support animation, can only support up to 256 colors., lastly, PNG or Portable Network Graphics, this is similar to GIF except it has smaller file size but does not support animation, it can display up to 16 million colors and allows the control of the transparency level or opacity of images.
The second material is Clip Art. This is generally a GIF type; line art drawings or images used as a generic representation for ideas and objects that you might want to integrate into your document.
The third is Shapes. These are printable objects or materials that you can integrate in your document to enhance its appearance or to allow you to have some tools to use for composing and representing ideas or messages. The fourth is Smart Art. Generally, these are predefined sets of different shapes grouped together to form ideas that are organizational or structural in nature.
The fifth is Chart. Another type of material that you can integrate into your Word document that allows you to represent data characteristics and trends.
The sixth is Screenshot. Sometimes, creating reports or manuals for training or procedure will require the integration of a more realistic image of what you are discussing on your report or manual.
Moving on to the most focused part of the lesson which is the Mail Merge. Mail Merge is a useful tool that allows you to produce multiple letters, labels, envelopes, name tags, and more using information stored in a list, database, or spreadsheet. When these two documents are combined (merged), each document includes the individual names and addresses you need to send it to. The two components of Mail Merge are the Form Document, this contains the main body of the message we want to convey or send., and the List or Data File, This is where the individual information or data that needs to be plugged in (merged) to our form document is placed and maintained.
It was demonstrated to us, how to use and make mail merge, and here’s mine:
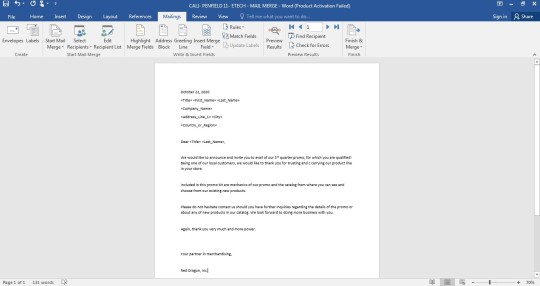

Before ending this blog, I would like to show you some of my modules for the subject Empowerment Technologies(ETech): ICT for Professional Track.
First, the open forum about the “How can you promote Netiquette?”

Second, an assignment about “Cyberspace: Share an experience that you have always tend to do but later did you discover that it is not a standard of ONLINE SAFETY, SECURITY, ETHICS, AND ETIQUETTE. “

Third, another open forum about “What is the importance of Microsoft office in your education?”

Lastly is another assignment, making an Infographic: Promoting your specific track/strand. My infographic is a promotion of my strand, STEM or Science, Technology, Engineering, and Mathematics.
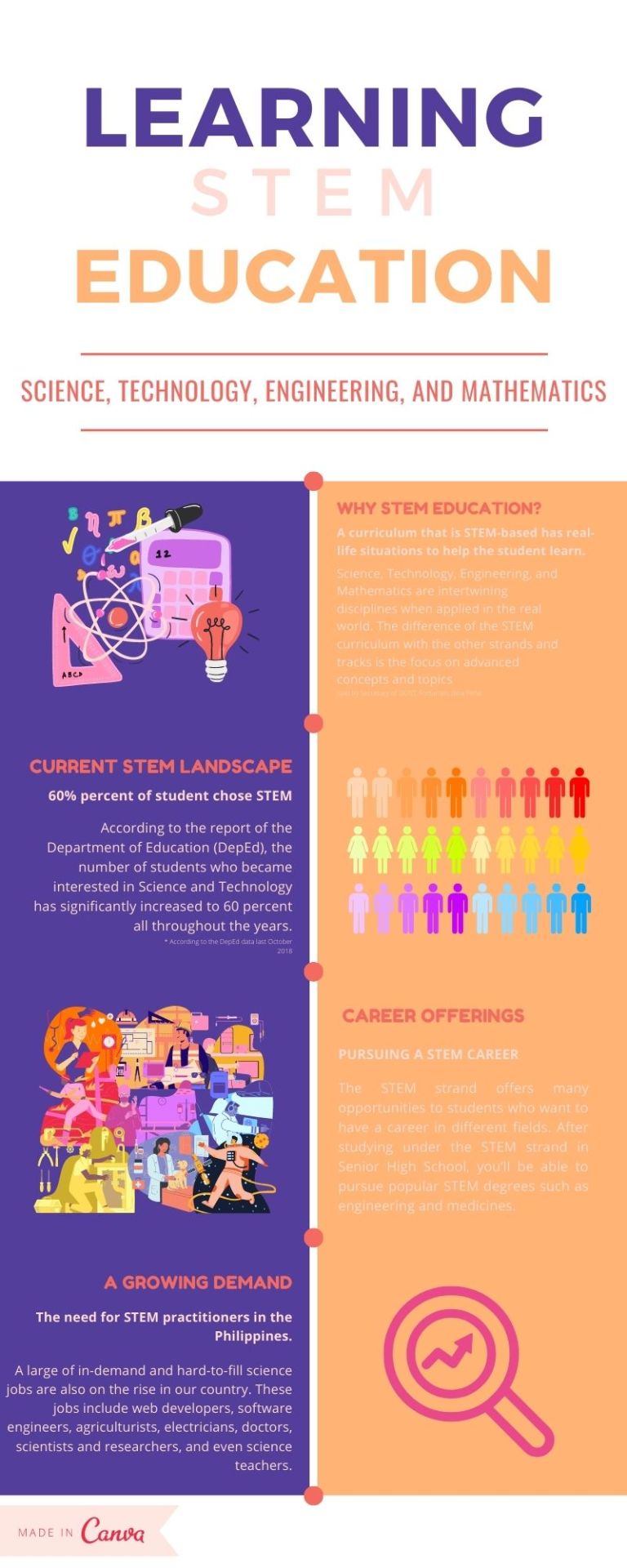
Hope you learn a lot from this blog as I learn a lot from my subject teacher for Empowerment Technologies(ETech): ICT for Professional Track.
Let this day be filled with success in all the ventures you make today. Have a great day!
Photo Credits:
1
https://curatti.com/wp-content/uploads/2019/11/WWW-Image-1.jpg
2
https://go4customer.com/articleimages/1581925569Safety_Internet_Day.png
3
https://futureofsourcing.com/sites/default/files/articles/internet_attacks.jpg
4
https://i.pinimg.com/originals/fc/37/e1/fc37e162244d19115d88ab58e07ccc2b.png
5
https://cdn.guidingtech.com/imager/assets/2019/05/226896/Image-Best-Microsoft-Word-Online-Tips-and-Tricks 2_4d470f76dc99e18ad75087b1b8410ea9.png?1558678050
2 notes
·
View notes
Text
LESSON 1: INTRODUCTION TO ICT
ICT– Information and Communication-
It deals with the use of different communication technologies such as mobile phones, telephone, Internet to locate, save, send and edit information
Is a study of computers as data processing tools. It introduces students to the fundamental of using computer systems in an internet environment.
ICT in the Philippines
Philippines is dub as the ‘’ICT Hub of Asia” because of huge growth of ICT-related jobs, one of which is BPO, Business Process Outsourcing, or call centers.
ICT Department in the Philippines is responsible for the planning, development and promotion of the country’s information and communications technology (ICT) agenda in support of national development.
Computer– an electronic device for storing and processing data, typically in binary form, according to instructions given to it in a variable program. Internet– is the global system of interconnected computer networks that use the internet protocol suite (TCIP/IP) to link billions of devices worldwide.
Means of connecting a computer to any other computer anywhere in the world via dedicated routers and servers.
Sometimes called simply ‘’the Net’’, is a worldwide system of computer networks- a network of networks in which the users at any one computer can get information from any other computer.
World Wide Web
An information system on the internet that allows documents to be connected to other documents by hypertext links, enabling the user to search for information by moving from one document to another.
Is an information space where documents and other web resources are identified by URLs, interlinked by hypertext links, and can be accessed via the Internet.
Invented by Tim-Berners Lee
Web Pages
Web page is a hypertext document connected to the World Wide Web. It is a document that is suitable for the World Wide Web.
The different online platforms of World Wide Web:
Web 1.0 – refers to the first stage in the World Wide Web, which was entirely made up of the Web pages connected by hyperlinks.
Web 2.0 – is the evolution of Web 1.0 by adding dynamic pages. The user is able to see a website differently than others.
– Allows users to interact with the page; instead of just reading the page, the user may be able to comment or create user account.
Web 3.0 – this platform is all about semantic web.
– Aims to have machines (or servers) understand the user’s preferences to be able to deliver web content.
Static Web Page- is known as a flat page or stationary age in the sense that the page is ‘’as is’’ and cannot be manipulated by the user. The content is also the same for all users that is referred to as Web 1.0
Dynamic Web Pages– web 2.0 is the evolution of web 1.0 by adding dynamic web pages. The user is able to see website differently than others e.g. social networking sites, wikis, video sharing sites.
FEATURES OF WEB 2.0
Folksonomy- allows user to categorize and classify information using freely chosen keywords e.g. tagging by FB, Twitter, use tags that start with the sign #, referred to as hashtag.
Rich User Experience – content is dynamic and is responsive to user’s input
User Participation- The owner of the website is not the only one who is able to put content. Others are able to place a content of their own by means of comments, reviews and evaluation e.g. Lazada, Amazon.
Long Tail– services that are offered on demand rather than on a one-time purchase. This is synonymous to subscribing to a data plan that charges you for the amount of time you spent in the internet.
Software as a services- users will be subscribe to a software only when needed rather than purchasing them e.g. Google docs used to create and edit word processing and spread sheet.
Mass Participation– diverse information sharing through universal web access. Web 2.0’s content is based on people from various cultures.
TRENDS IN ICT
Convergence– is the synergy of technological advancements to work on a similar goal or task. For example, besides using your personal computer to create word documents, you can now use your smartphone. 2. Social Media– is a website, application, or online channel that enables web users web users to create , co-create, discuss modify, and exchange user generated content.
Six types of Social Media:
a)Social Networks – These are sites that allows you to connect with other people with the same interests or background. Once the user creates his/her account, he/she can set up a profile, add people, share content, etc
Example: Facebook and Google+
b)Bookmarking Sites – Sites that allow you to store and manage links to various website and resources. Most of the sites allow you to create a tag to others.
Stumble Upon, Pinterest
c) Social News – Sites that allow users to post their own news items or links to other news sources. The users can also comment on the post and comments may also be rank.
Ex. Reddit and Digg
d) Media Sharing – sites that allow you to upload and share media content like images, music and video.
Ex. Flickr, YouTube and Instagram e) Microblogging – focus on short updates from the user. Those that subscribed to the user will be able to receive these updates. Ex. Twitter and Plurk
f) Blogs and Forums – allow user to post their content. Other users are able to comment on the said topic. Ex. Blogger, WordPress and Tumblr
Mobile Technologies– The popularity of smartphones and tablets has taken a major rise over the years. This is largely because of the devices capability to do the tasks that were originally found in PCs. Several of these devices are capable of using a high-speed internet. Today the latest model devices use 4G Networking (LTE), which is currently the fastest.
MOBILE OS
iOS – use in apple devices such as iPhone and iPad
Android – an open source OS developed by Google. Being open source means mobile phone companies use this OS for free.
Blackberry OS – use in blackberry devices
Windows phone OS – A closed source and proprietary operating system developed by Microsoft.
Symbian – the original smartphone OS. Used by Nokia devices
WebOS- originally used in smartphone; now in smart TVs.
Windows Mobile – developed by Microsoft for smartphones and pocket PCs
Assistive Media– is a non- profit service designed to help people who have visual and reading impairments. A database of audio recordings is used to read to the user.
e.g. Yahoo!, Gmail, HotmailCloud computing-distributed computing on internet or delivery of computing service over the internet.
-Instead of running an e-mail program on your computer, you log in to a Web
e-mail account remotely. The software and storage for your account doesn’t exist
on your computer – it’s on the service’s computer cloud.
It has three components
Client computers – clients are the device that the end user interact with cloud.
Distributed Servers – Often servers are in geographically different places, but server acts as if they are working next to each other.
Datacenters – It is collection of servers where application is placed and is accessed via Internet.
TYPES OF CLOUDS
PUBLIC CLOUD allows systems and services to be easily accessible to the general public. Public cloud may be less secured because of its openness, e.g. e-mail
PRIVATE CLOUD allows systems and services to be accessible within an organization. It offers increased security because of its private nature.
COMMUNITY CLOUD allows systems and services to be accessible by group of organizations.
HYBRID CLOUD is a mixture of public and private cloud. However, the critical activities are performed using private cloud while the non-critical activities are performed using public cloud.
LESSON 2: ONLINE SAFETY, SECURITY AND RULES OF NETIQUETTE
INTERNET SAFETY- it refers to the online security or safety of people and their information when using internet. NETIQUETTE- is network etiquette, the do’s and don’ts of online communication.
TEN RULES OF NETIQUETTE
Rule No. 1: Remember the human
You need to remember that you are talking to a real person when you are online.
The internet brings people together who would otherwise never meet.
Remember this saying when sending an email: Would I say this to the person’s face.
Rule No. 2: Adhere to the same standards online that you follow in real life.
You need to behave the same way online that you do in real life.
You need to remember that you can get caught doing things you should not be doing online just like you can in real life.
You are still talking to a real person with feelings even though you can’t see them.
Rule no. 3: Know where you are in cyberspace.
Always take a look around when you enter a new domain when surfing the web.
Get a sense of what the discussion group is about before you join it.
Rule no. 4: Respect other people’s time and bandwidth.
Remember people have other things to do besides read your email. You are not the center of their world.
Keep your post and emails to minimum by saying what you want to say.
Remember everyone won’t answer your questions.
Rule no. 5: Make yourself look good online.
Be polite and pleasant to everyone.
Always check your spelling and grammar before posting.
· Know what you are talking about and make sense saying it.
Rule no. 6: Share expert knowledge
Ask questions online
Share what you know online.
Post the answers to your questions online because someone may have the same question you do.
Rule no. 7: Help keep flame wars under control
Netiquette does not forgive flaming.
Netiquette does however forbid people who are flaming to hurt discussion groups by putting the group down.
Rule no. 8: Respect other people’s privacy.
Do not read other people’s mail without their permission.
Going through other people’s things could cost you, your job or you could even go to jail.
Not respecting other people’s privacy is a bad netiquette.
Rule no. 9: Don’t abuse your power.
Do not take advantage of other people just because you have more knowledge or power than them.
Treat others as you would want them to treat you if the roles were reversed.
Rule no. 10: Be forgiving of other people’s mistake.
Do not point out mistakes to people online.
Remember that you were once the new kid on the block.
You still need to have a good manners even though you are online and cannot see the person face to face.
Internet security
Security Requirement Triad
ConfidentIality Data confidentiality Privacy
Integrity Data integerity System integrity
Availability
Threat ConsequenceThreat Action ( Attack)
Unauthorized Disclosure
A circumstance or event whereby an entity gains access to data for which the entity is not authorized.
Exposure: Sensitive data are directly released to an unauthorized entity.
Interception: An unauthorized entity directly accesses sensitive data traveling between authorized sources and destinations.
Inference: A threat action whereby an unauthorized entity indirectly accesses sensitive data by reasoning from characteristics or byproducts of communications.
Intrusion: an unauthorized entity gains access to sensitive data by circumventing a system’s security protections.
Disruption
A circumstances or even that interrupts or prevents the correct operation of system services and functions.
Deception
A circumstance or event that may result in an authorized entity receiving false data and believing it to be true.
Incapacitation: prevents or interrupts system operation by disabling a system component.
Corruption: Undesirably alters system operation by adversely modifying system functions or data.
Obstruction: A threat action that interrupts delivery of system services by hindering system operation.
Masquerade: An unauthorized entity gains access to a system or performs a malicious act by posing as an authorized entity.
Falsification: False data deceive an authorized entity.
Repudiation: An entity deceives another by falsely denying responsibility for an act.
Usurpation
A circumstances or event that results in control of system services or functions by an unauthorized entity.
Misappropriation: An entity assumes
unauthorized logical or physical control of a
system resource.
Misuse: Causes a system component to perform a function or service that is detrimental to system security.
Types of System Intruders
Masquerader
Hackers
Clandestine user
Parts of Virus
Infection mechanism
Trigger
PayloaD
Virus stages
Dormant phase Virus is idle.
Propagation phase Virus places an identical copy of itself into other programs or into certain system areas on t the disk.
Triggering phase Virus is activated to perform the function for which it was intended. Caused by a variety of system events
Execution phase Function is performed
Key Terms
Cyber crime- a crime committed or assisted through the use of the Internet.
Privacy Policy/Terms of Services (ToS) – tells the user how the website will handle its data.
Malware- stands for malicious software.
Virus- a malicious program designed to transfer from one computer to another in any means possible.
Worms– a malicious program designed to replicate itself and transfer from one file folder to another and also transfer to other computers.
Trojan-a malicious program designed that is disguised as a useful program but once downloaded or installed, leaves your PC unprotected and allows hacker to get your information.
Spyware– a program that runs in the background without you knowing it. It has the ability to monitor what you are currently doing and typing through key logging.
Adware- a program designed to send you advertisement, mostly pop-ups.
Spam– unwanted email mostly from bots or advertisers.
Phishing- acquires sensitive personal information like passwords and credits card details.
Pharming- a more complicated way of phishing where it exploits the DNS system.
Copyright- a part of law, wherein you have the rights to work, anyone who uses it w/o your consent is punishable by law.
Fair Use- means that an intellectual property may be used w/o consent as long as it is used in commentaries, criticism, parodies, research and etc.
Keyloggers- used to record the keystrokes done by user. This is done to steal passwords or any other sensitive information.
Rogue security softwares– is a form of malicious software and internet fraud that misleads users into believing there is a virus on their computer, and manipulates them into paying money for a fake malware removal tool.
Four search strategies
Keyword searching
Enter terms to search
Use quotation marks to search as a phrase and keep the words linked together
Common words are ignored (That, to, which, a, the …)
+ and – can be used to include or exclude a word
Boolean
AND – enter words connect with AND- it will include sites where both words and found
Uses: joining different topics (i.e. global warming AND California)
OR – requires at least one of the terms is found.
Uses: join similar or synonymous topics (i.e. global warming OR greenhouse effect)
NOT – searches for the first term and excludes sites that have the second term.
(i.e. Washington NOT school)
Question
a question may be entered in the search field of search engine
Advanced Features are offered on many engines by going to an “Advanced search” page and making selections. Effective in narrowing search returns to a specific topic or phrase.
LESSON 3: Advanced Word Processing Skills
Lesson Discussion
In the professional world, sending out information to convey important information is vital. Because of ICT, things are now sent much faster than the traditional newsletters or postal mail. You can now send much faster than the traditional newsletters or postal mail. You can now use the Internet to send out information you need to share. What if we could still do things much faster – an automated way of creating and sending uniform letters with different recipients? Would that not be more convenient?
I. Mail Merge and Label Generation
A. Mail Merge
One of the important reasons in using computers per se is its ability to do recurring tasks automatically. But this ability has to be honed by learning the characteristics and features of the software you use with your computer. After all, no matter how good or advance your computer and software may be, it can only be as good as the person using it.
In this particular part of our lesson, we will learn one of the most powerful and commonly used features of Microsoft Word called Mail Merge. As the name suggests, this feature allows you to create documents and combine or merge them with another document or data file. It is commonly used when sending out advertising materials to various recipients.
The simplest solution for the scenario above is to create a document and just copy and paste it several times then just replace the details depending on whom you send it to. But what if you have hundreds or thousands of recipients? Would not that take too many hours? What if you have a small database of information where you can automatically generate those letters?
Two Components of Mail Merge
1. Form Document
The first component of our mail merged document is the form document. It is generally the document that contains the main body of the message we want to convey or send. The main body of the message is the part of the form document that remains the same no matter whom you send it to from among your list.
Also included in the form document is what we call place holders, also referred to as data fields or merge fields. This marks the position on your form document where individual data or information will be inserted. From our sample document, the place holders are denoted or marked by the text with double-headed arrows (<< >>) on each side and with a gray background. On a printed standard form, this will be the underlined spaces that you will see and use as a guide to where you need to write the information that you need to fill out. In its simplest form, a form document is literally a “form” that you fill out with individual information. A common example of a form document is your regular tax form or application form.
2. List or Data File
The second component of our mail merged document is the list or data file. This is where the individual information or data that needs to be plugged in (merged) to the form document is placed and maintained. One of the best things about the mail merge feature is that it allows data file to be created fro within the Microsoft Word application itself, or it gets data from a file created in Microsoft Excel or other data formats. In this way, fields that needed to be filled up on the form document can easily be maintained without accidentally altering the form or main document. You can also easily add, remove, modify, or extract your data more efficiently by using other data management applications like Excel or Access and import them in Word during the mail merge process.
B. Label Generation
Included in the mail merge feature on Microsoft Word is the Label Generator. It just makes sense that after you print out your form letters, you will need to send it to individual recipients in an envelope with the matching address printed directly on the envelope or on a mailing label to stick on. By using virtually the same process as a standard mail merge, Microsoft Word will print individual addresses to a standard form that it has already pre-formatted. Simply put, it creates a blank form document that simulates either a blank label or envelope of pre-defined size and will use the data file that you selected to print the information, typically individual addresses. So even in generating labels, the two essential components of creating a merged document are present: the form document and the data file. Only in this case, you did not have to type or create the form document yourself because it was already created and pre-formatted in Microsoft Word. All you need to do is select the correct or appropriate size for the label or envelope and select the data file that contains the addresses (data) to be printed. You can also preview your merged labels before printing if you want to.
II. Integrating Images and External Materials
Integrating or inserting pictures in your document is fun and it improves the impression of your document. A common use of inserting a picture on a document is when you are creating your resume. Though seemingly simple to do, your knowledge on the different kinds of materials that you can insert or integrate in a Word document and its characteristics can help you create a more efficient, richer document not only in content but also in physical form. A better understanding of the physical form of your document as well as the different materials you would integrate in it would allow you to be more efficient and versatile in using Microsoft Word.
A. Kinds of Materials
There are various kinds of materials Microsoft Word is capable of integrating to make the documents richer, more impressive, and more informative.
1. Pictures
Generally, these are electronic or digital pictures or photographs you have saved in any local storage device. There are three commonly used types of picture files. You can identify them by the extension on their file names.
a. .JPG/JPEG
This is pronounced as “jay-peg“ and is the short form of .jpeg or Joint Photographic Experts Group. Like all the rest of the image file extensions, it identifies the kind of data compression process that it uses to make it more compatible and portable through the Internet. This type of image file can support 16.7 million colors that is why it is suitable for use when working with full color photographic images. Unfortunately, it does not support transparency and therefore, images of this file type can be difficult to integrate in terms of blending with other materials or elements in your document. But if you are looking for the best quality image to integrate with your document then this is the image file type for you. .JPG does not work well on lettering, line drawings, or simple graphics. .JPG images are relatively small in file size.
b. .GIF
This stands for Graphics Interchange Format. This type of image file is capable of displaying transparencies. Therefore, it is good for blending with other materials or elements in your document. It is also capable of displaying simple animation. Apparently, this may not be too useful on a printed document but if you are sending documents electronically or through email, or even post documents into a website, then this could be quite impressive. The downside is that it can only support up to 256 colors so it is good mostly on logos and art decors with very limited, and generally solid colors. .GIF is much better for logos, drawings, small text, black and white images, or low-resolution files.
Example of a .gif format picture.
c. .PNG
This is pronounced as “ping“. It stands for Portable Network Graphics. It was built around the capabilities of .GIF. Its development was basically for the purpose of transporting images on the Internet at faster rates. It is also good with transparencies but unlike .GIFs, it does not support animation but it can display up to 16 million colors, so image quality for this image file type is also remarkably improved. .PNG allows the control of the transparency level or opacity of images.
Example of .png format picture.
2. Clip Art
This is generally a .GIF type; line art drawings or images used as generic representation for ideas and objects that you might want to integrate in your document. Microsoft Word has a library of clip arts that is built in or can be downloaded and used freely. There are still other clip arts that you can either purchase or freely download and use that come from third-party providers.
Clip Art Icon in Microsoft Office 2010.
3. Shapes
These are printable objects or materials that you can integrate in your document to enhance its appearance or allow you to have some tools to use for composing and representing ideas or messages. If you are designing the layout for a poster or other graphic material for advertising, you might find this useful.
Shapes Icon under the Insert ribbon tab.
4. Smart Art
Generally, these are predefined sets of different shapes grouped together to form ideas that are organizational or structural in nature. If you want to graphically represent an organization, process, relationships, or flow for infographic documents, then you will find this easy and handy to use.
Smart Art
5. Chart
Another type of material that you can integrate in your Word document that allows you to represent data characteristics and trends. This is quite useful when you are preparing reports that correlate and present data in a graphical manner. You can create charts that can be integrate in your document either directly in Microsoft Word or imported from external files like Microsoft Excel.
Chart – Used to illustrate and compare data.
6. Screenshot
Sometimes, creating reports or manuals for training or procedures will require the integration of a more realistic image of what you are discussing on your report or manual. Nothing can get you a more realistic image than a screenshot. Microsoft Word even provides a snipping tool for your screen shots so you can select and display only the part that you exactly like to capture on your screen.
III. Image Placement
Layout of text wrapping options.
A. In Line with Text
This is the default setting for images that are inserted or integrated in your document. It treats your image like a text font with the bottom side totally aligned with the text line. This setting is usually used when you need to place your image at the beginning of a paragraph. When placed between texts in a paragraph or a sentence, it distorts the overall appearance and arrangement of the texts in the paragraph because it will take up the space it needs vertically, pushing whole lines of texts upward.
B. Square
This setting allows the image you inserted to be placed anywhere with the paragraph with the text going around the image in a square pattern like frame.
C. Tight
This is almost the same as the Square setting, but here the text “hug” or conforms to the general shape of the image. This allows you to get a more creative effect on your document. This setting can mostly be achieved if you are using an image that supports transparency like a .GIF or .PNG file.
D. Through
This setting allows the text on your document to flow even tighter taking the contours and shape of the image. Again, this can be best used with .GIF or .PNG type of image.
E. Top and Bottom
This setting pushes the texts away vertically to the top and/or the bottom of the image so that the image occupies a whole text line on its own.
F. Behind Text
This allows your image to be dragged and placed anywhere on your document but with all the texts floating in front of it. It effectively makes your image look like a background.
G. In Front of Text
As it suggests, this setting allows your image to be placed right on top of the text as if your image was dropped right on it. That means whatever part of the text you placed the image on, it will be covered by the image.
IV. Key Terms
Mail Merge – a feature that allows you to create documents and combine or merge them with another document or data file.
Form Document – the document that contains the main body of the message we want to convey or send.
Data File – includes the individual information or data or the recipient’s information.
Merge Field/Place Holder – marks the position on your form document where individual data or information will be inserted.
.JPG – file extension for the Joint Photographic Experts Group picture file.
.PNG – file extension for Portable Network Graphics image file.
.GIF – file extension for the Graphics Interchange Format image file.
Clipart – line art drawings or images used as a generic representation for ideas and objects.
Smart Art – predefined sets of different shapes grouped together to form ideas that are organizational or structural in nature.
Text Wrap – adjusts how the image behaves around other objects or text.
LESSON 4: Advanced Spreadsheet Skills
What is a Spreadsheet Software? • allows users to organize data in rows an columns and perform calculations on the data • These rows and columns collectively are called worksheet.
3. Examples of Spreadsheet Software: • LibreOffice Calc • OpenOffice.org Calc • Google Sheets • Apple iWork Numbers • Kingsoft Office Spreadsheets • StarOffice Calc • Microsoft Excel
4. MICROSOFT EXCEL
5. To open Microsoft Excel, Press “Windows Logo” + R then type “excel” then enter.
6. Key Terms in MS Excel: • Row – horizontal line of entries in a table • Column – vertical line of entries in a table • Cell – the place where info. is held in a spreadsheet
7. Key Terms in MS Excel: • Active Cell – the selected cell • Column Heading – the box at the top of each column containing a letter • Row Heading – the row number
8. Key Terms in MS Excel: • Cell Reference – the cell address of the cell usually combine letter and number (ex. A1, B4, C2) • Merge – combining or joining two or more cells • Formula – is an expression which calculates the value of a cell.
9. Key Terms in MS Excel: • Functions – are predefined formulas and are already available in Excel • Formula Bar – the bar that displays the contents of a cell
10. FUNCTIONS
11. BASIC MATH OPERATIONS: • =SUM(x,y) or =SUM(range) – returns the sum of x and y or (all the numbers within the range) • =PRODUCT(x,y) – returns the product of x and y • =QUOTIENT(x,y) – returns the quotient of x divided by y • =x-y – returns the difference of x subtracted by y
12. BASIC MATH OPERATIONS: • =x+y – returns the sum of x and y • =x*y – returns the product of x and y • =x/y – returns the quotient of x divided by y • =x-y – returns the difference of x subtracted by y
13. OTHER FUNCTIONS: • =ABS(x) – returns the absolute value of x • =AVERAGE(x,y) – returns the average of x and y • =CONCATENATE(x,y) – joins x and y
14. OTHER FUNCTIONS: • =IF(Condition, x, y) – returns x if the condition is true, else it returns y • =ISEVEN(x) – returns true if x is an even number • =ISODD(x) – returns true if x is an odd number
15. OTHER FUNCTIONS: • =COUNT(range) – counts the number of cell containing a number within a range • =COUNTIF(range, criteria) – count the number of cell that fits with the criteria within the range
16. OTHER FUNCTIONS: • =ISNUMBER(x) – returns true if x is a number • =ISTEXT(x) – returns true if x is a text • =LEN(x) – returns the length of characters in x • =PROPER(x) – returns the proper casing of x
17. OTHER FUNCTIONS: • =LEFT(x,y) – returns the characters of x specified by y (from the left) • =RIGHT(x,y) – returns the characters of x specified by y (from the right) • =PI() – returns the value of pi
18. OTHER FUNCTIONS: • =MIN(x,y) – returns the smallest number between x and y • =MAX(x,y) – returns the largest number between x and y • =MIN(range) – returns the smallest number within the range • =MAX(range) – returns the largest number within the range
19. OTHER FUNCTIONS: • =POWER(x,y) – returns the value of x raised to the power of y • =ROUND(x,y) – rounds x to a specified number of digits (y) =COLUMN(x) – returns the column number of x • =ROW(x) – returns the row number of x
20. OTHER FUNCTIONS: • =SQRT(x) – returns the square root of x • =TRIM(x) – removes extra spaces in x • =UPPER(x) – returns x in all capital form • =LOWER(x) – returns x in non- capital form
21. OTHER FUNCTIONS: • =TODAY() – returns the current date • =NOW() – returns the current date and time
22. EXERCISES
23. Consider this data: NAME MATH GRADE SCIENCE GRADE FILIPINO GRADE ENGLISH GRADE A.P GRADE MARK 75 70 78 81 78 PETE 84 87 86 88 85 ANA 91 92 95 90 90 REA 73 75 74 75 70
24. Give the formulas to get : • Mark’s , Pete’s, Ana’s and Rea’s averages • The highest grade that Ana got • The lowest grade that Mark got? • Sum of all Math Grade? Science? A.P.? • Sum of all Rea’s Grades • The Lowest Number among all grades • The remarks (Passed or Failed)
25. Now, consider this data: FIRST NAME MIDDLE NAME LAST NAME MARK CURTIS WILLIAMS PETE MCCLOEY HARRISON ANA MONROE FRITZ REA TAN COLLINS
26. Give the formulas to get : • Mark’s Full Name • Ana’s Full Name in Proper Case • Count the number of letters that Pete’s Last Name has • “COLL” from Rea’s Last Name • “LOEY” from Pete’s Middle Name • Combining “WILL” and “LINS” from Mark and Rea’s Last Names respectively
LESSON 5: Advanced Presentation Skills
Powerpoint is a highly innovative and versatile program that can ensure a successful communication whether you’re presenting in front of potential investors, a lecture theatre or simply in front of your colleagues. The following are the five features you should be using-if youy aren’t already. Learn everything about these tips: they will improve your presentation skills and allow you to communicate your message successfully. The five features of powerpoint was
1)adding smart art
2)Inserting Shapes
3)Inserting and Image
4)Slide Transitions
5)Adding Animations
Creating an Effective Presentation
1.
Minimize
: Keep slides counts to a minimum to maintain a clear message and to keep the audience attentive. Remember that the presentation is just a visual aid. Most information should still come from the reporter.2.
Clarity
: Avoid being to fancy by using font style that is easy to read. Make sure that it is also big enough to be read by the audience. Once you start making your presentation, consider how big the screen is during your report.3.
Simplicity
: Use bullets or short sentences. Summarize the information on the screen to have your audience focus on what the speaker is saying than on reading the slide. Limit the content to six lines and seven words per line. This is known as the 6 x 7 rule.4.
Visual
: Use graphics to help in your presentation but not too many to distract the audience. In addition, instead of using table of data, use charts and graphs.5.
Consistency
: Make your design uniform. Avoid having different font styles and backgrounds.6.
Contrast
: Use a light font on dark background or vice versa. This is done so that it is easier to read. In most instances, it is easier to read on screen if the background is dark. This is due to the brightness of the screen. LESSON 6: Imaging and Design for Online Environment
PHOTO EDITING
Photo editing encompasses the processes of altering images, whether they are digital photographs, traditional photo chemical photographs, or illustrations. Traditional analog image editing is known as photo retouching, using tools such as an airbrush to modify photographs, or editing illustrations with any traditional art medium.
Graphic software programs
Which can be broadly grouped into vector graphics editors, raster graphics editors, and 3D modelers are the primary tools with which a user may manipulate, enhance, and transform images. Many image editing programs are also used to render or create computer art from scratch.
BASIC OF IMAGE EDITING
RASTER IMAGESare stored in a computer in the form of a grid of picture elements or pixels.
VECTOR IMAGESsuch as Adobe Illustrator, Inkscape and etc. are used to create and modify vector images, which are stored as descriptions of lines, Bezier curves and text instead of pixels.
DIFFERENCE BETWEEN RASTER AND VECTOR IMAGES
RASTER IMAGESuse many colored pixels or individual building blocks to form a complete image JPEGs, GIFs and PNGs are common raster image types. Almost all of the photos found on the web and in print catalogs are raster images.
VECTOR IMAGES alternatively, allow for more flexibility. Constructed using mathematical formulas rather than individual colored blocks, vector file types such as EPS, AI and PDF are excellent for creating graphics that frequently require resizing. 3. 3D MODELING (OR MODELLING) is the process of developing a mathematical representation of any three dimensional surface of an object via specialized software. The product is called a 3D model. It can be displayed as a two-dimensional image through a process called 3D rendering or used in a computer simulation or physical phenomena. The model can also be physically created using 3D printing devices.
IMAGE FORMATS
Ø JPEG is a commonly used method of lossy compression for digital images, particularly for those images produced by a digital photography.
Ø PNG (PORTABLE NETWORK GRAPHICS) is a raster graphics file format that supports lossless data compression.
Ø GIF a lossless format for image files that supports both animated and static images.
Ø BMP is a raster graphics image used to store bitmap digital images
Ø EPS used in vector-based images in Adobe Illustrator.
Ø SVG is an XML-based vector image format for two-dimensional graphics w/ support for interactivity and animation
Ø .3ds is one of the file formats used by the Autodesk 3Ds Max 3D Modelling, animation and rendering software.
Ø .fbx is an exchange format, in particular for interoperability between Autodesk products and other digital content creation software
FEATURES OF IMAGE EDITORS
SELECTION One of the prerequisites for many of the app mentioned below is a method of selecting part(s) of an image, thus applying a change selectively without affecting the entire picture
Ø MARQUEE TOOL for selecting rectangular or other regular polygon-shaped regions
Ø LASSO TOOL for freehand selection of a region
Ø MAGIC WAND TOOL selects objects or regions in the image defined by proximity of color or luminance
LAYERS which are analogous to sheets of transparent acetate, stacked on top of each other, each capable of being individually positioned, altered and blended with the layers below, w/o affecting any of the elements on the other layers. IMAGE SIZE resize images in a process often called image scaling, making them larger, or smaller. High image resolution cameras can produce large images which are often reduced in size for Internet use.
CROPPING creates a new image by selecting a desired rectangular portion from the image being cropped. The unwanted part of the image is discarded. Image cropping does not reduce the resolution of the area cropped.
CLONING uses the current brush to copy from an image or pattern. It has many uses: one of the most important is to repair problem areas in digital photos.
IMAGE ORIENTATION – Image editors are capable of altering an image to be rotated in any direction and to any degree. Mirror images can be created and images can be horizontally flipped or vertically flopped. Rotated image usually require cropping afterwards, in order to remove the resulting gaps at the image edges.
PERSPECTIVE – is the art of drawing solid objects on a two- dimensional surface so as to give the right impression of their height, width, depth and position in relation to each other when viewed from a particular point.
SHARPENING AND SOFTENING– Sharpening makes images clearer. Too much sharpening causes grains on the surface of the image. Softening makes images softer that removes some of the highly visible flaws. Too much causes the image to blur.
SATURATION- is an expression for the relative bandwidth of the visible output from a light source. As saturation increase, colors appear more “pure.’’ As saturation decreases, colors appear more ‘’ washed-out.’’
CONTRAST AND BRIGHTENING
Contrast of images and brighten or darken the image. Underexposed images can be often be improved by using this feature.
Brightening lightens the image so the photo brightens up. Brightness is a relative expression of the intensity of the energy output of a visible light source.
Adjusting contrast means adjusting brightness because they work together to make a better image.
PHOTO MANIPULATION
Photo manipulation involves transforming or altering a photograph using various methods and techniques to achieve desired results. Some photo manipulations are considered skillful artwork while others are frowned upon as unethical practices, especially when used to deceive the public, such as hat used for political propaganda , or to make a product or person look better.
DIFFERENCES PHOTO EDITING – signifies the regular process used to enhance photos and to create them ‘’Actual editing simple process’’. Also includes some of the regular programs used for editing and expose how to use them. PHOTO MANIPULATION – includes all simple editing techniques and have some manipulation techniques like erasing, adding objects , adding some graphical effects, background correction, creating incredible effect, change elements in an image, adding styles , eliminating blemishes from a person’s face and changing the features of a person’s body.
b.) Infographics
also known as data visualization, information design, and communication design
It is any graphic that display and explains information, whether that be data or words. When we use the term ‘’infographics’’, we’re using it as a general term used to describe data presented in a visual way.
Infographics are important because they change the way people find and experience stories. Infographics are being used to augment editorial content on the web, it create a new way of seeing the world of data, and they help communicate complex ideas in a clear and beautiful way.
TYPES OF INFOGRAPHICS
Statistical
Process Flow
Geographic
PROCESS OF MAKING INFOGRAPHICS
Research
a)Know what is needed
b)Take a reference
c)Know the audience
d)Decide the type of infographics
Brainstorm
a)Gather ideas
b)Build thought process
Design
a) Choose your tool and start designing
Review
a) Cross check the data to deliver flawless output
Launch
a) Make it viral
b) Share on social network
BEST PRACTICES WHEN CREATING INFOGRAPHICS
a)Maintain a structure
b)Don’t use more than 3 color palletes
c)Typography matters a lot
d)Include source and references
LESSON 7: Online Platforms for ICT Content Development
1.Facebook
Posted on
February 13, 2017
Marketplace – allows members to post, read and respond to classified ads.
Groups – allows members who have common interests to find each other and interact.
Events – allows members to publicize an event, invite guests and track who plans to attend.
Pages – allows members to create and promote a public page built around a specific topic.
Presence technology – allows members to see which contacts are online and chat.
Within each member’s personal profile, there are several key networking components. The most popular is arguably the Wall, which is essentially a virtual bulletin board. Messages left on a member’s Wall can be text, video or photos. Another popular component is the virtual Photo Album. Photos can be uploaded from the desktop or directly from a smartphone camera. There is no limitation on quantity, but Facebook staff will remove inappropriate or copyrighted images. An interactive album feature allows the member’s contacts (who are called generically called “friends”) to comment on each other’s photos and identify (tag) people in the photos. Another popular profile component is status updates, a microbloggingfeature that allows members to broadcast short Twitter-like announcements to their friends. All interactions are published in a news feed, which is distributed in real-time to the member’s friends.
Facebook offers a range of privacy options to its members. A member can make all his communications visible to everyone, he can block specific connections or he can keep all his communications private. Members can choose whether or not to be searchable, decide which parts of their profile are public, decide what not to put in their news feed and determine exactly who can see their posts. For those members who wish to use Facebook to communicate privately, there is a message feature, which closely resembles email.
2. Instagram
Instagram is an online mobile photo-sharing site that allows its users to share pictures and videos either publicly or privately on the app, as well as through a variety of other social networking platforms, such as Facebook, Twitter, Tumblr, and Flickr. Originally, a distinctive feature was that it confined photos to a square shape, similar to Kodak Instamatic and Polaroid SX-70 images, in contrast to the 4:3 aspect ratio typically used by mobile device cameras. In August 2015, version 7.5 was released, allowing users to upload media captured in any aspect ratio. Users can also apply digital filters to their images. Videos on Instagram debuted in June 2013, allowing prerecorded square standard definition resolution clips of up to 15 seconds to be shared; later improvements added support for widescreenresolutions of up to 1080p and longer recording times for either prerecorded (up to one minute) or disappearing live (up to one hour) videos.
Instagram was created by Kevin Systrom and Mike Krieger, and launched in October 2010 as a free mobile app. The service rapidly gained popularity, with over 100 million active users as of April 2012[10][11] and over 300 million as of December 2014.[12] Instagram is distributed through the Apple App Store and Google Play.[13]Support for the app is available for iPhone, iPad, iPod Touch, Windows 10 devices and Android handsets, while third-party Instagram apps are available for BlackBerry 10 and Nokia-Symbian Devices.
3. Twitter
Twitter is an online news and social networking service where users post and interact with messages, “tweets,” restricted to 140 characters. Registered users can post tweets, but those who are unregistered can only read them. Users access Twitter through its website interface, SMS or a mobile device app.[10] Twitter Inc. is based in San Francisco, California, United States, and has more than 25 offices around the world.
Twitter is about learning and adding value
It is also about adding value to others by giving or sharing something valuable to them so that they are able to learn something. That is why I usually tweet about stuff that I read, learned or have good value. I have learned so much from the others that is why I love twitter. It is also about helping others, I disagree with many‘experts’ that say you should only follow ‘influential’ users because I don’t judge someone that way, and because I believe the people at Twitter don’t believe in them either. I also disagree that you should only share your own stuff otherwise you will dilute your brand. Sure it makes sense but 24/7 sharing your own blog post and following influential people?
BLOGGING SITES
Weebly
Weebly is one of the easiest website builders in the market. They allow you to drag and drop content into a website, so it’s very intuitive to use (click here to see our opinion on Weebly).
By using Weebly’s website building elements, you can literally drag them into your website and have a website built relatively quickly, and painlessly. The beauty of this system is that you can pretty much drag the elements to wherever you want – so it’s not very restrictive on where and how you place your website content.
Weebly’s elements include pictures, paragraphs, videos, buttons, maps, contact forms – basically all the basics for website building.
2. Tumblr
Tumblr is a popular microblogging platform designed for creative self-expression. It is considered a mindful alternative to Facebook and other social media websites where users blog on a myriad of topics.
You can link your Tumblr account to other social networks you use and you can feed your traditional blog or other RSS feed to your Tumblelog. You can also create static pages such as your own Questions page that people are automatically taken to when they ask you a question. If you want to make your Tumblelog look more lie a traditional website, you can do it by adding pages. You can make your Tumblelog private or just make specific posts private as needed, and you can schedule posts to publish in the future.
Tumblr is perfect for people who don’t need a full blog to publish lengthy posts. It’s also great for people who prefer to publish quick multimedia posts, particularly from their mobile devices. Tumblr is also a great choice for people who want to join a larger community. If a blog is too much or too big for you, but Twitter is too small or too little for you and Instagram isn’t versatile enough for you, then Tumblr might be just right for you.
It’s also easy to invite other people to contribute to your Tumblelog.
If you want to track your stats, you can add any analytics tracking code to your Tumblelog. Some users will even burn a feed with Feedburner, create custom themes, and use their own domain names
3. Pinterest
Pinterest is a free website that requires registration to use.Users can upload, save, sort, and manage images—known as pins—and other media content (e.g., videos) through collections known as pinboards. Pinterest acts as a personalized media platform. Users can browse the content of others in their feed. Users can then save individual pins to one of their own boards using the “Pin It” button, with pinboards typically organized by a central topic or theme. Users can personalize their experience by pinning items, creating boards, and interacting with other members. The end result is that the “pin feed” of each user displays unique, personalized results.
Content can also be found outside of Pinterest and similarly uploaded to a board via the “Pin It” button, which can be downloaded to the bookmark bar on a web browser, or be implemented by a webmaster directly on the website. They also have the option of sending a pin to other Pinterest users and email accounts through the “Send” button. Some websites include red and white “pin it” buttons on items, which allow Pinterest users to pin them directly.
Initially, there were several ways to register a new Pinterest account. Potential users could either receive an invitation from an already registered friend, or they could request an invitation directly from the Pinterest website that could take some time to receive. An account can also be created and accessed by linking Pinterest to a Facebook or Twitter profile. When a user re-posts or re-pins an image to their own board, they have the option of notifying their Facebook and Twitter followers. This feature can be managed on the settings page.
On the main Pinterest page, a “pin feed” appears, displaying the chronological activity from the Pinterest boards that a user follows.
A “board” is where the user’s pins are located. Users can have several boards for various items such as quotes, travel or, most popularly, weddings. A “pin” is an image that has either been uploaded or linked from a website. Once users create boards and add pins, other users can now repin, meaning they can pin one user’s image to their board as well. Once the user has set up their account and boards, they can browse, comment, and like other pins. Users might be discouraged by repeated images and difficult-to-follow direct linking features. Pinterest has also added the option of making boards “secret” so that the user can pin to and view boards that only the user can see when logged into their own account.
Pinterest does not generate its own content; rather, it draws from many resources around the web and compiles them in one convenient location for users.
1 note
·
View note
Text
MIL REFLECTION #7 (JAN 13 2020) (UNIT 7)
LEGAL, ETHICAL AND SOCIETAL ISSUES IN MEDIA AND INFORMATION. So first things first, ethics. Ethics is a moral principles that govern a person's behavior or the conducting of an activity and there are areas of ethical concerns in digital media. Commonly for number 1 is social media. Social Networking. It has a wide range of variety in terms of platform but has one aim, it is to make people socially interact with one another, and hence, the use of dedicated websites and applications to interact with other users, or to find people with similar interests to oneself. There are also ethical concerns in social networking, privacy that we put on our social networking accounts, free speech where users think that it is acceptable to post anything regardless of how rude their action was, and authenticity which is the biggest problem in using social media. The second is blogging is a discussion or informational website published on the World Wide Web consisting of discrete, often informal diary-style text entries. The third is gaming that grows over the years and developed also some issues regarding excessive violence and its effect to the players. Fifth is downloading music/videos/media. Sixth is uploading and sharing original creations. Seventh is using work from another company, service, individual, or product, such as photography, logos or any other copyright patented or trademarked material. We have this thing called netiquette, a correct or acceptable way of communicating on the Internet.
25 notes
·
View notes
Text
SOCIAL MEDIA: Its Benefits, Advantages, and Disadvantages
is the term used to describe the different applications that people use to participate in the social networking and to socialize with others.

Most of us now are using social media applications like Facebook, Instagram, Twitter, etc. these applications are really a big help especially to others who has a family member that is far from them. they can use social media for communication. Others also use social media for education, entertainment, and politics.
Here are some of the benefits of using social media:
1. By using social media, we can easily communicate with other people. It’s more convenient to use social media for communication because unlike before, people were sending messages to others through mails, letters, that will be delivered by the mailman and it takes 4 days or a week to receive the letter. but now that we have social media applications, we can send messages easier and faster. it’s already in the tips of our fingers, in just one click, you are now able to send it to someone without being hassle, and other applications offers free usage and that will not cause you a big amount of money.
2. Students makes use of internet for their projects, researches, and for educational purposes. As a student, I can say that social media really helped me to educate myself, to learn more by just using internet and social media to gather reliable information that I can use to nurture my education.
3. You can share your knowledge through social media. There are different social media applications where you can share what you know ,like the blogging platforms wherein you can post your opinion, your knowledge that you want to share with others so that they will also learn from you.
4. Internet as an entertainment provider. YouTube, Facebook, Twitter, etc., are one of the applications that provides us entertainment. Most of us now find vlogging videos on the YouTube interesting and entertaining, not only or kids but also for the adults.
5. Use of internet for spreading news. We use social media to spread news faster. For example, #WALANGPASOK is used to inform people about the condition of the certain place that could be affected by some serious reasons.
We know that social media is very useful and it makes our life easier but using social media has advantages and disadvantages for us.
ADVANTAGES OF USING SOCIAL MEDIA
1. Social Media offers powerful search engines that can be used by students for educational purposes.
2. It provides entertainment for others who doesn’t find face-to-face socialization fun.
3. It has the ability to provide instant messaging services for others who has a family that is far from them.
4. It helps other people to grow their business by using different services.
5. Social Media is also used for spreading news online by posting it on blogs, websites, pages, etc.
DISADVANTAGES OF USING SOCIAL MEDIA
1. There is a lot of inaccurate information on the internet.
2. Others don’t know how to respect other people’s privacy in a way of hacking private social media accounts.
3. Pornography can easily seen by the users because there are a lot of websites that are free to use by the people that has a bad content.
4. When someone is having a fight with other people, they tend to post things that can hurt other’s feelings and it can lead to Cyberbullying.
5. Using internet for business purposes if helpful, but there are a lot of people who has this kind of confidence to scam them and they are called “bogus buyers.”
In using the internet, make sure to follow the rules of netiquette “network etiquette” to avoid problems. Know how to use it properly.
1 note
·
View note
Text
1.) Empowering the World with the use of technology. We're so lucky because the technologies are present everywhere it help us to make our work quickly and accurate. It is timely updated and always upgraded. In this generation, technology has many uses and important role to our lives and what we all to do is to empower it by doing some things that have value or good benefit to us by the use of gadgets and computers.
Features of Empowerment Technology
-ICT (information and communications technology - or technologies) is an umbrella term that includes any communication device or application, encompassing: radio, television, cellular phones, computer and network hardware and software, satellite systems and so on, as well as the various services and applications associated with them, such as videoconferencing and distance learning. ICTs are often spoken of in a particular context, such as ICTs in education, health care, or libraries. The term is somewhat more common outside of the United States.
Importance of Technology
-Empowerment technology is important , especially to the millennials to prepare, to teach the value and to introduce them/us to the proper world of ICT (Information and Communication Technologies) and also, of course to teach us the proper etiquette of using it and not the way where people use it in violence that could end up someone else’s precious life.
2.) I’ve learned that empowerment technologies is important. However, there are things that we need to follow ,to avoid danger or accidents. I learned what are the rules and netiquette to be follow .I also learned that ICT (Information and Communication Technology) deals with the use of different communication technologies such as mobile phones, telephone, Internet, etc. to locate, save, send and edit information . I also learned that Empowerment Technology or E-Tech often deals with the use of different technologies such as mobile phones, telephone, computer and other devices to locate, save, communicate and to inform. Empowerment Technology is important for its innovative uses is sufficient in our daily lives. I also learned how to make a blog and website. I also learned more about social media and its categories.I am thankful that I learned many things in Empowerment Technology
1 note
·
View note
Text
BLOG ME: Social Media
Life in 21st century is obviously more convenient and instant than before. In the past, people can only get information given by the media like television, radio, and print media (newspapers and magazines) but nowadays, news and updates are easily disseminated through gadgets, specifically the social media.
Social media are software, applications or platforms that allow users to communicate in an online network or community. There are different types of social media. These are Social Network, Bookmarking Site, Social News, Media Sharing, Micro Blogging, and Blogs and Forums. There are a lot of social media users all over the world and the most common platforms that are so popular to everyone specially to the youth are Facebook, Instagram, Snapchat, Twitter, Reddit, Viber, Telegram, Pinterest and more.
Because of social media, families are now more connected, just like in our situation last year, when we were not able to see one another, but because of social media applications/platforms, we still found a way to communicate. Also, social workers and businesses have benefits in this trend of ICT for social media made a lot opportunities in engaging, finding, and advertising services and products to people (e.g. Shopee, Lazada, Facebook marketplace and pages, Food Panda, etc.). Aside from that, it also created different job offers and opportunities to everyone. When it comes to government, social media became a big platform as well in discerning information during calamities like announcing on Facebook pages of different Local Government Units and Departments of the government.
Indeed, social media is a great platform that is very useful in our everyday lives. Without it, it would be difficult for us to communicate and receive information from time to time. But on the other hand, as users, we must put in mind to practice proper netiquette every time we use it in order to avoid insensitivity, violence, fake news, and internet threats.

0 notes
Text
Common issues and crimes in the Internet
1. CYBERBULLYING or Cyber harassment - It is a form of electronic means of intimidation or abuse. Online bullying is also known as cyberbullying and cyber abuse. - Cyberbullying is when someone on the internet, usually adolescents, threatens or harasses others, particularly on social media sites. Harmful bullying actions may include posting gossip, warnings, lewd comments, a victims' personal details, or pejorative labels (i.e. hate speech).

2. HACKING - Hacking usually refers to unauthorized entry into a device or a network. As a hacker, the individual engaged in hacking activities is identified. This hacker may change the device or security features to achieve a target that varies from the system's original intent. - Hacking may also refer to non-malicious operations, usually involving uncommon or improvised equipment or process modifications.

3. IDENTITY THEFT - Identity theft, also recognized as fraudulent activity, is a crime where a pretender gains key bits of individually identifiable information and the ability to impersonate someone else, such as Social Security or driver's license numbers.
TYPES AND EXAMPLE OF IDENTITY THEFT.
True-name identity theft - In order to open new accounts, the robber uses personal information. In order to acquire blank checks, the robber could open a new credit card account, set up a cellular phone service or open a new checking account.
Account-takeover identity theft - This implies that the impostor uses sensitive information to obtain access to the current accounts of the user.

4. PLAGIARISM - Plagiarism is a fraudulent act. It includes both stealing the work of someone else and lying about it afterwards.

5. NETIQUETTE - It is a mixture of the phrase net and label. This focuses on an individual's appropriate behavior while using the web resource.

THIS IS THE END OF LESSON 3. THANK YOU!
0 notes
Text

What is online safety?
Is the knowledge of maximizing the user's personal safety and security and security risk to private information, and self-protection from computer crime in general.
10 SAFETY TIPS
1. Know the Scams
Learn about diferrent kinds of scams and what you can do to avoid them.
2. Think before you click
Think twice, thrice and a zillion time before click any link or buttons.
3. Safety Peruse
These sites may have an Address that's very similar tp legitimate site, but the page can have misspelling, Bad Grammar, or low resolution Images.
4. Shop Safety
Don't shop on a site unless it has "https" and a padlock icon on the left or right or the URL.
5. Kick-butt Passwords
Use an Extremely uncrackable password One likw 9&4yiw2pxwys#"
6. Protect you Info's
Keep your guard up. Back up all your data on your computer, smartphone and tablet, theft or a cash.
7. Watch your Wi-Fi Connectivity
Protect your network by changing your router's setting and making sure that you have connection password-protected.
8. Install a Firewall
A firewall is a gate line of defense against cyber attracts.
9. Keep up to date
• The best security updates automatically to protect your computer.
• Use the manufacturer's latest security patches to make regular updates and make that you have the software set to do routine scam.
10. Use your Noggin
Use your common sense while surfing the web.
COMMON ISSUES AND CRIMES IN THE INTERNET
CYBERBULLYING
HACKING
IDENTITY THEFT
PLAGIARISM
COPYRIGHT ISSUES
CYBERBULLYING
Cyberbullying or cyberharassment is a form of bullying or harassment using electronic means. Cyberbullying and cyberharassment are also known as online bullying
Cyberbullying is when someone, typically teens, bully or harass others on the internet, particularly on social media sites. Harmful bullying behavior can include posting rumors, threats, sexual remarks, a victims' personal information, or pejorative labels (i.e. hate speech).
The Anti-Bullying Act of 2013
(RA 10627)
(Sec. 2, RA 10627) These acts are collectively called “cyber bullying” when committed online. (Sec. 2-D, RA 10627) This covers social bullying aiming to belittle another individual or group or gender-based bullying that humiliates another on the basis of perceived or actual sexual orientation and gender identity. (Sec. 3, B-1, RA 10627, Implementing Rules).
The Revised Penal Code and the Cybercrime Prevention Act
One who publicly or maliciously imputes to another a crime, vice, defect, real or imaginary, or any act, omission, condition, status or circumstance tending to cause the dishonor, discredit or contempt of a natural or juridical person, or blacken the memory of one who is dead may be liable for libel under this Code. (Art. 353, RPC) These acts are more severely punished when done online in addition to the civil action for damages which may be brought by the offended party. (Sec. 4(c-4), RA 10175) Cyberlibel holds liable only the original author of the post (Sec. 5(3), Implementing Rules of RA 10175). Likers or sharers of a post cannot be held liable under this law.
Slander may also be applicable to one who, in heat of anger, utters statements that are highly defamatory in character. (Art. 358, RPC) Intriguing Against Honour may also find applicability when the principal purpose is to blemish the honour or reputation of a person. (Art. 364, RPC) However, the requirement is that the post be directed to a specific person. Hence, a blind item is not as actionable as a named-post in social media.
HACKING
Hacking generally refers to unauthorized intrusion into a computer or a network. The person engaged in hacking activities is known as a hacker. This hacker may alter system or security features to accomplish a goal that differs from the original purpose of the system.
Hacking can also refer to non-malicious activities, usually involving unusual or improvised alterations to equipment or processes.
IDENTITY THEFT
Identity theft, also known as identity fraud, is a crime in which an imposter obtains key pieces of personally identifiable information, such as Social Security or driver's license numbers, in order to impersonate someone else.
Types and examples of identity theft
True-name identity theft means the thief uses personal information to open new accounts. The thief might open a new credit card account, establish cellular phone service or open a new checking account in order to obtain blank checks.
Account-takeover identity theft means the imposter uses personal information to gain access to the person's existing accounts.
PLAGIARISM
Plagiarism is an act of fraud. It involves both stealing someone else's work and lying about it afterward.
The following are considered plagiarism
turning in someone else's work as your own
copying words or ideas from someone else without giving credit
failing to put a quotation in quotation marks
giving incorrect information about the source of a quotation
changing words but copying the sentence structure of a source without giving credit
copying so many words or ideas from a source that it makes up the majority of your work, whether you give credit or not (see our section on "fair use" rules)
Copyright Issues
Republic Act No. 8293 [An Act Prescribing the Intellectual Property Code and Establishing the Intellectual Property Office, Providing for Its Powers and Functions, and for Other Purposes]otherwise known as the Intellectual Property Code of the Philippines.
Intellectual property rights under the I. P. Code: The intellectual property rights under the Intellectual Property Code are as follows:
1. Copyright and related rights;
2. Trademarks and service marks;
3. Geographic indications;
4. Industrial designs;
5. Patents;
6. Layout designs [topographies] of integrated circuits; and
7. Protection of undisclosed information.
The scheme of penalties for infringement has also been changed. From the previous fine of Php200 to Php2,000 and/or imprisonment of 1 year, the current range of penalties are as follows:
For first offenders - fine of PhP50,000 to PhP150,000 and/or imprisonment of 1 to 3 years
For second offenders - fine of PhP150,000 to PhP500,000 and/or imprisonment of 3 to 6 years
For third and subsequent offenders - fine of PhP500,000 to PhP1.5 Million and/or imprisonment of 6 to 9 years.
In case of insolvency, the offender shall furthermore suffer subsidiary imprisonment.
NETIQUETTE
Is a combination of the word net and etiquette.
It focuses on the acceptable behavior of a person while using the internet resource.
The Core Rules of Netiquette
Rule 1. Remember the human.
Never forget that the person reading yourj mail or posting is, indeed, a person, with feelings that can be hurt.
Corollary 1 to Rule #1: It's not nice to hurt other people's feelings.
Corollary 2: Never mail or post anything you wouldn't say to your reader's face.
Corollary 3: Notify your readers when flaming.
Rule 2. Adhere to the same standards of behavior online that you follow in real life.
Corollary 1: Be ethical.
Corollary 2: Breaking the law is bad Netiquette.
Rule 3. Know where you are in cyberspace.
Corollary 1: Netiquette varies from domain to domain.
Corollary 2: Lurk before you leap.
Rule 4. Respect other people's time and bandwidth.
Corollary 1: It's OK to think that what you're doing at the moment is the most important thing in the universe, but don't expect anyone else to agree with you.
Corollary 2: Post messages to the appropriate discussion group.
Corollary 3: Try not to ask stupid questions on discussion groups.
Corollary 4: Read the FAQ (Frequently Asked Questions) document.
Corollary 5: When appropriate, use private email instead of posting to the group.
Corollary 6: Don't post subscribe, unsubscribe, or FAQ requests.
Corollary 7: Don't waste expert readers' time by posting basic information.
Corollary 8: If you disagree with the premise of a discussion group, don't waste the time and bandwidth of the members by telling them how stupid they are. Just stay away.
Corollary 9: Conserve bandwidth when you retrieve information from a host or server.
Rule 5. Make yourself look good online.
Corollary 1: Check grammar and spelling before you post.
Corollary 2: Know what you're talking about and make sense.
Corollary 3: Don't post flame-bait.
Rule 6. Share expert knowledge.
Corollary 1: Offer answers and help to people who ask questions on discussion groups.
Corollary 2: If you've received email answers to a posted question, summarize them and post the summary to the discussion group.
Rule 7. Help keep flame wars under control.
Corollary 1: Don't respond to flame-bait.
Corollary 2: Don't post spelling or grammar flames.
Corollary 3: If you've posted flame-bait or perpetuated a flame war, apologize.
Rule 8. Respect other people's privacy.
Don't read other people's private email.
Rule 9. Don't abuse your power.
The more power you have, the more important it is that you use it well.
Rule 10. Be forgiving of other people's mistakes.
0 notes
Text
LESSON 3:Online Safety and Security
ONLINE SAFETY AND SECURITY,ETHICS AND NETIQUETTE











COMMON ISSUES AND CRIMES IN THE INTERNET
CYBERBULLYING
HACKING
IDENTITY THEFT
PLAGIARISM
COPYRIGHT ISSUES
CYBERBULLYING Cyberbullying or cyberharassment is a form of bullying or harassment using electronic means. Cyberbullying and cyberharassment are also known as online bullyingCyberbullying is when someone, typically teens, bully or harass others on the internet, particularly on social media sites. Harmful bullying behavior can include posting rumors, threats, sexual remarks, a victims’ personal information, or pejorative labels (i.e. hate speech). Unicef: Cyber bullying affects 70% of youth, he proportion of children and adolescents affected by cyberbullying ranges from five percent to 21 percent, with girls at higher risk than boys, according to data from the UN Educational, Scientific and Cultural Organization. The Anti-Bullying Act of 2013 (RA 10627) (Sec. 2, RA 10627) These acts are collectively called “cyber bullying” when committed online. (Sec. 2-D, RA 10627) This covers social bullying aiming to belittle another individual or group or gender-based bullying that humiliates another on the basis of perceived or actual sexual orientation and gender identity. (Sec. 3, B-1, RA 10627, Implementing Rules).
The Revised Penal Code and the Cybercrime Prevention Act One who publicly or maliciously imputes to another a crime, vice, defect, real or imaginary, or any act, omission, condition, status or circumstance tending to cause the dishonor, discredit or contempt of a natural or juridical person, or blacken the memory of one who is dead may be liable for libel under this Code. (Art. 353, RPC) These acts are more severely punished when done online in addition to the civil action for damages which may be brought by the offended party. (Sec. 4(c-4), RA 10175) Cyberlibel holds liable only the original author of the post (Sec. 5(3), Implementing Rules of RA 10175). Likers or sharers of a post cannot be held liable under this law.Slander may also be applicable to one who, in heat of anger, utters statements that are highly defamatory in character. (Art. 358, RPC) Intriguing Against Honour may also find applicability when the principal purpose is to blemish the honour or reputation of a person. (Art. 364, RPC) However, the requirement is that the post be directed to a specific person. Hence, a blind item is not as actionable as a named-post in social media.
HACKING Hacking generally refers to unauthorized intrusion into a computer or a network. The person engaged in hacking activities is known as a hacker. This hacker may alter system or security features to accomplish a goal that differs from the original purpose of the system. Hacking can also refer to non-malicious activities, usually involving unusual or improvised alterations to equipment or processes.
IDENTITY THEFT Identity theft, also known as identity fraud, is a crime in which an imposter obtains key pieces of personally identifiable information, such as Social Security or driver’s license numbers, in order to impersonate someone else.
Types and examples of identity theft 1. True-name identity theft means the thief uses personal information to open new accounts. The thief might open a new credit card account, establish cellular phone service or open a new checking account in order to obtain blank checks. 2. Account-takeover identity theft means the imposter uses personal information to gain access to the person’s existing accounts.
PLAGIARISM Plagiarism is an act of fraud. It involves both stealing someone else’s work and lying about it afterward.
-turning in someone else’s work as your own -copying words or ideas from someone else without giving credit -failing to put a quotation in quotation marks -giving incorrect information about the source of a quotation -changing words but copying the sentence structure of a source without giving credit -copying so many words or ideas from a source that it makes up the majority of your work, whether you give credit or not (see our section on “fair use” rules)
Republic Act No. 8293 [An Act Prescribing the Intellectual Property Code and Establishing the Intellectual Property Office, Providing for Its Powers and Functions, and for Other Purposes]otherwise known as the Intellectual Property Code of the Philippines. Intellectual property rights under the I. P. Code: The intellectual property rights under the Intellectual Property Code are as follows:
1. Copyright and related rights;
2. Trademarks and service marks;
3. Geographic indications;
4. Industrial designs;
5. Patents;
6. Layout designs [topographies] of integrated circuits
7. Protection of undisclosed information.
The scheme of penalties for infringement has also been changed. From the previous fine of Php200 to Php2,000 and/or imprisonment of 1 year, the current range of penalties are as follows:
For first offenders - fine of PhP50,000 to PhP150,000 and/or imprisonment of 1 to 3 years
For second offenders - fine of PhP150,000 to PhP500,000 and/or imprisonment of 3 to 6 years
For third and subsequent offenders - fine of PhP500,000 to PhP1.5 Million and/or imprisonment of 6 to 9 years.
In case of insolvency, the offender shall furthermore suffer subsidiary imprisonment
NETIQUETTE
Is a combination of the word net and etiquette.
It focuses on the acceptable behavior of a person while using the internet resource.The Core Rules of Netiquette
The Core Rules of Netiquette
Rule 1. Remember the human.
Never forget that the person reading your mail or posting is, indeed, a person, with feelings that can be hurt.
Corollary 1 to Rule #1: It’s not nice to hurt other people’s feelings.
Corollary 2: Never mail or post anything you wouldn’t say to your reader’s face.
Corollary 3: Notify your readers when flaming.
Rule 2. Adhere to the same standards of behavior online that you follow in real life.
Corollary 1: Be ethical.
Corollary 2: Breaking the law is bad Netiquette.
Rule 3. Know where you are in cyberspace.
Corollary 1: Netiquette varies from domain to domain.
Corollary 2: Lurk before you leap.
Rule 4. Respect other people’s time and bandwidth.
Corollary 1: It’s OK to think that what you’re doing at the moment is the most important thing in the universe, but don’t expect anyone else to agree with you.
Corollary 2: Post messages to the appropriate discussion group.
Corollary 3: Try not to ask stupid questions on discussion groups.
Corollary 4: Read the FAQ (Frequently Asked Questions) document.
Corollary 5: When appropriate, use private email instead of posting to the group.
Corollary 6: Don’t post subscribe, unsubscribe, or FAQ requests.
Corollary 7: Don’t waste expert readers’ time by posting basic information.
Corollary 8: If you disagree with the premise of a discussion group, don’t waste the time and bandwidth of the members by telling them how stupid they are. Just stay away.
Corollary 9: Conserve bandwidth when you retrieve information from a host or server.
Rule 5. Make yourself look good online.
Corollary 1: Check grammar and spelling before you post.
Corollary 2: Know what you’re talking about and make sense.
Corollary 3: Don’t post flame-bait.
Rule 6. Share expert knowledge.
Corollary 1: Offer answers and help to people who ask questions on discussion groups.
Corollary 2: If you’ve received email answers to a posted question, summarize them and post the summary to the discussion group.
Rule 7. Help keep flame wars under control.
Corollary 1: Don’t respond to flame-bait.
Corollary 2: Don’t post spelling or grammar flames.
Corollary 3: If you’ve posted flame-bait or perpetuated a flame war, apologize.
Rule 8. Respect other people’s privacy.
Don’t read other people’s private email.
Rule 9. Don’t abuse your power.
The more power you have, the more important it is that you use it well.
Rule 10. Be forgiving of other people’s mistakes.
0 notes
Text
ONLINE SAFETY AND SECURITY, ETHICS
AND NETIQUETTE

What is online safety?
Is the knowledge of maximizing the user's personal safety and security and security risk to private information, and self protection from computer crime in general.
10 safety tips
1. Know the scams
Learn about different kinds of scams and what you can do to avoid them
2. Think before you click
Think twice, thrice and a zillion of times before click any links or buttons
3. Safety Peruse
These sites may have an address. Thats very similar to a legitimate site, but the page can ve have a misspelling, bad grammar or low resolution images
4. Shop Safety
Don't shop on a site unless it has "https" and a padlock icon on the left or right if the URL
5. Kick-butt passwords
Use an extremely uncrakable passwords
6. Protect you info's
Keep your guard up. Back up all your data on your computer, smartphone, tablet, theft or a cash.
7. Watch your Wi-Fi connectivity
Protect your network by changing your router's setting and making sure that you have the connection password protected.
8. Install a Firewall
A firewall is agrate line of defense against cyber attracts..
• The best security updates automatically to protect your computer
• Use the maifacturers latest security patches to make a regular updates and make that you have the software set to do the routine scam
10. Use you Noggin
Use your common sense while surfing the web
CYBERBULLYING
HACKING
IDENTITY THEFT
PLAGIARISM
COPYRIGHT ISSUES
CYBERBULLYING

Cyberbullying or cyberharassment is a form of bullying or harassment using electronic means. Cyberbullying and cyberharassment are also known as online bullying
Cyberbullying is when someone, typically teens, bully or harass others on the internet, particularly on social media sites. Harmful bullying behavior can include posting rumors, threats, sexual remarks, a victims' personal information, or pejorative labels (i.e. hate speech).
The Anti-Bullying Act of 2013
(RA 10627)
(Sec. 2, RA 10627) These acts are collectively called “cyber bullying” when committed online. (Sec. 2-D, RA 10627) This covers social bullying aiming to belittle another individual or group or gender-based bullying that humiliates another on the basis of perceived or actual sexual orientation and gender identity. (Sec. 3, B-1, RA 10627, Implementing Rules).
The Revised Penal Code and the Cybercrime Prevention Act
One who publicly or maliciously imputes to another a crime, vice, defect, real or imaginary, or any act, omission, condition, status or circumstance tending to cause the dishonor, discredit or contempt of a natural or juridical person, or blacken the memory of one who is dead may be liable for libel under this Code. (Art. 353, RPC) These acts are more severely punished when done online in addition to the civil action for damages which may be brought by the offended party. (Sec. 4(c-4), RA 10175) Cyberlibel holds liable only the original author of the post (Sec. 5(3), Implementing Rules of RA 10175). Likers or sharers of a post cannot be held liable under this law.

Slander may also be applicable to one who, in heat of anger, utters statements that are highly defamatory in character. (Art. 358, RPC) Intriguing Against Honour may also find applicability when the principal purpose is to blemish the honour or reputation of a person. (Art. 364, RPC) However, the requirement is that the post be directed to a specific person. Hence, a blind item is not as actionable as a named-post in social media
HACKING

Hacking generally refers to unauthorized intrusion into a computer or a network. The person engaged in hacking activities is known as a hacker. This hacker may alter system or security features to accomplish a goal that differs from the original purpose of the system.
Hacking can also refer to non-malicious activities, usually involving unusual or improvised alterations to equipment or processes.
IDENTITY THEFT

Identity theft, also known as identity fraud, is a crime in which an imposter obtains key pieces of personally identifiable information, such as Social Security or driver's license numbers, in order to impersonate someone else.
Types and examples of identity theft
1. True-name identity theft means the thief uses personal information to open new accounts. The thief might open a new credit card account, establish cellular phone service or open a new checking account in order to obtain blank checks.
2. Account-takeover identity theft means the imposter uses personal information to gain access to the person's existing accounts.
PLAGIARISM

Plagiarism is an act of fraud. It involves both stealing someone else's work and lying about it afterward.
1 note
·
View note
Text
LESSON 1
Information and communications technology (ICT) is an extensional term for information technology (IT) that stresses the role of unified communications[ and the integration of telecommunications (telephone lines and wireless signals) and computers, as well as necessary enterprise software, middleware, storage and audiovisual, that enable users to access, store, transmit, and manipulate information.
The term ICT is also used to refer to the convergence of audiovisual and telephone networks with computer networks through a single cabling or link system. There are large economic incentives to merge the telephone network with the computer network system using a single unified system of cabling, signal distribution, and management.
ICT is an umbrella term that includes any communication device, encompassing radio, television, cell phones, computer and network hardware, satellite systems and so on, as well as the various services and appliances with them such as video conferencing and distance learning.ICT is a broad subject and the concepts are evolving.It covers any product that will store, retrieve, manipulate, transmit, or receive information electronically in a digital form (e.g., personal computers, digital television, email, or robots). Theoretical differences between interpersonal-communication technologies and mass-communication technologies have been identified by the philosopher Piyush Mathur.Skills Framework for the Information Age is one of many models for describing and managing competencies for ICT professionals for the 21st century.

Information technology (IT) is the use of computers to store, retrieve, transmit, and manipulate data or information. IT is typically used within the context of business operations as opposed to personal or entertainment technologies. IT is considered to be a subset of information and communications technology (ICT).

Communications technology, also known as information technology, refers to all equipment and programs that are used to process and communicate information. Professionals in the communication technology field specialize in the development, installation, and service of these hardware and software systems.

Emerging technologies are technologies whose development, practical applications, or both are still largely unrealized, such that they are figuratively emerging into prominence from a background of nonexistence or obscurity. These technologies are new, such as various applications of biotechnology including gene therapy. Emerging technologies are often perceived as capable of changing the status quo.
Emerging technologies are characterized by radical novelty (in application even if not in origins), relatively fast growth, coherence, prominent impact, and uncertainty and ambiguity. In other words, an emerging technology can be defined as "a radically novel and relatively fast growing technology characterised by a certain degree of coherence persisting over time and with the potential to exert a considerable impact on the socio-economic domain(s) which is observed in terms of the composition of actors, institutions and patterns of interactions among those, along with the associated knowledge production processes. Its most prominent impact, however, lies in the future and so in the emergence phase is still somewhat uncertain and ambiguous."


Artificial intelligence (AI) refers to the simulation of human intelligence in machines that are programmed to think like humans and mimic their actions. The term may also be applied to any machine that exhibits traits associated with a human mind such as learning and problem-solving.


Robotics is a branch of engineering that involves the conception, design, manufacture, and operation of robots. This field overlaps with electronics, computer science, artificial intelligence, mechatronics, nanotechnology and bioengineering.
Biometrics is the measurement and statistical analysis of people's unique physical and behavioral characteristics. The technology is mainly used for identification and access control or for identifying individuals who are under surveillance.

Quantum cryptography is the science of exploiting quantum mechanical properties to perform cryptographic tasks. The best known example of quantum cryptography is quantum key distribution which offers an information-theoretically secure solution to the key exchange problem.

online learning platform is an integrated set of interactive online services that provide trainers, learners, and others involved in education with information, tools and resources to support and enhance education delivery and management.

Computer-assisted translation (CAT) software translates one language to another using translation memory—which stores previously translated texts—or crowd assistance to provide translations that are consistent with previously used language to ensure proper spelling, grammar, and phrasing.

3D hologram is defined as a 3D projection that exists freely in space and is visible to everyone without the need for 3D glasses. Holography is the next stage of photography and conventional film and its three-dimensionality creates completely new possibilities for use, such as for product presentation.

Virtual reality (VR) refers to a computer-generated simulation in which a person can interact within an artificial three-dimensional environment using electronic devices, such as special goggles with a screen or gloves fitted with sensors.

Online systems – are online versions of information systems, which is “the process of and tools for storing, managing, using, and gathering of data and communications in an organization. An example of information systems are tools for sending out communications and storing files in a business.”

Social Media Platform means a mobile and/or internet-based platform used and controlled by a Seller or any of its Affiliates for the exclusive purpose of promoting the Business,
ecommerce platform is a software application that allows online businesses to manage their website, marketing, sales and operations.
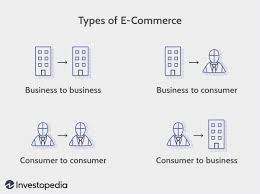
online video platform (OVP), provided by a video hosting service, enables users to upload, convert, store and play back video content on the Internet, often via a structured, large-scale system that may generate revenue. Users generally will upload video content via the hosting service's website, mobile or desktop application, or other interface (API). The type of video content uploaded might be anything from shorts to full-length TV shows and movies. The video host stores the video on its server and offers users the ability to enable different types of embed codes or links that allow others to view the video content. The website, mainly used as the video hosting website, is usually called the video sharing website.

Netiquette is a combination of the words network and etiquette and is defined as a set of rules for acceptable online behavior. Similarly, online ethics focuses on the acceptable use of online resources in an online social environment.

Online search is the process of interactively searching for and retrieving requested information via a computer from databases that are online. ... Research Skills “Research” sometimes just means finding out information about a topic.

online safety refers to the act of staying safe online. ... Being safe online means individuals are protecting themselves and others from online harms and risks which may jeopardise their personal information, lead to unsafe communications or even effect their mental health and wellbeing.


Cyberbullying or cyberharassment is a form of bullying or harassment using electronic means. Cyberbullying and cyberharassment are also known as online bullying. It has become increasingly common, especially among teenagers, as the digital sphere has expanded and technology has advanced.Cyberbullying is when someone, typically a teenager, bullies or harasses others on the internet and in other digital spaces, particularly on social media sites. Harmful bullying behavior can include posting rumors, threats, sexual remarks, a victims' personal information, or pejorative labels (i.e. hate speech).Bullying or harassment can be identified by repeated behavior and an intent to harm. Victims of cyberbulling may experience lower self-esteem, increased suicidal ideation, and a variety of negative emotional responses including being scared, frustrated, angry, or depressed.

Hacking is an attempt to exploit a computer system or a private network inside a computer. Simply put, it is the unauthorised access to or control over computer network security systems for some illicit purpose. ... They can destroy, steal or even prevent authorized users from accessing the system.

Identity theft is the crime of obtaining the personal or financial information of another person to use their identity to commit fraud, such as making unauthorized transactions or purchases.

Plagiarism is presenting someone else's work or ideas as your own, with or without their consent, by incorporating it into your work without full acknowledgement. All published and unpublished material, whether in manuscript, printed or electronic form, is covered under this definition.

WHAT I’VE LEARNED?
I’ve learned to this lesson to know what and how to use some online platforms and to have some knowledge in using it in a good way because there are some issues that we shouldn’t do in the internet. Also I’ve learned some techniques on searching like you should find your web browser based for what we are going to search, we should limit our search and we should check if our spelling is correct when searching ,the safety tips also I’ve learned that we should avoid some scams in the internet, to protect our info’s and our password should be a unique or hard to know so that our accounts will be safe, we should use this searching or using internet in a nice and good way we shouldn’t not use it in unnecessary things.
0 notes
Text
LESSON 3:Online Safety and Security
ONLINE SAFETY AND SECURITY,ETHICS AND NETIQUETTE











COMMON ISSUES AND CRIMES IN THE INTERNET
CYBERBULLYING
HACKING
IDENTITY THEFT
PLAGIARISM
COPYRIGHT ISSUES
CYBERBULLYING Cyberbullying or cyberharassment is a form of bullying or harassment using electronic means. Cyberbullying and cyberharassment are also known as online bullyingCyberbullying is when someone, typically teens, bully or harass others on the internet, particularly on social media sites. Harmful bullying behavior can include posting rumors, threats, sexual remarks, a victims' personal information, or pejorative labels (i.e. hate speech). Unicef: Cyber bullying affects 70% of youth, he proportion of children and adolescents affected by cyberbullying ranges from five percent to 21 percent, with girls at higher risk than boys, according to data from the UN Educational, Scientific and Cultural Organization. The Anti-Bullying Act of 2013 (RA 10627) (Sec. 2, RA 10627) These acts are collectively called “cyber bullying” when committed online. (Sec. 2-D, RA 10627) This covers social bullying aiming to belittle another individual or group or gender-based bullying that humiliates another on the basis of perceived or actual sexual orientation and gender identity. (Sec. 3, B-1, RA 10627, Implementing Rules).
The Revised Penal Code and the Cybercrime Prevention Act One who publicly or maliciously imputes to another a crime, vice, defect, real or imaginary, or any act, omission, condition, status or circumstance tending to cause the dishonor, discredit or contempt of a natural or juridical person, or blacken the memory of one who is dead may be liable for libel under this Code. (Art. 353, RPC) These acts are more severely punished when done online in addition to the civil action for damages which may be brought by the offended party. (Sec. 4(c-4), RA 10175) Cyberlibel holds liable only the original author of the post (Sec. 5(3), Implementing Rules of RA 10175). Likers or sharers of a post cannot be held liable under this law.Slander may also be applicable to one who, in heat of anger, utters statements that are highly defamatory in character. (Art. 358, RPC) Intriguing Against Honour may also find applicability when the principal purpose is to blemish the honour or reputation of a person. (Art. 364, RPC) However, the requirement is that the post be directed to a specific person. Hence, a blind item is not as actionable as a named-post in social media.
HACKING Hacking generally refers to unauthorized intrusion into a computer or a network. The person engaged in hacking activities is known as a hacker. This hacker may alter system or security features to accomplish a goal that differs from the original purpose of the system. Hacking can also refer to non-malicious activities, usually involving unusual or improvised alterations to equipment or processes.
IDENTITY THEFT Identity theft, also known as identity fraud, is a crime in which an imposter obtains key pieces of personally identifiable information, such as Social Security or driver's license numbers, in order to impersonate someone else.
Types and examples of identity theft 1. True-name identity theft means the thief uses personal information to open new accounts. The thief might open a new credit card account, establish cellular phone service or open a new checking account in order to obtain blank checks. 2. Account-takeover identity theft means the imposter uses personal information to gain access to the person's existing accounts.
PLAGIARISM Plagiarism is an act of fraud. It involves both stealing someone else's work and lying about it afterward.
-turning in someone else's work as your own -copying words or ideas from someone else without giving credit -failing to put a quotation in quotation marks -giving incorrect information about the source of a quotation -changing words but copying the sentence structure of a source without giving credit -copying so many words or ideas from a source that it makes up the majority of your work, whether you give credit or not (see our section on "fair use" rules)
Republic Act No. 8293 [An Act Prescribing the Intellectual Property Code and Establishing the Intellectual Property Office, Providing for Its Powers and Functions, and for Other Purposes]otherwise known as the Intellectual Property Code of the Philippines. Intellectual property rights under the I. P. Code: The intellectual property rights under the Intellectual Property Code are as follows:
1. Copyright and related rights;
2. Trademarks and service marks;
3. Geographic indications;
4. Industrial designs;
5. Patents;
6. Layout designs [topographies] of integrated circuits
7. Protection of undisclosed information.
The scheme of penalties for infringement has also been changed. From the previous fine of Php200 to Php2,000 and/or imprisonment of 1 year, the current range of penalties are as follows:
For first offenders - fine of PhP50,000 to PhP150,000 and/or imprisonment of 1 to 3 years
For second offenders - fine of PhP150,000 to PhP500,000 and/or imprisonment of 3 to 6 years
For third and subsequent offenders - fine of PhP500,000 to PhP1.5 Million and/or imprisonment of 6 to 9 years.
In case of insolvency, the offender shall furthermore suffer subsidiary imprisonment
NETIQUETTE
Is a combination of the word net and etiquette.
It focuses on the acceptable behavior of a person while using the internet resource.The Core Rules of Netiquette
The Core Rules of Netiquette
Rule 1. Remember the human.
Never forget that the person reading your mail or posting is, indeed, a person, with feelings that can be hurt.
Corollary 1 to Rule #1: It's not nice to hurt other people's feelings.
Corollary 2: Never mail or post anything you wouldn't say to your reader's face.
Corollary 3: Notify your readers when flaming.
Rule 2. Adhere to the same standards of behavior online that you follow in real life.
Corollary 1: Be ethical.
Corollary 2: Breaking the law is bad Netiquette.
Rule 3. Know where you are in cyberspace.
Corollary 1: Netiquette varies from domain to domain.
Corollary 2: Lurk before you leap.
Rule 4. Respect other people's time and bandwidth.
Corollary 1: It's OK to think that what you're doing at the moment is the most important thing in the universe, but don't expect anyone else to agree with you.
Corollary 2: Post messages to the appropriate discussion group.
Corollary 3: Try not to ask stupid questions on discussion groups.
Corollary 4: Read the FAQ (Frequently Asked Questions) document.
Corollary 5: When appropriate, use private email instead of posting to the group.
Corollary 6: Don't post subscribe, unsubscribe, or FAQ requests.
Corollary 7: Don't waste expert readers' time by posting basic information.
Corollary 8: If you disagree with the premise of a discussion group, don't waste the time and bandwidth of the members by telling them how stupid they are. Just stay away.
Corollary 9: Conserve bandwidth when you retrieve information from a host or server.
Rule 5. Make yourself look good online.
Corollary 1: Check grammar and spelling before you post.
Corollary 2: Know what you're talking about and make sense.
Corollary 3: Don't post flame-bait.
Rule 6. Share expert knowledge.
Corollary 1: Offer answers and help to people who ask questions on discussion groups.
Corollary 2: If you've received email answers to a posted question, summarize them and post the summary to the discussion group.
Rule 7. Help keep flame wars under control.
Corollary 1: Don't respond to flame-bait.
Corollary 2: Don't post spelling or grammar flames.
Corollary 3: If you've posted flame-bait or perpetuated a flame war, apologize.
Rule 8. Respect other people's privacy.
Don't read other people's private email.
Rule 9. Don't abuse your power.
The more power you have, the more important it is that you use it well.
Rule 10. Be forgiving of other people's mistakes.
0 notes
Text
LESSON 3 - Online Safety and Security
ONLINE SAFETY AND SECURITY, ETHICS AND NETIQUETTE

10 SAFETY TIPS










COMMON ISSUES AND CRIMES IN THE INTERNET
CYBERBULLYING
HACKING
IDENTITY THEFT
PLAGIARISM
COPYRIGHT ISSUES
CYBERBULLYING Cyberbullying or cyberharassment is a form of bullying or harassment using electronic means. Cyberbullying and cyberharassment are also known as online bullyingCyberbullying is when someone, typically teens, bully or harass others on the internet, particularly on social media sites. Harmful bullying behavior can include posting rumors, threats, sexual remarks, a victims' personal information, or pejorative labels (i.e. hate speech). Unicef: Cyber bullying affects 70% of youth, he proportion of children and adolescents affected by cyberbullying ranges from five percent to 21 percent, with girls at higher risk than boys, according to data from the UN Educational, Scientific and Cultural Organization. The Anti-Bullying Act of 2013 (RA 10627) (Sec. 2, RA 10627) These acts are collectively called “cyber bullying” when committed online. (Sec. 2-D, RA 10627) This covers social bullying aiming to belittle another individual or group or gender-based bullying that humiliates another on the basis of perceived or actual sexual orientation and gender identity. (Sec. 3, B-1, RA 10627, Implementing Rules).
The Revised Penal Code and the Cybercrime Prevention Act One who publicly or maliciously imputes to another a crime, vice, defect, real or imaginary, or any act, omission, condition, status or circumstance tending to cause the dishonor, discredit or contempt of a natural or juridical person, or blacken the memory of one who is dead may be liable for libel under this Code. (Art. 353, RPC) These acts are more severely punished when done online in addition to the civil action for damages which may be brought by the offended party. (Sec. 4(c-4), RA 10175) Cyberlibel holds liable only the original author of the post (Sec. 5(3), Implementing Rules of RA 10175). Likers or sharers of a post cannot be held liable under this law.Slander may also be applicable to one who, in heat of anger, utters statements that are highly defamatory in character. (Art. 358, RPC) Intriguing Against Honour may also find applicability when the principal purpose is to blemish the honour or reputation of a person. (Art. 364, RPC) However, the requirement is that the post be directed to a specific person. Hence, a blind item is not as actionable as a named-post in social media.
HACKING Hacking generally refers to unauthorized intrusion into a computer or a network. The person engaged in hacking activities is known as a hacker. This hacker may alter system or security features to accomplish a goal that differs from the original purpose of the system. Hacking can also refer to non-malicious activities, usually involving unusual or improvised alterations to equipment or processes.
IDENTITY THEFT Identity theft, also known as identity fraud, is a crime in which an imposter obtains key pieces of personally identifiable information, such as Social Security or driver's license numbers, in order to impersonate someone else.
Types and examples of identity theft 1. True-name identity theft means the thief uses personal information to open new accounts. The thief might open a new credit card account, establish cellular phone service or open a new checking account in order to obtain blank checks. 2. Account-takeover identity theft means the imposter uses personal information to gain access to the person's existing accounts.
PLAGIARISM Plagiarism is an act of fraud. It involves both stealing someone else's work and lying about it afterward.
-turning in someone else's work as your own -copying words or ideas from someone else without giving credit -failing to put a quotation in quotation marks -giving incorrect information about the source of a quotation -changing words but copying the sentence structure of a source without giving credit -copying so many words or ideas from a source that it makes up the majority of your work, whether you give credit or not (see our section on "fair use" rules)
Republic Act No. 8293 [An Act Prescribing the Intellectual Property Code and Establishing the Intellectual Property Office, Providing for Its Powers and Functions, and for Other Purposes]otherwise known as the Intellectual Property Code of the Philippines. Intellectual property rights under the I. P. Code: The intellectual property rights under the Intellectual Property Code are as follows:
1. Copyright and related rights;
2. Trademarks and service marks;
3. Geographic indications;
4. Industrial designs;
5. Patents;
6. Layout designs [topographies] of integrated circuits
7. Protection of undisclosed information.
The scheme of penalties for infringement has also been changed. From the previous fine of Php200 to Php2,000 and/or imprisonment of 1 year, the current range of penalties are as follows:
For first offenders - fine of PhP50,000 to PhP150,000 and/or imprisonment of 1 to 3 years
For second offenders - fine of PhP150,000 to PhP500,000 and/or imprisonment of 3 to 6 years
For third and subsequent offenders - fine of PhP500,000 to PhP1.5 Million and/or imprisonment of 6 to 9 years.
In case of insolvency, the offender shall furthermore suffer subsidiary imprisonment
NETIQUETTE
Is a combination of the word net and etiquette.
It focuses on the acceptable behavior of a person while using the internet resource.The Core Rules of Netiquette
The Core Rules of Netiquette
Rule 1. Remember the human.
Never forget that the person reading your mail or posting is, indeed, a person, with feelings that can be hurt.
Corollary 1 to Rule #1: It's not nice to hurt other people's feelings.
Corollary 2: Never mail or post anything you wouldn't say to your reader's face.
Corollary 3: Notify your readers when flaming.
Rule 2. Adhere to the same standards of behavior online that you follow in real life.
Corollary 1: Be ethical.
Corollary 2: Breaking the law is bad Netiquette.
Rule 3. Know where you are in cyberspace.
Corollary 1: Netiquette varies from domain to domain.
Corollary 2: Lurk before you leap.
Rule 4. Respect other people's time and bandwidth.
Corollary 1: It's OK to think that what you're doing at the moment is the most important thing in the universe, but don't expect anyone else to agree with you.
Corollary 2: Post messages to the appropriate discussion group.
Corollary 3: Try not to ask stupid questions on discussion groups.
Corollary 4: Read the FAQ (Frequently Asked Questions) document.
Corollary 5: When appropriate, use private email instead of posting to the group.
Corollary 6: Don't post subscribe, unsubscribe, or FAQ requests.
Corollary 7: Don't waste expert readers' time by posting basic information.
Corollary 8: If you disagree with the premise of a discussion group, don't waste the time and bandwidth of the members by telling them how stupid they are. Just stay away.
Corollary 9: Conserve bandwidth when you retrieve information from a host or server.
Rule 5. Make yourself look good online.
Corollary 1: Check grammar and spelling before you post.
Corollary 2: Know what you're talking about and make sense.
Corollary 3: Don't post flame-bait.
Rule 6. Share expert knowledge.
Corollary 1: Offer answers and help to people who ask questions on discussion groups.
Corollary 2: If you've received email answers to a posted question, summarize them and post the summary to the discussion group.
Rule 7. Help keep flame wars under control.
Corollary 1: Don't respond to flame-bait.
Corollary 2: Don't post spelling or grammar flames.
Corollary 3: If you've posted flame-bait or perpetuated a flame war, apologize.
Rule 8. Respect other people's privacy.
Don't read other people's private email.
Rule 9. Don't abuse your power.
The more power you have, the more important it is that you use it well.
Rule 10. Be forgiving of other people's mistakes.
0 notes