#inspiration4
Explore tagged Tumblr posts
Text
youtube
Discover the incredible journey of Jared Isaacman, billionaire entrepreneur, private astronaut, and now President Trump's pick to lead NASA. From founding Shift4 Payments at 16 to leading groundbreaking space missions with SpaceX, Isaacman's life is a testament to innovation and adventure. Learn how his leadership could transform NASA and redefine America's role in space exploration. Don't miss this fascinating story of ambition and achievement! Watch now for insights on Isaacman's remarkable career and what his appointment means for NASA's future.
#Jared Isaacman#NASA#NASA leader#Trump NASA pick#private astronaut#billionaire entrepreneur#SpaceX missions#Polaris Dawn#Inspiration4#NASA administrator#space exploration#Trump space policy#billionaire astronaut#space missions#future of NASA#Jared Isaacman biography#Elon Musk NASA#space technology#NASA private companies#billionaire NASA#Jared Isaacman SpaceX#Shift4 Payments#new NASA leader#NASA space exploration#Youtube
0 notes
Text

12 September 2024


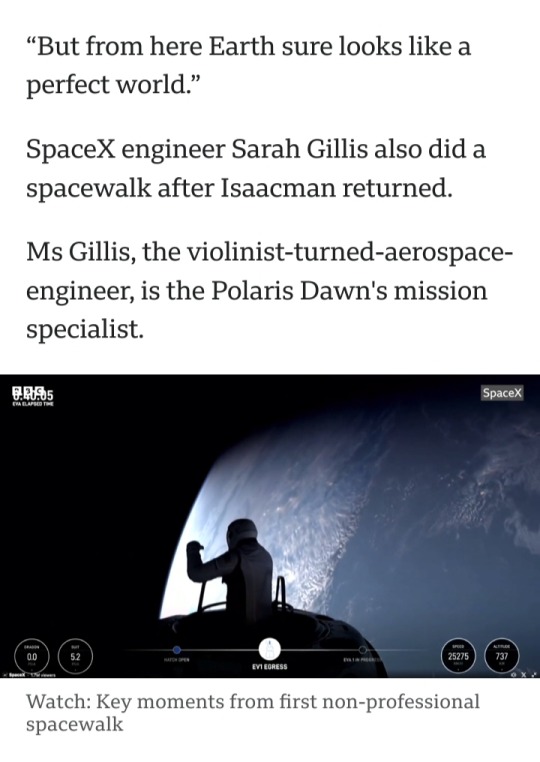





#Jared Isaacman#Polaris Dawn#SpaceX Crew Dragon spaceship#SpaceX#space walk#non-professional astronaut#astronaut#Shift4 Payments#Sarah Gillis#Inspiration4#Draken International#space#universe#Earth#entrepreneur#billionaire#historic spacewalk#spaceship#spacecraft
0 notes
Link
SpaceX Awaits Regulatory Breakthrough Following April Rocket Mishap SpaceX's Regulatory Journey: Aiming for October Milestone SpaceX, the visionary aerospace company led by Elon Musk, is on the verge of a significant regulatory achievement. After a major setback in April involving a Falcon 9 rocket explosion during a test flight, SpaceX has been diligently working to regain its standing. Here's the latest on SpaceX's quest for an upgraded launch license. SpaceX's Pursuit of an Enhanced Launch License Recent developments indicate that SpaceX's efforts to secure an upgraded launch license may yield positive results as early as October. The April incident, which unfolded during a Crew Dragon capsule test flight at SpaceX's Texas facility, resulted in the rocket's destruction. Fortunately, there were no casualties, but the incident prompted a thorough review of the company's safety protocols and procedures. The explosion also raised concerns at the Federal Aviation Administration (FAA), responsible for overseeing commercial space launches in the United States. [caption id="attachment_55332" align="aligncenter" width="688"] SpaceX License Advancement Possible As Early As October Following April Rocket Explosion[/caption] FAA's Reassessment and Upgraded License SpaceX had been operating under a license that granted certain privileges for its rocket launches. However, the April mishap prompted the FAA to reevaluate and potentially enhance SpaceX's license to ensure maximum safety. If approved, the new license would expand SpaceX's capabilities and provide greater flexibility for future missions. Insiders at the FAA have indicated their active collaboration with SpaceX to expedite the review process. While no official timeline has been confirmed, there is optimism that the upgraded license could be granted by October, contingent on SpaceX meeting all safety and regulatory requisites. Implications of an Enhanced License The potential approval of an upgraded license holds profound significance for SpaceX. It would empower the company to sustain its ambitious launch schedule, encompassing crewed missions to the International Space Station (ISS), satellite deployments, and even missions to Mars. Post the April incident, SpaceX has implemented substantial safety enhancements and executed successful launches, including the groundbreaking Inspiration4 mission, which transported an all-civilian crew to orbit. These endeavors underscore SpaceX's unwavering commitment to safety and reliability, further bolstering the case for a license upgrade. As October draws near, space enthusiasts and industry observers eagerly await the FAA's decision, which could herald an exciting new chapter in SpaceX's cosmic exploration journey. FAQs About SpaceX License Advancement Possible As Early As October Following April Rocket Explosion Q1: Why does SpaceX need an upgraded launch license? A1: SpaceX is pursuing an upgraded launch license to expand its capabilities and flexibility after a rocket incident prompted safety concerns. Q2: When did the rocket incident occur, and what were the consequences? A2: The rocket incident happened in April during a Crew Dragon test flight, resulting in the rocket's destruction. Thankfully, no casualties were reported. Q3: What is the role of the FAA in this process? A3: The FAA oversees commercial space launches in the United States and is reassessing SpaceX's license to ensure safety. Q4: What activities could SpaceX undertake with an enhanced license? A4: An upgraded license would allow SpaceX to conduct a wider range of activities, including crewed missions to the ISS, satellite deployments, and missions to Mars. Q5: How has SpaceX demonstrated its commitment to safety? A5: SpaceX has made substantial safety improvements and executed successful launches, such as the Inspiration4 mission, showcasing its dedication to safety and reliability.
#Crew_Dragon#FAA#falcon_9#Inspiration4#launch_license#regulatory_breakthrough#regulatory_requirements.#rocket_explosion#safety_protocols#space_exploration#spacex
0 notes
Text

🌍✨ Dragon Capsule: Gateway to the Void
Developed by SpaceX, the Dragon Capsule was designed to give NASA a reliable, American-made vehicle for accessing the International Space Station (ISS). It became essential after the retirement of the Space Shuttle, allowing NASA to break away from reliance on Russia's Soyuz for crewed flights.
Built to launch multiple times a year, Dragon not only ferries astronauts to and from the ISS but also handles frequent resupply missions. With its **RCS thrusters** for precise control and a cargo variant for delivering vital supplies, Dragon is a cornerstone of space exploration. It’s even ready for future **private missions**, like the breathtaking *Inspiration4* mission, where passengers enjoyed views from the **glass cupola**.
Are you ready to learn more about this incredible spacecraft? 🛰️🌌 Stay tuned for more!
#art#digital art#art community#space art#innovation#space exploration#spaceflight#spacex#rocket art#outer space
2 notes
·
View notes
Text
What's particularly interesting about these findings is that the Inspiration4 mission lasted only three days. So, not only do scientists now have consistent and reproducible data on telomeres' response to spaceflight, but we also know it happens quickly. These results suggest that even short trips, like a weekend getaway to space, will be associated with changes in telomere length. Scientists still don't totally understand the health impacts of such changes in telomere length. We'll need more research to figure out how both long and short telomeres might affect an astronaut's long-term health.
2 notes
·
View notes
Text
Astronauts face health risks—even on short trips in space
Ramin Skibba for Science:
In 2021, four passengers, including billionaire businessman Jared Isaacman, rode into space on a SpaceX rocket, orbiting Earth for 3 days in the company's Dragon capsule before splashing down in the Atlantic Ocean. The trip, financed by Isaacman and called Inspiration4, was the first privately funded orbital mission on a private rocket carrying private citizens—setting the stage for more routine tourist space travel today.
The astronauts also underwent intensive medical monitoring before, during, and after their flight. Now, researchers have analyzed how the space radiation and weightlessness they experienced affected their bodies, releasing a package of more than 40 studies, most of them based on Inspiration4 data. Published today in Nature journals, the Space Omics and Medical Atlas (SOMA) includes studies of the participants' genomes, microbiomes, transcriptomes (the messenger RNA made from their genes), and proteomes (their panoply of proteins).
…
One message from the SOMA studies, Mason says, is that the same health effects that professional astronauts experience over their long expeditions turn up among space tourists who only spend a few days in orbit.
You mean I can go to space recreationally and still suffer negative health effects? Sign me up immediately
2 notes
·
View notes
Text
Обратный отсчет: Космическая миссия Inspiration4 (#сериал 2021)
#StrimKino #смотретьфильмы #бесплатно

https://0o.strimkino.com/2418-obratnyj-otschet-kosmicheskaja-missija-inspiration4.html
0 notes
Text
Donald Trump Nominates Jared Isaacman To NASA Administrator Post
Jared Isaacman with his children in a 2024 Polaris Dawn publicity photo.Credit: John Kraus, Polaris Program Jared Isaacman, the billionaire entrepreneur, philanthropist, and private astronaut, has been nominated by Donald Trump to serve as the next Administrator of NASA. Isaacman, best known to the general public as the commander of both the groundbreaking Inspiration4 and Polaris Dawn space…
0 notes
Text
Elon Musk's SpaceX launches first all-civilian mission to space
Introduction: Elon Musk’s SpaceX has made history by launching the first-ever all-civilian mission to space, marking a significant milestone in the space exploration industry. This groundbreaking mission, known as Inspiration4, is set to revolutionize the way we think about space travel and exploration, as it includes four non-professional astronauts who will orbit the Earth for several days.…
#Breaking news updates#economic news and trends#entertainment news#global news highlights#health news updates#how to stay informed on current events.#latest headlines today#local news updates#major world events#news analysis and commentary#political news updates#sports news highlights#technology news#top news stories today#trending news topics
0 notes
Text

Update: Launch delayed due to thunder clouds within 10 miles of launch pad, new launch time of 10:23BST (09:23UT)
Polaris dawn is back on, tomorrow morning the second private independent flight Dragon mission, Polaris Dawn, will launch from LC-39A at Kennedy at 08:38BST. Billionaire Jared Isaacman is again paying for the mission, but this time in collaboration with SpaceX. The crew is seen here on their arrival at KSC on 19 August, in there Alpha Jets (Franco-German jet trainers). The crew left to right is Commander Jared Isaacman, Mission Specialist Sarah Gillis SpaceX, Medical Officer Anna Menon SpaceX and Lieutenant Colonel Scott Poteet USAF (ret).
The five day mission will attempt a record high (apogee) orbit of 190 x 1,400km (118x870mi), which will be higher than the record set by Gemini 11 in 1966, which attained 1,372km (853mi) (not counting the Apollo Lunar transfer orbits, which I suppose where not full orbits). Resilience will than drop down to a lower orbit of 750km when two of the crew will attempt the first private EVA. SpaceX has upgraded its IVA suits to EVA standard. Too do this the whole spacecraft will have to be depressurised (so all the crew need their suits on) and the hatch opened to space. Two of the crew, at least, will take turns standing in the hatchway on umbilicals (and tethered of course), rather than backpacks, in the same way that the first spacewalks were conducted in the early sixties. There won't be any free floating, off structure as it is termed.
C207 Resilience was also used for the first operational Crew Dragon mission to the ISS, USCV-1 or Crew 1, between 16 Nov 2020 to 2 May 2021 and the first independent mission, Inspiration4, also payed and flown on by Isaacman, on 16-18 Sep 2021.
Axiom Space has also charted SpaceX Dragon missions but these were three short commercial visits, with paying commercial astronauts, to the ISS in 2022 (AX-1), 2023 (AX-2) and 2024 (AX-3), another, AX-4, is planned for Oct-Nov 2024 and AX-5 in 2025 with an all British crew onboard. Pic: SpaceX
youtube
0 notes
Text
The Space Omics and Medical Atlas (SOMA) and international astronaut biobank | Nature
Here we present the Space Omics and Medical Atlas (SOMA), an integrated data and sample repository for clinical, cellular and multi-omic research profiles from a diverse range of missions, including the NASA Twins Study7, JAXA CFE study8,9, SpaceX Inspiration4 crew10,11,12, Axiom and Polaris. The SOMA resource represents a more than tenfold increase in publicly available human space omics data, with matched samples available from the Cornell Aerospace Medicine Biobank. The Atlas includes extensive molecular and physiological profiles encompassing genomics, epigenomics, transcriptomics, proteomics, metabolomics and microbiome datasets, which reveal some consistent features across missions, including cytokine shifts, telomere elongation and gene expression changes, as well as mission-specific molecular responses and links to orthologous, tissue-specific mouse datasets.
https://www.nature.com/articles/s41586-024-07648-x
Атлас SOMA (Space Omics and Medical Atlas) предлагает интегрированный репозиторий клинических, клеточных и мультиомных данных из различных миссий, включая исследование NASA Twins и SpaceX Inspiration4. Выявлены общие изменения, такие как сдвиги цитокинов и изменения экспрессии генов, а также уникальные реакции, характерные для отдельных миссий. Эти данные важны для разработки методов мониторинга здоровья и мер противодействия заболеваниям для будущих миссий на Луну, Марс и в глубокий космос.
0 notes
Text
💯 real video of the @SpaceX Inspiration4 launch is made of multiple telescope tracking shots, created by the talented MARS Scientific group — perfectly showcasing what a #Falcon9 rocket launch looks like after sunset.
—
The flight, dubbed "Inspiration4," was a privately chartered spaceflight by billionaire Jared Isaacman, which launched on 15 September 2021.
It became the first crewed orbital mission with no professional astronauts on board.
Aboard the SpaceX Crew Dragon capsule dubbed Resilience, Isaacman — a self-described space geek who has accrued more than 6,000 hours piloting various aircraft — was the commander of the flight.
Joining him were physician assistant Hayley Arcenaux, data engineer Chris Sembroski, and geoscientist and science communication specialist Sian Proctor. Resilience and its four occupants circled Earth for three days, splashing down off the Florida coast on September 18.
The primary purposes of Inspiration4, according to the mission's official website, were to raise awareness and funds for St. Jude Children's Research Hospital in Memphis, Tennessee, and to begin "a new era for human spaceflight and exploration."
https://www.space.com/inspiration4-spacex.html#section-how-was-the-crew-chosen-for-inspiration4
#Space X#Falcon 9#space#space rocket#Inspiration4#space launch#Mars Scientific#Jared Isaacman#Shift4 Payments#Elon Musk#space company#SpaceX Crew Dragon capsule#Resilience#spaceflight#space exploration#Earth#Kennedy Space Center#Launch Complex 39A#Inspirati④n#Space Exploration Technologies Corp#Florida#human spaceflight#Mobile Aerospace Reconnaissance System#long-range telescopic tracking#spacecraft imaging
1 note
·
View note
Text
0 notes
Text
SpaceX is preparing to launch its next private mission by the end of the month, featuring the first attempt to have the astronauts step out into space.

The Polaris Dawn mission - the first of three flights billionaire and Shift4 founder Jared Isaacman purchased from SpaceX in 2022 for his human spaceflight effort known as the Polaris Program - is set to launch from Florida in the early hours of Aug. 26.
Isaacman will commanding the mission, as he did while leading the historic Inspiration4 flight in 2021. The multi-day trip isn't headed to a destination, but instead will e a free-flying mission tracing orbits that the crew hopes will go far from Earth.
#allthenews
0 notes
Link
One of the most highly anticipated missions in 2024 is now mere days away from taking flight. The Polaris Dawn mission, scheduled to launch on SpaceX’s Falcon 9 and Crew Dragon with a four-person complement no earlier than Monday, Aug. 26, will see the introduction of new technologies and many records eclipsed — setting a high benchmark for the program going forward. This mission will be the first of three flights currently listed under the banner of Polaris, a private spaceflight program run by entrepreneur and aerospace tourist Jared “Rook” Isaacman. The New Jersey native founded the program to rapidly advance human spaceflight capabilities whilst making charitable contributions to and raising awareness for children’s medical research at St. Jude’s Hospital. In addition to organizing and managing the SpaceX-contracted venture, Isaacman will serve to command each Polaris flight (Dawn included), building upon his spaceflight résumé as commander of the all-civilian Inspiration4 mission that flew to low-Earth orbit in September 2021. We are targeting no earlier than August 26 for the launch of Polaris Dawn pic.twitter.com/tkkiRke64a — Polaris (@PolarisProgram) August 7, 2024 Polaris Dawn will see the first trips to space for the remainder of the mission’s crew, which consists of three individuals with prior experience within the aerospace industry. See AlsoPolaris Dawn Mission UpdatesSpaceX Missions SectionL2 SpaceX ResourcesClick here to Join L2 Scott “Kidd” Poteet, a retired United States Air Force pilot with 3,200 flight hours under his belt, will be the spacecraft pilot for the Polaris Dawn mission. Poteet has allied with Isaacman for many years, having held management positions at Isaacman’s companies Draken International and Shift4. Additionally, he served as mission director for the Inspiration4 mission. SpaceX lead space operations engineer Sarah Gillis will join the Polaris Dawn crew as one of the mission specialists. Her main responsibility at SpaceX has been to oversee the company’s astronaut training program, having prepared the crews of the Demo-2, Crew-1, and Inspiration4 for their respective flights on Crew Dragon. Anna Menon will hold the distinction of being Polaris Dawn’s onboard medical officer, alongside her role as a mission specialist. She previously served as a biomedical flight controller for the International Space Station at NASA’s Johnson Space Center, working in the post for six years before joining SpaceX to become a Dragon mission director. The crew is slated to spend up to five days in Earth orbit after launching from Kennedy Space Center in Florida and attempt to achieve a maximum altitude of 1,400 km (870 mi) — the furthest any human has been from Earth since the Apollo program. This will also result in the Dragon spacecraft passing through the Van Allen radiation belt, which will aid the mission objective of studying the health effects of space radiation. Visualization of a Polaris Dawn astronaut egressing Dragon as part of the mission’s planned spacewalk. (Credit: Polaris/SpaceX) After this, Dragon will move to a lower orbital altitude on the third flight day to meet one of the mission’s main objectives: the first commercial spacewalk in history. During the spacewalk, the crew will test the new SpaceX-designed extravehicular activity (EVA) suit in the vacuum of space for the first time. These suits are based on the company’s intravehicular activity (IVA) suit design and feature many structural and engineering upgrades. This two-hour EVA will see the mission crew donning the EVA suits before the Dragon spacecraft is depressurized. After this, commander Isaacman and mission specialist Gillis will egress the vehicle’s forward hatch and perform a tethered spacewalk. In addition to the new suits, the Dragon spacecraft has been appropriately modified to support this mission profile. Polaris Dawn will also feature the first crewed operational test of laser interlink communications from Dragon via SpaceX’s Starlink satellite internet constellation, aimed at reducing latency and increasing data bandwidth for human spaceflight missions. Following these tests and other experiments, Dragon will bring the Polaris Dawn crew back home and splashdown off the Florida coast, either in the Gulf of Mexico or the Atlantic Ocean. Jared, Kidd, Anna, & Sarah – welcome to the KSC! The crew of @PolarisProgram’s inaugural mission have arrived to America’s premier spaceport in a trio of Alpha Jets and pair of L-39’s. Standing by for the upcoming press conference ~12:45pm local time. 7 more days until game… pic.twitter.com/ufQZF4xyoi — Max Evans (@_mgde_) August 19, 2024 Dawn is only the beginning of Polaris’ mission plans. A second mission is also slated to launch on a SpaceX Falcon 9 and Crew Dragon, but the launch date, crew, and mission profile have not been announced at this time. Isaacman has offered to service or reboost NASA’s Hubble Space Telescope on this mission, but the agency has since indicated it has decided to not pursue the option. The third and currently final Polaris flight is set to be the first crewed mission launched on SpaceX’s next-generation Starship launch system, with a launch date, crew complement, or mission profile yet to be determined. As Starship is still in early flight testing as of 2024, the mission is understood not to occur until the vehicle is fully matured and certified for human spaceflight. With three ambitious flights ready to go in its catalog and a healthy contingent of support, Polaris is set to change the face of commercial and human spaceflight in short order, eventually leaving a ripple effect to be felt by future crews as they leave Earth for missions to the Moon, Mars, and possibly beyond. (Lead image: the crew of Polaris Dawn give a thumbs-up after their arrival at Kennedy Space Center in preparation for launch. Credit: Max Evans for NSF) The post Polaris aiming to break barriers, build experience with Dawn appeared first on NASASpaceFlight.com.
0 notes
Text
un ampio studio non rivela alcun calo di produttività Studio: Lavoro da Casa e Produttività Un ampio studio ha dimostrato che il lavoro ibrido può essere vantaggioso per le aziende senza compromettere la produttività. Un esperimento con oltre 1600 dipendenti ha rivelato che lavorare da casa può aumentare la fidelizzazione del personale, equiparandosi a un aumento del 10% di stipendio. Effetti del Volo Spaziale sul Corpo Umano Un nuovo studio ha esaminato gli effetti dei voli spaziali a corto raggio sul corpo umano. I dati raccolti durante il volo spaziale di breve durata della missione Inspiration4 di SpaceX hanno rivelato cambiamenti fisiologici simili a quelli osservati nei voli spaziali
0 notes