#gis tools for road condition assessment
Explore tagged Tumblr posts
Text
Road Condition Monitoring System(RCMS): Enhancing Efficiency with AI-Powered Solutions
The quality and sustainability of road infrastructure play a pivotal role in societal development, economic growth, and the safety of communities. To address the challenges of road construction and maintenance, advanced digital tools such as Road Condition Monitoring Systems (RCMS) are becoming indispensable. Leveraging technologies like AI-powered pothole detection, data analytics, and interactive visualization, RCMS ensures efficient planning, monitoring, and maintenance of road networks.

#ai and gis road monitoring solutions#geospatial road management solutions#geospatial road monitoring system#gis based pothole mapping and detection#gis based road condition monitoring system#gis based road inspection software#gis based road survey solutions#gis data analysis for road monitoring#gis mapping for road condition analysis#gis road maintenance solutions#land management system#gis tools for road condition assessment#pothole detection using gis technology#real time road condition monitoring gis#road condition assessment using gis#road condition monitoring using gis#road infrastructure monitoring with gis#road maintenance gis software#road safety monitoring with gis systems#road surface monitoring with gis#smart road condition monitoring gis
1 note
·
View note
Text
Your Digestive Health Matters: Find the Best Gastroenterologist in Vadodara

Digestive problems may seem minor at first—occasional gas, acidity, or stomach discomfort. But left untreated, they can point to deeper issues like ulcers, liver conditions, or inflammatory bowel disease. That’s why finding the Best Gastroenterologist in Vadodara is the first step toward long-term health and relief.
At Desai Surgical Hospital, we offer expert gastro care backed by years of experience, advanced diagnostics, and patient-first treatment. Whether you're facing routine digestion issues or chronic gastrointestinal disorders, our team is here to help.
When Should You See a Gastroenterologist?
You may not always know when to visit a GI specialist. But if you’re experiencing any of the following, it’s time to consult a gastroenterologist:
Persistent stomach pain or bloating
Chronic constipation or diarrhea
Acid reflux or heartburn that won’t go away
Blood in stool or black-colored stool
Jaundice (yellowing of eyes and skin)
Sudden weight loss or appetite loss
Frequent nausea or vomiting
These symptoms can be signs of underlying issues like gastritis, liver dysfunction, ulcers, IBS, or even more serious conditions. Early diagnosis is key—and the right specialist makes all the difference.
Why Desai Surgical Hospital Has the Best Gastroenterologist in Vadodara
Here's why thousands of patients across Gujarat trust our hospital for digestive care:
Expertise & Experience
Our lead gastroenterologists have years of hands-on experience treating complex GI cases, including liver diseases, pancreatitis, acidity disorders, and ulcers.
Comprehensive Diagnosis
We use the latest tools like endoscopy, colonoscopy, liver function tests, and ultrasound to provide precise and early detection of problems.
Personalized Treatment Plans
No two digestive issues are alike. We assess your symptoms, history, and lifestyle to design a treatment that fits you—not just the disease.
Full-Spectrum GI Care
From basic indigestion to chronic liver and bowel disorders, our gastro department covers it all under one roof.
Post-Treatment Support
We don’t stop at medication. Diet guidance, lifestyle coaching, and regular monitoring are part of your recovery plan.
Common Gastrointestinal Conditions We Treat
Acid Reflux / GERD
Gastric Ulcers
Gallbladder Stones
Liver Cirrhosis and Fatty Liver
Jaundice
Hepatitis B & C
Pancreatitis
Irritable Bowel Syndrome (IBS)
Constipation and Diarrhea
Food Intolerance and Bloating
Whether you have a one-time stomach issue or a long-standing concern, our experts will provide care that is both effective and comforting.
Advanced Liver & Jaundice Care in Vadodara
We’re not just about digestive care—we are also known for Jaundice Treatment in Vadodara and liver-related care. Our gastroenterologists work closely with liver specialists to ensure a comprehensive approach for:
Drug-induced liver damage
Alcoholic liver disease
Viral hepatitis
Liver enzyme elevation monitoring
Real People. Real Relief.
Thousands have found lasting relief from chronic digestive issues at Desai Surgical Hospital. Our patient-first approach, ethical care, and advanced facilities have earned us the reputation of having the Best Gastroenterologist in Vadodara.
Your Health Deserves Expert Attention
Don't let digestive issues hold you back. With expert care, most GI problems are completely treatable or manageable. And with the right guidance, you can enjoy a pain-free, confident lifestyle again.
Book an Appointment Today
📍 Desai Surgical & Eye Hospital Near G.P.O, Kharivav Road, Dandia Bazaar Rd, Raopura, Vadodara, Gujarat 390001 📞 Phone: 0265 2435153 📧 Email: [email protected] 🌐 Website: www.desaisurgical.com
OPD Timings: Monday – Friday: 12:30 PM – 02:30 PM | 06:00 PM – 07:00 PM Saturday: 12:00 PM – 02:30 PM Sunday: Closed
Emergency? 24/7 Emergency Services Available
Trust your gut—literally.
Choose Desai Surgical Hospital and meet the Best Gastroenterologist in Vadodara for lasting relief and expert care.
#gastrocare#digestivehealth#desaisurgicalhospital#shock wave lithotripsy (swl)#ureteral stone treatment#kidney stone removal#gastroenterology#gastrocarevadodara#best urologist in vadodara#ureteroscopy for stones#gastroenterologist#gastrodoctor#stomach#stomachcare#stomachhealth#stomach flu
0 notes
Text
Engineering Feasibility Study Company in Dubai: Precision Planning with F&M
In a city defined by iconic skylines, futuristic developments, and ambitious infrastructure, Dubai demands precision in every stage of its construction and engineering processes. Before any project begins—whether it's a towering skyscraper, a residential complex, a highway, or a commercial hub—it must pass through a critical phase of evaluation and validation. This is where the role of an Engineering Feasibility Study company in Dubai becomes indispensable. Among the leaders in this field, F&M stands out for delivering accurate, reliable, and strategically informed feasibility studies that serve as the blueprint for project success.
F&M is widely recognized in Dubai and the broader UAE for its deep technical knowledge, multidimensional approach, and commitment to excellence. With decades of experience across engineering, architecture, and infrastructure planning, F&M offers a comprehensive suite of feasibility study services that assess the technical, economic, and environmental viability of a project. The company supports private developers, government agencies, and investment firms in making informed decisions—minimizing risks while optimizing outcomes.
What sets F&M apart as a leading Engineering Feasibility Study company in Dubai is its holistic and methodical process. Every study begins with an in-depth understanding of the client’s vision, goals, and constraints. F&M’s expert team then conducts a rigorous site assessment, analyzes regulatory requirements, evaluates engineering challenges, and simulates potential risks. Factors such as soil conditions, structural systems, utility access, transport integration, environmental impact, and zoning laws are all meticulously examined.
Economic viability is another core element of the feasibility study. F&M provides detailed cost estimates, return on investment projections, and operational considerations, enabling stakeholders to make realistic and profitable decisions. This data-driven approach ensures that projects are not only technically sound but also financially sustainable over the long term.
F&M’s team includes civil engineers, architects, project managers, planners, and environmental experts—each contributing unique insights to create a 360-degree analysis. Their collaborative process allows for a multidiscipline review, which strengthens the reliability of every recommendation. As a result, clients receive feasibility reports that are comprehensive, precise, and tailored to Dubai’s unique urban landscape.
As regulations in the UAE grow more stringent—particularly around sustainability, safety, and urban planning—F&M ensures that all feasibility studies are fully aligned with local authorities such as Dubai Municipality, RERA, and the Roads and Transport Authority (RTA). Their understanding of regulatory frameworks helps expedite approvals and ensures projects are compliant from the outset.
Sustainability is also central to F&M’s approach. As part of their feasibility assessments, the team evaluates energy efficiency potential, water usage, environmental impact, and compliance with green building standards such as LEED and Estidama. These insights are invaluable for developers looking to future-proof their investments and align with Dubai’s vision of sustainable urban development.
F&M’s ability to integrate technology into the feasibility process further enhances its value. Using tools like Geographic Information Systems (GIS), Building Information Modeling (BIM), and advanced simulation software, the firm delivers data-rich insights that provide visual and numerical clarity. Clients can see potential outcomes, identify constraints early, and explore alternative solutions before committing capital and resources.
From mega infrastructure projects and commercial developments to residential communities and mixed-use complexes, F&M has successfully conducted engineering feasibility studies across a wide range of sectors. Their reputation is built not only on technical excellence but also on transparency, reliability, and an unwavering focus on client success.
Choosing F&M as your Engineering Feasibility Study company in Dubai means gaining a trusted partner who brings clarity to complexity. With a blend of innovation, expertise, and integrity, F&M empowers clients to move forward with confidence—knowing their project rests on a solid foundation of strategic insight and technical validation.
In a city where opportunities are vast but stakes are high, start your project the right way—with F&M. Accurate planning, expert guidance, and sustainable foresight—all delivered by a team that knows Dubai, and understands what it takes to build the future.
0 notes
Text
What Is Aerial Surveying and How Does It Work?
Introduction to Aerial Surveying
Aerial surveying is a powerful technique used to collect geographic and spatial data from an elevated perspective, typically with the help of drones, aircraft, or satellites. It allows professionals in various industries to obtain detailed, high-resolution images and measurements of the Earth's surface. This method is widely adopted in sectors such as construction, agriculture, mining, infrastructure planning, and environmental monitoring.
By capturing data from above, aerial surveying provides a fast, accurate, and cost-effective solution for mapping large or difficult-to-reach areas. In Australia, where expansive terrain and remote locations are common, this technology plays a critical role in improving project efficiency and data reliability.

How Aerial Surveying Works
Aerial surveying involves collecting imagery and data from the air using specialised equipment mounted on aerial platforms. These platforms can include:
Unmanned Aerial Vehicles (UAVs) or drones
Fixed-wing aircraft
Helicopters
Satellites
Sensors such as cameras, LiDAR (Light Detection and Ranging), multispectral sensors, and thermal imagers are used to capture specific types of data. The choice of sensor depends on the application and the desired output.
Once the raw data is collected, it is processed using photogrammetry software and Geographic Information System (GIS) tools. This data is then converted into accurate digital maps, 3D models, topographic surveys, and other valuable outputs.
Key Components of Aerial Surveying
Data Acquisition The first step in aerial surveying is flight planning. Routes and altitudes are calculated to ensure optimal coverage and resolution. The aircraft or drone flies over the area while capturing overlapping images or sensor readings.
Georeferencing Georeferencing is essential for aligning the captured data with real-world coordinates. GPS systems and ground control points (GCPs) are used to enhance the spatial accuracy of the results.
Data Processing Advanced software solutions process the raw data, generating orthomosaic images, digital elevation models (DEMs), and 3D reconstructions. This step ensures precision, clarity, and usability.
Data Analysis and Reporting After processing, the data is analysed to extract actionable insights. Professionals use the final outputs for planning, monitoring, and decision-making in various projects.
Applications of Aerial Surveying in Australia
The diverse landscape and vast land areas in Australia make aerial surveying particularly beneficial. Some common applications include:
Mining and Quarrying: Monitoring site changes, calculating stockpile volumes, and ensuring compliance with regulations.
Agriculture: Assessing crop health, irrigation efficiency, and soil variation using multispectral data.
Construction and Infrastructure: Surveying large construction sites, road alignments, and urban planning projects.
Environmental Studies: Tracking vegetation cover, mapping wetlands, and assessing the impact of natural disasters like bushfires or floods.
Land Development: Supporting subdivision planning, boundary determination, and topographical mapping.
Advantages of Aerial Surveying
The advantages of using aerial surveying over traditional ground-based methods are numerous:
Time Efficiency: Large areas can be surveyed in a fraction of the time.
Cost-Effective: Reduced manpower and quicker data collection lead to lower operational costs.
High Accuracy: When properly georeferenced, aerial surveying delivers precise and reliable data.
Safety: Eliminates the need to access hazardous or remote terrains on foot.
Versatility: Suitable for various industries and adaptable to multiple environmental conditions.
Regulations and Compliance in Australia
In Australia, aerial surveying operations must comply with aviation safety laws governed by the Civil Aviation Safety Authority (CASA). Drone operators are required to obtain the necessary licenses and adhere to flight regulations, especially in urban or restricted airspace. Ensuring legal and ethical use of airspace is vital for maintaining safety and protecting privacy.
Conclusion
Aerial surveying is revolutionising the way data is collected and analysed across numerous Australian industries. Its ability to deliver fast, accurate, and comprehensive geospatial information makes it an essential tool for modern project planning and management. As technology continues to evolve, the scope and effectiveness of aerial surveying will only expand, supporting smarter, safer, and more efficient workflows in both urban and remote environments.
0 notes
Text
The Growing Importance of Lidar in Mapping and Disaster Management
Lidar, which stands for Light Detection and Ranging, is an excellent technology that helps create detailed 3d maps with great accuracy to detect objects. It works by using laser light to measure distances. Nowadays, many areas use lidar mapping services and technology, from self-driving cars to studying the environment. Let’s understand the benefits of using lidar services.
Quick and Efficient Collection of Data:
Unlike traditional firms, which require more time for data collection, a professional lidar company takes less time and delivers fast and more efficient data collection. They use Lidar sensors that quickly scan the areas in a few minutes. It is most commonly used in disaster response, agriculture, forestry and urban planning.
Higher Accuracy and Precision:
Another significant advantage of Lidar services is that they offer higher precision and accuracy in mapping. They can work well in environmental conditions, capture data points in a few seconds and provide measurements in an appropriate way.
Enhances Topographic and Geographic Mapping:
Lidar services can also help analyse flood risks, monitor coastal erosion and assist in the development of roads, bridges and other constructions. The professional organisation uses these services to enhance geographic and topographic mapping. They have an expert team of professionals who have been doing their job for years.
Improve Disaster Management and Response:
In an emergency, having a rapid and accurate data collection device is crucial. That is why many organisations can opt for Lidar services. These services can be beneficial for identifying hazard zones, including landslides or earthquake fault areas, assessing damage by giving an immediate mapping and navigating areas filled with debris to help rescue teams.
Budget-Friendly and Scalable Technology:
Professional lidar companies often charge less for their services than others. They use top-quality sensors for data processing that are scalable and affordable. These technologies can be used for mapping projects based on large-scale, accessible data for researchers, government agencies, businesses and other automated systems
So, if you are also looking for the best lidar services for your company, you can hire professional experts from a trusted organisation!
About LETEL:
LETEL is a popular firm that provides the best GIS mapping Georgia. It has an expert team of professionals who have been doing their job for many years. They use modern tools and equipment for the process to deliver high-quality services at an affordable price.
To get more information, visit https://letelmetrics.com/
Original Source: https://bit.ly/3SwiMzL
0 notes
Text
Highway Engineering Consultancy: Shaping the Future of Road Connectivity

In an era where seamless transportation and connectivity are critical to economic prosperity, highway engineering consultancy services are playing an increasingly vital role. These specialized consultants ensure that the design, planning, and management of highway projects are executed efficiently, safely, and sustainably. By leveraging advanced engineering practices, cutting-edge technologies, and sustainable methods, highway engineering consultancy firms are significantly shaping the future of road connectivity.
Strategic Planning and Road Infrastructure Development
Effective road connectivity begins with strategic planning. Highway engineering consultancy firms meticulously plan road networks, aligning them with regional development goals, urban expansion needs, and traffic projections. These road consultants utilize comprehensive traffic studies, socio-economic analyses, and environmental assessments to devise infrastructure that meets both present and future demands.
Advanced Highway Design and Innovation
Highway design consultants integrate innovative approaches and technologies to create roads that are not only efficient but also resilient and adaptable. Modern highway designs feature sophisticated drainage systems, smart road technologies, and ergonomic road layouts. By employing advanced simulation software, these highway consultants optimize traffic flow, safety, and durability, ensuring minimal maintenance and maximized functionality over the project's lifespan.
Ensuring Safety and Compliance
Safety is paramount in highway construction and operation. Road consultants are experts in designing highways that adhere strictly to safety standards and regulatory compliance. From roadway geometry and intersection design to signage and illumination, every aspect is carefully planned to minimize accidents and ensure safe driving conditions. This emphasis on safety reduces risks, protects lives, and enhances overall user experience.
Environmental Sustainability
Today, sustainability is at the heart of infrastructure development. Highway engineering consultancy firms prioritize eco-friendly practices by incorporating green materials, promoting energy-efficient construction methods, and designing infrastructure to mitigate ecological impacts. This sustainable approach helps preserve biodiversity, reduce carbon footprints, and maintain ecological balance, ensuring road connectivity does not compromise environmental integrity.
Cost-Effective Solutions and Budget Management
Managing costs efficiently is another area where highway engineering consultancy firms excel. They provide meticulous budget planning, cost estimation, and financial management to ensure projects remain within allocated budgets. By employing value-engineering techniques, consultants identify cost-saving opportunities without sacrificing quality or functionality, ensuring projects deliver exceptional value for investment.
Use of Technology and Digital Tools
Digital transformation is revolutionizing highway engineering consultancy. Consultants use advanced tools such as Geographic Information Systems (GIS), Building Information Modeling (BIM), and Artificial Intelligence (AI) to enhance planning precision, streamline construction, and manage operational phases effectively. These technologies enable precise visualization, real-time tracking, and proactive issue resolution, significantly improving project outcomes and timelines.
Maintenance and Lifecycle Management
Effective highway management doesn't end at construction; it continues through ongoing maintenance and lifecycle management. Highway engineering consultancy firms provide strategic maintenance plans, asset management systems, and regular inspections, ensuring roads remain safe and functional throughout their lifecycle. These consultants ensure that highways maintain peak performance and safety standards long after completion.
Enhancing Economic Growth
Well-designed highways stimulate economic activity by improving connectivity, reducing transportation costs, and facilitating trade and commerce. Highway design consultants strategically plan infrastructure to maximize economic benefits, fostering regional development and attracting investments. Efficient road networks boost tourism, encourage regional trade, and create new opportunities, contributing significantly to local and national economies.
Eka Infra: Pioneering Highway Connectivity
A prominent example of excellence in highway engineering consultancy is Eka Infra. Renowned for their comprehensive expertise in strategic road planning, advanced highway design, and sustainability practices, Eka Infra delivers tailored solutions that significantly enhance road connectivity and performance. Their integrated approach, combining innovative engineering with sustainable development, positions Eka Infra at the forefront of highway consultancy services, making them an ideal partner for progressive infrastructure projects.
Capacity Building and Training
Knowledge transfer and capacity building form integral parts of highway engineering consultancy services. Road consultants regularly provide training to local teams, equipping them with the latest knowledge, skills, and best practices required for effective road management. This empowerment ensures that local authorities and communities can sustainably manage and maintain highway infrastructure, fostering long-term benefits.
Conclusion
Highway engineering consultancy is undeniably critical to shaping the future of road connectivity. Through strategic planning, innovative design, sustainability practices, and advanced technology, these consultants ensure that road infrastructure meets the growing demands of modern transportation. Firms like Eka Infra exemplify how specialized consultancy can profoundly impact infrastructure quality, economic growth, and environmental sustainability. As road connectivity remains a cornerstone of global development, the importance and influence of highway engineering consultancy will continue to grow.
0 notes
Text
Why Is GIS Surveying in High Demand in the UAE? Unlocking Accurate Data for Smarter Decisions
In the middle of the Arabian Peninsula, the United Arab Emirates shows off what people can accomplish through their ideas and the use of new technology. Among all the digital changes happening in this country, GIS surveys and data processing have become important tools for building roads and homes, planning cities, and taking care of the environment. Embracing GIS shows that the UAE values using data for decisions, helping the country progress sustainably in a world where things are getting more intricate.

The Evolution of GIS in the UAE started as a way to track and map important data for cities, and now it is used for almost all types of activities and services in the country.
The technology started as simple ways to map areas and has grown into tools that examine how different areas relate to each other across the country. The government of the UAE saw from the start that effective handling of spatial data would be key for achieving its big development plans. Today, GIS is used in many parts of life in the UAE, like helping people build things, plan roads, find doctors, and attract tourists.
Applications Transforming the Nation
The footprint of GIS survey and data processing covers different fields in the UAE. They make it possible for those working in urban planning to visualize, assess, and improve city designs before starting construction. GIS technology was used to design the Palm Jumeirah island in Dubai to provide strong structures and ensure that it does not harm the environment.
Scientists in the field use GIS to look out for changes in the shape of dunes and to locate places that might turn into deserts. By having this data, officials can work more effectively to manage and protect water resources where there is a long-standing problem with not having enough water.
Advanced-Data Collection Methods
The accuracy of GIS applications is mostly determined by how good the data are that people gather. Data collection in the UAE uses important methods such as LiDAR, imaging via drones, and imagery from satellites to ensure the highest level of accuracy. With mobile GIS, teams can catch data live and prevent mistakes made by humans.
showing how committed they are to data, the city’s Smart Geospatial Contact Center uses AI to check and correct geographical information used in different systems. The focus on data accuracy has made the UAE a leader in geospatial intelligence in the region.
Digital Transformation and Integration
It is not just the use of GIS that makes the UAE unique, but also how they connect GIS with different digital tools. By using GIS data, the country’s efforts to become a smart city create well-connected urban areas where different complimentary systems and services are together.
The Roads and Transport Authority in Dubai uses GIS to improve traffic management, cut down on congestion, and set up future transportation systems. As another example, telecom companies use precision mapping so that underground operations during maintenance and construction are less likely to disrupt visitors or everyday usage.

Overcoming Challenges Through Innovation
Certain problems arise when GIS surveys and data processing are used in the UAE. Difficult desert conditions influence the tasks conducted by oilfield workers and the performance of equipment. Fast growth in cities means that spatial databases must be updated often to remain precise.
As a result, people have devised new ways to tackle these issues. Companies in the UAE have both designed heat-resistant tools and developed new techniques for surveying deserts. Initiatives from the government, including the UAE Spatial Data Infrastructure, have helped to ensure standards for data sharing and compatibility, making the whole national spatial data system more unified.
Building Local Expertise
Understanding that the impact of technology depends on learning, the UAE has focused on developing GIS experts within the country. Colleges and universities offer courses in geospatial sciences, and there are professional certification courses available for already-employed individuals. As a result, the knowledge is shared and helps build lasting resources within the Emirates.
The Road Ahead
When we think about the future, GIS survey and data processing in the UAE will include emerging technologies such as artificial intelligence and blockchain to make both data analysis and security better. They will help the country achieve vital objectives, like ensuring enough food and adapting to climate change.
By embracing GIS in the UAE, the country has demonstrated that using spatial intelligence can help strengthen, organize, and sustain a society. With the help of GIS, Emirati agencies can now study and survey the regions of Abu Dhabi and Dubai, while mapping how the economy moves toward knowledge-work.
Accurate Survey UAE provides precise land, building, and construction surveys using advanced technology, ensuring reliable results for projects across the UAE. If you would like to learn more about GIS survey and data processing, you can visit the page.
0 notes
Text
Engineering Surveys Explained: From Blueprint to Build
In the world of construction and infrastructure development, accuracy and precision are paramount. Whether it’s a residential complex, a bridge, or a highway, every project begins with a deep understanding of the site. That’s where engineering surveys come into play. These critical assessments serve as the foundation upon which architects, engineers, and contractors build their plans and execute their visions.
This article provides a comprehensive overview of engineering surveys, their purpose, types, methods, and significance in the Australian construction landscape.

What Are Engineering Surveys?
Engineering surveys are specialised surveys conducted to collect data that supports the planning, design, and execution of engineering projects. These surveys help determine the positions of natural and man-made features on the land and ensure that construction is carried out with accuracy and efficiency.
By providing spatial information about terrain, elevations, boundaries, infrastructure, and utilities, engineering surveys eliminate guesswork, mitigate risks, and guide construction from concept to completion.
Importance of Engineering Surveys in Australia
Australia’s diverse landscapes—from coastal zones to rugged outback terrains—pose unique challenges in civil engineering. Engineering surveys enable project stakeholders to adapt to these conditions by offering critical insights that influence feasibility, cost estimation, environmental compliance, and structural safety.
Key reasons why engineering surveys are indispensable include:
Ensuring compliance with local planning and zoning regulations
Minimising costly construction errors or rework
Providing data for designing roads, drainage systems, and utility layouts
Supporting land development assessments and subdivision planning
Enhancing safety and reducing environmental impact
Types of Engineering Surveys
Depending on the nature and scope of the project, different types of engineering surveys may be utilised. The most common types in Australian construction projects include:
1. Topographic Surveys
These surveys map out the natural and artificial features of a land parcel, including elevations, contours, vegetation, buildings, and infrastructure. They are essential for understanding site conditions before initiating any design work.
2. Boundary Surveys
Boundary surveys define the exact legal limits of a property. They help resolve disputes, support subdivision developments, and ensure that construction activities remain within legal property lines.
3. Construction Set-Out Surveys
These surveys mark the precise location of proposed structures or infrastructures on the ground, as per the approved design plans. They ensure that the physical construction aligns with engineering specifications.
4. As-Built Surveys
Also known as "as-constructed" surveys, these are conducted after construction to verify that the work has been completed according to plan. They are often required for regulatory compliance and project documentation.
5. Utility Surveys
Utility surveys locate and map underground services such as water mains, sewerage, telecommunications, and electrical cables. This information is crucial for avoiding service disruptions during excavation and construction.
Techniques and Tools Used in Engineering Surveys
Modern engineering surveys rely on cutting-edge technology to collect and process data with precision. Tools commonly used include:
Total Stations: Instruments that measure angles and distances with high accuracy
GPS/GNSS Equipment: Global positioning systems used for geolocation and mapping
Drones/UAVs: Used for aerial photogrammetry and large-scale topographic surveys
3D Laser Scanners: Capture detailed spatial data for complex structures or terrain
Geographic Information Systems (GIS): Software for visualising and analysing spatial data
Each of these tools plays a vital role in ensuring that engineering surveys produce reliable, actionable information.
The Engineering Survey Process
While the exact workflow may vary by project, a typical engineering survey in Australia involves the following stages:
Initial Consultation – Understanding project requirements, timelines, and regulatory obligations.
Site Reconnaissance – A preliminary visit to identify key features and assess access and safety.
Data Acquisition – Using advanced instruments to collect accurate spatial and elevation data.
Data Processing – Converting raw data into maps, models, and CAD files.
Reporting and Delivery – Presenting the results in formats required by engineers, planners, and authorities.
Engineering Surveys and Australian Regulations
In Australia, engineering surveys must comply with standards set by professional bodies such as the Surveying and Spatial Sciences Institute (SSSI) and state-specific regulations. For example, in New South Wales, surveyors must adhere to the requirements of the Surveying and Spatial Information Act 2002. Similar regulatory frameworks exist across Queensland, Victoria, and other states, ensuring consistency and legal compliance.
Applications Across Industries
Although closely associated with construction, engineering surveys are crucial across various industries, including:
Transport and Infrastructure (e.g., railways, airports, motorways)
Mining and Resources
Urban Planning and Development
Water Management and Utilities
Renewable Energy Projects (e.g., solar farms, wind turbines)
These surveys support both public and private sector projects, contributing to Australia's ongoing urbanisation and infrastructure development.
Final Thoughts
From identifying land contours to marking construction set-out points, engineering surveys form the backbone of every successful project. Their role in minimising errors, ensuring regulatory compliance, and enhancing safety makes them an essential service in Australia’s dynamic built environment.
Whether you're initiating a residential development in Melbourne or planning a major infrastructure project in regional Queensland, investing in professional engineering surveys is the first step toward building with confidence.
By understanding the scope, significance, and processes involved in these surveys, project stakeholders can make informed decisions that streamline development and secure long-term success.
0 notes
Text
Hydrographic Survey

Hydrographic Survey: Mapping the World Beneath the Waves
When we think of maps, our minds often go to mountains, roads, or cityscapes. But just as the land above water is charted and studied, the vast and complex terrain beneath oceans, rivers, and lakes also demands careful measurement. That’s the role of a Hydrographic Survey—a specialized field dedicated to exploring, mapping, and understanding underwater environments. These surveys are vital for navigation, engineering, resource management, environmental protection, and scientific discovery.
A Hydrographic Survey doesn’t just capture depth; it reveals the character, structure, and dynamic processes of the aquatic world. As industries expand offshore and climate change intensifies the need for coastal resilience, the importance of accurate underwater data has never been greater.
What Is a Hydrographic Survey?
A Hydrographic Survey is the process of measuring and describing the physical features of oceans, seas, coastal areas, rivers, lakes, and the seabed. The primary focus is on bathymetry—measuring the depth of water and determining the topography of the underwater surface. However, it can also involve current profiling, tide and wave monitoring, sediment sampling, and shoreline analysis.
Using advanced equipment such as single-beam and multi-beam echo sounders, side-scan sonar, LiDAR, GPS, and autonomous vehicles, hydrographers gather precise data that inform critical decisions in construction, navigation, and environmental conservation.
The Evolution of Hydrographic Surveying
Historically, hydrographic surveys involved manual methods like lead line soundings, which were slow, labor-intensive, and prone to error. Today, however, the field has been revolutionized by technology. Multi-beam sonar systems can map vast seafloor areas in high resolution, while airborne LiDAR bathymetry allows for rapid coastal assessments. Unmanned Surface Vessels (USVs) and Autonomous Underwater Vehicles (AUVs) further increase coverage and safety.
Modern Hydrographic Surveys rely heavily on software for data processing, visualization, and integration into Geographic Information Systems (GIS). The ability to analyze and present detailed underwater models is essential for engineering, navigation, and policy-making.
Why Are Hydrographic Surveys Important?
Hydrographic Surveys serve multiple industries and public needs. Here are some of the most significant applications:
Safe Navigation Perhaps the most critical application of hydrographic surveys is supporting maritime safety. Accurate charts help ships avoid underwater hazards, navigate shallow waters, and approach ports and harbors with confidence. National and international hydrographic offices use survey data to produce official nautical charts and publications.
Marine Construction and Infrastructure Any construction project near or on water—such as bridges, tunnels, piers, or offshore wind farms—requires detailed hydrographic data. Engineers need precise depth measurements, seabed conditions, and current data to design safe and effective structures. Surveys are often performed before, during, and after construction to ensure alignment and structural integrity.
Dredging Operations Maintaining navigable waterways often involves dredging, where sediment is removed from the bottom of rivers, ports, or canals. Hydrographic Surveys guide dredging efforts by identifying sediment buildup and verifying post-dredging results. This helps avoid over-dredging or under-dredging, optimizing both costs and environmental impact.
Environmental Monitoring Understanding aquatic environments is essential for protecting ecosystems. Surveys can reveal erosion patterns, sediment transport, water quality indicators, and habitat changes. They are essential tools in managing marine protected areas, planning coastal resilience strategies, and evaluating environmental impact.
Subsea Cable and Pipeline Routing Telecommunication cables, gas pipelines, and power connectors laid underwater depend on hydrographic data for safe and efficient routing. Surveys identify suitable paths, assess potential obstacles, and monitor the condition of these critical infrastructures over time.
Disaster Response and Risk Management In the wake of natural disasters like tsunamis or hurricanes, hydrographic surveys help assess damage to underwater infrastructure, ports, and shorelines. They also aid in search and rescue efforts by identifying debris or submerged hazards.
Scientific Research and Exploration Oceanographers, marine biologists, and geologists rely on hydrographic surveys to understand seabed features, plate tectonics, coral reefs, and underwater volcanoes. These surveys contribute to our knowledge of the planet and uncover new opportunities for sustainable development.
Core Technologies in Hydrographic Surveys
To meet the growing demands for precision, speed, and safety, hydrographic surveyors utilize a suite of sophisticated tools:
Echo Sounders: These send sound pulses to the seabed and measure the time it takes for the echo to return. Multi-beam echo sounders provide wide swath coverage, creating detailed 3D maps.
Side-Scan Sonar: Produces high-resolution images of the seabed by emitting sound waves at an angle. It is especially useful for detecting objects like shipwrecks or pipelines.
GNSS and RTK GPS: Provide centimeter-level positioning accuracy for survey vessels and equipment.
LiDAR (Light Detection and Ranging): Especially useful in shallow or coastal areas, airborne LiDAR systems can map both land and water surfaces simultaneously.
Unmanned Vessels: Remote-controlled or autonomous survey vessels can operate in hazardous or shallow areas without risking human safety.
Challenges of Hydrographic Surveys
Conducting a Hydrographic Survey is not without obstacles. Environmental conditions such as rough seas, strong currents, and limited visibility can interfere with measurements. Equipment calibration, data processing, and georeferencing require expertise and careful attention to detail. Additionally, collecting data in politically sensitive or remote regions poses logistical and regulatory challenges.
Data management is another major consideration. The volume of information collected during a single survey can be enormous. Converting raw data into usable formats for charts, 3D models, or GIS applications takes time, processing power, and trained personnel.
Emerging Trends in Hydrographic Surveying
As the world continues to digitize and automate, Hydrographic Surveys are evolving in step. Key trends shaping the future of the industry include:
Integration with BIM and Digital Twins: Survey data is increasingly being used in Building Information Modeling (BIM) systems to create real-time, interactive representations of marine and coastal infrastructure.
Artificial Intelligence and Automation: Machine learning algorithms can now process and interpret large datasets faster and more accurately than ever, accelerating decision-making.
Cloud-Based Collaboration: Teams across continents can now work on the same survey projects using cloud-based platforms that allow for real-time data sharing and analysis.
Sustainability and Climate Resilience: Hydrographic data is crucial in modeling sea-level rise, storm surge, and erosion. This makes it a cornerstone of climate adaptation strategies for coastal cities and vulnerable communities.
Conclusion
A Hydrographic Survey is far more than a series of measurements—it is a gateway to understanding the underwater world and enabling human progress in harmony with natural forces. From ensuring the safety of maritime navigation to laying the groundwork for renewable energy, the applications are both vast and vital.
As technology continues to advance and the demand for coastal development increases, Hydrographic Surveys will play a central role in shaping the future of marine infrastructure, environmental protection, and ocean science. Whether you're steering a vessel, designing an underwater pipeline, or planning a resilient coastline, the accuracy and insight provided by hydrographic surveying are indispensable.
1 note
·
View note
Text
Epitome – Excellence in Accurate Land Surveying Services
In the dynamic world of construction, infrastructure, and urban development, precision is not a luxury—it’s a necessity. Every towering building, every road, and every bridge begins with one crucial step: a land survey. At Epitome Geotechnical Services, we recognize that land surveying is not just about marking boundaries—it’s about laying the foundation for everything that follows.
What is Land Surveying?
Land surveying is the process of determining the terrestrial or three-dimensional position of points and the distances and angles between them. This data is essential for planning and executing nearly every form of construction. It ensures that structures are built in the right place and that developers have an accurate understanding of the land’s topography, boundaries, and features.

From large-scale infrastructure projects to residential developments, surveying eliminates guesswork and provides actionable data for architects, engineers, and contractors.
Our Land Surveying Approach at Epitome Geotechnical
At Epitome Geotechnical Services, our approach to land surveying is defined by precision, innovation, and an unwavering commitment to quality. We understand that every land survey is the foundation of a successful project—so we go beyond standard practices to ensure accuracy and reliability at every stage.
Client-Focused Planning Every project begins with a thorough consultation to understand the client’s objectives, site-specific requirements, and regulatory needs. We believe that effective surveying starts with clear communication and a deep understanding of the end goal—whether it's construction, development, or land acquisition.
Advanced Technology Integration We employ cutting-edge technologies to deliver high-precision results:
Total Stations and GNSS/GPS Instruments for rapid, real-time data collection
Drone/UAV Surveys for detailed aerial mapping and 3D modeling
GIS Mapping Systems for large-scale data analysis and site visualization
CAD Software for accurate, professional survey reports and drawings
By embracing the latest tools, we ensure our surveys are not only accurate but also time-efficient and cost-effective.
Field-to-Office Collaboration Our survey teams in the field are supported by in-house engineers and drafting professionals who process the data with meticulous attention to detail. This collaborative approach bridges the gap between raw field data and actionable insights, reducing errors and accelerating turnaround times.
Integrated Geotechnical Insight Unlike traditional survey firms, we incorporate our deep geotechnical expertise into the surveying process. This means we assess not only the surface conditions but also the subsurface characteristics that could impact your project. From soil stability and water tables to terrain behavior under load, we provide a complete picture of the land’s potential challenges and opportunities.
Accuracy, Compliance & Certification Every survey we deliver meets local regulatory standards, zoning requirements, and legal frameworks. Our certifications and documentation are fully compliant with municipal, industrial, and governmental norms, making your approval process smoother and faster.
Custom-Tailored Solutions We recognize that no two projects are alike. Whether it's a compact urban lot, a sprawling industrial site, or a rugged terrain, we customize our methodology and deliverables to fit the unique needs of your project. Our scalable approach means we can support small residential plots just as effectively as large infrastructure developments.
Industries We Serve at Epitome Geotechnical Services
Real Estate & Urban Development We assist real estate developers, architects, and planners with accurate boundary surveys, topographical mapping, and site analysis. Our data helps optimize land use, ensure regulatory compliance, and support smooth project execution from planning to completion.
Infrastructure & Transportation From roads, railways, and bridges to airports and metros, infrastructure projects rely heavily on accurate geospatial and geotechnical information. We provide detailed construction layout surveys, alignment checks, and soil investigations to support safe and sustainable infrastructure development.
Industrial & Commercial Construction For factories, warehouses, industrial parks, and commercial buildings, we offer precise site surveys, foundation assessments, and layout planning. Our insights enable risk mitigation and long-term structural performance.
Renewable Energy Solar and wind energy projects require careful site planning and geotechnical evaluation. We deliver land grading surveys, foundation assessments, and environmental mapping to support the successful development of solar farms, wind parks, and related infrastructure.
Agriculture & Land Management We provide land mapping, irrigation planning, and soil analysis services to support agricultural development, farm layout optimization, and sustainable land use strategies.
Conclusion
At Epitome Geotechnical Services, we believe that accurate land surveying and geotechnical expertise form the backbone of successful development. Whether it’s a residential layout, a major infrastructure project, or a renewable energy installation, our commitment to precision, innovation, and client satisfaction remains unwavering. With a deep understanding of the industries we serve and a forward-thinking approach, we deliver data that drives informed decisions and builds a solid foundation for the future.
Partner with Epitome Geotechnical Services—where accuracy meets reliability, and every project starts with confidence.
#Detailed Project Report Preparation in India#Topographic Survey#Topographical Survey#Land Survey in India#DGPS Survey#Land Survey
0 notes
Text
Top 10 GIS Use Cases Across
Geographic Information Systems (GIS) have become an indispensable tool across various industries, offering powerful solutions to complex problems by integrating spatial data with analytical capabilities. Whether you’re in architecture, government, or health services, GIS provides unique insights that drive decision-making, efficiency, and innovation. In this blog, we’ll explore the top 10 GIS use cases for 18 different industries, showcasing the transformative impact of geospatial technology.
Architecture, Engineering & Construction
1. Site Selection & Analysis: Choosing the right site for a construction project is critical. GIS allows architects and engineers to analyze various factors such as topography, soil type, zoning regulations, and environmental constraints, ensuring the best possible location for development.
2. Infrastructure Management: Managing infrastructure such as roads, bridges, and utilities is simplified with GIS. It provides a real-time view of assets, helping engineers to monitor conditions, plan maintenance, and ensure compliance with safety standards.
3. 3D Modeling & Visualization: GIS enables the creation of 3D models that help in visualizing urban developments, construction projects, and architectural designs. These models provide a realistic view of how new structures will fit into the existing environment.
4. Environmental Impact Assessments: Before any construction begins, assessing the environmental impact is crucial. GIS helps in identifying potential risks to ecosystems, water sources, and communities, allowing for mitigation strategies to be put in place.
5. Construction Project Management: With GIS, managing large construction projects becomes more efficient. Project managers can track progress, allocate resources, and monitor timelines through spatial data integration.
6. Utilities Design & Mapping: Designing and mapping utilities such as water, gas, and electricity require precision. GIS ensures that all utilities are correctly planned and placed, avoiding costly errors during construction.
7. Urban Planning: Urban planning benefits immensely from GIS by providing a comprehensive view of city layouts, zoning laws, and population density. This data is essential for creating sustainable and efficient urban environments.
8. Flood Risk Assessment: Flood risks can be assessed using GIS, which analyzes historical flood data, topography, and climate patterns to identify areas at risk. This information is vital for planning resilient infrastructures.
9. Surveying & Land Development: GIS is revolutionizing the way land surveys are conducted. It allows for the precise mapping of land parcels, helping developers to plan and execute projects more efficiently.
10. Building Information Modeling (BIM): Integration Integrating GIS with BIM provides a powerful tool for architects and engineers. It enhances spatial analysis, offering a more comprehensive approach to construction planning and management.
Business
1. Market Analysis & Site Selection: GIS helps businesses identify optimal locations for expansion by analyzing demographics, customer behavior, and competitor locations. This data-driven approach ensures that businesses choose sites that maximize profitability.
2. Supply Chain Optimization: In the world of logistics, GIS plays a critical role in optimizing supply chains. It helps businesses map out the most efficient routes, reducing costs and delivery times.
3. Customer Segmentation: Understanding customer demographics is key to targeted marketing. GIS allows businesses to map customer locations and behavior, enabling more personalized marketing strategies.
4. Sales Territory Management: GIS assists in defining and managing sales territories by analyzing geographic data. This ensures that sales teams are deployed effectively, maximizing coverage and performance.
5. Competitor Analysis: GIS provides businesses with a competitive edge by mapping competitor locations and analyzing market share. This information is crucial for strategic planning and market entry.
6. Real Estate Analysis: In real estate, location is everything. GIS helps businesses analyze property values, market trends, and zoning laws, aiding in informed decision-making.
7. Risk Management: Businesses face various risks related to their geographic locations, such as natural disasters or political instability. GIS helps in assessing and mitigating these risks by providing detailed spatial analysis.
8. Advertising & Marketing: Targeted advertising is more effective when it considers geographic factors. GIS allows businesses to plan marketing campaigns based on location data, ensuring that they reach the right audience.
9. Franchise Expansion For businesses looking to expand through franchising, GIS provides insights into the best locations for new outlets. It considers factors like population density, income levels, and competitor presence.
10. Workforce Management Managing a geographically dispersed workforce is challenging. GIS helps businesses monitor employee locations, optimize routes, and ensure that resources are allocated efficiently.
Conservation
1. Habitat Mapping & Monitoring: GIS is a powerful tool for conservationists, allowing them to map and monitor critical habitats. This helps in protecting endangered species and managing biodiversity.
2. Species Distribution Modeling: Understanding where species are located and how they move is essential for conservation efforts. GIS enables the modeling of species distribution, helping in the creation of effective conservation strategies.
3. Protected Area Management: Managing protected areas requires detailed spatial information. GIS provides conservationists with the tools to monitor and manage these areas, ensuring that they remain protected.
4. Environmental Impact Assessments: Before any development occurs in sensitive areas, environmental impact assessments are necessary. GIS helps in identifying potential risks and developing strategies to mitigate them.
5. Land Use Planning: GIS supports sustainable land use planning by providing data on topography, soil types, and existing land use. This helps in making informed decisions that balance development and conservation.
6. Water Resource Management: Water is a critical resource for conservation. GIS helps in monitoring and managing watersheds, ensuring that water resources are protected and sustainably managed.
7. Climate Change Analysis: Climate change poses significant risks to ecosystems. GIS helps in analyzing these risks by modeling the impact of climate change on various habitats and species.
8. Restoration Planning: Restoring degraded habitats requires careful planning. GIS helps in identifying areas that need restoration and in monitoring the progress of restoration efforts.
9. Wildlife Corridor Mapping: GIS is used to identify and protect wildlife corridors, which are essential for the migration of species. This helps in maintaining genetic diversity and ecosystem health.
10. Natural Resource Management: Conservation efforts often involve managing natural resources such as forests and water bodies. GIS provides the tools needed to monitor and manage these resources effectively.
Education
1. Campus Mapping GIS allows educational institutions to create detailed campus maps, helping students, staff, and visitors navigate the campus with ease.
2. Student Demographic Analysis: Understanding student demographics is essential for educational planning. GIS helps institutions analyze where students are coming from, allowing for more targeted recruitment and support.
3. Curriculum Development: GIS can be integrated into various subjects, such as geography and environmental science, providing students with hands-on experience in spatial analysis.
4. Research Support: GIS supports academic research by providing tools for spatial analysis. This is particularly useful in fields such as environmental science, urban planning, and public health.
5. Resource Allocation: Educational institutions often face challenges in allocating resources effectively. GIS helps in analyzing the geographic distribution of students and resources, ensuring that they are allocated where they are needed most.
6. Community Outreach: Educational institutions often engage in community outreach programs. GIS helps in mapping out these programs, ensuring that they reach the communities that need them most.
7. Environmental Education: GIS provides a powerful tool for teaching students about the environment. It allows them to explore real-world data and understand the impact of human activities on the environment.
8. Alumni Tracking: GIS helps institutions track alumni, understanding where they are located and how they are contributing to their communities. This information is valuable for engagement and fundraising efforts.
9. Field Studies: Field studies are an essential part of many educational programs. GIS allows students to collect and analyze spatial data in the field, providing them with practical experience.
10. Emergency Planning: Educational institutions need to be prepared for emergencies. GIS helps in developing emergency response plans by providing detailed maps of the campus and surrounding areas.
Energy Utilities
1. Asset Management: Energy utilities have vast networks of assets, including power lines, substations, and pipelines. GIS helps in tracking and managing these assets, ensuring that they are maintained and operating efficiently.
2. Network Planning: Planning and designing utility networks requires detailed spatial analysis. GIS helps in optimizing the placement of new infrastructure, reducing costs, and improving service delivery.
3. Outage Management: When outages occur, utilities need to respond quickly. GIS provides real-time data on the location and extent of outages, helping utilities to restore service as quickly as possible.
4. Environmental Compliance: Energy utilities are subject to strict environmental regulations. GIS helps in monitoring compliance by providing data on the impact of utility operations on the environment.
5. Renewable Energy: Renewable energy sources such as wind and solar require precise site selection. GIS helps in identifying the best locations for renewable energy projects, considering factors such as sunlight, wind speed, and proximity to the grid.
6. Smart Grid: The smart grid is revolutionizing the way utilities deliver electricity. GIS plays a critical role in managing the smart grid by providing data on the location of smart meters, sensors, and other infrastructure.
7. Disaster Response: When natural disasters occur, energy utilities need to respond quickly to restore service. GIS helps in coordinating disaster response efforts by providing real-time data on the location and extent of damage.
8. Energy Demand Forecasting: Accurately forecasting energy demand is essential for ensuring that supply meets demand. GIS helps in analyzing factors such as population growth and economic activity, providing utilities with the data they need to forecast demand accurately.
9. Customer Engagement: Energy utilities need to engage with their customers, providing them with information on energy usage and efficiency. GIS helps in mapping out customer locations and tailoring engagement strategies to meet their needs.
10. Risk Management: Energy utilities face a variety of risks, including natural disasters, cyberattacks, and regulatory changes. GIS helps in assessing and mitigating these risks by providing detailed spatial analysis.
Facilities Management
1. Space Utilization: Managing space efficiently is a key challenge for facility managers. GIS helps in analyzing space utilization, identifying areas that are underused, and optimizing layouts.
2. Maintenance Management: GIS supports maintenance management by providing detailed maps of facilities and their assets. This helps in planning and scheduling maintenance tasks, ensuring that assets are kept in good condition.
3. Energy Management: Facility managers need to monitor and manage energy usage to reduce costs and environmental impact. GIS helps in analyzing energy usage patterns and identifying opportunities for efficiency improvements.
4. Emergency Planning: In the event of an emergency, facility managers need to respond quickly. GIS provides detailed maps of facilities, helping to develop and implement emergency response plans.
5. Asset Tracking: Facility managers are responsible for a wide range of assets, from furniture to HVAC systems. GIS helps in tracking these assets, ensuring that they are properly maintained and replaced when necessary.
6. Space Planning: GIS supports space planning by providing detailed maps of facilities and their layouts. This helps in optimizing the use of space, ensuring that it meets the needs of occupants.
7. Security Management: Facility security is a top priority for facility managers. GIS helps in monitoring and managing security systems, ensuring that facilities are protected from unauthorized access.
8. Environmental Compliance: Facility managers need to ensure that their facilities comply with environmental regulations. GIS helps in monitoring compliance by providing data on the impact of facility operations on the environment.
9. Fleet Management: For facilities with vehicle fleets, GIS helps in managing and optimizing fleet operations. This includes route planning, vehicle tracking, and maintenance scheduling.
10. Space Allocation: Allocating space effectively is essential for ensuring that facilities meet the needs of occupants. GIS helps in analyzing space requirements and allocating space based on usage patterns.
Health & Human Services
1. Disease Surveillance and Outbreak Management: GIS is crucial in tracking and managing disease outbreaks. By mapping the spread of diseases, health officials can identify hotspots, monitor trends, and allocate resources effectively to contain the spread.
2. Health Resource Allocation: GIS helps in analyzing the geographic distribution of health resources, such as hospitals, clinics, and pharmacies. This ensures that health services are accessible to the population, particularly in underserved areas.
3. Epidemiology and Public Health Research: GIS is used extensively in epidemiological studies to analyze the spatial patterns of health events. This helps in understanding the relationships between environmental factors and health outcomes, guiding public health interventions.
4. Emergency Response and Preparedness: In disaster situations, GIS is critical for coordinating emergency response efforts. It helps in mapping affected areas, identifying safe zones, and deploying resources where they are most needed.
5. Health Service Planning: GIS aids in the planning of health services by analyzing population demographics, health needs, and service availability. This ensures that health services are planned and delivered where they are most needed.
6. Environmental Health Monitoring: GIS helps in monitoring environmental factors that affect health, such as air and water quality. This data is crucial for assessing health risks and implementing public health measures.
7. Accessibility and Equity in Healthcare: GIS is used to analyze the accessibility of healthcare services across different regions, helping to identify disparities in service provision and guide efforts to improve equity.
8. Social Services Delivery: For human services, GIS supports the planning and delivery of services like child welfare, senior care, and food assistance programs, ensuring these services reach those in need.
9. Behavioral Health and Substance Abuse Treatment: GIS is increasingly being used to map and analyze the availability and accessibility of behavioral health services and substance abuse treatment centers. This helps in identifying gaps in service provision and directing resources to areas with the greatest need.
10. Telehealth Expansion and Planning: With the rise of telehealth, GIS is used to map and analyze broadband availability and identify regions where telehealth services can be expanded.
National Government
1. National Security and Defense: GIS is used for military planning, logistics, and operations. It helps in mapping terrain, planning missions, and monitoring threats, ensuring that national security is maintained.
2. Disaster Management: National governments rely on GIS for disaster preparedness, response, and recovery. It helps in mapping vulnerable areas, coordinating response efforts, and assessing damage after disasters.
3. Policy Development and Implementation: GIS provides valuable data for the development and implementation of national policies. Whether it’s infrastructure development, environmental protection, or economic planning, GIS ensures that policies are data-driven and geographically sound.
4. Natural Resource Management: Managing a nation’s natural resources, such as forests, water, and minerals, requires detailed spatial analysis. GIS helps in monitoring and managing these resources sustainably.
5. Census and Population Studies: National governments use GIS for conducting censuses and population studies. It helps in mapping population distribution, analyzing demographic trends, and planning services accordingly.
6. Infrastructure Development: GIS is crucial in the planning and development of national infrastructure, including roads, bridges, and utilities. It ensures that infrastructure projects are efficiently planned and executed.
7. Environmental Protection: National governments use GIS to monitor and protect the environment. It helps in tracking deforestation, pollution, and wildlife populations, ensuring that conservation efforts are effective.
8. Public Safety: GIS supports public safety initiatives by mapping crime patterns, planning law enforcement operations, and ensuring that emergency services are optimally located and deployed.
9. Transportation Planning: GIS is used for planning and managing national transportation networks, ensuring that roads, railways, and airports are efficiently planned and maintained.
10. Land Use and Zoning: GIS supports national governments in land use planning and zoning, ensuring that land is used efficiently and sustainably across the country.
Natural Resources
1. Resource Exploration: GIS is a powerful tool for natural resource exploration, helping companies identify potential sites for mining, drilling, and other activities.
2. Environmental Impact: Assessments Before any resource extraction occurs, environmental impact assessments are necessary. GIS helps in identifying potential risks and developing strategies to mitigate them.
3. Land Use Planning: Managing natural resources requires detailed spatial analysis. GIS helps in analyzing land use patterns and developing sustainable management strategies.
4. Water Resource Management: Water is a critical resource for many industries. GIS helps in monitoring and managing watersheds, ensuring that water resources are protected and sustainably managed.
5. Forestry Management: Managing forests requires detailed spatial data. GIS helps in monitoring forest health, planning timber harvests, and protecting wildlife habitats.
6. Wildlife Management: Managing wildlife populations requires detailed spatial analysis. GIS helps in tracking animal movements, monitoring populations, and protecting critical habitats.
7. Environmental Monitoring: Monitoring the environment is a critical function of natural resource management. GIS helps in tracking air and water quality, monitoring deforestation, and managing natural resources.
8. Land Degradation Monitoring: Land degradation is a significant problem for natural resource management. GIS helps in monitoring land degradation and developing strategies to combat it.
9. Oil & Gas Exploration: Exploring for oil and gas requires detailed spatial analysis. GIS helps in identifying potential drilling sites, optimizing exploration efforts, and minimizing environmental impact.
10. Sustainable Development: Sustainable development requires a balance between resource extraction and environmental protection. GIS helps in analyzing these factors and developing sustainable management strategies.
Conclusion
At Advintek Geoscience, we specialize in providing cutting-edge GIS solutions tailored to meet the unique needs of your industry. Our expertise ensures that you harness the full potential of GIS to achieve your goals, whether you’re improving public health, managing natural resources, or advancing business.
Ready to elevate your operations with advanced GIS solutions? Visit Advintek Geoscience to learn more about how we can help you integrate GIS into your workflow, or contact us today to discuss how we can support your specific needs.
0 notes
Text
A GIS-Based Approach to Infrastructure and Road Network Planning
Geographic Information Systems (GIS) offer a powerful platform for infrastructure development by enabling detailed spatial analysis, route optimization, and long-term urban planning. Through advanced mapping, terrain modeling, and data integration, GIS improves the efficiency, sustainability, and connectivity of transportation systems.
Why Use GIS for Infrastructure and Road Network Development? GIS provides planners and engineers with accurate, data-driven insights into land use, topography, and population density. It reduces development costs, enhances route planning, and ensures infrastructure aligns with environmental and social needs. This approach also supports transparent decision-making and continuous project monitoring.

GIS in Road Network Analysis Supports:
Spatial Planning: Analyzing terrain and land cover to determine optimal routes and avoid natural obstacles.
Traffic Flow Analysis: Using temporal traffic data to identify bottlenecks and improve route efficiency.
Environmental Assessment: Minimizing environmental impact by avoiding sensitive zones during construction planning.
Infrastructure Lifecycle Management: Enabling long-term monitoring and maintenance scheduling of road networks.
Using GIS for Infrastructure Mapping Includes:
Uploading and styling road and terrain layers.
Using elevation and slope data to design roads in complex topography.
Buffering critical areas (e.g., schools, rivers) for risk-aware planning.
Integrating socio-economic datasets for inclusive infrastructure design.
Procedure for Infrastructure Mapping and Road Network Analysis Using GIS
Road network analysis using GIS begins with acquiring and preparing data on traffic, fuel consumption, emissions, and environmental conditions. Administrative boundaries and road network layers are added and styled for better visualization. Buffer zones are created around current and proposed highways to assess impact areas. Spatial joins integrate land ownership, zoning, and environmental data. A multi-criteria analysis is then conducted to identify the most suitable road alignment. The results are compiled into a geospatial report for informed planning and stakeholder input.
Use Case: Urban Expansion and Road ConnectivityGIS helps urban planners overlay demographic data with existing transport networks to identify underserved areas and prioritize road expansions, promoting equitable access, economic growth, and reduced congestion.
Open-source GIS Mapping for Road Networks Open-source tools like MAPOG enable detailed, multi-layered infrastructure mapping with features like route tracking, real-time updates, and spatial analysis. These platforms empower planners to build smarter cities with sustainable mobility systems and increased public engagement.
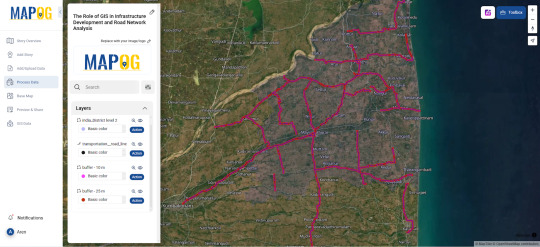
Conclusion Buffer zones and route analytics improve the precision of infrastructure projects. When used effectively, GIS supports proactive planning, better transport access, and reduced development risks across urban and rural areas.
#InfrastructureMapping#RoadNetworkPlanning#UrbanMobility#GISinInfrastructure#GeospatialTech#SmartCities#SmartMapping#DataDrivenPlanning#TransportationInnovation
1 note
·
View note
Text
Advancements in Gastrointestinal Diagnostics at Desai Surgical Hospital: What Patients Should Know
Contemporary medicine has evolved in identifying and managing gastrointestinal (GI) conditions. Modern diagnostic technologies, such as noninvasive imaging and sophisticated endoscopy, allow you to learn more about what's happening inside your digestive system more quickly, accurately, and comfortably. Because of technological advancements, patients are getting answers faster than ever before, whether they are dealing with problems like acid reflux, chronic stomach pain, or inexplicable weight loss.
What Are the New Advancements
1. High-Definition Endoscopy
Traditional endoscopy has long been the gold standard for visualizing the GI tract, but high-definition (HD) scopes now provide enhanced clarity. This allows more precise detection of ulcers, inflammation, tumors, and early-stage cancers. The best gastroenterologists in Vadodara use HD endoscopy to ensure patients receive accurate diagnoses with minimal discomfort.
2. Capsule Endoscopy
A revolutionary advancement, capsule endoscopy involves swallowing a tiny, pill-sized camera that captures thousands of images as it moves through your digestive tract. It's beneficial for examining the small intestine, an area difficult to reach with traditional methods. This noninvasive test is painless and ideal for patients with unexplained bleeding or suspected Crohn's disease.
3. Endoscopic Ultrasound (EUS)
EUS provides fine-grained pictures of the digestive tract and adjacent organs by combining endoscopy with ultrasound. It is useful for assessing bile duct obstructions, pancreatic disorders, and specific tumor types. The top gastroenterologists in Vadodara can use this technology to identify anomalies early and develop focused treatment plans.
4. Advanced imaging, including enterorrhaphy based on CT and MRI
These imaging methods allow for a cross-sectional view of the digestive tract. One can identify strictures, malignancies, and inflammatory bowel disease (IBD) using the digestive tract. CT and MRI enterorrhaphy give physicians a comprehensive grasp of anatomy and disease progression without requiring invasive treatments.
5. Molecular and Genetic Testing
Molecular diagnostics can offer early warnings for people with inherited cancer syndromes or gastrointestinal diseases in their family. These tests can identify genetic alterations that raise the likelihood of illnesses, including colon cancer and celiac disease. These findings can be used to create monitoring programs and individualized treatment regimens.
The Benefits of Timely Recognition
Many gastrointestinal disorders, including cancer, respond better to therapy when detected early. Clinical expertise and modern technologies are combined to guarantee accurate and timely disease diagnosis. Choosing the best gastroenterologists in Vadodara is essential since it gives you access to the most cutting-edge diagnostic equipment and evidence-based care in one place.
CONCLUSION
Thanks to advancements in diagnostic techniques, patients no longer have to undergo outdated or uncomfortable procedures to get clear answers about their digestive health. If you're experiencing persistent digestive symptoms, don't delay. Like Desai Surgical Hospital, the best gastroenterologists in Vadodara are equipped with the latest. We provide the tools to diagnose and treat your condition effectively and comfortably.
Visit Desai Surgical Hospital for Expert Gastro Care!
Location: Near G.P.O, Kharivav Road, Dandia Bazaar Road, Raopura, Vadodara,
Gujarat 390001
Contact: 0265 2435153
OPD Timings:
Monday - Friday: 12:30 PM - 02:30 PM & 06:00 PM - 07:00 PM
Saturday: 12:00 PM - 02:30 PM
Sunday: Closed
Emergency Services: Available 24/7Choose expert care at Desai Surgical Hospital, where the Top Gastroenterologists in Vadodara ensure optimal digestive health.
#GastroCare#DigestiveHealth#Endoscopy#Gastroenterologist#VadodaraDoctors#AdvancedDiagnostics#GIHealth#CapsuleEndoscopy#EarlyDetectionSavesLives#DesaiSurgicalHospital
0 notes
Text
Mapping the Unmapped – How A-THON’s ASHVA 4X4 ATV is Transforming Rural Infrastructure Access
India’s rural transformation depends on one thing—access. A-THON’s ASHVA 4X4 ATV is becoming an essential mobility solution for surveyors, engineers, and planners working in the most challenging terrains of India’s infrastructure growth story.
Building India Starts With Reaching It.
India’s development is no longer urban-centric. The future of economic progress and social transformation depends on infrastructure, connectivity, and services in over 6.4 lakh villages, spread across mountains, valleys, forests, deserts, and flood-prone regions.
Government initiatives like PM Gati Shakti, PMGSY (Pradhan Mantri Gram Sadak Yojana), and Digital Bharat all start with a critical first step—surveying, mapping, and terrain verification.
But how do teams access remote locations, navigate washed-out trails, or cross unstructured terrain to collect vital data?
The A-THON ASHVA 4X4 ATV provides the perfect mobility solution, allowing survey teams, infrastructure planners, and field engineers to reach, assess, and develop unmapped areas with precision and efficiency.
1. The Hidden Mobility Challenge in Rural Infrastructure Projects
Infrastructure development in remote and rural India relies on: ✔ Land surveys and GPS mapping ✔ On-ground engineering inspections ✔ Geo-tagging and elevation profiling ✔ Field validation for roads, bridges, borewells, telecom towers, and schools
The Challenge:
Despite technological advancements, rural terrain continues to present significant obstacles: ✔ Narrow, broken, or seasonally submerged paths ✔ Projects stall due to lack of physical access to survey sites ✔ Satellite maps and drone data fail to capture on-ground conditions ✔ On-foot surveys are slow, exhausting, and inconsistent
The Impact:
✔ Delays in Detailed Project Reports (DPRs) ✔ Inaccurate budget estimations ✔ Faulty infrastructure design due to incomplete data
The Solution – A-THON ASHVA 4X4 ATV
Designed for India’s toughest terrains, the ASHVA 4X4 ATV provides a robust, terrain-adaptive transport solution, ensuring that no project is delayed due to inaccessibility.
2. How A-THON ASHVA 4X4 ATV Enhances Rural Infrastructure Development
The ASHVA 4X4 ATV is specifically designed for infrastructure survey teams, government agencies, and engineering firms working in challenging, unstructured terrain.
Key Features for Survey and Site Validation:
✔ High-torque, 4x4 drivetrain – Tackles loose soil, riverbeds, and steep inclines ✔ Compact dimensions and tight turning radius – Navigates narrow village paths and jungle trails ✔ Seating for multiple field engineers – Supports government officers, planners, and contractors ✔ Rear utility bed – Transports survey equipment, drones, tripods, GIS gear, and power tools ✔ Tablet mounts and power outlets – Enables real-time data capture and geo-mapping ✔ All-weather resilience – Performs in monsoons, dust storms, and extreme heat
The Result:
✔ More accurate terrain data ✔ Faster project planning and execution ✔ Improved infrastructure outcomes
By ensuring uninterrupted mobility, the ASHVA 4X4 ATV is bridging the gap between data and development in rural India.
3. Key Government Use Cases for ASHVA 4X4 ATV
1. Rural Road and PMGSY Surveys
✔ Accessing remote villages for road connectivity assessments ✔ Verifying topography for optimal road alignment ✔ Assessing embankment risks post-monsoon
2. Jal Jeevan Mission (Water Infrastructure Development)
✔ Identifying feasible sites for borewells, water tanks, and pipelines ✔ Mapping terrain for gravity-fed water supply systems
3. Renewable Energy Microgrid Deployment
✔ Surveying un-electrified zones for solar and wind power projects ✔ Transporting panel prototypes and installation kits
4. BharatNet & Telecom Expansion
✔ Surveying for mobile towers and fiber optic routes ✔ Terrain validation for last-mile connectivity
5. Smart Village Infrastructure Planning
✔ Identifying locations for schools, health centers, and government offices ✔ Supporting digital service hubs like e-Mitra, CSC, and DigiGaon
The ASHVA 4X4 ATV empowers government agencies, private contractors, and survey teams to increase operational efficiency and execution speed in rural infrastructure projects.
4. Partnerships & Stakeholders in Rural Development Mobility
A-THON is actively partnering with government bodies, infrastructure firms, and technology innovators to support nationwide rural infrastructure projects.
Potential Collaborators:
✔ Rural Development Ministries & State Engineering Departments ✔ Survey of India, NIC, and Bhuvan GIS Teams ✔ Infrastructure & Construction Majors (L&T, Shapoorji Pallonji, NCC, etc.) ✔ District Collectorates and Panchayat Development Boards ✔ CSR-backed rural development projects ✔ Tech startups in geospatial mapping, AI surveying, and smart infra solutions
How ASHVA 4X4 ATV Supports Rural Infrastructure:
✔ Deployed as terrain mobility support for government and engineering teams ✔ Integrated with IoT sensors for field data collection and analysis ✔ Leased to infrastructure agencies for seasonal project demands
The ASHVA 4X4 ATV is not just a vehicle—it is an enabler of rural connectivity and progress.
5. Specialized ASHVA 4X4 ATV Variants for Infrastructure Surveying
A-THON offers customized ATV models optimized for rural infrastructure development and land surveying.VariantFeaturesSurveyor Scout ATVGIS tablet mount, tripod rack, weatherproof storage, laser rangefinder portsEngineering Inspection ATVSeating for multiple engineers, drone launch bay, blueprint rackSmart Village Data ATVPortable server, battery pack, and CSC digital terminalBridge & Culvert Inspection ATVCompact wheelbase, slope stability, moisture sensor toolkitHydro-Terrain ValidatorFlow sensors, GPS loggers, and camera mounts for stream path tracing
These specialized ATV models can be leased, integrated into PPP projects, or deployed in district administrations for on-demand field mobility.
6. Transforming Rural Infrastructure with Smarter Mobility
Measurable Impact of ASHVA 4X4 ATV Deployments:
✔ 25–40% increase in survey throughput per week ✔ Reduced need for re-surveys and corrections in DPRs ✔ Higher accuracy in terrain data, leading to better infrastructure design ✔ Lower long-term repair costs due to well-planned projects ✔ Enhanced training opportunities for rural workers in mobility tech
With ASHVA 4X4 ATVs in action, infrastructure projects become smarter, faster, and more effective.
Conclusion: Before You Build the Road, Reach the Road
In rural India, mobility is the foundation of development. Pipes, roads, and towers can only be built after the land is understood.
The A-THON ASHVA 4X4 ATV is the ultimate terrain mobility solution for India’s planners, engineers, and infrastructure pioneers.
This is more than transportation—it’s nation-building mobility, enabling real progress in Bharat’s most remote corners.
0 notes
Text
Exploring the Future of Mapping and Surveying with Lidar Technology
In the world of modern surveying, mapping, and robotics, one of the most revolutionary technologies that has emerged is Lidar (Light Detection and Ranging). Lidar technology utilizes laser pulses to measure distances, allowing for precise mapping and modeling of the environment. This article dives into the various applications and benefits of Lidar systems, including how they are transforming industries like road profiling, surveying, and robotics.
What is Lidar Mapping and Surveying?
Lidar mapping involves using laser light to scan and measure the surrounding environment, producing high-definition, accurate, and detailed 3D maps. These maps provide unparalleled detail for topographical surveys, infrastructure assessments, and environmental monitoring.
In surveying, Lidar technology is quickly becoming the go-to method for gathering geographic data. Traditional methods like total stations and GPS systems are often time-consuming and less accurate, particularly when dealing with complex terrains. In contrast, Lidar enables surveyors to capture massive amounts of data in a fraction of the time. Whether it’s mapping forests, coastal areas, or urban environments, Lidar ensures that even hard-to-reach areas are effectively surveyed.
Lidar Vision and Its Impact on Robotics
Lidar Vision plays a pivotal role in enhancing the capabilities of autonomous systems, particularly robots. By providing real-time data, Lidar sensors offer robots the ability to “see” their environment in 3D, enabling them to navigate with precision. The combination of Lidar Vision and artificial intelligence helps robots recognize objects, detect obstacles, and understand spatial relationships.
This capability is vital for mobile Lidar Vision For Robots used in industries such as warehousing, agriculture, and delivery services. With Lidar, robots can safely and effectively operate in dynamic environments. They can move around people, machinery, and obstacles while continuously updating their surroundings in real-time.
The integration of Lidar Vision is also important in the development of self-driving vehicles. Autonomous cars rely on Lidar to generate a 360-degree map of their surroundings, allowing them to make data-driven decisions when navigating streets, highways, and complex intersections. This technology is paving the way for the future of transportation.
The Role of Laser Systems in Lidar Technology
At the core of Lidar technology is the laser system, which emits pulses of light to measure distances with incredible accuracy. The laser beams bounce off objects, and the time it takes for the light to return is calculated to determine the distance from the sensor to the target. By emitting thousands to millions of laser pulses per second, Lidar systems can gather vast amounts of data quickly and precisely.
Laser systems used in Lidar can also capture various environmental details, such as vegetation, buildings, roads, and even underground structures. This makes Lidar an indispensable tool for urban planning, forestry, environmental conservation, and civil engineering.
Road Profiling with Lidar
One of the most impactful applications of Lidar is road profiling. Lidar systems are increasingly used to assess road conditions, identify damage, and map the road surface in detail. With the ability to quickly scan entire highways or city streets, Lidar offers road professionals accurate data that is vital for maintenance, repair, and construction projects.
Road profiling using Lidar technology allows for the measurement of pavement roughness, surface texture, and drainage patterns. These insights help transportation departments plan and prioritize road maintenance efficiently, ensuring a smooth and safe driving experience for all road users.
In addition to its efficiency, Lidar road profiling can also be combined with other technologies like Geographic Information Systems (GIS) to create integrated data platforms. These platforms enable cities to manage and analyze their road networks for long-term infrastructure planning.
The Future of Lidar and Its Applications
The potential applications for Lidar technology are vast and continue to expand across various industries. As Lidar technology becomes more accessible and affordable, it’s expected to revolutionize fields like urban planning, environmental conservation, agriculture, and even entertainment. Moreover, the ongoing advancements in Lidar sensors are making them smaller, more accurate, and even more affordable.
Robotics will continue to benefit from Lidar Vision, enabling smarter, safer, and more efficient robots. With more robots equipped with Lidar, industries can expect increased automation and reduced reliance on human intervention in various tasks.
Lidar's ability to collect high-resolution, 3D data with precision makes it an indispensable tool in sectors such as surveying, mapping, and road construction. Its future applications will likely lead to even more innovative solutions, further shaping the way we navigate and interact with the world around us.
For businesses and organizations looking to leverage the power of Lidar technology, Red Sensors offers cutting-edge Lidar solutions that cater to a variety of industries. Their advanced Lidar systems ensure accurate data capture and analysis for everything from autonomous robots to road profiling.
Explore how Red Sensors can help transform your surveying, mapping, and robotic operations. For more information, visit Red Sensors today.
0 notes
Text
Harnessing Geospatial Intelligence for Disaster Response and Resilience
Disasters can occur at any time and in any place, and then strike back at people with all the force they can muster, leaving everyone in the affected community to pick up the pieces. This is where fast and efficient Geospatial disaster technologies response have become an indispensable crucial factor in disaster response reducing as loss of help life in and fast property. evaluation and generation of appropriate recommendations for the emergency response teams. Advintek Geoscience uses advanced geospatial technologies to provide emergency teams with precise information and can plan to act any time quickly and can rebuild it properly.
The Role of Geospatial Tools in Emergency Network Restoration Rapid Damage Assessment with Geospatial Intelligence When a disaster disrupts wireless infrastructure, restoring communication networks is often the first priority. Geospatial tools play a pivotal role in assessing the extent of damage, pinpointing areas where communication has collapsed, and identifying accessible routes for emergency teams.
Satellite imagery and drone-based mapping provide high-resolution data that helps assess structural damage and prioritize repairs. GIS platforms can overlay this data with existing network maps to pinpoint which towers, antennas, or fiber-optic lines require immediate attention. For example, during hurricanes or earthquakes, geospatial analysis ensures response teams focus their efforts on the areas with the greatest need.
Enhancing Collaboration Among Stakeholders Geospatial tools enable seamless collaboration between government agencies, telecom providers, and emergency responders. Shared geospatial dashboards provide a unified view of the situation, ensuring all stakeholders are aligned on priorities and action plans. This collaborative approach accelerates decision-making and reduces downtime for critical communication services.
Temporary Coverage Solutions for Emergency Scenarios Planning Mobile Cell Site Deployments with GIS When communication towers are severely damaged, temporary coverage becomes essential. Mobile cell sites, often mounted on vehicles or portable structures, provide an interim solution to restore connectivity. GIS plays a crucial role in determining the optimal locations for deploying these mobile units.
Using real-time data, GIS tools analyze factors such as population density, terrain, and proximity to damaged infrastructure. This ensures that mobile cell sites are strategically placed to maximize coverage and minimize disruption. Additionally, GIS modeling can predict how these temporary solutions will perform under various scenarios, allowing teams to plan for contingencies.
Optimizing Deployment Routes In disaster-hit areas, navigating damaged roads and blocked access points can delay deployment efforts. GIS-based route optimization ensures that teams deploying mobile cell sites take the most efficient paths. By integrating live traffic and hazard data, GIS tools help emergency teams avoid delays and reach critical areas faster.
Building Long-Term Resilience Leveraging Geospatial Insights for Infrastructure Planning Disasters offer valuable lessons for building resilient infrastructure. Post-disaster geospatial analysis helps identify vulnerabilities in wireless networks and informs future planning. By understanding patterns of damage, telecom providers can reinforce at-risk infrastructure, ensuring greater resilience in the face of future events.
For instance, GIS tools can identify flood-prone areas where network equipment should be elevated or hurricane-prone regions where wind-resistant designs are necessary. These insights contribute to the development of robust communication networks that can withstand extreme conditions.
Integrating Early Warning Systems with GIS Geospatial tools are not only reactive but also proactive in disaster management. By integrating real-time monitoring systems with GIS, organizations can establish early warning mechanisms. For example, sensors monitoring seismic activity or river levels can feed data into GIS platforms, triggering alerts and enabling preemptive action to protect infrastructure and communities.
Why Geospatial Tools Are the Future of Disaster Management The ability to visualize and analyze data in real-time is revolutionizing the way we approach disaster management. Geospatial tools bring clarity and structure to chaotic situations, enabling emergency teams to respond with precision and confidence. They are not only tools of reaction but also instruments of prevention and long-term planning. Here’s why they are set to define the future of disaster management.
Real-Time Situational Awareness In the critical hours following a disaster, real-time information can save lives. Geospatial tools integrate live data feeds from satellites, drones, sensors, and social media, creating a comprehensive situational awareness map. This allows responders to see the full scope of the disaster, from flooded areas to collapsed infrastructure, and prioritize efforts accordingly. For instance, during wildfires, GIS can provide dynamic fire progression maps, helping teams strategize evacuations and resource allocation.
Enhanced Decision-Making Through Data Integration Disaster management often involves a plethora of data sources: meteorological data, infrastructure maps, population density, and real-time updates from the field. Geospatial tools excel at integrating these diverse datasets into a single, interactive platform. This integration enables emergency teams to make decisions backed by a holistic view of the situation, rather than relying on fragmented or outdated information.
Predictive Modeling for Preemptive Actions The future of disaster management is moving toward prediction rather than reaction. Geospatial tools enable predictive modeling by analyzing historical disaster data alongside current conditions. For example, by studying historical flood data and weather patterns, GIS can predict areas most likely to be affected in upcoming storms. This foresight allows governments and organizations to pre-position resources, evacuate populations, and protect critical infrastructure before disaster strikes.
Streamlined Coordination Across Agencies Disasters often require coordinated efforts from multiple agencies, including emergency responders, government bodies, utility companies, and non-profits. Geospatial platforms act as a common operating picture for all stakeholders, ensuring seamless communication and coordination. Shared geospatial dashboards enable each entity to contribute to and access vital information, reducing redundancy and increasing efficiency.
Advancing Recovery and Mitigation Efforts Geospatial tools are as critical in recovery as they are in response. After a disaster, GIS can assess long-term impacts, track recovery progress, and inform mitigation strategies to reduce vulnerability in the future. For instance, post-earthquake GIS analyses can help identify areas where building codes need strengthening, while flood impact maps can guide the construction of levees or drainage systems.
Advintek Geoscience: Leading the Charge in Disaster Response Innovation At Advintek Geoscience, we specialize in providing advanced geospatial solutions tailored to the unique challenges of disaster response and resilience. Our expertise in GIS, and data analytics ensures that our clients are equipped to navigate emergencies effectively.
We collaborate with telecom providers, government agencies, and emergency responders to deliver customized solutions that restore connectivity and strengthen infrastructure. With Advintek Geoscience, you’re not just responding to disasters — you’re building a future that’s better prepared for them.
Ready to transform your disaster response strategy? Discover how Advintek Geoscience can empower your organization with geospatial intelligence today.
0 notes