#food waste into cooking gas and fertilizer
Explore tagged Tumblr posts
Text
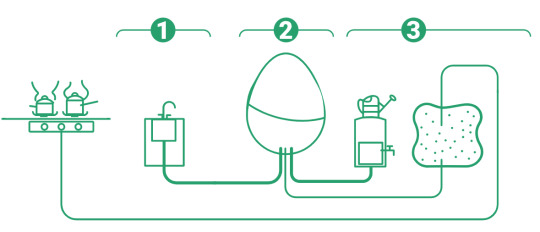
Kieran, a longtime mechanical engineer, had just invented Ireland’s first micro-scale anaerobic biodigester.

What does one even do with a micro-scale anaerobic biodigester?
Well, this particular anaerobic biodigester takes care of nearly 100% of your food waste.
You feed in all your scraps and waste – even hard-to-compost foods like cooked meats, dairy, cakes and liquids go in. Then the anaerobic bacteria get to work breaking down the waste.
After that, out come two very different ready-to-use products: a biogas for cooking and a nutrient-rich liquid fertiliser for gardening.
Food waste goes in. Gas and fertiliser come out.

‘We were never really into gardening or growing food. That was the biggest thing to change with the digester,’ Kieran says.
‘During lockdown, we set up the polytunnel and started using the fertiliser from the egg to grow tomatoes and courgettes. Because not only have you got a way to get rid of your food waste, you’ve also got a way to grow more food. And the taste was extraordinary. We had loads of tomatoes so we gave them to friends. They couldn’t get over how tasty they were compared to what they were buying from shops.’
Fiona and Kieran have only seen positives come out of using the egg. They love cooking with the biogas they produce themselves, and having no bill for fertiliser.
#solarpunk#solar punk#reculture#solarpunk aesthetic#solarpunk AF#mygug#ireland#solarpunk innovation#biodigester#food waste into cooking gas and fertilizer#circular food
49 notes
·
View notes
Text
Let me start with the following principle: “Energy is the only universal currency: One of its many forms must be transformed to get anything done.” Economies are just intricate systems set up to do those transformations, and all economically significant energy conversions have (often highly undesirable) environmental impacts. Consequently, as far as the biosphere is concerned, the best anthropogenic energy conversions are those that never take place: No emissions of gases (be they greenhouse or acidifying), no generation of solid or liquid wastes, no destruction of ecosystems. The best way to do this has been to convert energies with higher efficiencies: Without their widespread adoption (be it in large diesel- and jet-engines, combined-cycle gas turbines, light-emitting diodes, smelting of steel, or synthesis of ammonia) we would need to convert significantly more primary energy with all attendant environmental impacts.
Conversely, what then could be more wasteful, more undesirable, and more irrational than negating a large share of these conversion gains by wasting them? Yet precisely this keeps on happening—and to indefensibly high degrees—with all final energy uses. Buildings consume about a fifth of all global energy, but because of inadequate wall and ceiling insulation, single-pane windows and poor ventilation, they waste at least between a fifth to a third of it, as compared with well-designed indoor spaces. A typical SUV is now twice as massive as a common pre-SUV vehicle, and it needs at least a third more energy to perform the same task.
The most offensive of these wasteful practices is our food production. The modern food system (from energies embedded in breeding new varieties, synthesizing fertilizers and other agrochemicals, and making field machinery to energy used in harvesting, transporting, processing, storing, retailing, and cooking) claims close to 20 percent of the world’s fuels and primary electricity—and we waste as much as 40 percent of all produced food. Some food waste is inevitable. The prevailing food waste, however, is more than indefensible. It is, in many ways, criminal.
Combating it is difficult for many reasons. First, there are many ways to waste food: from field losses to spoilage in storage, from perishable seasonal surpluses to keeping “perfect” displays in stores, from oversize portions when eating outside of the home to the decline of home cooking.
Second, food now travels very far before reaching consumers: The average distance a typical food item travels is 1,500 to 2,500 miles before being bought.
Third, it remains too cheap in relation to other expenses. Despite recent food-price increases, families now spend only about 11 percent of their disposable income on food (in 1960 it was about 20 percent). Food-away-from-home spending (typically more wasteful than eating at home) is now more than half of that total. And finally, as consumers, we have an excessive food choice available to us: Just consider that the average American supermarket now carries more than 30,000 food products.
Our society is apparently quite content with wasting 40 percent of the nearly 20 percent of all energy it spends on food. In 2025, unfortunately, this shocking level of waste will not receive more attention. In fact, the situation will only get worse. While we keep pouring billions into the quest for energy “solutions”—ranging from new nuclear reactors (even fusion!) to green hydrogen, all of them carrying their own environmental burdens—in 2025, we will continue to fail addressing the huge waste of food that took so much fuel and electricity to produce.
20 notes
·
View notes
Text
BLU Spy headcanon and Sniper pee
What if… BLU Spy was from rural France originally, and not the city?
Because the way he acts, you would assume he’d throw a hissy fit over getting dirt under his nails or something minor like that…
But what if it’s an act? As stuck up as he is, he pretends to be grossed out and prissy about everyday messes to keep up his image. And the only thing that actually grosses him out is human waste like Sniper pee?



[Throwing dirty bottles from the trash]
Think about it. He doesn’t tell people his name or where he’s from, he doesn’t let them see his face, and he tries to stay aloof. Even to someone as friendly as Soldier. Wouldn’t it make sense to play a part that doesn’t fit your background, so people couldn’t use your behavior to extrapolate your origin?
Animals are not clean, they poop and pee wherever it seems right to them and it accumulates. Farm animals included. And beyond that, gardening and farming requires you to get your hands up in the dirt. But that’s nature, animals don’t have souls and human intelligence. We know what viruses and diseases are; livestock, wildlife and pets do not.
So, in the absence of his suit or reasons to pretend to be a germaphobe, it wouldn’t bother BLU Spy to clean up a horse stable; they need their feces to be taken away so they don’t get worms. It wouldn't bother him to give food scraps to pigs or chickens, and it wouldn’t bother him to get the eggs from the coop.
Walking around cow patties in a field, helping a farm animal with a difficult delivery, and fertilizing a garden or field would not bother him. Killing a farm animal and preparing it to be cooked would not make him squeamish.
But Sniper is a grown man who throws his pee at people intentionally. And to BLU Spy, that’s extra nasty because how does an adult think that’s acceptable behavior? It’s waste; it’s water with all the toxins and ammonia and refuse that your body doesn’t use for energy. And it can make you sick if you get it in an open wound [likely on the battlefield] or drink it, which Snipes may well do.
And it’s probably worse considering the fact that Sniper takes those kidney enlarging pills; they may not be filtering waste out of the body like they were meant to do. I think that when RED Medic brought him back, he replaced his messed up kidneys with some from an exotic animal, since he wouldn’t have gotten the chance prior.






This is an interesting interaction for a few reasons.
The sewage they’re currently walking in is up to Soldier’s knees and almost Spy’s.
Soldier is talking about trench warfare, which is notorious for wet sloppy ground and rats causing gangrene and other illnesses. But the way he talks about it makes it sound less terrible than the situation they’re currently in. I think he was just trying to make conversation, not tell Spy to get over himself because he’s been through worse.
2. Soldier is looking straight ahead while Spy is looking into the water to watch his steps.
Sewage pipes are meant to take feces, pee, and toilet paper away from people to keep them from getting sick. But animals such as rats and random trash end up in the sewers; and given their location, they may well step on a fallen gun, bullets, or an engineer’s tools by mistake.
They’re both being smart in different ways; Soldier is watching for enemies ahead, and Spy is watching for objects that might go through his shoe and cause an infection. Or cause him to slip and get more sewage on himself.
3. In WWI, trench warfare was concentrated in France.
The Germans were trying to take Paris, and the French fought fiercely in the countryside between the city and Belgium, which had already fallen and been razed. WWI had more trench warfare, because the inventions needed to break a stalemate between two trenches of enemy soldiers had to be developed during those years. Chemical warfare like the use of Mustard gas was not condemned legally until after the war at the Geneva convention.
Meanwhile, America was ever the land far away that didn’t suffer the same effects on their land. Their soldiers died, their elderly and children did not. Their farms were not scarred with razor wire and trenches and bullets. But those scars were concentrated in France.
So to Spy -who did not live through the first war, but did hear the stories, and of the rebuilding, and live through WWII- Soldier is the one who hasn’t really been through it. War is hell on all soldiers, but it was a wildly different experience for a foreigner to come in, help, and go back to the land of plenty, than to be a citizen of one of the countries invaded by the N*zis.
4. In WWII, France fell to Germany in stark contrast to their valiant performance in WWI. The Resistance and anyone who tried to save persecuted undesirables were about the only people who showed courage.
I won’t go into so much detail here, since this will be relevant in my Emesis Blue fanfic later, but you should know that the country of France was not heroic and brave in WWII. It brought great shame on their people, even if it was mostly forgotten by the rest of the world later.
So in a way, Soldier being someone who kept up the fight against the Germans makes him “better” than the French military, alongside his platoon. But he would also be unaware of the wider hardships faced by the people of France during those years, as someone who was rushing to stop Germany and on the frontlines. He didn’t live in a village or city in Europe, living the misfortune of the civilians who called that country home. And he didn’t live through the years after the war, when these countries had to rebuild.
Him looking forward and ignoring whatever might be in the water is a good representation of this. So is the fact that he’s the one in front, setting their pace, while Spy is lagging a little.
#tf2#emesis blue#tf2 spy#tf2 soldier#character analysis#this started out lighthearted and got sad quick.#Angst#historical context
50 notes
·
View notes
Text
Biogas Plants in Kerala: Powering a Greener Tomorrow

Introduction
Kerala, a state known for its natural beauty and progressive mindset, is increasingly turning to sustainable solutions for energy and waste management. Among these, biogas plants in Kerala are gaining widespread adoption across households, institutions, and farms. These systems not only address the growing waste crisis but also provide a clean and renewable energy source for everyday use.
Why Biogas Plants Are Important in Kerala
With high population density and limited land availability, managing organic waste efficiently is a major challenge. Biogas technology provides a smart solution by:
Reducing organic waste at the source
Generating clean fuel for cooking and heating
Producing organic fertilizer for agriculture
Decreasing dependence on LPG and fossil fuels
Current Status of Biogas Plants in Kerala
Kerala has seen a steady rise in the installation of biogas plants in urban and rural areas alike. The Suchitwa Mission and other government-backed initiatives promote biogas adoption through subsidies, awareness campaigns, and technical support.
Thousands of household biogas units have been set up in cities like Ernakulam, Trivandrum, and Kozhikode.
Institutional plants are installed in schools, hospitals, and markets to handle bulk organic waste.
Panchayats and municipalities are implementing decentralized waste-to-energy models.
Types of Biogas Plants Used in Kerala
Fixed Dome Biogas Plants — Long-lasting, low-maintenance units ideal for rural households.
Portable Biogas Plants — Compact and suitable for urban homes with space constraints.
Community Biogas Plants — Shared systems in residential complexes or local markets.
Industrial Biogas Plants — For large-scale operations like slaughterhouses and food processing units.
Government Support for Biogas in Kerala
The Kerala government offers financial assistance and training programs to promote biogas adoption. Agencies like ANERT (Agency for Non-Conventional Energy and Rural Technology) and the Suchitwa Mission provide:
Subsidies for household and institutional plants
Technical guidance and installation support
Awareness campaigns for sustainable waste management
Benefits of Biogas Plants in Kerala
✅ Clean and renewable energy ✅ Organic fertilizer for farming ✅ Waste volume reduction ✅ Reduced greenhouse gas emissions ✅ Cost-effective and low maintenance
Challenges and the Way Forward
While the uptake is promising, challenges such as lack of awareness, maintenance issues, and improper waste segregation still exist. To scale adoption, Kerala must focus on:
Educating the public
Encouraging local manufacturing
Strengthening after-sales service
Integrating biogas into broader climate action policies
Conclusion
Biogas plants in Kerala represent a vital step toward a cleaner, self-sufficient, and eco-friendly future. As the state continues to champion green practices, embracing biogas technology can help every household and community become part of the sustainability movement.
#biogas in kerala#biogas plant for home#incinerator manufacturers in kerala#portable biogas plant for home#incinerators in kerala#biogas#kerala
0 notes
Text
Biogas Generator: A Sustainable Energy Solution for a Greener Future
What Is a Biogas Generator?
A biogas generator is a system that converts organic waste—such as food scraps, animal manure, and agricultural residue—into biogas through a process called anaerobic digestion. This biogas, mainly composed of methane and carbon dioxide, can be used as a renewable source of energy for electricity, heat, or even as a clean fuel for vehicles.
How Does a Biogas Generator Work?
Feedstock Collection: Organic waste is gathered and placed into an airtight chamber known as a digester.
Anaerobic Digestion: Microorganisms break down the organic matter in the absence of oxygen, producing biogas.
Gas Storage and Utilization: The biogas is collected and stored in gas holders, then used for generating electricity or heating.
Byproduct Management: The leftover slurry, rich in nutrients, is used as an organic fertilizer.
Benefits of Using a Biogas Generator
✅ Renewable Energy Source
Biogas is a clean, renewable alternative to fossil fuels, helping reduce greenhouse gas emissions and dependence on non-renewable energy.
✅ Waste Management
Biogas systems effectively manage organic waste, converting potential pollutants into valuable energy.
✅ Cost-Effective
Once set up, biogas generators significantly lower energy costs for households, farms, and industries.
✅ Eco-Friendly Fertilizer
The digestate—a byproduct of the process—is a high-quality organic fertilizer that enhances soil health and crop yields.
Applications of Biogas Generators
Agricultural Farms: Convert livestock manure into energy and fertilizer.
Households: Provide cooking gas and electricity in rural or off-grid areas.
Municipalities: Process food waste and sewage sludge sustainably.
Industries: Reduce energy costs and carbon footprint by utilizing factory waste.
Biogas Generator Types
Small-Scale Biogas Generators – Ideal for homes and small farms.
Medium-Scale Digesters – Suitable for community or cooperative use.
Industrial Biogas Plants – Designed for municipalities or large agricultural operations.
Factors to Consider When Choosing a Biogas Generator
Feedstock Availability
Energy Requirements
Space and Installation Area
Budget and Maintenance Costs
Local Regulations and Incentives
Conclusion
Investing in a biogas generator is a smart and sustainable step toward energy independence, environmental responsibility, and long-term cost savings. Whether you are a homeowner, farmer, or business owner, biogas technology offers a scalable and eco-friendly energy solution.
0 notes
Text
How to Start a Profitable Bio CNG Business with Government Support in India
As the focus on renewable energy and environmental responsibility continues to grow, the Bio CNG business is gaining momentum as a smart and sustainable option. With increasing awareness about clean energy solutions, this sector is showing significant potential across both rural and urban India. It not only provides an eco-friendly substitute for traditional fuels but also plays a key role in effective organic waste management.
What is Bio CNG?
Bio CNG (Compressed Natural Gas) is a purified form of biogas produced from organic waste materials like agricultural waste, cow dung, food waste, and sewage. After purification, it becomes methane-rich gas, which can be used just like traditional CNG for vehicles, cooking, and industrial use.
Why Choose Bio CNG Business?
The Bio CNG business is ideal for entrepreneurs looking to enter the renewable energy sector with long-term growth and government support. It contributes to waste management, reduces pollution, and promotes rural development. Moreover, it helps reduce dependency on imported fuels.
Let’s understand how you can start and succeed in this eco-friendly business.
How to Start Bio CNG Business in India
Starting a Bio CNG business in India involves careful planning, investment, and meeting certain approvals. Here’s a step-by-step overview:
Research and Feasibility Study – Understand the demand, location, availability of raw materials (like organic waste), and target users.
Land and Infrastructure – You will need around 1 to 2 acres of land, preferably near waste sources like dairy farms or food processing units.
Bio CNG Plant Setup – The setup includes waste collection units, anaerobic digesters, gas purification units, and a compression and bottling system.
Licenses and Approvals – You must obtain pollution control clearance, local municipal approval, and fire safety certificates. The process for Bio CNG license and approval in India can vary state-wise.
Connect with Government or Private Partners – You can tie up with energy companies or take a Bio CNG franchise opportunity to reduce risks and get faster market entry.
Bio CNG Plant Cost and Profit
The total cost of setting up a medium-scale Bio CNG plant ranges between ₹2 crore to ₹5 crore, depending on the capacity and technology used. However, the profit margins are good if operations are managed efficiently.
Monthly income can range from ₹5 lakh to ₹15 lakh depending on production and supply contracts. Selling the slurry as organic fertilizer adds extra income.
Bio CNG Production from Waste
One of the best things about this business is that it uses waste as raw material. Bio CNG production from waste not only ensures proper disposal but also converts waste into wealth. Around 100 tonnes of wet waste can generate over 500 kg of Bio CNG daily, which can power vehicles or be used in industries.
Government Support and Subsidy
The Indian government is promoting the Bio CNG sector under schemes like SATAT (Sustainable Alternative Towards Affordable Transportation). Under this, entrepreneurs can receive a Bio CNG government subsidy, capital support, and long-term purchase agreements from oil companies like IOCL, BPCL, and HPCL.
These schemes help reduce the initial investment burden and offer assured income.
Bio CNG Manufacturing Process
The Bio CNG manufacturing process involves anaerobic digestion of organic waste, where bacteria break down the material without oxygen. The resulting biogas is purified to remove carbon dioxide and hydrogen sulfide, leaving behind 90%+ pure methane gas. This purified gas is compressed and stored for transportation or direct supply.
Bio CNG Franchise Opportunity
For those who do not want to set up a full-scale plant from scratch, there are multiple Bio CNG franchise opportunities available. Many private companies offer ready business models with support in plant installation, training, raw material sourcing, and buyer tie-ups.
This option suits entrepreneurs with moderate investment and interest in the renewable energy space.
Conclusion
The Bio CNG business is not just a profitable venture but a step toward a greener and cleaner India. With increasing demand for sustainable energy, strong government support, and abundant raw materials, this industry has a bright future.
If you're thinking about starting a business that benefits both you and the planet, then the Bio CNG business is the right path to explore.
0 notes
Text
Leading the Green Energy Revolution: Biogas Plant Manufacturers in India – GasProcessing
As the world shifts toward sustainable energy, biogas has emerged as a powerful solution for clean and renewable fuel. In India, where agricultural waste, food waste, and organic materials are abundant, biogas technology offers a game-changing opportunity to reduce carbon emissions and generate energy. At the forefront of this movement are the top biogas plant manufacturers in India, with GasProcessing leading the way.
What is a Biogas Plant?
A biogas plant is a system that processes organic waste such as animal dung, food waste, or crop residue through anaerobic digestion, producing biogas (a mix of methane and carbon dioxide) and organic fertilizer. The methane-rich gas can be used for:
🔥 Cooking fuel
⚡ Power generation
🚛 Vehicle fuel (when upgraded to CBG – Compressed Biogas)
🇮🇳 Why India Needs Biogas More Than Ever
India generates millions of tons of organic waste every year. Converting this waste into energy not only solves the problem of waste management but also helps in:
✅ Reducing dependence on fossil fuels
✅ Lowering greenhouse gas emissions
✅ Empowering rural and agricultural communities
✅ Creating sustainable livelihoods
As one of the top biogas plant manufacturers in India, GasProcessing is proud to contribute to India’s clean energy mission.
Why Choose GasProcessing for Your Biogas Plant?
At GasProcessing, we bring decades of engineering expertise and a passion for sustainability to every project. Here’s why businesses, farms, and institutions across India trust us:
Turnkey Biogas Plant Solutions: From design to commissioning, we manage everything
Custom Plant Sizes: Scalable solutions from small rural plants to large industrial units
Advanced Digester Technology: High-yield biogas production using the latest anaerobic digestion systems
Quality Components: Durable gas holders, scrubbers, and feeding mechanisms
End-to-End Support: Training, maintenance, and operational assistance
Applications of Biogas Plants in India
Our biogas plants serve a wide range of sectors:
Dairy Farms – Manage cattle waste and generate electricity
Institutions – Handle food waste from canteens and hostels
Agriculture – Utilize crop residue for fuel and organic manure
Municipal Corporations – Convert solid waste into energy
Industries – Reduce energy costs and improve sustainability
💬 Client Success Story
A large dairy farm in Maharashtra partnered with GasProcessing to install a 500 m³ biogas plant. Within six months, they were generating enough biogas to power their milk chilling units and save 40% on electricity costs — while also producing nutrient-rich slurry for their crops.
Why We Stand Out Among Biogas Plant Manufacturers in India
In-house design and fabrication
Environment-first approach
Experienced team of engineers and biogas experts
Pan-India project execution
Commitment to quality, safety, and performance
Join the Clean Energy Movement with GasProcessing
If you're looking for reliable, innovative, and sustainable biogas plant manufacturers in India, look no further than GasProcessing. We are committed to turning waste into energy — one plant at a time.
Contact Us Today
Ready to build a biogas plant? Reach out to GasProcessing for customized solutions and expert guidance. Let’s power India’s future, sustainably.
Visit us https://gasprocessing.in/biogas/
0 notes
Text
Food Waste Composter: Good for Your Garden, Great for the Planet
Every year, millions of tons of food waste end up in landfills, releasing harmful greenhouse gases and taking up valuable space. But what if there was a simple, eco-friendly solution that could turn this waste into something valuable? Enter the food waste composter — a powerful tool that not only enriches your garden but also helps save the planet.
Turning Scraps into Soil Gold
A food waste composter takes everyday kitchen scraps like vegetable peels, fruit rinds, coffee grounds, and even leftover cooked food and transforms them into nutrient-rich compost. This natural fertilizer is often called “black gold” for gardeners because it improves soil structure, boosts microbial activity, and enhances water retention.
Why It's Great for the Planet
When food waste decomposes in landfills, it releases methane, a potent greenhouse gas far more damaging than carbon dioxide. Composting diverts this waste from landfills, significantly reducing methane emissions.
By composting food waste, you’re participating in a circular economy where waste is not discarded but returned to the earth to nourish new life. It’s a simple yet powerful way to lower your carbon footprint and promote environmental sustainability.
Types of Food Waste Composters
Home Compost Bins: Ideal for backyard composting using natural processes.
Electric Composters: Speed up composting indoors, perfect for urban homes.
Community Composting Units: Handle larger volumes, great for apartments or neighborhoods.
Industrial Food Waste Composters: Used by businesses like hotels, restaurants, and food processors.
Benefits Beyond the Garden
Reduces Household Waste: Less trash means lower waste collection costs and fewer landfill trips.
Odor Control: Composting properly reduces kitchen odors from rotting waste.
Educational Impact: The term educational impact teaches children and communities about sustainability and the value of waste reduction.
Get Started Today
Whether you have a sprawling backyard or a small kitchen, there’s a composting solution for everyone. Starting with a food waste converter is not only a win for your garden but a big step toward protecting the environment. Turn your scraps into soil, and let your garden and the planet thrive together.
1 note
·
View note
Text
Is Maintenance of a Biogas Plant Difficult or Expensive?

Website: https://www.grunerrenewable.com
⚙️ Introduction: Biogas Plants – Sustainable, but Practical?
As India turns towards sustainable energy, biogas plants have emerged as a powerful solution for waste management and clean fuel production. Whether you're a dairy farmer, panchayat, FPO, or commercial investor, a bio gas plant offers long-term value—from cooking fuel to electricity to Bio-CNG.
But one common concern remains: “Is maintaining a biogas plant difficult or expensive?”
The short answer: Not if done right.
In this article, we’ll break down the maintenance needs, cost factors, and smart strategies to keep a biogas plant running efficiently—especially in Indian conditions.
🧰 What Does Biogas Plant Maintenance Involve?
Biogas plant maintenance is largely about ensuring consistency in four key areas:
✅ 1. Feedstock Management
Supplying the right type and quantity of organic waste (e.g., cow dung, food waste, paddy straw)
Avoiding toxic materials like plastics or chemicals
Ensuring proper C:N ratio for efficient gas production
✅ 2. Digester Health
Checking pH levels, temperature, and retention time
Avoiding foam formation or solid scum
Preventing overloading of waste
✅ 3. Gas Collection & Storage
Inspecting pipelines, valves, and pressure gauges
Checking for gas leaks
Regular maintenance of gas scrubbers if Bio-CNG is being produced
✅ 4. Equipment Servicing
Maintaining mixers, agitators, and pumps (in large-scale plants)
Ensuring gensets or compressors are serviced as per schedule
Keeping motors and control panels clean and dry
💰 Is It Expensive? Understanding the Real Costs
Biogas plant maintenance is generally low to moderate in cost, especially when compared to diesel or LPG systems. Let’s break it down:
Maintenance Component
Cost Estimate (Small/Medium Plant)
Daily labor for cleaning/feed
₹150–300/day
pH test kits or sensors
₹200–₹500/month
Oil and filter changes (genset)
₹1,000–1,500 every 3–4 months
Digester desilting (annual)
₹5,000–₹10,000/year
Equipment service & spares
₹10,000–₹15,000/year (avg.)
✔️ Monthly Maintenance Estimate:
Small Plant (5–10 m³): ₹2,000–3,500/month Medium Plant (50–100 m³): ₹6,000–10,000/month
These costs can be further reduced through:
On-site training
Using digester slurry as organic fertilizer (saves ₹ on chemical fertilizers)
Preventive maintenance schedules to avoid breakdowns
🧑🔧 Is It Technically Difficult?
No. Most daily and weekly tasks can be done by a trained local worker or farmer with basic skills.
Tasks That Are Easy to Handle:
Feeding the digester at fixed intervals
Stirring or mixing feedstock (manually or with agitators)
Checking slurry outlet flow
Basic pH checks and temperature observation
When You Need Technical Support:
Gas pressure is abnormally low or high
Equipment like compressors or gensets need professional servicing
Unusual smells or visible gas leaks
Structural cracks in dome or tank
👉 At Gruner Renewable, we provide full O&M training and helpline support to minimize external dependencies.
✅ Tips to Reduce Biogas Plant Maintenance Hassles
Use consistent feedstock (same type every day)
Filter impurities before feeding (no plastic, hair, or metals)
Use solar dryers or shade to control slurry moisture
Schedule monthly checks for pipe leakage or blockage
Follow preventive maintenance of pumps and mixers
Also, using a co-digestion strategy (e.g., cow dung + food waste or paddy straw) can balance the microbial activity, improving plant stability and reducing issues like acidification.
🏡 Perfect for Rural and Decentralized Setups
For rural India, where LPG refills or diesel costs are high, biogas plants offer:
Reliable fuel supply
Low maintenance with training
No recurring commercial fuel purchase
Over 25,000 small and medium-scale biogas plants across India have proven that maintenance is manageable—even at the village level.
🧠 Final Thought: Simpler Than You Think, Smarter Than You Expect
So, is maintenance of a biogas plant difficult or expensive?
Not really—especially if planned properly. With the right training, minimal tools, and regular checks, even a small team can manage a biogas plant efficiently.
At Gruner Renewable, we provide:
End-to-end training for plant operators
Maintenance manuals and preventive care plans
Remote support and annual AMC services (optional)
👉 Learn more at www.grunerrenewable.com and start your journey to clean, self-sustained energy—without the maintenance headaches.
0 notes
Text
The Economic Benefits of Installing a Biogas Plant in 2025
In 2025, the demand for sustainable and cost-effective energy solutions continues to grow rapidly, driven by environmental concerns, rising energy costs, and a global shift towards renewable sources. Among the standout innovations gaining traction is the biogas plant—a powerful solution that transforms organic waste into clean energy. This technology not only addresses waste management but also offers substantial economic benefits for both residential and commercial users.

Understanding the Function of a Biogas Plant
A biogas plant is a system designed to convert organic waste materials—such as food scraps, agricultural residues, and animal manure—into biogas through the process of anaerobic digestion. During this natural decomposition process, microorganisms break down the waste in an oxygen-free environment, producing a mixture of methane and carbon dioxide. The methane-rich gas can then be used as a source of energy for cooking, heating, electricity generation, or even fuel for vehicles.
The byproduct of this process is a nutrient-rich slurry that serves as an organic fertilizer, promoting sustainable agriculture and reducing reliance on chemical alternatives. This dual output—energy and fertilizer—makes biogas technology a practical and highly beneficial investment in 2025.
Substantial Savings on Energy Costs
One of the most significant advantages of a biogas plant is its ability to reduce energy bills. By generating a steady supply of methane, users can replace conventional energy sources like electricity, natural gas, and liquefied petroleum gas. For agricultural operations, industries, and households with access to sufficient organic waste, this translates to significant monthly savings.
Given the continuing rise in fossil fuel prices, investing in a biogas plant allows long-term budget control. The energy generated can be used on-site, reducing dependency on external providers and shielding users from fluctuating market rates.
Reducing Waste Disposal Costs
Another major economic benefit comes from minimizing waste disposal expenses. Industries, restaurants, farms, and households often spend substantial amounts on waste management services. With a biogas system in place, organic waste is processed on-site, eliminating the need for third-party removal or landfill tipping fees.
In urban and rural settings alike, this benefit streamlines operations and promotes environmental responsibility. Over time, these savings can significantly offset the initial installation and maintenance costs associated with biogas plant construction.
Revenue Generation Opportunities
In addition to cost savings, a biogas plant can serve as a source of income. Excess biogas produced can be sold to neighboring homes, businesses, or even injected into the natural gas grid in areas where such infrastructure is supported. Moreover, the organic fertilizer byproduct is marketable to local farmers, especially as demand grows for eco-friendly farming practices.
For entrepreneurs and agribusinesses, this opens the door to new business models, from energy reselling to organic fertilizer production. As environmental regulations tighten and green energy incentives expand, revenue generation from biogas ventures will likely become even more accessible.
Government Incentives and Policy Support
In many regions, national and local governments offer incentives to encourage renewable energy adoption. These can include tax credits, grants, subsidies, and low-interest loans specifically geared toward biogas plant installation. In 2025, with global climate goals pressing on decision-makers, such incentives are expected to increase.
Investing in a biogas plant aligns with these policy goals, allowing owners to take advantage of available financial support and compliance benefits. This support reduces the financial barrier to entry, making the technology more accessible to farmers, rural communities, and small-scale industries.
Low Operating and Maintenance Costs
Compared to other renewable energy systems, biogas plants have relatively low operating and maintenance costs. Once the system is in place and optimized, it requires minimal human intervention. Regular feedstock input and occasional maintenance of mechanical components are typically the only routine tasks.
Furthermore, the materials used in biogas production—organic waste—are readily available and cost-free in most cases. This makes the system self-sustaining and budget-friendly, especially in agricultural settings where waste is constantly generated.
Enhancing Energy Security and Independence
Biogas technology contributes significantly to local energy security. By producing energy at the point of use, it minimizes exposure to geopolitical risks, supply chain disruptions, and market volatility associated with fossil fuels. For remote or off-grid communities, a biogas plant can be a reliable and decentralized solution that ensures constant power supply.
This independence reduces reliance on national grids and international energy sources, giving communities and industries more control over their energy use and future planning.
Supporting Job Creation and Local Economies
The expansion of biogas infrastructure promotes job creation, particularly in rural areas. From plant construction and maintenance to feedstock collection and fertilizer distribution, the industry generates employment across various skill levels.
Moreover, supporting a circular economy through waste-to-energy conversion stimulates local economies and attracts investments. It encourages innovation, entrepreneurship, and sustainable business practices that uplift communities while addressing energy and waste challenges.
Long-Term Return on Investment
Although the initial setup of a biogas plant requires capital, the long-term return on investment is both measurable and dependable. Cost savings, income generation, government incentives, and reduced dependency on external resources all contribute to a fast and sustainable payback period.
In many cases, the full investment can be recovered within a few years, after which the benefits continue to accumulate for decades. This financial viability makes it a strategic asset for farms, factories, cooperatives, and even residential complexes looking for durable energy solutions.
Contribution to a Circular and Green Economy
Beyond economic gain, investing in a biogas plant contributes to a cleaner and more circular economy. Organic waste, once viewed as a problem, is transformed into valuable resources. This aligns with the principles of sustainability, resource efficiency, and ecological balance—objectives that are increasingly demanded by governments, investors, and consumers.
As 2025 unfolds, businesses and individuals adopting biogas technology are not only improving their bottom line but also becoming key players in the transition toward a greener future.
Final Thoughts
A biogas plant is more than a tool for energy production—it is an economic engine that generates cost savings, new revenue streams, and broader societal benefits. In 2025, its value proposition has never been clearer. From reducing waste and energy bills to contributing to job growth and environmental sustainability, the technology stands out as a smart, future-proof investment.
With ongoing advancements and growing policy support, installing a biogas plant is not only a sound economic decision but a powerful step toward energy resilience and environmental stewardship.
1 note
·
View note
Text
Biogas Plant in Kerala: A Green Energy Initiative for Sustainable Development
Abstract
The biogas plant in Kerala is rapidly becoming an essential component of the state’s strategy for renewable energy and sustainable waste management. With Kerala facing challenges related to increasing organic waste and rising energy demands, the biogas plant in Kerala presents an eco-friendly solution that converts biodegradable waste into usable biogas and organic fertilizer. This article explores the relevance, application, and potential of the biogas plant in Kerala, emphasizing its environmental, economic, and social benefits.
Introduction
The biogas plant in Kerala has emerged as a sustainable model for addressing waste management and clean energy production. Given Kerala’s dense population, agricultural activities, and growing urban centers, the state produces significant amounts of organic waste daily. The installation of a biogas plant in Kerala offers an effective solution by recycling this waste into biogas, which can be used for cooking, electricity, and other energy needs, thereby promoting a circular economy and reducing dependence on fossil fuels.
Main Body
The adoption of the biogas plant in Kerala is driven by the state’s commitment to reducing greenhouse gas emissions and promoting renewable energy sources. Various government and private initiatives encourage households, institutions, and industries to install a biogas plant in Kerala to manage organic waste efficiently while producing sustainable energy. The tropical climate of Kerala, combined with a high generation of food and agricultural waste, makes the biogas plant in Kerala a viable and practical technology.

The government has played a pivotal role in promoting the biogas plant in Kerala by offering subsidies, technical guidance, and awareness programs. The Suchitwa Mission and Haritha Keralam initiatives actively promote the biogas plant in Kerala as a part of their integrated waste management systems. These efforts aim to improve waste disposal practices, minimize the use of landfills, and promote decentralized energy production through the biogas plant in Kerala.
Communities and institutions that have adopted the biogas plant in Kerala have reported reduced household energy costs and improved sanitation practices. The slurry produced as a byproduct of the biogas plant in Kerala serves as a high-quality organic fertilizer for agricultural purposes. As a result, the biogas plant in Kerala not only addresses energy and waste management issues but also contributes to sustainable agricultural development.
In rural areas, the biogas plant in Kerala has empowered small farmers by providing a reliable and low-cost energy source, which is especially useful for cooking and lighting. Urban centers have also embraced the biogas plant in Kerala through community-based models, where multiple households collectively process their organic waste and share the biogas output. This model has helped strengthen Kerala’s efforts to become a zero-waste state, positioning the biogas plant in Kerala as a cornerstone of environmental policy.

Conclusion
The biogas plant in Kerala exemplifies how simple yet innovative technologies can transform waste into a valuable resource, supporting both environmental sustainability and energy security. With increasing government support, public participation, and technological advancements, the biogas plant in Kerala is poised to become a widespread solution across the state. The future of waste management and clean energy in Kerala depends significantly on the adoption and integration of the biogas plant in Kerala into both rural and urban infrastructure.
0 notes
Text
Biogas in Kerala: Harnessing Renewable Energy from Organic Waste
Introduction to Biogas in Kerala

What is Biogas?
Biogas is a renewable energy source produced through the anaerobic digestion of organic materials such as food waste, animal manure, and agricultural residues. The process of breaking down these organic substances by microorganisms in the absence of oxygen results in the production of methane gas. This methane, which is the main component of biogas, can be used for cooking, heating, and electricity generation, making it a versatile and sustainable energy source.
In Kerala, with its vast agricultural sector, abundant organic waste, and focus on sustainability, biogas technology is gaining attention as an effective solution for generating clean energy.
The Role of Biogas in Kerala’s Renewable Energy Landscape
Kerala’s agricultural and livestock industries generate a considerable amount of organic waste, making the state an ideal location for biogas production. With large quantities of waste such as cow dung, poultry litter, and crop residues, the state can tap into these resources to produce biogas. Biogas plants can convert these organic materials into valuable energy, thus reducing the state’s dependency on fossil fuels.
In addition, Kerala’s large rural population and its reliance on traditional cooking fuels like firewood and kerosene create an opportunity to replace these harmful energy sources with cleaner, more sustainable alternatives like biogas.
Benefits of Biogas in Kerala
1.Sustainable Waste Management: One of the key benefits of biogas technology is its ability to address waste management issues. Kerala’s cities and rural areas often face challenges in managing organic waste. Biogas plants offer a solution by converting food waste, agricultural residue, and animal waste into energy, thus reducing landfill usage and minimizing harmful methane emissions.
2.Renewable and Clean Energy: By utilizing biogas, Kerala can reduce its dependence on non-renewable energy sources like LPG, firewood, and kerosene. The methane produced in biogas plants can be used as a clean cooking fuel, significantly lowering household energy costs and providing energy security in rural areas.
3.Reduction of Greenhouse Gas Emissions: Biogas production reduces the release of methane, a potent greenhouse gas, into the atmosphere. When organic waste is left to decompose in landfills, it emits large quantities of methane. By converting waste into biogas, Kerala can reduce the environmental impact of waste disposal and contribute to mitigating climate change.
4.Economic Opportunities: Biogas plants offer potential economic benefits, particularly in rural areas. Farmers can use biogas to meet their energy needs and reduce their dependency on expensive, non-renewable fuels. Moreover, the byproduct of biogas production, bio-slurry, can be used as an organic fertilizer, promoting sustainable agriculture and reducing the need for chemical fertilizers.
5.Energy Independence: Biogas technology provides Kerala with the potential for local energy production. By tapping into organic waste, the state can produce energy locally, reducing its reliance on imported fuels and contributing to a more self-sufficient energy system.
Government Initiatives Supporting Biogas in Kerala
The Kerala government has been active in promoting renewable energy solutions like biogas through various schemes and incentives. These initiatives aim to encourage the widespread adoption of biogas plants among households, farmers, and local communities.
1.Subsidies for Biogas Plants: The government provides financial incentives and subsidies for the installation of biogas plants. These subsidies help reduce the initial capital investment required, making it easier for households and rural communities to adopt biogas technology.
2.Public Awareness Campaigns: The Kerala government, in collaboration with various NGOs, has been working to increase awareness about the environmental and economic benefits of biogas. Educational campaigns aim to inform citizens about how biogas plants can improve waste management and provide clean energy.
3.Waste-to-Energy Projects: Several municipalities in Kerala, including Kochi and Thiruvananthapuram, have initiated waste-to-energy projects that incorporate biogas technology to process municipal solid waste. These projects help address urban waste challenges while generating renewable energy.
4.Support for Rural Development: Biogas initiatives are being integrated into Kerala’s rural development programs, where biogas plants are being promoted as a sustainable energy source for farmers. By using biogas for cooking and electricity, rural communities can reduce energy costs and improve their standard of living.
Challenges to Biogas Adoption in Kerala
Despite its potential, several challenges must be addressed for biogas to become a mainstream energy source in Kerala:
1.High Initial Costs: The cost of installing biogas plants can be a significant barrier, especially for low-income households. Although subsidies are available, the initial investment remains a challenge for many, particularly in rural areas where economic conditions may not be ideal.
2.Technical Expertise: Installing and maintaining biogas systems requires specialized knowledge. There is a need for skilled technicians to install and maintain biogas plants, and a shortage of such professionals in rural areas can hinder widespread adoption.
2.Space Constraints: In urban areas, limited space for installing biogas plants can be a barrier to their adoption. The infrastructure for collecting and processing organic waste in cities may also require significant improvements to ensure the effectiveness of biogas systems.
3.Sustainability and Maintenance: Ensuring the long-term sustainability of biogas plants is critical. Regular maintenance and proper operation are necessary for the efficient functioning of biogas systems, and without adequate support and education, many projects may fail to deliver on their potential.
The Future of Biogas in Kerala
The future of biogas in Kerala holds great promise. As awareness grows and technology improves, Kerala can become a leader in biogas adoption in India. The state’s rich agricultural resources, coupled with its commitment to environmental sustainability, make biogas a promising solution to its energy and waste management challenges.
Key factors for the successful integration of biogas technology include:
Expanding biogas plant installations, especially in rural areas.
Increasing investment in waste-to-energy infrastructure in urban centers.
Providing continuous training and support for biogas plant maintenance.
Encouraging public-private partnerships to scale up biogas production.
Conclusion
Biogas in Kerala represents a sustainable solution to some of the state’s most pressing challenges. By leveraging organic waste for energy production, Kerala can reduce waste, cut down on harmful emissions, and provide clean, renewable energy to its citizens. With government support, increased public awareness, and technological advancements, biogas can become a cornerstone of Kerala’s green energy future.
0 notes
Text
What Happens to Waste from Slaughterhouses?

Slaughterhouses play a crucial role in the food industry, providing meat for consumption. However, they also generate large amounts of waste, including blood, fat, bones, hides, feathers, and wastewater. Proper management of this waste is essential to prevent environmental pollution and ensure sustainability.
Types of Slaughterhouse Waste
Slaughterhouse waste can be categorized into the following types:
Solid Waste – This includes bones, hooves, hides, feathers, and undigested food from the animal’s stomach and intestines.
Liquid Waste – Blood, fats, and wastewater from cleaning processes fall into this category.
Gaseous Emissions – Byproducts processing plant such as rendering plants, hide processing unit, gelatine manufacturing unit (Ossein manufacturing unit) etc will release odour. In addition to that the decomposition of organic waste (be it liquid or solids described above) can release gases like ammonia, hydrogen sulfide, mercaptons, Volatile Organic Compounds (VOCs), etc. contributing to foul odours and air pollution.
Environmental Impact of Slaughterhouse Waste
If not managed properly, slaughterhouse waste can have significant negative effects on the environment:
Water Pollution – Wastewater rich in organic matter and pathogens can contaminate water sources, leading to health hazards.
Air Pollution – The odourous gas release from the above sources and the release of methane due to decomposing organic matter contribute to odour problems and air quality deterioration.
Soil Contamination – Improper disposal of solid and liquid waste can lead to soil pollution and disrupt ecosystems.
Slaughterhouse Waste Management Solutions
To mitigate environmental risks, various waste management techniques are employed:
1. Wastewater Treatment
Slaughterhouses generate large amounts of wastewater containing blood, fats, and organic matter. This water needs to be treated before being discharged into natural water bodies. Elixir Enviro Systems offers advanced wastewater treatment solutions that help in removing contaminants through biological and physical treatment processes, ensuring compliance with environmental regulations.

2. Rendering Process
Rendering is a common method used to convert animal by-products into useful materials like meat and bone meal, tallow, and gelatin. These products are then used in industries such as animal feed, soap manufacturing, and biodiesel production.
3. Anaerobic Digestion for Energy Recovery
Anaerobic digesters can be used to break down organic slaughterhouse waste, producing biogas that can be utilized for energy generation. This process helps in reducing greenhouse gas emissions while providing a renewable energy source.

4. Composting and Fertilizer Production
Organic slaughterhouse waste can be composted to create nutrient-rich fertilizers for agricultural use. This process not only helps in waste reduction but also promotes sustainable farming practices.
5. Odour Control Measures
Managing odours from slaughterhouses is essential to maintain a healthy working environment and minimize complaints from surrounding communities. Elixir Enviro Systems provides biofilters – Standard rate Biofilters, High rate biofilters, containerised biofilters etc, scrubbers - water scrubbers, Acid scrubbers, Alkali scrubbers, Bioscrubber etc, and other odour control technologies such as Biotrickling filters, thermal oxidisers, activated carbon filters etc that help neutralize foul smells efficiently.
The major odour releasing operations are
Rendering plants: The process where byproducts such as soft tissues and bones of the large animals are crushed, cooked and dried for further processing to byproducts such as meat-meal. In case of Poultry slaughterhouses, rendering will be used for feathers, soft tissues (intestines and others), head and feet to make the byproducts such as the chicken-meal, feather meal etc. These byproducts are generally used in the pet feed industry.
Bonemeal Plants: The process wherein only the bones of large animals are processed to produce crushed bones (sometimes gel bones) and bonemeal etc. The crushed bones & gel bones are used in gelatin manufacturing and the bonemeal is generally used as organic fertiliser. The warehousing (storage), cooking and the drying stage releases odour.
Hide processing units: In general, hide processing happens in two stages – salting stage and leather manufacturing stage(tannery). Generally the salting stage alone happens in the slaughterhouse premises and the leather processing happens at a different unit called Tannery. In the salting stage, the hides are kept one on top of the other with a good quantity of sea salt in between. After salting for several days, the same shall be transported to tannery for further processing to leather. This temporary storage itself will cause huge odour pollution and high TDS wastewater generation. The tannery is yet another process wherein the odour and wastewater pollution is huge.
Animal fat processing plant: Animal fat or tallow processing plant also releases odour and wastewater. The cooking phase and the storage stage generally release odour. The product is purified animal fats is used in generally in the pet feed industry and sometimes in soap manufacturing and some areas of the world it is used for direct consumption as well.
Gelatin manufacturing unit: The gelatin manufacturing happens in several stages – crushed bone (gel bone) manufacturing, Ossein manufacturing unit – where ossein and dicalcium phosphate is being produced and the final gelatin manufacturing unit. The product of each stage is the raw material to the next. Crushed bones and gel bones are used for ossein manufacturing, and this ossein is used in gelatin manufacturing.
For a detailed approach to managing exhaust air in poultry and meat processing facilities, check out our article: How to Treat the Exhaust Air from Poultry and Meat Processing Companies?
Regulatory Compliance and Best Practices

Governments and environmental agencies impose strict regulations on slaughterhouse waste management. Companies must comply with standards related to water discharge, waste disposal, and air quality to avoid legal penalties. Implementing best practices such as regular waste audits, efficient treatment systems, and sustainable waste disposal methods ensures environmental responsibility.
As of today, in India we do not have a concrete odour control law, but instead what we have is nuisance law, due to which many companies faces closure of their factories and are allowed to operate only with the proper odour pollution mitigation system. Elixir Enviro System has rescued many companies and brought them back to operation when many went to closure.
Elixir Enviro Systems' Services
Elixir Enviro Systems specializes in providing comprehensive environmental solutions for slaughterhouse waste management. Our services include:
Industrial Wastewater Treatment – Advanced treatment technologies for removing organic contaminants, fats, and pathogens from slaughterhouse wastewater
Odour Control Solutions – Elixir Enviro Systems provides biofilters – Standard rate Biofilters, High rate biofilters, containerised biofilters etc, scrubbers - water scrubbers, Acid scrubbers, Alkali scrubbers, Bioscrubber etc, and other odour control technologies such as Biotrickling filters, thermal oxidisers, activated carbon filters etc that help neutralize foul smells efficiently.
Anaerobic Digesters – Sustainable solutions for biogas production from organic waste.
Sludge Handling Equipment – Efficient processing and disposal of sludge generated in wastewater treatment and from anaerobic digestion.
Monitoring Equipment – Real-time monitoring systems to ensure compliance with environmental regulations.
Consultancy Services – Expert guidance on waste management strategies and regulatory compliance.
Onsite Wastewater Quality Assessment – Analysis and optimization of wastewater treatment processes.
Onsite Odour Assessment – Analysis and optimization of odour control units.
Pilot Studies for Wastewater Treatment – Customized pilot projects to evaluate and enhance treatment efficiency.
Conclusion
Slaughterhouse waste, if not managed properly, can have severe environmental consequences. However, with efficient treatment technologies, resource recovery methods, and odour control solutions, it is possible to turn waste into valuable resources. Elixir Enviro Systems specializes in providing cutting-edge solutions for industrial wastewater treatment, odour control, and sustainable waste management, ensuring a cleaner and greener future.
#slaughterhouse 5#environment#odourcontrol#elixirenvirosystems#blog#sustainability#airpollution#anaerobicdigestion#biofilter#ecofriendly#wastewatertreatment
0 notes
Text
Environmental Benefits of Food Waste Biogas Plants
Introduction
Food waste is a growing global issue, contributing to environmental pollution, greenhouse gas emissions, and landfill overflow. However, food waste biogas plants provide an innovative and sustainable solution by converting organic waste into renewable energy. This article explores the key environmental benefits of food waste biogas plants and their role in promoting a greener future.
Reduction of Greenhouse Gas Emissions Food waste decomposition in landfills produces methane, a potent greenhouse gas that is significantly more harmful than carbon dioxide. Biogas plants capture and utilize methane for energy production, thereby preventing its release into the atmosphere. This process helps mitigate climate change and reduces the carbon footprint of waste management.
Waste Diversion from Landfills Landfills are a major source of pollution and contribute to soil and water contamination. By diverting food waste to biogas plants, the pressure on landfills is reduced, extending their lifespan and minimizing environmental hazards. This practice also reduces the release of leachate, a toxic liquid that contaminates groundwater.
Production of Renewable Energy Food waste biogas plants generate biogas, which can be used as a clean energy source for electricity, heating, and cooking. Unlike fossil fuels, biogas is renewable and does not contribute to the depletion of natural resources. This transition to sustainable energy reduces dependence on non-renewable sources and supports the global shift towards green energy solutions.
Reduction of Air Pollution Traditional waste disposal methods, such as incineration, release harmful pollutants into the air, including carbon monoxide and particulate matter. Biogas plants provide a cleaner alternative by processing waste anaerobically, minimizing air pollution and improving air quality.
Soil and Water Protection Biogas plants produce nutrient-rich digestate as a byproduct, which can be used as an organic fertilizer. Unlike chemical fertilizers, digestate enhances soil health, improves water retention, and reduces soil degradation. Additionally, by preventing landfill overflow, biogas plants protect water bodies from contamination caused by leachate runoff.
Circular Economy and Sustainable Waste Management Food waste biogas plants support the principles of a circular economy by transforming waste into valuable resources. Instead of discarding food waste, it is repurposed for energy production and soil enrichment. This sustainable waste management approach promotes responsible consumption and waste reduction. Conclusion Food waste biogas plants play a crucial role in addressing environmental challenges by reducing greenhouse gas emissions, diverting waste from landfills, producing renewable energy, and protecting soil and water resources. As the world seeks sustainable solutions for waste management, biogas technology emerges as an essential tool for a cleaner and greener future. Governments, industries, and communities must collaborate to expand the adoption of food waste biogas plants and maximize their environmental benefits.
0 notes
Text
How Biogas in Kerala is Turning Waste into Wealth

Introduction: As waste management becomes a growing concern, biogas in Kerala is proving to be a game-changer. This clean, renewable energy source is helping the state turn food and organic waste into a valuable resource.
The Working of a Biogas Plant: Biogas plants decompose organic waste — like food scraps, vegetable peels, and animal manure — into methane gas and organic fertilizer. Kerala’s high biodiversity and agricultural background make it an ideal place for such systems.
Key Drivers of Biogas Growth in Kerala:
Urban households adopting compact biogas units
Farmer cooperatives using agricultural waste for energy
Municipalities setting up centralized biogas plants
Impact on Society and Environment:
Clean cooking fuel for thousands of homes
Less landfill waste, reduced soil and water contamination
Affordable organic fertilizer for local farmers
Government Initiatives: The Kerala State Biodiversity Board and Suchitwa Mission are actively promoting biogas adoption through training, subsidies, and awareness programs.
Conclusion: By adopting biogas in Kerala, the state is leading by example in building a circular economy — where waste is no longer a burden but a source of clean energy and prosperity.
#biogas in kerala#biogas plant for home#incinerator manufacturers in kerala#portable biogas plant for home#incinerators in kerala#biogas#kerala
0 notes
Text
Biogas Generator: A Sustainable Solution for Clean Energy
In the quest for renewable and eco-friendly energy sources, biogas generators have emerged as a practical and efficient option. These systems convert organic waste into valuable energy, reducing reliance on fossil fuels and minimizing environmental impact. In this article, we’ll explore what a biogas generator is, how it works, its benefits, and why it’s becoming increasingly popular worldwide.
What is a Biogas Generator?
A biogas generator is a device that produces biogas through the process of anaerobic digestion, where microorganisms break down organic materials such as agricultural waste, food scraps, manure, and sewage in the absence of oxygen. The resulting biogas primarily consists of methane (CH4) and carbon dioxide (CO2), which can be used as a clean fuel for cooking, heating, electricity generation, and even vehicle fuel.
How Does a Biogas Generator Work?
The biogas generation process occurs in several key steps:
Feedstock Collection: Organic waste materials are collected and fed into the biogas digester.
Anaerobic Digestion: Inside the digester, bacteria break down the waste in an oxygen-free environment, producing biogas.
Gas Collection: The biogas is captured in a gas holder attached to the digester.
Energy Conversion: The captured biogas is burned in a generator or stove to produce electricity, heat, or cooking fuel.
Digestate Use: The leftover material, called digestate, is a nutrient-rich fertilizer that can enhance soil health.
Benefits of Using a Biogas Generator
Renewable Energy Source: Biogas is produced from waste materials, making it a sustainable energy option.
Reduces Greenhouse Gas Emissions: By capturing methane that would otherwise escape into the atmosphere, biogas generators help combat climate change.
Waste Management: Converts organic waste into energy, reducing landfill use and environmental pollution.
Cost Savings: Lowers energy costs by providing a local, inexpensive fuel source.
Soil Fertilization: The digestate byproduct improves agricultural productivity as an organic fertilizer.
Energy Independence: Useful in rural areas where grid electricity is limited or unavailable.
Applications of Biogas Generators
Electricity Generation: Small and large-scale generators power homes, farms, and businesses.
Cooking Fuel: Biogas stoves offer a cleaner alternative to wood or charcoal.
Heating: Biogas can be used in boilers and heaters for residential or industrial purposes.
Vehicle Fuel: Purified biogas (biomethane) can replace natural gas in vehicles.
Choosing the Right Biogas Generator
When selecting a biogas generator, consider the following factors:
Feedstock Availability: Ensure a steady supply of organic waste.
Energy Needs: Match the generator size to your household or industrial power requirements.
Budget: Balance upfront costs with long-term savings.
Maintenance: Opt for systems with accessible maintenance and local support.
Future of Biogas Generators
As global demand for sustainable energy grows, biogas generators are poised to play a vital role in the energy transition. Innovations in digester technology, combined with supportive policies, are making biogas more accessible and cost-effective for communities worldwide.
Conclusion
A biogas generator is more than just a machine—it’s a pathway toward cleaner energy, effective waste management, and a greener future. Whether for small-scale home use or larger industrial applications, investing in biogas technology can deliver environmental and economic benefits. Embrace the power of biogas today and contribute to a sustainable tomorrow.
0 notes