#flexor digiti minimi
Explore tagged Tumblr posts
Text
Note Cards (February 2024)
2nd Law and Acceleration
3' Untranslated Region
3rd Cuneiform Facet Shape
4th Rib and Age
18-Aldocorticosterone
30S Initiation Factors
Actions of Adductor Magnus
Age and Cranial Sutures
Ancylostoma duodenale Pathogenesis
Anthropological Linguistics
Brachialis OIA
Breeding Isolates
Causes of Negative Nitrogen Balance
Chemokines
Components of Hill Plots
Derivatives of Oxaloacetate
Echinococcosis
Endocrinology
Femoral Popliteal Surface
Fibularis Brevis
Flexor Digiti Minimi Brevis OIA
H. erectus at Ceprano Site
IgE
Ilex verticillata Names
Intermediate Filament
LCL vs MCL
Malate Dehydrogenase 1
Nail Matrix
Neanderthal Metabolism
Obturator Nerve Muscles
Parts of Epiphyses
Peptide Bond Structure
Primary vs Secondary Metabolites
sanguino-
Selective Pressures
Siding Metacarpal 3
Skull of Arago 21
Steps of Whole-Genome Shotgun Sequencing
Strongyloides stercoralis
Structure of α-Helix
T. Dale Stewart
T. trichiuria Appearance
Talus - Plantar View
Taphonomy
Teres Minor
Transcriptional Fusion
Trichuris trichiuria Pathogenesis
Vena Cava Inferior
venulo-
Zygomatic - Lateral View
.
Patreon
#studyblr#notes#studying#masterlist#study masterlist#master list#study master list#studyblr resources#study resources#learning#learning resources#school#school resources#free learning#science#academics#academia#learning science#mcat resources#mcat notes#mcat studyblr#mcat masterlist#resource masterlist#scienceblr#medblr
20 notes
·
View notes
Text
Sole Of Foot
0 notes
Text
Sole Of Foot
0 notes
Note

why do you want to draw the hand muscles, which in brief are the lateral volar consisting of thenar (opponens pollicis, flexor pollicis brevis, abductor pollicis brevis) and adductor pollicis, the medial volar consisting of hypothenar (opponens digiti minimi, lexor digiti minimi brevis, abductor digiti minimi) and palmaris brevis, the intermediate consisting of lumbrical and interossei (dorsal and palmar), and the fascia (posterior: extensor retinaculum, extensor expansion; anterior: flexor retinaculum, palmar aponeurosis)
Hand muscles
go away
7 notes
·
View notes
Text
Which foot exercises activate the intrinsics?
So, your goal is to strengthen the intrinsics. What exercise is best? Probably the most specific one, right? Well....maybe. These 4 exercises seem to all hit them.
This study looked at the muscle activation of the abductor hallucis, flexor digitorum brevis, abductor digiti minimi, quadratus plantae, flexor digiti minimi, adductor hallucis oblique, flexor hallucis brevis, and interossei and lumbricals with the short foot, toe spreading, big toe extension and lesser toes extension exercises with T2 weighted MRI post exercises (perhaps not the best way to look at it) and shows they all work to varying degrees.
"All muscles showed increased activation after all exercises. The mean percentage increase in activation ranged from 16.7% to 34.9% for the short-foot exercise, 17.3% to 35.2% for toes spread out, 13.1% to 18.1% for first-toe extension, and 8.9% to 22.5% for second- to fifth-toes extension."
Gooding TM, Feger MA, Hart JM, Hertel J. Intrinsic Foot Muscle Activation During Specific Exercises: A T2 Time Magnetic Resonance Imaging Study. Journal of Athletic Training. 2016;51(8):644-650. doi:10.4085/1062-6050-51.10.07.
link to full text: https://www.ncbi.nlm.nih.gov/pmc/articles/PMC5094843/
#foot#exercise#exercises#rehab#intrinsic#muscles#quadratus plantae#flexor hallucis brevis#adductor hallucis#lumbricals#abductor digiti minimi
3 notes
·
View notes
Text
MRI SUMMARY:
** IMPRESSION **:
1. High-grade near complete chronic tear of the anterior talofibular ligament.
2. High signal or edema at the lateral fibular tip, consider contusion or stress changes.
3. Acute grade 2 mild sprain of the proximal deep deltoid ligament/deep tibiotalar ligament from the medial malleolus attachment.
4. 6 x 4 mm chondral fissuring with subchondral cystic changes in the anterior central tibial plafond.
5. Small tibiotalar and posterior subtalar joint effusion.
6. Mild fatty atrophy of the flexor digiti minimi muscle likely from chronic denervation changes.
---
i know what, like, some of those words mean by themselves, but have a podiatry appointment wednesday morning (virtual) who will hopefully explain it in not-a-doctor terminology and figure out options. but hey, diagnoses!
2 notes
·
View notes
Text

Location and Function of the Feet Muscles
Feet muscles play a great role in enhancing movement, and as shown in the diagram below, the feet muscles can be classified into superficial layer, deep, and deeper layer. According to my view, I believe that feet works almost the same as fingers and being controlled with the same mechanism, for instance, the movement of the toes is powered by the extensor and flexor muscles, furthermore, the muscles plays a sententious balancing role of the feet. Most of the muscles used in foot’s movement are connected to the back of the knee, and just as shown in the image below, some muscles that affect the foot’s movement include; flexor digitorum brevis, abductor halluces, abductor digiti minimi, and calcaneus located within the superficial layer. Within the deep layer there are lumbricals, flexor halluces longus, and flexor digitorum longus. Finally, the deeper layer of the foot has abductor halluces, abductor digiti mini, quadratus plantae, flexor digiti mini brevis, flexor halluces brevis, and abductor halluces.
Image 1: Location of the feet muscles
Retrieved from: https://www.custompilatesandyoga.com/flexor-hallucis-brevis-flexor-digitorum-brevis-learn-your-muscles/
The online article “Learn your muscles”by Sarah Stockett (2019) classifies the function of the feet muscles into two major categories, that is;
Flexor Hallucis Brevis: within the foot this muscle extends from the medial portion of the planter surface within the cuboid bone, and the cuboid bone is situated almost outside of the foot. Basically, the function of this muscle according to the article is the flexion of the toes, specifically the big toe (Custom Pilates & Yoga, 2019).
Flexor Digitorum Brevis: Generally, this muscle stems from two different places, that is; medial process of the tuberosity of the calcaneus and the middle section of the internuscular septa and plantar aponeurosis (Custom Pilates & Yoga, 2019). Just like its name, the flexor halluces brevis is responsible for the flexing of metatarsophalangeal joint of the big toe.
Reference
Custom Pilates and Yoga. (2019). Flexor Hallucis Brevis and Flexor Digitorum Brevis: Learn Your Muscles - Custom Pilates and Yoga. [online] Available at: https://www.custompilatesandyoga.com/flexor-hallucis-brevis-flexor-digitorum-brevis-learn-your-muscles/ [Accessed 17 Aug. 2019].
2 notes
·
View notes
Video
tumblr
Hypothenar compartment:
Opponens digiti minimi
Originates on the hook of the hamate and the flexor retinaculum
Inserts on the medial side of the fifth metacarpal
Opposes digit 5.
Flexor digiti minimi brevis
Originates on the hook of the hamate and the flexor retinaculum
Inserts on the medial side of the base of the proximal phalanx of digit 5
Flexes digit 5.
Abductor digiti minimi
Originates on the pisiform (and, in some cases, from the tendon of flexor carpi ulnaris)
Inserts near flexor opponens digiti minimi on the base of the proximal phalanx of digit 5
Abducts digit 5.
Visit drawittoknowit.com to learn more about our vast collection of medical science tutorials! Save 15% with code: SAVE15
#hypothenar#pinkyfinger#digit 5#digitabduction#muscles#musculoskeletal#hands#anatomy#handanatomy#handmuscles#abductor digiti minimi#medicalschool#medstudyblr#gross anatomy#studyanatomy#anatomystudyblr#anatomytutorial#anatomyvideo#anatomylab#occupationaltherapy#physicaltherapy#student doctor#ditki#pisiform#hamate#ulnar
5 notes
·
View notes
Photo
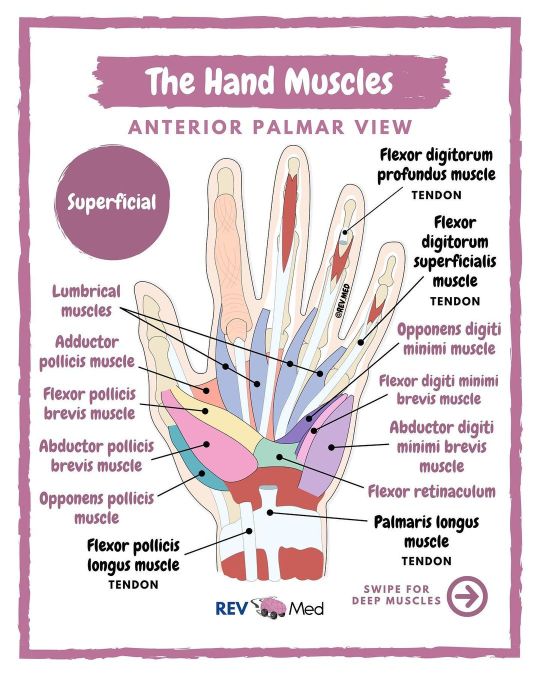
Hand Muscles brought to you by @rev.med ✋🏽 Also notes here ⤵️ 🧠 Tell us below in the comments - which class are you currently struggling with? ✅ Overview Today: Intrinsic muscles, which means they are located within the hand, and responsible for fine motor functions of the hand. See if you want to really memorize and know them.. then follow this method: 1️⃣ Thenar (thumb) muscles 2️⃣ Hypothenar (pinky) muscles 3️⃣ Other muscles: Interossei, palmaris brevis & Lumbricals @rev.med ✅ Intrinsic Muscles ✋🏾 1️⃣ Thenar (Thumb) Muscles All Innervated by Median nerve - Except Adductor Pollicis Muscle *Adductor pollicis muscle (Ulnar nerve) Insertion - Both attach into base of proximal phalanx of the thumb Action - Adductor of the thumb *Flexor pollicis brevis muscle Insertion - Base of the proximal phalanx of thumb Action - Flexes MCP joint of the thumb *Abductor pollicis brevis muscle Insertion - Lateral side of proximal phalanx of thumb Action - Abducts the thumb *Opponens pollicis muscle Insertion - Lateral margin of the first metacarpal of thumb Action - Opposes thumb, medially rotates and flexes metacarpal on the trapezium @rev.med 2️⃣ Hypothenar (Pinky) muscles All innervated by Ulnar nerve *Abductor digiti minimi brevis muscle Insertion - Base of proximal phalanx of little finger Action - Abducts little finger *Flexor digiti minimi brevis muscle Insertion - base of proximal phalanx of little finger Action - Flexes MCP joint of little finger *Opponens digiti minimi muscle Insertion - Medial margin of 5th metacarpal Action - Rotates metacarpal of little finger towards palm, producing opposition. 3️⃣ Other muscles *Lumbricals (4) - Index & middle fingers innervated by median nerve. Little and ring finger innervated by ulnar nerve. *Interossei (2) - Dorsal and palmar interossei innervated by ulnar nerve *Palmaris Brevis muscle - innervated by ulnar nerve @rev.med @rev.med #handmuscle #REVMED #REVupyourbrain #REVmedicine https://www.instagram.com/p/CTclvrwM5Tu/?utm_medium=tumblr
1 note
·
View note
Text
Foot/Ankle - Muscles
Layer 1 - most outside

outside licorice: abductor digiti minimi
middle licorice: flexor digitorum brevis
inside licorice: abductor hallucis
Layer 2 - some inside

thick middle ankle licorice: quadratus plantae
smaller near ball-of-foot licorice: lumbricals
Layer 3 - more inside

outside swedish fish: flexor digiti minimi brevis
across middle toes swedish fish: adductor hallucis (transverse)
thick swedish fish near big toe: adductor hallucis (oblique)
v-shape big toe swedish fish: flexor hallucis brevis with sesamoids
Layer 4 - innermost

inside the balls of foot area: interossei muscles
0 notes
Photo

Table des matières
Abstract 2
Keywords: 2
Introduction.
I./ Who was Homo Sapiens?.
II./ the long-distance fast bipedal running mutations.
III./ Ritualization of Impregnation, Pregnancy, and Delivery.
IV./ The Representation of Women.
V./ Human Articulated Language.
FIRST ARTICULATION.
SECOND ARTICULATION.
THIRD ARTICULATION.
Summary.
Conclusion.
Bibliography of Direct References.
WOMEN’S ROLE AND POSITION IN THE EMERGENCE OF HOMO SAPIENS Dr. Jacques COULARDEAU[1]
Abstract
Homo Sapiens (HS) started emerging around 300,000 BP. HS, a long-distance fast bipedal runner had a 29-year life expectancy. The ensuing physiological mutations caused the birth of long-dependent children. Their side-effect was enhanced vocal articulation. Linguistic phylogeny produced language with three time-ordered articulations: 1- rotation vowels-consonants into roots; 2- space- and time-categorization of roots into stems; 3- functional and temporal specifications of stems into fronds. Full communicational discursive syntax over 200,000 years and migrations out of Black Africa at each stage.
Between 13-29, women were pregnant every 18 months to raise at least three individuals to full procreational adult age. Women enjoyed a special division of labor to care for children for 3-5 years each.
This required observing menstrual and pregnancy cycles to guarantee impregnation, safe pregnancy, and delivery. These cycles are close to moon cycles: menstrual cycle = 1 moon cycle; pregnancy cycle = 10 moon cycles. Marshack rightly studied cycles but missed their menstrual dimension pinpointing fertility. Then we do have moon cycles till birth.
Women henceforth developed as spiritual members in their communities, hereinafter their place in the production of symbolic cave and mobiliary art. The spiritual dimension of such symbolism must heavily be centered on women.
Around 45,000 BCE all over the world, HS communities who had migrated out of Black Africa between 250,000 and 70,000 BP developed women-centered symbolism for the first time on durable media, though male-centered hunting weapons and tools had been produced even by previous Hominins.
Keywords: Linguistic Phylogeny; Homo Sapiens Emergence; Women’s Position; Menstrual Cycle; Durable Media; Symbolism.


FULL AND UNABRIDGED ARTICLE AT WOMEN’S ROLE AND POSITION IN THE EMERGENCE OF HOMO SAPIENS https://www.academia.edu/44383032/WOMEN_S_ROLE_AND_POSITION_IN_THE_EMERGENCE_OF_HOMO_SAPIENS
INTRODUCTION
I will only consider the place of women in the emergence of homo sapiens in this presentation keeping the sexual division of labor for the raising of children for the face-to-face presentation
“We are, however, here concerned only with that kind of selection, which I have called sexual selection. This depends on the advantage which certain individuals have over other individuals of the same sex and species, in exclusive relation to reproduction.”
But Darwin is centered on animal species, and a lot of insects and fish, not human species or higher mammal species, though he seems to approach the Homo Genus with the following quotation when envisaging this sexualized mate choice within the concept of pairs of partners (same reference, Part I, p. 263):
“Such pairs would have an advantage in rearing offspring, more especially if the male had the power to defend the female during the pairing-season, as occurs with some of the higher animals, or aided in providing for the young.”
This bipedal upright position is thus typical of the Homo species (plural) and that’s the difference with apes, including the top ones who are still able to use their grasping feet to climb in trees and who are able to run with the help of their arms and hands, which Hominins normally do not do, certainly from Homo Erectus onward.
But Homo Sapiens goes one stage further than all other Hominins: they became long-distance bipedal fast runners when they got out of the forest and the protection of trees to develop in the savanna, and their whole bodily structure was transformed by this fundamental evolution, first of all, brought to the species by the mutation of the foot, seen as follows.

Fig. 1. Salient features of the human foot, and the windlass mechanism in action. (A) A medial view of the human foot bones highlighting the pronounced longitudinal arch (LA, dashed line) and a schematic illustration of the Cal-Met angle that we used as a measure of dynamic arch compression (the angle formed between the calcaneus and metatarsal segments of the foot model, as defined in ref. 43). (B) Superior view of the human foot bones with a depiction of how the human hallux (bold outline) is greatly adducted from the opposable hallux found in fossil remains of our hominin ancestors (e.g., dashed outline). (C) A plantar view of the human foot showing the largest superficial PIMs that span the LA and MTP joints: Abductor hallucis (AH) and FDB. The PIMs also include abductor digiti minimi, quadratus plantae, flexor hallucis brevis, the lumbricals, and adductor hallucis (17), which have not been included here for clarity. (D) Depicts the windlass mechanism in action from mid to late stance in human walking. From left to right, the foot rotates about the MTP joints, tensioning the plantar aponeurosis (PA) and raising the LA (decreasing the Cal-Met angle) before the toes are plantar-flexed as the PA recoils just before toe-off.
(“The functional importance of human foot muscles for bipedal locomotion” Dominic James Farris, Luke A. Kelly, Andrew G. Cresswell, and Glen A. Lichtwark, Published online January 17, 2019.)
[1] University Paris I, Panthéon-Sorbonne, Paris, France, [email protected], 33+(0)7 88 84 22 57
0 notes
Photo


Meiwo science co ltd has send the superficial muscles of upper limb and deep blood vessels and nerves of upper limb human plastinated specimens to Malaysia medical university. The superficial muscles of upper limb human plastinated specimen shows deltoid, biceps brachii, brachialis, musculus subscapularis, pectoralis major, brachioradialis, flexor carpi radialis, palmaris longus, flexor carpi ulnaris, pronator supraspinatus muscle, infraspinatus, teres minor, teres major, musculus triceps brachii, extensor carpi radialis longus, extensor carpi radialis brevis, extensor digitorum, extensor digiti minimi, extensor carpi ulnaris, musculus anconeus, abductor pollicis longus, extensor pollicis brevis, extensor retinaculum, flexor retinaculum, abductor pollicis brevis, flexor digiti minimi brevis, lumbrical.


The deep blood vessels and nerves of upper limb plastinated specimen shows blood vessels, median nerve, ulnar nerve, radial nerve, superficial branch of radial nerve, flexor digitorum profundus, deep branch of ulnar nerve, common palmar digital nerves, axillary nerve, posterior antebrachial cutaneous nerve, teres minor, musculus triceps brachii, posterior interosseous nerve, dorsal branch of ulnar nerve, anterior interosseous nerve, etc.
0 notes
Photo

FLEXOR DIGITORUM BREVIS & ABDUCTOR DIGITI MINIMI MUSCLE PAIN ⠀ [PATHOLOGY AND SELF-TREATMENT] ⠀ For the anatomy of the flexor digitorum brevis (FDB) and the abductor digits minimi (ADM) muscles check my previous posts! ⠀ If these muscles are tense or carriy trigger points (TP’s), it can cause various ailments and pains. ⠀ Tensions in the FDB and ADM often lead to foot pain and local sensitivity to pressure. TP“s can trigger pain in the area of the forefoot. ⠀ Additional symptoms: ▪️Metatarsal head pain ▪️Plantar midfoot pain ⠀ Self-massage of the FDB and ADM with a @Blackroll Ball 08: ▪️Place the Blackroll Ball under your foot in sitting or standing position. ▪️Now roll the ball in the area of the FDB (plantar, middle of the foot) and ADM (plantar, outside of the foot), use the weight of your leg for pressure. You may let your heel rest on the floor. ▪️Execute short and slow movements over the entire length of the muscles and look for painful tensions & TP’s. ▪️Once you find one, move a few times from just before to just behind the painful spot until you feel it eases in the tissue. ⠀ Check and subscribe my YouTube channel for more information about treatment and exercises: www.youtube.com/stefanduell ⠀ #anatomy #flatfeet #footpain #foot #fascia #soccer #biomechanics #biotensegrity #running #football #functionalanatomy #functionalrehab #sprint #yoga #bigtoe #turftoe #bunion #chiropractic #massage #physicaltherapy #acupuncture #dryneedling #arch #yogaanatomy #strongfeet #tensegrity #footarch #physiotherapy #osteopathy #sport https://www.instagram.com/p/B_j_LyMptc2/?igshid=1wjynf8qhwy5j
#anatomy#flatfeet#footpain#foot#fascia#soccer#biomechanics#biotensegrity#running#football#functionalanatomy#functionalrehab#sprint#yoga#bigtoe#turftoe#bunion#chiropractic#massage#physicaltherapy#acupuncture#dryneedling#arch#yogaanatomy#strongfeet#tensegrity#footarch#physiotherapy#osteopathy#sport
2 notes
·
View notes
Photo

Bridgman hand studies pt. 19 1. Abductor pollicis 2. Flexor brevis pollicis 3. Adductor transversus pollicis 4. Lumbriacles 5. Annular ligament 6. Abductor minimi digiti 7. Flexor minimi digiti
8 notes
·
View notes