#finalmbbs
Explore tagged Tumblr posts
Photo
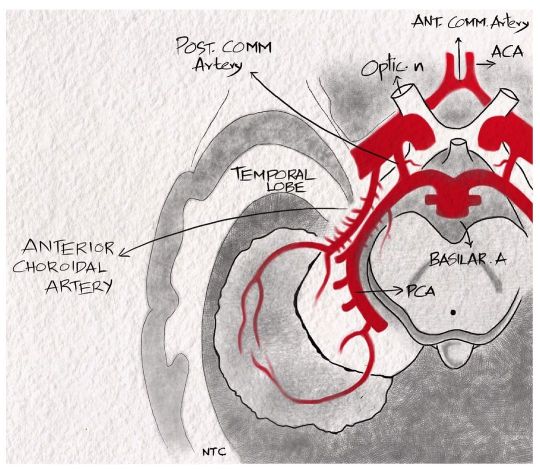
Anterior choroidal artery For discussion of this image, follow episode seven of ‘Clinical neurology with KD’ in Apple podcast, Spotify or Google podcast. The anterior choroidal artery is a branch of distal internal carotid artery. It passes posterolaterally and supplies the posterior two-thirds of the posterior limb of the internal capsule, optic tract, lateral geniculate body, optic radiation, amygdala, uncus, adjacent medial temporal lobe, posterior paraventricular corona radiata and a small supply to the thalamus. The symptoms produced by the anterior choroidal artery infarct include hemiparesis due to the posterior limb of internal capsule involvement, hemianopia due to the lateral geniculate body involvement and hemianesthesia due to thalamic supply. A middle cerebral artery infarct can cause the same triad, but the patient will be sicker and have cortical features like aphasia or neglect. There are no cortical features with an anterior choroidal artery infarct. #neurologyteachingclub #clinicalneurology #mbbs #medicineresidency #dnbmedicine #neetpg #neetsuperspeciality #finalmbbs #anteriorchoroidalartery #internalcarotidartery #circleofwillis #neuroanatomy #neurologypodcast #teachingneuroimages #nejm #lancet https://www.instagram.com/p/CZeKb58Pdub/?utm_medium=tumblr
#neurologyteachingclub#clinicalneurology#mbbs#medicineresidency#dnbmedicine#neetpg#neetsuperspeciality#finalmbbs#anteriorchoroidalartery#internalcarotidartery#circleofwillis#neuroanatomy#neurologypodcast#teachingneuroimages#nejm#lancet
1 note
·
View note
Text
Mai chahu mai chahu
Dil se mai ye chahu
Ye Dharti abhi phat jaaye
Aur mai isi me samaa jaau
#finalmbbs
#dragon tales
0 notes
Photo

One can only hope & pray! ✌ #lastnight #finaltheorypaper #hopefullyso #itsbeenacrazytime #definitelychangedme #finalmbbs #okiamoutofhashtags (at Beliaghata Building More)
#definitelychangedme#itsbeenacrazytime#finaltheorypaper#okiamoutofhashtags#finalmbbs#lastnight#hopefullyso
0 notes
Photo

#Today #finalmbbs #predicitingthefutureofmedstudentseverywhere #alcoholics #LOL #marchingfavabeans
0 notes
Photo

Parinaud's syndrome. For full discussion of the image hear ‘Clinical neurology with KD’ 🎙podcast episode 9. The link is given in the profile. A dorsal rostral midbrain lesion causes it. The vertical gaze palsy is due to the involvement of riMLF and the Interstitial nucleus of Kajal in the thalamo-midbrain junction. The lid retraction and convergence retraction nystagmus are due to the loss of supranuclear inhibition to the third nerve nucleus. The light near dissociation is due to damage of the pretectal nucleus or the decussating fibres of the pretectal nucleus in the posterior commissure. The pupillary reflex will be absent, while the accommodation reflex will be present. The accommodation reflex is preserved because the accommodation pathway enters the Edinger- Westphal nucleus more ventrally. #clinicalneurologywithkd #neurologyteachingclub #neurologypodcast #NTC #neurology #neurosciences #neuro #clinicalneurology #medicine #clinicalmedicine #kdpodcast #mbbs #medicos #doctors #neuroanatomy #casediscussion #medicineresidents #residency #medschool #futureneurologist #neuroimages #NEET #finalmbbs #neetpg #neetsuperspeciality #neetmedicine #eanneurology #nejm #aanbrain #neuroimage https://www.instagram.com/p/CcdZWYVvJfE/?igshid=NGJjMDIxMWI=
#clinicalneurologywithkd#neurologyteachingclub#neurologypodcast#ntc#neurology#neurosciences#neuro#clinicalneurology#medicine#clinicalmedicine#kdpodcast#mbbs#medicos#doctors#neuroanatomy#casediscussion#medicineresidents#residency#medschool#futureneurologist#neuroimages#neet#finalmbbs#neetpg#neetsuperspeciality#neetmedicine#eanneurology#nejm#aanbrain#neuroimage
3 notes
·
View notes
Photo

Today(06-03-2022) in Clubhouse at 8 PM IST(7:30 AM Pacific time), we will have a case discussion of a patient presenting with acute onset right-sided weakness, paresthesia, and visual deficits. We will revise the approach to a patient with hemiplegia and arterial localization of stroke while discussing this case. Hearing episodes 3 and 7 of the 'Clinical neurology with KD' podcast https://t.co/wxlIdYdPO9 before the discussion will be helpful. #clinicalneurologywithkd #neurologyteachingclub #stroke #NTC #neurology #neurosciences #neuro #clinicalneurology #medicine #clinicalmedicine #kdpodcast #mbbs #medicos #doctors #neuroanatomy #casediscussion #medicineresidents #residency #medschool #futureneurologist #neuroimages #NEET #finalmbbs #neetpg #neetsuperspeciality #neetmedicine #eanneurology #nejm https://www.instagram.com/p/Cav_aZwrVhB/?utm_medium=tumblr
#clinicalneurologywithkd#neurologyteachingclub#stroke#ntc#neurology#neurosciences#neuro#clinicalneurology#medicine#clinicalmedicine#kdpodcast#mbbs#medicos#doctors#neuroanatomy#casediscussion#medicineresidents#residency#medschool#futureneurologist#neuroimages#neet#finalmbbs#neetpg#neetsuperspeciality#neetmedicine#eanneurology#nejm
2 notes
·
View notes
Photo

Extra medullary compression of the spinal cord. For discussion of these images, follow episode five and six of podcast ‘Clinical neurology with KD’ in Apple podcast, Spotify or Google podcast. An extramedullary compressive lesion goes through three stages, according to Oppenheim. An initial stage of radicular pain and segmental motor and sensory symptoms. The initial phase is followed by a Brown-Sequard syndrome and finally a complete transection of the cord. The rapidity of development of these stages depends on the aetiology and can be acute or chronic. Some of the cardinal features of extramedullary compression include Radicular or root pain, which is a unilateral lancinating pain down the dermatome on coughing, straining, or Valsalva. The patient will have early corticospinal tract involvement with lower limb spasticity more than the upper limb. The leg is more involved as leg fibres are laterally placed in the corticospinal tract than arm fibres. The LMN findings are rare and, if present, occur at the segmental level at the site of compression. The patient will have only late bladder involvement. They have ascending paresthesia as sacral fibres are laterally placed in the spinothalamic tract. Funicular or tract pain is less common. The patient can have vertebral pain and tenderness, which suggest extramedullary extradural lesion. #clinicalneurologywithkd #neurologyteachingclub #paediatricneurology #NTC #neurology #neurosciences #neuro #clinicalneurology #medicine #clinicalmedicine #criticalcaremedicine #mbbs #medicos #doctors #neuroanatomy #casediscussion #medicineresidents #residency #medschool #futureneurologist #neuroimages #NEET #finalmbbs #neetpg #neetsuperspeciality #neetmedicine #eanneurology #nejm #emergencymedicine #spinalcord https://www.instagram.com/p/Cds4asLpst1/?igshid=NGJjMDIxMWI=
#clinicalneurologywithkd#neurologyteachingclub#paediatricneurology#ntc#neurology#neurosciences#neuro#clinicalneurology#medicine#clinicalmedicine#criticalcaremedicine#mbbs#medicos#doctors#neuroanatomy#casediscussion#medicineresidents#residency#medschool#futureneurologist#neuroimages#neet#finalmbbs#neetpg#neetsuperspeciality#neetmedicine#eanneurology#nejm#emergencymedicine#spinalcord
0 notes
Photo
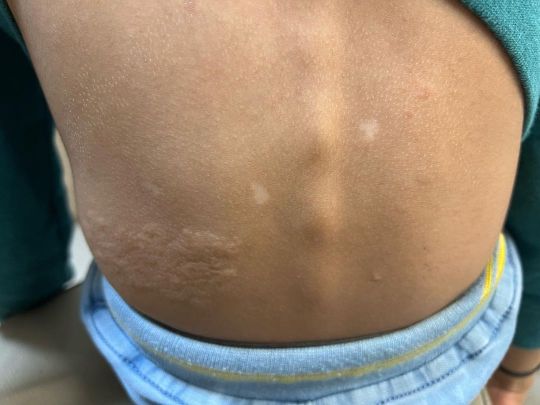
🚨Spotter🚨Five year old boy came with episodes of stare of few seconds. He won’t respond to call at that time. Diagnosis was made from general examination. Please DM me the answers. Follow Clinical neurology with KD podcast at Apple podcast, Google Podcast and Spotify. #clinicalneurologywithkd #neurologyteachingclub #neurologypodcast #NTC #neurology #neurosciences #neuro #clinicalneurology #medicine #clinicalmedicine #kdpodcast #mbbs #medicos #doctors #neuroanatomy #casediscussion #medicineresidents #residency #medschool #futureneurologist #neuroimages #NEET #finalmbbs #neetpg #neetsuperspeciality #neetmedicine #eanneurology #nejm #seizure #epilepsy. https://www.instagram.com/p/CdJKLJOvxO8/?igshid=NGJjMDIxMWI=
#clinicalneurologywithkd#neurologyteachingclub#neurologypodcast#ntc#neurology#neurosciences#neuro#clinicalneurology#medicine#clinicalmedicine#kdpodcast#mbbs#medicos#doctors#neuroanatomy#casediscussion#medicineresidents#residency#medschool#futureneurologist#neuroimages#neet#finalmbbs#neetpg#neetsuperspeciality#neetmedicine#eanneurology#nejm#seizure#epilepsy
0 notes
Photo
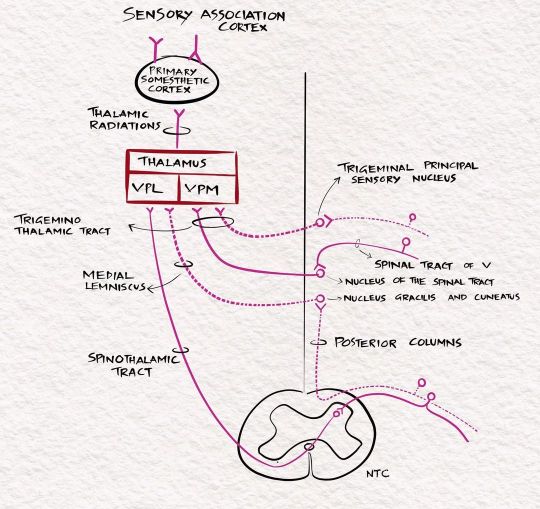
The sensory pathways. For full discussion of this image, follow 'Clinical neurology with KD' podcast episode 10 in Apple podcast, Spotify or Google podcast. Full notes are available on the neurologyteachingclub.com website. The primary modalities of sensation, including touch, pain, temperature, JPS, and vibration, are recognised at the level of the opposite thalamus. So all these sensations are carried to the opposite thalamus by the sensory pathways. The fine touch, vibration and JPS ascend in the posterior column- medial lemniscus pathway, while the pain and temperature through the lateral spinothalamic tract. From the thalamus, they are then projected to the sensory cortex in the postcentral gyrus through the posterior limb of the internal capsule. The sensory cortex helps identify the cortical sensations, namely tactile localisation, two-point discrimination, graphesthesia, stereognosis and sensory attention. #clinicalneurologywithkd #neurologyteachingclub #neurologypodcast #NTC #neurology #neurosciences #neuro #clinicalneurology #medicine #clinicalmedicine #kdpodcast #mbbs #medicos #doctors #neuroanatomy #casediscussion #medicineresidents #residency #medschool #futureneurologist #neuroimages #NEET #finalmbbs #neetpg #neetsuperspeciality #neetmedicine #eanneurology #nejm #aanbrain #neuroimage https://www.instagram.com/p/CdI1u4oP9cY/?igshid=NGJjMDIxMWI=
#clinicalneurologywithkd#neurologyteachingclub#neurologypodcast#ntc#neurology#neurosciences#neuro#clinicalneurology#medicine#clinicalmedicine#kdpodcast#mbbs#medicos#doctors#neuroanatomy#casediscussion#medicineresidents#residency#medschool#futureneurologist#neuroimages#neet#finalmbbs#neetpg#neetsuperspeciality#neetmedicine#eanneurology#nejm#aanbrain#neuroimage
1 note
·
View note
Photo
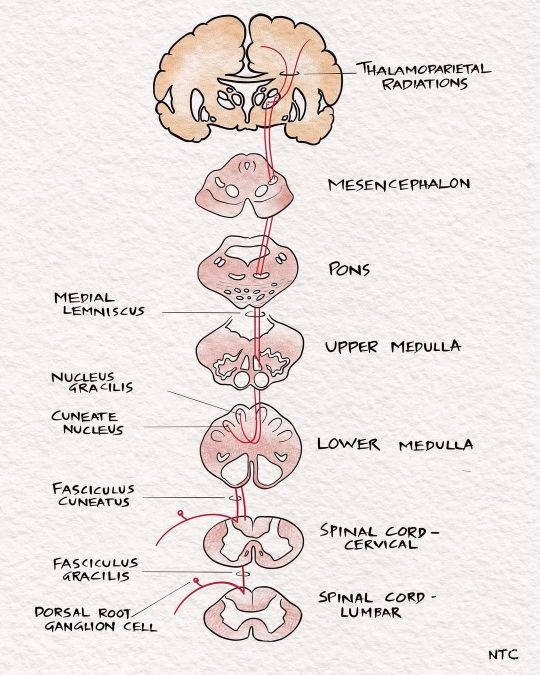
Light touch pathway For discussion of these image, follow 'Clinical neurology with KD' podcast episode ten in Apple podcast, Spotify or Google podcast. Full notes are available on the neurologyteachingclub.com website. The receptors for touch sensation include free nerve endings, Merkel cell endings, and encapsulated nerve endings such as Meissner's corpuscles, Pacinian corpuscles and Ruffini endings. The Pacinian corpuscles act as rapidly adapting mechanoreceptors and are especially sensitive to high-frequency vibration. Others are slowly adapting mechanoreceptors. Light touch sensation is conveyed over large myelinated peripheral nerve fibres to unipolar DRG cells. Tactile sensation follows several different pathways within the central nervous system. The central processes of DRG enter the spinal cord via the medial division of the posterior roots. It then projects through the ipsilateral posterior column to reach the cervicomedullary junction. The fibres from the sacral area will be arranged most medially in the posterior column. The lumbar will be just lateral, followed by the thoracic. The cervical fibres are lateral most as they are the last to enter while going up. The second-order neuron lies in the cuneatus and gracillis nucleus at the cervicomedullary junction. All the fibres below T8 are grouped in the fasciculus gracilis; fibres above T8 form the fasciculus cuneatus. The second-order neurons in the nucleus cuneatus and gracillis project to the opposite thalamus. They immediately sweep anteriorly as the internal arcuate fibres and cross over to the opposite side at the cervicomedullay junction. It ascends in the brainstem as the medial lemniscus to reach the thalamus. The Third-order neuron lies in the ventral posterolateral nucleus of the thalamus and project to the sensory cortex. #sensory #touchpathway #neuro#neurologyteachingclub #neurologypodcast #NTC #neurology #neurosciences #neuro #clinicalneurology #medicine #clinicalmedicine #kdpodcast #mbbs #medicos #doctors #neuroanatomy #casediscussion #medicineresidents #residency #medschool #futureneurologist #neuroimages #NEET #finalmbbs #neetpg https://www.instagram.com/p/CdDx2tIvefO/?igshid=NGJjMDIxMWI=
#sensory#touchpathway#neuro#neurologyteachingclub#neurologypodcast#ntc#neurology#neurosciences#clinicalneurology#medicine#clinicalmedicine#kdpodcast#mbbs#medicos#doctors#neuroanatomy#casediscussion#medicineresidents#residency#medschool#futureneurologist#neuroimages#neet#finalmbbs#neetpg
1 note
·
View note
Photo
New episode of the podcast’Clinical neurology with KD’ released. In this episode, we will discuss the clinical localisation of sensory symptoms. We will learn the sensory pathways and study the clinical features of lesions involving these pathways. You can hear it at Apple podcast, Spotify or wherever you get your podcast #clinicalneurologywithkd #neurologyteachingclub #neurologypodcast #NTC #neurology #neurosciences #neuro #clinicalneurology #medicine #clinicalmedicine #kdpodcast #mbbs #medicos #doctors #neuroanatomy #casediscussion #medicineresidents #residency #medschool #futureneurologist #neuroimages #NEET #finalmbbs #neetpg #neetsuperspeciality #neetmedicine #eanneurology https://www.instagram.com/p/CdACTF5PaTR/?igshid=NGJjMDIxMWI=
#clinicalneurologywithkd#neurologyteachingclub#neurologypodcast#ntc#neurology#neurosciences#neuro#clinicalneurology#medicine#clinicalmedicine#kdpodcast#mbbs#medicos#doctors#neuroanatomy#casediscussion#medicineresidents#residency#medschool#futureneurologist#neuroimages#neet#finalmbbs#neetpg#neetsuperspeciality#neetmedicine#eanneurology
0 notes
Photo
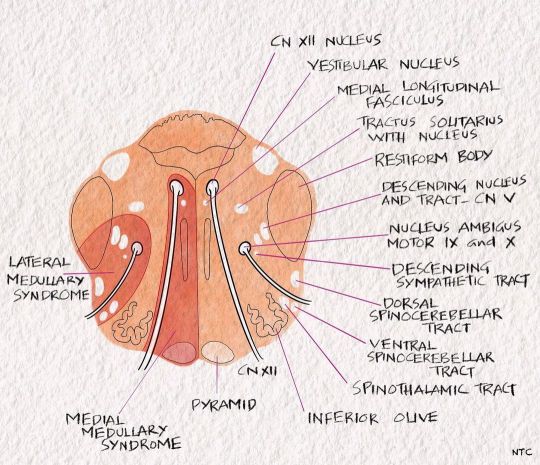
Medial medullary syndrome of Dejerine The 'rule of four' tells us that the 4M lies medially in the brainstem, including the motor pathway or pyramidal tract, motor nuclei of hypoglossal, medial lemniscus and medial longitudinal fasciculus. So a medial medullary syndrome produces opposite side weakness with loss of posterior column sensation and ipsilateral hypoglossal nerve palsy. The MLF involvement can cause upbeat nystagmus occasionally. #clinicalneurologywithkd #neurologyteachingclub #neurologypodcast #NTC #neurology #neurosciences #neuro #clinicalneurology #medicine #clinicalmedicine #kdpodcast #mbbs #medicos #doctors #neuroanatomy #casediscussion #medicineresidents #residency #medschool #futureneurologist #neuroimages #NEET #finalmbbs #neetpg #neetsuperspeciality #neetmedicine #eanneurology #nejm #aanam #medulla https://www.instagram.com/p/Cc2uhA7PxCd/?igshid=NGJjMDIxMWI=
#clinicalneurologywithkd#neurologyteachingclub#neurologypodcast#ntc#neurology#neurosciences#neuro#clinicalneurology#medicine#clinicalmedicine#kdpodcast#mbbs#medicos#doctors#neuroanatomy#casediscussion#medicineresidents#residency#medschool#futureneurologist#neuroimages#neet#finalmbbs#neetpg#neetsuperspeciality#neetmedicine#eanneurology#nejm#aanam#medulla
0 notes
Photo

Cerebellar nuclei For full discussion of this topic, hear episode 8 of Clinical neurology with KD podcast at Apple podcast, Spotify or Google podcast. The cerebellar nuclei are the main source of cerebellar efferents. All of the efferent projections of the deep cerebellar nuclei are excitatory, except for projections to the inferior olive, which are inhibitory. These nuclei from medial to lateral include the fastigial nucleus, the nucleus interpositus (composed of the globose and emboliform nuclei), and the dentate nucleus. The arrangement can be remembered by the code Fast Girls Eat Dates. The fastigial nucleus assists stance and gait. Therefore its lesion may cause abasia. You can remember it by the code- Fast Gait. The nucleus interpositus assists segmental reflexes. It speeds the initiation of movements triggered by somatosensory cues. It guides the response, stop unwanted and promotes wanted oscillations. Therefore, nucleus- interpositus lesions may result in delayed check or rebound responses, truncal titubation, abnormal rapid alternating movements, action tremor, and ataxia on finger-nose-finger and heel-knee-shin manoeuvres. The dentate nucleus assists in tasks requiring fine dexterity. You can remember it like D for D [Dentate for Dexterity]. Lesions of this nucleus or its projections cause delays in initiating and terminating movements, terminal and intention tremors, temporal incoordination in activities that require multiple joints, and abnormalities in the spatial coordination of hand and finger movements. #clinicalneurologywithkd #neurologyteachingclub #neurologypodcast #NTC #neurology #neurosciences #neuro #clinicalneurology #medicine #clinicalmedicine #kdpodcast #mbbs #medicos #doctors #neuroanatomy #casediscussion #medicineresidents #residency #medschool #futureneurologist #neuroimages #NEET #finalmbbs #neetpg #neetsuperspeciality #neetmedicine #eanneurology #nejm #cerebellum #dnbneurology https://www.instagram.com/p/CbsjK-9vv0p/?utm_medium=tumblr
#clinicalneurologywithkd#neurologyteachingclub#neurologypodcast#ntc#neurology#neurosciences#neuro#clinicalneurology#medicine#clinicalmedicine#kdpodcast#mbbs#medicos#doctors#neuroanatomy#casediscussion#medicineresidents#residency#medschool#futureneurologist#neuroimages#neet#finalmbbs#neetpg#neetsuperspeciality#neetmedicine#eanneurology#nejm#cerebellum#dnbneurology
0 notes
Photo

The blood supply of the internal capsule. For full discussion of these images follow ‘Clinical neirology with KD’ podcast in Apple podcast, Spotify or Google podcast. The blood supply of the internal capsule is variable. The superior part of the anterior limb, Genu and posterior limb are supplied by lenticulostriate branches of the middle cerebral artery. The recurrent artery of Heubner supplies the inferior aspect of the anterior limb. The inferior part of Genu is supplied by direct branches from the internal carotid artery and posterior communicating artery. The anterior choroidal artery supplies the inferior part of the posterior limb of the internal capsule. The retrolentiform and sublentiform parts of the internal capsule are supplied by the anterior choroidal artery and the branches of the posterior cerebral artery. #clinicalneurologywithkd #neurologyteachingclub #neurologypodcast #NTC #neurology #neurosciences #neuro #clinicalneurology #medicine #clinicalmedicine #kdpodcast #mbbs #medicos #doctors #neuroanatomy #casediscussion #medicineresidents #residency #medschool #futureneurologist #neuroimages #NEET #finalmbbs #neetpg #neetsuperspeciality #neetmedicine #eanneurology #nejm https://www.instagram.com/p/CakAflPPXQC/?utm_medium=tumblr
#clinicalneurologywithkd#neurologyteachingclub#neurologypodcast#ntc#neurology#neurosciences#neuro#clinicalneurology#medicine#clinicalmedicine#kdpodcast#mbbs#medicos#doctors#neuroanatomy#casediscussion#medicineresidents#residency#medschool#futureneurologist#neuroimages#neet#finalmbbs#neetpg#neetsuperspeciality#neetmedicine#eanneurology#nejm
0 notes
Photo

Blood supply of the brain. For discussion of these images, follow 'Clinical neurology with KD' podcast episode seven in Apple podcast, Spotify or Google podcast. Full notes are available on the neurologyteachingclub.com website .The brain's blood supply is from two systems, the anterior and posterior circulation. The anterior circulation is formed from the right and left internal carotid artery, which arises from the corresponding common carotid artery. The right common carotid artery arises from the right brachiocephalic trunk and the left common carotid directly from the aortic arch. The posterior circulation is formed by the two vertebral arteries which arise from corresponding subclavian arteries. The two vertebral arteries join together to form the basilar artery at the pontomedullary junction. The basilar artery terminates as the two posterior cerebral arteries. The anterior and posterior circulation communicates through the posterior communicating artery, a branch of the distal internal carotid artery. #clinicalneurologywithkd #neurologyteachingclub #neurologypodcast #NTC #neurology #neurosciences #neuro #clinicalneurology #medicine #clinicalmedicine #kdpodcast #mbbs #medicos #doctors #neuroanatomy #casediscussion #medicineresidents #residency #medschool #futureneurologist #neuroimages #NEET #finalmbbs #neetpg #neetsuperspeciality #neetmedicine #eanneurology #nejm https://www.instagram.com/p/CZwP99dvV3Y/?utm_medium=tumblr
#clinicalneurologywithkd#neurologyteachingclub#neurologypodcast#ntc#neurology#neurosciences#neuro#clinicalneurology#medicine#clinicalmedicine#kdpodcast#mbbs#medicos#doctors#neuroanatomy#casediscussion#medicineresidents#residency#medschool#futureneurologist#neuroimages#neet#finalmbbs#neetpg#neetsuperspeciality#neetmedicine#eanneurology#nejm
0 notes
Photo

New episode of the podcast released. In this episode, we will learn the brain's blood supply and various symptoms produced by the occlusion of an individual artery or its branches. We will use that knowledge to localise the artery involved in a stroke patient from the clinical symptomatology. The podcast is available in Apple podcast, Spotify, Google podcast and Amazon music. https://podcasts.apple.com/in/podcast/clinical-neurology-with-kd/id1587263975?i=1000549547006. #clinicalneurologywithkd #neurologyteachingclub #neurologypodcast #NTC #neurology #neurosciences #neuro #clinicalneurology #medicine #clinicalmedicine #kdpodcast #mbbs #medicos #doctors #neuroanatomy #casediscussion #medicineresidents #residency #medschool #futureneurologist #neuroimages #NEET #finalmbbs #neetpg #neetsuperspeciality #neetmedicine #eanneurology #bloodsupplyofbrain #stroke #neuroanatomy https://www.instagram.com/p/CZZtgRKv8HV/?utm_medium=tumblr
#clinicalneurologywithkd#neurologyteachingclub#neurologypodcast#ntc#neurology#neurosciences#neuro#clinicalneurology#medicine#clinicalmedicine#kdpodcast#mbbs#medicos#doctors#neuroanatomy#casediscussion#medicineresidents#residency#medschool#futureneurologist#neuroimages#neet#finalmbbs#neetpg#neetsuperspeciality#neetmedicine#eanneurology#bloodsupplyofbrain#stroke
0 notes