#edit: 28 official programme
Explore tagged Tumblr posts
Text
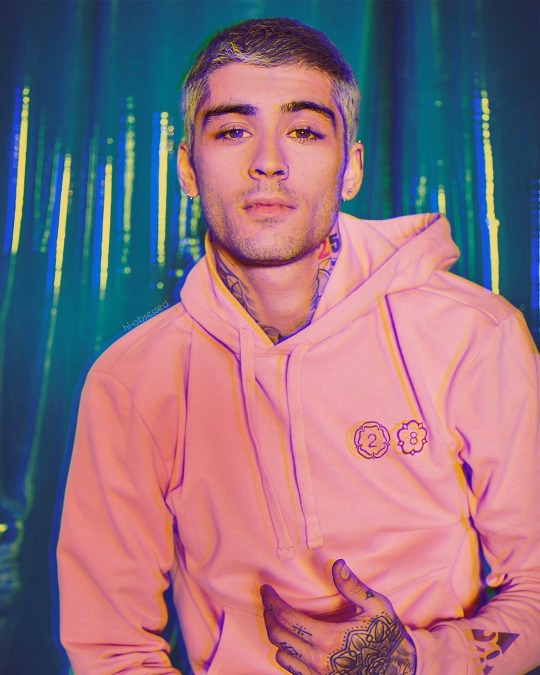

part 2
#zayn malik#28op#28 official programme#28 clothing#louis tomlinson#zouis#manip#manips#mine#I TOTALLY BLAME ASH#zayn in 28op series#to be updated#boys in 28op#modeling for lou#zouis edits
125 notes
·
View notes
Note
Hii, I don't know if people have spoken about this but I saw a video of Kit Connor's recent photoshoot on his Insta page. One of the outfits is Louis's 28 brand hoodie. Is he the first celeb model for the brand? If so, that's so awesome!
And not to make unnecessary connections but they wore a lot of blue green this season. I didn't think about until Kit specifically mentioned it in BTS. And in one of the episodes, Nick tells Charlie he couldn't find mint chocolate chip ice cream. All of these could be just coincidences but it also feels like subtle thing one would do for a friend (LT). He must know him if he's wearing his hoodie
Just thought I'll point this out
Hi nonnie, that’s such a wonderful topic to talk about!
Yes, we saw it and were super excited to see that Helen Seamons put Kit into 28 clothing! They also linked the brand website to it (the IG is confirmed too) and now we’re all patiently waiting for something to drop.
I don’t know much about the show but it’s definitely interesting that bluegreening was specifically mentioned. And the mint chocolate chip ice cream would definitely make me go 👀 Maybe there’s a Larrie or two in the writers room. LOL.
Btw @lovingstheantidote sent me a Harry edit by @brightgoldanne and while Kit looks already amazing in it, the Harry edit is 😙👌


33 notes
·
View notes
Text
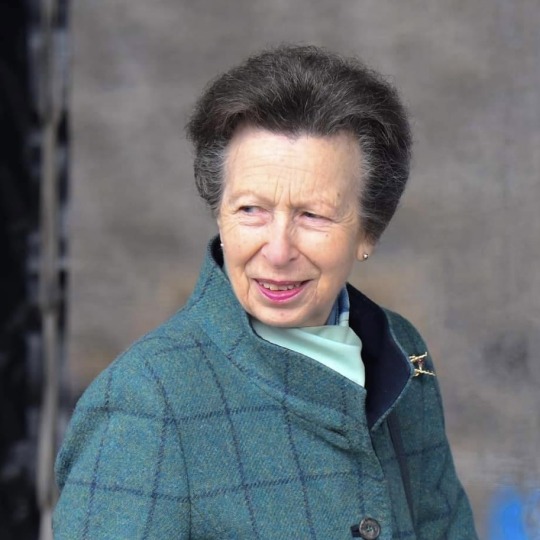
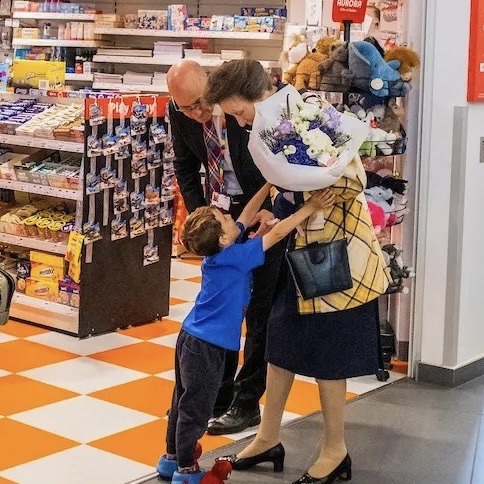
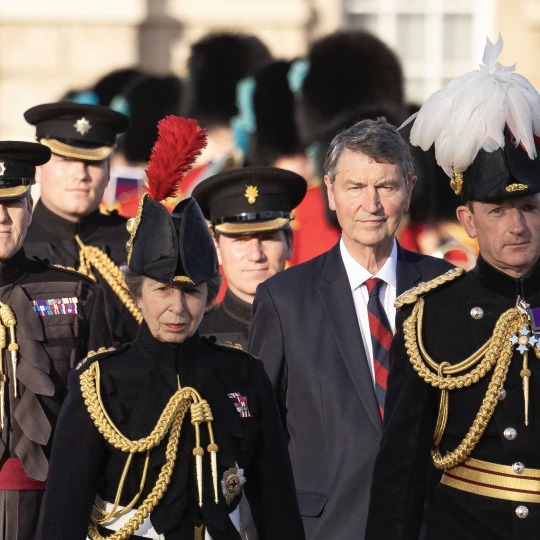
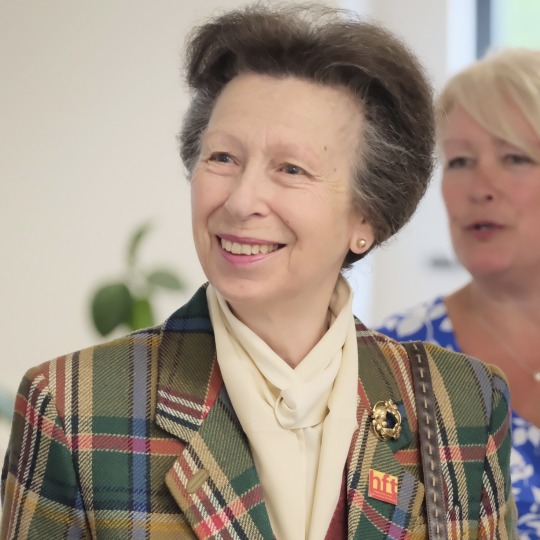
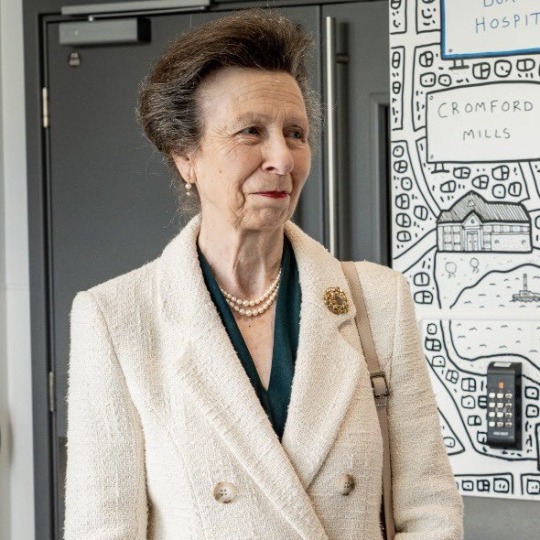
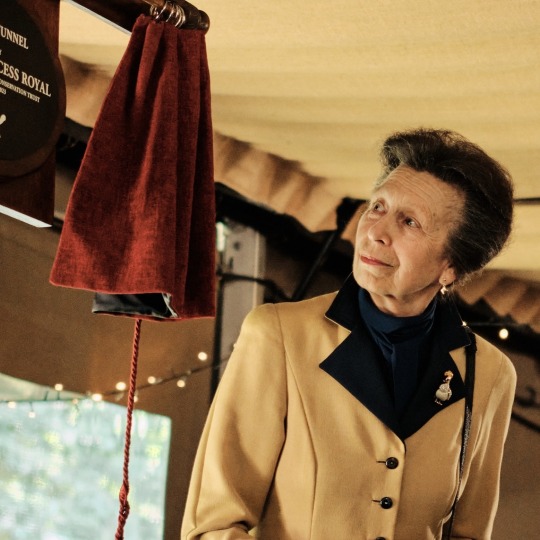
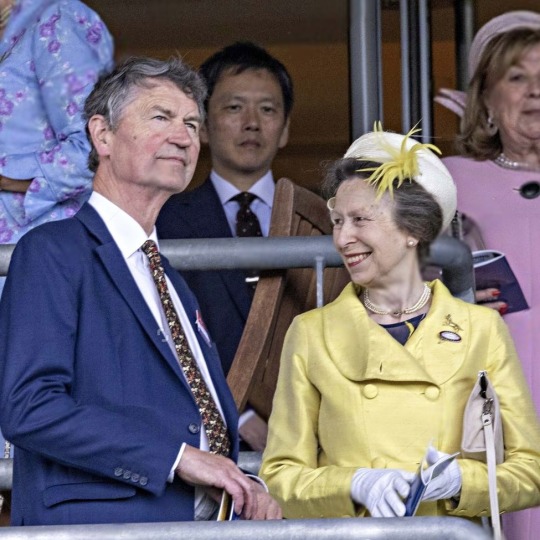









The Princess Royal’s Official Engagements in July 2023
01/07 Princess Anne accompanied by Sir Tim, opened the 30th Scottish Traditional Boat Festival at Portsoy Harbour. ⛴️
03/07 As Chancellor of Harper Adams University, visited the University’s Future Farm, Edgmond and met the 2023 Marshal Papworth Foundation Scholars. 👩🎓
As Patron, Scottish Fisheries Museum’s Reaper Appeal visited the Scottish Fisheries Museum in St. Ayles, Anstruther. 🎣
04/07 Visited Strathcarron Hospice, Denny. 👩⚕️
As Colonel-in-Chief of the Intelligence Corps, attended a 5 Military Intelligence Battalion Training Night at the Army Reserve Centre, Edinburgh. 💂
05/07 As part of Holyrood week in Edinburgh, Princess Anne carried out the following engagements;
Opened the Royal Hospital for Children and Young People and the Department of Clinical Neurosciences, at NHS Lothian as part of #NHS75 celebrations. 🧸
Opened King’s Buildings Nucleus Building at the University of Edinburgh. 👩🎓
Launched WETWHEELS EDINBURGH Accessible Boat at Port Edgar Marina. 🦽🛥️
Attended a Dinner at the Waldorf Astoria for Eric Liddell 100 programme. 🍽️
06/07 As President of the UK Fashion and Textile Association, attended the Textile Institute World Conference at the University of Huddersfield. 🪡
Opened Bradford Teaching Hospitals NHS Foundation Trust’s Maternity Theatre at Bradford Royal Infirmary.🤰
As Colonel of The Blues and Royals, with Sir Tim, took the salute at the Household Division Beating Retreat on Horse Guards Parade. 🫡
07/07 Attended a Charity Polo Day at Cirencester Park Polo Club for the Spinal Injuries Association 🐎
11/07 Visited Flintshire Adult Day Care Centre, Hwb Cyfle in Queensferry, Wales. 🏴
HRH, as the new Patron of BASC (British Association for Shooting and Conservation) visited their Headquarters at Marford Mill, Wrexham, Wales. 🦡
12/07 Visited St Helena’s Nursing Campus at the University of Derby in Chesterfield. 👩⚕️
Opened Chesterfield Royal Hospital NHS Foundation Trust’s new Urgent and Emergency Care Department. 🏥
Attended a Reception at Rolls-Royce Learning and Development Centre for the Motor Neurone Association. 🚘
13/07 Sir Tim represented the Princess Royal at a service of thanksgiving for the life of Admiral of the Fleet Lord Boyce at Westminster Abbey. ⚓️
Princess Anne opened the King’s Arch at Government House, visited the Tortoise Takeover Trail at Gorey Castle and subsequently opened the Tortoise Tunnel at Jersey Zoo. 🇯🇪🐢
Princess Anne with Sir Tim, later attended the Royal Academy of Engineering Annual Awards Dinner at the Londoner Hotel in Leicester Square, London. 🏆
14/07 Opened the new Southampton Citizens Advice Bureau and visited DP World Shipping Container Terminal. ⛴️
15/07 As Colonel-in-Chief of the Intelligence Corps, attended their Annual Corps Day at Chicksands. 🪖
18/07 Princess Anne and Sir Tim carried out the following engagements in Kent;
Opened a new affordable housing development at Bartlett Close, Staple, Canterbury, followed by a Reception at Staple Village Hall. 🏡
Visited St James’s Cemetery in Dover in her role as Patron of the Remembrance Trust 🫡
Visited Folkestone National Coastguard Institution Station in Folkestone to mark its 25th Anniversary, followed by a Reception at Folkestone Yacht and Motorboat Club. 🚨
19/07 In South Wales, visited Barry Citizens Advice Bureaux in her role of Patron of the National Association of Citizens Advice Bureaux and later visited HM Prison Cardiff in her role of Patron of the Butler Trust. 🏴
20/07 Joined the ship’s company of HMS Albion and visited Clyde Marina near Glasgow, Scotland. 🏴
21/07 Princess Anne and Sir Tim attended a Dinner at the Royal Ocean Racing Club Clubhouse, to celebrate the 50th Edition of the Fastnet Race in Cowes, Isle of Wight. 🛥️
27/07 Attended the Tall Ships Races Captains’ Dinner at Lerwick Town Hall, Lerwick, Shetland Islands. 👨✈️🍽️
28/07 Visited ships in Lerwick Harbour taking part in the Tall Ships Races. 🚢🏁
29/07 With Sir Tim, attended the King George Day at Ascot Racecourse. 🏆🐎
30/07 Princess Anne and Sir Tim visited Cowes, Isle of Wight for Cowes Week and carried out the following engagements;
Viewed Cowes Week Racing and met Squadron Staff at the Royal Yacht Squadron. 🛥️
Visited HMS Tyne and The Royal Navy Stand. ⛴️
Attended a Church Service at Holy Trinity Church. ⛪️
Attended a Reception for Members, Racing Crews, Flag Officers and Sailing Associates at the Royal Yacht Squadron. 🥂
Total official engagements for Anne in July: 42
2023 total so far: 304
Total official engagements accompanied by Tim in July: 14
2023 total so far: 70
#hardest working royal 🫡#no choice but to stanne#this is based on the court circular#monthly engagement count#july 2023#and yes i’m doing a separate count for tim too#because i’m rooting for…#operation working royal tim 🫡#STILL WAITING CHARLES…#not all engagements are listed on this post#if you want a full list plz dm me 💕#princess anne#princess royal#tim laurence#timothy laurence
61 notes
·
View notes
Text
🕯️ 28 official programme purple edition 🕯️
9 notes
·
View notes
Text
[ad_1] Smile International Film Festival for Children & Youth (SIFFCY), hosted by Smile Foundation, in partnership with the European Union (the delegation of the European Union in India) announces the official selection for its 11th edition. The annual film festival is scheduled to take place between Jan 28-30, 2025 at Siri Fort Auditorium, New Delhi and several other locations across India in a hybrid mode, in order to reach out to maximum young Indian audience. Enthusiastic children pose for a photo op at the film festival venue during the 10th edition of SIFFCY Major activities, from the opening ceremony to the award ceremony, will be held at the iconic Siri Fort Auditorium, New Delhi on 28,29 and 30 January 2025. Simultaneously, multiple screenings and festival-related activities are scheduled in various schools and communities across a hundred locations across India. Selected programmes will also be streaming on a dedicated, secured, geo-blocked virtual platform throughout the week. Santanu Mishra, SIFFCY Chairman and Producer of the much-acclaimed film 'I am Kalam', says, “Childhood is the decisive phase of human life. The lessons we learn, the habits we make as children, it stays with us forever. Therefore, it is important that we sensitise our youngsters with a positive value system, early.” He adds, “Good cinema can play a crucial role in shaping the young minds, and can even help fight issues such as depression, loneliness, and aggression that children and young adults are getting prone to.” Official Selection SIFFCY 2025 Feature films in competition: Lampo - The Dog who travelled by train, by Magdalena Niec, Poland Doubles Match, by Hung Po-Hao, Taiwan Bigman, by Camiel Schouwenaar, The Netherlands Winners, by Soleen yusef, Germany Soaring Wings, by Palash Das, India Greetings from Mars, by Sarah Winkenstette, Germany 7600, by Behrooz Bagheri, Iran A Butterfly’s Heart, by Inesa Kurklietyte, Lithuania The Tiger’s Nest, by Brando Quilici, Italy Niko - Beyond the Northern Lights, by Kari Juusonen, Jorgen Lerdam, Finland, Germany The boy with pink Pants, by Margherita Ferri, Italy Itty Bitty Princess, By Lauri Maijala, Finland Teacher, Veterinarian, Astronaut, by Reynaldo Escoto, Mexico Short films in competition: Above the Tamarind Tree, by Buthyna Al-Mohammadi, Qatar Dandelions Girl, Azadeh Masihzadeh, Iran Ballad of the Mountain, by Tarun Jain, India Skin Color, by Fidel Alfonso Barboza Gómez, Sebastián Castaño, Colombia Travelling Past, by Rory Power-Gibb, The United Kingdom Skipping Rope, by Wu Meryl, Taiwan Who needs Teachers? by Ekal Deep Kaur, India Forever Seven, by Antje Heyn, Alexander Isert, Germany AB OVO, by Oleksandr Viken, Stas Marchenko, Ukraine Films nominated for Next-Gen Award (Films made by Students) A Dragon in name only, New Zealand And the boy was a bird, India Bedtime Guardian, The United Kingdom Cut the Tie, Greece I am Mutya and I Thank You! The Philippines Until the bell rings, Colombia The Day you were gone, France What is A.D.H.D, China Rebell, India Poland is the country of honour, whereas Italy is the country of focus in SIFFCY 2025. A curated selection of some of the finest Polish and Italian films for the young audience is going to be presented during the festival. Jitendra Mishra, SIFFCY, www.siffcy.org, Festival Director says, “We have carefully selected films from a diverse range of genres and countries of origin, ensuring that each one offers a unique narrative. Most of the feature films will have their Indian premiere at our festival, with some even making their world debut. We hope our efforts will not only showcase the best of global cinema but also inspire young audiences to think critically, broaden their horizons, and foster a deeper appreciation for the cultural, social, and emotional stories that shape our world.”
The 11th edition of the Smile International Film Festival for Children and Youth (SIFFCY) will feature over 150 films, that include feature films, animation, short films, and documentaries, created by professional filmmakers, children, and students from more than 40 countries. The participating countries include the USA, Australia, the UK, Germany, Czech Republic, France, Greece, Belgium, Bulgaria, Croatia, Chile, Poland, the Netherlands, Spain, Italy, Portugal, Luxembourg, Estonia, Slovenia, Sweden, Malaysia, Argentina, Colombia, Lithuania, Brazil, Iran, China, Russia, Ukraine, Nepal, Romania, Serbia, Korea, Singapore, Canada, Japan, Bahrain, Cuba, and India. The selected films will be showcased in five distinct sections, viz. International Competition (both feature and short films), 70MM Smile (World Panorama), The Yellow Carpet (Indian Showcase), Next-Gen (Films made by film students), and Take One (Films made by children). The festival organised by Smile Foundation will also host prestigious awards such as the ECFA Award (European Children’s Film Association), CIFEJ Award (formed under UNESCO), and the Film Critics Circle of India Award (FCCI). SIFFCY, siffcy.org, is an initiative of Smile Foundation, www.smilefoundationindia.org, to entertain, engage, educate and empower young minds. It is based on a strong belief that good cinema represents much more than entertainment; rather this is the most powerful medium to depict the reality and emulate values. Film becomes an interesting and engaging alternative to stimulate discussion among young people about vital personal, societal, moral and world issues. Link: siffcy.org. !function(f,b,e,v,n,t,s) if(f.fbq)return;n=f.fbq=function()n.callMethod? n.callMethod.apply(n,arguments):n.queue.push(arguments); if(!f._fbq)f._fbq=n;n.push=n;n.loaded=!0;n.version='2.0'; n.queue=[];t=b.createElement(e);t.async=!0; t.src=v;s=b.getElementsByTagName(e)[0]; s.parentNode.insertBefore(t,s)(window,document,'script', 'https://connect.facebook.net/en_US/fbevents.js'); fbq('init', '311356416665414'); fbq('track', 'PageView'); [ad_2] Source link
0 notes
Text
[ad_1] Smile International Film Festival for Children & Youth (SIFFCY), hosted by Smile Foundation, in partnership with the European Union (the delegation of the European Union in India) announces the official selection for its 11th edition. The annual film festival is scheduled to take place between Jan 28-30, 2025 at Siri Fort Auditorium, New Delhi and several other locations across India in a hybrid mode, in order to reach out to maximum young Indian audience. Enthusiastic children pose for a photo op at the film festival venue during the 10th edition of SIFFCY Major activities, from the opening ceremony to the award ceremony, will be held at the iconic Siri Fort Auditorium, New Delhi on 28,29 and 30 January 2025. Simultaneously, multiple screenings and festival-related activities are scheduled in various schools and communities across a hundred locations across India. Selected programmes will also be streaming on a dedicated, secured, geo-blocked virtual platform throughout the week. Santanu Mishra, SIFFCY Chairman and Producer of the much-acclaimed film 'I am Kalam', says, “Childhood is the decisive phase of human life. The lessons we learn, the habits we make as children, it stays with us forever. Therefore, it is important that we sensitise our youngsters with a positive value system, early.” He adds, “Good cinema can play a crucial role in shaping the young minds, and can even help fight issues such as depression, loneliness, and aggression that children and young adults are getting prone to.” Official Selection SIFFCY 2025 Feature films in competition: Lampo - The Dog who travelled by train, by Magdalena Niec, Poland Doubles Match, by Hung Po-Hao, Taiwan Bigman, by Camiel Schouwenaar, The Netherlands Winners, by Soleen yusef, Germany Soaring Wings, by Palash Das, India Greetings from Mars, by Sarah Winkenstette, Germany 7600, by Behrooz Bagheri, Iran A Butterfly’s Heart, by Inesa Kurklietyte, Lithuania The Tiger’s Nest, by Brando Quilici, Italy Niko - Beyond the Northern Lights, by Kari Juusonen, Jorgen Lerdam, Finland, Germany The boy with pink Pants, by Margherita Ferri, Italy Itty Bitty Princess, By Lauri Maijala, Finland Teacher, Veterinarian, Astronaut, by Reynaldo Escoto, Mexico Short films in competition: Above the Tamarind Tree, by Buthyna Al-Mohammadi, Qatar Dandelions Girl, Azadeh Masihzadeh, Iran Ballad of the Mountain, by Tarun Jain, India Skin Color, by Fidel Alfonso Barboza Gómez, Sebastián Castaño, Colombia Travelling Past, by Rory Power-Gibb, The United Kingdom Skipping Rope, by Wu Meryl, Taiwan Who needs Teachers? by Ekal Deep Kaur, India Forever Seven, by Antje Heyn, Alexander Isert, Germany AB OVO, by Oleksandr Viken, Stas Marchenko, Ukraine Films nominated for Next-Gen Award (Films made by Students) A Dragon in name only, New Zealand And the boy was a bird, India Bedtime Guardian, The United Kingdom Cut the Tie, Greece I am Mutya and I Thank You! The Philippines Until the bell rings, Colombia The Day you were gone, France What is A.D.H.D, China Rebell, India Poland is the country of honour, whereas Italy is the country of focus in SIFFCY 2025. A curated selection of some of the finest Polish and Italian films for the young audience is going to be presented during the festival. Jitendra Mishra, SIFFCY, www.siffcy.org, Festival Director says, “We have carefully selected films from a diverse range of genres and countries of origin, ensuring that each one offers a unique narrative. Most of the feature films will have their Indian premiere at our festival, with some even making their world debut. We hope our efforts will not only showcase the best of global cinema but also inspire young audiences to think critically, broaden their horizons, and foster a deeper appreciation for the cultural, social, and emotional stories that shape our world.”
The 11th edition of the Smile International Film Festival for Children and Youth (SIFFCY) will feature over 150 films, that include feature films, animation, short films, and documentaries, created by professional filmmakers, children, and students from more than 40 countries. The participating countries include the USA, Australia, the UK, Germany, Czech Republic, France, Greece, Belgium, Bulgaria, Croatia, Chile, Poland, the Netherlands, Spain, Italy, Portugal, Luxembourg, Estonia, Slovenia, Sweden, Malaysia, Argentina, Colombia, Lithuania, Brazil, Iran, China, Russia, Ukraine, Nepal, Romania, Serbia, Korea, Singapore, Canada, Japan, Bahrain, Cuba, and India. The selected films will be showcased in five distinct sections, viz. International Competition (both feature and short films), 70MM Smile (World Panorama), The Yellow Carpet (Indian Showcase), Next-Gen (Films made by film students), and Take One (Films made by children). The festival organised by Smile Foundation will also host prestigious awards such as the ECFA Award (European Children’s Film Association), CIFEJ Award (formed under UNESCO), and the Film Critics Circle of India Award (FCCI). SIFFCY, siffcy.org, is an initiative of Smile Foundation, www.smilefoundationindia.org, to entertain, engage, educate and empower young minds. It is based on a strong belief that good cinema represents much more than entertainment; rather this is the most powerful medium to depict the reality and emulate values. Film becomes an interesting and engaging alternative to stimulate discussion among young people about vital personal, societal, moral and world issues. Link: siffcy.org. !function(f,b,e,v,n,t,s) if(f.fbq)return;n=f.fbq=function()n.callMethod? n.callMethod.apply(n,arguments):n.queue.push(arguments); if(!f._fbq)f._fbq=n;n.push=n;n.loaded=!0;n.version='2.0'; n.queue=[];t=b.createElement(e);t.async=!0; t.src=v;s=b.getElementsByTagName(e)[0]; s.parentNode.insertBefore(t,s)(window,document,'script', 'https://connect.facebook.net/en_US/fbevents.js'); fbq('init', '311356416665414'); fbq('track', 'PageView'); [ad_2] Source link
0 notes
Text
Reality TV and the sinister side of it
Reality TV, one of the most recognised genres of TV shows and has been appreciated by generations, is a form of television programming that exposes unscripted and frequently spontaneous circumstances, captures genuine occurrences, and includes everyday people involved in unscripted action and interaction.

Reality TV shows frequently use social media as a tool for promotion, audience participation, and interactivity (Mcbride 2015). Many reality TV shows have official social media profiles where they post behind-the-scenes videos, and live updates, and interact with their viewers in real-time. This contact makes fans feel more connected to the show and its players, which frequently leads to increased watching and engagement.
Reality TV shows frequently use social media as a tool for promotion, audience participation, and interactivity (Mcbride 2015). Many reality TV shows have official social media profiles where they post behind-the-scenes videos, and live updates, and interact with their viewers in real-time. This contact makes fans feel more connected to the show and its players, which frequently leads to increased watching and engagement. On the other side, reality TV viewers utilise social media platforms to discuss and share their ideas on the shows, as well as to follow and interact with the participants. This creates excitement and awareness for the shows outside of their scheduled broadcast times (Mcbride 2015).
Although social media is the primary medium for fans to engage with TV show participants and express their feelings about them. However, incidents of celebrities being subjected to cyber-assault by fans are not uncommon (Lin. 2023). It is regrettably not uncommon for public individuals, especially reality TV show contestants, to receive rude and abusive remarks on social media. The combination of a huge audience, strong emotions, and relative anonymity on social media can occasionally lead to cyberbullying. This can have serious consequences for the mental health and well-being of everyone affected. For example, cyberbullying Kimura, a cast member on the popular television show Terrace House, was discovered dead at her home on May 23 following an apparent suicide after bombarding a barrage of harsh comments on her social media channels (Knowseeker 2023).

Not only cyberbullying, editing causes misinterpretation are also a downside of reality TV shows. In reality programmes, the editing process can be used to depict a competitor's behaviour as adversarial to a future popular contestant, creating a more interesting story for the audience at home (Mast). The reason there are ethical concerns is that how a candidate is depicted might have major life-changing consequences. According to Cultivation theory, prolonged exposure to important themes in the symbolic worlds of mass media encourages people to overestimate the likelihood and potency of those themes in the psychosocial worlds of themselves and significant others. (ScienceDirect 2012)
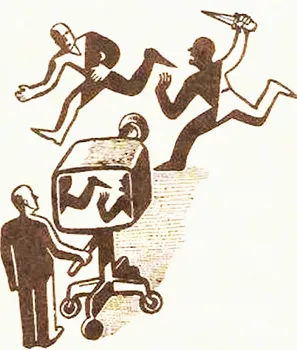
References
Jelle Mast. “The Dark Side of “Reality TV”: Professional Ethics and the Treatment of “Reality”-Show Participants.” International Journal of Communication, vol. 10, no. 0, 2016, p. 22, ijoc.org/index.php/ijoc/article/view/2444/1646.
Knowseeker. “Cyberbulling in Reality Shows: A New Culture or an Innocent Fun? - Knowseeker.” Knowseeker - a Blog about Lifestyle, Relationships, Health, Business and Others; All Thoroughly Spelt out in the Most Relatable and Exciting Way., 17 June 2022, www.knowseeker.com/lifestyle/cyberbulling-in-reality-shows-a-new-culture-or-an-innocent-fun/#google_vignette. Accessed 4 Feb. 2024.
Langguth, Jake. “After the Torch Is Snuffed: The Ethics of Reality TV Editing.” Medium, 28 Apr. 2021, jlangguth2.medium.com/after-the-torch-is-snuffed-the-ethics-of-reality-tv-editing-a5e0021d5450.
Lin, Jingning, et al. “Cyberbullying in Fandom.” Communications in Humanities Research, vol. 7, no. 1, 31 Oct. 2023, pp. 179–192, https://doi.org/10.54254/2753-7064/7/20230875. Accessed 4 Feb. 2024.
Mast, Jelle. “The Dark Side of Reality TV: Professional Ethics and the Treatment of Reality Show Participants.” International Journal of Communication, vol. 10, 2016, pp. 2179–2200, ijoc.org/index.php/ijoc/article/viewFile/2444/1646.
Mcbride, Jean. IdeaExchange@UAkron Social Media & Audience Participation in Regard to Television. 2015.
Nabi, Robin L. “Determining Dimensions of Reality: A Concept Mapping of the Reality TV Landscape.” Journal of Broadcasting & Electronic Media, vol. 51, no. 2, 12 July 2007, pp. 371–390, https://doi.org/10.1080/08838150701307111.
ScienceDirect. “Cultivation Theory - an Overview | ScienceDirect Topics.” Www.sciencedirect.com, 2012, www.sciencedirect.com/topics/social-sciences/cultivation-theory#:~:text=Cultivation%20theory%20explains%20how%20repeated.
0 notes
Text
PM Modi's vision will be realised with the success of the Viksit Bharat Sankalp Yatra: Dr Banwari Lal
IEP Chandigarh, January 28 Haryana Cooperation, Public Health, and Engineering Minister, Dr. Banwari Lal, today listened carefully with party workers and officials to the 109th edition of Prime Minister Sh. Narendra Modi’s monthly programme ‘Mann Ki Baat’ at Shri Krishna Yadav Dharamshala in Jhajjar. He emphasised everyone to convey the messages shared by the Prime Minister to the public. He…
View On WordPress
0 notes
Text
choppy video i'm too lazy to edit at the moment - sorry - posting for personal archiving purposes
featuring Helen Seamons's IG post in which she's styled Kit Connor in merch from Louis's 28 Official Programme line - which has its own IG account now (?) which i'd not even realized 😬
Sunday, July 23rd, 2023; as of 4:55 p.m. DST
0 notes
Text

#modeling for lou#zayn malik#manip#manips#28op#28 official programme#28 clothing#louis tomlinson#zouis#boys in 28op#mine#one direction#one direction manip#1d#zouis edits
73 notes
·
View notes
Text
@doombrigade
1988
Edit
26 September 1988: The novel is published in the UK.
Khushwant Singh, while reviewing the book in Illustrated Weekly, proposed a ban on The Satanic Verses, apprehending the reaction it may evoke among people.[citation needed]
5 October 1988: India bans the novel's importation, after Indian parliamentarian and editor of the monthly magazine Muslim India Syed Shahabuddin petitioned the government of Rajiv Gandhi to ban the book.[127][128][129] In 1993, Syed Shahabuddin tried unsuccessfully to ban another book (Ram Swarup's Hindu View of Christianity and Islam).[130][131]
October 1988: Death threats against Rushdie compel him to cancel trips and sometimes take a bodyguard. Letter writing campaign to Viking Press in America brings "tens of thousands of menacing letters".[132]
20 October 1988: Union of Muslim Organisations of the UK writes the British government pressing for a ban of The Satanic Verse on grounds of blasphemy.[133]
21 November 1988: Grand sheik of Egypt Al-Azhar calls on Islamic organisations in Britain to take legal action to prevent the novel's distribution.
24 November 1988: The novel is banned in South Africa and Pakistan; bans follow within weeks in Saudi Arabia, Egypt, Somalia, Bangladesh, Sudan, Malaysia, Indonesia, and Qatar.
2 December 1988: First book burning of The Satanic Verses in UK. 7000 Muslims attend rally burning the book in Bolton,[134] though the event is barely noticed by the media.[135]
1989
Edit
14 January 1989: A copy of the book is burned in Bradford. Extensive media coverage and debate. Some support from non-Muslims.[134]
January 1989: Islamic Defense Council demands that Penguin Books apologise, withdraw the novel, destroy any extant copies, and never reprint it.
February 1989: The first copies of the United States edition appear in bookstores, along with book reviews in the US press.
12 February 1989: Six people are killed and 100 injured when 10,000 attack the American Cultural Center in Islamabad, Pakistan protesting against Rushdie and his book.[136]
13 February 1989: One person is killed and over 100 injured in anti-Rushdie riots in Srinagar, Jammu and Kashmir.[137][138]
14 February 1989: Ayatollah Ruhollah Khomeini of Iran issues a fatwa calling on all Muslims to execute all those involved in the publication of the novel; the 15 Khordad Foundation, an Iranian religious foundation or bonyad, offers a reward of $US1 million or 200 million rials for the murder of Rushdie, $3 million if done by an Iranian.
16 February 1989: Armed Islamist groups, such as Islamic Revolutionary Guard Corp and Hezbollah of Lebanon, express their enthusiasm to "carry out the Imam's decree".[139] Rushdie enters the protection programme of the British government. The bounty on his head is raised to $6 million.[39]
17 February 1989: Iranian president Ali Khamenei says Rushdie could be pardoned if he apologises.[140]
17 February 1989: Book store chains including B. Dalton, Barnes & Noble, Waldenbooks, and Coles Book Stores say that they will no longer sell the book.[141]
18 February 1989: Rushdie apologizes as President Khamenei suggested; initially, IRNA (the official Iranian news agency) says Rushdie's statement "is generally seen as sufficient enough to warrant his pardon".[142]
19 February 1989: Ayatollah Khomeini issues edict saying no apology or contrition by Rushdie could lift his death sentence.
22 February 1989: The novel is published in the US; major bookstore chains Barnes & Noble and Waldenbooks, under threat, remove the novel from one-third of the nation's bookstores.
24 February 1989: Twelve people die and 40 are wounded when a large anti-Rushdie riot in Bombay, Maharashtra, India starts to cause considerable property damage and police open fire.[143]
28 February 1989: Bookstores, including Cody's and Waldenbooks in Berkeley, California, USA, are firebombed for selling the novel.[144]
28 February 1989: 1989 firebombing of the Riverdale Press: The offices of the Riverdale Press, a weekly newspaper in the Bronx, is destroyed by firebombs. A caller to 911 says the bombing was in retaliation for an editorial defending the right to read the novel and criticising the chain stores that stopped selling it.[145]
7 March 1989: Iran breaks diplomatic relations with Britain.
March 1989: Independent book stores including Cody's in Berkeley, California, United States and Powell's in Portland, Oregon, United States continue to sell the book.[146]
March 1989: The Organisation of the Islamic Conference calls on its 46 member governments to prohibit the novel. The Revolutionary Government of Zanzibar sets the punishment for possession of the book as three years in prison and a fine of $2,500; in Malaysia, three years in prison and a fine of $7,400; in Indonesia, a month in prison or a fine. The only nation with a predominantly Muslim population where the novel remains legal is Turkey. Several nations with large Muslim minorities, including Papua New Guinea, Thailand, Sri Lanka, Kenya, Tanzania, Liberia, and Sierra Leone, also impose penalties for possessing the novel.
May 1989: Musician Yusuf Islam (formerly known as Cat Stevens) indicates his support for the fatwa and states during a British television documentary, according to The New York Times, that if Rushdie shows up at his door, he "might ring somebody who might do more damage to him than he would like... I'd try to phone the Ayatollah Khomeini and tell him exactly where this man is".[147] Yusuf Islam later denied giving support to the fatwa. For more on this topic see Cat Stevens' comments about Salman Rushdie.
27 May 1989: 15,000 to 20,000 Muslims gather in Parliament Square in London burning Rushdie in effigy and calling for the novel's banning.[148]
3 June 1989: Khomeini dies. Former president Khamenei takes over as the new Supreme Leader.
31 July 1989: The BBC broadcasts Tony Harrison's film-poem The Blasphemers' Banquet in which Harrison defends Rushdie by likening him to Molière, Voltaire, Omar Khayyam and Byron.
Following the broadcast of his film-poem, Harrison published a poem titled The Satanic Verses in The Observer in which he wrote:[149]
I shall not cease from mental strife
nor shall my pen sleep in my hand
till Rushdie has a right to life
and books aren't burned or banned
3 August 1989: A man using the alias Mustafa Mahmoud Mazeh accidentally blew himself up along with two floors of a central London hotel while preparing a bomb intended to kill Rushdie.[150]
Kerstin Ekman and Lars Gyllensten, members of the Swedish Academy (which awards the Nobel Prize in Literature), stopped participating in the Academy's work in protest at the Academy's refusal to support an appeal to the Swedish cabinet in support for Rushdie.[151][152] Gyllensten dies in 2006, while Ekman leaves in 2018 after the Academy changed its rules, permitting resignations.[153]
1990
Edit
1990: Rushdie apologises to Muslims.
1990: Rushdie publishes an essay on Khomeini's death, "In Good Faith", to appease his critics and issues an apology in which he seems to reaffirm his respect for Islam; however, Iranian clerics do not retract the fatwa.
1990: Five bombings target bookstores in England.
24 December 1990: Rushdie signs a declaration affirming his Islamic faith and calls for Viking-Penguin, the publisher of The Satanic Verses, neither to issue the book in paperback nor to allow it to be translated.[91]
1991
Edit
11 July 1991: Hitoshi Igarashi, the novel's Japanese translator, is stabbed to death;[154] and Ettore Capriolo, its Italian translator, is seriously wounded.
1993–1994
Edit
2 July 1993: Thirty-seven Turkish intellectuals and locals participating in the Pir Sultan Abdal Literary Festival die when the conference hotel in Sivas, Turkey, is burnt down by a mob of radical islamists. Participating in the conference was Aziz Nesin, who had previously announced that he was going to get the book translated and published. The mob demanded he be handed over for summary execution. The mob set the hotel alight when Nesin was not turned over. Nesin escaped the fire and survived.[155]
11 August 1993: Rushdie makes a rare public appearance at U2's concert in Wembley Stadium on their Zoo TV Tour in London. Bono, donned as stage character/devil Mr. MacPhisto, placed a call to Rushdie only to find himself face to face with Rushdie on stage. Rushdie told Bono that "real devils don't wear horns".
October 1993: The novel's Norwegian publisher, William Nygaard, is shot and seriously injured.
1997–1998
Edit
1997: The bounty is doubled, to $600,000.
1998: Iranian government publicly declares that it will "neither support nor hinder assassination operations on Rushdie".[63] This is announced as part of a wider agreement to normalise relations between Iran and the United Kingdom. Rushdie subsequently declares that he will stop living in hiding, and that he is not, in fact, religious. According to some of Iran's leading clerics, despite the death of Khomeini and the Iranian government's official declaration, the fatwa remains in force. Iran's foreign minister Kamal Kharazi stated,
The Government of the Islamic Republic of Iran has no intention, nor is it going to take any action whatsoever, to threaten the life of the author of The Satanic Verses or anybody associated with his work, nor will it encourage or assist anybody to do so".[2]
1999
Edit
1999: An Iranian foundation places a $2.8 million bounty on Rushdie's life.
14 February 1999: on the tenth anniversary of the ruling against Rushdie, more than half of the deputies in (Iranian) Parliament sign a statement declaring, "The verdict on Rushdie, the blasphemer, is death, both today and tomorrow, and to burn in hell for all eternity".[156]
2000–2004
Edit
14 February 2000: Ayatollah Hassan Saneii, the head of the 15th of Khordad Foundation, reiterates that the death sentence remains valid and the foundation's $2.8 million reward will be paid with interest to Rushdie's assassins. Persians take this news with some scepticism as the foundation is "widely known" to be bankrupt.[156]
January 2002: South Africa lifts its ban on The Satanic Verses.[157]
16 February 2003: Iran's Revolutionary Guards reiterate the call for the assassination of Rushdie. As reported by the Sunday Herald, "Ayatollah Hassan Saneii, head of the semi-official Khordad Foundation that has placed a $2.8 million bounty on Rushdie's head, was quoted by the Jomhuri Islami newspaper as saying that his foundation would now pay $3 million to anyone who kills Rushdie".[158]
2005–2007
Edit
Early 2005: Khomeini's fatwa against Rushdie is reaffirmed by Iran's spiritual leader, Ayatollah Ali Khamenei, in a message to Muslim pilgrims making the annual pilgrimage to Mecca. Iran has rejected requests to withdraw the fatwa on the basis that only the person who issued it may withdraw it.
14 February 2006: Iran's official state news agency reports on the anniversary of the decree that the government-run Martyrs Foundation has announced, "The fatwā by Imam Khomeini in regard to the apostate Salman Rushdie will be in effect forever", and that one of Iran's state bonyad, or foundations, has offered a $2.8 million bounty on his life.[3]
15 June 2007: Rushdie receives knighthood for services to literature sparking an outcry from Islamic groups. Several groups invoking The Satanic Verses controversy renew calls for his death.
29 June 2007: Bombs planted in central London may have been linked to the Knighthood of Salman Rushdie.[159]
2008–2012
Edit
24 January 2012: The vice-chancellor of Darul Uloom Deoband, an Islamic school in India, issued a demand that Rushdie be denied a visa for his scheduled appearance at the Jaipur Literature Festival at the end of January. The Indian government replied that there were no plans to bar Rushdie from entering the country, and that Rushdie, who had visited India several times in the past, did not need a visa because he held a Persons of Indian Origin Card "that entitles holders to travel to the country of their origin without other documentation".[160] Rushdie ultimately decided not to attend the festival, citing reports of possible assassination attempts.[161] Rushdie investigated police reports of paid assassins and suggested that the police might have lied.[162] Meanwhile, police were seeking Ruchir Joshi, Jeet Thayil, Hari Kunzru and Amitava Kumar who fled Jaipur on the advice of officials at the Jaipur Literature Festival after reading excerpts from The Satanic Verses, which is banned in India.[163] A proposed video link session between Rushdie and the Jaipur Literature Festival ran into difficulty after the government pressured the festival to stop it.[162]
17 September 2012: Rushdie expressed doubt that The Satanic Verses would be published today because of a climate of "fear and nervousness".[164]
2016
Edit
22 February 2016: A group of forty state-run media organisations in Iran raised $600,000 to add to the Fatwa on Rushdie.[165]
24 March: In a press release, the Swedish Academy, who awards the Nobel Prize in Literature, condemns the death sentence for Rushdie for the first time, saying:
"The death sentence and the reward money are flagrant breaches of international law and rules of civilised interaction within the world community and therefore can in no way be compatible with normalisation.
The fact that the death sentence has been passed as punishment for a work of literature also implies a serious violation of free speech. The principle of the independence of literature from political control is of fundamental importance for civilisation and must be defended against attacks by avengers and the adherents of censorship.
The Swedish Academy decries the retention of the death sentence for Salman Rushdie and that state-controlled media are permitted to encourage violence directed at a writer."[166]
2022
Edit
Main article: Stabbing of Salman Rushdie
12 August 2022: Rushdie was stabbed in the neck and abdomen when he was set to give a lecture in Chautauqua, New York.[167][168] Commenting on the extent of his injuries, Rushdie's agent said that he had likely lost an eye, in addition to sustaining liver damage and severed nerves in one arm.[169][170] Rushdie was placed on a ventilator the day of the attack, but within 48 hours, he was taken off of it and reportedly able to speak.[171]
14 August 2022: Two days after Rushdie's stabbing, the government-run newspaper of Iran called the attack an "implementation of divine decree".[172]

“A guy who has an open bounty placed on him for decades which has resulted in a near fatal stabbing as well as the murders of people connected to him and the bombing of a hotel building is a lot like people on the internet saying JK Rowling is transphobic”
4K notes
·
View notes
Photo


28 OFFICIAL PROGRAMME
#louis tomlinson#2022#fashionlouist: by louis tomlinson#edit: 28 official programme#lfltracks#tomlinsonedits#louisgalaxy#tracksintheam#louisprojectstracks#louistomlinsonuk
538 notes
·
View notes
Text


#louis edit#28 official programme#ltwt22: São Paulo n1#my ltwt22 content#mindofwalls#louisprojectstracks#tomlinsonedits#louisupdates#lfltracks#dailytomlinson#💗💜💙#louis tomlinson#designer Louis rise
125 notes
·
View notes
Text
Hello everyone !
We didn’t want to have to do this, but sometimes you’re left with no other option.
FLT prides itself in sourcing everything posted into the account. It’s our priority to create quality content, because we don’t just ID garments: we’re an archive.
With that being said, last tuesday 13th we updated about Louis wearing his own brand, 28 Official Programme. For both Instagram and Tumblr, we used a graphic we created ourselves for the hoodie — a graphic we didn’t authorise anyone else to use.
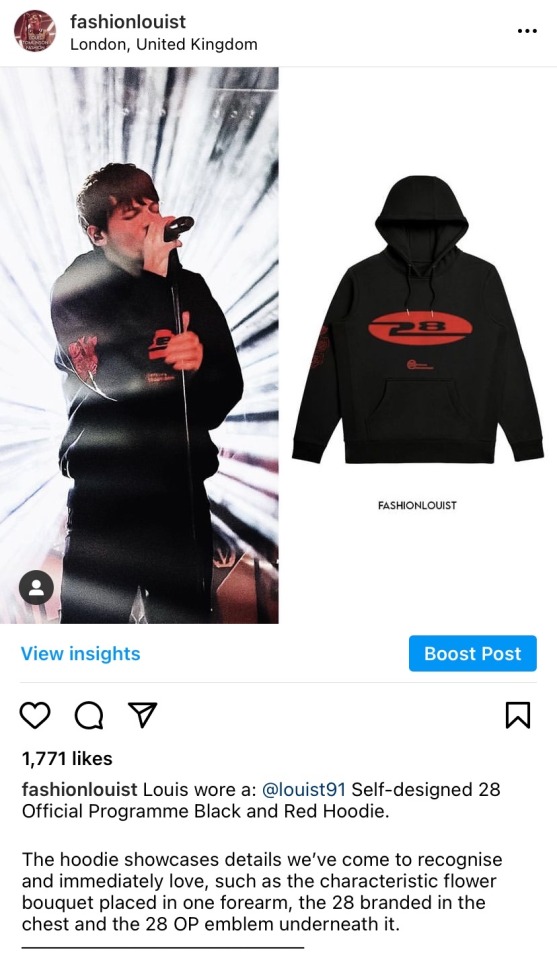

Sadly, another account that also ID’s his clothes (@/louiswearbook) took our edit and posted it without giving us any kind of credit or bothering to ask us if they could use it.
We have spoken to them about this and despite reaching an agreement that they would delete their post because we didn’t authorise for anyone else to use our graphic, it is still up — almost 12 hours later.


Following this, some ID’s we’ve posted haven’t been accurate — which we have always put up as a disclaimer — but we leave them up because it’s an alternative to what Louis wore.
So imagine our faces when accounts like the previous one “identify” the same garment as we did, hours later — when we know for a fact it’s not a confirmed ID due to new, HQ/closer pictures. Or when the same typos we accidentally make in our ID’s are present in their posts too.
This is a public announcement: we do not authorise anyone (be it louiswearbook or any other account) to repost our edits, our descriptions, or use our ID’s without credit. We might not always say it — but we notice when it happens and when things are directly copied from us.
This is why your support means the world to us — because of things like this. We know we aren’t the biggest account on all the platforms we use, but that doesn’t justify stuff like this happening several times.
We will continue running the archive as we normally do. But please know — there’s a lot of work behind it you might not see. Please appreciate that.
We hope this is the last time we have to do this. Thank you. 🤍
78 notes
·
View notes
Text
September 28 Official Programme
📣 Announcing our first project! 📣
🟢Title: September 28 Official Programme
📅 Date: Posts have to be published on Tuesday September 28, 2021
☀️Theme: Freeform - we are inviting you to create anything you want! Why not finalize that edit you've been working on for so long? Or finally write the lyrics analysis of Change you've been thinking about since AFHF? Take this as an opportunity to challenge yourself and clean your drafts!
# Tag: Tag your post(s) #S28OP
🎁Surprise! To celebrate our first project, we're doing a giveaway amongst participants! Details to follow.
🎵 What's the Project's Playlist?: Stream DLIBYH to contribute to the streaming project!
✨In need of inspiration?
Suggested Content: Gifs and gif sets, moodboards, lyrics edits, quotes edits, lyrics parallels, drawings, "Louis as" pics post, videos edits/TikToks, song analysis, text posts about a specific topic (ex. Louis’ fashion, Louis’ charity, Louis and fans, etc)
Suggested Themes: The Away From Home Festival performance/ documentary, Change (song), LT2, what does 369 means, the DLIBYH lyrics, celebrating live music, Louies, the number 28, the Yorkshire rose...
🚫Are There Restrictions? Your creation(s) must focus on Louis as a solo artist.
🎈What Will the LouisProjects Blog Do?: We will reblog posts that have been tagged #S28OP and respect the project's rules and spirit.
85 notes
·
View notes
Note
when will he give us 28 Official Programme Tank Top edition

Can louis hear us asking for this🗣
#okay don't know why Tumblr didn't let me see this ask until now#but SONIII#🗣🗣#asking the real questions here!!!!#soni⚡#asks
5 notes
·
View notes