#early mid Victorian doll clothes are so fun
Explore tagged Tumblr posts
Text
Ah now I could stand to do some sewing lol
6 notes
·
View notes
Text
The Legacy of Meadham Kirchhoff
by MODE GENESIS

Known for their outrageous interloping of romanticism and rebellion, Meadham Kirchoff had become an iconic brand in the early to mid-2000s. The brand was founded by designers Edward Meadham and Benjamin Kirchoff, both graduates from Central Saint Martins, which gained fame through its extravagant expression of whimsicality. An interview by Glamcult with Kirchoff verbalizes how he designs from instinct in a state of “aborted happiness,” and both feel the fashion industry is “based on a repetition of ideas, often aimed at product placement.”

Their inspirations ranging from Victorian dolls to Courtney Love lookalikes in the SS 2012 show, the duo expressed a fresh approach to fashion which became one of the signatures of their brand identity.

Each show transported you into a carefully crafted almost theatrical performance with scent, visuals, light, and music accompanying. Their rebellious spirit brought new design innovation through patchwork dresses in velvet and leather, stacked glittering platform shoes, and a runway decorated with what looked like blood-dipped tampons. Each piece in their collection was carefully made through tailoring research and using techniques such as Elizabethan lacework. The handwork which came in forms of hand embroidery showed in garments in almost all seasons, and detailed construction of each piece became a standard for the brand

Although their womenswear lines achieved most of the media attention, their menswear emerged as out of the ordinary on the London scene. The collections set the direction of modern-day menswear, anticipating the arrival of gender-fluid casting and boy-meets-girl styling. One of their final shows, SS 15, was reclaimed as a celebration of different bodies, genders, and races. The use of rubber, chiffon, color, and layered drapery was an ode to the liberation they stand for. They were chosen as LVMH Young Fashion Designers but weren’t included as finalists so in their show notes they elaborated, “Fuck LVMH corporate fashion,” which is admirable considering the nature of the fashion industry, LVMH, and celebrity culture. As a Dazed article states, “Because fashion doesn’t just have to be about seasonal trends; it can, at its best, be a broader reflection of society, and like riot grrl, BodyMap, Westwood, and Leigh Bowery before them, Meadham Kirchhoff is making clothes for the people they love: the dykes, fags, slappers, and freaks.”

The brand met its demise when most of their clothes they were making weren’t sellable; the market was too niche, and production costs of garments became too high. While it was believed for Meadham Kirchoff as a whole for their clothes to be either too expensive or costume-like, critics praised them, and many designers looked at them as an inspiration. As a Dazed Article states, “They were showing detailed lace on par and on time with the wonders that Alexander McQueen was showing on its runway. Some have even likened the brand’s jackets—particularly from years ago—as foreshadowing those that made Christophe Decarnin a star at Balmain.”

Most of the brand’s pieces have been long lost, as the archive was taken by their landlord and sold in 2015, leaving only pictures and memories of what once was. Since the brand shut down, the duo has gone on separate paths. Meadham launched a new label called Blue Roses, and Kirchoff has become a stylist and menswear consultant. While Meadham Kirchoff could not have survived in the corporate fashion world, they live on as a martyr of sorts through their fun, cheeky, whimsical yet rebellious spirit, which inspires the future of the industry and may even have been ahead of its time.
References:
#fashion blog#blog#meadham kirchhoff#fashion week#london#fashion design#fashion designer#runway fashion#runway
7 notes
·
View notes
Text
There is Joy in Simplicity: 19th century Optical Toys

A late 19th century advertisement for the Stereoscope. It advertises the ability to be “Around the World in 60 minutes” reflecting the educational quality people believed the Stereoscope to have. Source.
I have become engrossed in the world of Yo-Yos lately. This little hunk of plastic with the name Duncan painted on the side, flying through the air on a string. By itself it seems so perfectly simple, however the world of Yo-Yos is deeper than one would think. For instance, there’s several different types of Yo-Yos with their own advantages and disadvantages based on their material and shape. While a Yo-Yo may seem like a simple toy, they also demonstrate a humans ability to learn reflexes. At first, I could barely get the Yo-Yo to come back up but after weeks of continued use I can shoot a dog across the wooden floor of my mother’s kitchen. Toys in a society are truly significant, because they represent what that society wants the young to learn or what they themselves want to play with. They are a form of experimentation.
Just as the yo-yo represents a learning of reflexes, the toys of 19th century America reflect the societal obsession with illusion and vision. Granted, people of the 19th century already had stuff like dolls (which I would argue is still related to vision of the human form), wooden tops and yoyos, dominos, balls, and all other means of play, but the late 19th century sees a boom of vision-based toys. We see the kleidoskope, the thaumatrope, the phenakistoscope, the stereoscope, the zoetrope, and the praxinoscope emerge as these fun little practices in vision. The early hints of film, the basics of animation, the play of illusion all appear in this era.
These toys exist as echoes of the 19th century American societal interest in deception, vision, and representation of self. In the early 19th century, the American faced challenges of identity, the crowd, later on they faced the mass societal grief and crisis of war, the camera as a view of reality, and the concept of the showman like P.T. Barnum, going into the late years of the era we see the early hints of film come out and the concepts of reality. Throughout the 19th century we see visions-based gadgets appear as supplements to the already ongoing discussions of view. Toys like the kaleidoscope, the thaumatrope, the phenakistoscope, the stereoscope, and the zoetrope and praxinoscope all represent a growing societal interest in vision and experimentation throughout the 19th century.

An 1818 illustration titled “Human Nonsense”, the man in the top hat is so entranced by the kaleidoscope, he doesn’t notice he’s walking directly in front of a bike. The Victorians had what Is now called a “craze” over kaleidoscopes as they allowed exploration of vision. Source.
The first optical toy to be invented in the Victorian age was the Kaleidoscope in 1816, by David Brewster, who we will see appear again. Jason Farman of Atlas Obscura describes the 19th century kaleidoscope design as, “made from a range of materials, such as tubes made of brass with embellishments of wood or leather or those cheaply made of tin. The base of the tube was typically filled with broken pieces of glass, ribbons, or other small trinkets.” When viewed from one side, the other would appear as a range of fantastical colors, patterns, and shapes. It almost immediately gained massive popularity, amongst both children and adults, scientists, artists, and industry professionals. Scientists “found it useful as a tool to visualize massive numbers” while artists and industrials used it “for patterns on china, paper, carpets, floor-cloths, and other fabrics” (Farman).
It was experimentation in the role of the eye in light, and shape, along with the illusions of beauty, or reality, when viewed close with a magnifier. Truthfully, some people felt betrayed when they found out what was inside of a kaleidoscope, R.S. Dement, a playwright, writes he was “deceived (as a child) into believing that what he saw was at least the shadow of something real and beautiful, when in truth it was only a delusion” (Farman). However, this only further intrigued some of the Victorian viewers:
These new visual tricksters fed into the fascination in the deficits of the human eye and how it could be misled. As people began understanding human vision differently because of these objects, people also began seeing the world through machines like trains, moving walkways, and steamships (Farman).
While the kaleidoscope is simplistic, it is not to be denied it is important as a starting point for the 19th century conversation on vision. A tube that presents to the viewer an illusionary range of symmetrical colors and patterns, created by broken glass, ribbons, and random scraps.

Vignette by George Cruikshank from Philosophy in Sport, 1827. Source.
The next optical toy to appear was the thaumatrope, appearing in the mid-1820s (when it was first published) by John Aryton Paris. The history of the thaumatrope is a mixed and complex mess of early 19th century scientific figures making a bet, including John Herschel (A popular astronomer), Charles Babbage (A mathematician who made the calculating engine), and David Brewster, however it stands clear as a true foundation of visual interest (Herbert). As much as I talk it up, the toy is extremely simple. It consists of a piece of cardboard with two strings on each end, with a picture on both sides (the classic example is bird on one side and a cage on the other) and when the user twists the strings fast enough the two images appear to become one (The bird appears inside of the cage). The same effect had been created by spinning a coin previously, however the thaumatrope was the first to give “the phenonium a scientific explanation and a device produced to be sold as a popular entertainment” (Gunning 499).

Bird-in-Cage Thaumatrope, the classic example and believed to be the first thaumatrope image created as an example, by Dr. Fitton. This depiction pictures the expected result of twisting the strings. Source.
While it is basic, its an extremely effective toy for teaching a core concept of the 19th century. There is flaw in the human vision, or moreso, the human vision has depths and conditions. From 1827’s Philosophy in Sport by Paris, “I will now show you that the eye also has its source of fallacy” says “Mr. Seymour” as he operates the device (501). Its simplicity allows there to be no questions about interference from the toy’s design, there is no mirror, or screen, or other window the viewer is looking at the toy at through.
“We can operate it and understand its process. But the image it produces is not fixed in space, embodied in pigment or canvas; it occurs in our perception. Yet while it may be defined as a subjective image, taking place through our individual processes of perception, it is not a fantasy or, in a psychological sense, a hallucination” (513).
There is simply vision, and the effect of the lasting image (called an afterimage) the human eye creates with the reality the user is the sole reason the illusion continues. Tom Gunning captures perfectly what the Thaumatrope meant as a foundational toy, “This device introduces to the Victorian era a new class of images simultaneously technological, optical, and perceptual” (500). It is the perfect device to start the 19th century with a magical simplicity that allows the user to experience illusion in their own hands through natural processes of the eye.
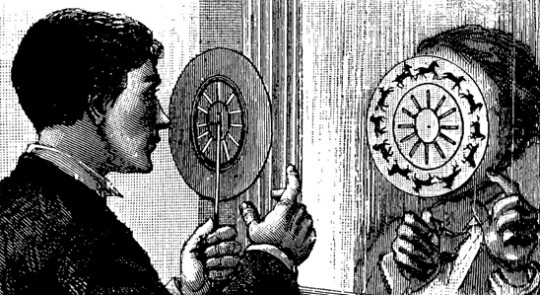
An illustration depicting a person using the phenakistoscope. Of course, it’s impossible to depict the movement accurately in a drawing. Source.
Later, in 1832, the phenakistoscope was “simultaneously invented…by Joseph Plateau in Brussels and by Simon von Stampfer in Berlin” though other concepts were in the works at the same time (“Phenakistoscopes (1833)”). The so called “parlour toy” is a cardboard disc on a handheld stick with an outer circle of images and an inner circle of slits which the viewer would look through. The “trick” of the toy is to spin it while looking through the slits into a mirror, where the images on the outer circle jump to life in animation through the distortion and the flicker of light as the disc moves. “The scanning of the slits across the reflected images kept them from simply blurring together, so that the user would see a rapid succession of images that appeared to be a single moving picture” (“A Short History of the Phenakistoscope”). Its one of the earliest forms of animation, completely using human sight as its method.
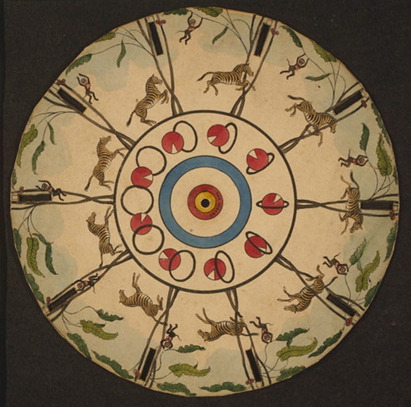

A Phenakistoscope featuring zebras and monkeys in a jungle setting, the zebras would run, and the monkeys would swing when viewed through a mirror. This particular phenakistoscope is from a competing product of the original production, “Mclean’s Optical Illusions or Magic Panorama” from 1833. This is a simplistic image, but phenakistoscopes became more complex as years went on. Source.
Like how the thaumatrope represents a flaw in human vision, the phenakistoscope fully represents the conditionality of vision. The human eye is susceptible to condition, to light, to distortion of light, to illusion. The illusion is only possible through a window, the mirror, showing the young the new concepts of the human eye as an unreliable “narrator” by itself. However, at the same time it shows it through an exciting illusion of movement. The Phenakistoscope saw mass popularity, being published under names like Fantoscope and “Magic Wheel”, leading to further visual toys being produced which would eventually overtake the simple phenakistoscope and thaumatrope. However, before we get into them let us take a quick sideroad into the world of photography.

A 1908 advertisement for a stereoscope viewer in the Pittsburgh Daily Post. It presents the stereoscope as a tool, and as entertainment. Source.
In 1838, Charles Wheatstone published a paper reporting an odd illusion he had discovered where two drawings of the same object, at slightly different perspectives, were placed next to each other the two would be fused together by the eye into a three-dimensional view of it. It is realized this is exactly how the eye functions, each eye taking its own perspective and the two images fusing together for a full three-dimensional view (Thompson). From Oliver Wendell Holme’s 1859 essay on the Stereoscope (After it gained mass popularity):
The two eyes see different pictures of the same thing, for the obvious reason that they look from points two or three inches apart. By means of these two different views of an object, the mind, as it were, feels round it and gets an idea of its solidity. We clasp an object with our eyes, as with our arms, or with our hands (Jacobi).
Wheatstone created a table-top device to demonstrate this effect more easily and clearly, thus the world’s first stereoscope was created, a product of the 19th century’s scientific endeavors.
However, the mass market version of the stereoscope would not be refined and produced until a decade later, by Davis Brewster (who you may remember as the inventor of the kaleidoscope and involved with the thaumatrope) who crafted it into a handheld model in 1849, enabling a scene to appear anywhere.
The refinement of the stereoscope just so happened to align with the release of the first photographs (the specific type called daguerreotypes) as well, enabling the device to show its true potential. “Once Brewster’s design hit the market, the stereoscope exploded in popularity” writes Clive Thompson of the Smithsonian, “The London Stereoscopic Company sold affordable devices; its photographers fanned out across Europe to snap stereoscopic images. In 1856, the firm offered 10,000 views in its catalog, and within six years they’d grown to one million.” The stereoscope, at least its phenomenon, is possibly one of the most long-lasting of these optical toys, considering 3D magic books are on the shelves that use stereoscope technology and some virtual reality headsets rely on the same visual illusion to function.

A stereograph of Indian people gathered outside of a building, created between 1860 and 1930. Stereographs were viewed as tools for exploring the world without literally traveling, however it also led to people objectifying different cultures as they were not people but depictions of people that lacked relation. Source.
The stereoscope equipped with the stereograph became a scientific tool, a toy, and an educational object. Astronomers used it to peer closer at celestial objects. “Astronomers realized that if they took two pictures of the moon—shot months apart from each other—then it would be like viewing the moon using a face that was the size of a city: “Availing ourselves of the giant eyes of science,” as one observer wrote. (The technique indeed revealed new lunar features)” (Thompson). It also became a tool of education, as a way for the child to view far off locations and immerse in a select scene, which the Victorian believed sharpened the child’s attention as their mind was “chaotic and unfocused”. The mass popularity of the stereoscope enabled mass collections of stereographs to develop, which further allowed people to see far off regions, of India, of Asia, of Africa, and the landmarks of Europe, South America, and their own America. However, overall, it remains a toy, a device for entertainment, a way to immerse oneself in another world, another plane, another region.
The stereoscope reflects the society’s interest in vision, the world, and the depths of the human eye. The lighting illusionary discovery reveals the eye to be more than seen, a thing to be further explored. The use of the stereograph reveals the human eye to have complex mechanisms of sight, what you see if not simplistic it is made up of two images. People collected hundreds of stereographs that depicted America, landmarks, animals, people, and any other thing you could imagine into countless to indulge in. However, it is important for the Victorian, and us, to remember however, a person inside of a photograph is not a person, it is the depiction of a person.

A 19th century advertisement for the Zoetrope from T.H. McAllister, describing the Zoetrope as “an instructive Scientific Toy, illustrating in an attractive manner the persistence of an image on the retina of the eye.” The nickname “Wheel of Life” comes from the way the images appear to “jump to life”. Source.
The direct improvement of the phenakistoscope was the cylindrical Zoetrope, first invented by William George Horner in 1834 (only a year or two after the phenakistoscope) who originally named it the Daedalum (the “Wheel of the Devil”) but only marketed in 1887 under the new name of Zoetrope (A combination of the Greek words for life and turn). It improves on the phenakistoscope in two aspects, the user did not need a mirror to observe the effect, and the device could be enjoyed by more than one person at a time. The Zoetrope works in a similar method, along with also being constructed of cardboard, to the phenakistoscope:

Photo included with the article, showing the construction of the zoetrope. Source.
The zoetrope is a mechanical device that produces the effect of motion through a rapid succession of static images, seen through the slits in a rotating cylinder. The sequenced drawings or photographs lie beneath the slits on the inner surface of the cylinder, and as the cylinder spins the viewer looks through the slits at the opposite side of the interior. This scanning action prevents the images from blurring together, and the viewer is treated to a repeating motion picture (Kumar).
The device is considered an early work of animation, along with the flipbook, and acts as a supplement to the evolving concept of human vision, deception, and illusion in the 19th century. From the time of its creation to its market appearance, P.T. Barnum rose to worldwide fame, the Civil war ended, the concept of photographs and spirit photography had arrived, and the societal concept of children had evolved. It is only just then, that the Zoetrope is succeeded by yet another evolution of vision, the Praxinoscope.

An advertisement for the Praxinoscope theatre at the 1878 Exposition Universal in Paris, highlighting its winning of a bronze medal. Source.
The Praxinoscope was created in 1877 by Emile Reynaud, a Frenchman. It is similar in design to the Zoetrope, however it has one innovation that makes it superior, it replaces the slits used to create the effect with narrow vertical mirrors placed in the center of the drum (Greenslade). This enabled even further wider audiences, along with cleaner, brighter animation which was vital in an era before the lightbulb. The praxinoscope garnered massive popularity, being used in homes, and presented as theatres like the one above.
The zoetrope and the praxinoscope both represent the later ends of the 19th century in terms of the view of vision, as this concept that exists to be explored, a thing that can view through windows into other realities, that of film, of moving pictures, of the modern cinema experience. They stand as foundational objects to the modern film industry, with film coming quickly after their creation in the late 1800s and early 1900s. While these toys are simplistic to the modern viewer, they stand as important milestones of concepts of human vision, of looking askance, and of the eye.
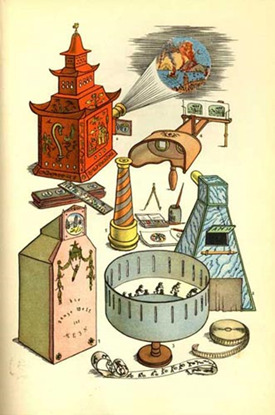
Lithograph by Alfred Mahlau from “Spielzeug, eine Bunte Fibel”, a german book from 1938 by Hans-Friedrich von Geist. The lithograph shows a Kaleidoscope, A Stereoscope, a Zoetrope, along with later film mediums. Source.
The 19th century was an era of vision, the exploration of it, the evolution of it, and the play of it. Within the century we see the concepts of vision evolve, from the simple exploration of tricks of the eye to the questioning of the credibility of it, alongside it we see these optical toys appearing as exploration of the concepts. The kaleidoscope appears in the early 19th century as an exploration of the interaction of the eye and light. The thaumatrope flips as a exploration of an illusionary sticking image of the eye. The phenakistoscope spins to look at how the interaction of the eye and light can create illusions of movement. The stereoscope appears as another exploration of an illusion the eye creates, being used to explore other regions and concepts. Finally, the Zoetrope and the Praxinoscope make their way in, becoming early concepts of animation by building off the concepts of the phenakistoscope, and enhancing the effect with more slits and mirrors.
While these toys may seem laughably simplistic to us, there is a reason things like yoyos, balls, and dolls are still so amazingly popular along with these very optical toys being recreated and sold. There is a joy in simplicity, there is joy exploring the human eye.
Farman, Jason. “The Forgotten Kaleidoscope Craze in Victorian England”. Atlas Obscura, November 9th, 2015. https://www.atlasobscura.com/articles/the-forgotten-kaleidoscope-craze-in-victorian-england
Greenslade, Thomas B. “Praxinoscopes”. Instruments for Natural Philosophy, Keyton College. http://physics.kenyon.edu/EarlyApparatus/Optical_Recreations/Praxinoscopes/Praxinoscopes.html
Gunning, Tom. “Hand and Eye: Excavating a New Technology of the Image in the Victorian Era” Victorian Studies, Vol. 54, No. 3, Indiana University Press, Spring 2012. Pgs. 499-501, 513.
Herbert, Stephen. “The Thaumatrope Revisited; or: "a round about way to turn'm green". The Wheel of Life, https://www.stephenherbert.co.uk/thaumatropeTEXT1.htm
Jacob, Carol. “Tate Painting and the Art of Stereoscopic Photography”. ‘Poor man’s picture gallery’: Victorian Art and Stereoscopic”. Tate, https://www.tate.org.uk/whats-on/tate-britain/display/bp-spotlight-poor-mans-picture-gallery-victorian-art-and-stereoscopic/essay
Kamar, Julie. “The Wheel Of The Devil - The History Of The Zoetrope From Ancient China To Pixar”. June 1st, 2012. Thalo, https://www.thalo.com/articles/view/343/the_wheel_of_the_devil_the_history_of_the
Thompson, Clive. “Stereographs Were the Original Virtual Reality”. Smithsonian Magazine, October 2017. https://www.smithsonianmag.com/innovation/sterographs-original-virtual-reality-180964771/
“A Short History of the Phenakistoscope” June 28, 2014. Juxtapoz: Art & Culture, https://www.juxtapoz.com/news/news/short-history-of-the-phenakistoscope/
“Phenakistoscopes (1833)”. The Public Domain Review, https://publicdomainreview.org/collection/phenakistoscopes-1833
9 notes
·
View notes
Note
>:) Personality + Background for Helena, Basics + Appearance for Erin
YES thank u... vampire time
Helena
PERSONALITY
What’s their alignment?
Probably neutral good ehehehe
What are their hobbies and interests? Do they have any particular “favorites” (food, books, and so on)?
Her number one passion is acting, it’s not really a hobby since she does it professionally (or is trying to lol).. She enjoys learning history though, especially the mid-18th century :^) Also music, corny movies, she’s also a huge sims fan >:)
As for her favorites uhhh her favorite band is My Chemical Romance DUH, fav movies are Shakespeare in Love, Valley of The Dolls (yeah ik it sucks),... Shark Tale.... aaaaand her favorite food is fries. Or it was, she can’t eat it anymore :(
What are they bad at?
Within the game’s mechanics and all that.. she’s not much good in a fight (thank u faelike background). She’s still significantly stronger than the average human of course, but very fragile for vampire standarts :/ Noodle arms bitch
Do they have any vices/addictions/mental illnesses?
None that I can think of
What are their goals and motivations?
Before her embrace it was to become a famous actress.. which isn’t possible anymore, she’s still craving that kind of lifestyle though. She grew up not being very well off and not being very popular either, so it’s kinda... wanting to be someone important? Like that Will Smith fish from shark tale :)
What are their manners like? Any habits?
She’s rather well-mannered, not exactly posh but she doesn’t do anything weird in public either.. usually.
What are they most afraid of?
irrelevance... something like that :/
BACKGROUND
Where were they born? What was their childhood like?
She’s originally from San Francisco, grew up with a single mom and her younger sister. They weren’t very well off so her mom had to work a lot, it was pretty much just her and her sister :/ She wasn’t very popular either so she made only few friends in school, it was lonely :(
What’s their family like?
Her mom Jenny is a nice lady, very goal-oriented.. she was very popular in high school, which is how she met Helena’s dad. He’s originally from germany and comes from a long line of vampire hunters and religious zealots (Society of Leopold hoes..), doesn’t really know anything about it though. His family are just a bunch of weird catholics. They had two children, miss Helena & her little Sister, Elizabeth before he divorced his wife and fucked off 👋. He cut off all contact and doesn’t pay child support bc he’s a freak. Also Elizabeth is currently studying law somewhere, their mother insisted they make something of themselves >:(
What factions or organizations are they a part of? What ranks and titles do they hold?
She’s with the camarilla, mostly due to the fact that Christian is in it too. She came to them all starry-eyed because the other members were all sexy, powerful and rich vampires which is pretty much what she wants to be like lmao.. She works directly for Lacroix, kinda like the fledgling except with better pay, slightly less shitty jobs and a tiny bit more respect (only a tiny bit everyone still thinks she’s dumb af). She just has to run small errants lol. There’s no official rank or title though lol.
She’s not really loyal to them or anything and quickly becomes disillusioned by it all. Vampire society is fucked up... she kinda starts spending more time with the Hollywood anarchs because toreador solidarity, doesn’t join their cause though. The anarchs can’t stand her lmao. She’s really mostly independent...
How do they fit into their “story”?
She’s just your good ol’ regular La Croy foundations employee, she was initially my fledgling but I don’t want Christian (her sire) to die, I suppose she’s just like.. there.. idk its kind of a wip
Where do they currently live? What’s their place like?
She has that little apartment in downtown LA during the events of bloodlines :^) It’s a nice place, modern interior and all that... she does miss her old apartment with the victorian furniture though :(( Post bloodlines she probably leaves LA after the whole thing with Lacrosse lol... she’s friends with Ash now they can go on a road trip or something
How do they eventually die?
she doesn’t... shes a vampire >:)
Erin
BASICS
What’s their full name?
Cassandra Erin Winters :~)
What does their name mean? Why were they named that?
Cassandra (from greek “to excel, to shine “) is a little nod to the seer Cassandra, who appears somewhere in her bloodline :^) In-universe it’s one of those names that appear throughout her family.. there are a bunch of important great-grandmothers, aunts and other relatives so her parents named her that to make it look like they’re an important dynasty or something. Rich people bs. Erin is an english derivative of the irish word for.. Ireland lmao. It was just one of those names that were popular in the early 80′s and her mother liked it, there’s no real reason behind it!
Do they have any nicknames?
jhdfjhfd Cammy by Damsel even though she helped them out 😒 also “Newbie” by her bf sdkjskjdf romance ❤
How old are they?
22 in 2004, I suppose she’s 37 in 2020 aka during the events of bloodlines 2
When’s their birthday?
December 13th, 1982
What’s their zodiac sign/element/birthstone/etc.? Do they believe that holds any significance?
I had to take a whole quiz for this but she’s a Sagittarius 😌 I’d say it definitely does lol... she reads her horoscope almost daily
What’s their species/subspecies? Do they have any special/magical abilities?
Vampire lol... specifically of clan Malkavikan. As for magical abilities yknow, typical vampire stuff, plus the voices & Malkavian insight and all that. Her abilities are Auspex and Obfuscate :^)
What “class” do they belong to (for fantasy characters)? If none, what weapon do they favor?
No class but her favorite weapon was the axe she found in the haunted hotel
APPEARANCE
What do they look like?
goddd.... small, pretty blonde, pale skin bc she’s dead, yellow-ish eyes (used to be blue)... big eyes, sliightly overplucked eyebrows bc it’s 2004 :( she’s still cute though
Do they have a face claim?
Mostly Bella Heathcote and Christina Ricci in one image I found on pinterest lol.. I never have faceclaims that are 100% what they look like :(
What’s their style like? Clothes, hair, makeup?
goddd jt was pretty much regular late 90s/early 2000s popular girl before her embrace.. short skirts, juicy tracksuits, tube tops, those awful tinted glasses, coats with fake fur. Her hair was often in those late 90′s updos with a few streaks hanging loose in the front... makeup is just regular looks from the time, lipgloss, frosty eyeshadow and all that 🤢 she’s a big fan of turtleneck sweaters though 😌
It’s still the same but a bit more fucked up post-embrace because she’s just like go crazy aaahh go stupid aaahhh and digs out some of her weirder clothes because half of these vampire bitches wear dumber clothes than her anyway... an old white lace dress that looks like it’s from the early 1900s or something like that... her standard outfits are still low-rise jeans with tank tops and those giant early 2000s shoes though, she just adds in a few weird looking clothes for fun sometimes
How do they carry themselves? What’s their default expression?
Honestly she looks like this emoji 😳 most of the time, Malkavian voices, weird doomsday visions and all that... She had a very cheerful attitude before her embrace and it still shows sometimes, most of the time it’s kinda weird though :(
Do they have any physical ailments or disabilities?
nope!
5 notes
·
View notes