#dairy farming machinery price in india
Explore tagged Tumblr posts
Text
Lactoscane Spare Parts – High-Quality Replacement Components for Reliable Performance
Lactoscane Spare Parts provide high-quality replacement components designed for durability and optimal performance. Ensure seamless operation with reliable spare parts tailored to meet industry standards. Perfect for maintenance and repairs, these components enhance efficiency and longevity, minimizing downtime. Keep your equipment running smoothly with precision-engineered Lactoscane spare parts.

#dairy machines#dairy machinery#dairy farming machinery price in india#dairy equipment#dairy machines for sale#electronic poducts#data processing unit
0 notes
Text
Best Agriculture Loan Services in Bharuch, Gujarat: Empowering Farmers for Growth
Agriculture is the backbone of India's economy, and Gujarat, particularly the region of Bharuch, has always been a significant contributor to the agricultural sector. With a strong emphasis on farming and cultivation, Bharuch offers a range of opportunities for farmers to grow their businesses and improve their livelihoods. However, one of the biggest challenges faced by farmers in this region is securing adequate funding for their agricultural ventures. This is where the Best Agriculture Loan Services in Bharuch, Gujarat play a crucial role.
Understanding the Importance of Agriculture Loans
Agriculture loans are designed to provide financial assistance to farmers, enabling them to meet their farming needs, buy seeds, fertilizers, equipment, and even finance the expansion of their agricultural activities. With access to the right kind of financial support, farmers can improve their productivity, adopt modern farming techniques, and ensure better yields. The availability of agricultural loans is a critical factor in promoting sustainable growth in the farming sector, especially in a region like Bharuch, which is known for its rich soil and diverse crops.
Types of Agriculture Loans Available in Bharuch, Gujarat
In Bharuch, farmers can access various types of agriculture loans, each catering to different needs:
Crop Loans: These loans are offered to farmers to cover the costs of seeds, fertilizers, pesticides, and other inputs required for growing crops. They are short-term loans that are repaid after the harvest, providing immediate financial relief during the growing season.
Long-Term Loans: These loans are designed for purchasing land, machinery, or other assets that are necessary for the long-term sustainability of the farm. They help farmers in investing in modern equipment, improving irrigation systems, and enhancing infrastructure.
Kisan Credit Card (KCC): The KCC scheme is a popular loan option for farmers, providing them with an easy and quick way to access credit. The card helps farmers avail of short-term loans for agricultural purposes, as well as for personal and family needs, at low interest rates.
Agri-Equipment Loans: Farmers often need machinery such as tractors, harvesters, and plows to enhance their productivity. These loans offer easy financing options to purchase such equipment, making farming more efficient and less labor-intensive.
Post-Harvest Loans: These loans are designed to help farmers manage their post-harvest expenses, including storage, transportation, and marketing. They ensure that farmers can sell their produce at the right time and price without facing financial constraints.
Horticulture and Animal Husbandry Loans: For farmers involved in horticulture or livestock farming, these loans provide funding for setting up greenhouses, buying seeds, planting orchards, or raising animals for dairy or poultry production.
Key Features of the Best Agriculture Loan Services in Bharuch, Gujarat
When seeking Best Agriculture Loan Services in Bharuch, Gujarat, it’s essential to choose the right service provider. Here are some key features that make an agriculture loan service stand out:
Low Interest Rates: The most crucial factor when selecting an agriculture loan service is the interest rate. The best services offer competitive rates, ensuring that farmers don’t burden themselves with high repayment costs. Lower interest rates enable farmers to focus on growing their businesses without worrying about loan repayments.
Flexible Repayment Options: Agriculture is often unpredictable, with crops and produce being affected by weather, market prices, and other external factors. The best loan services offer flexible repayment options, allowing farmers to repay loans based on their harvest cycles or cash flow.
Quick Disbursement: Time is of the essence when it comes to farming. Farmers require immediate access to funds to meet their seasonal needs. The best agriculture loan services in Bharuch provide fast disbursement of loans, ensuring that farmers get the financial support they need without delay.
Minimal Documentation: Traditional loan processes can be time-consuming and require a lot of paperwork. The best agriculture loan services in Bharuch simplify the process by offering minimal documentation, making it easier for farmers to apply for and obtain loans.
Tailored Loan Solutions: Every farm is unique, and the financial needs of farmers vary. The best loan services offer customized loan products based on the specific needs of the farmer, whether it’s for crop cultivation, equipment purchase, or infrastructure development.
Government Subsidies and Schemes: Several government schemes are designed to support farmers, and the best agriculture loan services help farmers take advantage of these schemes. Whether it’s through subsidies, interest rate concessions, or loan guarantees, these services ensure that farmers benefit from government initiatives.
How Agriculture Loans Benefit Farmers in Bharuch, Gujarat
Agriculture loans play a significant role in the growth and development of the farming community in Bharuch. Some of the key benefits include:
Increased Productivity: With access to timely funding, farmers can invest in high-quality seeds, fertilizers, and equipment, which directly contributes to better yields and higher productivity.
Improved Livelihoods: Agriculture loans provide farmers with the means to improve their standard of living by allowing them to invest in their farms and generate higher income.
Risk Mitigation: With financial support, farmers can better manage risks related to crop failure, poor weather conditions, or market fluctuations. Loans enable them to cope with challenges and recover faster.
Sustainable Growth: By investing in modern farming techniques and technologies, farmers can ensure sustainable agricultural practices that benefit both the environment and their business in the long term.
Conclusion
The Best Agriculture Loan Services in Bharuch, Gujarat provide a crucial lifeline for farmers, helping them overcome financial barriers and ensuring they can grow their agricultural ventures. By offering a variety of loan products, competitive interest rates, and quick processing times, these services empower farmers to achieve higher productivity, improve their livelihoods, and contribute to the region’s agricultural growth. With the right support, farmers in Bharuch can continue to thrive, ensuring a prosperous future for both themselves and the broader community.
0 notes
Text
Challenges and Opportunities in Dairy Farming

Dairy farming has been a vital component of rural livelihoods for generations. In India, it serves as a key source of income and support for millions of farmers. However, like other agricultural activities, it faces unique challenges while offering numerous opportunities.
Challenges
Animal Health and Nutrition Ensuring proper nutrition and veterinary care for livestock is critical to their health and milk production. Poor feeding practices and diseases can significantly affect productivity and herd well-being.
Limited Access to Modern Equipment Many small-scale farmers still depend on traditional methods. While advanced machinery can boost efficiency, its high cost often makes it inaccessible to them.
Market Accessibility Farmers often struggle to get fair prices for their milk due to limited access to local markets and exploitation by middlemen.
Impact of Climate Change Changes in weather patterns disrupt the availability of fodder and water, making dairy farming less cost-effective and sustainable.
Financial Barriers The high costs of starting and maintaining a dairy farm deter many farmers. Limited availability of credit further adds to their financial struggles.
Opportunities
Technological Innovations Advances in milking systems, refrigeration, and veterinary tools can enhance productivity and improve the quality of milk.
Government Support Various government initiatives offer subsidies, training programs, and better access to credit, encouraging farmers to adopt modern practices.
Organic Dairy Farming The growing demand for organic milk, due to its health benefits, provides farmers an opportunity to earn premium prices.
Value-Added Products Diversifying into products such as cheese, yogurt, and butter can help farmers increase profits and reduce reliance on selling raw milk alone.
Cooperative Models Joining farmer cooperatives allows for collective bargaining, shared resources, and access to better market opportunities and knowledge.
Conclusion
Dairy farming in India has vast potential, and innovative approaches combined with supportive policies can help overcome existing challenges. Reliable tools and services are essential for successful farming operations. Tractor Seva is committed to ensuring uninterrupted farming activities by providing timely tractor services.
Explore more at tractorseva.com.
0 notes
Text
Hay and Forage Rakes Market is estimated to Witness Steady Growth Due to Growing Dairy Farm Industry
The hay and forage rakes market has been growing significantly over the past couple of years. Hay and forage rakes are agricultural equipment used for collecting and accumulating wet or dry hay, straw or silage during harvesting into windrow. They are widely used for their capacity to handle various crop types gently without substantial losses and offer high work rates. Owing to their ability to pick up and gather hay and forage crops smoothly and uniformly, they help improve efficiency and consistency during harvesting. The global hay and forage rakes market size was valued at US$ 1.84 billion in 2023 and is expected to reach US$ 2.49 billion by 2031, growing at a compound annual growth rate (CAGR) of 3.8% from 2024 to 2031.
Key players operating in the hay and forage rakes market are Philips Healthcare, Cerner Corporation, Agfa Healthcare, Fujifilm Holdings Corporation, Allscripts Healthcare Solutions Inc., Sectra, Epic Systems Corporation, General Electric Company, Siemens AG, McKesson Corporation, Wellbeing Software, Merge Healthcare Incorporated, Medinformatix Inc., eRAD, Inc., and RamSoft Inc. Key Takeaways Key players: Key players operating in the hay and forage rakes market are Philips Healthcare, Cerner Corporation, Agfa Healthcare, Fujifilm Holdings Corporation, Allscripts Healthcare Solutions Inc., Sectra, Epic Systems Corporation, General Electric Company, Siemens AG, McKesson Corporation, Wellbeing Software, Merge Healthcare Incorporated, Medinformatix Inc., eRAD, Inc., and RamSoft Inc. Key opportunities: Growing adoption of mechanization in agriculture and rise in precision farming are expected to offer lucrative opportunities for players in the global hay and forage rakes market over the forecast period. Global expansion: Increasing export of dairy products worldwide is driving the demand for quality fodder like hay and silage. Hay and Forage Rakes Market Size is further propelling equipment manufacturers to expand their global footprint. Market drivers: The dairy industry has been growing at a notable pace over the past few years. Rising dairy production is increasing the demand for high-quality hay and silage, which is the primary driving force for the sales of hay and forage rakes globally. PEST Analysis Political: Agriculture is a regulated industry, and changes in farm bills and subsidies can impact demand for hay and forage rakes. Tariffs on imported goods could also influence prices. Economic: Overall economic conditions determine discretionary farm spending. During periods of economic recession or uncertainty, equipment purchases may be deferred to prioritize other expenses. Declining crop prices could dampen demand. Social: Changes affecting the agriculture labor force, such as an aging farmer population, can drive Hay and Forage Rakes Companies for machinery that reduces physical work requirements. Health and safety regulations may require equipment upgrades. Technological: Advances in engine efficiency and autonomous functionality are enhancing rake productivity. Variable-rate and GPS technologies optimize field coverage and decrease waste. Connected equipment platforms facilitate equipment monitoring and maintenance planning. Geographical regions: North America and Europe are major markets due to large-scale farming operations and agricultural mechanization. The U.S. is the largest country market globally. Asia Pacific is growing rapidly led by increases in livestock production and government support for agriculture infrastructure modernization in China and India. Fastest growing region: Asia Pacific is projected to have the fastest CAGR during the forecast period. Population and income growth are increasing demand for animal products and the need to expand forage harvesting capacity in the region's developing economies. Government efforts to boost productivity through farm mechanization will further support market expansion.
Get more insights on Hay And Forage Rakes Market
Alice Mutum is a seasoned senior content editor at Coherent Market Insights, leveraging extensive expertise gained from her previous role as a content writer. With seven years in content development, Alice masterfully employs SEO best practices and cutting-edge digital marketing strategies to craft high-ranking, impactful content. As an editor, she meticulously ensures flawless grammar and punctuation, precise data accuracy, and perfect alignment with audience needs in every research report. Alice's dedication to excellence and her strategic approach to content make her an invaluable asset in the world of market insights.
(LinkedIn: www.linkedin.com/in/alice-mutum-3b247b137 )

#Coherent Market Insights#Hay And Forage Rakes Market#Hay And Forage Rakes#Agricultural Equipment#Hay Harvesting#Forage Harvesting#Farm Implements#Hay Tools#Raking Equipment#Windrower
0 notes
Text
Alfalfa Market: Global Industry Analysis and Forecast 2023 – 2030
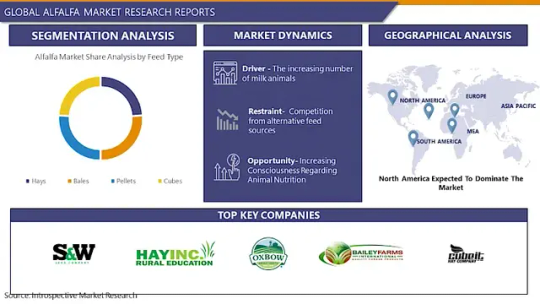
Global Alfalfa Market Size Was Valued at USD 265.33 metric tons In 2022 And Is Projected to Reach USD 426.11 metric tons By 2030, Growing at A CAGR of 16.2% From 2023 To 2030.
Alfalfa is a tonic plant rich in proteins, minerals, enzymes, and vitamins. A bulk quantity of the whole plant is required in the pharmaceutical industries, especially for homeopathic pharmacies. The increasing awareness regarding animal nutrition among the people is one of the important key factors driving the growth of the market. This can be attributed to the increasing consumer demand for chemical-free meat and milk-based products. Product manufacturers are using innovative processing and harvesting machinery to produce long-fiber hay cubes and hay products with enhanced fiber content.
In the US, beef industries have the most influence over alfalfa and hay prices. In terms of regional analysis, North America, particularly the US is the largest producer as well as exporter of alfalfa owing to the country's excellent geographical conditions. The country is known for its various best-quality alfalfa products.
Get Full PDF Sample Copy of Report: (Including Full TOC, List of Tables & Figures, Chart) @
https://introspectivemarketresearch.com/request/14112
The latest research on the Alfalfa market provides a comprehensive overview of the market for the years 2023 to 2030. It gives a comprehensive picture of the global Alfalfa industry, considering all significant industry trends, market dynamics, competitive landscape, and market analysis tools such as Porter's five forces analysis, Industry Value chain analysis, and PESTEL analysis of the Alfalfa market. Moreover, the report includes significant chapters such as Patent Analysis, Regulatory Framework, Technology Roadmap, BCG Matrix, Heat Map Analysis, Price Trend Analysis, and Investment Analysis which help to understand the market direction and movement in the current and upcoming years. The report is designed to help readers find information and make decisions that will help them grow their businesses. The study is written with a specific goal in mind: to give business insights and consultancy to help customers make smart business decisions and achieve long-term success in their particular market areas.
Leading players involved in the Alfalfa Market include:
S&W Seed (US), Hay USA Inc. (US), Oxbow Animal Health (US), Bailey Farms International (US), Haykingdom Inc (US), Mc Cracken Hay (US), Cubeit Hay (US), Standlee Hay (US), Al Dahra ACX Global Inc. (US), Anderson Hay & Grain (US), Green Prairie International Inc- (Canada), Carli Group (Italy), Border Valley (India), Riverina (Australia)
If You Have Any Query Alfalfa Market Report, Visit:
https://introspectivemarketresearch.com/inquiry/14112
Segmentation of Alfalfa Market:
By Feed Type
Hays
Bales
Pellets
Cubes
By Application
Dairy Cow Feed
Cattle and Sheep Feed
Pig Feed
Horse Feed
Poultry Feed
By Animal Type
Cattle
Horse
By Regions: -
North America (US, Canada, Mexico)
Eastern Europe (Bulgaria, The Czech Republic, Hungary, Poland, Romania, Rest of Eastern Europe)
Western Europe (Germany, UK, France, Netherlands, Italy, Russia, Spain, Rest of Western Europe)
Asia Pacific (China, India, Japan, South Korea, Malaysia, Thailand, Vietnam, The Philippines, Australia, New Zealand, Rest of APAC)
Middle East & Africa (Turkey, Bahrain, Kuwait, Saudi Arabia, Qatar, UAE, Israel, South Africa)
South America (Brazil, Argentina, Rest of SA)
What to Expect in Our Report?
(1) A complete section of the Alfalfa market report is dedicated for market dynamics, which include influence factors, market drivers, challenges, opportunities, and trends.
(2) Another broad section of the research study is reserved for regional analysis of the Alfalfa market where important regions and countries are assessed for their growth potential, consumption, market share, and other vital factors indicating their market growth.
(3) Players can use the competitive analysis provided in the report to build new strategies or fine-tune their existing ones to rise above market challenges and increase their share of the Alfalfa market.
(4) The report also discusses competitive situation and trends and sheds light on company expansions and merger and acquisition taking place in the Alfalfa market. Moreover, it brings to light the market concentration rate and market shares of top three and five players.
(5) Readers are provided with findings and conclusion of the research study provided in the Alfalfa Market report.
Our study encompasses major growth determinants and drivers, along with extensive segmentation areas. Through in-depth analysis of supply and sales channels, including upstream and downstream fundamentals, we present a complete market ecosystem.
If you require any specific information that is not covered currently within the scope of the report, we will provide the same as a part of the customization.
Acquire This Reports: -
https://introspectivemarketresearch.com/checkout/?user=1&_sid=14112
About us:
Introspective Market Research (introspectivemarketresearch.com) is a visionary research consulting firm dedicated to assisting our clients to grow and have a successful impact on the market. Our team at IMR is ready to assist our clients to flourish their business by offering strategies to gain success and monopoly in their respective fields. We are a global market research company, that specializes in using big data and advanced analytics to show the bigger picture of the market trends. We help our clients to think differently and build better tomorrow for all of us. We are a technology-driven research company, we analyse extremely large sets of data to discover deeper insights and provide conclusive consulting. We not only provide intelligence solutions, but we help our clients in how they can achieve their goals.
Contact us:
Introspective Market Research
3001 S King Drive,
Chicago, Illinois
60616 USA
Ph no: +1-773-382-1047
Email: [email protected]
#Alfalfa#Alfalfa Market#Alfalfa Market Size#Alfalfa Market Share#Alfalfa Market Growth#Alfalfa Market Trend#Alfalfa Market segment#Alfalfa Market Opportunity#Alfalfa Market Analysis 2023
0 notes
Text
Khoya Making Machine Manufacturer and Suppliers in India
The revolutionary Khoya Making Machine is now available on Indian Trade Bird—discover the ideal option for hassle-free khoya preparation! The platform offers a wide selection of superior machinery aimed at streamlining the process of producing Khoya for dairy farms, confectioneries, and food manufacturing establishments. Whether you're preparing savory meals or classic Indian sweets, you can consistently obtain the ideal consistency for your khoya with our khoya making machine. Our machines, outfitted with cutting-edge technology and accurate controls, guarantee consistent texture and maximum production of Khoya. Indian Trade Bird connects you with trusted manufacturers and suppliers specializing in Khoya Making Machines, ensuring access to top-quality equipment at competitive prices.
For more details clicks here - https://www.indiantradebird.com

0 notes
Text
Top 10 Agriculture Businesses in India
Agriculture plays a pivotal role in India's economy, providing employment to a significant portion of its population and contributing to the country's food security. In recent years, the agricultural sector has witnessed a significant transformation, driven by technological advancements and innovative business models.
This article explores the top 10 agriculture businesses in India that have been instrumental in shaping the industry, promoting sustainable practices, and driving economic growth.
I. Agrochemicals and Fertilizers:
The agrochemicals and fertilizers industry in India has experienced remarkable growth, aiding farmers in improving crop productivity and yield. Leading companies such as IFFCO, UPL, and Dhanuka Agritech have made substantial investments in research and development, manufacturing high-quality fertilizers and pesticides.
These businesses not only contribute to enhanced agricultural practices but also play a critical role in ensuring food security by providing farmers with the necessary inputs for healthy crop growth.
II. Agricultural Machinery and Equipment:
The mechanization of agriculture has been a game-changer in India, improving efficiency and productivity. Companies like Mahindra & Mahindra, Escorts Group, and TAFE (Tractors and Farm Equipment Limited) are at the forefront of manufacturing and supplying advanced agricultural machinery, including tractors, harvesters, and irrigation systems.
These businesses enable farmers to optimize their operations, reduce labor-intensive tasks, and achieve higher yields, thereby transforming the agricultural landscape.
III. Agri-Food Processing:
The agri-food processing industry in India plays a vital role in reducing post-harvest losses, increasing value addition, and enhancing the shelf life of agricultural produce.
Companies like ITC Limited, Nestlé India, and Britannia Industries have established state-of-the-art processing facilities to convert raw agricultural commodities into consumer-ready products.
These businesses contribute significantly to rural employment, provide farmers with fair prices for their produce, and meet the growing demands of the domestic and international markets.
IV. Organic Farming and Sustainable Practices:
In recent years, there has been a surge in demand for organic and sustainably grown produce. Businesses like Nature Bio Foods, Sresta Natural Bioproducts, and Organic India have been pioneers in promoting organic farming practices and offering certified organic products.
These companies emphasize environmentally friendly techniques, minimize the use of chemical inputs, and adhere to sustainable farming methods.
By embracing organic agriculture, they not only cater to health-conscious consumers but also preserve the long-term fertility of the soil.
V. Agri-Tech Startups
The emergence of agri-tech startups in India has revolutionized the agriculture sector, leveraging technology to address various challenges faced by farmers.
Companies such as AgroStar, CropIn, and DeHaat have developed innovative digital platforms, providing farmers with access to information, advisory services, and market linkages.
These startups empower farmers with real-time data, weather forecasts, and crop monitoring solutions, and facilitate seamless interactions with buyers, thereby enhancing efficiency and profitability in agriculture.
VI. Dairy and Livestock Farming
India is the largest milk producer globally, and the dairy industry has been a significant driver of rural income and employment generation.
Companies like Amul, Mother Dairy, and Parag Milk Foods have played a pivotal role in establishing robust dairy supply chains, promoting cooperative models, and ensuring fair returns to farmers.
These businesses not only focus on milk production but also encourage livestock rearing, breed improvement, and animal healthcare, contributing to the overall development of the livestock sector.
VII. Seed Industry
The seed industry forms the foundation of agricultural production, providing farmers with high-quality seeds for diverse crops. Companies like Advanta India, Nuziveedu Seeds, and Mahyco (Maharashtra Hybrid Seeds Company) have been instrumental in developing and distributing hybrid and genetically modified seeds. These businesses invest heavily in research and development to create seeds that offer improved traits such as higher yield potential, disease resistance, and tolerance to adverse climatic conditions. By providing farmers with superior seeds, they contribute to enhancing productivity and profitability in agriculture.
VIII. Agri-Exports
India has emerged as a significant player in the global agri-export market, exporting a wide range of agricultural commodities. Companies such as Adani Wilmar, Ruchi Soya Industries, and Olam International have established strong supply chains and processing facilities to meet the demands of international buyers.
These businesses play a crucial role in connecting farmers to global markets, ensuring fair prices for their produce, and promoting India's agri-export potential. Through their efforts, they contribute to foreign exchange earnings, job creation, and economic growth.
IX. Agri-Input Retail
Agri-input retail businesses have gained momentum in recent years, providing farmers with a one-stop shop for agricultural inputs and services. Companies like BigHaat, Hariyali Kisaan Bazaar, and KisanKraft have established retail networks, offering a comprehensive range of seeds, fertilizers, pesticides, and farm machinery.
These businesses aim to improve farmers' access to quality inputs, provide technical knowledge, and enable the timely availability of agricultural products.
By ensuring convenience and affordability, they empower farmers to make informed decisions and optimize their farming practices.
X. Horticulture and Floriculture
The horticulture and floriculture sectors in India have witnessed remarkable growth, catering to domestic and international markets with a diverse range of fruits, vegetables, and flowers.
Companies like FieldFresh Foods (a joint venture between Bharti Enterprises and Del Monte Pacific Limited), M&M Agritech, and Karuturi Global have made significant investments in horticulture production, post-harvest infrastructure, and value addition.
These businesses have played a pivotal role in promoting contract farming, setting up cold storage facilities, and establishing reliable supply chains. They contribute to the nutritional well-being of consumers and generate employment opportunities in rural areas.
The Future of Agriculture in India
The Indian agricultural sector continues to evolve, driven by technological advancements, innovative business models, and government initiatives. The top 10 agriculture businesses, along with other notable players, are at the forefront of this transformation, fostering sustainable practices, increasing productivity, and promoting inclusive growth.
However, there are still several challenges that need to be addressed. These include fragmented land holdings, water scarcity, climate change impacts, and access to finance and markets for smallholder farmers. To overcome these obstacles, it is crucial for businesses, government agencies, and stakeholders to collaborate and implement comprehensive solutions.
Furthermore, leveraging emerging technologies such as precision agriculture, artificial intelligence, and blockchain can further enhance the efficiency, traceability, and sustainability of Indian agriculture. By integrating these technologies, agriculture businesses can optimize resource utilization, minimize wastage, and improve decision-making processes.
Conclusion
The top 10 agriculture businesses in India showcased in this article have been instrumental in transforming the sector, driving growth, and fostering sustainability.
Through their innovations, investments, and commitment to improving farmers' livelihoods, these companies have demonstrated the potential of agriculture as a key driver of economic development.
As India continues to strive towards food security and sustainable agricultural practices, these businesses will play a crucial role in shaping the future of the agricultural landscape, ensuring a prosperous and resilient farming community.
0 notes
Text
Development Of Dairy Industry By TDP Government in Andhra Pradesh
The TDP government in Andhra Pradesh has revolutionized the dairy industry. The state government has transformed Andhra Pradesh into a leading producer and exporter of milk and dairy products. From empowering farmers with modern technology to promoting entrepreneurship among women, this comprehensive guide will leave you amazed at their dedication towards building a sustainable future for the dairy industry.

The start of Dairy Industry in AP
The dairy industry in Andhra Pradesh started with the launch of the TDP government's Dairy Development Scheme in 1985. The scheme was implemented with the help of World Bank funds and was designed to promote the growth of the dairy industry in the state. The scheme had two components: one was aimed at increasing milk production and the other at processing and marketing of milk products. Under the scheme, dairy farmers were given loans to purchase animals and build infrastructure. The government also provided technical assistance and training to help them improve their husbandry practices. In addition, Nara Chandrababu Naidu who had worked as the Chief minister of Andhra Pradesh had added many of the dairy cooperatives and were set up to provide marketing support to farmers. The scheme was successful in increasing milk production in Andhra Pradesh, which rose from 1 million liters per day in 1985-86 to 2.6 million liters per day by 1989-90.
The success of the Dairy Development Scheme led to the establishment of a number of private dairy companies in Andhra Pradesh. These companies set up modern infrastructure for milk collection, processing, and marketing. With the help of the Top TDP Leaders and many of the ongoing TDP MLAs made sure that they were also introduced to new technologies for quality control and value addition. As a result, the state's dairy industry has grown rapidly, making Andhra Pradesh one of the leading states in India for milk production. And the development of the Dairy industry in the state is said to be one of the greatest TDP Achievements of all times in Andhra Pradesh.
How the people benefited from the Dairy Development
The development of the dairy industry in Andhra Pradesh by the TDP government has been a boon for the people of the state. It has provided employment opportunities for the youths, and has also helped in the development of the rural areas. The dairy industry has also helped in the development of infrastructure in the state. And by this way the government is said to have done the unique Contributions of the TDP Government to its state people and followed on TDP Live Updates.
How it changed the farmers and many village residents throughout the state
The dairy industry in Andhra Pradesh has undergone a massive transformation in recent years, thanks to the efforts of the TDP government. Prior to this, the sector was largely unorganized and small-scale, with most farmers relying on traditional methods of milk production. This all changed when the government launched its ambitious Dairy Development Project in 2016. Under this initiative, a number of modern dairy farms were set up across the state, equipped with the latest technology and machinery. This allowed farmers to significantly increase their milk production levels, while also providing them with much needed employment opportunities.
In addition, the project also resulted in the setting up of a large number of village level Milk Producers’ Societies (MPS). These MPS provide farmers with a platform to sell their milk at competitive prices, while also offering them access to quality inputs and services. The dairy industry in Andhra Pradesh is now flourishing like never before. Farmers are earning more money than ever before, and many village residents who were earlier dependent on manual labor are now employed in various aspects of the dairy value chain. The TDP government’s development of the dairy sector has truly been a game changer for both farmers and rural residents across the state.
0 notes
Text
Development Of Dairy Industry By TDP Government in Andhra Pradesh
The TDP government in Andhra Pradesh has revolutionized the dairy industry. The state government has transformed Andhra Pradesh into a leading producer and exporter of milk and dairy products. From empowering farmers with modern technology to promoting entrepreneurship among women, this comprehensive guide will leave you amazed at their dedication towards building a sustainable future for the dairy industry.
The start of Dairy Industry in AP
The dairy industry in Andhra Pradesh started with the launch of the TDP government's Dairy Development Scheme in 1985. The scheme was implemented with the help of World Bank funds and was designed to promote the growth of the dairy industry in the state. The scheme had two components: one was aimed at increasing milk production and the other at processing and marketing of milk products. Under the scheme, dairy farmers were given loans to purchase animals and build infrastructure. The government also provided technical assistance and training to help them improve their husbandry practices. In addition, Nara Chandrababu Naidu who had worked as the Chief minister of Andhra Pradesh had added many of the dairy cooperatives and were set up to provide marketing support to farmers. The scheme was successful in increasing milk production in Andhra Pradesh, which rose from 1 million liters per day in 1985-86 to 2.6 million liters per day by 1989-90.

The success of the Dairy Development Scheme led to the establishment of a number of private dairy companies in Andhra Pradesh. These companies set up modern infrastructure for milk collection, processing, and marketing. With the help of the Top TDP Leaders and many of the ongoing TDP MLAs made sure that they were also introduced to new technologies for quality control and value addition. As a result, the state's dairy industry has grown rapidly, making Andhra Pradesh one of the leading states in India for milk production. And the development of the Dairy industry in the state is said to be one of the greatest TDP Achievements of all times in Andhra Pradesh.
How the people benefited from the Dairy Development
The development of the dairy industry in Andhra Pradesh by the TDP government has been a boon for the people of the state. It has provided employment opportunities for the youths, and has also helped in the development of the rural areas. The dairy industry has also helped in the development of infrastructure in the state. And by this way the government is said to have done the unique Contributions of the TDP Government to its state people and followed on TDP Live Updates.
How it changed the farmers and many village residents throughout the state
The dairy industry in Andhra Pradesh has undergone a massive transformation in recent years, thanks to the efforts of the TDP government. Prior to this, the sector was largely unorganized and small-scale, with most farmers relying on traditional methods of milk production. This all changed when the government launched its ambitious Dairy Development Project in 2016. Under this initiative, a number of modern dairy farms were set up across the state, equipped with the latest technology and machinery. This allowed farmers to significantly increase their milk production levels, while also providing them with much needed employment opportunities.
In addition, the project also resulted in the setting up of a large number of village level Milk Producers’ Societies (MPS). These MPS provide farmers with a platform to sell their milk at competitive prices, while also offering them access to quality inputs and services. The dairy industry in Andhra Pradesh is now flourishing like never before. Farmers are earning more money than ever before, and many village residents who were earlier dependent on manual labor are now employed in various aspects of the dairy value chain. The TDP government’s development of the dairy sector has truly been a game changer for both farmers and rural residents across the state.
0 notes
Text
Eko Milkanalyzer in Bikaner – Advanced Milk Testing Solutions
Eko Milkanalyzer in Bikaner offers advanced milk testing solutions designed for accuracy and efficiency. Our state-of-the-art milk analyzers ensure precise measurement of key milk parameters, helping dairy farmers, milk processors, and cooperatives maintain quality standards.

#dairy machines#dairy machinery#dairy equipment#dairy farming machinery price in india#dairy machines for sale#data processing unit#milk machine price in india#electronic poducts
0 notes
Text
Best Agriculture Loan Services in Navsari, Gujarat
Agriculture plays a vital role in the economy of India, and Gujarat, especially Navsari, is no exception. Farmers in this region rely heavily on loans to enhance their agricultural activities, whether it's for buying seeds, fertilizers, equipment, or expanding their farms. With the increasing demand for agricultural loans, many financial institutions have emerged offering various types of loans to meet the diverse needs of farmers. In this article, we’ll explore the Best Agriculture Loan Services in Navsari, Gujarat, and how they can help you achieve your farming goals.
Understanding Agriculture Loans
Agriculture loans are financial products designed specifically for farmers and agricultural businesses to help them with the costs of cultivation, purchasing machinery, or expanding their operations. These loans come with flexible terms and conditions to cater to the specific needs of the agricultural community. Whether you are a small-scale farmer or run a large farming business, there are different loan options available, such as crop loans, farm equipment loans, and working capital loans.
Importance of Agriculture Loans in Navsari, Gujarat
Navsari, located in the southern part of Gujarat, is an agricultural hub known for its production of crops like rice, cotton, groundnut, and sugarcane. The region also has a thriving horticulture industry, including the cultivation of fruits like bananas and pomegranates. However, the challenges of unpredictable weather, fluctuating crop prices, and the need for modern equipment make it difficult for farmers to thrive without external financial assistance.
This is where the Best Agriculture Loan Services in Navsari, Gujarat come into play. These services are tailored to support farmers in every step of their agricultural journey, from planting seeds to harvesting and marketing their crops. With the right loan service, farmers can access the capital needed to invest in better technology, high-quality seeds, and modern irrigation techniques.
Types of Agriculture Loans Available in Navsari
In Navsari, Gujarat, several financial institutions offer agriculture loans that cater to various needs. Here are the main types of agriculture loans available:
Crop Loans Crop loans are short-term loans provided to farmers to meet the expenses of crop production. This includes costs for seeds, fertilizers, pesticides, and labor. These loans usually come with low-interest rates and flexible repayment terms, which makes them ideal for seasonal farming needs.
Farm Equipment Loans For farmers who wish to purchase machinery or tools such as tractors, plows, or harvesters, farm equipment loans are the best option. These loans help farmers upgrade their equipment, making their farming practices more efficient and cost-effective.
Horticulture Loans Navsari’s farmers involved in horticulture, including fruit and vegetable cultivation, can benefit from horticulture loans. These loans provide financial assistance for purchasing plant saplings, irrigation systems, and other related resources to improve the productivity of horticultural crops.
Dairy and Poultry Loans For farmers in the dairy or poultry business, specialized loans are available to help with purchasing livestock, setting up sheds, and other infrastructure. These loans can help diversify farming activities and increase income from livestock farming.
Kisan Credit Cards (KCC) The Kisan Credit Card scheme is a popular loan service for farmers in Gujarat. It offers credit to farmers for crop production, post-harvest expenses, and other farming-related needs. The KCC scheme also allows farmers to withdraw cash as needed, making it a flexible and convenient option.
Key Features of Agriculture Loan Services in Navsari
The Best Agriculture Loan Services in Navsari, Gujarat offer several key features that make them ideal for farmers:
Low-Interest Rates: Agriculture loans in Gujarat typically come with lower interest rates compared to other types of loans. This helps farmers repay their loans without facing financial strain.
Flexible Repayment Terms: Many agriculture loans offer repayment terms that align with the agricultural cycle. Farmers can repay their loans after harvest when they have sufficient income.
Easy Documentation: To make the loan process smoother, financial institutions in Navsari provide easy documentation requirements. This ensures that farmers can quickly access the financial assistance they need without bureaucratic delays.
Subsidies and Government Schemes: The government of India and the state government of Gujarat offer various subsidies and schemes to encourage farmers to take loans for agricultural development. These include interest subsidies and loan waivers under specific conditions.
Personalized Financial Guidance: Many financial institutions provide personalized guidance to farmers, helping them understand which loan product is best suited for their needs. This helps farmers make informed decisions and maximize the benefits of their loans.
How to Apply for Agriculture Loans in Navsari
Applying for agriculture loans in Navsari is a straightforward process. Farmers can approach banks, cooperative societies, or microfinance institutions to apply for loans. The process typically involves the following steps:
Eligibility Check: Ensure that you meet the eligibility criteria set by the lender, which may include factors like age, landholding, and previous credit history.
Loan Application: Submit a loan application form along with the required documents, such as land records, identity proof, and income proof.
Processing and Approval: Once the application is reviewed, the lender will process it and provide approval. In some cases, the loan may be disbursed directly to the farmer's bank account.
Loan Disbursement: After approval, the loan amount is disbursed based on the type of loan and the requirements of the borrower.
Conclusion
Access to financial resources is crucial for the success of farmers in Navsari, Gujarat. The Best Agriculture Loan Services in Navsari, Gujarat provide farmers with the tools they need to enhance their agricultural practices and improve their livelihood. By choosing the right loan service, farmers can overcome financial challenges and focus on increasing productivity, improving sustainability, and growing their farming businesses.
If you are a farmer in Navsari looking for the right agriculture loan, it is important to research the various loan options available, compare interest rates, and choose a financial institution that best meets your needs. With the right financial support, your farming venture can flourish and contribute to the growth of the agricultural sector in Gujarat.
0 notes
Text

NK Dairy Farm Equipment Supplier & Manufacturer
NK Dairy farm equipment supplier & manufacturer in India. Know the products list, and machinery prices. For affordable & premium-quality plants, Contact us.
0 notes
Text
Rise of a Digital Agriculture Platform-Agrojay Innovations Pvt Ltd.
Digital agriculture alludes to tools that carefully gather, store, examine and share electronic information as well as data along the farming value chain.
Now and then known as “smart farming” or “e-agriculture, digital farming incorporates exactness agribusiness. In contrast to exactness agriculture, advanced agribusiness impacts the whole agri-food value chain — previously, during, and after on-farm creation. Therefore, on-farm advancements, similar to yield mapping, GPS direction frameworks, and variable-rate application, fall under the space of exactness agriculture and digital agriculture. Then again, digital innovations engaged with e-commerce business stages, e-extension administrations, stockroom receipt frameworks, blockchain-empowered food traceability frameworks, tractor rental applications, etc. fall under the umbrella of digital agriculture however not accurate agriculture.
Digital agriculture encompasses a wide range of technologies, most of which have multiple applications along the agricultural value chain. These technologies include, but are not limited to:
· Cloud computing/big data analysis tools
· Artificial intelligence (AI)
· Machine learning
· Distributed ledger technologies, including blockchain and smart contracts
· Digital communications technologies, like mobile phones
· Digital platforms, such as e-commerce platforms, agro-advisory apps, or e-extension websites
· Precision agriculture technologies, including
o Sensors, including food sensors and soil sensors
o Guidance and tracking systems (often enabled by GPS, GNSS, RFID, IoT)
o Variable-rate input technologies
o Automatic section control
o Advanced imaging technologies, including satellite and drone imagery, to look at temperature gradients, fertility gradients, moisture gradients, and anomalies in a field
o Automated machinery and agricultural robots
On-farm efficiency
On-farm, accuracy agriculture innovations can limit inputs required for a given yield. For example, variables rate application (VRA) innovations can apply exact measures of water, fertilizer, pesticide, herbicide, etc. Various exact examinations find that VRA improves input use proficiency. Utilizing VRA nearby geo-spatial mapping, ranchers can apply contributions to hyper-confined areas of their homestead — here and there down to the individual plant level. Diminishing info use brings down expenses and decreases negative ecological effects. Besides, observational proof shows accuracy agriculture innovations can build yields.
Digital agriculture improves work profitability through improved farmer knowledge. E-extension takes into account cultivating information and abilities to diffuse requiring little to no effort. E-extension administrations can likewise improve farm profitability by means of choice to help benefits on portable applications or other advanced stages. Utilizing numerous wellsprings of data — climate information, GIS spatial mapping, soil sensor information, satellite/drone pictures, etc — e-extension stages can give ongoing proposals to farmers.
At long last, advanced farming improves work profitability through reduced work requirements. Robotization innate inaccuracy agribusiness — from “milking robots on dairy farms to greenhouses with automated climate control — can make yield and domesticated animals the executives increasingly proficient by lessening required labor.
Off-farm/market efficiency
Reducing information asymmetry
Value data influence serious markets’ productivity since it impacts price scattering, exchange, and farmers and customer welfare. Since the negligible expense of carefully conveying data approaches zero, digital agriculture can possibly spread value data. Likewise, cost data gave by Internet booths (“e-choupals”) in India prompted an expansion in farmers’ net benefits as profits lost monopsony power.
Matching buyers and sellers
Online business brings down the inquiry expenses of coordinating purchasers and sellers, possibly shortening the worth chain. Instead of experience many delegates, farmers can sell straightforwardly to consumers. Market get to administrations can likewise take care of the coordinating issue without fundamentally facilitating online transactions. These coordinating stages assist smallholders with organizing with purchasers and enter both local and worldwide worth chains. At last, it’s critical to take note of digital technologies that can likewise encourage coordination in financial and input markets, not only producer to-consumer output sales.
Lowering transaction costs in commercial markets:
Digital payments — whether integrated into e-commerce platforms or in mobile money accounts, e-wallets, etc. — reduce transaction costs inside rural markets. The requirement for sheltered, fast money related exchanges is especially evident in rustic territories. In addition, Digital payments can give passage to financial balances, protection, and credit. Utilizing conveyed record advances or brilliant agreements is another approach to lessen trust-related exchange costs in business markets. Numerous retail and food organizations have collaborated with IBM to create blockchain pilots related to food safety and traceability.
Agrojay is one of the best platforms for Digital agriculture
Agrojay Digital Agricultural platform will help the farmers for the following: 1. Farmers can directly connect with labs and research institutes.
2. Farmers can find agronomist for his crop, also he can give ratings and feedback to him.
3. Farmers can get pre harvesting predictions.
4. Farmers can directly connect with buyers and before harvesting, they can sell.
5. Farmers can easily connect with manufacturers of pesticides, fertilizer, Agri equipment.
6. Farmers can discuss their problems and solution with each other.
Download the app: https://play.google.com/store/apps/details?id=com.wowinfotech.agrojay
Agrojay Innovations Pvt. Ltd.
Check other blogs
Why Agronomist is Important in Agri Sector
Farmer Producer Organization
TOP 10 PROBLEM FACED BY FARMERS
Farmer Producer Organization
Digital Platform for Farmers
2 notes
·
View notes
Link
COMBINE HARVESTER
Combine Harvester is a machine which was designed for three process in one machine i.e. reaping, threshing and winnowing. The modern combine harvester, is a unique machine designed to efficiently harvest various type of crops. Combine harvester have reduced the cost and time of harvesting in India drastically. Today, major manufacturers of combine harvesters have designed combine not only for harvesting of wheat, rice, sorghum, but for forage, cotton, potato, soybean, sun-flower, sugarcane, beetroot, sweet potato, turmeric and onions etc. Earlier most of companies from Belarus, Russia, USA, Germany and Europe were only manufacturing the machine and utilising for their own purpose. Company like Gomselmash, Claas, John Deere and New Holland have started their manufacturing units in India and making their machines available for India and exporting their combine harvester and other agricultural machines to Africa, Nepal, Bangladesh, Sri Lanka and other countries. Now, Forage Harvester is available for forage harvesting which are self-propelled having technology for chopping the maize or similar crops and crushing corn cob. Silage is a best nutrient feed for animal which make them healthy and increase the milk production. Many silage manufacturers are using forage harvester either tractor mounted & pull type and few farmers are using self-propelled forage harvesters for cutting and chopping of maize in India. Now silage is available in India at best price which is being made with the help of high efficient forage harvester and compressed and wrap by high quality of Silage baler and wrapper. Most of Silage balers are imported from the companies of Turkey and Europe i.e. Celikel, Orkel, Mofem etc. Earlier Indian farmers were not aware about forage meaning, forager and silage. Initially farmers of Punjab and Andhra Pradesh have introduced Silage in India. But now harvester machine have change the life of dairy farming by providing them machinery at low price in India. One can easily understand silage meaning, foraging meaning in Hindi, forage meaning in Tamil, forage meaning in Telugu. Forage synonym is hara chara or silage, makki ka achar in India. Government of India is providing subsidy for buying of modern agriculture equipments, one can check about subsidy through dbt agriculture, agriculture, agriculture department, up agriculture, agriculture department bihar, bihar agriculture, dbt bihar gov in, dbt agriculture bihar, dbt agriculture bihar govt, Assam agriculture in, ap agriculture, mp agriculture. Modern agricultural farmers have stopped many questions in India with the significant change in their ways of farming i.e., un, forage crops, what is sustainable development, what does agriculture means, what is community development, what is animal husbandry, what is the green revolution, what is sustainable agriculture, what is water quality, what is ground water, what was the agricultural revolution, what is agricultural science, why is agriculture important, what is agricultural engineering. Combine Harvester are developed by many companies in wheel mounting facilities with 2x2 wheel for utilisation in dry areas or 4x4 wheel operations in muddy or wet lands. Most of companies are now providing track type combine harvesters for rice or paddy harvesting. These harvesters are useful for big or small farms. Mini rice combine harvesters are useful for small farmers who hold small size agricultural fields. Gomselmash, Lovol, Zoomlian, Preet, Dasmesh are the main supplier of track combine harvesters and there are many other manufacturers who make tractor mounted mini combine harvesters in India. After harvesting of crop farmers were burning the residue Parali in the fields which was making pollution very high. Government of India has announced good quantum of subsidies on Combine harvesters, tractor implements and, straw baler, zero till seed drills and other farm equipment’s to make the viability for good agriculture farming. Now farmers have many options for buying the machines as many companies are offering new, old and used harvester for sale, tractor mounted mini combine harvester and self-propelled harvester.
#agricultulre#mini rice harvesting machine price in india#mini combine harvester#combine harvester companies in India#combine harvester price#combine harvester price in india#combine harvester india#combine harvester in India#combine harvester machine#forage harvester
1 note
·
View note
Text
BUILDING UP A FOREIGN TRADE ACTIVITY IS PRECEDED BY BUILDING UP A BUSINESS

picture: modern lace worker, Brussels
Introduction
I have written this text to share it with my postgraduate students from the VUB. They start a year of International Trade and Investment full of courage from various nationalities and from various study backgrounds. They do this with a great deal of diligence and dedication but often find that they do not master the premises: the fact that the course deals with doing business, producing, trading, buying and selling. For many of them, who are at the start of a professional life, even the theoretical knowledge about this is lacking.
That is why I have decided, during an hour and a half, with many examples, to try and guide them in doing business.
1. Doing business
Doing business takes only three forms: it is either about producing something or about purchasing items and then reselling them, or about selling one’s own knowledge and skills to third parties. People sometimes need material for the latter, but they don't sell it. People only sell their workforce and intelligence. The latter are called services. Although they account for between 75% and 80% of the economic activities in most countries, in this article I will deliberately limit myself to agriculture and the manufacturing industry. Because in this presentation we want to end up at trading with foreign partners, and this is primarily about tangible products.
Two stories can support this:
The company F.E. T* 2011, 100 km from the Ukrainian capital Kiev has 2000 ha of land, which it owns partially and leases mostly (long lease 50 y). 80% of the farm’s turnover comes from traditional crops, such as wheat and corn. In order to make future oriented products, the farmer started to develop an entire line (30 items) of dairy products from goat milk, to yoghurt and kephir and even ice cream since 2016. Today the income of this activity line is good for 20% of the turnover. The farmer aims at reaching 50% over 5 years. The goats have been purchased in France and a breeding process started. They now have 1500 goats and intent to increase the amount to up to 3000 goats. They have a milk production capacity for up to 7000 l/day. They are at 2000 l/day. The equipment for milk treatment is Israeli, as well as the milk production supervisor. Cheese production equipment comes from France and Italy as well as their cheese making consultant. The ice cream consultant comes from Italy. The farmer goes yearly to a large goat fair Caprina in France where he learns about gear and equipment and meets potential consultants. This dairy line is a typical example of vertical integration. The production is entirely mastered by the farm from the breeding of goats, the collection and distillation of the milk, the production of the dairy products, the production of the bottles out of small plastic objects purchased in China, the bottling, the development of logo and packaging design, the packaging and the transportation to the retailers. Important is that the farm does and finances market research, developed its own brand Z*, as well as its own design with colour codes. They even intend to create in the future a second high-end brand. These steps enables them to grow organically and in a sustainable way. They declined until now to produce for private labels of retailers. Even with Auchan, with whom they negotiate now, they declined the private label production.
The company W* close to Chisinau in Moldova sells tractors and agricultural equipment from the brand C*, of which they have a dealership agreement during 3 years in Moldova. Before they had a dealership with the Italian M* G*. They also sell equipment from the Swedish brand V*. The company recently built new premises as rep office for C*. They built a state of the art show room and offices with workshop for repairing. The company also sells fertilisers and pesticides as well as seeds for crops. They don’t sell liquids but solid boxes. Their suppliers are BASF, Bayer, Pioneer for the seeds. They produce also seeds themselves (sunflowers).
Services companies are often related to ICT development. Until five years ago, ICT focused primarily on processes and their management. Because of our increasingly complex society, which demands more transparency, which requires faster and more thorough reporting, and which is monitored more and more, large companies have to manage such large volumes of data that they can use help for this. Data is becoming very important, now even more for large, say, listed companies. But medium-sized companies will suffer the same fate in the future. The engineers at the -nowadays “unicorn”- company C* in Brussels are active in data governance and in data stewardship. In this way they do not address the IT departments within a company, but rather the business people themselves.. There are 20 potential customers in Belgium. That is why they had resolutely gone international from the start. They are mainly talking to banks, insurance companies, pharmaceutical companies, etc. But also large governments, large public companies, universities.
2. Import and export
Import and export are often activities that go together in the same company. A company often needs products that are not present in its own country or that are present at too high a price or of poor quality. The company needs these products both to make its own products and to sell them to other customers. He will therefore have to import them. A company is sometimes approached at a trade fair or thanks to its website via e-mail by foreign companies who are convinced that they can use the semi-finished products or raw materials that our company produces in their own production process. In other circumstances our company finds a foreign-interested company at a trade fair that is convinced that there is a market for our company's products in its country and that it wants to sell it there.
3. Producing and selling products.
A company from the manufacturing industry needs raw materials or semi-finished products to make its own products. Depending on the type of quality that they wish to deliver, they must determine where they will purchase their raw materials. Are these present in the country itself or do they have to import them? They also need machines to manufacture their products. Depending on the quality that they are trying to deliver, on their financing options and on the number of staff they have at their disposal, they will purchase their machines, either abroad or domestically but often from abroad.
The company O* in Obuchov,Ukraine has machinery for 2 types of products: polyamide and cotton for women and children socks. They are the second producer in Ukraine. The cotton comes from Turkey, the polyamide from Italy, the elastane from Korea through Poland, the yarn from Italy.
The company D* in Chisinau, Moldova produces fiberglass mesh for construction, especially walls and insolation. It produces 1,2 M m²/month. Thanks to a new machine of the K* from Chemnitz they will be able to double their production to 2.5 M m²/month. They export 90% of his product to Romania, Bulgaria, Germany, Spain and Italy. The company has 100 staff members and is looking this to extend by recruiting 40 new staff members. They have difficulties to find qualified staff. The raw material comes by 80 % from Bielarus, by 20% % from Germany, Switzerland, Latvia and Poland.
4. Buying and selling products
This activity is often performed by a permanent sales representative in a region or a country. This person or company can be established as self-employed in the country (agent, shop / webshop), or can be established as a subsidiary of the foreign company (sales office, shop / webshop) with its own legal status. A representative on the payroll of the foreign company may also be located in the country: he may sell the products but the deal is concluded by the main house abroad and the invoice also comes from the main house. The company W* described above, also houses the rep office of the company for whom they do the sales in the Chisinau region.
Why are companies entering and selling products from abroad? There can be several reasons for this. It is possible that a specific type of machine or product is not produced on the local market because the size of the country is too small for it. It may also be that the importer can deliver in a cheaper way than the products already on the market. It may also be that the new products are much more sophisticated and can therefore make them work much more productively. It may also be that products have built up such a reputation or became a brand that is in demand throughout the world. This last one is the case for many fancy clothing brands like Gucci, Dolce & Gabbana, Dior etc.
Which products do companies offer abroad? That can be anything: from raw materials such as seeds for agriculture, yarns for textiles or fiberglass for construction, to semi-finished products such as fabrics for clothing, goats for milk and cheese production to finished products such as luxury clothing, refrigerators but also cooling installations for cold storage.
The company V* – Groups Ltd in Kiev, Ukraine is a trader. He buys cereals and looks for opportunities. He does business with Sri Lanka, Myanmar, India and many other countries. His warehouse capacity was insufficient and obsolete. He stocked on the ground floor. With a bank loan he has been able to construct 2 grain silos of 3,018 tons capacity each. The silos are erected close to a railway platform, thus avoiding logistical problems and damage to the goods. He found a new business opportunity with Sri Lanka for sale of split yellow peas and next requires an optical sorting machine.
5. The production or purchasing process and its financial aspects
A production company might purchase raw materials or semi-finished products from elsewhere. Before the production of their new product is finished, several weeks or months sometimes pass. And then the new product must still be put on the market, sold and the invoice must be paid. A company therefore needs a financial buffer: that is called working capital. Chocolate producers in Belgium and Switzerland who supply products for the Chinese New Year, which often takes place in February, start their production in September of the year before! Companies often purchase large quantities of raw materials at times when they are offered cheaply and stock them for later production. The same applies to a store: it purchases finished products to resell in the store. There is also a lead time of several days, weeks or months. Here, too, the store needs a buffer called working capital.
The company O* in Ukraine makes pavement tiles out of concrete with artistic top layers. They produce 300 different types of pavement in 60 different shapes. They also produce stone levelling machines of the brand W*. They have offices in Lviv, Ukraine but have their production is set-up 80 km further, where they have 4 separate plants. During winter season, because of the cold, the production is stopped. They received a loan from the bank over 3 year for working capital, since January 2017. The additionality of this loan type for O* is the tenor: 3 years’ working capital enables a company to plan strategically: buy raw material when prices are low and stock it in order to produce through a longer period. And also have a 5-month buffer stock in times of scarcity through political crisis. They have large storage capacities (70.000 tons) for as well raw as finished material.
But those companies also need machines for their production, storage areas, large stores for their sales, trucks for their transport, tractors to work their land. They purchase them or build them with a bank loan. The cost of that loan must be passed on in the selling price. These loans, which are usually of a longer duration, are called investment capital. A company can also invest with its own resources.
The company K* , a wine production company in Georgia specialises in making wines for the lower and medium segment, priced at USD 5 to 8 /bottle. 75% of its production goes to the former CIS countries, of which 50% to Russia, where they have a distributor with the necessary connections, the remainder goes to Ukraine, Belarus, Kazakhstan, Armenia. The final 25% goes to China, US and recently, the UK. In 2016 the company invested in new reservoir tanks, fermentation facilities, refrigerators, a steam generator and a filling & labelling line. The client received in total a loan from BoG. In 2017, the company reapplied for a second loan for land, construction, production facilities over 36 months. Additionally, they invested in health and safety procedures for the workers, environmental protection (by reducing ozone depleting substances), low voltage machinery, electromagnetic compatibility and in measures for materials that come in contact with food. Thanks to the investments the company increased its production volume from 4,6 m litres in 2016 to 6 m litres in 2017, an impressive 35% increase. In labelling and bottling they were able to increase production by 50%.
6. Access to finance
All research reports around the world reveal that access to finance is the aspect that most often blocks the growth of SMEs. Working capital is usually requested for relatively short periods, such as three, six or twelve months. However, the amounts required are often important. The duration of the loan for capital goods is longer: this depends on the price and durability of the good: a computer is outdated after 4 years, a car or light truck starts to show signs of wear after 5 years, machines will certainly be operational during 10 to 20 years, industrial buildings as well. But do the banks have any loans with this duration for all those terms?
A bank's assignment is simple and difficult at the same time. A bank collects money from people who can spare the cash for a certain period of time and gives a fee for this. In Western Europe and North America, this allowance has been peanuts for several years. In Eastern Europe, Africa, large parts of Asia and Latin America, this allowance is quite substantial. Yet most of these “savers” are wary of leaving their money with the banks for too long: they want to buy things with it, or they do not trust the monetary policy of their country and are always afraid of a devaluation of their currency. With the money that banks collect from citizens and companies, they finance loans. They earn their profit through the spread between the interest rate they give for the savings and the interest rate they charge for the credits. But it is difficult for them to grant 10-year loans if they can only collect one-year savings. Moreover, there are few citizens who put away savings for 20 years. The only ones that do that are the pension funds. But what if there aren't any in a country? Which is the case in many countries. The international financial institutions such as African Development Bank, Asian Development Bank, European Investment Bank and European Bank for Reconstruction and Development offer longer-term loans to local banks, that can then transfer them to their customers. Only: most of those loans are in dollars or euros. Again a problem. Because the citizens and companies of the country usually do not have repayment capacity in dollars or euros but in the local currency. And if that local currency is not stable and has a tendency to devalue frequently, local banks are not keen to withdraw long-term dollars or euro loans. Hedging is the only option that remains. Hedging is a type of contract that a bank concludes with a specialized institution to mitigate the risk of devaluation: the contract foresees the exchange rate of euro / dollar to the local currency at the time of repayment, even if the local currency has meanwhile been devalued. Hedging in this case can be considered as a type of insurance. And there are now some companies that also dare to hedge "exotic" currencies. The price ,for this insurance is important though: up to 7 % of the amount.
Banks also do not like to take risks. It is often the central bank of the country that obliges them to be very restrictive in giving loans. Because they have been confronted in the past with bad loans to large outdated government companies that were poorly managed and therefore worked with losses. Governments that have to bear such a burden then hit back with the blunt ax and prevent any loan that is not covered by collateral. Where all statistics indicate that lending to SMEs is much less risky!
Therefore: collateral. In many countries, the way collaterals can be offered to guarantee credit is limited to tangible assets: buildings, land, machines. Intangible assets like the company’s goodwill are not accepted. The valuation of the tangible assets is by law done by the Association of property evaluators. These experts apply the principle of “market value coverage”. Based upon their valuation the size of collateral is put by the bank. It mostly comes to 140% of the loan. Once a credit is taken, the bank declares it to the central credit reporting system. Based upon the regularity of the reimbursement a company is classified class 1, 2, 3 or 4. Class 1 is all payments are done on a regular basis. Class 2 is a company of which arrears were limited from 30 to 60 days. Companies with arrears of between 60 and 90 days are class 3. Companies with arrears of more than 90 days are sent to recovery as class 4. Recovery is compulsory and taken from the profit automatically and can therefore jeopardise the existence of the company. In certain cases the collateral will be sold without warning.
7. Difficulties to tackle
Managing a company goes further than ensuring that people and machines work, that stocks are replenished, that bills are paid and that sales run smoothly. There are constant obstacles that need to be overcome: the financial aspect, the transport aspect, the legal aspect and - once a company starts exporting - the political aspect.
7.1. The banking aspect
A company is practically obliged to work with a bank: it has to make payments and it often needs funds for working capital and for investments.
Payments go faster and smoother nowadays thanks to automation and now also thanks to fintech applications. There are payment cards and credit cards that allow customers to pay without cash and give the collecting company the assurance that the money will be in the account. There are international transaction systems such as SWIFT or the European IBAN that create uniformity between banks and countries and thereby make payment transactions run faster and more efficiently. The currency aspect remains a stumbling block. Although more and more currencies are freely exchangeable, there are still a lot of them that are not convertible. Contracts with companies from such countries are therefore often in USD, EUR or CNY. Banks that operate in those countries are not always considered reliable by the others and must therefore be patterned by an internationally respected confirming bank. There are even countries with which the US in particular are in conflict. They then oblige all banks in the world not to do transactions with banks from that country. Iran, Cuba and North Korea have been assigned such a fate. There are always solutions, but they are complicated and time-consuming.
We have already explained the credit aspect: the fact that in many countries long-term loans are far more the exception than the rule. The extravagant guarantees that are requested. The non-customer-oriented thinking of banks that only wait until a loan is repaid and have no eye for the growth of companies and the usefulness that these can have for the further development of a country. But also the positive role for SMEs that IFIs play such as African Development Bank, Asian Development Bank, European Investment Bank.
Last but not least is the interest charged on loans. In many countries, the interest rate is a double digit, and companies think this is freakish. Where do those freak interest rates come from? The Central Bank of a country offers its banks short-term loans to banks that need them to clear a deficit for one or a few days ("overnight" or tomorrow-next day = “tom-next”). The Central Bank itself is able to provide with these loans because it borrows money on the international money market and pays interest for that. The interest rate the central has to pay for that depends on the country's rating, which is the appreciation of the economy and the way a country makes economic progress. That appreciation is indicated depending on the rating agency with numbers and letters and reflects on the local currency. The lower those ratings are, the more risk premium a central bank has to pay on the international money market. She therefore passes on the risk premium to the local banks, which naturally also pass it on to their customers. Hence countries where the banks demand a double digit interest, when they provide with loans in local currency.
7.2. The transport system
Goods must reach the customer from the workplace. That requires transport. Road transport and train transport are usually the first choice for domestic transport. River transport is still very limited in Europe, is much more present in Asia. When it comes to transport to foreign destinations for import or export, the nature of the product - its weight, its durability, the urgency of the customer - determines the choice between truck, train, ship or plane. All these means of transport have their own international documents, luckily. International rules have also been worked out that determine who becomes the owner of the goods and when. These rules are called the Incoterms, and there are so 11 containing 3 letters each. There are RULES FOR EVERY TYPE OF TRANSPORTATION and there are RULES FOR OVERSEAS AND INLAND TRANSPORTATION BY VESSEL.
Import and export is also about customs and import duties to be paid. It is important to realize the value of customs zones such as the EU and free trade zones such as NAFTA, Mercosur, ECOWAS or ASEAN. The service provider that is most approached by companies to steer this aspect of transport in the right direction is the freight forwarder.
Transporting also entails risks: goods can be damaged or stolen, incidents such as harbor strikes can occur, so that perishable goods do not reach the customer in time. There are insurance policies for these types of problems, but they obviously cost and there is not always room to pass them on to the end customer.
7.3. The legal aspect
Trading within the same country offers few surprises once one knows the legal framework in which one operates. Foreign managers are often surprised that things are not treated in the same way everywhere. Anglo-Saxon legislation is based on a completely different approach than the European continental one. A contract based upon Anglo-Saxon law contains minimum 30 pages, a continental European one can be limited to three-four pages because everything is in the law. In the other continents, the laws were partly inspired by Americans and partly by Europeans. A treacherous aspect in the U.S. is, for example, the principle of litigation: one is going to provoke newcomers and then be able to sue them for not respecting the legislation.
A second aspect is the lack of certain pieces of legislation such as the law on bankruptcy, the law on pledging commercial goods, the law on claiming goods and objects, the mortgage legislation.
A third aspect is the independence of the courts. This is essential if the rule of law is to work objectively. But in many countries, judges are nationalistic, so a case brought to court by a foreign company, or where the foreign company needs to defend itself, is lost in advance.
7.4. The tax aspect
Taxes are the deepest expression of the deepest emotion of a country: there are hundreds and they take different aspects everywhere, even within a country. Brazil, the US and India are federal countries in which the states can collect taxes. And do so with pleasure. Informing yourself in advance is of the utmost importance because it can drastically influence the price worked out by consultants to the end consumer. And one must also know that the principle of VAT is not used all over the world, especially not in the US. Tax declarations are another aspect that one needs to check beforehand. In the US, certain spontaneous declarations are assumed, the consequences of a non-spontaneous declaration can be horrendous.
The last aspect that should be taken into account are the double taxation treaties. Thanks to this, a company only has to pay tax once, either in its home country or in the trading country. That is, for example, the reason why Belgian companies trade with China via Hong Kong.
7.5. The business development aspect
The Access to finance aspect has many consequences. Opportunities can pass because companies in a country have insufficient production capacity. This requires heavier and more efficient machines that cannot be purchased due to the lack of collateral.
The pharmaceutical production company I* in Cape Verde, Africa exported since 1995 to Angola and Mozambique. Those markets became too large and the company’s production capacity was unable to produce the required quantities based upon the governmental tenders they won. The quality is good, but the production capacity is not adapted to large markets.
The same goes for the printing sector in Rwanda, Africa who cannot fulfill orders to print packaging material on time because the local industry is unable to produce cardboard of the correct quality. All packaging cardboard has to be imported. And transportation over road in Africa is perilous and time consuming.
Another aspect that triggers problems is the cultural one. Our company I* in Cape Verde limits its export to Portuguese speaking countries, because otherwise they have to print several packaging types and product information, and they can’t stock it. Coca Cola has been active in China since 1995. That does not mean that the first years of the sales effort were a success. The Chinese were not used to drinking ice-cold drinks: their preference was for hot drinks. So it took Coca-Cola a lot of marketing effort to convince them that ice-cold drinks could quench their thirst. Eastern European wine producers from Romania, Bulgaria and Moldova have had to put a lot of effort into adapting their wines to Western European tastes. Eastern Europeans simply like semi-sweet wines and do not touch dry wines. In Western Europe, semi-sweet wines can only be sold to a very limited segment. It has therefore required a great deal of investment in new storage and maturing capacity (wooden or metal barrels) to produce specifically for Western Europe at a competitive price.
8. Geography and geopolitics
An International Trade and Investment student can be expected to find countries on a map. He can also be expected to realize that there are numerous free trade agreements between countries and groups of countries such as EU, NAFTA, Mercosur, ECOWAS, East-African Community, Association of Southeast Asian Nations (ASEAN countries).
While a customs union and a free trade area are similar in some ways, they are also different. A customs union represents a higher level of economic integration than a free trade area does. The key distinction between customs unions and free trade areas, however, involves their approach to non-treaty nations. While a customs union, by definition, requires all parties to the agreement to establish identical external tariffs with regard to trade with non-treaty nations (those nations that are not signatories to the agreement), members of a free trade area are free to establish whatever tariff rates with respect to foreign imports from non-signatory nations that they deem necessary or desirable. An example of a customs union is the Southern African Customs Union (SACU). An example of free trade area is the ASEAN Free Trade Area (AFTA). Members of the EU, the largest and most productive customs union in existence,, have agreed to, among other criteria for membership, maintain a common external tariff system with respect to outside nations. Free trade areas, like the North American Free Trade Agreement (NAFTA), are less cohesive to the extent that each of the three member nations, the United States, Canada and Mexico, are free to establish tariff policies distinct from each other.
But it is also important for him to grasp that some organizations and initiatives are not only created or organized inspired by goodwill. Certain organizations have been established for power reasons. Some have old-colonial some have also neo-colonial intentions. They exist, one has to work with them and sometimes for them, one can do business with them. One should not necessarily respond enthusiastically to them.
Students are invited to study the background, objectives and history of the following organizations: the Road and Belt initiative, Eurasian economic union, USAid, Eastern Partnership Agreement + DCFTA, Union for the Mediterranean (UfM), West African Economic and Monetary Union (UEMOA) , Organization international de la Francophonie (OIF), the Commonwealth of Nations.
ATTACHMENT
Do you want to import products from non EU countries into the European Union?
https://www.brusselsnetwork.be/do-you-want-to-import-products-from-non-eu-countries-into-the-european-union/
If you want to import a product from a non European country into the European Union, you need to comply with import rules and taxes.
The Trade Helpdesk is specially designed for businesses based outside the EU or importing into the EU.
You’ll find all you need to know about exporting to the EU, including:
health, safety and technical standards you’ll need to meet
customs duties you’ll need to pay at the border
internal taxes in each of the 28 countries
the rules of origin that define where a product is from and whether it profits from preferential duty rates
forms to send with your shipments
Find your way on the Trade Helpdesk through the 6 easy steps for importing into Europe:
Open the search box.
Browse the classification tree or type a keyword.
Define your product, the exporting country and the importing country.
Check ‘Requirements’: the health, safety or technical standards your product needs to meet
Check the ‘Internal taxes’: the VAT or excise duties for your product in the importing country.
the standard rate of EU import duty for your product
a possibly reduced rate if the exporting country has a trade agreement with the EU or benefits from a preferential scheme
any quota or antidumping duties
they indicate the minimum processing your product must undergo in your contry to be considered as ‘originating’ there
the origin depends also on where the inputs you use for your final product are from
the customs offices at EU borders will verify your origin certificate
find out how much other countries are already exporting to the EU of your kind of product
more on product codes
chambers of commerce and customs offices in each EU country or
additional information for your country
1 note
·
View note
Text
Gomselmash India
Gomselmash India Private Limited is a JV company of OJSC "Gomselmash", Republic of Belarus. Gomselmash India Private Limited was incorporated in India for Manufacturing, assembling, sales and after sales services in India, other SAARC and African countries.
Holding "Gomselmash" is one of the largest manufacturers of agricultural machinery ranking among the world market leaders of combine harvesters and other complexes of agricultural machines since 1930.
Today "Gomselmash" is a modern multi-manufacturer producing under the brand name "PALESSE" all range of Harvesting and farming equipments i.e.-
Combine harvesters for Grains & Pulses
· Forage harvesters
· Maize harvesters
· Potato-picking harvesters
· Cotton picking harvesting machine
· Combine harvesters for Soy bean and Sunflower
· Pull type harvesters, mowers, Cultivators, Ridgers and other agricultural machinery.
· Sowing equipments – Precision Seed and fertilizer drills, Tractor mounted Sprayers
· Dairy farming equipments- Total Mix Ration machine, Silage and Hay balers, Cow Brushes, Maize Choppers, Forage Harvesters, Drum Mowers, Feed Crushing Machines, Bale Loading Machines, Leveling Blades, Row independent maize choppers, Mixer Feeder Wagons and Cow Brush Machines .
Gomselmash agricultural equipments are manufactured and sold in brand name "PALESSE". We produce more than 16 categories of farm machinery, including 75 basic models and model types, 70 adapters and units for harvesting different agricultural crops. Agricultural producer with any acreage and crops can choose from these machines a set of most effective models for their conditions.
With a full range of modern production technologies "Gomselmash" independently produces the main parts and components for combine harvesters. It’s providing an opportunity to control the quality, to produce at the same time different types of machines, to maintain reasonable prices for the products.
Combine harvesters "PALESSE” are running in Russia, Ukraine, Kazakhstan, Czech Republic, Slovakia, Romania, Bulgaria, the Baltics, Argentina, Brazil, China, South Korea , Africa, Gulf and other countries. The company has a wide distribution and service network, a range of joint ventures and assembly plants.
#gomselmash#india#harvest#forage#harvester#combine#dairyfarm#equipment#machinery#silage#baler#celikel
1 note
·
View note