#carbon capture and storage market analysis
Explore tagged Tumblr posts
Text
Carbon Capture and Storage (CCS) Market is Set to Exhibit 15.7% CAGR Between Between 2022-2026
Worldwide, the carbon capture and storage (CCS) market is expected to grow at a stellar CAGR of 15.7% and 101 MTP over the prophesied period of 2020-to 2026. Moreover, the market value is projected to reach US$ 9.42 Bn in 2026 from US$ 4.17 Bn in 2020.
With rapid growth in industrialization, carbon dioxide emissions into the atmosphere have scaled up. The rising CO2 emissions have raised concerns of the industries and government. In order to achieve net-zero, several governments have framed favorable policies and schemes for carbon capture and storage adoption. Furthermore, in several countries, the industries are provided with diverse benefits to work considering net-zero emissions.
Major sources of CO2 emissions across the globe include electricity production via natural gas and fossil fuels. Carbon capture and storage activities enable effortless capture, utilization, and storage of carbon dioxide; hence underpins the market growth. Besides, the change in climatic conditions due to such emissions is also a pressing factor that determines the growth of the carbon capture and storage (CCS) market.
For More Industry Insights Read: https://www.fairfieldmarketresearch.com/report/carbon-capture-and-storage-ccs-market
Rising Demand for Enhanced Oil Recovery Provides Impetus to Carbon Capture and Storage
Offshore oil and gas exploration and production activities are thriving with technical upgrades; thus, increasing the adoption of enhanced oil recovery (EOR). Additionally, with 61% of the share, the EOR sector singlehandedly dominates in the carbon capture and storage market across the globe. The EOR activity enables effortless crude oil extraction using carbon dioxide. Onshore and offshore wells are widely opting for EOR techniques for maturing and depleting the oil reserves. Also, these reserves suffice the need for temporary as well as permanent storage of oil in the reservoirs. Consequently, the carbon capture and storage (CCS) market is envisaged to flourish on the solid turf of surging demand for carbon dioxide in order to enhance oil recovery processes.
Sweeping Developments and Higher Adoption Rates Hurls Exponential Growth Across North American Market
With 13 active carbon capture and storage facilities, North America holds the largest share in the global market for carbon capture and storage. Large-scale development and adoption of carbon capture and storage from end-use industries are key factors driving growth to the markets in the region. Collaborative financial assistance of around US$270 million from the U.S. Department of Energy further fosters the growth of the CCS market.
The European CCS market is anticipated to proliferate as it garners 11 new projects to be operated by 2030. In the view of CCS, Norway, Ireland, U.K, and the Netherlands are prominent regions of Europe. Further, the planning, construction, and operations of CCS are primarily backed by the EU’s Innovation fund that impels the growth of the CCS market. Besides, CCS markets in the emerging economies of the Asia Pacific such as South Korea, China, and Australia are likely to grow at a promising pace.
Looking For a Sample Copy of This Report? Request the Same Here: https://www.fairfieldmarketresearch.com/report/carbon-capture-and-storage-ccs-market/request-sample
The eminent market players in the global carbon capture and storage (CCS) domain are GE, Carbon Engineering Ltd., Siemens AG, Mitsubishi Heavy Industrial Ltd., Babcock & Wilcox Enterprises, Inc., Air Liquid, Air Products & Chemical Inc., Global Thermostat, CO2 Solutions, Linde AG, Royal Dutch Shell plc, Total SE, and Climeworks.
About Us
Fairfield Market Research is a UK-based market research provider. Fairfield offers a wide spectrum of services, ranging from customized reports to consulting solutions. With a strong European footprint, Fairfield operates globally and helps businesses navigate through business cycles, with quick responses and multi-pronged approaches. The company values an eye for insightful take on global matters, ably backed by a team of exceptionally experienced researchers. With a strong repository of syndicated market research reports that are continuously published & updated to ensure the ever-changing needs of customers are met with absolute promptness.
#carbon capture and storage#carbon capture and storage (CCS)#carbon capture and storage market#carbon capture and storage market size#carbon capture and storage market share#carbon capture and storage market trends#carbon capture and storage market demand#carbon capture and storage market growth#carbon capture and storage market analysis#carbon capture and storage market report#fairfield market research
0 notes
Text
#United States Carbon Capture and Storage Market#Market Size#Market Share#Market Trends#Market Analysis#Industry Survey#Market Demand#Top Major Key Player#Market Estimate#Market Segments#Industry Data
0 notes
Text

Meet Degrowth, the Green New Deal & Green Authoritarians
When it comes to conversations on socio-ecological solutions, the Green New Deal, degrowth and authoritarian leftism are some of the alternative solutions debated right now. The Degrowth school, while containing multiple and differing voices, can all agree that in order to avert socio-ecological catastrophe, a planned reduction of energy and resource throughput must be organized until the economy is back in “balance with the living world in a way that reduces inequality and improves human well-being.”[1] The expansive tendencies of capitalism – transforming the planet into urbanized environments that produce toxic and nuclear wastes – consumes labor, hydrocarbon, mineral, timber, and kinetic energy resources, which is placed front and center in the degrowth analysis. A key strength of degrowth is that its focus on reducing material throughput – the “taking” and “grabbing” – which positions it, in the word of Corinna Burkhart and colleagues, as “the most radical rejection of the eco-modernist mainstream of growth-centredness, extractivism and industrialism.”[2] Degrowth confronts the dominant myths of ecological modernism and “green growth,” which believe that technological solutions (e.g. low-carbon infrastructures, carbon capture storage, nuclear power, geoengineering) can remediate climate change and socio-ecological degradation while maintaining economic growth as we know it.[3] While there are various eco-modernist positions, which believe in state administration of large-scale technological projects and a command economy, others believe that capitalism and market mechanisms can correct ecological degradation through market-mechanisms and by decoupling economic growth from ecological degradation. The economy can grow, while ecological degradation can decrease. Eco-modernism, importantly, is an expression and continuation of the existing modernist, capitalist or state capitalist trajectories, even if many eco-modernists might argue the state is not doing enough with geoengineering, nuclear development, increasing urban densities and investing in technological innovation.[4] This position, however, has been thoroughly discredited at length by ecological economists and degrowthers.[5] Jason Hickel and Giorgos Kallis, for example, conclude:
This review finds that extant empirical evidence does not support the theory of green growth. This is clear in two key registers. (1) Green growth requires that we achieve permanent absolute decoupling of resource use from GDP. Empirical projections show no absolute decoupling at a global scale, even under highly optimistic conditions. While some models show that absolute decoupling may be achieved in high-income nations under highly optimistic conditions, they indicate that it is not possible to sustain this trajectory in the long term. (2) Green growth also requires that we achieve permanent absolute decoupling of carbon emissions from GDP, and at a rate rapid enough to prevent us from exceeding the carbon budget for 1.5°C or 2°C. While absolute decoupling is possible at both national and global scales (and indeed has already been achieved in some regions), and while it is technically possible to decouple in line with the carbon budget for 1.5°C or 2°C, empirical projections show that this is unlikely to be achieved, even under highly optimistic conditions. The empirical evidence opens up questions about the legitimacy of World Bank and OECD efforts to promote green growth as a route out of ecological emergency, and suggests that any policy programmes that rely on green growth assumptions – such as the Sustainable Development Goals – need urgently to be revisited. That green growth remains a theoretical possibility is no reason to design policy around it when the facts are pointing in the opposite direction.[6]
Other studies find similar results. Reviewing 179 articles that contain evidence of decoupling, Vadén and colleagues conclude that “the empirical evidence on decoupling is thin” and “the evidence does not suggest that decoupling towards ecological sustainability is happening at a global (or even regional) scale.” Vadén and colleagues continue that the analysis of decoupling “needs to be supported by detailed and concrete plans of structural change that delineate how the future will be different from the past.”[7] These findings, indeed, raises serious questions of legitimacy concerning international financial, governance and higher-learning institutions that ignore the reality of ecological modernism and the necessity of degrowing material and energy production/consumption.
Degrowth, as opposed to capitalist liberalism and eco-modernism, gets to the root of human exploitation and nonhuman extraction, questioning developmental modes requiring enormous amount of raw materials and energy. This also includes critically reflecting on the productivist work regimes organized, whether liberal capitalist, state capitalist or otherwise. Degrowth, while retaining differing tendencies within it, seeks to create a public space for socio-ecological remediation and promotes a largely anti-authoritarian developmental pathway by advocating “degrowth values,” such as autonomy, care, conviviality, equity and direct democracy.[8] Degrowth is the organized and planned reduction of energy and material consumption with the intention of improving the quality of people’s lives by moving towards more convivial and fulfilling lifeways rooted in community-supported agriculture, commoning land, cooperative economies, switching to localized low-carbon energy production and political systems built around direct democracy and more.[9] Degrowth represents an autonomous, feminist, democratic and anarchistic approach to social development. Degrowth, as you can imagine, is not without its critics, from ecological modernists to authoritarian leftists chastising their failure to have a planned program or pronounced focus on the working class.[10] Likewise, there are sympathetic critiques from feminists and anarchists North and South of the Globe, pointing out their relevance, but also how degrowthers’ appear detached from political struggles (with middleclass positionalities) and failure to be clear about political strategy and action.[11] Degrowthers, however, are working through these criticisms,[12] which is compounded by the conflictive reality of capitalism and the state. This means charting a viable path towards social transformation and that degrowthers’ “strategic orientation thus needs a strategy for [how to engage] the state.”[13]
The issue of the state quickly leads to the hopes surrounding the Green New Deal in all of its variants. While readers might be more familiar with The Green New Deal (GND) as it spread across headlines in 2019, it was initially a term proposed by the infamous conservative economist and New York Times columnist Thomas Friedman in 2007. The GND refers to President Franklin D. Roosevelt’s New Deal that responded to the Great Depression with social and economic reforms. In January 2019, congressional representative Alexandria Ocasio-Cortez and Senator Ed Markey proposed the GND in United States Congress. While it failed to pass in the Senate, it created enormous enthusiasm for renewing public policy with a variety of energy, housing, agricultural and industrial reforms. Numerous authors advocated the Green New Deal,[14] among them Noam Chomsky, and the program was further elaborated on by economist Robert Pollen.[15] Later, again, the GND was further developed under Bernie Sanders presidential campaign.[16] Meanwhile the European Commission began enacting the European Green Deal (EGD). Trade unions and non-governmental organizations also began articulating their proposals, only slightly departing from the original US proposal.
The GND and EGD remained “green growth” strategies that claimed to organize a (socio-technical) energy transition from fossil fuels to so-called renewable energy, all the while ignoring the amount of minerals, hydrocarbon resources, manufacturing and transportation supply-chains necessary to rollout low-carbon infrastructures. Sanders’ fiery rhetoric against hydrocarbon industries did not account for this material reality for “achieving 100% renewable energy” in the United States[17]—or similar claims within Europe.[18] The GND, however, offered a valuable proposal to create “green jobs,” agricultural reform, recognizing Indigenous rights, housing reform and promoting “just transitions” among others, which could have made incrementally positive social changes domestically, potentially redirecting and restricting the use of hydrocarbons. Then again, unless the economic, energy and material growth imperatives of capitalism and corresponding low-carbon infrastructures and electrification are capped—or have a limit—nothing structurally changes within this socio-technical shift that continues private or state capital accumulation. In the end—as usual—ecologies and habitats would be overlooked and sacrificed in the name of low-carbon infrastructures that leave untouched the (neo)colonial global supply-chains predicated on unequal exchange, violence and racist discrimination.[19] Not to forget, nobody really knows the quantity of fossil fuels actually used to produce a wind turbine, solar panel or a dam. These issues are discussed further in the next chapter, with an emphasis on the arithmetic, models and science propelling these aspirations.
While degrowth advocates initially advocated the GND, seemingly uncritically—overlooking the realities discussed in this book[20]—it still led to heated and antagonistic debates with environmental economists and modernist socialists.[21] Despite the needed social reforms of the GND, the mainstream versions still never questioned economic growth, energy markets and the expansive reality of capital accumulation responsible for socio-ecological catastrophe. Because, as James O’Conner reminds us, “over time, capital seeks to capitalize everything and everybody.”[22] If the GND is anything like Roosevelt’s New Deal, Gelderloos reminds us, then it is designed to prevent “a real solution” and “to save capitalism,” placing “the brunt of this new industrial onslaught” onto the laps of the marginalized and poor of this world lower on the capitalist pyramid scheme.[23] From this perspective, the GND proposals sought to blunt revolutionary demands for socio-ecological transition, meanwhile developing and expanding green capitalism.
Implicit, and most appealing, about the GND is the state as an agent of administering social change. Experts, however, agree governments across the world, especially Euro-American governments influencing international policy, have resolutely failed for thirty—if not forty—years to develop adequate environmental policies that produce results.[24] Some people blame this on hydrocarbon companies lobbying politicians, hiding and falsifying science,[25] but this accepts the other deleterious socio-ecologically destructive impacts of urbanization, the proliferation of plastics, chemically intensive industrial production and low-carbon infrastructures (dependent on fossil fuels) that are normalized by capitalist states in their quest for territorial control and technological supremacy. This fossil fuel versus renewable energy dichotomy emblematic of the GNDs, and inundating corporate propaganda, remains central to the socialist modernist position.
The socialist modernist position takes on various intensities, yet have a core set of beliefs. “Softer” socialist modernist positions join the GND bandwagon, which celebrates centralized planning and technological innovation. “Solving climate change undoubtedly requires massive new industrial infrastructure in energy, public transit and housing,” explains Matt Huber.[26] This perspective, however, breaks with capitalism with a presumed ethic of egalitarianism and a pronounced concern with the “working class” and “global proletariat.” This position celebrates and encourages “techno-fixes” such as carbon capture storage (CCS), nuclear power and the state as administrator.[27] “Clearly, the productive forces must develop beyond their historically entrenched reliance upon fossil fuels,” explains Huber.[28] This somehow implies, possibly influenced by Marxian stage theory, that low-carbon infrastructures and electrification can be separated from hydrocarbons to enter a ‘new stage’ of decarbonized and renewable (socialist) industry. This tendency, moreover, tends to operate in the abstract with repeated references to Marxian theorists, for example, criticizing degrowthers for missing “the concrete class relationships that both inhabit such transformations or might bring them about.” While Huber has been rebuked by other Marxian scholars,[29] it is strange how he failed to engage with Joan Martinez-Alier’s “environmentalism of the poor,”[30] which connects ‘the poor’—Indigenous and working class—to ecological struggles. Socialist modernism, we can say, is eco-modernism with egalitarian intentions. Huber’s variety does not depart from representative democracy, strengthening electoral political strategies and union organizing.[31] Degrowth, from this perspective, is understood as a “hard sell” to the working class and political campaigns, because challenging economic growth and the consumerist lifestyles—or ‘imperial modes of living’—have become habitual and questioning this is not a popular position in the voting polls. While both agree on some form of democracy, socialist modernism confronts degrowth by asking how their proposed socio-ecological transition will be accomplished.
#climate crisis#climate change#Climate Justice#Direct Action Movement#Earth First#Earth Liberation Front#Green anarchism#How to Blow Up a Pipeline#United Kingdom#uk politics#Andreas Malm#anarchism#anarchy#anarchist society#practical anarchy#practical anarchism#resistance#autonomy#revolution#communism#anti capitalist#anti capitalism#late stage capitalism#daily posts#libraries#leftism#social issues#anarchy works#anarchist library#survival
4 notes
·
View notes
Text
Global Decarbonization Service Market Is Estimated To Witness High Growth Owing To Growing Environmental Concerns
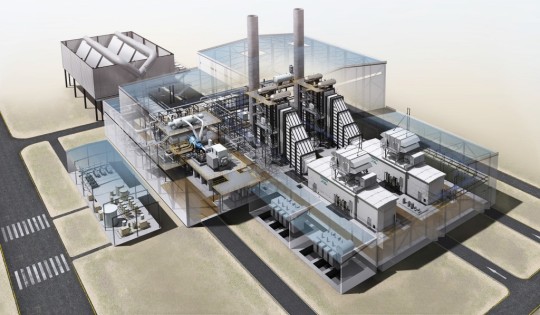
The Global Decarbonization Service Market is estimated to be valued at US$69.73 billion in 2023 and is expected to exhibit a CAGR of 12.3% over the forecast period 2023 to 2030, as highlighted in a new report published by Coherent Market Insights. This market involves the provision of decarbonization services that help reduce carbon emissions and promote sustainable energy practices. With increasing concerns over climate change and the need to transition towards clean energy sources, organizations and governments around the world are seeking decarbonization solutions. These services offer various advantages, such as reduced environmental impact, improved energy efficiency, and compliance with regulatory standards. Market key trends: Technological advancements driving decarbonization efforts One key trend in the global Decarbonization Service Market is the increasing focus on technological advancements to drive decarbonization efforts. Advancements in renewable energy technologies, energy storage systems, and carbon capture technologies are enabling organizations to adopt more sustainable practices. For example, the implementation of smart grids and advanced metering infrastructure allows for better monitoring and management of energy consumption, leading to optimized energy usage and reduced carbon emissions. Similarly, the development of carbon capture and storage technology enables the capture and sequestration of CO2 emissions from industrial processes, reducing their impact on the environment. PEST Analysis: - Political: Governments worldwide are implementing policies and regulations to encourage decarbonization. This includes carbon pricing mechanisms, renewable energy targets, and incentives for clean energy adoption. - Economic: The economic benefits of decarbonization, such as cost savings from improved energy efficiency and the creation of green jobs, are driving market growth. Additionally, the declining costs of renewable energy technologies make them more affordable and attractive alternatives to fossil fuels. - Social: Increasing public awareness and concern about climate change are driving demand for decarbonization services. Consumers and organizations are actively seeking sustainable solutions to reduce their carbon footprint and contribute to a greener future. - Technological: Technological advancements, as mentioned earlier, are playing a crucial role in accelerating decarbonization efforts. The development of innovative solutions and the integration of renewable energy sources into existing infrastructure are enabling a more sustainable energy transition. Key Takeaways: 1: The Global Decarbonization Service Market Size is expected to witness high growth, exhibiting a CAGR of 12.3% over the forecast period. This growth is driven by increasing environmental concerns and the need for sustainable energy practices. For example, the rising global temperatures and extreme weather events are motivating governments and organizations to adopt decarbonization services. 2: In terms of regional analysis, North America is expected to be the fastest-growing and dominating region in the Decarbonization Service Market. This can be attributed to government initiatives promoting clean energy adoption, favorable regulatory frameworks, and high awareness among consumers about the importance of decarbonization. 3: Key players operating in the global Decarbonization Service Market include Schneider Electric, ENGIE, Siemens, AECOM, EDF Group, Johnson Controls, DNV, Honeywell, Carbon Clean Solutions, Green Charge Networks (ENGIE Impact), ERM (Environmental Resources Management), First Solar, Tesla, CarbonCure Technologies, and Ørsted. These companies are actively providing decarbonization services and developing innovative solutions to address the increasing demand for sustainable energy practices.
#Decarbonization Service Market#Decarbonization Service Market Insights#Decarbonization Service Market Forecast#Decarbonization Service Market Analysis#Decarbonization Service Market Values#Decarbonization Service#climate change#carbon footprint#stor#age technologies#renewable energy#Coherent Market Insights
6 notes
·
View notes
Text
0 notes
Text
Harnessing Technology: The Future of Carbon Capture and Sequestration Market - UnivDatos
As per International Energy Agency data for 2020, globally, roughly 40 million metric tons of CO2 (MtCO2) is being captured and stored each year (mostly as part of enhanced oil recovery [EOR]). However, as per energy outlook analyses, to meet the emission target, it is estimated that CCS would be needed on the scale of upwards of 1,500 MtCO2 being captured per year by 2030 and between 5,000-10,000 MtCO2 being captured per year by 2050. If the Carbon Capture and Sequestration technology is deployed globally to address emissions as part of a broad suite of zero or low carbon technologies, the carbon capture industry would employ between 70,000-100,000 construction workers and between 30,000-40,000 facility operators by 2050, with additional employees to build and maintain CO2 transport and storage network
Request To Download Sample of This Strategic Report - https://univdatos.com/get-a-free-sample-form-php/?product_id=48768&utm_source=LinkSJ&utm_medium=Snehal&utm_campaign=Snehal&utm_id=snehal
Covid-19 pandemic have impacted all section of the society and industry and Carbon Capture and Sequestration market is no exception. Covid-19 pandemic has resulted in slow growth of the energy and power sector in most of the economies globally, as many countries are resorting to nationwide lockdowns to prevent a spread of the virus. Globally, as of 2020, there were 26 large-scale facilities capture approximately 40 millions of CO2 per year in operation, with US being home of 12 commercial-scale carbon capture facilities, with the capacity to capture approximately 23.5 million tons of CO2 annually.
According to UnivDatos Market Insights (UMI)’ research report “Global Carbon Capture and Sequestration Market”, the market is expected to witness a CAGR growth of 22.8% during the forecast period 2023-2030F. Rising number of EOR Projects to reduce Carbon Emissions, rising Government investments on Carbon Capture technology and Growing investments from the private sector companies are the major factors driving the growth of global Carbon Capture and Sequestration market. However, lack of fund (majorly in the developing regions) to act as a major challenge for the growth of the industry. Furthermore, Prevalence of Carbon Capture Plants in the US, to provide growth opportunity for the North America Region.
Based on the Service, the Global Carbon Capture and Sequestration Market is bifurcated into Capture (combustion and industrial separation), Transport, Sequestration. Currently, Carbon Capture segment dominate the market and is expected to maintain its dominance during the forecast period.
Based on capture source, the market is segmented into segmented into Chemicals, Natural Gas Processing, Power Generation, Fertilizers Production, Others. Natural Gas Processing and Power Generation together generated major revenue share in 2020.
Based on source category, the Global Carbon Capture and Sequestration Market is bifurcated into EOR and dedicated geological straoge. Currently, EOR segment dominated the market. However, during the forecast period, dedicated geological storage category is likely to showcase the fastest growth rate.
Europe to witness highest growth
Based on region, the report provide detail analysis for overall adoption of Carbon Capture and Sequestration in major region including North America (US, Canada), Europe (Germany, UK, France, Italy, Spain), Asia-Pacific (China, India, Japan, Australia), Middle East & Africa (South Africa, UAE, Saudi Arabia), and South America (Brazil, Argentina). Europe is likely to showcase the fastest growth rate during the forecast period owing to expected commissioning of large-scale commercial projects in the region.
According to UnivDatos Market Insights (UMI)’, the key players with a considerable market share in the Global Carbon Capture and Sequestration market are Fluor Corporation, Linde AG, Shell, Petrobras, Chevron, TotalEnergies, Equinor, China National Petroleum Corporation, ExxonMobil, ADNOC Group. These companies are investing heavily on technology to increase their customer base.
Some of the instances are:
§ Total, Equinor, and Shell together invested over US$ 680 million on the Northern Lights CCS project for phase 1. The ongoing project aims at developing robust infrastructures for the transportation and storage facilities for 1.5 metric tons per annum (MTPA) carbon dioxide
§ US Department of Energy (DOE) granted US$11.05 million for projects FLExible Carbon Capture (FLECCS). The project when completed would provide an efficient natural gas power generation system and upgrade the existing technology
§ Exxonmobil, recently announced a US$3 billion investment over the next 5 years in new carbon capture and storage (CCS) projects
§ In 2021, ExxonMobil announced the creation of a new business “ExxonMobil Low Carbon Solutions” to commercialize and deploy emission-reduction technologies. The unit would initially focus on carbon capture and storage (CCS), one of the critical technologies required to achieve net zero emissions and the climate goals outlined in the Paris Agreement
“Global Carbon Capture and Sequestration Market” provides comprehensive qualitative and quantitative insights on the industry potential, key factors impacting sales and purchase decisions, hotspots, and opportunities available for the market players. Moreover, the report also encompasses the key strategic imperatives for success for competitors along with strategic factorial indexing measuring competitor's capabilities on different parameters. This will help companies in the formulation of Go to Market Strategies and identifying the blue ocean for its offerings.
Ask for Report Customization - https://univdatos.com/get-a-free-sample-form-php/?product_id=48768&utm_source=LinkSJ&utm_medium=Snehal&utm_campaign=Snehal&utm_id=snehal
Market Segmentation:
1. By Service (Capture (Combustion and Industrial Separation), Transport, Sequestration)
2. By Capture Source (Chemicals Production, Natural Gas Processing, Power Generation, Fertilizers Production, Others)
3. By Storage (EOR and Dedicated Geological Storage)
4. By Region (North America (US, Canada), Europe (Germany, UK, France, Italy, Spain), Asia-Pacific (China, India, Japan, Australia), Middle East & Africa (South Africa, UAE, Saudi Arabia), and South America (Brazil, Argentina))
5. By Company (Fluor Corporation, Linde AG, Shell, BP, Chevron, Total SA, NRG Energy, China National Petroleum Corporation, ExxonMobil, ADNOC Group etc.)
0 notes
Text
The Carbon Capture and Sequestration Market is projected to grow from USD 4202.5 million in 2024 to an estimated USD 18434.55 million by 2032, with a compound annual growth rate (CAGR) of 20.3% from 2024 to 2032. The Carbon Capture and Sequestration (CCS) market is emerging as a cornerstone of global efforts to combat climate change by reducing carbon dioxide (CO₂) emissions. CCS technology captures CO₂ from industrial and power generation sources and stores it underground, preventing it from entering the atmosphere. With increasing environmental concerns, stringent government regulations, and the growing need for sustainable energy solutions, the CCS market is poised for significant growth in the coming years.
Browse the full report https://www.credenceresearch.com/report/carbon-capture-and-sequestration-market
Market Overview
The CCS market comprises three key stages: capture, transportation, and sequestration. Carbon capture involves isolating CO₂ from industrial processes, power plants, or direct air capture systems. Transportation of captured CO₂ often relies on pipelines, ships, or tankers to reach storage sites. Finally, sequestration involves injecting CO₂ into deep geological formations, such as depleted oil and gas reservoirs or saline aquifers, where it is stored permanently.
In 2024, the CCS market is expected to witness robust investments from both public and private sectors. Countries around the globe are implementing aggressive carbon neutrality targets, making CCS an essential technology for industries that are hard to decarbonize, such as cement, steel, and chemical manufacturing.
Key Market Drivers
1. Stringent Regulatory Frameworks
Governments worldwide are imposing strict regulations to reduce greenhouse gas emissions. The European Union's Green Deal and the United States' Inflation Reduction Act include provisions to promote CCS technology. Tax credits, grants, and incentives are making CCS projects more financially viable.
2. Corporate Net-Zero Commitments
Many multinational corporations are committing to net-zero emissions by 2050 or earlier. These commitments drive investments in CCS as part of comprehensive strategies to reduce operational and supply chain emissions.
3. Technological Advancements
Innovations in carbon capture technologies, such as solvent-based capture, solid sorbents, and direct air capture systems, are improving efficiency and reducing costs. The development of integrated hubs that serve multiple emitters is also boosting the scalability of CCS.
4. Rising Carbon Pricing
The increasing adoption of carbon pricing mechanisms, such as carbon taxes and emission trading systems, is incentivizing businesses to adopt CCS to mitigate financial penalties associated with high carbon emissions.
Challenges and Opportunities
While CCS has immense potential, challenges such as high costs, public opposition to CO₂ storage, and regulatory hurdles remain. However, the market is ripe with opportunities:
Development of CCUS (Carbon Capture, Utilization, and Storage), which involves repurposing captured CO₂ for products like synthetic fuels and building materials.
Expansion of carbon credit trading to create additional revenue streams for CCS projects.
Collaboration among governments, industries, and NGOs to standardize regulations and build public trust.
Future Outlook
The CCS market is expected to grow at a compound annual growth rate (CAGR) of 12–15% from 2024 to 2032. As the world transitions toward a low-carbon future, CCS will play a critical role in decarbonizing hard-to-abate sectors and achieving global climate goals. With continued innovation, investment, and collaboration, the CCS market holds the promise of a sustainable and resilient future.
Key Player Analysis:
ADNOC Group (UAE)
Aker Solutions (Norway)
BP (U.K.)
Carbon Engineering Ltd (Canada)
Chevron (U.S.)
China National Petroleum Corporation (China)
Dakota Gasification Company (U.S.)
Equinor (Norway)
Exxonmobil (U.S.)
Fluor Corporation (U.S.)
Linde Plc (Ireland)
NRG Energy (U.S.)
Shell (Netherlands)
Total Energies (France)
Segmentation:
By Capture Source Analysis
Natural Gas Processing
Power Generation
Fertilizer’s Production
Chemicals
Others
By End-use
Dedicated Storage & Treatment
Enhanced Oil Recovery (EOR)
By Region
North America
U.S.
Canada
Mexico
Europe
Germany
France
U.K.
Italy
Spain
Rest of Europe
Asia Pacific
China
Japan
India
South Korea
South-east Asia
Rest of Asia Pacific
Latin America
Brazil
Argentina
Rest of Latin America
Middle East & Africa
GCC Countries
South Africa
Rest of the Middle East and Africa
Browse the full report https://www.credenceresearch.com/report/carbon-capture-and-sequestration-market
Contact:
Credence Research
Please contact us at +91 6232 49 3207
Email: [email protected]
Website: www.credenceresearch.com
0 notes
Text

Saudi Arabia Distributed Energy Generation Market Analysis 2030
Saudi Arabia had been witnessing a significant level of development in its distributed energy generation market. The Saudi Arabia Distributed Energy Generation market is projected to reach USD 1339.82 million by 2030 from USD 418.1 million in 2022 with a CAGR of 15.67% for the country has been working towards diversifying its economy, reducing its dependency on oil, and promoting sustainable development. Hence, distributed energy systems, including renewable energy sources like solar power, wind power, etc. play a crucial role in this strategy by providing alternative sources of power thereby facilitating the market growth.
In Saudi Arabia, solar energy is the most dominant renewable energy source that is being harnessed for electricity generation. The country has abundant solar resources, making it an ideal location for solar power projects. Moreover, solar energy is particularly valuable in remote and off-grid areas of Saudi Arabia. In regions where extending the traditional grid infrastructure is not feasible, solar power provides a reliable and cost-effective solution. Numerous solar power projects are launched across the country by the Saudi Arabian government in order to increase its solar energy capacity. Sakaka PV Solar Project in Sakaka City within the Al Jouf Province of Saudi Arabia is a solar project with a capacity of 300MW that harnesses solar energy though photovoltaic panels. By being integrated into the national electricity grid, the power plant is anticipated to provide a sufficient amount of clean energy to meet the needs of over 75,000 households in Saudi Arabia. This will result in a substantial reduction of over 430,000 tonnes of carbon dioxide (CO₂) emissions annually.
A Continuous Increase in Renewable Energy Deployment
Saudi Arabia has been actively promoting the adoption of renewable energy sources for distributed energy generation. There has been a significant emphasis on solar energy, with the country aiming to install 58.7 GW of solar capacity by 2030. This push towards renewable energy has led to a rise in distributed solar installations, both on rooftops and in ground-mounted projects. According to the General Authority for Statistics of Saudi Arabia, the country has set a target to generate 15.1 terawatt-hours (TWh) of renewable energy annually by 2024. This amount of renewable energy production will be sufficient to fulfill the electricity needs of approximately 692,557 households. Furthermore, the National Renewable Energy Program of Saudi Arabia comprises a total of 13 projects, with a combined capacity of 4,870 megawatts (MW).
The Advent of Bifacial Solar Panels
Bifacial solar panels have the potential to generate more electricity compared to monofacial panels and are widely used for distributed energy generation. By capturing sunlight from both sides, they can utilize the reflected light, which increases the overall energy yield of the system. This is particularly beneficial in desert regions like Saudi Arabia, where the ground reflects a significant amount of sunlight. Hence the key players operating in this region are sheer focusing on the installation of bifacial solar panels.
LONGi Solar Technology Co., Ltd. – (LONGi) has recently reported the successful provision of 406MW worth of its Hi-MO 5 bifacial photovoltaic (PV) panels to the Solar plant created by PowerChina SEPCO III. This solar plant is part of Saudi Arabia’s Red Sea Solar PV Project. At present, this undertaking stands as the largest energy storage project worldwide that is currently being constructed and holds the title of the world’s largest off-grid integrated smart energy project.
Government Regulations
The government of Saudi Arabia has implemented various regulations and policies to support and regulate the distributed energy generation market in the country. These regulations aim to promote renewable energy, enhance energy efficiency, and create a favorable environment for bidding of distributed energy projects. For example – REPDO (Renewable Energy Project Development Office), introduced in 2017, initiated the initial phase of renewable energy projects, including the Sakaka 300 MW solar PV project, which is now integrated into the national power grid, and the Dumat Al Jandal 400 MW wind project, currently in the construction phase. The development of a prosperous renewable energy sector is a fundamental aspect of Saudi Vision 2030, a comprehensive economic and social roadmap, with an initial objective of generating 9.5 GW (gigawatts) of renewable energy. The plan also envisions the involvement of public-private partnerships and gradual liberalization of the fuel market. Hence, it can be stated firmly that the implication of govt programs has facilitated market growth greatly.
Impact of COVID-19
The COVID-19 crisis highlighted the importance of resilient and decentralized energy systems. The distributed energy generation market, with its potential for energy independence and local resilience, gained further recognition as a viable solution for future energy needs. Moreover, in response to the pandemic, government of Saudi Arabia emphasized the importance of renewable energy and sustainable development for economic recovery. Saudi Arabia has continued to demonstrate its commitment to renewable energy, including distributed energy generation, by announcing initiatives and regulatory reforms to support the sector. While the COVID-19 pandemic initially posed some economic challenges to the distributed energy generation market in Saudi Arabia, the long-term impacts are likely to result in a renewed focus on renewable energy and the acceleration of the energy transition. As economies recover and adapt to new realities, distributed energy generation is expected to play a crucial role in building more resilient and sustainable energy systems.
Download Sample Report
Saudi Arabia Distributed Energy Generation Market: Report Scope
Markets and Data’s report titled “Saudi Arabia Distributed Energy Generation Market Assessment, Opportunities, and Forecast, 2016-2030F” offers a thorough examination and assessment of the current state of the Saudi Arabia Distributed Energy Generation market. The study provides a detailed analysis of the industry’s dynamics, opportunities, and future projections from 2023 to 2030. Moreover, the report delves into the key players within the industry, focusing on their business models, market share, competitive intelligence, and other relevant aspects.
Click here for full report- https://www.marketsandata.com/industry-reports/saudi-arabia-distributed-energy-generation-market
Latest reports-
Contact
Mr. Vivek Gupta 5741 Cleveland street, Suite 120, VA beach, VA, USA 23462 Tel: +1 (757) 343–3258 Email: [email protected] Website: https://www.marketsandata.com
0 notes
Text
The Green Hydrogen Market is projected to reach $12.8 billion by 2030
Meticulous Research®, a prominent global market research firm, has recently published an insightful report titled, “Green Hydrogen Market by Generation Process (PEM, Alkaline, Solid Oxide), Energy Source (Wind, Hydropower), Application (Fueling, Feedstock), End User (Transportation, Chemical Production, Power Generation), and Geography - Global Forecast to 2030.”
This report forecasts that the green hydrogen market will grow to $12.8 billion by 2030, exhibiting a remarkable CAGR of 40.9% during the forecast period. Key drivers of this growth include the increasing demand for green hydrogen in fuel cell electric vehicles (FCEVs), a surge in green hydrogen utilization in chemical production, and robust government initiatives aimed at achieving net-zero emissions. However, high production costs present a significant barrier to market expansion.
Download Sample Report @ https://www.meticulousresearch.com/download-sample-report/cp_id=5580
On the flip side, growing investments in electrolysis technology and the rising preference for green hydrogen due to its zero-carbon footprint are expected to open new avenues for growth. Yet, the challenges posed by complex and costly storage and transportation methods remain a major concern for industry players. Notably, recent trends indicate a growing reliance on water and electricity for green hydrogen production.
Market Segmentation Overview
The green hydrogen market is meticulously segmented by various factors, including the generation process, energy source, application, end user, and geographic location. This segmentation allows for a comprehensive analysis of competitors and market dynamics at regional and country levels.
Generation Process: The market is divided into proton exchange membrane electrolysis, alkaline electrolysis, and solid oxide electrolysis. In 2024, proton exchange membrane (PEM) electrolysis is expected to dominate, driven by its ability to operate at high current densities and the growing focus on fuel cell technologies.
Energy Source: The energy sources fueling green hydrogen production include wind, solar, hydropower, and other renewable sources. The hydropower segment is predicted to hold the largest market share in 2024, attributed to the increasing demand for renewable energy and governmental support for reducing fossil fuel dependency.
Application: The market applications encompass fueling, feedstock, heat processing, and energy storage. The feedstock segment is expected to be the largest, primarily due to the rising adoption of green hydrogen in chemical production and its appeal as a zero-carbon energy source.
End User: The end-user categories include transportation, chemical production, healthcare, and power generation. The chemical production segment is projected to capture the largest market share, driven by the increasing adoption of green hydrogen for sustainable chemical processes.
Browse in Depth @https://www.meticulousresearch.com/product/green-hydrogen-market-5580
Regional Insights
Geographically, the green hydrogen market is divided into North America, Europe, Asia-Pacific, Latin America, and the Middle East & Africa. North America is anticipated to lead the market in 2024, fueled by the increasing adoption of clean energy solutions and government initiatives to promote green hydrogen production. However, the Asia-Pacific region is set to exhibit the highest growth rate, thanks to strategic partnerships and investments in the clean hydrogen economy.
Key Market Players
The report includes a competitive landscape based on an extensive assessment of the key growth strategies adopted by the leading market participants in the green hydrogen market in the last three to four years. The key players profiled in the green hydrogen market report are FuelCell Energy, Inc. (U.S.), Bloom Energy Corporation (U.S.), Plug Power Inc. (U.S.), Air Products and Chemicals, Inc. (U.S.), China Petrochemical Corporation. (China), L’AIR LIQUIDE S.A. (France), Linde plc (Ireland), Green Hydrogen Systems A/S (Denmark), McPhy Energy (France), ITM Power PLC (U.K.), Nel ASA (Norway), Ballard Power Systems Inc. (Canada), ENGIE SA (France), Repsol S.A. (Spain), and Iberdrola, S.A. (Spain).
These companies are actively investing in research and development to advance green hydrogen technologies and expand their market presence.
Request for Customization Report @https://www.meticulousresearch.com/request-customization/cp_id=5580
Related Research Reports:
Cable Assembly Market >> https://www.meticulousresearch.com/product/cable-assembly-market-4975
North America Electric Scooter Market >> https://www.meticulousresearch.com/product/north-america-electric-scooter-market-5245
ADAS Market >> https://www.meticulousresearch.com/product/adas-market-5377
Electric Vehicle Charging Stations Market >> https://www.meticulousresearch.com/product/electric-vehicle-charging-stations-market-5078
North America Electric Vehicle Charging Stations Market >> https://www.meticulousresearch.com/product/north-america-electric-vehicle-charging-stations-market-5222
Electric Scooter Market >> https://www.meticulousresearch.com/product/electric-scooter-market-5191
Europe Electric Scooter Market >> https://www.meticulousresearch.com/product/europe-electric-scooter-market-5239
Asia-Pacific Electric Scooter Market> > https://www.meticulousresearch.com/product/asia-pacific-electric-scooter-market-5242
0 notes
Text
Methanol Market Analysis: Trends, Growth, and Opportunities Through 2031
The methanol market is witnessing significant growth due to its versatility and increasing adoption across energy, automotive, and chemical industries. This vital chemical compound plays a key role in fostering sustainability, especially with its applications in clean energy and environmental solutions. Below, we explore the market dynamics, segmental insights, regional trends, and emerging opportunities shaping the methanol industry's future.
Market Insights: Methanol as a Catalyst for Sustainability
Methanol’s extensive use in the production of formaldehyde, acetic acid, and fuel additives positions it as an essential feedstock in the chemical and energy industries. With rising concerns about carbon emissions, methanol is also being used as an alternative fuel and in renewable energy storage systems. The market is projected to grow steadily, supported by advancements in production processes, such as the synthesis of methanol from biomass and CO2 recycling.
Request Sample of the Report - https://www.skyquestt.com/sample-request/methanol-market
Segmental Analysis: Diverse Applications Driving Growth
The methanol market is segmented into key applications, feedstocks, and end-user industries:
Applications:
Chemical Manufacturing: Methanol is a key ingredient in producing a variety of chemicals, including formaldehyde and dimethyl ether (DME).
Energy: Its adoption as a clean fuel and in methanol fuel cells is expanding rapidly.
Other Uses: Methanol is used in pharmaceuticals, adhesives, and as an anti-freeze agent.
Feedstocks:
Natural gas dominates methanol production, while coal and renewable sources like biomass are gaining attention for their sustainability benefits.
End-User Industries:
Automotive, energy, and construction industries are among the largest consumers of methanol, reflecting its diverse applications.
Get Customized Reports with your Requirements, Free -https://www.skyquestt.com/speak-with-analyst/methanol-market
Regional Insights: A Global Perspective
Asia-Pacific:
The region leads in methanol production and consumption, driven by rapid industrial growth in China and India.
Investments in coal-to-methanol projects further bolster the region's dominance.
North America:
Shale gas exploitation provides an abundant and cost-effective feedstock, making the U.S. a significant player in methanol production.
Europe:
Stringent environmental regulations drive the adoption of green methanol, particularly in energy and transportation sectors.
Middle East & Africa:
With rich natural gas reserves, this region is emerging as a key hub for methanol production, catering to both local and global markets.
Is this report aligned with your requirements? Interested in making a Purchase -https://www.skyquestt.com/buy-now/methanol-market
Key Market Trends: Innovations and Sustainability
· Green Methanol Production: The push toward sustainability is fostering innovations in producing methanol from renewable feedstocks such as biomass and captured carbon dioxide.
· Expanding Fuel Applications: Methanol is gaining recognition as a marine fuel and as a potential hydrogen carrier in fuel cell technologies.
· Advances in Chemical Synthesis: Methanol-to-olefins (MTO) and methanol-to-gasoline (MTG) technologies are enabling efficient and sustainable chemical production.
Market Dynamics: Drivers, Challenges, and Opportunities
The methanol market is shaped by several factors influencing its growth trajectory:
Market Drivers:
o The rising demand for eco-friendly fuels and chemicals aligns methanol with global sustainability goals.
o Expanding industrialization in emerging economies fuels the demand for methanol in construction and automotive industries.
Challenges:
o Fluctuations in feedstock prices and the development of competing renewable energy sources could impede market growth.
o Regulatory pressures on environmental impacts remain a critical challenge.
Opportunities:
o Technological advancements in producing methanol from renewable sources present significant opportunities for growth.
o Growing interest in methanol as a marine fuel and in hydrogen fuel cells highlights its potential in future energy applications.
Methanol's Role in the Future Economy
The methanol market is on a growth trajectory, supported by its versatile applications and alignment with global sustainability goals. Despite challenges such as feedstock price volatility, the market is poised for expansion due to increasing demand in energy and chemical sectors and innovations in green methanol production. As industries adapt to a greener future, methanol is set to play a critical role in reducing emissions and driving industrial transformation worldwide
1 note
·
View note
Text
#Ireland Carbon Capture and Storage Market#Market Size#Market Share#Market Trends#Market Analysis#Industry Survey#Market Demand#Top Major Key Player#Market Estimate#Market Segments#Industry Data
0 notes
Text
PV Solar Panel Market Analysis: Challenges, Innovations, and Winning Strategies for 2024-2030
The PV solar panel market is at a critical juncture, poised for significant growth between 2024 and 2030. The increasing urgency to address climate change and the rising cost of traditional energy sources have placed renewable energy, especially solar power, at the forefront of global energy strategies. Despite its immense potential, the market faces challenges that require innovative solutions and well-crafted strategies to ensure sustainable growth.

One of the primary challenges is the fluctuating cost of raw materials, such as silicon, a key component in solar panel manufacturing. Supply chain disruptions, geopolitical tensions, and rising global demand for semiconductors have made resource procurement more complex. Manufacturers are exploring ways to minimize dependency on traditional materials by researching alternatives like perovskite solar cells, which promise lower production costs and higher efficiency.
Another critical issue is the intermittency of solar energy. Since solar panels rely on sunlight, energy generation fluctuates based on weather conditions and time of day. This challenge underscores the importance of integrating advanced energy storage solutions. Battery technologies, such as lithium-ion and emerging solid-state options, are evolving rapidly, making energy storage more efficient and cost-effective. Companies investing in hybrid systems that combine solar panels with robust storage capabilities are likely to gain a competitive edge.
Innovation continues to be a driving force in the PV solar panel market. Technological advancements have led to the development of bifacial panels, which capture sunlight from both sides, and thin-film panels, known for their flexibility and adaptability in unconventional settings. Smart technologies are also reshaping the industry. Solar systems integrated with AI and IoT enable real-time monitoring, predictive maintenance, and energy optimization, offering end-users more control and efficiency.
The transition to decentralized energy systems is another trend shaping the market. Rooftop solar installations, microgrids, and community solar projects are gaining traction, especially in regions with limited access to centralized power grids. These systems empower consumers by reducing dependency on traditional energy providers and fostering energy independence. Companies focusing on localized solutions can tap into underserved markets and strengthen their position in the industry.
Policy and regulatory frameworks play a pivotal role in the market's trajectory. Governments across the globe are implementing renewable energy mandates, offering subsidies, and setting ambitious carbon neutrality goals. However, inconsistent policies and bureaucratic hurdles can deter growth. Companies must actively engage with policymakers to ensure favorable conditions for renewable energy adoption while addressing region-specific regulatory challenges.
Consumer education and affordability remain vital components of market strategy. While solar energy is increasingly recognized as a sustainable alternative, misconceptions about installation costs and efficiency still persist. Financial models such as leasing, pay-as-you-go systems, and green financing options can make solar energy accessible to a broader audience. Companies that prioritize customer education and offer flexible financial solutions are likely to build trust and expand their market share.
Looking ahead, collaboration will be key to overcoming challenges and unlocking growth opportunities. Partnerships between manufacturers, tech companies, and financial institutions can drive innovation and scalability. Investments in research and development will also be critical, enabling breakthroughs in panel efficiency, durability, and recycling.
The PV solar panel market’s future depends on a blend of strategic planning, technological innovation, and proactive adaptation to challenges. With global energy demands rising and the imperative to reduce carbon emissions intensifying, the market holds immense potential for those ready to innovate and lead. By addressing obstacles head-on and leveraging emerging opportunities, the industry is set to play a transformative role in shaping a sustainable energy future.
Get Free Sample and ToC : https://www.pristinemarketinsights.com/get-free-sample-and-toc?rprtdtid=NDUz&RD=PV-Solar-Panel-Market-Report
#PVSolarPanelMarket#PVSolarPanelMarketInsights#PVSolarPanelMarketTrends#PVSolarPanelMarketGrowth#PVSolarPanelMarketOutlook#PVSolarPanelMarketAnalysis
0 notes
Text
0 notes
Text
Oil and Gas Entrepreneur Matt Pouldar: Innovating the Energy Industry with Sustainability and Vision
Matt Pouldar is an influential oil and gas entrepreneur whose innovative approach has significantly impacted the global energy sector. As the founder and visionary leader behind Matt Pouldar Oil, he has built a reputation for not only excelling in the traditional oil and gas industry but also for championing sustainability and clean energy solutions. His work exemplifies the evolving role of entrepreneurship in driving both economic growth and environmental responsibility within the energy market.
The Rise of Oil and Gas Entrepreneur Matt Pouldar
Matt Pouldar’s journey to becoming a prominent figure in the oil and gas sector wasn’t one of overnight success, but rather a product of years of hard work, strategy, and an unwavering commitment to the energy industry. With a strong background in energy markets, production technologies, and business operations, Pouldar quickly recognized the complexities of the oil and gas sector. But rather than seeing these challenges as obstacles, he viewed them as opportunities to innovate.
His early career began at some of the largest oil and gas companies, where he honed his skills in exploration, production, and market analysis. Through these experiences, Pouldar gained a comprehensive understanding of the energy landscape, the financial dynamics of energy markets, and the technological advancements that could transform the industry.
However, Matt Pouldar’s entrepreneurial spirit led him to start his own company, Matt Pouldar Oil, where he sought to disrupt traditional oil and gas operations by integrating advanced technologies and sustainable practices into his business model. His goal was clear: to build a company that could not only meet the growing global demand for energy but also lead the way in minimizing environmental impact.
The Innovation Behind Matt Pouldar Oil
Under the leadership of Matt Pouldar, Matt Pouldar Oil has become a prominent player in the global oil and gas market. The company stands out for its integration of innovative technologies and a deep commitment to sustainability. Pouldar has led the charge in implementing state-of-the-art extraction and production techniques, such as horizontal drilling and automated systems, to improve efficiency, reduce costs, and enhance the overall productivity of oil and gas operations.
Moreover, as a gas entrepreneur, Matt Pouldar has prioritized the development of cleaner, more sustainable energy solutions. One of the company's flagship initiatives is its focus on liquefied natural gas (LNG), which serves as a cleaner alternative to coal and traditional oil products. With global demand for natural gas rising, Pouldar has positioned Matt Pouldar Oil as a key player in the LNG market, helping to meet both energy needs and climate goals.
Pouldar’s company has also made significant strides in environmental sustainability by investing in carbon capture and storage (CCS) technologies. This technology allows for the safe capture of carbon dioxide emissions produced by energy operations, preventing them from being released into the atmosphere. For Pouldar, this is not just about meeting regulatory requirements, but about setting new standards for environmental stewardship within the oil and gas industry.
Expanding Global Reach
An essential element of Matt Pouldar Oil’s success has been its global expansion. Recognizing that energy demand is increasing in emerging markets, Pouldar has strategically extended the company’s operations into key regions like Southeast Asia, Africa, and South America. These regions offer significant growth potential, and Pouldar’s ability to navigate the regulatory, economic, and political complexities of these markets has enabled Matt Pouldar Oil to establish a strong international presence.
Through partnerships and joint ventures, Matt Pouldar has also fostered relationships with local governments, stakeholders, and other energy companies. This collaborative approach has helped Matt Pouldar Oil tap into new markets while ensuring the company’s operations align with regional energy policies and sustainable development goals.
A Vision for a Sustainable Energy Future
At the core of Matt Pouldar’s entrepreneurial success is his forward-thinking vision of a more sustainable energy future. While the oil and gas industry has long been associated with environmental challenges, Pouldar believes that innovation within the sector can drive positive change. He has consistently advocated for the integration of renewable energy sources, such as wind and solar power, into the traditional oil and gas infrastructure. This hybrid approach not only helps diversify energy portfolios but also supports global efforts to transition toward a low-carbon future.
Pouldar’s vision extends beyond just operational sustainability. He is a passionate advocate for addressing climate change and has used his position to influence policy discussions, calling for more robust frameworks that support both oil and gas production and renewable energy growth. For Pouldar, the energy transition is not a matter of replacing fossil fuels entirely but finding ways to combine them with clean energy solutions to create a more resilient and sustainable energy system.
Conclusion: The Impact of Entrepreneur Matt Pouldar
As an oil and gas entrepreneur, Matt Pouldar has made an indelible mark on the energy sector. Through his leadership of Matt Pouldar Oil, he has successfully merged traditional oil and gas expertise with innovative, sustainable practices that are shaping the future of energy production. By focusing on technology-driven solutions, environmental sustainability, and global expansion, Pouldar has positioned his company to lead the energy industry into a new era—one that is both economically viable and environmentally responsible.
Looking ahead, Gas Entrepreneur Matt Pouldar will undoubtedly continue to drive transformative change in the energy sector, helping to bridge the gap between fossil fuels and renewable energy while meeting the world’s growing demand for cleaner, more efficient energy solutions. His entrepreneurial journey is a testament to the power of innovation, sustainability, and visionary leadership in shaping the future of the global energy landscape.
0 notes
Text
Explore the role of AI in the oil and gas theme analysis. Learn how artificial intelligence is transforming operations, enhancing efficiency, and driving innovation in the sector. The oil and gas industry, traditionally known for its reliance on heavy machinery, exploration, and labor-intensive processes, is undergoing a transformative shift. Artificial intelligence (AI) is emerging as a critical tool that is reshaping the sector. With its ability to process vast amounts of data, optimize operations, and predict outcomes, AI is driving efficiency, reducing costs, and enhancing decision-making processes across the industry.
Key Applications of AI in the Oil and Gas Industry
Predictive Maintenance and Asset Management One of the most significant applications of AI in the oil and gas industry is predictive maintenance. AI algorithms can analyze historical data from equipment and machinery to predict potential failures before they occur. This predictive capability reduces downtime, minimizes costly repairs, and ensures continuous operations. AI also helps in optimizing asset management, ensuring that critical assets are maintained at peak performance levels and extending their operational lifespan.
Exploration and Drilling Optimization In exploration, AI-driven data analytics helps geologists and engineers make more accurate predictions about where oil and gas deposits are likely to be located. Machine learning models process geological data, seismic surveys, and well logs to identify patterns and predict the most promising drilling locations. During drilling operations, AI can also optimize drilling parameters, such as pressure, temperature, and rotation speed, to increase efficiency and reduce the risk of costly mistakes.
Supply Chain and Logistics Optimization The oil and gas sector often operates with complex global supply chains that require seamless coordination of resources, products, and services. AI enhances supply chain management by improving demand forecasting, route optimization, and inventory management. AI-driven algorithms can analyze market data, weather patterns, and geopolitical factors to ensure that materials are delivered efficiently and at the right time, reducing delays and costs.
Reservoir Modeling and Production Forecasting AI plays a vital role in enhancing reservoir modeling and production forecasting. By analyzing massive amounts of data from sensors and well logs, AI models can create more accurate models of underground reservoirs. These models help companies understand the flow of oil and gas, optimize recovery rates, and predict production levels. This improves decision-making, leading to more efficient resource extraction and enhanced profitability.
Safety and Risk Management Safety is a top priority in the oil and gas industry, and AI technologies are helping to improve safety protocols by detecting hazards before they cause accidents. AI systems can analyze real-time data from equipment sensors and environmental factors to identify potential risks, such as gas leaks or equipment malfunctions. Furthermore, AI is used to monitor workers’ conditions in hazardous environments, ensuring that safety regulations are followed and incidents are prevented.
Energy Efficiency and Sustainability As the oil and gas industry faces growing pressure to reduce its environmental footprint, AI is helping companies increase energy efficiency and reduce emissions. AI algorithms can optimize production processes to minimize waste and improve the energy efficiency of operations. Additionally, AI is playing a role in helping companies identify opportunities for carbon capture and storage (CCS), as well as in analyzing data related to environmental impacts to support sustainability initiatives.
0 notes
Text
0 notes