#by talking about the original land grant and the uncertainty around the definitions of the borders
Explore tagged Tumblr posts
Text
@loryer496 replied to your post “Easy solution to the duplicate bird problem: if...”:
no wait, maine was originally part of massachusetts. why would it not just revert to all being massachusetts?
The inhabitants of Maine are proud of their state's name, and even though there are only seven of them, it would still be a little too tyranny-of-the-majority to completely erase their state identity just to clean up a bird chart.
#loryer496#mainesachusetts#found this in my drafts where I had started a long essay#by talking about the original land grant and the uncertainty around the definitions of the borders#but it was all factual and I have no idea where I was planning to go with it#so sorry#you get an obvious 'haha nobody lives in maine' joke#instead of whatever apparently had me researching the merrimack river and the 1691 Province charter
2 notes
·
View notes
Text
Forgotten Stories is an Amazing Skyrim Mod, and You Should Play It
May 26, 2020 1:00 PM EST
Sometimes, you find a mod that defies expectations and becomes a worthy game in its own right. Enderal: Forgotten Stories is one such mod.
Enderal: Forgotten Stories is a total conversion mod for The Elder Scrolls V: Skyrim. Developed by a dedicated team of German modders by the name of SureAI, the first version of Enderal was released back in 2016. The updated Forgotten Stories expansion from 2019 saw a number of additions to quests and content, as well as a standalone release on Steam. It’s the definitive and complete version of the tale, and is worth playing again if you’ve only dabbled in the original previously.
This mod completely replaces the landmass and setting of Skyrim with an original one, and overhauls most of the gameplay systems as well. Skyrim’s general DNA is still inevitably present in movement and systems, but the way it works is wholly redone. It is less the freeform “do whatever you want” simulator that Skyrim quickly becomes; Enderal is instead a focused, story-driven RPG with a splash of open-world content that better utilizes the space. There’s less reliance on scaling enemies, and more on not reaching into areas beyond your means, as the story will nudge you there when you’re ready.
That story, world, the characters contained within, and the full span of Enderal’s adventure? Those are so fantastically realized that it feels disingenuous to call Enderal a mere mod. It easily transcends the boundaries of Skyrim, overcoming many of the gameplay issues and lacking elements of its source material. Having finished it recently, I now find myself thinking of Enderal not as just a Skyrim mod, nor even its own standalone game and RPG.
I now think of Enderal: Forgotten Stories as one of the best video games I’ve ever played.
youtube
Since Enderal hasn’t left my mind for long since completing it, I feel that it’s important to I write this down and share it. I want to talk a bit about Enderal’s design and gameplay systems. I’ll cover a little about the story and characters (in non-spoiler terms), as well as how emotionally devastating its ending is. And finally, I’ll briefly touch on the many ways it shines a light on all of Skyrim’s greatest weaknesses. I’ve come to develop a more negative view of Bethesda’s most recent mainline Elder Scrolls foray, and Enderal has helped me put all of that into words.
In the interim, I urge you to go and check out Enderal: Forgotten Stories at your earliest convenience if any of this has sounded slightly appealing to you. It’s comprehensive enough to have its own standalone Steam page and installer, with many Skyrim mods that are considered “mandatory” baked into it already. In fact, it’s comprehensive enough to have its own mods also! Go there now, pick it up, and see for yourself. This is something special, and the SureAI team deserves the attention and spotlight.
Skyrim: New Vegas

Enderal takes absolutely no time in laying its cards on the table for you. The opening scene is a gorgeous, sun-baked vista of a lush garden near sunset. It’s idyllic, pushing the graphics of both the base game and the included ENBoost and graphical mods to the max. It’s also very clearly wrong, with something uncanny about the whole scene lurking just below the surface. A quick glance around the place will see that uncertainty grow, with the culmination of that scene making it crystal clear. I won’t spoil specifics; once again, I urge you to check it out, and the introduction alone should demonstrate that you’re in for a ride.
More cutscenes and important setup will follow, including character creation. The first area or two play out like a tutorial, helpful both for newcomers and those familiar with the workings of Skyrim. All throughout, the placing of story elements and themes has begun, and seeing that all eventually culminate more than makes up for its “slow” start. More importantly, you’ll get through the first scripted dungeon and be greeted by a sun-swept vista not unlike the one from the intro. This game is utterly gorgeous. The continent of Enderal beckons forth.

Mechanically, the game might be a little bit off-putting for Skyrim veterans. That’s not to say it isn’t good; Enderal simply does away with the learn-by-doing skill system for something more focused. Killing creatures and completing quests give experience, and experience thresholds grant you a level-up. You’ll choose health, magicka, or stamina and get a selection of points with which to invest into specific skills. You can’t just plug these points straight into your skills, though.
“It feels disingenuous to call Enderal a mere mod.”
Memory points are your big talent/perk purchases, which are applied through a much fancier in-game version of the Skyrim perks. It’s not just opening a menu and clicking a constellation: here, you meditate to reach a bizarre shrine in your mind, where physical stones reflecting the perk trees are represented to interact with. In addition to the passive powers here, you’ll unlock talents which function like dragon Shouts. These have individual cooldowns rather than global ones though, so mixing and matching them in combat is far more useful than Skyrim‘s counterparts.
For general skill levels, you need to acquire and study a learning book of the appropriate skill and quality. Doing so increases that skill by 1. Want to get One-Handed from 15 to 16? You’ll have to scavenge or buy a One-Handed learning book of the apprentice difficulty. To get beyond 25, you’ll need an adept book, and so on. Skills have been split between learning and crafting, with the latter being less directly tied into combat trees (Alchemy, Enchanting, Lockpicking and such).
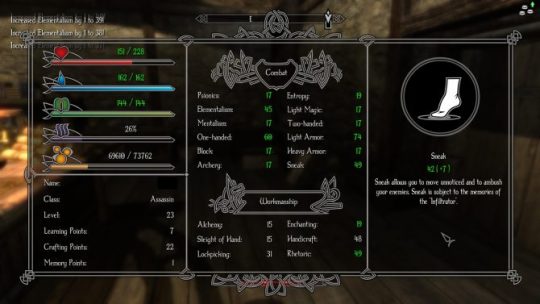
This means that you cannot master everything in a single playthrough like you might in Skyrim. Builds become important, and swapping to a new combat style on a whim requires some investment. This would probably not go down well in Skyrim; open exploration carries that game, and diversity in one’s playstyle can alleviate a sense of repetition after long sessions. Enderal wants you to think about your build and develop a roleplay attachment to your avatar, instead. As you’ll see from the heavier story focus, that becomes increasingly clear as you play.
Experience also becomes a premium resource. Enderal isn’t as large as Skyrim, but it’s far more curated. Leveled lists and scaling rewards are barely a factor here, and bandits won’t suddenly find late-game armor. Completing side quests and exploring where you can now helps you progress your build. Given that the game can be pretty difficult in the early hours, that’s a good mindset to embrace. Exploring is a good idea, right up until you cross a boundary you probably shouldn’t have and get completely murdered.
“Enderal feels to Skyrim as Fallout: New Vegas did to Fallout 3.”
There’s further incentives for exploring carefully as well, with rare pickups that can grant bonus experience or even permanently increase your carry capacity. Set items now exist and are quite powerful when combined, and rare crafting schematics or learning books are scattered across the land. The fact that everything feels hand-designed instead of just generated en masse helps the world seem more real. Thus, when the plight of the story starts to ramp up and affect the continent I’d grown attached to, I felt it all the more from seeing it myself.

Still, even with all the benefits for exploring, Enderal is a comparatively more linear game than its source. Modern Elder Scrolls games are happy to let you wander off the beaten path for a hundred hours and ignore the main story entirely. That’s not at all encouraged for Enderal; in fact, unlike Skyrim, you are seriously missing out if you don’t engage with the main quest. Major biomes of Enderal’s landmass are gated off by the challenge they represent. You can go there and try to survive, but generally the main story will introduce you to it once you’ve progressed far enough to be ready.
In this way, Enderal feels to Skyrim as Fallout: New Vegas did to Fallout 3. Obsidian’s Fallout foray was more linear and focused than its predecessor’s open-world jaunt around post-apocalyptic Washington, D.C.; wandering too far would get you torn apart by Deathclaws. This lack of freedom was exchanged for much sharper writing, a better plot, and more narrative options and choice. Enderal feels as if it’s done much the same to Skyrim, and given how fantastic the story and characters are, it’s a trade I’d make a million times over.
The Adventures of Jespar (featuring the Player Character)
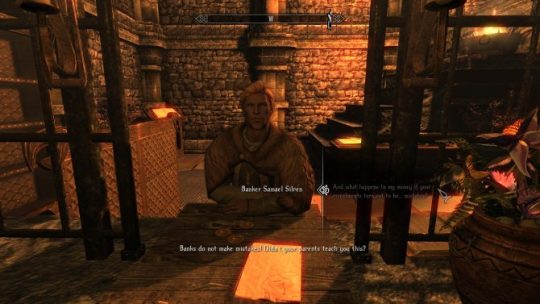
Leaving the tutorial dungeon brings you to a secluded valley within Enderal proper. There’s a few treasures and hidden secrets to be found there, but eventually you will have to follow the path that leads beyond. That one path will see you encounter a couple of apothecary NPCs, who explain a little more about the world you’re in.
Attempting to leave will see you overcome with Arcane Fever; this is both a story point, and one of Enderal’s new gameplay mechanics. It functions similarly to Fallout’s radiation, increasing when exposed to magically dense areas. Most importantly, Arcane Fever is exacerbated by using magical healing and potions. No longer can you just open your inventory and chug twenty potions to heal up, as this’ll quickly raise your Fever. Get too high and you’ll start having negative side effects, and at 100% you die outright. Food items don’t heal much in combat either, but out of combat? You’ll get a satiated buff that will regenerate your health over time, so you still want to stay fed. It’s a clever little way of balancing Enderal’s combat and making it less absurd than Skyrim.

Nonetheless, you find out about this system shortly after the apothecary conversation ends. It’s here that you’ll meet Jespar Dal’Varek, one of the major NPCs of the game. He leads you into the main story quest for Enderal, but he’ll also take the time to chat you with if you want to ask questions. By the end of that first segment of the game, I was ready to follow him anywhere. Jespar is one of the more well-written and constructed NPC companions I’ve had the pleasure of encountering in video games. He’s a very easy-going sort and it’s clear why they introduce you to him first, but the cynical and anti-idealist side of him comes to the fore if you start asking.

In fact, there will be side quests and conversations entirely focused on getting to know some of the side characters better. These were usually highlights in my playthrough, which should give you an indication of the quality of these characters. In Jespar’s case, this is further strengthened by such fantastic voice acting that you’d almost forget this was a free mod. In fact, his voice actor Ben Britton has springboarded into the industry off his work here. Small wonder that Jespar is the focus character in the writer’s spin-off novel (the audiobook is also voiced by Ben).
“By the end of that first segment of the game, I was ready to follow Jespar anywhere.”
Jespar might be the first and most prominent, but he is far from the only character worth remembering in Enderal. Throughout the main quest lines, you’ll be introduced to a slew of primary characters, many of which have just as much depth as him. The interactions of these characters both with you and each other really sell the narrative being told, and it was very easy to grow attached to them (or to loathe them, as the situation demands).
I cannot stress how strong the writing for Enderal truly is. It’s not just the characters either; the entire game world is incredibly well designed and presented. The continent is built on a religious caste-based society with heavy stratification, and you’ll have the opportunity to investigate and interact with each level of it. You’ll argue the pros and cons of religiosity, discuss the nature of life, death and reality, or dive into a magic system which literally plucks aspects from alternate timelines in order to function. Whether through its world-building, characters, or overall narrative, I found myself hopelessly drawn in by Enderal and wanted more.
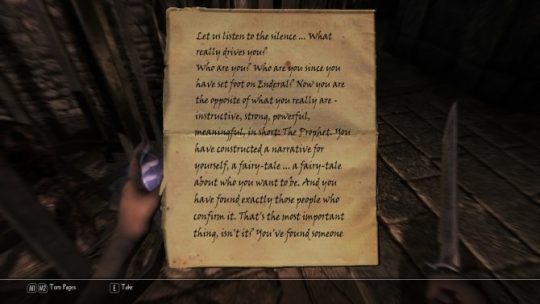
All throughout, the main quest runs through the bulk of the continent and takes you to appropriately leveled zones when the time comes. Each arc of the quest finds new ways to introduce spectacle, to develop the characters, and to ramp up the stakes and scope of the plot. There’s sections that are presented with better tension and horror than most horror games can manage. New difficulties will arise, characters will be hurt or even killed, and victories will be tempered with losses. Before I knew it, I’d been playing for over a hundred hours and had fully cleared the map; that’s something I’d never care to bother with in Skyrim.
Very quickly, you’ll realize just how big the implications of the story are, and this will continue without letting up until the conclusion of the game. And that conclusion is something else. There’s a sense of uncertainty and tension throughout the entire story, and neither the characters nor the player are ever quite sure that what they’re doing is the correct answer. Like everything else, this will build up to a finale that was so brilliantly handled and emotionally charged that I was reeling for days afterwards.

Finding the right words to describe it all without delving into spoilers is a difficult task. Much as I’d love to do so and start gushing in fantastic detail, that’s not the point of this editorial. Besides, it’s really something that I would rather people experience firsthand. Suffice it to say that Enderal’s writing and story is excellent, with quality that holds true until the very end. I expect that I’ll be thinking of some of the climactic moments for a long time to come. It really is that fantastic a tale.
“This will build up to a finale that was so brilliantly handled and emotionally charged that I was reeling for days afterwards.”
I have to take a moment to credit the sound, also. Enderal: Forgotten Stories might be a free mod, but it has an excellent and fully original soundtrack composed by Marvin Kopp. It’s so strong that I’ve been using it as background music while writing this piece, and will probably do so for future writing sessions. It also is fully voice acted, with absolutely fantastic voice direction. Not every actor is as professional as another, and there’s a couple of outliers that really hurt to listen to in the cities and side quests. But the primary cast deliver some fantastic performances, and most seem to have at least one scene that catapulted them from good to exceptional. All of the sound really helps carry the narrative that much further into greatness.

It’s not without flaw, of course. The pacing is generally good, but there is one quest near the end of the game that comes across as quite rushed. An important detail for the plot is revealed, and then immediately an NPC blurts ahead three steps in rapid succession. It was such a sudden guess about what was happening that it felt like random speculation, yet it was completely accurate. I suspect this was to get things in position for the finale without compromising that sequence, so it’s forgivable. Even so, the good far outweighs what little bad I could muster. Enderal is a story worth experiencing, and I’m genuinely glad I did so.
The Post-Enderal Lens on Elder Scrolls

It’s probably quite obvious at this point, so let’s address the elephant in the room: I don’t particularly like Skyrim.
That statement is usually enough to tank a game writer’s credibility given its reputation and scores, but hear me out. It wasn’t a case where I hated the game on purpose and refused to touch it from there. Skyrim took up a good hundred hours of my time, and even more once mods (besides Enderal) entered the scene. I completed the main quest and all the major faction quests, played through the DLC, and tried numerous different builds. There was a fun enough experience to be had, but I won’t lie and say I didn’t enjoy my time with it.
The problems that I have with Skyrim emerged only after time and reflection. My first Elder Scrolls game was Morrowind, and it is still possibly my absolute favorite game ever. Skyrim was unlikely to live up to that completely, but it still falls short in almost every metric. I replayed Morrowind in full a few months ago, and I only came away from that slow, ancient game loving it even more than previously. Nostalgia is not what pushes that game ahead of its follow ups in my eyes: it’s the richly detailed and exotic world, the flexible design, and the many guilds and factions to dive into that make Morrowind so strong. We will probably never get another game quite like it.

When I think back to Skyrim, I don’t think of any of that. I think of going off on random adventures and losing myself in the wilderness for a few hours. I’ll accumulate gear, get stronger, tick off increasingly more quest markers from my list, and just continue going through the motions. Bethesda’s approach nowadays seems less about making high quality content, and instead making more content. Whenever Skyrim has the opportunity to provide depth or meaning, it comes away lacking. The gameplay is more action than RPG when compared to its predecessors, but the mechanics are lackluster and simplistic.
Most don’t even seem to bother with Skyrim‘s main quest, though I pushed through and completed it. Still, barely any aspect of it really stands out in my mind or impressed me. By contrast, the main questline in Morrowind is the highlight; so too is the main quest line in Enderal. So many moments of Skyrim that could’ve been something more end up feeling like yet another item crossed off the list. I could go back now and still probably play it for tens of hours if I wanted, and I’d probably enjoy it. But if I wanted depth, I’d only find an ocean-sized puddle. For all its vaunted freedom to play it as you want, that’s all Skyrim can ever offer you, no matter what else you might desire from it.

Enderal: Forgotten Stories felt incredibly refreshing to me as a result. It took all the potential of Skyrim’s size, condensed it into a large but focused story, amped up the presentation and mechanics, and proceeded to deliver one of the best experiences I’ve had from any RPG I’ve played. If ever there was a game that nearly elicited the same sense of wonder I got from Morrowind, it would be Enderal, not Skyrim.
Morrowind isn’t the only titan of RPGs I’ve had the pleasure of playing recently, either. In the last year, I’ve sought to play or replay many of the titans of PC RPGs. I grew up with the likes of Baldur’s Gate 2 and Planescape: Torment, and I revisited them recently with fondness. Contemporary RPGs like NieR: Automata, The Witcher 3, and even Final Fantasy 14: Shadowbringers all have stirred strong responses in me. Yet even amongst all these heavy hitters, Enderal left such an imprint on me that it absolutely deserves to be discussed and compared alongside them.
“If ever there was a game that nearly elicited the same sense of wonder I got from Morrowind, it would be Enderal, not Skyrim.”
The Elder Scrolls 6 is a long ways off, and the last few showings of Bethesda’s games have been less than spectacular. I have no real anticipation for what’s to come from them. When you consider what a German modding team managed to make with that framework and deliver it for free, it just cements that feeling all the more. Instead of looking to that distant horizon, I’m instead prepping to go back and visit SureAI’s earlier works. Enderal isn’t their first game; they made a similar mod for Oblivion called Nehrim, set in the same world and apparently of equal quality. Nehrim is getting its own stand-alone Steam release in June, and there is no game I’m looking forward to more than it right now.

If you happen to like RPGs, I heartily urge you to go check out Enderal: Forgotten Stories. Regardless of whether or not you think highly of Skyrim, there’s a really incredible experience here that is a worthy game in its own right. You don’t even need to install Skyrim to run it, just own it. Even if you have to buy the unlisted original edition of Skyrim to play, since it doesn’t run on the Special Edition, you should still consider it. Believe me when I say that it’s worth it.
May 26, 2020 1:00 PM EST
from EnterGamingXP https://entergamingxp.com/2020/05/forgotten-stories-is-an-amazing-skyrim-mod-and-you-should-play-it/?utm_source=rss&utm_medium=rss&utm_campaign=forgotten-stories-is-an-amazing-skyrim-mod-and-you-should-play-it
0 notes
Text
Direct Trade In The Shadows
In the first entry in this series, author Michaele Weissman explored the promise and problems associated with Direct Trade, the ethical sourcing model for specialty coffee in which producers and roasting work as partners. In her research—for this series and for her book, God In A Cup—more questions were raised than answered. The exploration continues.
“If you want to see Direct Trade in action look no further than your local Whole Foods or specialty grocery,” says Matt Lounsbury, Stumptown’s former veteran vice president. “Everyone in the industry is promoting coffee farmers and putting reference to farms and farmers on their packages. And if they are not, they had better start.” (Lounsbury recently left Stumptown; his departure was amicable.)
It’s hard to dispute that customers find stories about coffee farmers uplifting. But is the uplift justified? Is the wealth generated by Direct Trade shared and are lives being changed at origin? These questions have dogged Direct Trade since its inception. Today, as the high-end coffee industry grows and consolidates, new questions emerge.
When we refer to Direct Trade, are we still talking about small roasting companies partnering with small farmers? What about large roasters? Is it Direct Trade when a behemoth specialty roaster negotiates with a coffee smallholder?
Answering these questions requires a nitty gritty examination at how Direct Trade operates, not in theory but in practice. That’s the task I set for myself in this, the second installment of my series, “Is Direct Trade Fair?” for Sprudge Media Network.
The Microlots
First, a definition. Direct Trade coffees are NOT beans with high cupping scores from outstanding regions such as Yirgacheffe in Ethiopia or Guatemala’s Huehuetenango. A coffee company with cool branding is not automatically Direct Trade. Skyping with the farmer doesn’t make your coffee DT.
Direct Trade is a sales practice related to the growing, selling, and buying of microlots–small amounts of coffee grown with an unusual attention to detail on pinpricks of land. Microlots grow on terroir that is comparable to a neighborhood, not a zip code. A microlot might come from, for example, one half hectare of land on a south-facing hillside, at 1817 meters elevation, protected from extreme winds and weather by a canopy of tall trees or a rocky outcropping.
Beans from microlots are strictly segregated–the technical term is disaggregated–when picked, processed, bagged, and shipped. Microlots are small, maybe 5 or 10 bags of coffee, with the most prized of these lots clocking in with cupping scores of 88 and above. And they are expensive. Four to five dollars a pound is more or less standard for the best lots, and prices often rise higher than that.
The Direct Trade label can also apply to single-origin coffees. Single-origin refers to disaggregated beans grown in somewhat larger areas of a single farm or possibly several farms. A single-origin may produce as much as 50 or even 100 bags of unusually high-quality coffee. These beans, too, are often the product of Direct Trade or quasi-Direct Trade relationships and may also earn impressive quality premiums when cupped.
Tim Hill, Counter Culture Coffee’s quality director and head buyer, says the practice of designating and segregating microlots was a game changer for the specialty industry when it emerged a dozen years ago. “Sellers and buyers working in partnership pushed specialty into a realm that no one had imagined possible in terms of scarcity, flavor, quality, and value.”
Hill credits early collaboration among the industry’s most influential buyers—including Counter Culture’s Peter Giuliano, now with SCA; Intelligentsia’s Geoff Watts; and Stumptown founder Duane Sorenson, now a restaurateur–with nurturing this revolution into existence. “They rewrote the rules of the specialty game,” says Hill. “I don’t think any one of our companies alone could have brought about this new system.”
What Hill describes is a win for roasters, and for coffee lovers, but it is not automatically a win for producers. The extra costs associated with growing a few bags or a few dozen bags of super high-quality coffee do not always pay off. This is the finding of Hannah Popish of Catholic Relief Services, whose case study for Counter Culture titled “The Social Impact of Microlots” explores what it takes to make Direct Trade profitable for growers. “The decision to pursue microlots… has to be made independently by smallholder farmers and their organizations on a case-by-case basis,” Popish wrote in her report. In order to do so, farmers need to undertake what she describes as an “inventory of assets,” determining if they have what it takes to be “conducive to successful microlot production and marketing.”
Among the assets Popish lists: well-situated land, water, labor, access to financing, “hardware” up to and including the farmer’s own wet mill, software such as communications, transportation, and roads. As a takeaway Popish suggests that roasters interested in developing direct relationships with farmers help them determine ahead of time if they have the necessary “assets”.
The Sellers
So why bother? If you are a grower, why make the expensive effort to develop relationships with specialty buyers and jump through all their hoops? Your coffee might not make the grade. And if it does win the jackpot one year, it may not perform so well the next (this story is sadly common among Cup of Excellence winners). Isn’t there a better way?
The question presumes that farmers have choices. “Direct Trade is the worst system for buying (or selling) green coffee…except for all the others,” says Michael Sheridan. Today he’s the Director of Sourcing at Intelligentsia, but in a previous role he oversaw Catholic Relief Services’ path-breaking Borderlands research project, studying the impact of Direct Trade on farmers in Colombia.
Sheridan’s quote doesn’t pull any punches—nothing about this process is easy. Yet despite the uncertainty and added labor associated with Direct Trade, many coffee producers have embraced the challenge. Take Maria Elena de Botto, co-owner of Finca Nombre de Dios in the northwest Alotepec-Metapan region of El Salvador (she wears a second hat as “presidente” of El Salvador’s Alianza de Mujeres en Café). Botto has no doubts about this interactive way of selling coffee.
Direct Trade, she believes, is a lot more than a sales model—it’s a top to bottom reorientation that opened her eyes to coffee’s potential. “It taught me what coffee was and what I could do with it,” Botto recalls. “If you just hand your cherry over to someone else for wet milling and drying and selling—that’s how the C-market operates. If you make the additional effort to wet mill and dry mill the way your buyers want, that’s Direct Trade.” Without the innovations promoted by Direct Trade “coffee farming in my region would not be sustainable,” she says.
Her enthusiasm is only secondarily about the promise of greater earnings. In her view, the most important issue is price stability. Direct Trade frees farmers from the commodities market where coffee prices peaked in 2012 at $3.00 a pound and then fell to around $1.40 a pound in early 2017—a baffling free fall that coincides with the fast rising global demand for specialty coffee on the consumer end of the supply chain.
Direct Trade has transformed Botto and those like her: Previously they were resource extractors in a commodities chain. Now they are entrepreneurs and artisans.
Botto first encountered ideas about selling and buying direct at El Salvador’s Cup of Excellence competition in 2003. Drawn by the country’s abundance of washed Bourbons, Pacamaras and other high-quality Arabicas, COE chose El Salvador as the site of one of its first Central American competitions. Following the competition, Geoff Watts and Peter Giuliano remained in El Salvador to conduct a series of introductory lectures familiarizing Salvadoran growers with the basics of cupping and roasting. That was the first of many visits by roasters from around the world.
Until then even educated growers—Botto has a degree in marketing from Universidad Jose Simeon Canas—knew little about their crop and less about the taste preferences of buyers. This is not unusual. Coffee growers in many parts of the world traditionally do not drink coffee—tea, for example, is the preferred drink in much of Kenya, a holdover from its colonial history. If they do drink coffee, oftentimes it’s the low-quality stuff international buyers reject, hence their unfamiliarity with coffee’s potential. (This generality is fast changing, with many producing countries developing their domestic coffee sectors and cities like San Salvador, Nairobi, Bogota, and others hosting lively coffee scenes.)
Botto believes Direct Trade’s focus on building relationships and its principle of, as she says, “incentivizing quality,” saved the day in 2012 when catastrophe struck. A devastating outbreak of coffee leaf rust exacerbated by hotter, wetter weather wrought by climate change swept through her region, cutting production in half.
The dual promise of a stable marketplace and high prices for high-quality beans gave farmers a reason to rebuild, she says. As part of a program funded by the US Department of Agriculture, they ripped out diseased trees, planted new disease resistant varieties and adopted agricultural practices that help coffee plants withstand extreme weather. Other improvements were made as well. Botto, for example, bought a wet mill and she now does the milling for her own farm and for some of her neighbors. Then she applied for and was granted a license to export, and this, too, benefited her and her neighbors.
“Quality is profitable even with greater costs,” Botto insists, noting that the promise of Direct Trade has encouraged many young people, including two of her sons, to study agronomy with the intention of returning to their families’ farms to grow coffee. Other forward-looking growers interviewed for this article also described making improvements and adopting strategies benefitting themselves and their communities.
Growers in other parts of South and Central America share Botto’s enthusiasm for Direct Trade. Among them: Felipe Croce, whose family farm, Fazenda Ambiental Fortaleza, in the Mococca region of Brazil produces highly ranked organic coffees, many of them naturally processed that it sells via Direct Trade to several thousand buyers worldwide. On its website, Fazenda Ambiental Fortaleza describes itself as “a farm, a network of farmers, a center of coffee studies, and an export company that mills and ships coffee worldwide.” Croce credits Direct Trade with making his family’s farm profitable enough to sustain a vertically integrated operation in which nearly 100 nearby farms now participate, with more eager to join. His goal in Brazil is the same as Maria Botto’s in El Salvador: growth that expands outward to benefit an entire region’s agricultural sector.
Direct Trade programs, at their best, have a multiplier effect. Improving incomes and outlooks encourages farmers to take pride in what they do. That, in turn, encourages a new generation to reconsider coffee farming as a life’s work. “Most of the farmers I work with are my age, 29,” Croce says. “Their children are proud of their parents. I think a lot of farmers were embarrassed, but now roasters from around the world are coming to visit them.”
Meanwhile in Panama, Wilford Lamastus—whose family owns the famed Elida Estate in Boquete—tells a similar story. Panama is an unusual case study in Direct Trade, due to its small size, advanced infrastructure, and international fame brought about by the Geisha/Gesha cultivar, first pioneered by the Peterson family at Hacienda Esmeralda. And yet, the Boquete region is home to the Ngobe-Bugle indigenous peoples, who live in the remote highlands and work as pickers, and are among the poorest farm laborers in the world. Lamastus says the prosperity generated by Direct Trade is rewriting the story of laborers on his farm and throughout the Boquete region. (I spoke at length about the Ngobe-Bugle peoples with third-generation Boquete coffee farmer Maria Ruiz of Boquete, in researching the Panama chapters of God In A Cup). Lamastus and his neighbors are now able to pay better wages and provide better housing, they are building schools and clinics, hiring teachers, and providing a raft of services not provided by the government that address intergenerational poverty.
“Because of Direct Trade, some of the Ngobe-Bugle are learning to cup,” says Lamastus. “Some are learning to roast, to operate dryers, and now they have health insurance and a permanent job. They live in Boquete and their kids are going to school. Some study English and learn how to work computers. Direct Trade has changed the future of these people.”
Beyond Latin America
Outside the Western Hemisphere, upbeat stories about Direct Trade are harder to find, and more nuanced. Where infrastructure and transportation systems are wanting, maintaining high standards is difficult.
Rwanda is somewhat anomalous because the specialty sector there goes back more than a dozen years. In 2004, a US AID-funded project helped hundreds of thousands of Rwanda farmers owning as few as 200 coffee trees upgrade their agronomic practices and processing protocols. Mitigating extreme poverty in rural areas, it was hoped, would have a positive impact on political stability. The experiment was an apparent success: stability in Rwanda has prevailed and the quality of Rwandan coffee soared. Specialty buyers from the US, Europe, and Asia were induced to travel to Rwanda in search of growers with whom to partner. There was, however, a disconnect, as virtually all farmers in Rwanda are members of growers’ groups and cooperatives. Small roasters found these entities a challenge.
Enter Gilbert Gatali, a Rwandan-born coffee professional whose family fled to Toronto following the genocide in the 1990s. Gatali, a Sprudgie Award winner in 2012 for Notable Producer, is today the CEO of Roots Imizi Ltd, operating a chain of coffee shops across this small country. “Direct Trade is a positive development that has improved the outlook for Rwandan farmers in several different ways,” he tells me.
As with farmers in Central America, Direct Trade benefits in Rwanda began with education. Gatali, who worked for more than 10 years with the exporter KZ Noir and the influential Rwandan producers group Rwashoscco, describes coffee farmers in Rwanda as “hungry for knowledge”, from the field to the mill to the cupping lab. Given their poverty, one of the central tenets of Direct Trade—that “roasters were willing to pay whatever price was warranted for better coffee”—was almost beyond their ken. But beyond financials, engagement with buyers has another benefit for farmers in Rwanda. “The sense of self-respect farmers felt when they realized that buyers in the US, Europe, and Asia were telling a positive story about coffee in Rwanda cannot be understated,” says Gatali.
Still, Direct Trade’s positives were sometimes more apparent than real. Some buyers simply didn’t get the challenges farmers faced. He cites the example of the roaster who spent four or five days touring farms with him and then ordered five bags of coffee. Or the roaster who worked with a farm group to produce 100 bags of coffee for Direct Trade who at harvest time bought 30 bags, representing the cream of the crop. That left the coop with 70 bags to sell that were rejected by other buyers who might have taken all 100 bags.
“With larger roasters there are problems too. There is a lot of demand for excellence, but the rejection rate is much higher,” Gatali says. “A Direct Trade coffee may leave the warehouse in Kigali in tiptop shape but a lot can happen in transit that is beyond the producer’s control,” he explains. “A guy in Mombasa can ruin a shipment of coffee packed in hermetically sealed Grainpro bags with just a slip of the loading hook.” If the coffee is damaged or degraded when it arrives in Oakland, depending on the nature of the contract, the seller, not the buyer eats the cost.
But Gatali doesn’t see all this as an indictment of Direct Trade. The takeaway for him is the gap between the worldview of growers and buyers and the understanding that problems outside farmers’ control—infrastructure especially—can undermine efforts to use Direct Trade to hoist their communities out of poverty.
The Buyers
Recognizing the difficulty of cultivating Direct Trade relationships in Africa and Asia, many specialty buyers stay away. Others go in with unreasonable expectations that lead them to give up. Counter Culture’s Tim Hill, working in Kenya, is trying to short circuit that cycle of defeat. For the past two and a half years, he has been working intensively with farmers in the Kamavindi region of Kenya to upgrade their agricultural practices, improve quality, and regularize the supply chain in hopes of avoiding some of the problems that Gilbert Gatali described in Rwanda. Most hopeful, he says, is “the desire of farmers to learn from other farmers.”
Jeff Taylor of PT’s Coffee in Topeka, Kansas and San Diego, California, takes a more classical approach. He sells nearly 400,000 pounds of coffee a year, 80 percent of which is labeled Direct Trade. Up to now, Taylor, whose company bought San Diego’s Bird Rock Coffee in early 2017, has exemplified DT as it was originally conceived.
“Our standards are pretty much what Geoff Watts spelled out a dozen years ago,” says Taylor. “I buy from producers who are passionate about coffee. I consider most of them to be my friends. We’ve worked together for years,” he says. None of the farmers he works with are desperately poor, according to Taylor. He considers this uniformity a shortcoming, but understands having stability ensures consistency and makes doing business easier. He negotiates price face to face, paying at a minimum 25 percent above Fair Trade or the C-market, although “we generally pay twice that.” For Taylor and his partner Fred Polzin, coffee has been a calling first and a business second. “It was more important to both of us to succeed on our terms. This was a labor of love, not money.”
It’s an admirable position, but as the number of high-quality specialty coffee roasters increases, attitudes like theirs are less common. Many younger roasters cannot afford to preference their passion for coffee over an awareness of the bottom line.
Back in 2009 when Wille Yli-Luoma, the straight-talking co-owner of Heart Coffee in Portland, Oregon, was getting started, he recalls being “slightly jealous of big companies that had pictures of farms on their bags and Direct Trade stories to tell.” After buying his first Direct Trade coffee, he realized what he’d done, to a large extent, was buy himself a sales pitch because, in fact, equally great coffees were available from traditional channels.
Yli-Luoma hasn’t given up on Direct Trade. He likes building relationships with farmers—“that’s the biggest benefit,” he tells me—and he enjoys “buying nice lots that a lot of energy is being put into.”
Problem is, the way he sees it, Direct Trade as it now plays out often favors larger roasters. Though growing, Heart bought some 250,000 pounds of coffee in 2016, a tiny fraction compared to larger specialty brands. He explains: “Say we find some new coffee and we work with the farmer to develop it,” a process that may entail being in near daily contact with the grower. If the coffee cups well and everyone wants it, larger roasters who can absorb more volume may scoop up the entire supply, cutting off Heart’s access to the very microlot Yli-Luoma helped nurture into existence. He doesn’t blame the farmer when this happens—“the farmer knows he isn’t going to make all his money on me”—but the power of pragmatism to console is limited. It must be enormously frustrating to invest time and money into a project, only to see your best efforts swooped up by monied interlopers.
Yli-Luomo hasn’t given up on Direct Trade, but feels that the system is getting “trickier and trickier.” It’s possible, he concedes, for farmers to earn $4 maybe $5 a pound for their most spectacular microlots. But ironically, the very success of specialty and Direct Trade—success that has led to the industry’s growth and consolidation—is threatening the higher prices farmers earn. That’s because, according to Yli-Luomo, when large specialty roasters show up at a farm able to buy a huge amount of coffee –including the best lots–the roaster “holds the quantity card,” and can force growers’ prices down.
“This is still Direct Trade,” he notes ruefully. Call it Direct Trade in the Shadows , perhaps—the shaded details of how deals get done, long before the coffee touches your lips. And then Yli-Luoma told me something really surprising: “Honestly, I think buying through importers may be the way to go for this industry.”
The Importers
Back in the first splash of Third Wave coffee—around a decade ago, when I was researching God In A Cup—influential buyers, only half in jest, spoke of importers as “blood-sucking middlemen.” In their view, the fees middlemen charged robbed farmers of their hard-won earnings. Such posturing was disingenuous. In the specialty coffee business then and now, no legitimate buyer goes it alone. Unless you as a roaster are smuggling green coffee from the farm out of the country in your backpack, your Direct Trade program is not, in fact, entirely direct.
Standing in the middle between farmers and roasters are the importers, who, when doing their job well, absorb some of the pressures crushing both sides. In tandem with carefully chosen exporters, importers create the supply chain ensuring that microlots are properly separated, processed, labeled, shipped, stored in warehouses, and shipped to roasters, sometimes in bulk, but more often, a few bags at a time. At origin, roasters rely on importers’ knowledge of coffee, their webs of global relationships, and their financial, technical, and bureaucratic know-how.
All this explains why Dan Streetman, the Relationship Buyer at Irving Farm Coffee Roasters, says his first act after being hired was to reach out to his importer. That was in 2011. “My directive was to travel to origin and buy coffees that would change how we tell our story,” Streetman says. “To develop relationships with farmers, I realized I would have to work backwards. I called our importer and said I am looking for coffees with these characteristics. I am going to buy this amount. I am going to travel, and I want to cup coffees and meet producers.” His importer made the introductions and six years later, Streetman, whose company sells half a million pounds of coffee a year is still buying from some of these producers.
On the grower side of the equation, the single most important service provided by importers is financial. Importers do what small and medium-sized boutique roasters can rarely do: provide farmers with pre-financing to buy seed and fertilizer, pay pickers, and underwrite other expenses incurred prior to harvest. “Most coffee farmers are poor,” says Café Imports VP of Sales Noah Namowicz, who spoke to me at length for this feature series. “Believe me, we had to fight our bank to do this,” he explains. “Borrowing money to give to a coffee farmer in Colombia whose whole crop can get wiped out in a hailstorm is not something money people want you to do.”
A new generation of importers has emerged to serve the thousands of small and medium-sized specialty roasters making their mark today. These importers look, dress, and think like their customers. Among them, Minneapolis-based Café Imports; Seattle’s Atlas Coffee; Oakland’s Red Fox Coffee Merchants, co-founded by former Stumptown green buyer Aleco Chigounis (who declined to be interviewed for this series); Genuine Origin, the boutique division of the global trading company Volcafe; Coffee Shrub, the influential small-format green coffee purveyor owned by Thompson Owen of Sweet Maria’s; and Royal Coffee, whose newly launched Crown Jewels program separates out high-rated microlots for customers looking to buy small lots of green coffee.
There is another, often overlooked dimension to the importer’s role. By absorbing large amounts of coffee, these quality-focused importers ensure the financial viability of the specialty market and Direct Trade. Microlots are expensive to grow, but when volume increases, costs are amortized. Cafe Imports bought 19 million pounds of specialty coffee in 2015, enough to tip the scale in favor of specialty. As Namowicz explained, “When we work with a farm, we feel an obligation to buy everything that we can find a home for.” Only the largest (consolidated) roasters can approach this.
You might say Café Imports and other importers help level the playing field by absorbing risk while enabling small and medium-sized roasters to push quality coffee into all corners of the world. “I pour a ton of time and money into developing infrastructure to benefit farmers,” Namowicz continues. “When a roaster buys thirty bags from me, the purchase is part of a larger structure benefiting the producer.” When looked at closely this importer-funded structure, plus the quality premium Café Imports and others pay for the highest-rated microlots, lines start to blur, and the importers’ work begins to resemble Direct Trade.
If it looks like Direct Trade, and cups like Direct Trade, well…perhaps Wille Yli-Luoma is right, and the role these importers play will be integral to the future of the Direct Trade business model. If that role has been overshadowed, well, perhaps it’s time we bring it out of the shadows and into the light.
To get there we need transparency, which is one focus of my third and final installment of this series. Join us again in late April for the conclusion.
Michaele Weissman is a special correspondent to Sprudge Media Network. Weissman is the author of God In A Cup: The Obsessive Quest for the Perfect Coffee, published in 2008 by Houghton Mifflin Harcourt, and a freelance journalist writing for The New York Times, The Washington Post, The Wall Street Journal, and many more. Read more Michaele Weissman on Sprudge.
The post Direct Trade In The Shadows appeared first on Sprudge.
seen 1st on http://sprudge.com
0 notes