#biparietal
Text
Module 10 Assignment
Question 9.1:
Conduct ANOVA (analysis of variance) and Regression coefficients to the data from cystfibr (> data (" cystfibr ") database.
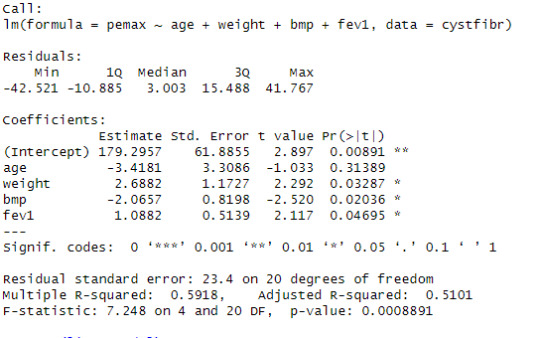
I chose the variables pemax(intercept), age, sex, weight, and fev1. I used the code 'lm(formula = cystfibr$pemax ~ age + weight + bmp + fev1, data=cystfibr)' to calculate the coefficients shown below.

I then conducted the ANOVA test using the function 'anova()', and the result is shown below.

Interpretation of ANOVA Results:
'age' has a high f-value of 18.4385 and a significantly low p-value of 0.0003538. This tells us to reject the null hypothesis and we can determine that the variation of 'age' on 'pemax' is not equal to 0.
'weight' has a somewhat low f-value of 1.7258 and a non-significant p-value of 0.2038195. This does not warrant the rejection of the null hypothesis.
The f-value of 'bmp' is 4.3450, which is not low, and the p-value of 0.0501483 may be considered significant as it is just greater than 0.05 (5% significance level). In this case, we can reject the null hypothesis.
'fev1' has an f-value of 4.4836, which is also not low, and a significant p-value of 0.0469468 because it is less than 0.05 (5% significance level). This tells us we can reject the null hypothesis.
Last, I used the "summary()" function to conduct and calculate a multivariate analysis.

Interpretation of Multivariate Results:
The estimated value of the intercept is 179.2957 with a significant p-value. The value of the intercept represents the predicted mean of 'pemax' when all independent variables = 0. The significant p-value tells us that the results are more extreme than the expected probability, as it is between 0.001 and 0.01 (less than a 1% significance level), therefore, we can reject the null hypothesis.
The estimated value of 'age' is -3.4181, meaning we predict that for every unit change in 'age', there will be a change of -3.4181 units in 'pemax'. This p-value is not significant and does not warrant the rejection of the null hypothesis, as it is greater than 0.1 (10% significance level).
The estimated value of 'weight' is 2.6882. This indicates that for every unit change in 'weight', there will be a change of 2.6882 units in 'pemax'. This p-value can be considered significant because it is less than 0.05 (less than a 5% significance level).
The estimated value of 'bmp' is -2.0657. This indicates that for every unit change in 'bmp', there will be a change of -2.0657 units in 'pemax'. This p-value can also be considered significant because it is less than 0.05 (less than a 5% significance level).
The estimated value of 'fev1' is 1.0882. This indicates that for every unit change in 'fev1', there will be a change of 1.0882 units in 'pemax'. This p-value can be considered significant because it is less than 0.05 (less than a 5% significance level).
Question 9.2:
Fit a prediction weight as well as abdominal and biparietal diameters. How much is gained by using both diameters in a prediction equation? Can this be given a nice interpretation to our analysis?
Step 1: I first saved the logarithms of the 3 variables, birth weight ('bwt'), abdominal diameter ('ad'), and biparietal diameter ('bpd'), as columns.

Step 2: I used 'ad' and 'bpd' as predictor variables to create two linear regression models using the 'lm()' function.

Step 3: I added the two predictor coefficients to get a sum of 5.569.
Step 4: I made another model to join the two coefficients in one linear model, again using the 'lm()' function. Adding the two coefficients, we end up with a sum of 3.019.

Step 5: I used the 'summary()' function on the model containing both predictor variables.

Both predictors hold considerable statistical significance, as illustrated by the p-value, which is < 2.2e-16.
By employing both diameters within a predictive equation, we observe that their combined total approximates 3, aligning with our expectations. This suggests the accuracy and correctness of the results. I have concluded that both predictors hold significance in predicting 'bwt', with each contributing nearly equally, given their proximity to 1.5 out of the total sum of around 3. These findings offer valuable insights into the data, revealing the impactful interactions and influences between these variables.
0 notes
Text
Ultrasound in obstetrics and gynaecology
Ultrasound technology has revolutionized the field of obstetrics and gynecology (OB/GYN), offering a non-invasive and highly effective method for imaging and diagnosing various conditions. Here are some key applications of ultrasound in obstetrics and gynecology:
Prenatal Care: Ultrasound is routinely used during prenatal care to monitor fetal development, growth, and well-being. It helps determine gestational age, assess fetal anatomy, detect abnormalities, and evaluate the placenta and amniotic fluid levels.
Dating and Viability: Ultrasound is used to accurately determine the gestational age of the fetus, helping to confirm the due date and assess fetal viability in early pregnancy.
Anomaly Scan: Anomaly scans, typically performed around 18–20 weeks of pregnancy, use ultrasound to assess the fetal anatomy in detail. This helps detect structural abnormalities, congenital anomalies, and markers for genetic disorders.
Multiple Gestations: Ultrasound is essential for diagnosing and monitoring multiple pregnancies, including twins, triplets, or higher-order multiples. It helps determine chorionicity, amnionicity, and assess the growth and well-being of each fetus.
Fetal Growth Assessment: Serial ultrasound measurements of fetal biometry, including biparietal diameter, head circumference, abdominal circumference, and femur length, are used to assess fetal growth and detect intrauterine growth restriction (IUGR) or macrosomia.
Fetal Doppler Studies: Doppler ultrasound evaluates blood flow in the umbilical artery, middle cerebral artery, and ductus venosus to assess fetal well-being, detect signs of fetal distress, and monitor placental function.
Fetal Echocardiography: Specialized ultrasound techniques are used to evaluate the fetal heart, detect congenital heart defects, and assess cardiac function in cases of suspected cardiac abnormalities or high-risk pregnancies.
Amniocentesis and Chorionic Villus Sampling (CVS): Ultrasound guidance is often used during invasive prenatal procedures such as amniocentesis and CVS to ensure accurate placement of the needle and minimize the risk to the fetus.
Gynecological Disorders: Ultrasound is used to diagnose and monitor various gynecological conditions such as ovarian cysts, fibroids, endometrial abnormalities, and pelvic inflammatory disease (PID). It helps evaluate the size, location, and characteristics of these abnormalities.
Infertility Evaluation: Ultrasound plays a crucial role in evaluating infertility by assessing ovarian reserve, detecting structural abnormalities in the uterus or ovaries, and monitoring follicular development during assisted reproductive techniques (ART) such as in vitro fertilization (IVF).
Overall, ultrasound is an indispensable tool in obstetrics and gynecology, providing valuable diagnostic information, guiding interventions, and facilitating optimal care for pregnant women and gynecological patients. If you are preparing ultrasound courses. join StudyUltrasound.
0 notes
Text
Module 10 Assignment
library(base)
library(ISwR)
cystfibr
attach(cystfibr)
linearmodel <- lm(pemax ~ age + weight + bmp + fev1, data = cystfibr)
summary(linearmodel)
anova(linearmodel)
anovamodel <- aov(pemax ~ age + weight + bmp + fev1, data = cystfibr)
summary(anovamodel)
Looking at the linear progression model, we can see that the estimate of the value for the intercept is 179.2957 with significant p-value. The estimate of the variable age is -3.4181 for that unit change in the variable age in the dependent variable pemax with a non-significant p-value. The estimate of the variable weight is 2.6882 for that unit change in the variable weight in the dependent variable pemax with a significant p-value. The estimate of the variable bmp is -2.0657 for that unit change in the variable bmp in the dependent variable pemax with a significant p-value. The estimate of the variable fev1 is 1.0882 for that unit change in the variable fev1 in the dependent variable pemax with a significant p-value.
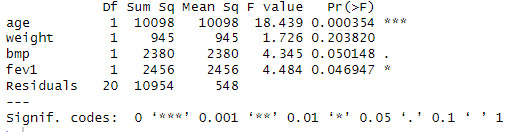
Looking at the ANOVA table, see that the p value of age is 0.00354, less than 0.001 so, we can reject the null hypothesis and can interpret it as the variation the effect of the variable age on the dependent variable pemex is not equal to zero. The p value of weight is 0.203820, greater than 0.05 so, we can not reject the null hypothesis and can interpret it as the variation the effect of the variable weight on the dependent variable pemex is equal to zero. The p value of bmp is 0.050148, less than or equal to 0.05 so, we can reject the null hypothesis and can interpret it as the variation the effect of the variable bmp on the dependent variable pemex is not equal to zero. The p value of fev1 is 0.046947, less than or equal to 0.05 so, we can reject the null hypothesis and can interpret it as the variation the effect of the variable fev1 on the dependent variable pemex is not equal to zero.
Importing Data
library(ISwR)
Data <- secher
head(Data)
Creating a model using birthweight and biparietal diameter
model1 <- lm(log(bwt) ~ log(bpd) , data = Data)
summary(model1)
Creating a model using birthweight and abdominal diameter
model2 <- lm(log(bwt) ~ log(ad), data = Data)
summary(model2)
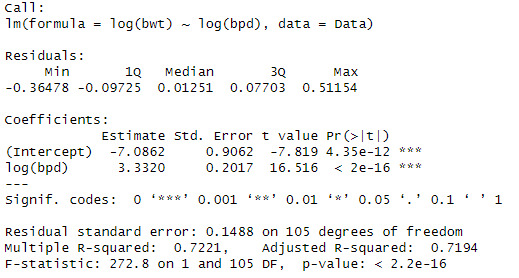
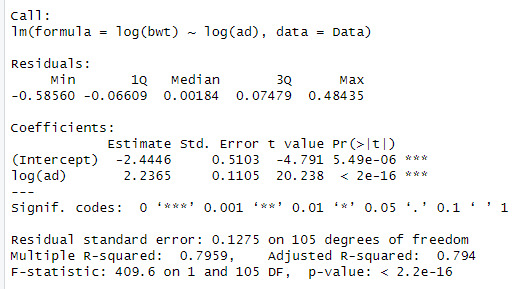
When looking at the data, we can see that the log(bpd) is a significant variable of the log(ad). The model also explains 79.5% of the variation in log(bwt)
Creating a model using birthweight and both abdominal and biparietal diameter
model3 <- lm(log(bwt) ~ log(ad) + log(bpd), data = Data)
summary(model3)
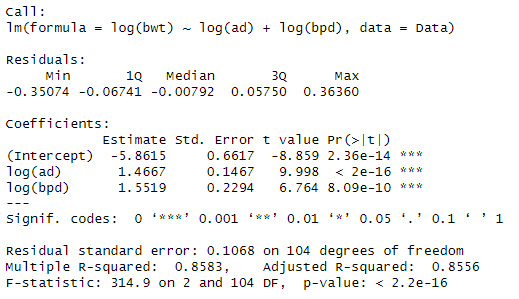
We can see that when both variables are added that the significance and Rsqaured increases to 85.5%.
The interpretation is, when there is a 1% increase in abdominal diameter increases the birthweight by 1.4667% and when there is a 1% increases in the biparietal diameter there is a 1.5519% increase in the birthweight.
0 notes
Text
Multivariate Regression
From our textbook, Introductory Statistics with R pp. 159 Exercises 9.1 & 9.2
9.1. I revised this question, so please follow my description only. Conduct ANOVA (analysis of variance) and Regression coefficients to the data from cystfibr (> data (" cystfibr ") database. You can choose any variable you like. in your report, you need to state the result of Coefficients (intercept) to any variables you like both under ANOVA and multivariate analysis. I am specifically looking at your interpretation of R results.

Extra clue:
The model code:
i. lm(formula = cystfiber$spemax ~ age + weight + bmp + fev1, data=cystfiber)
ii. anova(lm(cystfibr$spemax ~ age + weight + bmp + fev1, data=cystfiber))
9.2 The secher data (> data("secher") are best analyzed after log-transforming birth weight as well as the abdominal and biparietal diameters. Fit a prediction weight as well as abdominal and biparietal diameters. For a prediction equation for birth weight. How much is gained by using both diameters in a prediction equation? The sum of the two regression coefficients is almost identical and equal to 3.

Extra clue:
Model10 <-lm(log(bwt))~I(log(ad)), data=secher
summary(model10)
UNFINISHED
0 notes
Photo

There's a video that talks about fetal biometry. BPD = Biparietal Diameter = diameter of skull from one parietal bone to the other. See video here: https://accessmedicine.mhmedical.com/MultimediaPlayer.aspx?MultimediaID=6130500
0 notes
Text
Best torrent download sites for 2021
Simple Calculator - Free Online CalculatorIn a conventional report sharing setup that uses a document server, sharing a 2 hundred MB software to 1,000 human beings might speedy exhaust all of my upload bandwidth, especially if they all requested the report straight away. Torrents take away this hassle via letting clients scrape just a little bit of the records from me, a bit bit from some other user, and so forth till they have downloaded the complete record.
Once a couple of character has the complete document downloaded, the original sharer can stop dispensing it without it affecting absolutely everyone else. The record will remain available for any other users of that torrent because of the decentralized, P2P foundation of BitTorrent.
A magnet link is a simple way to pick out the torrent on the BitTorrent community while not having to address a TORRENT document. It's particular to that unique torrent, so despite the fact that the link is only a string of characters, it's just as desirable as having the report.
Magnet links and TORRENT files are regularly indexed on torrent indexes, that are websites constructed mainly for sharing torrents. You can also share torrent data over e-mail, text, etc.
Since magnet links and TORRENT documents are simply the commands for a BitTorrent consumer to recognize a way to get the data, sharing them is short and easy. This is glaringly only a fallback because this clone steals the hyperlinks of OxTorrent for its gain. To pass back to Caesar what belongs to Caesar it will therefore be vital to return to OxTorrent brief
Even despite the fact that streaming structures are attracting more and more human beings, online downloading still represents a large a part of net site visitors. Despite the controversies and illegality of many web sites, masses of thousands of human beings though use them. Among the torrent web sites is OxTorrent. We will find out what this website on line has to provide and solution your questions in element. We will cowl specially its history, its actual address (website) or its felony (or instead unlawful) thing.

Simple Calculator - Free Online Calculator
Fast forward to the 21st century and we don’t only have calculators that healthy in small computers but advanced ones that don’t require users to have them established on their tool.
Here are the 10 superb websites for making calculations ranging from fundamental math operations to solving complex monetary questions. Want to resolve a complex Mathematical hassle or want to transport-check any problem associated with Physics? Here is a simplified answer for you. Online Calculator is a tool so you can will let you do multiple calculations related to Maths, Physics, Chemistry and so on. At one skip.
All you need to do is input numbers and equations and loose on-line calculator will resolve it for you. Online calculator reduces the complexity of solving difficult problems and because of this lets in in quick and clean gaining knowledge of of any project. Learning might be tons less difficult and amusing with online Calculator. The online calculator is in reality loose and is an clean way of hassle-solving. Solve equations, flow into test sums and issues related to Maths, Physics and Chemistry. Mathematical and Scientific equations can be solved again and again without any problem with the calculator.
Whether it's far an Improper Fraction or Mixed Number, Percentage or Cross Product, Area or Perimeter of any figure, you can calculate it all with this device.Check the development and weight of your baby on the same time as though in fetal diploma with this week with the useful resource of week fetal development calculator and get perception into the early development stages of the fetus.
The on-line fetal development calculator tells you the expected fetal weight while you provide fetal biparietal diameter and fetal belly circumference. Know greater about the health of your fetus via using checking it's miles weight often to make certain comfortable shipping of your toddler. Also check the not unusual fetal weight for a selected week to check the specified not unusual top and weight of the fetus to apprehend the general increase that the fetus ought to have. Also get descriptions and insights into the week via the use of using week boom of the fetus.
1 note
·
View note
Text
The Online Calculator
3D LED Acrylic BoardsThe online fetal improvement calculator tells you the predicted fetal weight after you provide fetal biparietal diameter and fetal belly circumference. Know extra about the health of your fetus by checking it's weight often to make sure safe transport of your baby. Also take a look at the average fetal weight for a specific week to test the required common top and weight of the fetus to understand the general growth that the fetus have to have. Also get descriptions and insights into the week by using week boom of the fetus.
This everyday distribution calculator (also a bell curve calculator) calculates the region underneath a bell curve and establishes the possibility of a fee being better or lower than any arbitrary fee X. You can also use this opportunity distribution calculator to find the probability that your variable is in any arbitrary range, X to X₂, just by the use of the everyday distribution imply and widespread deviation values. This article explains some basic terms regarding the standard ordinary distribution, offers you the formula for regular cumulative distribution feature (ordinary CDF) and gives examples of the everyday distribution opportunity.
Normal distribution (additionally called the Gaussian) is a non-stop chance distribution. Most records is close to a principal cost, without a bias to left or right. Many observations in nature, along with the height of human beings or blood strain, follow this distribution.
In a normal distribution, the imply cost (common) is also the median (the "center" range of a looked after list of facts) and the mode (the fee that looks most usually). As this distribution is symmetric approximately the center, 50% of values are lower than the imply, and 50% of values are higher than the suggest.
Another parameter characterizing the ordinary distribution is the standard deviation. It describes how tremendous the numbers are. Generally, sixty eight% of values have to be within 1 trendy deviation from the suggest, 95% - within 2 standard deviations, and 99.7% - within three popular deviations. The wide variety of popular deviations from the imply is called the z-score. It can be the case which you recognise the variance, however not the same old deviation of your distribution. However, it's easy to workout the latter through simply taking the square root of the variance.
You can say that an boom in the imply cost shifts the whole bell curve to the proper. Changes in wellknown deviation tightens or spreads out the distribution around the suggest. In strongly dispersed distributions, there's a better probability for a random facts point to fall a long way from the imply. The shape of the bell curve is decided simplest by those two parameters.
You can test that this tool via using the standard normal distribution calculator as nicely. If you input the mean, μ, as 0 and standard deviation, σ, as 1, the z-score can be identical to X.
3D LED Acrylic Boards
The light additives embedded in the letters or within the base-board to provide hues and mild results to the above-cited acrylic letters. Modern signs are normally lit up by means of LEDs
You can study the special description of the substances, above additives and production technique of the forums in a phase at the end of this page. It does make for an thrilling study.
But for now, allow’s explore the distinctive kinds of boards indexed above, in element: Detailed clarification and photos of 10 extraordinary varieties of LED ACP Acrylic Glow Sign Boards
1. 3D Acrylic Letters Mounted on a ACP Base Frame
Three-dimensional letters constant on top of an ACP base is the form of sign board that maximum keep owners opt for. As the name shows, those acrylic call forums consist of:
Hollow acrylic letters or emblems which can be about 3 inches thick.
LEDs are embedded in the hollow area below those letters.
These 3-d letters and emblems are hooked up on an ACP field frame.
This aluminium body, together with the backlit acrylic letters, are then mounted on-website online.
1 note
·
View note
Text
Importance of Ultrasound in Pregnancy
Introduction
In pregnant women, tests that use radiation, such as x-rays and computerized tomography, should be avoided due to the obvious risks they bring to the baby. So, ultrasound in Delhi is the imaging test of choice for prenatal follow-up. Ultrasound is a cheap test, without risks for the fetus, which causes no side effects and has no contraindications.
In this article, we will briefly review the role of obstetric ultrasound scan in Delhi. We will address issues such as nuchal translucency, morphological ultrasound, estimating gestational age and 3D and 4D ultrasound.

WHEN MUST THE OBSTETRIC ULTRASOUND BE DONE?
Ultrasound can be performed several times during pregnancy, but it is not necessary in each consultation. In fact, many international Gynecology and Obstetrics societies agree that, if the patient is healthy, she has no complaints or risk factors, only one or two ultrasound evaluations, carried out between the 10th and 13th weeks and between the 16th and 20th weeks of gestation, they are really necessary during pregnancy.
However, since many obstetricians have an ultrasound device in their office, it is very common for the test to become part of many, if not all, prenatal consultations. It is good to make clear that, being pregnant well, there are no studies that indicate advantages in terms of health of the mother and the fetus when we compare pregnant women who did serial ultrasounds throughout pregnancy with pregnant women who made only a single ultrasound between the 16th and 20th week of gestation. Therefore, in places with structure and limited access to medical resources, there is nothing wrong with requesting only a single ultrasound during pregnancy.
In places with more resources, the obstetrician usually performs at least 3 or 4 prenatal ultrasound exams, divided during the 3 trimesters of pregnancy:
1- In the first or second prenatal consultation with the aim of confirming the existence of an embryo within the gestational sac and intrauterine pregnancy, visualize the heartbeat of the fetus, early identification of a twin pregnancy, estimate the gestational age and evaluate possible changes Anatomical aspects of the female gynecological tract, such as ovarian cysts, myomas, uterine malformations, etc.
2- In the second trimester of pregnancy, the pregnancy scan in Delhi should be performed, preferably, between the 18th and 24th week of pregnancy, to evaluate the formation of the fetal anatomy. This test is called morphological ultrasound (or morphological ultrasound) and is the most important ultrasound of pregnancy since it is capable of detecting fetal malformations.
Then in the beginning of the 2 trimester, around the 12th week of gestation, it is also very common to perform an ultrasound to measure the nuchal translucency, which is a test that evaluates the amount of fluid in the region of the nape of the fetus. An increased nuchal translucency suggests the possibility of a chromosomal alteration, such as Down syndrome.
3- In the third trimester, ultrasound is used to control the growth rate of the fetus, the placenta of the uterus, the amount of amniotic fluid, the vitality of the fetus, its position inside the uterus and the position of the umbilical cord.
FIRST ULTRASOUND OF THE BABY
Obstetric ultrasounds performed in the first 12 weeks of pregnancy are usually done through the transvaginal route. From the 12th week, the abdominal route is more indicated.
The first pregnancy ultrasound in Karol Bagh can be performed after the 5th week of pregnancy, when it is already possible to visualize the gestational sac, the first identifiable structure of a pregnancy. The gestational sac is usually visible after the 4th or 5th week of gestation. Before the 4th week it is useless to do the ultrasound since he is not able to identify any sign of gestation.
A few days after the beginning of the 5th week of pregnancy it is possible to identify, within the gestational sac, the vitelline vesicle, structure that provides nutrients to the embryo. The presence of the gestational sac and the vitelline vesicle inside the uterus confirms the existence of an intrauterine pregnancy, ruling out the possibility of an ectopic pregnancy, although the embryo is still incapable of being seen.
The embryo itself is usually visible from the 6th week and its heartbeat can be identified between the 6th and 7th week.
In general, we indicate the realization of the first ultrasound during the 7th week of pregnancy, when all the data referred to above will already be available to the obstetrician.
ESTIMATION OF THE GESTATIONAL AGE BY ULTRASOUND
In the first trimester of pregnancy, the human embryo presents a more or less stable and predictable growth and development rate, thus being possible to estimate the gestational age according to its ultrasonographic characteristics. From the second trimester, babies begin to grow at different speeds according to their genetic characteristics and pregnancy conditions, being it more difficult to estimate gestational age through ultrasound.
The estimate of the gestational age and the probable date of delivery (PPD) are made more accurately by the obstetric ultrasound in Delhi in the first trimester than by the date of the last menstruation (DUM), mainly in women who have a cycle Irregular menstrual or that are not remembered with certainty of the day of the beginning of the last menstruation. If the DPP calculated by the DUM is different from the DPP calculated by the ultrasound, the latter should be the one used by the obstetrician to assess the most accurate gestational age.
The size of the gestational sac and, mainly, a measure called head-buttock length (CCN), are the most used measures to estimate gestational age. Data, such as the presence of the heartbeat, the vitelline vesicle and an embryo visible inside the uterus, also help in the estimation of gestational age in still very early pregnancies.
From the 12th week of pregnancy, other measures allow to estimate the gestational age, such as the biparietal diameter (DBP), the cephalic circumference (CC) and the length of the femur (LF).
NUCAL TRANSLUCENCY
The evaluation of the nuchal translucency (TN), which some call morphological ultrasound of the first trimester, is an examination performed between the 11th and 13th week of pregnancy, whose objective is to identify the amount of fluid present in the nape of the fetus. Studies show that fetuses with chromosomal abnormalities, fetal malformations and genetic syndromes tend to have more fluid in this region, making the neck look wider.
As liquids create less echo than solid structures to ultrasound, they appear darker, that is, with greater translucency or increased nuchal translucency. The examination of the nuchal translucency only has value when performed on fetuses with head-buttock length between 45 and 84 mm and with less than 14 weeks of gestation
Normal values of the nuchal translucency are less than 2.5 mm. These values, however, must be evaluated according to the age of the pregnant woman. A nuchal translucency greater than 2.5 mm in a 22-year-old pregnant woman is less worrisome than the same value in a 40-year-old pregnant woman. The greater the value of the nuchal translucency, the greater the possibility of the fetus having some genetic alteration.
The increased nuchal translucency may be an indicator of several genetic diseases or malformations, with Down syndrome being the most important. About 75% of babies with Down syndrome have increased nuchal translucency.
It is necessary to reinforce that the nuchal translucency is only a screening test, and does not serve as a definitive diagnosis. The false positive rate is relatively high, around 5%. In the same way, a normal TN, below 2.5 mm, does not rule out the possibility of a chromosomal disease since around 20 to 25% of fetuses with Down present normal TN.
When we find an increased nuchal translucency, other ultrasonographic evaluations must be performed to obtain more data. Generally, the absence of nasal bone and an altered blood flow in the venous duct (communication between the umbilical vein and the inferior vena cava of the fetus) are alterations that reinforce the possibility of genetic problems.
When the tracing by the nuchal translucency, nasal bone or venous duct is altered, an investigation with blood analysis of the mother (beta hCG and Plasmatic Protein A (PAPP-A)) is necessary.
With the TN data and the results of the blood tests, the obstetrician can calculate the risk of chromosomal diseases of the fetus. If the value is much higher than expected for age, amniocentesis (collection of amniotic fluid) is usually indicated for the definitive diagnosis.
MORPHOLOGICAL ULTRASOUND
Fetal morphological ultrasound is the most important ultrasound examination of pregnancy. It should be done abdominally between the 18th and 24th weeks of pregnancy. In this stage, the fetus is already fully formed, being possible to identify present malformations with relative ease.
The morphological ultrasound is the slowest and most detailed of the pregnancy, being able to take more than half an hour, since the doctor at ultrasound centre in Delhi needs to individually evaluate different structures. In many cases, it is not your obstetrician who performs this test, but a radiologist in Delhi or another obstetrician specializing in fetal morphologic ultrasound.
In the morphological ultrasound it is possible to confirm the sex of the baby, verify its heart and its chambers, evaluate the formation of the brain, digestive organs, limbs, face and other systems of the fetus. The use of Doppler is used to check the blood flow in the placenta and uterus. In this ultrasound it is also possible to determine the location of the placenta to know if it may be blocking the exit of the uterus, a condition called placenta previa.
The morphological ultrasound also serves to measure the head of the baby, the femur and the abdominal circumference to know if its growth is adequate.
ULTRASOUND 3D
3D ultrasound has gained popularity in recent years due to the greater sharpness and beauty of its images. For parents, 3D ultrasound is much more interesting, because it shows the appearance of the fetus in more detail. For the doctor, however, in most cases, there is no indication for its realization because 3D ultrasound adds little information in relation to the common 2D ultrasound.
In some cases of suspected facial abnormality or neural tube defects seen by common ultrasound, 3D ultrasound seems to show the defects with a little more clarity. Except situations like this, there are few cases in which 3D ultrasound is really useful.
The 4D ultrasound is only a 3-D ultrasound in real time, capable of showing the movements of the fetus and its internal structures, such as the heart. It can be recorded as a video, which makes it even more attractive to parents.
#Radiologist in Delhi#Ultrasound in Delhi#Ultrasound Centre in Delhi#Ultrasound Scan in Delhi#Pregnancy Scan in Delhi#Ultrasound in Karol Bagh
1 note
·
View note
Text
BPD And FL Chart in Pregnancy – Biparietal Diameter and Femur Length in Ultrasound
Pregnancy term and ultrasound imaging go hand in hand. Not only do you get to witness your baby’s growth, but the ultrasound report also ascertains the health of the fetus, their gestational period, and even their development in the mother’s womb.
After an ultrasound, your OBGYN will likely discuss “BPD and FL chart in pregnancy.” This stands for Biparietal diameter (diameter of the baby’s developing skull bone and structure) and the Femur length (length of the baby’s growing and developing femur).
Through ultrasound imaging, these factors can help ascertain the overall fetal weight and the baby’s gestational age. Comparing the numbers of BPD and FL with the standard chart also allows the doctors to look out for underdevelopment, overdevelopment and other developmental anomalies in the fetus.
If this is your first pregnancy and you are confused about these pregnancy-related terminologies like BPD and FL, let us explain them to you in simpler words and in more detail.
Read Full Article: http://pregajunction.com/blog/bpd-and-fl-chart-in-pregnancy/
0 notes
Text
Isobutane Market Trends and Prospects by 2030
Isobutane Market: Overview
The isobutane market may record good growth across the forecast period of 2020-2030 on the back of its widespread use across various applications such as aerospace, rubbers, additives, lubricants, additives, household cleaners, and cosmetics. On the basis of purity, the isobutane market may be classified into Purity 99.7%, Purity 99.5%, Purity 99%, and others. Furthermore, based on the source, the isobutane market can be segmented into synthetic and bio-based. Pure-grade isobutane holds great importance in the market and may show significant growth across the forecast period.
This report on the isobutane market has research based on various parameters for analyzing the ideal growth generating factors. This aspect proves to be of great help to the market stakeholder and helps them design their business strategies accordingly. This report also covers the rapidly changing isobutane market scenario. The report also sheds light on the effects of COVID-19 on the isobutane market through 2020 – 2030.
Are you a start-up willing to make it big in business? Grab an exclusive PDF Brochure for this report!
Isobutane Market: Industrial Analysis
The isobutane market comprises a highly fragmented landscape with a mix of local and international players in tough competition with each other. The manufacturers in the isobutane market are also focusing on expansion activities for generating isobutene. For instance, last year, the Kuwait Integrated Petroleum Industries Company announced its intentions to expand the production capacity of Al-Zour Refinery. Two UOP MErox units will be used for treating isobutene and an 11,800 biparietal diameter (BPD) Butamer unit will be used for converting normal butane to isobutene. Such developments bring good growth opportunities for the isobutane market.
REQUEST FOR COVID19 IMPACT ANALYSIS –
The participants in the isobutane market are also involved in activities such as mergers, acquisitions, collaborations, joint ventures, and partnerships to strengthen their foothold. These activities also prove to be growth multipliers for the isobutane market. Some well-established players in the isobutane market are Jinling Petrochemical, PBG Energy Inc., Sinopec Zhongyuan Petroleum Co., Praxair Distribution Inc., CryoCarb-Beloit, Conoco Philips, Amcor Inc., and Linde LLC.
Read our Case study at :
https://www.transparencymarketresearch.com/casestudies/chemicals-and-materials-case-study
Isobutane Market: COVID-19 Perspective
The COVID-19 pandemic has led to the disruption of growth across numerous sectors across the world. The lockdown orders imposed for containing the deadly SARS-CoV-2 outbreak by various countries resulted in the complete shutdown of manufacturing facilities and production units, thus hitting a pause button on the economic activities. This aspect has left a negative impact on almost all businesses, including the isobutane sector. However, many countries are relaxing lockdown measures to revive the economy. This factor will help the isobutane market to rise steadily and recover from the losses incurred due to the pandemic.
Isobutane Market: Growth Boosters
Applications of isobutane across diverse end-users may sow the seeds of growth for the isobutane market throughout the forecast period. The use of isobutane as a replacement for chlorofluorocarbons (CFCs) in cosmetic products may bring promising growth for the isobutane market. It also finds use in shaving creams as it is a foaming agent as well. In addition, isobutane is highly preferred by synthetic rubber manufacturers due to lower resistance to liquids and gas. Petrochemicals are the most prominent end-users and may bring good growth opportunities for the isobutane market across the forecast period.
Isobutane Market: Regional Landscape
The isobutane market is spread across North America, Central America, South America, the Middle East and Africa, Europe, and Asia Pacific. The large presence of isobutane manufacturers across North America and Europe may prove to be a significant growth generating factor.
Asia Pacific may emerge as a rapid growth-generating region. Rising industrial infrastructure across developing economies like India and China is serving as a significant growth booster for the isobutane market across the forecast period. The Middle East and Africa may record medium growth throughout the forecast period.
0 notes
Photo

☢️Feliz día! ¡Hoy quiero hablarles de algo que las mamis ven en los informes de la ecografía de sus bebes! Me encanta realizar estudios maternos para ver a los bebés y quiero ayudarlo a perfeccionar su análisis también. ☢️Hoy hablare de la circunferencia de la cabeza y el diámetro biparietal. Para obtener las mediciones de la cabeza fetal perfecta, ¡debe conocer los puntos de referencia! En las mediciones de BPD (bi parietal diameter) y HC (head circumference), debemos incluir 4 cosas: -Talamo -Cavum Septum Pellucidum -3er ventriculo -Linea media Falx ☢️Una vez que todas estas se incluyen en nuestra imagen, debemos asegurarnos de que la línea media Falx sea perpendicular al Transductor ¡Ahora estás listo para medir! 🎉 ☢️El diámetro biparietal se mide de oreja a oreja, la pared exterior del calvario anterior a la pared interior del calvario posterior. Para la circunferencia de la cabeza, la elipse debe colocarse herméticamente alrededor del borde exterior del calvario. ☢️Es bueno realizar estas medidas pare determinar anomalías congénitas y el peso del bebé así que si las vez no te asustes, solo son parametros a tener en cuenta. ¡Deja un comentario si encontraste útiles estos recordatorios! 💛 #medicina #ultrasound #ultrasoundstudent #ultrasounds #docescalona #medicina #radiologia #radiologiamedica #radiology #radiologystudent #radiologycases #imagenologia (en Isla de Margarita- Tu Destino Ideal) https://www.instagram.com/p/CVeP0KJFbhE/?utm_medium=tumblr
#medicina#ultrasound#ultrasoundstudent#ultrasounds#docescalona#radiologia#radiologiamedica#radiology#radiologystudent#radiologycases#imagenologia
0 notes
Text
An 18 week woman came in because she had back pain. The resident I was with did a sonogram and urinalysis to see if there might be any urinary infection. Things you have to evaluate on sonogram:
MVP = Most Vertical Pocket (of amniotic fluid); should be at least 2 cm.
AC = Abdominal Circumference
FL = Femur Length
HC = Head Circumference
BPD = Biparietal Diameter
HR = 110 to 160 bpm is normal
Position of placenta (anterior or posterior)
5 notes
·
View notes
Text
Type of fetal malformation in a referral clinic in Beirut Lebanon and compare to the literature by Kariman Ghazal* in Open Access Journal of Biogeneric Science and Research

Abstract
Background: Ultrasonography has been shown to be an important tool for detecting congenital malformation. The objective of this study was to assess the feasibility and value of first trimester ultrasonography in the detection of fetal anomaly and how the information from ultrasound can influence the outcome of pregnancy.
Methods: A retrospective observational study was conducted between December 2018 and December 2020 on singleton pregnant women visiting the antenatal private clinic. All patients were screened for congenital anomalies by ultrasound scan during the first trimester. Demographics, maternal characteristics, and complications as well as malformation prevalence and types were recorded.
Results: A total of 159 women visited the antenatal clinic during the study period. The mean age was 28.15±5.53 years. The rate of consanguinity was 8.8%. Almost 99% of the women consumed folic acid during pregnancy while 45.3% took folic acid before pregnancy. Regarding symptoms complications during pregnancy, 93.7% of the women had vomiting, and around 20% had gestational diabetes and hypertension. The first trimester ultrasound of 31 women (19.5%) showed congenital anomalies of their fetus. Of the 31, 9 (29.0%) had malformation in the central nervous system (CNS) and brain, 7 (22.6%) had cardiac malformation, 2 (6.5%) had gastrointestinal anomaly, renal malformation, and skeletal defect, while 12 (38.7%) had other types of anomaly such as Down Syndrome and anomaly in the umbilical cord and limbs. As for pregnancy outcome, of the 31 who had malformation, 10 (32.3%) aborted, 1 (3.2%) had IUFD, 9 (29.0%) delivered through NVD, and 11 (35.5%) had CS. Of the 20 who delivered by NVD or CS, 8 (40.0%) of the neonates died directly after delivery or after few days.
Conclusion: First trimester ultrasound is an important tool for early detection of congenital anomalies. This would assist in initiating timely and multidisciplinary interventions.
Keywords: Pelvic ultrasound first trimestre malformations.
Introduction
The prevalence of congenital anomalies prenatal and posnatal ranges between 1.8% and 3% in different regions of the world [1-4] . Ultrasonography has been shown to be an important tool for detecting congenital malformation. The common practice is to perform an ultrasound evaluation of fetal anatomy during the second trimester (at 18 to 22 weeks’ gestation) [5]. The number of ultrasound scans varies depending on medical practice, the availability of qualified providers and equipment, in addition to the incurred costs [5].
Although some organ systems develop after the first trimester; yet, the importance of first-trimester ultrasound is being emphasized since it has the utility for confirming fetal viability, determining gestational age, detecting multiple gestation, identifying ectopic and cesarean scar pregnancies, evaluating the risk of chromosomal disorders and fetal anomalies, as well as assessing nuchal translunary [6-8]. There is an association between increased nuchal translucency and chromosomal abnormalities, specifically trisomy 21, and structural anomalies, such as cardiac abnormalities [9, 10].
Several fetal anomalies develop before 12 weeks of gestation. Hence, appropriate visualization of the fetus at this stage allows early detection of congenital anomalies [11]. The ultrasound detection rates for major structural anomalies in the first trimester was reported to be more than 40% [12]. Early detection of structural anomalies would assist the parents and physicians in planning multidisciplinary interventions during pregnancy or the early postpartum period, which could decrease neonatal and infant morbidity and mortality [7, 13].
Given that first trimester ultrasound is not just a screening tool for chromosomal anomalies, but also a method to identify anatomic anomalies, the aim of this study was to assess the feasibility and value of first trimester ultrasonography in the detection of fetal anomaly and how the information from ultrasound can influence the outcome of pregnancy.
Material and Methods
A retrospective observational study was conducted between December 2018 and December 2020 on pregnant women visiting the antenatal private clinic. Women with singleton pregnancies whom gestational age was established using the last menstrual period date and was confirmed through first trimester ultrasound were included in the study. Exclusion criteria were poor fetal visualization because of technical factors and multiple gestation.
Data collected included patients’ demographic and maternal characteristics such as age, body mass index (BMI), detailed obstetric history (gravida, parity, and abortions), consanguinity, smoking, and folic acid consumption. Moreover, maternal complications, illness (gestational diabetes and hypertension), and delivery characteristics were noted. In addition, neonatal characteristics and malformation were recorded.
All patients were screened for congenital anomalies by ultrasound scan during the first trimester as part of routine antenatal care. For the purposes of this study, first trimester included all examinations before 14 weeks of gestation. First trimester anomaly scan was performed by SAMSUNG R7 Expert ultrasound machine using 2.5 – 3.5 MHz probe.. The scan included demonstration of fetal location (intrauterine or ectopic), spontaneous fetal movements, and fetal organs. For gestational age calculation, fetal growth measurements such as crown-rump length, biparietal diameter, head and abdominal circumference, and femur length were done. Nuchal translucency was also measured. Fetal head was examined for shape, bilateral ventricular size, and choroid plexus. Fronto-maxillary facial angle, nasal bone, and ductus venosus Doppler were done. Examination also included abdominal organs, spine, limbs, fetal heart rate and cardiac chambers. Fetal echocardiography was done if there was any sign of cardiac anomaly. Umbilical cord and position of placenta were inspected. Neonates were examined by pediatricians after delivery.
The ultrasound findings were correlated with the results, chromosome analysis, further ultrasound studies performed in the second and third trimesters, fetal echocardiography, and results of postnatal follow-up when available. Termination with dilation and curettage prevented detailed pathologic examination in some cases.
Data Analysis
Data were analyzed using the Statistical Package for Social Sciences (SPSS) version 24. Descriptive analysis was performed. Categorical variables were presented as number and percent and were compared using Chi-square test or Fisher’s exact test. Continuous variables were presented as mean ± standard deviation and were compared using t-test. P-value less than 0.05 was considered statistically significant.
Results
1A total of 159 women visited the antenatal clinic during the study period. The demographic and maternal characteristics are presented in Table 1. The mean age was 28.15±5.53 years. Around 53% of the parturients had BMI ≥35 kg/m2 and 32.7% had one previous abortion. The rate of consanguinity was 8.8%. About 7% had thyroid diseases before pregnancy. Almost 99% of the women consumed folic acid during pregnancy while 45.3.0% took folic acid before pregnancy (Table 1).
Regarding symptoms during pregnancy, 93.7% of the women had vomiting, and around 20% had gestational diabetes and hypertension (Table 2). The majority of women experienced headache, cough, dizziness, nasal discharge, and sore throat during their pregnancy. Around 10% visited the emergency department during their pregnancy; the main reason was due to experiencing contractions.
For the delivery mode, 82 (51.6%) had cesarean section (CS), 60 (37.7%) had normal vaginal delivery (NVD), 16 (10.1%) aborted and 1 (0.6%) had intra-uterine fetal death (IUFD) (Table 2).
Neonatal characteristics, 35 (25.2%) were admitted to the neonatal intensive care unit; the main reason was for respiratory distress. The first trimester ultrasound of 31 women (19.5%) showed congenital anomalies of their fetus (Table 3). Of the 31, 9 (29.0%) had malformation in the central nervous system (CNS) and brain acrania 3 (9.7%) Ventriculomegaly3(9.7%) Encephalocele 2 (6.5%) Dandy-Walker syndrome1(3,2%)as well as face and neck absent nasal bone 6 (19.4%) cystic hygroma 3(9.7%), 7 (22.6%) had cardiac malformation complete atrioventricular canal defect (CAVC)4 (12.9%) tetralogy of Fallot 1(3.2%)Ventricular septal defect2 (6.5%), 2 (6.5%) had gastrointestinal anomaly esophageal atresia 1(3.2%) imperforate anus 1(3.2%), renal malformation polycystic kidney 2 (6.5%), and skeletal defect, spina bifida 1 (3.2% )dysplasia of the spine 1 (3.2%) while 12 (38.7%) had other types of anomaly such as Down Syndrome8 (25.8%) and anomaly in the umbilical cord 1( 3.2%) and limbs absent hand 1 (3.2%) symbrachydactyly 1 (3.2%) nanism 1( 3.2%)(Table 3). Multiple anomalies were more common than isolated malformation (71.0%% vs. 29.0% respectively).
For pregnancy outcome, of the 31 who had malformation, 10 (32.3%) aborted, 1 (3.2%) had IUFD, 9 (29.0%) delivered through NVD, and 11 (35.5%) had CS. Of the 20 who delivered by NVD or CS, 8 (40.0%) of the neonates died directly after delivery or after few days.(Table 4).
The relation between maternal characteristics and fetal malformation, of the women who consumed folic acid before pregnancy, 88.9% did not have fetal malformation and only 11.1% had malformation (p-value=0.02). Other factors such as age, consanguinity, and maternal illness were not significantly associated with fetal anomaly (Table 5).
The following are ultrasound images of some of the women included in the study.
Discussion
The major outcome of the present study was that the prevalence of fetal anomaly detected using first trimester ultrasound was 19.5%. The most common types of malformation were in the central nervous system and brain as well as face and neck (29.0%), followed by Down Syndrome (25.8%), then comes cardiac anomaly (22.6%). Of those with fetal anomaly, 10 cases had abortion, 1 case had IUFD, and 8 neonates passed away directly or within few days after delivery.
The prevalence of congenital anomalies and types vary depending on the population assessed as well as the time of diagnosis. Dulgheroff et al reported in their study conducted in Brazil that the prevalence of structural defects was 2.95% during the prenatal period and 7.24% in the postnatal period [13]. A study in India showed that 1.95% of congenital anomalies were detected in the first trimester [14]. Another study reported that the overall rate of congenital anomalies in the studied population was 2.6%. Out of them, 64.4% were detected during first trimester anomaly scan while 35.6% were detected during mid gestation scan [7]. A study carried out by Sallout et al in Saudi Arabia reported that the antenatal prevalence of major congenital anomalies was 5.2% and the birth prevalence of major congenital anomalies was 4.6% [15]. A study in Egypt mentioned that anatomical anomalies were detected in 9.4% of cases who were in their late first or early second trimester [6]. We postulate that the higher prevalence of anomalies observed in the present study may have been due to the fact that the study was conducted in a private clinic and physicians refer to that private clinic when they have anomalies cases. Additionally, other studies were conducted in medical centers that have large number of patients in comparison to the small number of patients at the clinic.
Regarding the most common types of fetal anomalies, similar to our study, Kashyap et al reported that central nervous anomalies had the highest prevalence (33%) [8]. Dulgheroff et al and Sallout et al mentioned that genitourinary tract anomalies were the most frequently diagnosed [13, 15]. Other studies found that neck and abdominal wall defects were the most common [14, 16]. Similarly, multiple anomalies were more likely to be identified than isolated malformations. Rajesh et al reported 60% multiple versus 44% single defects while Sallout et al had 66.6% multiple and 33.4% isolated anomalies [14, 15].Similar to our study multiple anomalies were more common than isolated malformation (71.0%% vs. 29.0% respectively).
Several factors influence the occurrence of fetal anomalies. One of these factors is consanguinity [13, 15]. However, in the current study, the percentage of consanguinity was similar in the malformation versus no malformation cases ; this is because most of patients are from Beirut and consanguinity rate is decreasing in urban areas . Moreover, prenatal folic acid deficiency has been correlated with neural tube defects, a common congenital anomaly [15]. A study concluded that there was a significant reverse relationship between folic acid consumption during the first trimester and the risk of developing anatomical anomalies [6]. The present study also showed that women who consumed folic acid before pregnancy had less fetal malformation Around 45% of the women in this study took folic acid preconception. This rate is higher than that reported by Dulgheroff et al (8.3%) and Fouad et al (6.8%) [6, 13] These patients have knowledge about importance of folic acid from previous pregnancy and some woman takes iron and acid folic routine. A study also found that the rate of anomalies was significantly higher among women with chronic diseases such as diabetes and hypertension [6]. However, this association was not observed in our study.
Regarding the pregnancy outcome of women with fetal malformation in this study, 32.3% had abortion, 3.2% had IUFD, and 64.5% had live births of which 40.0% experienced neonatal death. A study by Bardi et al mentioned that 56.3% of women with fetal anomaly resulted in termination of pregnancy, 6.3% in spontaneous fetal demise, and 37.5% in live births [17]. Another study reported lower rates such as 3.4% had termination of pregnancy and 0.2% had abortion in high-risk patients [7]. More live birth because more woman refuse termination of pregnancy like our study.
Detection of congenital malformation has improved in the past few years mainly due to advancement in ultrasound technology and enhancement in the skills of sonographers [7, 15]. Furthermore, several studies reported that detailed examination of fetal anatomy during the first trimester provides a comprehensive assessment of fetal anatomy and can detect a considerable percentage of major structural defects [14, 16, 18]. This might explain the increased number of malformation cases currently being diagnosed compared to the past [15]. This in turn would aid in improving the management of cases with anomaly during both the prenatal and postnatal periods [15]. Multidisciplinary teams that may include obstetricians, fetal medicine specialists, geneticists, and neonatologists would help in the diagnosis and management processes [16].
Our study has some limitations. First, the data were collected from a private clinic in Beirut and not were not multi-centered. Second, the retrospective nature of the study ,and the small sample size, and being a referral clinic make it less possible to generalize the outcomes to other populations.
Discussion
In conclusion, first trimester ultrasound is essential for early diagnosis of congenital malformation. Being equipped with advanced ultrasound machines and having experienced sonographers who dedicate enough time to perform the scan would improve the quality of the imaging and increase the accuracy of the diagnosis. This in turn would help in providing counseling to parents thereby guiding them during the antenatal and postnatal periods.
More information regarding this Article visit: OAJBGSR
https://biogenericpublishers.com/pdf/JBGSR.MS.ID.00194.pdf
https://biogenericpublishers.com/jbgsr-ms-id-00194-text/
#Pelvic ultrasound#malformations#fetal malformation#Beirut Lebanon#Kariman Ghazal#oajbgsr#jbgsr#bgsr#biogeneric publishers
0 notes
Text
How to Calculate Your Pregnancy Due Date
There are a number of different ways to calculate your due date, including:
Conception or ovulation date
Date of your last period
Measurements taken during an ultrasound
Transfer date (if you had in vitro fertilization)
Calculating Due Date
Your due date is considered to be 40 weeks (280 days) after the first day of your last menstrual period or 38 weeks (266 days) after ovulation. Even if an early ultrasound is used to determine or shift your due date, it’s still based on the basic idea of a 280-day gestational period.
Assuming you know the date of your last period, your primary care provider will use this to figure out the due date. Many midwives and obstetricians use a pregnancy wheel, which is a simple tool that quickly gives the 280th day from your last period.
There is a formula known as Naegele's rule. This is what is used for the due date calculator at the top of this page. It's also how a pregnancy wheel works. You can calculate the date yourself using Naegele's rule.
What Is Naegele's Rule?
To get your due date based on your menstrual period:
Record the date of your last period
Add one year
Add seven days
Move the date back three months
For example, if the first day of your last period was August 11, 2019, you would:
Add 1 year (making the date August 11, 2020)
Add 7 days (becomes August 18, 2020)
Move the date back 3 months (to May 18, 2020)
Your due date would be May 18, 2020.
If your fertility app gives you a different date than the one calculated by your doctor, it most likely because it was based on the ovulation date and not the date of your last period. If you ovulated earlier or later than day 14 of your cycle, this would shift your due date accordingly.
Ovulation vs. Menstruation
Your due date in relation to ovulation is considered to be more accurate than one calculated based on your last menstrual period. If you know when you ovulated, or you know your cycles are longer than average, share that information with your doctor.
The dates might be a week apart, but that week can make a big difference. For example, if you’re having a scheduled C-section, you wouldn’t want to schedule it too early. If your doctor is trying to decide whether your pregnancy has gone too far beyond your due date, you might want to wait another week before considering induction.
Using Ultrasound
An ultrasound in the first trimester of pregnancy—prior to 13 weeks—can be used to provide an estimated date of delivery or confirm a due date determined by your last period. Not every expectant mother will need one unless the date is uncertain.
A transvaginal ultrasound is usually performed between 9 weeks and 13 weeks of gestation. During the procedure, the technician will measure the fetus’s length from crown to rump. This is how they estimate how old the fetus is, and from that, provide an estimated due date.
Another method, called a biparietal diameter (BPD) ultrasound, measures the diameter of the baby's skull and may even be more accurate than the other methods.
Over 30% of pregnancies went past 41 weeks when using Naegele's rule.
Around 25% went past 41 weeks when using the crown-to-rump measurement.
Only 17% went past 41 weeks when using the biparietal diameter.
With all that said, ultrasound due dates are still not perfect. If the ultrasound due date is different from the date determined by your last period, both dates should be noted in your medical records.
If the ultrasound due date is less than seven days different from the menstrual cycle due date, your due date wouldn't change. If it is off by more than seven days, your due date may be altered.
What to Ask If Your Due Date Changes
Using IVF Due Date
If you had IVF treatment, your due date will never change. IVF due dates aren’t determined by your last period, the date of conception, or even the egg retrieval day. They are determined by embryo transfer day and the age of the embryo at the time of the transfer.
With IVF, the due date is determined by the date that the embryo implants in the uterus. As the transfer day is a fixed day relative to when the initial blood work is done, doctors are able to make more accurate calculations.
Role of Fundal Height
Your midwife or doctor may measure your fundal height at your pregnancy well-checks. The fundal height is the measurement in centimeters from your pubic bone to the top of your uterus. It should grow at a predictable rate as your pregnancy continues.
After 20 weeks, your fundal height in centimeters will typically be the same as the number of weeks you are pregnant. In other words, at 21 weeks pregnant, your fundal height should be around 21 centimeters (10 inches).
Sometimes, the fundal height won't match perfectly. Slight variations are normal, but if you are measuring much smaller or larger than expected, your primary care provider may want to investigate with another ultrasound.
While useful, the fundal height is not an accurate measurement of gestational age and would not affect the estimated due date in any way.
Why Your Due Date Is Important
Your due date is likely one of the first bits of information you’ll seek out after you find out you’re pregnant. Friends and family will want to know so they can look forward to greeting your new baby (and supporting you).
Doctors, midwives, and nurses will want to know so they can track important health milestones and make decisions about interventions and prenatal testing.
Your due date (sometimes called the estimated date of delivery) is less of a deadline and more like a time marker. Your due date indicates the 40th week since your last menstrual period or the 38th week from ovulation.
Once your due date is calculated, you're likely to give birth within a four-week period that surrounds your due date. In other words, sometime during the two weeks prior to and two weeks after your assigned due date, you'll likely meet your baby.
Around 70 out of every 100 women will have their baby within 10 days of their due date. Assuming there are no complications, others will deliver either a little earlier or a little later than that.
The due date is valuable for many reasons, including the preparation of your home and family for the new arrival. There are also several other reasons it's helpful to know your due date.
Tracking Fetal Development
Your healthcare provider will consider which week of pregnancy you are in when determining if the pregnancy and fetal development are on track. Your doctor will look for several indicators, such as:
When a heartbeat should appear on a transvaginal ultrasound
When a heart tone should be detectable with a handheld Doppler
When the baby should start moving
What the fundal height should be
Scheduling Tests
Some prenatal tests need to be conducted during a particular time frame. For example, an ultrasound to determine viability shouldn’t be done before six weeks.
An AFP blood test—used as a screening for birth defects—should ideally occur between week 16 and week 18. An ultrasound to determine whether twins are sharing a placenta or amniotic sac needs to occur between week 11 and week 14 of the pregnancy.
Schedule of Prenatal Tests
Determining If Labor Is Premature
Babies who are born too early are at risk for numerous health problems. There are steps we can take to slow or halt preterm labor. With that said, there are also risks to the medications used to stop preterm labor, both to the mother and the baby.
You and your doctor have to decide together when the risks of allowing labor to continue to outweigh the risks of intervention. This is partially determined by knowing which week of pregnancy you are in.
There are also risks to the baby and mother if a pregnancy goes on for too long. Post-term pregnancy is when birth does not occur by week 42 (14 days after the estimated date of delivery). If this happens, your midwife or doctor may decide to induce labor.
Average Length of Pregnancy
While 40 weeks is the average, it’s not unusual to deliver your baby earlier or later. In the past, 37 weeks was considered to be a full-term pregnancy. This definition carried implications on as two when it would be safe to induce labor or schedule a cesarean section.
However, we now know that being born at 37 weeks can increase health risks. It’s not nearly as risky as being born before 37 weeks, but it’s not ideal either.
In response, the American College of Obstetricians and Gynecologists (ACOG) has created new definitions to describe the timing of labor:
ACOG Definition of Pregnancy
Early-term: 37 weeks through 38 weeks and six days
Full-term: 39 weeks through 40 weeks and six days
Late-term: 41 weeks through 41 weeks and six days
Post-term: any pregnancy that goes beyond 42 weeks
Sometimes, when talking about twins or triplets, you will hear people say things like, “Twins are full-term at 37 weeks.” But this isn’t truly accurate. All pregnancies—including twins, triplets, or more—aren’t truly full-term until they reach 39 weeks.
While you might be at greater risk of earlier labor with twins, that doesn't affect how the timing of labor would be classified.
Factors Affecting Due Date
With so much focus and excitement over an assigned day, you’d think it’d be an accurate number—but it’s not always the case. The simple truth is that only 5 out of 100 women will deliver their babies on their actual due date.
Still, determining which week of pregnancy you’re in is crucial to receiving good prenatal care and planning for your upcoming life change.
The majority of babies are born over a 35-day span, with birth occurring anywhere from about 37.5 weeks to 42.5 weeks. Due dates also not deadlines. You could have your baby a week later than your due date and still be considered on time.
There are many factors that can influence your due date.
Each pregnant person has their own predetermined schedule. Many people will tell you that their pregnancies were all about the same length. If you had two kids, each delivered around 41 weeks, your third kid is likely to arrive around 41 weeks.
People pregnant for the first time tend to go into labor later. You’re more likely to go a few days past your due date with your first baby.
Some people are at risk of preterm labor. About one in 10 pregnancies end with premature delivery. Maternal risk factors for prematurity babies include having a previous preterm birth, vaginal bleeding during pregnancy, diabetes, high blood pressure, smoking, and even periodontal disease.
Signs of Preterm Labor
Your due date helps you and your healthcare providers track your pregnancy and plan for labor and delivery. It’s an important date, but it’s not a deadline. You may have your baby before or after your due date—and either can be OK.
If your due date comes and goes, you might start to wonder if you’re going to be pregnant forever. Don’t worry. While those last days can feel like an eternity, your baby will arrive when it’s ready and not a minute earlier.
To be sure the baby isn’t brought into the world too soon, ACOG recommends that induction of labor not be considered until week 41 begins (or seven days past your official due date).
5 Reasons to Avoid the Induction of Labor
0 notes
Text
Intel and Samsung detail AI-powered fetal ultrasound tools
Intel and Samsung Medison, a division of Samsung developing ultrasound devices, today detailed AI-powered, FDA-cleared ultrasound solutions — BioAssist and LaborAssist — that automate fetal health measurements. The companies claim BioAssist and LaborAssist can deliver a better understanding of a patient’s birthing progress by automatically taking metrics like fetal angle of progression during labor.
According to the World Health Organization, about 295,000 women died during pregnancy and following childbirth in 2017. Research from the Perinatal Institute shows that tracking fetal growth can help prevent stillbirths, as it allows physicians to recognize growth restrictions. But there’s little standardization around fetal measurement because doctors often disagree on where to start.
Intel and Samsung Medison say BioAssist and LaborAssist perform measurements in as little as 85 microseconds, courtesy of Intel’s machine learning toolkit OpenVino. BioAssist and LaborAssist estimate the baby’s head direction and fetal position, suggesting the right mode of delivery and potentially reducing the number of unnecessary cesarean sections. Using machine vision algorithms to analyze ultrasounds, the apps are ostensibly capable of measuring head angle within 8 degrees with 95% confidence. (That metric comes from an internal Samsung test on Intel hardware.)
Algorithms that ship with BioAssist and LaborAssist also guide caliper placement around the fetus. In addition to the biparietal diameter — one of the basic biometric parameters used to assess fetal size — they can measure femur length, head circumference, and abdominal circumference. Moreover, they’re able to segment outlines for the head, taking measurements in an average of 1.5 seconds.
Clinicians can play a demo animation for patients based on the measurements to show labor progress. Other visualization tools reveal a full labor history, including images and measurements in a 3×2 layout.
Intel and Samsung Medison say BioAssist and LaborAssist are already in use in 80 countries, including the U.S., Italy, France, Brazil, Russia, and South Korea. Going forward, the companies plan to collaborate on emerging ultrasound technologies, like nerve tracking.
AI is increasingly being applied to ultrasound scans, in part because the high-frequency waves are able to penetrate skin and soft tissue structures, making them ideal for noninvasive imaging of the gallbladder, kidney, pancreas, liver diseases, and blood clots. In August 2018, Dia Imaging Analysis raised $5 million for machine learning tools that analyze ultrasound scans. In September 2018, Butterfly raised $250 million to further develop its semiautomated full-body ultrasound technology. And last month, Exo raised $40 million to bring an AI-powered cloud-based workflow to ultrasound scanners.
0 notes