#because obviously the first thing i did was open up macrostrat to see what the geology was like
Explore tagged Tumblr posts
Text
Geology and The Terror
As a geologist who is incapable of turning off their geology brain even while watching shows for fun, one of the things that baffles me a bit about The Terror is why they continuously refer to the landscape as shale when both King William Island and the filming location in Pag, Croatia are dominated by limestone. Given the desolation of the landscape, the geology is rather at the forefront of many scenes so it was fun to try and parse it out as I watched.
King William Island, Nunavut, Canada
According to the official map of the bedrock of the region as published by the Canadian government (Harrison et al., 2015), the entirety of King William Island is mapped as dolostone, dolomitic limestone, and limestone with only minor components of shale, sandstone, conglomerate, and breccia. This is a shelf marine deposit dating back to the Late Cambrian, so this is very old sedimentary rock but younger than most of the surrounding hard rock that composes various parts of the Canadian shield. Notably, the pink units mapped on the Boothia Peninsula are Paleoproterozoic in age (2.5-1.6 billion years old), potentially up to 2 billion years older than the limestones of King William Island.

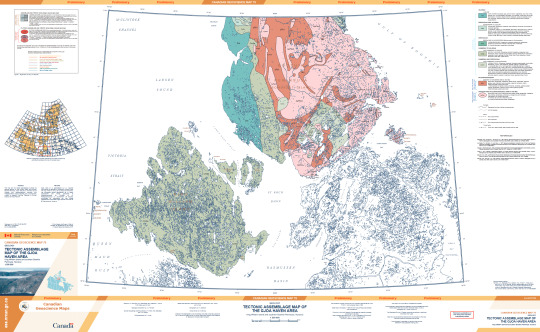
(This is an absolutely massive .pdf file with some scaled features so I would recommend viewing via the official publication to actually read anything or see fine details: publications.gc.ca/pub?id=9.557274&sl=0)
Notably, this map was published in 2015, 8 years after the novel was written. However, according to the bibliography for the map (which can be accessed via the previous link) a preliminary geologic map has existed for the area since at least 1967, though I was unable to track this publication down online. The novel was clearly thoroughly researched and Dan Simmons could have easily accessed this publication and others through multiple institutions.
The surficial geology of King William Island has also been mapped, and is predominantly glacial, as one would expect given it's location. For those unfamiliar with glacial geology processes, this is basically saying that the bedrock is buried under a bunch of glacial deposits. Glacial till is composed of rocks and sediments plucked from the bedrock and ground up. This is why the surface of the island is not one big rock, but a bunch of smaller pieces. Interestingly, the material on the southern part of the island is sandier because it contains more material derived from the Canadian Shield further south. If you're interested in glacial geology, I highly recommend zooming around a bit on Google Earth because the features here are GORGEOUS.

(This map is absolutely massive and the lines scale with zoom so it's hard to see at this resolution, access it here: publications.gc.ca/pub?id=9.834073&sl=0)
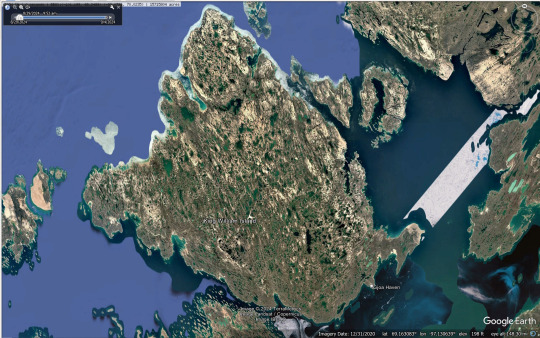
(Google Earth Pro, satellite imagery from 2020)
According to the surface geology map and Google Earth, the actual landscape of King William Island is much more water logged than it appears in the show. It's not entirely impossible that there has been some geomorphological change since 1848, but most of the features mapped would have been formed during the last ice age and as the glaciers melted and not more recently. This would have been handy for the men of the Franklin Expedition because each of these pools is filled with freshwater.
Pag, Croatia
Tracking down a geologic map of Croatia was somewhat challenging as I don't speak Croatian. I was able to find a map of the whole country, and while it's all in Croatian the symbol for the geologic time periods is universal so time periods can be correlated. This shows that the units that make up Pag are Cretaceous and Paleocene-Eocene in age.
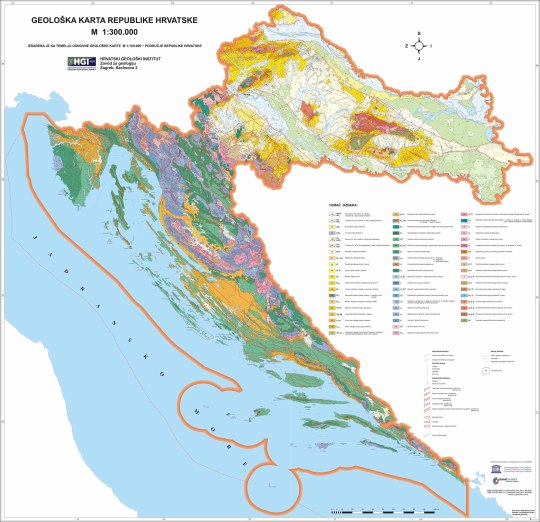
(Map accessed here: https://www.hgi-cgs.hr/en/geoloska-karta-republike-hrvatske-1300-000/)
I was able to find a .pdf (access here: http://kig.kartografija.hr/index.php/kig/article/view/158/274) that had a bit more information on the map above but at a lower resolution. This states that the Cretaceous units are dominantly carbonates from the Adriatic sea and the Eocene units are also carbonates. This makes sense as both the Cretaceous and Paleocene-Eocene boundary/PETM are times of increased global temperature correlated with increases in global sea level.
As always, the best geology website out there, Macrostrat, also came through on the unit lithologies. I was unable to access the source listed on Macrostrat, but both the Cretaceous (green) and Paleocene-Eocene units (orange) are listed as limestone.
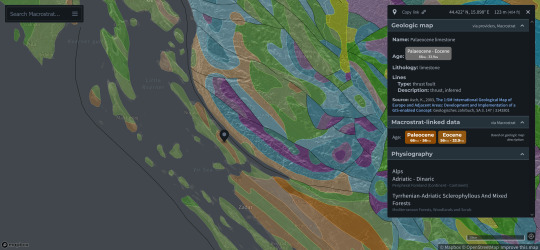
(Source: https://macrostrat.org/map/#x=16&y=23&z=2)
One of the best views that we get of the geology on Pag is the last scene with Bridgens in episode 9. During the zoom out of this scene we get a really nice view of the bedrock and debris covering it.

Given all of this, I'm really not sure where the landscape description as shale came from. If there is historical precedence for calling the rocks on the island shale, let me know! I have read a few books but none of the primary sources from the expeditions to this region, so if it comes from that I wouldn't be surprised.
Overall though, I have to say that the filming location was well chosen given the similarities it holds to the geology of King William Island.
#the terror#i have no idea whether this is of interest to anybody else#but i haven't been able to stop thinking about it since i started the show#because obviously the first thing i did was open up macrostrat to see what the geology was like#geology#peter posts#fr though the scene with bridgens is top tier in terms of getting a good view of the geology#it only took me three watches of the show to cave and make a post about it#franklin expedition
133 notes
·
View notes