#automation actuators
Explore tagged Tumblr posts
Text

Powerful Motion with Rotary Actuators!
A rotary actuator is a pneumatic cylinder that provides smooth, turning movement. It delivers strong torque in a small size and works through a defined angle, making it perfect for many applications.
Upgrade your system with rotary actuators for better performance!
👇 Contact Us for More Details👇
📞 +91 9787878732
🌐 https://www.nayagi.in/iminorgren/
#RotaryActuator#PneumaticPower#IndustrialTech#Automation#norgren#imi#iminorgren#business#industries#Actuators#industrialsupplier#industrialproducts#supplychainactivities#machineries#maintenanceservices#India#bengaluru#NayagiIndustrialTechnologies#industrialequipmentsupplier
2 notes
·
View notes
Text
Discover Tecnik Valves' multiple spring pneumatic actuators—compact, field-reversible, and engineered for high thrust and precise control in throttling, modulating, and on-off applications across industrial processes.
#Multiple spring actuators#pneumatic actuators#high-thrust actuators#Tecnik Valves#linear valve actuators#industrial valve automation#field-reversible actuators#diaphragm actuators#control valve actuators#compact actuator design
0 notes
Text
Why Electric Actuators Are Now the Core of Robotic Automation❓
From manufacturing lines to service robots, automation is everywhere—and at the heart of it all lies one powerful component: the electric actuator.
An electric actuator converts electrical energy into precise motion using a motor and a reducer. It's the key to enabling robots to move smoothly, lift accurately, and repeat tasks reliably without human intervention.
As robots get smaller and more advanced, actuators must follow suit. Bon Systems’ BCSA series answers this demand with its slim yet high-torque design, using in-house developed cycloidal gear technology. This structure not only maximizes torque but also minimizes space, allowing for more innovative and compact robot designs.
Whether it’s for an autonomous mobile robot in a warehouse or a collaborative arm in manufacturing, reliable actuators make the difference between a demo and real-world performance.
BonSystems offers custom actuator design, scalable production, and engineering support to bring your automation to life.
📌Explore our solutions or start a project consultation at our website.
0 notes
Text
The real house wife of Eureka.
#this is a joke about Sarah being a house and basically a wife#idk its late#S.A.R.A.H#Self Actuated Residential Automated Habitat (Sarah)#eureka tv show#a town called eureka#eureka
1 note
·
View note
Text
6 Types of Pneumatic Actuated Ball Valves You Should Know About
A pneumatic actuated ball valve is a reliable and efficient solution for controlling fluid and gas flow in industrial applications. These valves use compressed air to operate, making them ideal for automation in various industries, from manufacturing to water treatment. If you're looking for the right automated ball valve, here are six types you should know about.
1. Single-Acting Pneumatic Actuated Ball Valve
Single-acting (or spring-return) pneumatic actuated ball valves use compressed air to open or close and a spring mechanism to return them to their default position when the air supply is removed. They are energy-efficient and provide a fail-safe option in case of air supply failure.
2. Double-Acting Pneumatic Actuated Ball Valve
Unlike single-acting valves, double-acting models require compressed air for both opening and closing. These valves provide more precise control and are commonly used in high-performance automation systems. Many industries in Saint Clair rely on pneumatic actuated ball valve suppliers in Saint Clair to source high-quality double-acting valves for their applications.
3. V-Port Pneumatic Actuated Ball Valve
V-port valves have a uniquely shaped ball that allows for more precise flow control. These are often used in applications requiring throttling rather than simple on/off operation. If you're sourcing an automated ball valve in suppliers in Saint Clair, consider a V-port model for better control in process automation.
4. Three-Way Pneumatic Actuated Ball Valve
Three-way valves allow fluid to be diverted, mixed, or shut off in multiple directions. These are useful in industries that require frequent switching between different pipelines. Many pneumatic actuated ball valve suppliers in Saint Clair offer three-way configurations for more complex automation needs.
5. Stainless Steel Pneumatic Actuated Ball Valve
For industries handling corrosive fluids or extreme temperatures, stainless steel valves provide durability and resistance to chemical exposure. These valves are widely used in chemical processing plants and food industries.
6. High-Pressure Pneumatic Actuated Ball Valve
Designed for handling high-pressure systems, these valves ensure safety and reliability in industries such as oil and gas. If you're searching for a pneumatic actuated ball valve in Saint Clair, high-pressure options are available for demanding applications.
Conclusion
Selecting the right automated ball valve depends on your specific industry needs. Whether you require precision control, durability, or high-pressure resistance, understanding these six types will help you make an informed decision. If you're looking for reliable pneumatic actuated ball valve suppliers in Saint Clair, be sure to choose a trusted provider for the best quality and performance.

#pneumatic actuated ball valve#automated ball valve#automated ball valve in suppliers in saint clair#pneumatic actuated ball valve in saint clair#pneumatic actuated ball valve suppliers in saint clair#missouri#usa
0 notes
Text
Actuator Valve: Enhancing Precision and Efficiency in Industrial Applications
In the fast-paced world of industrial operations, efficient control over fluid and gas flow is paramount. Actuator valves play a critical role in ensuring this control with precision, reliability, and automation. Whether you’re managing complex chemical processes, oil and gas operations, or manufacturing systems, actuator valves offer a streamlined solution that improves productivity while reducing manual intervention.
What is an Actuator Valve?
An actuator valve is a type of valve used to control the flow of a liquid or gas in a system, operated by an external actuator. Unlike traditional valves that require manual operation, actuator valves rely on pneumatic, hydraulic, or electric mechanisms to open, close, or adjust the valve position. This automation makes them an ideal choice for systems that require consistent and accurate regulation without the need for direct human input.
Types of Actuator Valves
There are several types of actuator valves, each designed for specific industrial requirements:
Pneumatic Actuator Valve: Powered by compressed air, these valves are commonly used in applications requiring fast response times and cost-effective operation.
Electric Actuator Valve: Using electric motors to operate, these valves are ideal for applications where energy efficiency is critical. They offer precise control and are often used in high-precision industries like manufacturing and automation.
Hydraulic Actuator Valve: Hydraulic-powered actuator valves are known for their strength and ability to operate under high-pressure systems, making them suitable for heavy-duty applications.

Key Benefits of Using Actuator Valves
Improved Efficiency: Automation of valve operations allows for better process control, minimizing errors and downtime. This leads to enhanced efficiency across your systems.
Precision and Consistency: Actuator valves are designed for accurate control, ensuring that flow rates are precisely regulated, which is crucial in industries where minor variations can lead to significant disruptions.
Safety: By automating the control process, actuator valves reduce the need for manual intervention in potentially hazardous environments, enhancing safety for workers.
Durability: Built from high-grade materials, actuator valves are designed to withstand extreme environments, from high pressure to corrosive conditions, ensuring long-lasting performance.
Applications of Actuator Valves
Actuator valves are used across a variety of industries, including:
Oil and Gas: In the oil and gas sector, precise flow control is critical to the success of operations. Actuator valves help regulate the flow of gas and liquids through pipelines, ensuring smooth and safe operation.
Chemical Processing: In chemical plants, where accurate control of different fluids is necessary for reactions, actuator valves provide reliability and safety.
Manufacturing: Automation is the backbone of manufacturing, and actuator valves help in maintaining the precision and consistency needed in automated processes.
Why Choose Prabha Electronics' Actuator Valves?
At Prabha Electronics, we are committed to providing high-quality actuator valves that meet the unique demands of your industry. Our valves are engineered for durability, precision, and safety, ensuring reliable performance in even the most demanding applications. Whether you need pneumatic, electric, or hydraulic actuators, our extensive range is designed to seamlessly integrate with your systems, offering unmatched efficiency.
Conclusion
In today’s industrial landscape, actuator valves are more than just components; they are vital to the smooth functioning of critical systems. By choosing Prabha Electronics' actuator valves, you invest in quality, performance, and reliability. Explore our range today and take the first step toward optimizing your flow control systems for enhanced productivity and safety.
#Actuator valve#industrial actuator valve#flow control valve#automation valve#pneumatic actuator valve#electric actuator valve#fluid control valve#industrial valves
0 notes
Text
#automation#robotics#ckdgripper#fanucrobots#seimitsu#Gripper#exporters#distributors#automationsolutions#manufacturers#AutomationTechnology#linearmotion#actuator#actuatortechnology#motorlessactuators#suppliers#dealers#channelpartners
0 notes
Text
The Power of Rotation: A Comprehensive Look at Rotary Actuators
Transform Pneumatic, Hydraulic, or Electric Energy to Mechanical Rotation
In the realm of industrial automation, precise control over movement is paramount. Rotary actuators play a vital role in achieving this control, converting various forms of energy into rotary motion to power a wide range of applications. From the delicate movements of robotic arms to the powerful operation of valves and gates, rotary actuators offer a versatile and efficient solution for driving rotational tasks. This article delves into the world of rotary actuators, exploring their types, working principles, functionalities, and their diverse applications across various industries.
Understanding Rotary Actuators:
At their core, rotary actuators are mechanical devices that translate energy into rotary motion, or torque, around a specific axis. This energy source can be electric, pneumatic, hydraulic, or even manual. By converting this energy, rotary actuators enable precise control of angular displacement and rotational force, making them ideal for applications requiring positioning, opening, closing, or rotating various mechanisms.

Types of Rotary Actuators:
The diverse world of rotary actuators encompasses various types, each catering to specific needs and applications:
Electric Rotary Actuators: Powered by electric motors, these actuators offer precise control and are well-suited for automated applications. They come in various configurations, including stepper motors, servo motors, and DC gear motors, each offering distinct torque and speed characteristics.
Pneumatic Rotary Actuators: Utilizing compressed air as the energy source, these actuators are known for their speed and force output. They are commonly used in applications requiring high-speed actuation or limited space availability. Rack and pinion and vane types are two common configurations of pneumatic rotary actuators.
Hydraulic Rotary Actuators: These actuators rely on hydraulic fluid for power, offering exceptional force and torque capabilities. They are ideal for heavy-duty applications requiring high power output, such as operating large valves or manipulating massive machinery components.
Working Principles of Rotary Actuators:
The specific working principle of a rotary actuator depends on its type. Here's a simplified breakdown of the primary types:
Electric Rotary Actuators: An electric motor converts electrical energy into rotational motion of the motor shaft. This rotation can be geared down or up to achieve the desired output speed and torque. In stepper motors, the rotation occurs in discrete steps, offering precise positioning control. Servo motors provide continuous rotation with precise control over speed and position based on feedback signals.
Pneumatic Rotary Actuators: Compressed air enters the actuator body, pushing against a piston or vane, causing it to rotate. The direction of rotation is controlled by valves that direct the compressed air flow. Rack and pinion actuators convert the linear motion of the piston or vane into rotary motion using a gear rack and pinion gear. Vane actuators utilize the direct rotation of the vane within the actuator body.
Hydraulic Rotary Actuators: Hydraulic fluid, pressurized by a pump, enters the actuator body and exerts force on a piston or vane. The resulting linear motion is converted into rotary motion through a gear mechanism similar to pneumatic rotary actuators.
Functionalities of Rotary Actuators:
Rotary actuators perform a wide range of functions in various applications. Some key functionalities include:
Positioning: Rotary actuators can precisely position mechanical components or robotic arms to specific angles.
Opening and Closing: They can be used to open and close valves, gates, dampers, and other mechanisms requiring rotational movement.
Mixing and Stirring: Rotary actuators can power mixing blades or stirrers in various industrial processes.
Indexing and Material Handling: They can be used for precise indexing of materials in automated production lines or material handling equipment.
Clamping and Gripping: Rotary actuators can be used to clamp or grip objects in robotic applications or assembly lines.
Selection Considerations for Rotary Actuators:
Choosing the right rotary actuator for your application requires careful consideration of several factors:
Torque and Speed Requirements: The actuator's torque output and speed capabilities need to match the application's specific demands.
Power Source: Electric, pneumatic, or hydraulic power sources should be chosen based on available resources and desired control characteristics.
Duty Cycle: The frequency and duration of operation for the actuator must be considered to ensure proper sizing and prevent overheating.
Accuracy and Repeatability: The level of precision required for positioning or control should be factored in when selecting the actuator type.
Environmental Conditions: The operating environment, including temperature, humidity, and potential exposure to dust or liquids, should be considered to ensure proper material selection and protection for the actuator.
Applications of Rotary Actuators (Continued):
Building upon the previous section, here's a detailed look at some key industry applications of rotary actuators:
Oil & Gas: Rotary actuators are crucial in the oil & gas industry for:
Valve operation: Opening and closing valves for flow control in pipelines, refining processes, and wellheads.
Actuating blowout preventers (BOPs): Ensuring safety by closing wellbores in case of emergencies.
Positioning drilling equipment: Providing precise control over drilling heads and other downhole tools.
Power Generation: Rotary actuators are used in power plants for:
Valve actuation: Regulating fluid flow in cooling systems, boiler operations, and steam turbines.
Damper control: Adjusting air intake and exhaust dampers for combustion efficiency.
Positioning solar tracker systems: Optimizing the angle of solar panels to maximize sun exposure.
Food & Beverage: Rotary actuators contribute to automation in food processing by:
Operating valves for ingredient mixing, filling lines, and sterilization processes.
Positioning robotic arms for food handling, packaging, and palletizing.
Controlling conveyor belts for product movement within the production line.
Automotive Industry: Rotary actuators play a role in:
Robotic welding and painting applications: Precise movement of robotic arms for welding and painting car bodies.
Assembly line automation: Positioning and manipulation of components during vehicle assembly.
Climate control systems: Adjusting air flow dampers for heating, ventilation, and air conditioning within vehicles.
Aerospace & Defense: Rotary actuators find application in:
Aircraft control surfaces: Moving rudders, ailerons, and flaps for aircraft maneuverability.
Landing gear deployment and retraction: Precise actuation of landing gear mechanisms.
Radar positioning: Controlling the movement of radar antennae for target detection and tracking.
Construction: Rotary actuators contribute to automation in construction by:
Operating valves in concrete mixing trucks and other heavy machinery.
Positioning robotic arms for automated welding and material handling.
Controlling the movement of construction equipment attachments like excavator buckets and bulldozer blades.
Beyond these specific examples, rotary actuators are present in countless other applications across diverse industries. Their versatility, reliability, and ability to convert various energy sources into precise rotational motion make them a cornerstone of industrial automation.
Freture Techno: Your Partner in Rotary Actuator Solutions
Freture Techno Pvt. Ltd., a leading manufacturer of rotary actuators in Mumbai, India, offers a comprehensive range of high-quality electric, pneumatic, and hydraulic rotary actuators. With a commitment to innovation and engineering excellence, Freture Techno caters to diverse industry needs. Their team of experts can assist you in selecting the optimal rotary actuator for your specific application, ensuring optimal performance, reliability, and efficiency. Visit their website today to explore their product portfolio and discover how Freture Techno can be your trusted partner in rotary actuator solutions.
#valves#automation#Pneumatic#Hydraulic#Electric#Rotary Actuators#Freture Techno#Manufacturer#Mumbai#India
0 notes
Text
The Global Robotics and Automation Actuators Market Size was valued at USD 18.7 billion in 2022 and is estimated to reach USD 35.8 billion by 2027, growing at a CAGR of 13.9% during the forecast period. Industries across all the regions are expected to adopt robotics and automation actuators that have simple designs, are easy to operate, and are cost-effective.
Driver: Ongoing technological advancements in Robotics and automation actuators
The demand for improved performance Robotics and automation actuators for use in various industries has led to the development of new and advanced actuators such as electrical actuators, compact pneumatic actuators, and explosion- proof actuators. Electrical actuators are the most advanced actuators in terms of technology. They are increasingly used in the mining, automation, aerospace & defense, and chemical industries as they are silent, clean, non-toxic, and energy competent. These actuators are more efficient than pneumatic and hydraulic actuators. Electrical actuators can be integrated with critical systems using data bus communication. They offer instant feedback of movements of end effectors and provide accurate variable control over motor speed acceleration and velocity. They are also easy to install. Electrical actuators have a long shelf life and require low maintenance, leading to low total functional costs as compared to other actuators.
Moreover, several other types of actuators, such as mini-electrical actuators, digital linear actuators, and idle speed controllers, have also been developed and introduced in the market. Thus, continuous technological advancements in actuators are expected to lead to their increased application in various industries, thereby fueling their demand across the globe. This increased demand for different types of actuators is expected to contribute to the growth of the Robotics and Automation Actuators Industry during the forecast period.
#Robotics and Automation Actuators#Robotics and Automation Actuators Market#Robotics and Automation Actuators Industry#Global Robotics and Automation Actuators Market#Robotics and Automation Actuators Market Companies#Robotics and Automation Actuators Market Size#Robotics and Automation Actuators Market Share#Robotics and Automation Actuators Market Growth#Robotics and Automation Actuators Market Statistics
0 notes
Text
The Silent Guardians: Unveiling the Role of Valve Automation in Modern Industry

The intricate network of pipes that snake through industrial facilities plays a vital role in keeping processes running smoothly. But the true unsung heroes of this network are the industrial valves – the silent guardians that control the flow of fluids and gases. Traditionally, these valves were operated manually, requiring constant human intervention. However, with advancements in technology, industrial valve automation has emerged as a game-changer, transforming the way these guardians operate and unlocking a multitude of benefits for modern industry.
Industrial Valves: The Backbone of Process Control
Industrial valves come in various types, each designed for a specific function. From regulating pressure and flow rates to completely isolating sections of piping, valves ensure the smooth and efficient operation of various processes. However, manual operation can be time-consuming, labor-intensive, and prone to human error.
Valve Automation: A Symphony of Efficiency and Control
Valve automation replaces manual operation with a combination of actuators and control systems. Actuators, powered by sources like compressed air, electricity, or hydraulics, provide the physical force to open, close, or adjust the position of the valve. Control systems, ranging from simple timers to sophisticated computer-based systems, provide the brains of the operation, sending signals to the actuators based on pre-programmed parameters or real-time process data.
The Symphony's Benefits: How Valve Automation Enhances Industry
The integration of valve automation offers a multitude of advantages:
Enhanced Process Control: Automated valves ensure precise and consistent control over flow rates and pressure, leading to improved product quality and process efficiency.
Improved Safety: Automated systems can react faster to process deviations or emergencies, minimizing safety risks associated with manual intervention.
Reduced Operational Costs: Valve automation minimizes labor requirements for valve operation and allows for remote monitoring, leading to reduced manpower needs and improved overall operational efficiency.
Optimized Production: Automated valves enable faster response times and precise control, leading to optimized production cycles and increased output.
Data-Driven Decision Making: Advanced control systems can collect and analyze data from automated valves, providing valuable insights for process optimization and predictive maintenance.
The Future of Valve Automation: A Glimpse into a Smarter Industrial Landscape
The future of valve automation is brimming with possibilities. The integration of smart technologies like sensors and communication capabilities is paving the way for "smart" valve actuators. These actuators provide real-time feedback on valve position, performance parameters, and potential issues, enabling predictive maintenance and remote monitoring within the framework of the Industrial Internet of Things (IIoT).
Freture Techno: Your Partner in Industrial Valve Automation
Freture Techno, a leading manufacturer of industrial valves and automation solutions in Mumbai, India, understands the critical role of valve automation in modern industry. They offer a comprehensive range of high-quality industrial valves, actuators, and control systems to cater to diverse industrial needs. Their commitment to innovation ensures that their solutions are reliable, efficient, and integrate seamlessly with modern automation technologies.
Embrace the Silent Guardians of Efficiency:
By partnering with Freture Techno, you can leverage the power of valve automation to unlock a new era of process control, safety, and efficiency in your industrial operations. Consider Freture Techno as your trusted partner for all your industrial valve automation needs, and experience the silent symphony of enhanced performance in your industry.
0 notes
Text
🔧 Motor Actuators: The Unsung Heroes of Automation
Automation is all around us, from factory floors to delivery robots and even in hospitals. But what makes these systems move with precision and reliability? The answer lies in motor actuators, the hidden force behind automation.
At Bon Systems, we specialize in high-torque, slim actuators designed to enhance efficiency across industries. Whether it’s industrial robotics, logistics automation, or next-gen service robots, our technology is pushing the boundaries of innovation.
Want to know how motor actuators power the future? Dive into the details!
0 notes
Text
Unlocking Precision and Power: A Guide to Hydraulic Servo Actuators
Introduction: In the realm of automation and motion control, hydraulic servo actuators reign supreme for their unmatched blend of raw power and exceptional precision. These marvels of engineering combine the potent force of hydraulics with the meticulous control of electronic systems. This comprehensive guide delves into the world of hydraulic servo actuators, exploring their inner workings,…
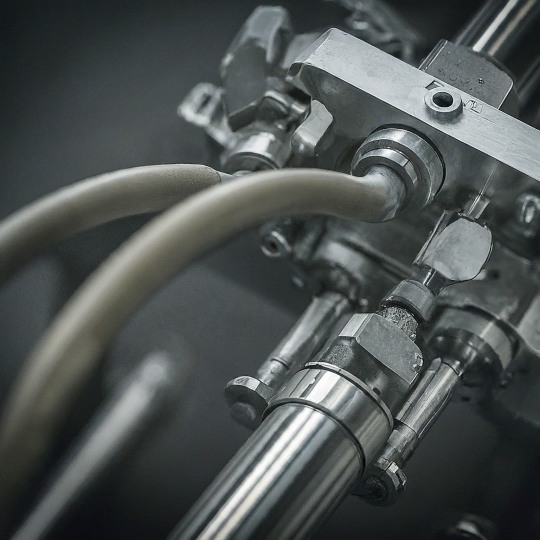
View On WordPress
#Electrohydraulic Actuators#Feedback Mechanisms#Flight Control Systems#High Force Applications#Hydraulic servo actuators#Industrial automation#Linear Actuators#Motion Control Systems#Proportional Valves#Robotics#Rotary Actuators
0 notes
Text
#pneumatic actuated ball valve#automated ball valve#pneumatic actuated ball valve suppliers in saint clair#pneumatic actuated ball valve in saint clair#automated ball valve in suppliers in saint clair#missouri#usa
0 notes
Text
Actuator Valves in Modern Gas Control Systems
Actuator valves are crucial components in various industrial and commercial applications, offering precision, safety, and efficiency in gas control systems. Whether in heating, ventilation, or automated gas distribution, actuator valves provide the necessary automation that enhances operational efficiency and safety. In this blog, we delve into the key features, benefits, and applications of actuator valves and why choosing a high-quality valve like the one from Prabha Electronics can make a significant difference.
What is an Actuator Valve?
An actuator valve is an automated control device that regulates the flow of gases or fluids through a system. It combines a valve with an actuator that uses electric, hydraulic, or pneumatic power to move the valve to the desired position. This automation eliminates manual intervention, ensuring consistent and precise control, which is especially important in complex or hazardous environments.

Key Features of Actuator Valves
Precision Control: Actuator valves provide accurate flow control, crucial in applications requiring fine-tuning of gas pressure or volume.
Durability and Reliability: Built with robust materials, these valves are designed to withstand harsh environments, including high temperatures, corrosive substances, and continuous operation.
Safety: Automation reduces the risk of human error, enhancing overall safety by ensuring valves operate within set parameters.
Ease of Integration: These valves are compatible with various control systems, making them easy to integrate into existing setups without extensive modifications.
Energy Efficiency: Actuator valves help reduce energy consumption by optimizing gas flow, making systems more sustainable and cost-effective.
Applications of Actuator Valves
Actuator valves find applications in various industries, including:
Oil and Gas: Ensuring precise flow control in pipelines and gas distribution networks.
HVAC Systems: Regulating airflow in heating, ventilation, and air conditioning systems to maintain optimal indoor conditions.
Manufacturing: Used in automated production lines to control the flow of gases essential for various processes.
Water Treatment: Controlling the flow of chemicals and gases in water and wastewater treatment plants.
Why Choose Prabha Electronics’ Actuator Valve?
Prabha Electronics offers a high-performance actuator valve designed to meet the demands of modern industrial applications. Our valves are engineered for durability, reliability, and precise control, ensuring your systems operate at their best. Here’s why our actuator valves stand out:
Superior Build Quality: Made with high-grade materials to resist corrosion and wear, ensuring a long service life.
Advanced Engineering: Our valves are designed to deliver smooth operation, even under challenging conditions.
Cost-Effective Solutions: We provide value without compromising on quality, making our actuator valves a wise investment for any gas control system.
Conclusion
Choosing the right actuator valve is essential for maintaining efficiency, safety, and performance in any gas control system. Prabha Electronics’ actuator valves offer the precision and reliability needed for industrial and commercial applications, ensuring your operations run smoothly and safely. Invest in quality, and experience the difference that our advanced actuator valves can make in your system.
#Actuator Valve#Gas Control Valve#Industrial Actuator Valve#Automation Valve#Precision Gas Control#Gas Flow Valve
0 notes