#and limited to 4 times on a trial basis.
Explore tagged Tumblr posts
Text
Day 11

Liber Libræ
0. Learn first — Oh thou who aspirest unto our ancient Order! — that Equilibrium is the basis of the Work. If thou thyself hast not a sure foundation, whereon wilt thou stand to direct the forces of Nature?
1. Know then, that as man is born into this world amidst the Darkness of Matter, and the strife of contending forces; so must his first endeavour be to seek the Light through their reconciliation.
2. Thou then, who hast trials and troubles, rejoice because of them, for in them is Strength, and by their means is a pathway opened unto that Light.
3. How should it be otherwise, O man, whose life is but a day in Eternity, a drop in the Ocean of time; how, were thy trials not many, couldst thou purge thy soul from the dross of earth?
Is it but now that the Higher Life is beset with dangers and difficulties; hath it not ever been so with the Sages and Hierophants of the past? They have been persecuted and reviled, they have been tormented of men; yet through this also has their Glory increased.
4. Rejoice therefore, O Initiate, for the greater thy trial the greater thy Triumph. When men shall revile thee, and speak against thee falsely, hath not the Master said, “Blessed art thou!”?
5. Yet, oh aspirant, let thy victories bring thee not Vanity, for with increase of Knowledge should come increase of Wisdom. He who knoweth little, thinketh he knoweth much; but he who knoweth much hath learned his own ignorance. Seest thou a man wise in his own conceit? There is more hope of a fool, than of him.
6. Be not hasty to condemn others; how knowest thou that in their place, thou couldest have resisted the temptation? And even were it so, why shouldst thou despise one who is weaker than thyself?
7. Thou therefore who desirest Magical Gifts, be sure that thy soul is firm and steadfast; for it is by flattering thy weaknesses that the Weak Ones will gain power over thee. Humble thyself before thy Self, yet fear neither man nor spirit. Fear is failure, and the forerunner of failure: and courage is the beginning of virtue.
8. Therefore fear not the Spirits, but be firm and courteous with them; for thou hast no right to despise or revile them; and this too may lead thee astray. Command and banish them, curse them by the Great Names if need be; but neither mock nor revile them, for so assuredly wilt thou be lead into error.
9. A man is what he maketh himself within the limits fixed by his inherited destiny; he is a part of mankind; his actions affect not only what he calleth himself, but also the whole universe.
10. Worship and neglect not, the physical body which is thy temporary connection with the outer and material world. Therefore let thy mental Equilibrium be above disturbance by material events; strengthen and control the animal passions, discipline the emotions and the reason, nourish the Higher Aspirations.
11. Do good unto others for its own sake, not for reward, not for gratitude from them, not for sympathy. If thou art generous, thou wilt not long for thine ears to be tickled by expressions of gratitude.
12. Remember that unbalanced force is evil; that unbalanced severity is but cruelty and oppression; but that also unbalanced mercy is but weakness which would allow and abet Evil. Act passionately; think rationally; be Thyself.
13. True ritual is as much action as word; it is Will.
14. Remember that this earth is but an atom in the universe, and that thou thyself art but an atom thereon, and that even couldst thou become the God of this earth whereon thou crawlest and grovellest, that thou wouldest, even then, be but an atom, and one amongst many.
15. Nevertheless have the greatest self-respect, and to that end sin not against thyself. The sin which is unpardonable is knowingly and wilfully to reject truth, to fear knowledge lest that knowledge pander not to thy prejudices.
16. To obtain Magical Power, learn to control thought; admit only those ideas that are in harmony with the end desired, and not every stray and contradictory Idea that presents itself.
17. Fixed thought is a means to an end. Therefore pay attention to the power of silent thought and meditation. The material act is but the outward expression of thy thought, and therefore hath it been said that “the thought of foolishness is sin.” Thought is the commencement of action, and if a chance thought can produce much effect, what cannot fixed thought do?
18. Therefore, as hath already been said, Establish thyself firmly in the equilibrium of forces, in the centre of the Cross of the Elements, that Cross from whose centre the Creative Word issued in the birth of the Dawning Universe.
19. Be thou therefore prompt and active as the Sylphs, but avoid frivolity and caprice; be energetic and strong like the Salamanders, but avoid irritability and ferocity; be flexible and attentive to images like the Undines, but avoid idleness and changeability; be laborious and patient like the Gnomes, but avoid grossness and avarice.
20. So shalt thou gradually develop the powers of thy soul, and fit thyself to command the Spirits of the elements. For wert thou to summon the Gnomes to pander to thine avarice, thou wouldst no longer command them, but they would command thee. Wouldst thou abuse the pure beings of the woods and mountains to fill thy coffers and satisfy thy hunger of Gold? Wouldst thou debase the Spirits of Living Fire to serve thy wrath and hatred? Wouldst thou violate the purity of the Souls of the Waters to pander to thy lust of debauchery? Wouldst thou force the Spirits of the Evening Breeze to minister to thy folly and caprice? Know that with such desires thou canst but attract the Weak, not the Strong, and in that case the Weak will have power over thee.
21. In the true religion there is no sect, therefore take heed that thou blaspheme not the name by which another knoweth his God; for if thou do this thing in Jupiter thou wilt blaspheme יהוה and in Osiris יהשוה. Ask and ye shall have! Seek, and ye shall find! Knock, and it shall be opened unto you!
#thelema#thelemic holy season#argentum astrum#holy days#silver star#tarot#adjustment#justice tarot#maat
10 notes
·
View notes
Text










My name is Elena Litvinova, I am Russian living in Spain for past 18 years. I have been doing photography for 6 years. Trying to see what is invisible otherwise, this is what photography means to me.
There is a great film about photography and not just about that, called “The salt of the Earth”, featuring Sebastião Salgado. There are many memorable ideas mentioned, but today I would quote the one that stuck with me the most and which I agree with.
“The eyes speak volumes, the expression of the face. When you are taking a picture, it’s not just you who’s doing the job, it’s the person in front of you who’s letting you take a photo, the person offers a photo.”
Related to that on a metaphysical level is a story from my grandfather regarding photography maybe 100 years ago, when people in his small Russian village believed that one shouldn’t go overboard about letting oneself being photographed, since every time one gives a part of oneself away and cannot do so indefinitely. This idea of offering, giving oneself away to a photographer is what unites these two ideas. And I believe in that.
There were many times when I couldn’t understand what was wrong with a picture I took, everything seemed fine, but something was missing. I reckon that the person being photographed influences the outcome. One can shut oneself off completely and whereas you will capture perfectly the looks, there will be nothing more, just a superficial depiction.
There is no active participation on behalf of the subject, the only thing he/she needs to do is to relax and open oneself just as if it was a silent conversation. Then pictures speak.
I started using film when my friend Victoria Ilina , a talented photographer, who was also one of my mentors in its’ day, suggested almost offhandedly that I should have tried it to see if I liked it. Another thing that played its’ part is that my father was always using the film, well, there was no other way of taking photos anyway, so I was growing up observing him using his Zenith and FED cameras. So I tried and got into it.
Gradually I have grown to actually prefer analogue photography. For me it is more about implicit things rather than the explicit ones, for example, the look of the photos (grain, etc) taken using a film camera is not a decisive factor.
Logically it was stressing me out since I just had to see the result straight away, but slowly I have learned to let it go. In the end I enjoyed more looking through the photos after actually disconnecting from the session completed. It allowed me to view the images more objectively and profoundly, as if they were not mine.
It is about limitations coming with usage of a film camera, some self imposed, some that I have no influence over. With that comes discipline, patience and improvement.
I remember spending time with my father in the darkroom, helping him with the film development and printing, however it was long ago. So about 4 years ago I decided to acquire necessary skills but instead of going trial and error route I opted for an intensive course with an experienced Spanish photographer Juan Carlos Marugán and I learnt from him everything I needed to know related both to the development process and to the photography itself. Now I feel in the darkroom as if at home. Also, I knew how to shoot before, but he gave me invaluable insights into details. He is an old school perfectionist and I really like his photos. They are, as they say, picture perfect).
I have seen so many wonderful photographs made by the photographers I like and respect, using digital cameras or even phones. I have discovered that using film perfectly matches my goals and way of working, it has been very beneficial to me. There are times when using an analogue camera is not convenient due to the session particularities, but apart from those singular times I clearly prefer using film. However, this is on a personal, even more intuitive rather than calculated, basis, it doesn’t mean that it would work for anyone who tries it.
In parallel to regular secondary school I attended an arts school in Sevastopol, the town where I was born. Then it was time for a pragmatic university economics degree in Moscow, followed by a masters degree in Spain, where I worked in the export department for a few years. However, I have never lost appreciation for art and as soon as I could I co founded with my friend an arts school-workshop in Barcelona specialising in Japanese sculpture and handcraft techniques.
Some years passed by and I gave birth to my first son, which made me leave that project and consider something which would enable me to manage maternity and professional development. That was how my interest in photography began, for then as an observer.
I watched, admired, watched again and analysed. Some images I liked, some didn’t. Some reached out to me, some left me untouched. Dozens of photographers, hundreds of images. Gradually I was discovering a new world. At a certain point I couldn’t stay put and started a project , which would let me share this new world with other people. Texts accompanied by photographs. Photographs intensified with texts.
Then I started trying myself. Heavy handedly I tried to reproduce beauty. I learnt simple things, wondered, got upset, uplifted by little revelations and success, I studied
So by now I have been doing photography for 6 years. People, their portraits are what attracts and interests me the most.
#women photographers#support female artists#female photographers#film photograhers#fine art photography#analog photography
5 notes
·
View notes
Text
Okay, here are the lists of human rights and child rights.
Human Rights
1. All human beings are free and equal
All human beings are born free and equal in dignity and rights. They are endowed with reason and conscience and should act towards one another in a spirit of brotherhood.
2. No discrimination
Everyone is entitled to all the rights and freedoms, without distinction of any kind, such as race, colour, sex, language, religion, political or other opinion, national or social origin, property, birth or other status. Furthermore, no distinction shall be made on the basis of the political, jurisdictional or international status of the country or territory to which a person belongs.
3. Right to life
Everyone has the right to life, liberty and security of person.
4. No slavery
No one shall be held in slavery or servitude; slavery and the slave trade shall be prohibited in all their forms.
5. No torture and inhuman treatment
No one shall be subjected to torture or to cruel, inhuman or degrading treatment or punishment.
6. Same right to use law
Everyone has the right to recognition everywhere as a person before the law.
7. Equal before the law
All are equal before the law and are entitled without any discrimination to equal protection of the law. All are entitled to equal protection against any discrimination in violation and against any incitement to such discrimination.
8. Right to treated fair by court
Everyone has the right to an effective remedy by the competent national tribunals for acts violating the fundamental rights granted him by the constitution or by law.
9. No unfair detainment
No one shall be subjected to arbitrary arrest, detention or exile.
10. Right to trial
Everyone is entitled in full equality to a fair and public hearing by an independent and impartial tribunal, in the determination of his rights and obligations and of any criminal charge against him.
11. Innocent until proved guilty
Everyone charged with a penal offence has the right to be presumed innocent until proved guilty according to law in a public trial at which he has had all the guarantees necessary for his defence. No one shall be held guilty of any penal offence on account of any act or omission which did not constitute a penal offence, under national or international law, at the time when it was committed.
12. Right to privacy
No one shall be subjected to arbitrary interference with his privacy, family, home or correspondence, nor to attacks upon his honour and reputation. Everyone has the right to the protection of the law against such interference or attacks.
13. Freedom to movement and residence
Everyone has the right to freedom of movement and residence within the borders of each state. Everyone has the right to leave any country, including his own, and to return to his country.
14. Right to asylum
Everyone has the right to seek and to enjoy in other countries asylum from persecution. This right may not be invoked in the case of prosecutions genuinely arising from non-political crimes or from acts contrary to the purposes and principles of the United Nations.
15. Right to nationality
Everyone has the right to a nationality. No one shall be arbitrarily deprived of his nationality nor denied the right to change his nationality
16. Rights to marry and have family
Men and women of full age, without any limitation due to race, nationality or religion, have the right to marry and to found a family. They are entitled to equal rights as to marriage, during marriage and at its dissolution. Marriage shall be entered into only with the free and full consent of the intending spouses. The family is the natural and fundamental group unit of society and is entitled to protection by society and the State.
17. Right to own things
Everyone has the right to own property alone as well as in association with others. No one shall be arbitrarily deprived of his property.
18. Freedom of thought and religion
Everyone has the right to freedom of thought, conscience and religion; this right includes freedom to change his religion or belief, and freedom, either alone or in community with others and in public or private, to manifest his religion or belief in teaching, practice, worship and observance.
19. Freedom of opinion and expression
Everyone has the right to freedom of opinion and expression; this right includes freedom to hold opinions without interference and to seek, receive and impart information and ideas through any media and regardless of frontiers.
20. Right to assemble
Everyone has the right to freedom of peaceful assembly and association. No one may be compelled to belong to an association.
21. Right to democracy
Everyone has the right to take part in the government of his country, directly or through freely chosen representatives. Everyone has the right of equal access to public service in his country.
22. Right to social security
Everyone, as a member of society, has the right to social security and is entitled to realization, through national effort and international co-operation and in accordance with the organization and resources of each State, of the economic, social and cultural rights indispensable for his dignity and the free development of his personality.
23. Right to work
Everyone has the right to work, to free choice of employment, to just and favourable conditions of work and to protection against unemployment. Everyone, without any discrimination, has the right to equal pay for equal work. Everyone has the right to form and to join trade unions for the protection of his interests.
24. Right to rest and holiday
Everyone has the right to rest and leisure, including reasonable limitation of working hours and periodic holidays with pay.
25. Right of social service
Everyone has the right to a standard of living adequate for the health and well-being of himself and of his family, including food, clothing, housing and medical care and necessary social services, and the right to security in the event of unemployment, sickness, disability, widowhood, old age or other lack of livelihood in circumstances beyond his control. Motherhood and childhood are entitled to special care and assistance. All children shall enjoy the same social protection.
26. Right to education
Everyone has the right to education. Education shall be free, at least in the elementary and fundamental stages. Elementary education shall be compulsory. Technical and professional education shall be made generally available and higher education shall be equally accessible to all on the basis of merit.
27. Right of cultural and art
Everyone has the right freely to participate in the cultural life of the community, to enjoy the arts and to share in scientific advancement and its benefits. Everyone has the right to the protection of the moral and material interests resulting from any scientific, literary or artistic production of which he is the author.
28. Freedom around the world
Everyone is entitled to a social and international order in which the rights and freedoms set forth in this Declaration can be fully realized.
29. Subject to law
Everyone has duties to the community in which alone the free and full development of his personality is possible. In the exercise of his rights and freedoms, everyone shall be subject only to such limitations as are determined by law solely for the purpose of securing due recognition and respect for the rights and freedoms of others and of meeting the just requirements of morality, public order and the general welfare in a democratic society.
30. Human rights can’t be taken away
Nothing in this Declaration may be interpreted as implying for any State, group or person any right to engage in any activity or to perform any act aimed at the destruction of any of the rights and freedoms set forth herein.
So those are all Universal Declaration of Human Rights list by United Nations General Assembly. All universal human rights list above commonly known as 30 basic human rights that must be respected and protected by the law.
1. All human beings are free and equal
All human beings are born free and equal in dignity and rights. They are endowed with reason and conscience and should act towards one another in a spirit of brotherhood.
2. No discrimination
Everyone is entitled to all the rights and freedoms, without distinction of any kind, such as race, colour, sex, language, religion, political or other opinion, national or social origin, property, birth or other status. Furthermore, no distinction shall be made on the basis of the political, jurisdictional or international status of the country or territory to which a person belongs.
3. Right to life
Everyone has the right to life, liberty and security of person.
4. No slavery
No one shall be held in slavery or servitude; slavery and the slave trade shall be prohibited in all their forms.
5. No torture and inhuman treatment
No one shall be subjected to torture or to cruel, inhuman or degrading treatment or punishment.
6. Same right to use law
Everyone has the right to recognition everywhere as a person before the law.
7. Equal before the law
All are equal before the law and are entitled without any discrimination to equal protection of the law. All are entitled to equal protection against any discrimination in violation and against any incitement to such discrimination.
8. Right to treated fair by court
Everyone has the right to an effective remedy by the competent national tribunals for acts violating the fundamental rights granted him by the constitution or by law.
9. No unfair detainment
No one shall be subjected to arbitrary arrest, detention or exile.
10. Right to trial
Everyone is entitled in full equality to a fair and public hearing by an independent and impartial tribunal, in the determination of his rights and obligations and of any criminal charge against him.
11. Innocent until proved guilty
Everyone charged with a penal offence has the right to be presumed innocent until proved guilty according to law in a public trial at which he has had all the guarantees necessary for his defence. No one shall be held guilty of any penal offence on account of any act or omission which did not constitute a penal offence, under national or international law, at the time when it was committed.
12. Right to privacy
No one shall be subjected to arbitrary interference with his privacy, family, home or correspondence, nor to attacks upon his honour and reputation. Everyone has the right to the protection of the law against such interference or attacks.
13. Freedom to movement and residence
Everyone has the right to freedom of movement and residence within the borders of each state. Everyone has the right to leave any country, including his own, and to return to his country.
14. Right to asylum
Everyone has the right to seek and to enjoy in other countries asylum from persecution. This right may not be invoked in the case of prosecutions genuinely arising from non-political crimes or from acts contrary to the purposes and principles of the United Nations.
15. Right to nationality
Everyone has the right to a nationality. No one shall be arbitrarily deprived of his nationality nor denied the right to change his nationality
16. Rights to marry and have family
Men and women of full age, without any limitation due to race, nationality or religion, have the right to marry and to found a family. They are entitled to equal rights as to marriage, during marriage and at its dissolution. Marriage shall be entered into only with the free and full consent of the intending spouses. The family is the natural and fundamental group unit of society and is entitled to protection by society and the State.
17. Right to own things
Everyone has the right to own property alone as well as in association with others. No one shall be arbitrarily deprived of his property.
18. Freedom of thought and religion
Everyone has the right to freedom of thought, conscience and religion; this right includes freedom to change his religion or belief, and freedom, either alone or in community with others and in public or private, to manifest his religion or belief in teaching, practice, worship and observance.
19. Freedom of opinion and expression
Everyone has the right to freedom of opinion and expression; this right includes freedom to hold opinions without interference and to seek, receive and impart information and ideas through any media and regardless of frontiers.
20. Right to assemble
Everyone has the right to freedom of peaceful assembly and association. No one may be compelled to belong to an association.
21. Right to democracy
Everyone has the right to take part in the government of his country, directly or through freely chosen representatives. Everyone has the right of equal access to public service in his country.
22. Right to social security
Everyone, as a member of society, has the right to social security and is entitled to realization, through national effort and international co-operation and in accordance with the organization and resources of each State, of the economic, social and cultural rights indispensable for his dignity and the free development of his personality .
23. Right to work
Everyone has the right to work, to free choice of employment, to just and favourable conditions of work and to protection against unemployment. Everyone, without any discrimination, has the right to equal pay for equal work. Everyone has the right to form and to join trade unions for the protection of his interests.
24. Right to rest and holiday
Everyone has the right to rest and leisure, including reasonable limitation of working hours and periodic holidays with pay.
25. Right of social service
Everyone has the right to a standard of living adequate for the health and well-being of himself and of his family, including food, clothing, housing and medical care and necessary social services, and the right to security in the event of unemployment, sickness, disability, widowhood, old age or other lack of livelihood in circumstances beyond his control. Motherhood and childhood are entitled to special care and assistance. All children shall enjoy the same social protection.
26. Right to education
Everyone has the right to education. Education shall be free, at least in the elementary and fundamental stages. Elementary education shall be compulsory. Technical and professional education shall be made generally available and higher education shall be equally accessible to all on the basis of merit.
27. Right of cultural and art
Everyone has the right freely to participate in the cultural life of the community, to enjoy the arts and to share in scientific advancement and its benefits. Everyone has the right to the protection of the moral and material interests resulting from any scientific, literary or artistic production of which he is the author.
28. Freedom around the world
Everyone is entitled to a social and international order in which the rights and freedoms set forth in this Declaration can be fully realized.
29. Subject to law
Everyone has duties to the community in which alone the free and full development of his personality is possible. In the exercise of his rights and freedoms, everyone shall be subject only to such limitations as are determined by law solely for the purpose of securing due recognition and respect for the rights and freedoms of others and of meeting the just requirements of morality, public order and the general welfare in a democratic society.
30. Human rights can’t be taken away
Nothing in this Declaration may be interpreted as implying for any State, group or person any right to engage in any activity or to perform any act aimed at the destruction of any of the rights and freedoms set forth herein.
Now, doesn’t this sound like the complete opposite to these new laws, stated above? It sure does. Specifically the last one.
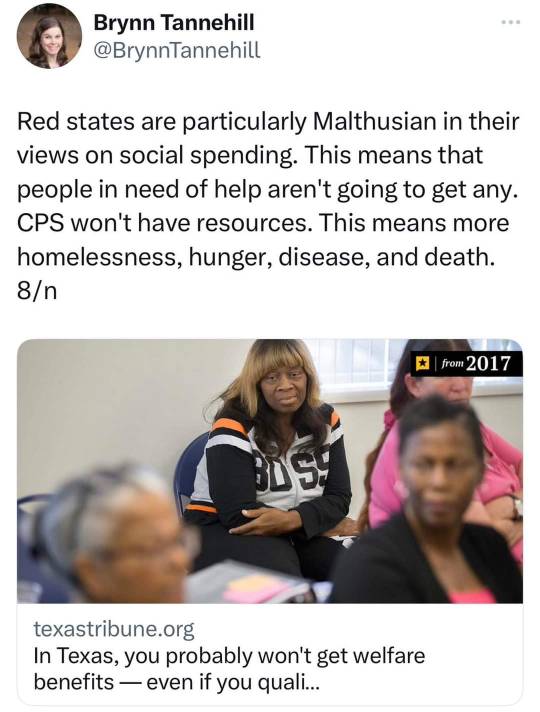
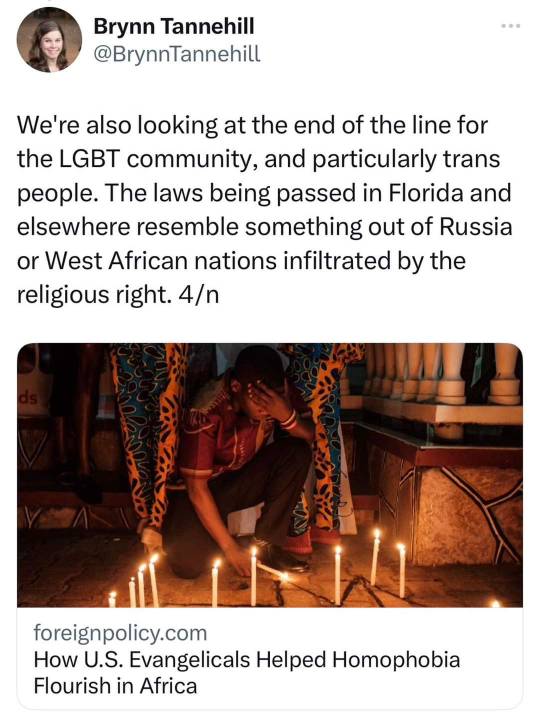
Child Rights (I can screenshot this one so I will)
This is the list of children’s rights in Australia at least. Did you get treated like this? Are your children going to be treated like this if THIS is the way we are going to make laws? No! So get your shit together, America.







#sorry long post#this is getting out of hand#get your shit together america#human rights#child’s rights
30K notes
·
View notes
Text
Understanding Personal Injury Lawyers in Sydney: What You Need to Know

Navigating the legal landscape after a personal injury can be daunting, especially if you are unfamiliar with the intricacies of the law. In Sydney, personal injury lawyers are invaluable allies for individuals seeking justice and compensation for their injuries. This article will provide a comprehensive guide to understanding personal injury lawyers in Sydney, covering common topics, challenges, a step-by-step guide, a case study, and a conclusion.
The Role of Personal Injury Lawyers in Sydney
Personal injury lawyers specialize in providing legal representation to individuals who have been injured due to the negligence or wrongdoing of another party. They handle various cases, including car accidents, workplace injuries, medical malpractice, and slip-and-fall incidents. These lawyers aim to help victims secure compensation for medical expenses, lost wages, pain and suffering, and other damages.
Common Topics in Personal Injury Law
Types of Personal Injury Claims: Personal injury claims can arise from different scenarios. Understanding the types of claims can help you determine if you have a case.
Statute of Limitations: This refers to the time limit within which you must file a personal injury claim. In New South Wales, the statute of limitations for personal injury claims is generally three years from the date of injury.
Negligence and Liability: Proving negligence is crucial in personal injury cases. You must show that the other party's actions or inactions caused your injury.
Compensation and Damages: This includes understanding the types of compensation you can receive, such as economic and non-economic damages.
The Legal Process: From filing a claim to reaching a settlement or going to trial, understanding the legal process can help you navigate your case more effectively.
Challenges in Personal Injury Cases
Proving Negligence: One of the biggest challenges in personal injury cases is proving that the other party was negligent. This requires gathering evidence, such as witness statements, medical records, and expert testimony.
Insurance Companies: Dealing with insurance companies can be challenging, as they often aim to minimize payouts. A personal injury lawyer can negotiate on your behalf to ensure you receive fair compensation.
Legal Costs: The cost of hiring a lawyer can be a concern for many individuals. However, many personal injury lawyers work on a contingency fee basis, meaning they only get paid if you win your case.
Emotional Stress: The legal process can be stressful and emotionally draining, especially if you are dealing with injuries and recovery.
Step-by-Step Guide to Hiring a Personal Injury Lawyer in Sydney
Step 1: Identify Your Needs
Determine the specifics of your case and what type of personal injury lawyer you need. For example, if you were injured in a car accident, look for a lawyer who specializes in car accident claims.
Step 2: Research Potential Lawyers
Look for personal injury lawyers in Sydney with good reputations and positive client reviews. Check their websites, read testimonials, and review their case histories.
Step 3: Schedule Consultations
Meet with several lawyers to discuss your case. Many personal injury lawyers offer free initial consultations. Use this opportunity to ask questions about their experience, approach, and fees.
Step 4: Evaluate Your Options
Consider the lawyers’ experience, success rate, and your comfort level with them. Choose a lawyer who you feel confident will represent your best interests.
Step 5: Understand the Fee Structure
Make sure you understand the lawyer’s fee structure before signing any agreements. Most personal injury lawyers in Sydney work on a contingency fee basis, but it’s important to confirm this.
Step 6: Sign a Retainer Agreement
Once you have chosen a lawyer, you will sign a retainer agreement that outlines the terms of your representation. This document will specify the lawyer’s fees and other important details.
Step 7: Work with Your Lawyer
Provide your lawyer with all necessary information and documentation related to your case. Stay in regular contact and follow their advice to ensure the best possible outcome.
Case Study: A Successful Personal Injury Claim
To illustrate the process, let's look at a case study involving a successful personal injury claim in Sydney.
The Incident
Jane, a Sydney resident, was involved in a car accident caused by a distracted driver. She suffered significant injuries, including a broken leg and a concussion, leading to substantial medical expenses and time off work.
Hiring a Lawyer
Jane researched personal injury lawyers in Sydney and chose a reputable firm with experience in car accident cases. She scheduled a consultation and decided to hire them on a contingency fee basis.
Building the Case
Jane’s lawyer gathered evidence, including police reports, medical records, and witness statements. They also consulted with medical experts to establish the extent of her injuries and their impact on her life.
Negotiating with the Insurance Company
The lawyer negotiated with the at-fault driver’s insurance company, presenting a strong case for compensation. After several rounds of negotiations, the insurance company offered a fair settlement that covered Jane’s medical expenses, lost wages, and pain and suffering.
Outcome
Jane received a substantial settlement, allowing her to focus on her recovery without financial stress. The lawyer's expertise and negotiation skills were crucial in achieving this outcome.
Conclusion
Personal injury lawyers in Sydney play a vital role in helping individuals navigate the complex legal system and secure the compensation they deserve. By understanding the common topics, challenges, and steps involved in personal injury cases, you can be better prepared to handle your situation. Whether you are dealing with a car accident, workplace injury, or any other type of personal injury, having a knowledgeable lawyer by your side can make a significant difference in the outcome of your case.
If you need a personal injury lawyer in Sydney, start by identifying your needs, researching potential lawyers, and scheduling consultations to find the right fit. Remember, the right lawyer can help you overcome challenges, negotiate with insurance companies, and achieve a successful outcome, just like in Jane’s case study. With the right support, you can focus on your recovery and move forward with your life.
0 notes
Text
daily forex signals
Daily Forex signals are trade recommendations provided on a daily basis, indicating optimal entry and exit points for various currency pairs. These signals are generated through comprehensive analysis by expert traders or sophisticated algorithms, and are designed to help traders make informed decisions. How Do Daily Forex Signals Work? Daily Forex signals typically include the following components: - Entry Point: The specific price level at which to enter the market. - Exit Point: The price level at which to close the trade to secure profit or limit loss. - Stop Loss: A predetermined price level at which the trade will automatically close to minimize losses. - Take Profit: A predetermined price level at which the trade will close to lock in profits. These signals are usually delivered through various channels such as email, SMS, mobile apps, and trading platforms, allowing traders to receive real-time updates and act quickly on trading opportunities. Benefits of Using Daily Forex Signals 1. Timeliness: Daily signals ensure traders receive up-to-date recommendations based on the latest market conditions, allowing them to act quickly on trading opportunities. 2. Expert Analysis: Signals generated by experienced traders or advanced algorithms provide valuable insights and enhance the accuracy of trading decisions. 3. Convenience: Receiving daily signals saves traders the time and effort required for continuous market analysis, enabling them to focus on executing trades. 4. Consistency: Daily signals help traders maintain a disciplined and consistent approach to trading, reducing emotional decision-making. Risks and Considerations While daily Forex signals offer numerous advantages, it is essential to be aware of potential risks and considerations: - Accuracy: The accuracy of signals can vary. It is crucial to choose reputable providers with a proven track record. - Over-reliance: Relying solely on signals without understanding the underlying market dynamics can be risky. Traders should use signals as part of a broader trading strategy. - Market Conditions: Signals may not perform well in all market conditions. Traders must adapt and adjust their strategies based on changing market environments. Choosing the Right Daily Forex Signal Provider When selecting a daily Forex signal provider, consider the following factors: 1. Reputation: Look for providers with positive reviews and a history of delivering accurate signals. 2. Transparency: Ensure the provider offers clear information on how signals are generated and provides performance data. 3. Trial Period: Opt for providers that offer a trial period to test the quality and reliability of their signals. 4. Support: Good customer support can help address any questions or issues that may arise. How to Get Started with Daily Forex Signals 1. Research Providers: Start by researching and comparing different daily Forex signal providers. Look for those with strong reputations and positive user feedback. 2. Understand the Signals: Take time to understand the reasoning behind the signals you receive. This will help you develop your trading knowledge and skills. 3. Implement Risk Management: Use stop-loss and take-profit levels as recommended by the signals, but also have your own risk management strategy in place. 4. Stay Informed: Keep yourself updated on market news and trends. This will help you make more informed decisions and better understand the signals you receive. Conclusion Daily Forex signals can be a powerful tool for traders seeking timely and accurate trading recommendations. By providing up-to-date insights and fostering a disciplined approach to trading, these signals help traders stay informed and make better decisions in the Forex market. However, it is essential to use them wisely, choose reputable providers, and integrate them into a comprehensive trading strategy. With the right approach, daily Forex signals can significantly enhance your trading performance and help you achieve your financial goals.
0 notes
Text
10 Popular Examples of SaaS Applications

Software as a Service (SaaS) is one of the most admired and adopted business models, providing increased ROI for companies and users alike, creating a win-win situation for all involved. Gartner predicts that by the end of 2021, end-user spending on public cloud services will reach $396 billion, projected to increase by 21.7% in 2022 to $482 billion, with approximately $171 billion of this occupied by SaaS.
From software development to the entertainment and finance industries, SaaS application development solutions have permeated almost every niche. Today, many examples of SaaS applications are visible around us. Before diving into popular SaaS examples and their companies, let’s first understand what exactly the Software as a Service model is and why so many businesses are inclined toward investing in it.
What is a SaaS (Software as a Service) application?
There are three major cloud-based services: SaaS, PaaS, and IaaS, with SaaS being the most popular. It is a cloud-based model in which all the maintenance work of software, including updates, delivery, and improvements, is managed by the operating organization. Users only need to pay subscription charges on a monthly or yearly basis. Many popular SaaS-based services are available for free with certain limitations, like Google Drive and Slack.
Why Have SaaS Application Development Services Become So Popular?
The most remarkable feature of web-based SaaS apps is that anyone around the globe can access the data by simply logging in. This means there is no need to store data on a computer's hard drive. Sounds amazing, doesn’t it? Anyone with an internet connection and login credentials can use the software.
In this unprecedented time of the COVID-19 pandemic, these SaaS applications have grown enormously to cater to the needs of remote working teams. Besides the cloud-based data storage advantage, essential for remote teams, let’s look at other perks that make these SaaS application development solutions even more convincing.
Benefits of SaaS Applications:
Low initial cost: Developing custom software is expensive and time-consuming. SaaS applications reduce initial costs and are more affordable.
Reduced time: SaaS applications save time as all updates and improvements are handled by the provider, allowing businesses to focus on their core operations.
Scalability: SaaS applications are subscription-based, offering flexibility to change plans according to needs.
Try and use: Many premium providers offer free trials, allowing users to try the SaaS app first and pay only if it meets their needs.
10 Popular Use Cases of SaaS Application Development
Now let’s look at popular examples of SaaS apps and see how big brands and startups have revolutionized the IT industry by providing successful SaaS applications.
1. Salesforce
Salesforce is a top cloud-based CRM (customer relationship management) platform aimed at boosting sales by managing leads and prospects in one place.
USP: Offers comprehensive solutions for CRM and sales team management.
Launch Year: 1999
Revenue: $33.954 billion (2022)
Website: Salesforce
2. Zoom
Zoom is a video conferencing platform that gained popularity during the pandemic for virtual meetings, conferences, webinars, and events.
USP: All-in-one video communications platform with a user-friendly interface.
Launch Year: 2011
Revenue: $4.527 billion (2023)
Website: Zoom
3. Google Workspace
Formerly known as G Suite, Google Workspace offers applications like Gmail, Google Docs, Google Sheets, and Google Drive, essential for businesses and individuals.
USP: Comprehensive product line available on all devices, connected with Android.
Launch Year: 2006
Revenue: $305.63 billion (2023 - Google Cloud)
Website: Google Workspace
4. Slack
Slack is a business communication platform offering private messaging, group discussions, file sharing, and end-to-end encryption.
USP: Ideal communication and collaboration tool with app integration.
Launch Year: 2013
Revenue: $273 million (2023)
Website: Slack
5. HubSpot
HubSpot is a CRM focused on inbound marketing, offering sales processes like social media marketing and content management.
USP: Automates marketing and sales efforts with easy access to relevant information.
Launch Year: 2006
Revenue: $2.17 billion (2023)
Website: HubSpot
6. Shopify
Shopify is a CMS for eCommerce stores, allowing retailers to create functional websites with various plans.
USP: Enables users to set up e-commerce platforms with built-in SEO and multiple payment gateway integration.
Launch Year: 2006
Revenue: $7.06 billion (2023)
Website: Shopify
7. SAP Concur
SAP Concur streamlines travel and expense management services into complete automation.
USP: Effective expense management platform accessible via web, smartphone, or tablet.
Launch Year: 1998
Revenue: €31 billion (2023)
Website: Concur
8. Adobe Creative Cloud
Adobe Creative Cloud offers applications for graphic design, web design, and photo & video editing.
USP: Access to creative apps like Photoshop, Premiere Pro, and Illustrator with team collaboration.
Launch Year: 2000
Revenue: $11.5 billion (2023)
Website: Adobe
9. Netflix
Netflix is a subscription-based streaming service offering a variety of television shows, movies, anime, and documentaries.
USP: High-quality, diverse content with on-demand streaming and no advertisements.
Launch Year: 1997
Revenue: $33.7 billion (2023)
Website: Netflix
10. Atlassian Jira
Jira is a project management tool for developers and project managers to track and manage software development workflows.
USP: Suitable for various users with integration capabilities for effective project management.
Launch Year: 2002
Revenue: $3.5 billion (2023)
Website: Jira
Final Thoughts
SaaS signifies a new way of doing things, allowing you to reach a larger audience, launch apps quickly, and streamline business operations. SaaS software allows you to focus on core businesses while removing the hassle of maintenance and upgrades. This is why the number of SaaS development agencies has nearly tripled in recent years.
For software providers, SaaS offers recurring revenue, faster release cycles, regular upgrades, stronger customer relationships, and more efficient maintenance. Thus, SaaS is a win-win for all parties involved. As long as we have the internet, the demand for SaaS will only continue to grow.
For more information, visit Facile Technolab.
Related Resources
Top 5 mistakes when hiring SaaS Development Team and How to avoid them
Related Services
SaaS Development
Related Case Studies
FinTech Modernization and SaaS Development Case Study
Manufacturing Execution System - SaaS Platform Development Case Study
Parking Management SaaS Platform Case Study
Job Management System SaaS Platform MVP for precision component manufacturing company in Australia
More Articles related to SaaS:
Why .NET Core is a popular choice for SaaS Development?
How to Build a 10x More Efficient B2B SaaS Platform in 2024
The Future of B2B SaaS Platform Development: 9 Emerging Trends to Watch in 2024
Creating Your First B2B SaaS Platform MVP: A Comprehensive Tutorial
Building Cloud-Native B2B SaaS Software Solutions: Advantages and Strategies
The 3 Hidden Obstacles Holding Back Your B2B SaaS Dream
The Cost-Effectiveness Myth: Ensuring Value Beyond Cost Savings in Offshore Software Development
Finding Your Perfect Fit: How to Choose the Right SaaS Development Partner in India
How Much Does a B2B SaaS Software MVP Development Really Cost?
#SaaS application development solutions#saas development company#saas app development services#saas development services#saas application development company
0 notes
Text
How AIML Helps Clinical Data Managers Improve Trial Efficacy

Clinical trials drive the essence of medical progress and form the basis for innovations in new treatments, drugs, and interventions, through which treatment efficacy is later established. However, there are associated difficulties, such as complex data management, high costs, long timelines, and strict regulatory requirements that impede the process.
This is where Artificial Intelligence and Machine Learning become game changers in maximizing the efficiency of clinical trials. AIML is used to harness the data in optimizing the process, improving the quality of the data, which consequently speeds up the overall timeline for the trial. The following discusses how AIML can help the CDM to improve the effectiveness of the trial.
1. Improving Data Quality and Integrity
Automated Data Cleaning and Validation Two significant tasks CDMs perform are the integrity and clarity check of data. The AIML algorithms will automatically correct disparities that naturally exist in the datasets without necessarily going through a process of data cleaning manually. Induction of knowledge from history in machine learning models for prediction and correction of common errors, such as data entry mistakes, missing entries, and outliers, enables this not only to mean better data quality but also lets CDMs focus on other more complex tasks.
Natural Language Processing for Unstructured Data Clinical trials usually generate large amounts of unstructured data from, for example, physician notes, patient reports, and medical records. NLP, a domain within AIML, helps to process and extract critical information out of text sources in a way that converts them into structured data with the ease of analysis, hence leaving no valuable data undiscovered and increasing the comprehensiveness of the data set.
2. Ensuring Optimal Patient Recruitment and Retention
Predictive Modelling for Patient Recruitment Recruiting appropriate subjects is one of the significant challenges in the clinical trial process. AIML can mine past trial data and patient records, thereby finding patterns that will enable it to predict which patients are most likely to be eligible and willing to participate in a given study. Targeting such individuals with a lot more precision would allow CDMs to increase the recruitment rate, hence reducing time-to-patient enrollment.
Personalized Retention Strategies Retaining subjects in a study has similar, if not more significant challenges than recruitment. AIML can harness the power of the patient engagement data to predict the subjects at high risk of dropout and deployment of personalized interventions that CDMs can undertake, including but not limited to tailored communication or added support, to increase these rates.
3. Streamlining Data Collection and Monitoring
Remote Monitoring and Wearable Technology The integration of AIML with wearable technology enables constant real-time monitoring of subjects. These devices can collect a vast range of health information, including heart rate, levels of activity, and sleep patterns, which can automatically be transferred into the trial database.
Following this, the AIML algorithms process that information for trend identification and abnormal patterns to manage health proactively and, in the event, detect adverse events as fast as possible.
AIML allows for adaptive designs of clinical trials where the protocol can change according to interim analysis results. For example, machine learning models could be used in real-time to analyze trial data for dosing regimen calibration, to change patient cohorts, or even to pull the plug for issues on efficacy and safety. This dynamic nature of treatment would make these trials more effective while cutting costs and reducing risks for trial participants.
4. Enhanced Data Analysis and Interpretation
Advanced Analytics and Predictive Modeling AIML enables advanced analytic techniques to be used with clinical trial data. Predictive modeling offers forecasting for trial outcomes and risk profiling, with optimum resource allocation. For instance, machine-learning algorithms might be deployed to identify the variables most likely to impact trial results so that CDMs can narrow down to critical factors and better structure and implement a trial.
Real-time Data Visualization Data visualization tools, supported by AIML, allow CDMs to have real-time views of the evolving trends in a clinical trial. Interactive dashboards can give heads-up indicators like enrollment rates, data quality metrics, and safety signals. All these visualizations allow CDMs to make on-the-go informed decisions for quick issue resolution, therefore contributing to improving efficiency within projects.
5. Regulatory Compliance and Data Security
Automated Compliance Monitoring The aim of clinical trials is regulatory compliance, but this area is most prone to risk and error.
With AI and ML, it is easy to automate compliance monitoring according to protocols and under regulatory requirements. For instance, machine learning algorithms could trace entries of data and raise a flag when any one of the data is not according to the set standard operating procedure, hence assuring the trial's compliance with all the regulation requirements that have to be adhered to.
6. Improved Data Security
Protecting patient data in clinical trials is paramount. AIML will be used to enhance the security of data through the detection and prevention of possible threats. Machine learning models can trace unusual patterns in accessing or transmitting data as an alarm for potential security breaches.
AIML can also help encrypt and anonymize patient data to protect sensitive information.
7. Efficient Resource Allocation
CDMs can optimize the allocation of resources for the trial using predictive analytics. AIML will help to predict in which stages of the trial there will be an increased need for staff, funding, or supplies, thereby better planning and cost management.
Such effectiveness can contribute to cost savings and shorten the time a trial takes to complete.
8. Expedited Data Processing
Automation of data processing by AIML could reduce the time spent analyzing data from clinical trials. It requires much time, and techniques such as entering, cleaning, and data analysis are quite a job error.
AIML can do such jobs much faster and more precisely; hence, the time taken to conclude the overall trial is considerably shortened.
Conclusion
The adoption of AIML in clinical trial management involves many benefits that are bound to raise the effectiveness of the trials. From improved data quality and better patient recruitment to smoother data collection, not forgetting regulatory compliance, AIML offers the CDMs a toolset replete with the capability to surmount conventional challenges in clinical trials.
As the healthcare industry continues to evolve, adopting AIML technologies will be essential for the ultimate success of future clinical trials and drive faster and more effective medical advancements. Want to know more about how Octalsoft’s eClinical suite can help streamline and expedite the efficiency of your next clinical trial? Book a demo with us today!
#ai and machine learning in clinical trials#clinical data management#clinical data management system
0 notes
Text
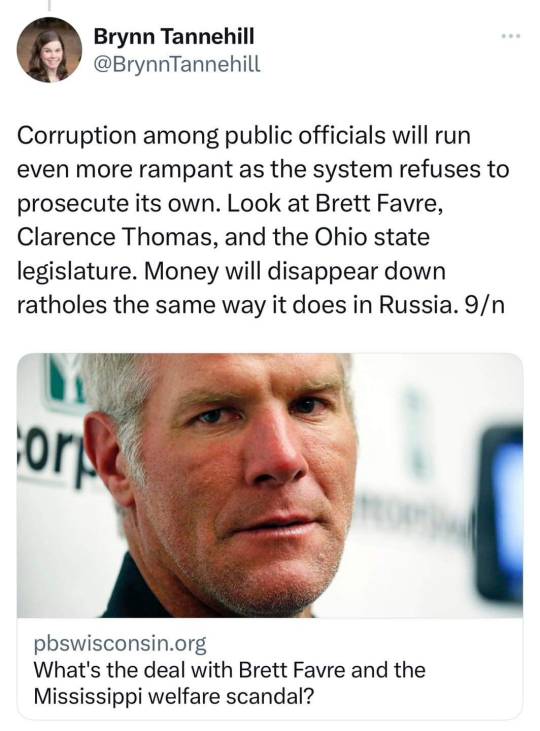
Walk-In Interview for Project-Based Vacancies at Mahamana Pandit Madan Mohan Malaviya Cancer Centre Advt. No.: HBCH/MPMMCC/PROJECT/2024/024 Walk-In Interview for Fresher Clinical Research and JRF Positions Date: Wednesday, 3rd July 2024 Time: Between 9:00 am to 10:00 am Venue: Mahamana Pandit Madan Mohan Malaviya Cancer Centre, Sunder Bagiya, BHU Campus, Varanasi, Uttar Pradesh - 221005 Contact Number: 0542-2517699 We are inviting applications for project-based vacancies on a contract basis. Interested and eligible candidates can attend the walk-in interview with their bio-data, recent passport-size photograph, original documents (PAN card, Aadhar card, experience certificates, education certificates), and one set of self-attested copies of all certificates. Note: The appointment will be initially for a period of six months or till the continuation of the project, whichever is earlier. Vacancy Details 1. Clinical Trial Coordinator (Project A/c No. 9243) Essential Qualification: Graduate in Life Science or B. Pharma and P.G. Diploma in Clinical Research. Age Limit: 30 years Monthly Remuneration: ₹25,000/- Number of Posts: 01 (one) 2. Clinical Trial Coordinator (Project A/c No. 9256) Essential Qualification: Graduate in Life Science with relevant experience in Clinical Research. Post Graduate Degree in Life Science and Diploma in Clinical Research is desirable. Age Limit: 30 years Monthly Remuneration: ₹25,000/- to ₹35,000/- Number of Posts: 01 (one) 3. Junior Research Fellow (Non-Medical) (Project A/c No. 9247) Essential Qualification: Graduate in Life Science or B. Pharma and Diploma in Clinical Research with 02 years relevant experience in Clinical Research is mandatory. Age Limit: 35 years Monthly Remuneration: ₹35,000/- to ₹40,000/- Number of Posts: 01 (one) 4. Junior Research Fellow (Non-Medical) (Project A/c No. 9259) Essential Qualification: Graduate in Life Science or B. Pharma and Diploma in Clinical Research with 02 years relevant experience in Clinical Research is mandatory. Age Limit: 35 years Monthly Remuneration: ₹35,000/- to ₹45,000/- Number of Posts: 01 (one) [caption id="attachment_85499" align="aligncenter" width="1200"] Walk-In Interview for Fresher Clinical Research and JRF Positions at MPMMCC[/caption] Online Interview for Outstation Candidates Outstation candidates may attend the interview online. To participate, candidates are required to send their resume along with supporting documents in a single PDF file to [email protected] on or before 30.06.2024. Please mention the advertisement number and post in the subject line of the email. Only shortlisted candidates who fulfill the norms will be contacted for the online interview. For recruitment-related queries, candidates may contact the Recruitment Cell, MPMMCC, Varanasi via email at [email protected] or phone at 0542-2517699 (Extn. 1106 / 1128). Walk-In Interview for Fresher Clinical Research and JRF Positions at MPMMCC
0 notes
Text
6 Very Simple Things You Can Do To Save on a Car Accident Lawyer Madison
When you're involved in a car accident, the legal and financial aftermath can be daunting. Hiring a car accident lawyer is often necessary to navigate the complexities of insurance claims, liability issues, and potential litigation. However, legal fees can quickly add up, straining your finances even further. Fortunately, there are several straightforward steps you can take to save on a car accident lawyer Madison without compromising on the quality of legal representation. Here are six simple strategies to help you manage legal costs effectively.
1. Choose a Lawyer Who Works on a Contingency Fee Basis
One of the most effective ways to save money on legal fees is to hire a lawyer who works on a contingency fee basis. This means that the lawyer only gets paid if you win your case or secure a settlement. The fee is typically a percentage of the compensation you receive, which aligns the lawyer's interests with your own. This arrangement not only makes legal services more affordable but also motivates your lawyer to work diligently on your behalf.
2. Obtain a Free Initial Consultation
Many car accident lawyers in Madison offer free initial consultations. Take advantage of this opportunity to discuss your case with multiple attorneys without any financial commitment. During these consultations, you can evaluate the lawyer's expertise, communication style, and strategy for your case. This allows you to make an informed decision without incurring any costs. Additionally, these consultations can provide valuable insights into the strengths and weaknesses of your case.
3. Gather and Organize Documentation Yourself
One way to reduce legal fees is to do some of the groundwork yourself. Lawyers often charge by the hour, and the time spent gathering documents and information can add up quickly. To minimize these costs, collect and organize all relevant documentation before meeting with your lawyer. This includes police reports, medical records, insurance information, photographs of the accident scene, witness statements, and any correspondence with insurance companies. Providing a well-organized file can save your lawyer time and reduce your overall legal expenses.
4. Communicate Efficiently
Having clear and concise communication with your attorney can also help you save money. Be concise and clear in your communications, and avoid unnecessary phone calls or emails. Instead, compile your questions and concerns and address them in a single communication or during scheduled meetings. This approach minimizes the time your lawyer spends on your case, which can significantly reduce hourly fees. Additionally, using email instead of phone calls for non-urgent matters can help keep communication costs down.
5. Consider Alternative Dispute Resolution (ADR)
Alternative Dispute Resolution (ADR) methods, such as mediation or arbitration, can be more cost-effective than going to trial. These methods are often quicker and less formal, which can reduce legal fees and other related expenses. Discuss with your lawyer whether ADR is a viable option for your case. If both parties agree to ADR, it can lead to a faster resolution and lower costs compared to a prolonged court battle.
6. Negotiate a Payment Plan
If paying a lump sum for legal fees is challenging, consider negotiating a payment plan with your lawyer. Many attorneys are willing to accommodate clients' financial situations by allowing them to pay fees in installments over time. This can make legal services more accessible and manageable without causing financial strain. Be upfront about your financial constraints and work with your lawyer to establish a payment plan that suits both parties.
Additional Tips for Managing Legal Costs
Research Lawyer's Reputation: Choosing a reputable lawyer with a strong track record can save money in the long run by increasing the likelihood of a successful outcome.
Limit Legal Scope: Clearly define the scope of legal services to avoid unnecessary costs. Ensure your lawyer focuses on essential tasks.
Stay Organized: Keep all correspondence and documents organized to streamline the legal process and avoid duplicative efforts.
Utilize Paralegals: Ask if paralegals can handle certain aspects of your case. Their hourly rates are usually lower than those of attorneys.
Conclusion
Navigating the aftermath of a car accident can be overwhelming, but hiring a car accident lawyer Madison doesn’t have to break the bank. By implementing these six simple strategies—choosing a contingency fee arrangement, obtaining free consultations, gathering documents yourself, communicating efficiently, considering ADR, and negotiating a payment plan—you can manage legal costs effectively. These steps will help ensure you receive quality legal representation without unnecessary financial strain, allowing you to focus on recovering and moving forward.
0 notes
Text
How to Find and Hire the Best Dedicated Developers for Your Team
In the constantly evolving technology world, businesses of all sizes frequently require dedicated developers to build or maintain their digital offerings. When you're creating an app, a mobile application, or a custom software, locating and hiring the most dedicated developers is vital to successful completion of the endeavor. In this article we'll look at how to proceed and the strategies that will assist you in locating and bringing on board the most dedicated developers to your team.
1. Define Your Project Requirements
Before you begin searching for a developer who is dedicated it is essential to have a thorough understanding of the scope of your project objectives, goals, and the technology stack. Knowing what you need will allow you to find candidates with the appropriate capabilities and knowledge.
2. Determine Your Budget
Set a budget for your project, which includes developer wages and any additional costs like software, tools licenses and project management costs. Having a budget-friendly your mind will allow you to limit your options and help you determine if you are able to afford the skills you require.
3. Decide on the Hiring Model
There are a variety of models of hiring to take into consideration when you are looking to bring dedicated developers to your team:
In-House It is possible to hire dedicated developers on a full-time basis working in your office. This is the most efficient method of control, but it is also more expensive.
Freelancers are freelancers who work remotely on a per-project basis. This type of model is economical, but it may not have the commitment to long-term contracts you require.
outsourcing: You could work with a development company or an outsourcing firm that can provide dedicated developers. This method combines experience and flexibility.
4. Search Online Job Portals
Job portals online as well as freelance websites are fantastic options to begin your search for developers who are dedicated. Websites such as LinkedIn, Upwork, Toptal and GitHub Jobs provide a huge collection of developers with varying capabilities and experiences. You can create a job opening or look for candidates that meet your needs.
5. Leverage Social Media and Professional Networks
Social media platforms such as LinkedIn and Twitter are powerful instruments for connecting prospective developers. Join groups and communities of developers and participate in discussions and build relationships with industry professionals. Your personal recommendations from your network could be helpful in locating reliable developers.
6. Review Portfolios and Resumes
When you've identified candidates, take a close look at the resumes and portfolios of each. Check for projects from the past which align with your mission and the technology stack. Take note of their abilities or experience as well as any awards or certifications they might have won.
7. Conduct Technical Interviews
Interviews with technical experts are an essential method of evaluating the developer's abilities and skills. Make a set of questions that are technical or code issues that relate to your particular project. Think about involving your current development team or enlisting an expert in technical matters to help in the interview process.
8. Check References
Get in touch with the references of the candidate to gain insight into their attitude to work ability to communicate, their skills in communication, and their ability to adhere to deadlines. References can give valuable insight regarding the developer's performance and credibility.
9. Evaluate Soft Skills
Alongside the technical capabilities take a look at the soft capabilities of committed developers. Communication and teamwork, as well as problem-solving and flexibility are the most important qualities to ensure a successful collaboration.
10. Begin with a trial period
To ensure that you have a great match, you should consider beginning with an initial trial period or smaller project prior to signing the long-term agreement. This will allow you to assess the performance of the developer and their compatibility with your team and the project.
11. Define Clear Terms and Contracts
After you've identified the most skilled developers on your staff, create specific terms and agreements which define obligations, roles along with payment structure and timelines for projects. This will ensure that the parties have a common understanding of what is expected.
12. Establish Effective Communication
Effective communication is essential to a successful collaboration with dedicated developers. Utilize tools for managing projects, frequent meetings and clear communication channels to ensure that everyone is on the on the same on the same page.
Conclusion
Finding the most dedicated developers to your team is an essential step towards reaching your goals in software development. When you define your project's requirements as well as establishing a budget and implementing a systematic hiring process, you will be able select dedicated developers for hire who can aid in an overall success for your initiatives. Keep in mind that finding the best match may take some long, but the time spent in choosing the most talented developers will be worth it over time since they will become valued part on your staff.
0 notes
Text
The First Amendment and the Chilmark Library
By Emma Babashak, Columbia University, Class of 2024
July 14, 2023

Last summer, The Chilmark Free Public Library, located on the island of Martha’s Vineyard, did not invite defense attorney and retired Harvard law professor Alan Dershowitz to speak at its library. Dershowitz, a frequent Martha’s Vineyard visitor, claimed that this lack of invitation was a form of censorship and infringed on his First Amendment right of free speech. Dershowitz threatened to sue the library, but he later issued a letter of apology.
Dershowitz is known for his work in American criminal law and constitutional law. In his career, he has represented many high-profile clients, including Jeffrey Epstein, Mike Tyson, and O.J. Simpson. From 2009 to 2017, Dershowitz spoke at the Chilmark library seven times – four times by invitation and three times at his own request.[1]
In 2020, he was a part of President Trump’s defense team for the president’s first impeachment trial. However, Dershowitz claimed that after speaking at the library on a regular basis, this new role is one reason he was “cancelled” not only at the Chilmark Library, but at multiple venues in Martha’s Vineyard.
In an interview last year, Dershowitz stated, “Every year, they would have an overflow crowd to hear me speak about whatever book I was writing, or whatever I was doing. But suddenly, after I represented the Constitution on behalf of President Trump, the library found excuses for never having me. Their first excuse was that my crowds were too big. So I said, “Well, why don’t you limit the crowds?” They said, “Oh, we hadn’t thought of that.” … So I’ve been cancelled, basically, by the Chilmark Library”.[2]
The First Amendment states that, “Congress shall make no law respecting an establishment of religion, or prohibiting the free exercise thereof; or abridging the freedom of speech, or of the press; or the right of the people peaceably to assemble, and to petition the Government for a redress of grievances”.[3] Because of this fundamental right, the Chilmark Library had to show that there was “compelling reason” to disallow someone from utilizing the First Amendment and speaking in the space.
According to the MV Times, library director Ebba Hierta said that in past years, “The reason I grew reluctant to extend invitations to Alan [Dershowitz] is this: The circus that surrounds this man who so ably courts controversy got in the way of the library’s important mission — serving the residents and visitors of Chilmark. When 200-plus people crammed into the library, with dozens more milling about harassing staff because they couldn’t hear the lecture; when local businesses lost money because our patrons filled their parking lots; when patrons not interested in hearing Alan could not take care of their library business; that’s when I realized the eminent Harvard professor emeritus had outgrown our little library”.[4] In addition, the trustees of the library claimed that last summer, Dershowitz had requested to talk after the summer schedule had already been finalized.
In contrast to last summer, Dershowitz was allowed to speak in Summer 2023. At the Chilmark Library, he gave a talk on his new book, “Dershowitz on Killing: How the Law Decides Who Shall Live and Who Shall Die”. While the library had set an attendance limit at 25 for Dershowitz’s event, this capacity was not exceeded by listeners. In this talk, Dershowitz highlighted his advocacy for organ donation and belief against the death penalty, but he did not mention his previous controversy with the library.[5]
______________________________________________________________
Emma Babashak is currently a rising senior attending Columbia University. She is majoring in Operations Research - Engineering Management Systems and minoring in both Economics and Psychology.
______________________________________________________________
[1] https://vineyardgazette.com/news/2022/08/17/chilmark-library-trustees-discuss-dershowitz-request
[2] https://www.newyorker.com/news/q-and-a/alan-dershowitzs-marthas-vineyard-cancellation
[3] https://constitution.congress.gov/constitution/amendment-1/
[4] https://www.mvtimes.com/2023/06/14/dershowitz-flap-chilmark-free-public-library/
[5] https://vineyardgazette.com/news/2023/06/21/dershowitz-returns-chilmark-library
0 notes
Text
Benefits and Challenges of Monthly Bike Rentals in Delhi
In bustling cities like Delhi, commuting can be a daunting task, especially with heavy traffic and limited parking options. Monthly bike rental in Delhi offers a practical and affordable solution for individuals seeking a convenient mode of transportation. In this blog post, we will delve into the benefits and challenges of opting for bike rentals in Delhi, shedding light on how this service can enhance your daily commute and address common concerns.

Benefits of Monthly Bike Rentals
1. Cost-Effective Solution
One of the primary advantages of monthly bike on rent in Delhi is the cost-effectiveness they offer. Owning a bike involves expenses such as maintenance, insurance, parking fees, and depreciation. With monthly rentals, you can avoid these costs and pay a fixed rental fee, often at a fraction of the price of owning a bike. This budget-friendly option allows you to allocate your finances efficiently and save money in the long run.
2. Convenience and Flexibility
Bike on rent in Delhi on a monthly basis provide unparalleled convenience and flexibility. You can choose a bike that suits your preferences and daily commuting needs. Rental services usually offer a diverse range of bikes, including scooters, sports bikes, and cruisers. This flexibility allows you to select a vehicle that aligns with your style, comfort, and requirements. Moreover, you can enjoy the convenience of pick-up and drop-off locations, making it hassle-free to commute to different parts of the city.
3. No Maintenance Hassles
When you get a bike rental in Delhi on a monthly basis, you eliminate the responsibilities of maintenance and repairs. Rental companies are responsible for keeping the bikes in optimal condition. In case of any issues, they handle the servicing, ensuring that you have a well-maintained vehicle at all times. Without any charges, Delhi bike rental company will take care of your comfort. This saves you from the hassle of finding a reliable mechanic and managing maintenance tasks, allowing you to focus on enjoying your ride.
4. Access to Latest Models
Monthly bike on rent in Delhi offer the advantage of accessing the latest models and technology. Rental companies often update their fleet regularly, providing you with the opportunity to ride the newest bikes available in the market. This ensures a superior riding experience, enhanced safety features, and access to advanced technologies that might be beyond your budget if you were to purchase a bike.
5. Trial Period for Potential Buyers
Getting a bike on rent in Delhi on a monthly basis can serve as a trial period for individuals considering purchasing a bike in the future. It allows you to test different models and gauge their suitability for your needs, riding style, and comfort. By experiencing firsthand the performance and features of various bikes, you can make an informed decision when it comes to investing in your own vehicle.
Challenges of Monthly Bike Rentals
1. Limited Personalization
Since monthly bike rentals in Delhi offer a fleet of standardised vehicles, personalization options may be limited. You may not have the freedom to customise the bike to your liking, such as adding specific accessories or modifications. However, the rental companies usually ensure that the bikes are well-equipped with essential features to meet general commuting requirements.
2. Availability and Booking
During peak seasons or high demand periods, securing a monthly rental bike of your choice may become challenging. It's advisable to make reservations in advance to ensure availability. Additionally, last-minute cancellations or changes in plans may incur penalties or impact future bookings. Therefore, it's crucial to plan your rental duration and communicate any changes promptly to avoid any inconvenience.
3. Responsibility and Liability
While monthly bike rentals provide convenience, it's essential to understand your responsibilities and liabilities as a renter. Carefully read the rental agreement to familiarise yourself with terms and conditions, including insurance coverage, security deposit requirements, and damage liabilities. Adhering to traffic rules, safe riding practices, and proper care of the rental bike is crucial to avoid any penalties or additional charges.
Conclusion
Monthly bike rentals in Delhi present an attractive alternative to traditional commuting methods. It is an appealing option for anyone looking for a hassle-free and affordable method to get around the city because of the advantages, which include cost effectiveness, convenience, flexibility, and maintenance-free experience. However, it's critical to understand the restrictions and obligations related to monthly bike rentals. You can make an informed choice and take advantage of the many benefits that monthly bike rentals or even scooty on rent in Delhi have to offer by taking into account the benefits and drawbacks stated above.
#bike on rent in delhi#scooty on rent in delhi#bike rental in delhi#two wheeler on rent in delhi#monthly bike on rent in delhi#bike rentals in delhi#haybhusa on rent in delhi#super bike on rent in delhi#motorcycle on rent in delhi
0 notes
Text
Is US Patent Policy Strong Enough to Withstand the Winds of Change: A Study of the Need to Change United States Patent Policy

Author by Kent R Acheson
Abstract
The purpose of this case study was to learn how US patent policy requirements differ for the Software and Pharmaceutical Industries, specifically if United States Patent Policy adequately protects intellectual property rights [1] for two divergent industries while still encouraging research and development (R & D) investment sufficient to increase profits and innovation. Data for this study consisted of 38 witness testimonies delivered to US Congress between the years 2005 and 2010 by experts representing the two industries of interest: pharmaceutical and software. Key findings from the data analysis of these 38 testimonies revealed both within industry differences and between industry differences in patent law protection. Within industry differences showed variance based on size of the company and the degree to which they relied on their own R & D. Between industry differences reflected divergent ‘products’ with Pharmaceutical Industries needing long-term protection to recover R & D expenditures that include expenses for human trials research to proceed from patent application to market. Software industry, on the other hand, uses follow-on innovation of others to continue technological advancement by constantly improving upon existing software. The data show that these two industries use patent policy protection in different ways for different reasons. This information will enable Policymakers to develop another form of product protection in lieu of the current patent law to better meet the needs of these two industries rather than try to modify the existing law.
Introduction
Patent law was developed in parts, building on one another with a single purpose in mind of protecting all innovations in a society and this created the basis for patent laws imposed on the current and future generations. Bessen [2,3] stressed that patents may not be valuable in protecting innovation [4-6] but are used solely to diffuse new ideas in the public. Bessen and Maskin [7] had previously highlighted that little research and development (R&D) in the Software Industry is used to gain patent protections and the enforcement issue with patents is difficult, as many patents are issued for products that are not new. Levin [8] and others found much earlier that patents were rated weak at protecting the returns on innovation, far behind the protection gained through lead time and learning curve advantages.
Patent’s role in different industries
The purpose of this qualitative case study was to explore the different requirements for patent policy for the Software and Pharmaceutical Industries. All transcripts from testimonies from the spokespersons representing the two industries introduced to either House between the years 2005 to 2010 concerning the U.S. Patent Reform Bills were collected and analyzed to answer the research question in this case study. The findings could be useful in further adjusting patent policy to encourage innovation for diverse industries, or suggest the creation of another form of idea protection.
A similar problem may be in the type of intellectual property protection that a company chooses to obtain to avoid the constraints of getting a patent and extend the time frame for protection, such as copyright protection that extends protection from the 20 years for a patent to 120 years. Apple Inc. obtained a copyright protection for their popular iPhone [9], which recently lost in a suit against the Federal Government. The landmark decision helps to control copyright creep. Initially when buying an iPhone, Apple Inc. limited the service provider to AT&T and applications had to be bought from the Official Apple Store. Now, however, through a hack on the iPhone, users can choose a different service provider and load other, unofficial, applications not supported by Apple Inc., and hackers are not in violation of Copyright Law.
Policy Makers can use the findings of this study to explore new directions for the United States Patent Policy to optimize advancement of technology in the Software and Pharmaceutical Industries. Historically in the United States, there has been one patent policy. Scholars, academicians, and the United States Government still do not know the ideal amount of IPRs mainly because the objective has been to uphold one uniform policy. This study clarified if further changes were needed for patent policy through a Patent Reform Act, which enables Policy Makers to understand the needs of the Software Industry, or design another form of protection designed specifically for the Software Industry.
Crowe [10] and others stated that a case study design is most appropriate when little is known of a phenomenon in its natural context. A case study is “used to generate an in-depth, multifaceted understanding of a complex issue in its real-life context” (p. 1). The Pharmaceutical Industry has a profitable track record using the existing Patent Law to protect their R&D investments. The Software Industry is comparatively new and therefore their issues are only just now becoming obvious. Case law is outside the boundaries of this study.
The multiple dimensions of the phenomenon of the nature of protecting intellectual property rights in the Software Industry property and the Pharmaceutical Industry are worthy of study to allow all voices to be heard, including large corporations from both software and pharmaceutical companies, generic drug companies, and smaller software startups. After carefully examining all relevant transcripts, these diverse opinions can be given venue to state their needs.
Methodology and main results
The research question addressed in this study was: How do the patent policy requirements differ for the Software and Pharmaceutical Industries? From the Software and Pharmaceutical Industries’ objectives and needs for the United States Patent Policy to address, the questions spotlighted the sufficiency and effectiveness of the United States Patent Policy.
The focus of this study has two parts, they are:
1. What is the evidence United States Patent Policy adequately protects Intellectual Property Rights (IPRs) for both the Software and Pharmaceutical Industries?
2. How does the United States Patent System encourage companies to make R&D investment in the Software and the Pharmaceutical Industry?
The first research question dealt with the effectiveness of the United States Patent Policy in protecting IPRs in two industries: software and pharmaceutical. The second research question related to how companies invest in R&D with support of the United States Patent Policy. The study explored the ability of the United States Patent Policy to foster innovation with satisfactory IPR protection to encourage R&D spending focusing on two specific industries. The Software Industry experiences a sequential and complementary nature of innovations, building on previous discoveries; and may not use the patent policy in effect in the United States. If patent policy does not consider the different requirements within the Pharmaceutical Industry and is too lax then enough R&D spending will not be invested and technological advancements, including new medications, may come to the market slower or not at all.
The scope of the study is to understand how the Software and Pharmaceutical Industries use the patent system and how better to adjust the patent system to optimize technological advancement. As discussed in assumptions, because of the nature of the source of data and the possible bias that was not fully known, the assumptions may or may not have had a credible or dependable basis and may therefore have biased the findings. Qualitative designs such as the case study have inherent limitations that may threaten validity, they may lack rigor and they may not be generalizable. These limitations may be mitigated with transparency in data analysis and reporting. Crowe 5 and others explains on page 8 “seeking potential, alternative explanations, and being explicit about how interpretations and conclusions were reached, helped readers to judge the trustworthiness of the case study report.
Evidence from various sources highlight the United States Patent system does not work as intended and needs a solution to continue or increase innovative activity. The principal problem deals with innovative activity that is sequential in nature and innovative activity that involves much R&D investment to bring a product to market. Sequential inventions build on previous breakthroughs and do not require much R&D investment. Secrecy would hinder follow-on discoveries of sequential innovative products.
This study used a content analysis of witness [11] testimonies to Congress on the Software and Pharmaceutical Industries from the years 2005 to 2010, and the possibility to develop more than one patent policy to accommodate different sectors of the economy. The study concentrated on software and pharmaceutical companies, as these two industries are most at odds with each other, and have prevented the passage of the Patent Reform Act of 2005 through 2010. The Patent Reform Act of 2010 [12,13] is the result of non-passage of the 2009 Act, as was each successive year from 2005. The stance of the Software and Pharmaceutical Industries remained relatively unchanged in their requirements, but the patent reform acts changed to incorporate the majority opinion of industry. The most important recommendations of the Federal Trade Commission (FTC 11) and National Academies of Sciences (NAS) studies that were first introduced in 2005 by Senator [14] Lamar Smith were considered.
The purpose of this descriptive analysis was to examine the current United States Patent Policy and the proposed changes to United States Patent Policy, and answer the research question – How do the patent policy requirements differ for the Software and Pharmaceutical Industries? This study will help decide if the Software and Pharmaceutical Industries effectively use the U.S. Patent Policy through protecting Intellectual Property Rights (IPRs) and encouraged investment research and development (R&D). The qualitative case study was the most suitable approach to study the issues and answer the research questions because it explored real-life experiences of industries looking to patent Intellectual Property (IP).
Data and Sample Statistics
Data were collected and analysis began using the Content Analysis Guide developed for this study. The testimonies of the BSA representatives, other computer software witnesses, Computing Technology Industry Association, PhRMA representatives, other generic pharmaceutical representatives, and the Generic Pharmaceutical Association, Biotechnology Industry Association (BIO), Intellectual Property Owners Association (IPO) [15-18], and venture capital organizations were included in this study. The IPO was included because IPO members represent 30% of patent applications at the USPTO and include members from the Software and Pharmaceutical Industries, among others. The study included Venture capitalists because some members of BSA [19] and other smaller software companies began with venture capital dollars. Each data point was examined for inclusion of any reference to R&D, including duration and support for R&D, the need for patent protections [20,21], and future needs for patent policy.
The 38 documents submitted to the congressional hearings were analyzed. Documents relating to software and pharmaceutical companies reviewed were not ambiguous but very clear and straight forward following a consistent format, so that anyone conducting another study would reach the same conclusions. They all stated who authored the document, who the document represented, who presented opinion to Congress, their position on the patent reform act, and agreements and disagreements with specific points of the patent reform act. No ambiguity existed and no information required subjective judgments to interpret the information reported. The nature of the data supported the reliability of the findings.

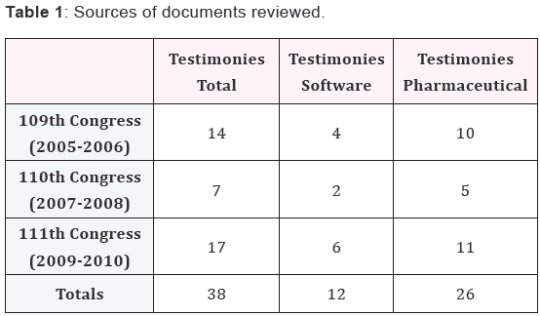

Cisco, Hewlett-Packard, and other big high-tech companies began pushing for reform legislation to limit the number of patent infringement lawsuits and therefore the amounts paid in damages. The United States Patent and Trademark Office’s (USPTO) proceedings’ transcript from the public hearings showed the patent policy needs for BSA’s principle member and founder Microsoft. The public hearing titled Use of the Patent System to Protect Software Related Inventions took place in 1994 at the San Jose Convention Center, California, and at the Crystal Forum in Arlington, Virginia. A brief summary of Microsoft’s speech follows. Microsoft (BSA) recommended that patent protection allow an accused infringer to identify readily the activity forbidden under the claim. The success of a particular claim in meeting these objectives may depend less on the form and more on claim substance and the supporting details.
BSA represents a large base of computer software and hardware companies in the United States. Phelps (2005) from Microsoft Corporation stated that BSA does not want the patent holder to have automatically injunctive relief. Injunctive relief occurs when the courts rule an infringement occurred and automatically issue a ruling to stop the infringer from continuing operations. From the congressional hearing in 2005 on harmonization and other matters, Phelps for BSA supports publication in 18 months. Phelps [39] expressed support for establishing a post grant opposition procedure and supported third-party opportunity to alert USPTO to questionable patents during review. Phelps also supported allowing third parties the opportunity to suggest relevant prior art to examiner during review, supported a limit on damages for willful infringement to include only egregious behavior, and supported limiting damages to only the contributing, patented piece of the invention and not the market value of the whole product, as it is now.
In a congressional hearing in 2005, Simon [40] from Intel , a BSA representative, stated the patent system is difficult to maneuver because of many pieces that comprise computers and software contain “potentially hundreds of patents [that] may be relevant to a particular computer or software technology” [40]. The primary way to challenge a patent under current law is through costly litigation. Intel suggests Congress create a balanced post grant opposition enabling third parties to challenge issued patents that includes a post grant opposition of 2 years from patent grant or 1 year from receiving notice of patent infringement. Simon also encouraged Congress to create a second window to make the post grant review meaningful. Simon suggested a limit on patent application continuations and for the court not to issue a continuation on any claim broader than the broadest claim previously published or issued. BSA suggested a stay on the lower court’s decision in interlocutory appeals before final determination by the Federal Circuit Court of Appeals. Micron Technology, Inc., a non-BSA member, suggested the same patent law reforms as BSA.
In a congressional hearing in 2006, Chandler [41] of Cisco (BSA) suggested a second window triggered by receipt of an infringement complaint. During the first window, the patent issues with thousands or millions of parts making the effectiveness of the patent examination questionable. Chandler (2006) encouraged Congress to make changes to remove venue shopping, and prevent suits from worldwide damages in United States Courts like the Microsoft and AT&T case. The only patent policy need described on the BSA website dated 1994 had no updates, which is understandable because United States Patent Policy has not changed significantly for more than 50 years and the proposed changes have not made it into law. The agreement with the Patent Reform Act was from the most influential voice for the Software Industry; nevertheless, there were disagreements within the Software Industry mainly arising from smaller companies and individual inventors. Software companies wanted patent reform by Congress but differences remained among large software companies and smaller organizations. An overhaul of the patent system and other measures to promote tech development efforts are top priorities of the Business Software Alliance, Cisco, Hewlett-Packard, and other big high-tech companies . BSA members began pushing for reform legislation to limit the number of patent infringement lawsuits, and therefore, the amounts paid in damages.
In an article in PC World dated March 9, 2008, patent reform leads a list of five legislative priorities expressed by BSA in 2008. The opinion article stated that BSA members want Congress to approve the Patent Reform Act but the legislation stalled in the United States Senate because of objections from inventors, pharmaceutical companies and some small tech (computer software) firms. In addition the article proclaimed, more than 170 California businesses and organizations oppose the Patent Reform Act in its current form. They mention that research to stay competitive is both expensive and risky, but strong protections from patent policy attract the necessary investments to commercialize a new product. This is especially the case for the hundreds of smaller, venture capital-backed firms in the state, of which many spun from California’s world-class research universities and private research institutes. According to GlaxoSmithKline, California Wireless and Mi5 Networks in paragraph eight on page one of Gross [42] (2008), the Patent Reform Act “would increase costs to obtain and maintain patents, undermine patent certainty, incentivize infringement, and weaken the enforceability of patent rights and intellectual property protections.”
Dr. Myhrovold [43-45] started Dynamical Systems, a software company, in 1984 that Microsoft bought in 1986. He worked with Microsoft from 1986 to 2000 (14 years). Myhrovold retired from Microsoft in 2000 to start another company, Intellectual Ventures, which files more than 300 patents a year making it the 25th largest inventing organization in America. Dr. Myhrovold stated “[Software is] a complex topic…and it’s all about company culture and how companies use patents” (Perspectives on Patents [46,47]. Continuing Dr. Myhrovold stated “…for most tech companies patents have never been important; they have never been a way to make money” (p. 76, para. 2), and “…patents are, at best, a distraction and most tech companies have made a deliberate decision to ignore the patent system” (p. 76, para. 5). Many other non-BSA members agreed with Myhrovold.
Defensive patenting by software companies explains if a company holds enough patents then this company can steal another product company’s ideas with impunity, but the problem enters when the other entity does not create a product to attack (Myhrovold, 2006, p. 77, para 3). These are the battle lines in the patent reform debate with universities, small inventors and pharmaceutical companies whose lifeblood is the patent system on one side, and companies who decide to infringe or at least do not care about infringing on the other side. Dr. Myhrovold is a witness from the vantage point of a Microsoft senior executive in the 1990s who discussed this role with other firms in the earlier rounds of patent reform debate.
Technology companies exaggerate the problem when over the last 20 years patents have remained in last place of lawsuits for the three forms of idea protection: trademark, copyright, and patents. A study of four high-tech companies that are active in the patent reform debate paid out $3.7 billion in patent lawsuit settlement from 1993 to 2005, but those same four companies earned $1.4 trillion in revenue over the same period making the sums for infringement only 0.26% of revenues on average. The company with the highest number of lawsuits experienced sums for infringement at only 0.51% of revenues. “Patent trolls” are companies that do not market a product but only the idea for a product. Companies that do not produce a product comprise only 2% of the patent infringement lawsuits. Software companies like to blame an innocuous group of patent troll companies when they themselves perform the same litigious practices blamed on trolls. Myhrovold stated the need to embrace the trend to make the alternate resolutions more like a court trial by creating a separate Patent Court, much like the Tax Court, Bankruptcy Court, or Divorce Court to try only specific cases.
Inter Digital is a technology and software company that disagrees with BSA’s proposed changes to patent law. Inter Digital’s Bernstein summarized the differences in the Software industry on page 220 last paragraph at the 2007 congressional hearings: “…the IT industry is absolutely not united in its support for mandatory apportionment, post grant opposition, expansive USPTO rulemaking authority, and interlocutory appeals fall outside the realm of patent ‘reform’.” Bernstein continues by expressing how such an action would degrade patent rights and increase litigation for smaller innovators. The weakening of legitimate patents would protect a few corporate giants and increase the number of lawsuits Bernstein (2007), [48,49].
An article by Mc Dougall [50] and Chabrow (2006), [51,52] in InformationWeek explains the problems as they perceive them with the Patent Reform Act from other software and computer companies. Hans Hxu, founder of online gift registry Felicite.com, says the industry’s large players want the appearance of IP openness but do not practice it. “IBM patents almost everything they do, and then they sit on it, which does not encourage innovation” (Microsoft Agenda, para. 3) says Hxu, a McKinsey consultant although other critics suggest the sellers’ moves cement their advantages when they face rising [53] competition from startups. In an August 2005 essay, Harvard Law School professor and tech entrepreneur James Moore argued the collaborative patent review proposed by IBM, Microsoft, and others would result in fewer patents issued because it would give examiners more ammunition to shoot down patent applications. “If fewer patents are issued, but existing patents are not revoked, IBM and Microsoft win because they already possess vast existing portfolios,” Moore writes (Microsoft Agenda, para. 4). Some Web 2.0 companies dismiss IBM’s argument that business-method patents protect obvious ideas. “Everything is obvious after someone has done it,” says a spokesperson for online movie renter Netflix (Microsoft Agenda, para. 5), which has patents on its queue-ordering system--and is suing Blockbuster for allegedly copying the system.
Small tech companies are taking matters into their own hands, forming patent cooperatives through which they share IPRs. Search company Wink shares in Creative Commons, a group that encourages sharing of copyrights and open source licenses, but there is a line between sharing and protecting intellectual property that creates competitive advantage, says Wink’s Chief Executive Officer (CEO) Michael [54,55] Tanne. “When companies have invested in the development of technologies, they really ought to be able to protect it,” Tanne says (Microsoft Agenda, para. 6). Resolving these issues will influence developing and commercializing tech innovations. Too many lengthy and expensive legal battles will persuade IT departments to stick with familiar technology, and this is something tech vendors should consider as they take one another to court.
The largest and best known pharmaceutical companies in the Pharmaceutical Industry represented by Pharmaceuticals Researchers and Manufacturers of America (PhRMA), Biotechnology Industry Organization (BIO), and the Professional Inventors Alliance disagree with the weakening of patent protection and the long, time frame proposed for patent reexamination. High R&D characterizes these industries and the Pharmaceutical Industry realizes a shortened patent protection because patent protection begins before FDA approval. This shortens patent protection to commercialize the product to the remaining years.
On September 17, 2007, The Professional Inventors Alliance expressed through a letter to President Bush the flaws in the Patent Reform Act of 2007. The Patent Reform Act of 2007 did not pass the United States Senate because of the opposition from PhRMA, small inventors, and small tech firms . The letter from the Professional Inventors Alliance expressed that if the Patent Reform Act of 2007 passed into law it would harm the United States’ innovative character because of the inability to enforce patents and would reduce the royalties associated with a patented technology. In 1980, PHRMA’s members invested $2 billion in R&D for new medicines; although, nearly 30 years later (in 2009), PHRMA’s members invested $50.3 billion in R&D out of the $65.2 billion industry-wide total. Pharmaceutical companies rely on government-granted patents to protect their substantial investments in researching and developing new drugs. It takes 10-15 years and costs $800 million on average to bring a new medicine to market. The Pharmaceutical Research and Manufacturers of America (PhRMA) represents the country’s leading pharmaceutical research and biotechnology companies.
Without patents to protect all the inventions necessary to develop a drug for a limited time, others could simply copy the drugs immediately, offering their versions at a reduced price because they did not incur the high costs to develop the drug. This would seriously affect the pharmaceutical companies’ ability to recoup their costs and reinvest in other research projects. PhRMA stated in 2010 that “a strong patent system is crucial to our economic [56,57] competitiveness, especially in these economically trying times” (PhRMA’s website, 2001, p. 1). The companies in favor and against the Patent Reform Act of 2010 divided into the companies that have favored and opposed the previous patent reform acts, that is, computer software favoring patent reform and pharmaceutical companies and biotechnology companies opposing patent reform. Those opposing and in favor of the patent reform acts through the six years in this study have not changed their needs but, instead, Congress changed trying to create a patent policy agreeable to most patent users.
The large pharmaceutical companies also known as the name brand pharmaceutical companies and the smaller, generic pharmaceutical companies were in general agreement on most issues. Both wanted strong patent protection and both sides were against the Patent Reform Bill [58] of 2005 and 2006 as stated in the congressional hearings on patent reform. The firstinventor- to-file patent system while harmonizing with the large United States trading partners also poses some difficulties and disagreements with United States patentees. The problems lay in the grace period of 1-year and the best mode requirement in the patent application. Harmonizing with other countries’ patent systems as currently written, such as Japan and Europe, would remove the United States grace period of 1 year to file a patent application and would remove the best mode requirement when filing a patent application. The best mode requirement is the descriptive part of the patent application the inventor has to include the inventor’s idea of how best to use or combine the chemicals for complete effectiveness.
The differences between the brand name and generic pharmaceutical companies lay in eliminating the best mode factor of the patent application and the inequitable conduct defense. Brand name pharmaceutical companies say the best mode provision of the patent law is subjective, and therefore should be removed. The generic pharmaceutical companies believe the best mode provision should remain because they cannot copy the patented medication without the recipe or the “best mode” of making the drug. By removing the inequitable conduct defense, brand name pharmaceutical companies will misuse the patent system to the harm of the public and generic pharmaceutical companies. Differences exist between the brand name pharmaceuticals and the generic pharmaceuticals. One example is the issue of patent quality: Best mode. Generic pharmaceuticals want to keep the “best mode” in the patent law language because it lowers cost of medications by allowing generic companies to copy name brand drugs more easily. Ely Lilly [59,60] and PhRMA want to remove the best mode language . The Generic Pharmaceutical Association also has qualms with weakening the inequitable conduct saying that weakening this provision gives brand-name pharmaceutical companies incentive to misrepresent their inventions.
The differences between the brand name and generic pharmaceutical companies lay in eliminating the best mode factor of the patent application and the inequitable conduct defense. Brand name pharmaceutical companies say the best mode provision of the patent law is subjective, and therefore should be removed. The generic pharmaceutical companies believe the best mode provision should remain because they cannot copy the patented medication without the recipe or the “best mode” of making the drug. By removing the inequitable conduct defense, brand name pharmaceutical companies will misuse the patent system to the harm of the public and generic pharmaceutical companies. Differences exist between the brand name pharmaceuticals and the generic pharmaceuticals. One example is the issue of patent quality: Best mode. Generic pharmaceuticals want to keep the “best mode” in the patent law language because it lowers cost of medications by allowing generic companies to copy name brand drugs more easily. Ely Lilly [59,60] and PhRMA want to remove the best mode language . The Generic Pharmaceutical Association also has qualms with weakening the inequitable conduct saying that weakening this provision gives brand-name pharmaceutical companies incentive to misrepresent their inventions.
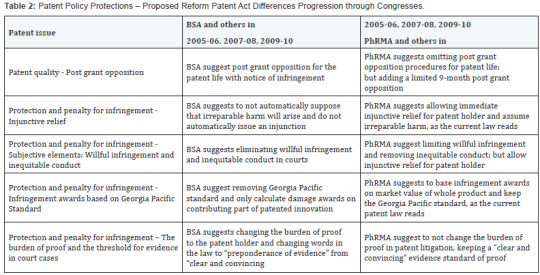
Together the Case Lawre presented the most comprehensive line of court-led patent reforms, which makes patent reform substantially different in 2010 than 2005. Patent lawyers and the law association, AIPLA [63,64], believe that legislation is not necessary and the court system will eventually find a solution for compromise for the different users of the patent system and will define patent law through successive Case Law. Larger, more market capitalized firms make more noise and are heard more clearly than smaller, less capitalized companies or individual inventors, including companies that specialize in innovation but do not concurrently produce a product, also known as patent trolls. More innovation comes from smaller firms and individual inventors than large entities. The larger software enterprises that often infringe on patents held by companies that do not produce a product (patent trolls) behave similarly to the patent trolls. IBM and Microsoft sit on patents without an accompanying product, when another company discovers something similar the patent surprises the unsuspecting company, and a licensing or royalty agreement can avoid costly litigation. IBM earned over a billion dollars in 2005 solely from license agreements and royalties. Licensing and royalty agreements are another possible direction that companies take to avoid patent infringement suits; however, their use threatens other companies to ransom licensing or royalty agreements but is cheaper and the outcome more certain than litigation.
The Pharmaceutical Industry appreciates the current patent policy and is leery of any changes that would disrupt the current manner in which they use the patent system to optimize patent protection; also the Pharmaceutical Industry like the Software Industry makes the best of the current patent policy . Although pharmaceutical firms have to wait until after drug trials and resulting FDA approval to market the medication, which includes the 20-year patent term and drug approval sometimes lasts as much as 10 years, they too have found ways to evade current patent law to extend the patent length. The Pharmaceutical Industry commonly increases the shortened patent length by adding a known chemical to the patent protected drug therapy, and adds another patent protection term of 20 years by increasing the number of patents on a drug. One specific drug therapy created by a name-brand pharmaceutical firm that a generic company was exploring to copy had patent protection by more than 200 patents spanning 40 years.
Discussion and Conclusions
The specific research questions that framed this qualitative case study were 1. What is the evidence United States Patent Policy adequately protects Intellectual Property Rights [65] (IPRs) for both the Software and Pharmaceutical Industries? 2. How does the United States Patent Policy encourage companies to make research and development (R&D) investment in both the Software Industry and in the Pharmaceutical Industry? Based on the differences on how patent policy should read, issues of effectiveness of the United States Patent Policy to both protect and encourage IPRs and R&D investment should be considered. Patent policy in the United States has remained unchanged for the last 55 years, and has been effective in protecting IPRs and encouraging R&D investment. Pharmaceutical firms have been around many years and have flourished in the current patent policy environment. Only with the creation of the personal computer have software companies entered the scene and have expressed concern for the patent policy changes to reduce the software company’s purposeful infringement. In a few words, the large software companies want to weaken patent protections and reduce their costs to defend against patent infringement lawsuits because big software companies do not care about patents or patent infringement.
Three important findings from this study are
1. The Pharmaceutical and Software Industries use patent policy differently
2. BSA explicitly states they want a strong patent policy, but, in effect, want to weaken the current patent policy, and
3. Differences exist within each industry. Congress has attempted to improve patent law 6 years without success because there is not agreement pleasing all industries, but the principle differences embodied the Software and Pharmaceutical Industries.
Firstly, pharmacy and software use patent policy differently: Pharmacy to protect R&D and Software for defensive purposes. Software Industry (BSA) does not use the patent policy as designed to protect R&D, but to defend against the threat of patent infringement lawsuits. The testimonies to Congress provided evidence to answer my research question of how the patent policy requirements differ between the Software and Pharmaceutical Industries. The testimonies to Congress were clear and straightforward. I did not have to infer the meaning or needs of the witnesses. They clearly stated their position and what they wanted in patent policy. Many people in the Pharmaceutical Industry and smaller software companies specifically stated that larger software and computer companies began calling for patent reform to limit the many patent infringement suits against them. Myhrovold shared his experience working for Microsoft in the late 90s stating that large software companies are not concerned with infringing on another’s patents and the only reason they care at all about patents is to defend against patent infringement lawsuits.
Secondly, the data from congressional testimonies clearly showed that the Software Industry (BSA) verbalized they want a strong patent policy but, instead, they want to weaken the rights of patent holders. This weakening is from: An unlimited post patent review period, placing the burden of proof for infringement on the patent holder (instead of the offender), and limiting the damage awards for infringement to only the infringing part of an innovation. The testimonies clearly stated their position and what they wanted. The previous list clearly communicated to Congress what the Software Industry (BSA) wanted in a patent policy, and refuted by other expert testimonies in the Software Industry.
All BSA representatives stated they wanted strong patent protection, and continued with the above reasons, which amount to weakening a patent holders’ legal rights to their Intellectual Property Rights (IPRs). Many testimonies contrary to BSA stated specifically the reasons BSA wants to limit a patent holders’ IPRs is to stave off patent infringement lawsuits. Myhrovold (2006) shared that patent policy did not enter into Microsoft’s and other BSA members’ culture. Patents are not how software companies protect innovation, but, rather, secrecy, and lead time or economies of scale are more effective to protect innovation in a short product lifecycle industry. Thirdly, the entire Software Industry is not united with BSA, and the entire Pharmaceutical Industry is not united with PhRMA. Differences exist between the two industries and differences exist within each industry, such as difference between larger companies and smaller companies in Software Industry and brand name pharmaceutical versus generic pharmaceutical. Each expert clearly stated what they wanted, why they wanted it, and differences within their respective industries. The witnesses to the congressional hearings succinctly stated that the BSA or PhRMA did not represent the entire industry, and the industry was not united in its desires for patent policy. Siwik [66] said in the exact words that the Pharmaceutical Industry is not united, and based on the non-BSA members’ testimonies with them vehemently disagreeing with BSA’s stance, anyone would reach the same conclusions that BSA is far from united too.
The evidence suggests the two industries use patent policy in different ways. For instance, The Software Industry does not use the patent system to protect intellectual property but rather use the patent system for defensive purposes not so much to protect innovation but to defend against infringement lawsuits. Pharmaceutical industry relies heavily on a patent protection to recover large R&D spending. The evidence was found in examples of how each industry effectively uses the patent system. Based on research of the patent system and the evidence of how each industry uses the patent system, the data would suggest agreement with many of the pharmaceutical, biotechnology, and other industries that use the patent system effectively to protect research and development dollars that the system does not need major change. Research shows the answer to the question of how the United States Patent System encourages R&D and promotes innovation; the patent system performs well according to its design. It protects ideas. The current patent policy is effective in protecting innovation and encouraging research and development spending.
For more Open Access Journals please visit our site: Juniper Publishers For more articles, please click on Journal of Organic Medicinal Chemistry
0 notes
Text
Daily Forex Signals
Daily Forex signals are trading recommendations provided on a daily basis. These signals indicate optimal entry and exit points for various currency pairs, helping traders make informed decisions. They are generated through a combination of technical analysis, fundamental analysis, and market sentiment analysis performed by experienced traders or sophisticated algorithms. How Do Daily Forex Signals Work? Daily Forex signals typically include the following components: - Entry Point: The price level at which a trader should enter the market. - Exit Point: The price level at which a trader should close their position to secure profit or limit loss. - Stop Loss: A predetermined price level at which the trade will automatically close to prevent further losses. - Take Profit: A predetermined price level at which the trade will automatically close to lock in profits. These signals are often delivered through various channels such as email, SMS, mobile apps, and trading platforms. Traders can choose to act on these signals manually or integrate them into automated trading systems. Benefits of Using Daily Forex Signals 1. Timeliness: Daily signals ensure traders receive up-to-date recommendations based on the latest market conditions, allowing them to act quickly on trading opportunities. 2. Expert Analysis: Signals generated by experienced traders or advanced algorithms provide valuable insights and enhance the accuracy of trading decisions. 3. Convenience: Receiving daily signals saves traders the time and effort required for continuous market analysis, enabling them to focus on executing trades. 4. Consistency: Daily signals help traders maintain a disciplined and consistent approach to trading, reducing emotional decision-making. Risks and Considerations While daily Forex signals offer numerous advantages, it is essential to be aware of potential risks and considerations: - Accuracy: The accuracy of signals can vary. It is crucial to choose reputable providers with a proven track record. - Over-reliance: Relying solely on signals without understanding the underlying market dynamics can be risky. Traders should use signals as part of a broader trading strategy. - Market Conditions: Signals may not perform well in all market conditions. Traders must adapt and adjust their strategies based on changing market environments. Choosing the Right Daily Forex Signal Provider When selecting a daily Forex signal provider, consider the following factors: 1. Reputation: Look for providers with positive reviews and a history of delivering accurate signals. 2. Transparency: Ensure the provider offers clear information on how signals are generated and provides performance data. 3. Trial Period: Opt for providers that offer a trial period to test the quality and reliability of their signals. 4. Support: Good customer support can help address any questions or issues that may arise. How to Get Started 1. Research Providers: Start by researching and comparing different daily Forex signal providers. Look for those with strong reputations and positive user feedback. 2. Understand the Signals: Take time to understand the reasoning behind the signals you receive. This will help you develop your trading knowledge and skills. 3. Implement Risk Management: Use stop-loss and take-profit levels as recommended by the signals, but also have your own risk management strategy in place. 4. Stay Informed: Keep yourself updated on market news and trends. This will help you make more informed decisions and better understand the signals you receive. Conclusion Daily Forex signals can be a powerful tool for traders seeking timely and accurate trading recommendations.
0 notes
Text
CONTRACT RESEARCH ORGANIZATION LIST Is Crucial To Your Business. Learn Why!
CONTRACT RESEARCH ORGANIZATION LIST Is Crucial To Your Business. Learn Why!

1. What is a contract research organization (CRO)?
A contract research organization (CRO) is defined as a company that provides services to the pharmaceutical, biotechnology, and medical device industries to help them outsource and conduct clinical trials. A CRO may also provide other services such as laboratory testing, regulatory affairs consulting, and marketing research.
The main reason why pharmaceutical and biotech companies use CROs is to save time and money. Conducting clinical trials is a very costly and time-consuming process. Therefore, by outsourcing this process to a CRO, companies can focus on their core competencies and save on costs.
CROs are classified into two main types: full-service and functional. Full-service CROs offer a complete range of services from start to finish, whereas functional CROs only offer specific services such as data management, biostatistics, or regulatory affairs.
The global CRO market was valued at around $32.5 billion in 2018 and is expected to grow to $42.8 billion by 2024, at a CAGR of 5.1%. The increase in demand for CROs is mainly due to the growing number of clinical trials, the increasing complexity of these trials, and the rising costs of conducting these trials.
The top 10 CROs in the world are Parexel, IQVIA, Charles River Laboratories, Laboratory Corporation of America Holdings (LabCorp), Covance, INC Research Holdings, Inc., ICON plc, Fujirebio, and WuXi AppTec Contract research organization list.
2. What are the benefits of using a CRO?
A CRO can provide a number of benefits to a company, including access to expertise and resources, cost savings, and increased efficiency. Here are some of the ways a CRO can help your business:
1. Access to Expertise and Resources
One of the main benefits of using a CRO is that it gives you access to a team of experts with a wealth of experience and resources. This can be especially helpful if you are a small or start-up company with limited in-house resources. A CRO can help you with everything from designing and conducting clinical trials to analyzing data and preparing regulatory submissions.
2. Cost Savings
Another benefit of using a CRO is that it can save you money. Hiring a CRO can be more cost-effective than hiring full-time staff or consultants. Additionally, a CRO can help you optimize your clinical trials, which can lead to reduced costs.
3. Increased Efficiency
A CRO can also help you increase the efficiency of your clinical development program. A CRO can help you streamline processes, reduce duplication of effort, and improve communication. This can help you get your products to market faster and improve your bottom line.
4. Flexibility
Another benefit of using a CRO is that it provides you with flexibility. A CRO can help you scale up or down your clinical development program as needed. This can be helpful if you have a limited budget or if you need to quickly ramp up your program.
5. Focus on Your Core Business
Using a CRO can also help you focus on your core business. By outsourcing your clinical development program, you can free up your time and resources to focus on your core competencies. This can help you improve your overall business performance.
3. How can a CRO help your business?
A contract research organization, or CRO, is a company that provides research and development services to pharmaceutical and biotechnology companies on a contract basis. A CRO can help your business in a number of ways, including:
1. Conducting clinical trials
One of the main services that a CRO can provide is conducting clinical trials. A clinical trial is a research study that is done in order to test a new medical treatment, drug, or device. Clinical trials are essential in order to get new treatments approved by the FDA. A CRO can help you by conducting clinical trials on your behalf.
2. Managing regulatory affairs
Another way that a CRO can help your business is by managing regulatory affairs. Regulatory affairs is the process of getting a new medical treatment, drug, or device approved by the FDA. This process can be very complex and time-consuming. A CRO can help you by managing the regulatory affairs process on your behalf.
3. Providing market research
A third way that a CRO can help your business is by providing market research. Market research is the process of collecting data about the market for a particular product or service. This data can be used to make decisions about marketing and product development. A CRO can help you by conducting market research on your behalf.
4. Managing clinical data
A fourth way that a CRO can help your business is by managing clinical data. Clinical data is the data that is collected during clinical trials. This data must be managed in a certain way in order to be useful. A CRO can help you by managing clinical data on your behalf.
5. Providing other services
In addition to the services listed above, a CRO can also provide other services that can help your business. These services can include project management, financial management, and administrative support.
4. What should you look for in a CRO?
A Contract Research Organization (CRO) is a company that provides services to the pharmaceutical, biotechnology, and medical device industries. CROs offer a variety of services, including clinical research, data management, biostatistics, and regulatory affairs. CROs help companies to develop new drugs and therapies and bring them to market faster.
When choosing a CRO, it is important to consider the following factors:
1. Services offered: Make sure that the CRO you choose offers the services you need.
2. Experience: Choose a CRO with experience in your therapeutic area and with the type of study you are planning.
3. Location: Consider the location of the CRO and whether it is convenient for you and your study participants.
4. Cost: Get quotes from several CROs and compare their prices.
5. References: Ask for references from companies that have used the CRO's services.
When selecting a CRO, it is important to choose one that is a good fit for your company and your needs. By considering the factors above, you can be sure to select a CRO that will help you successfully develop and bring new drugs and therapies to market.
5. How do you choose the right CRO for your business?
Choosing the right CRO (contract research organization) for your business is crucial to ensuring the success of your clinical trials. With so many CROs to choose from, it can be difficult to know where to start. Here are five tips to help you choose the right CRO for your business:
1. Define your goals and objectives.
Before you start looking for a CRO, it is important to know what you want to achieve with your clinical trial. What are your goals and objectives? What are your key performance indicators? Once you have a clear idea of your goals, you will be able to narrow down your search to CROs that have experience in your particular area.
2. Consider your budget.
CROs can vary widely in terms of cost, so it is important to consider your budget when choosing a CRO. You should get quotes from several CROs to get an idea of the range of prices. Keep in mind that the cheapest CRO may not necessarily be the best option for your business.
3. Check the CRO’s credentials.
Make sure to check the credentials of any CRO you are considering. What is their experience in conducting clinical trials? Do they have a good track record? Are they accredited by any reputable organizations? Checking the credentials of a CRO will give you peace of mind that you are working with a reputable and experienced organization.
4. Ask for references.
When you are considering working with a CRO, be sure to ask for references. Talk to other companies that have worked with the CRO to get their opinion on the quality of the services provided.
5. Meet with the CRO.
Once you have narrowed down your choice of CROs, it is important to meet with them in person. This will give you a chance to ask any remaining questions and to get a feel for the CRO’s culture and values.
Choosing the right CRO for your business is vital to the success of your clinical trial. By following these tips, you can be sure that you are working with a reputable and experienced organization that will help you achieve your goals
0 notes
Text

#Enroll Now | Our Private K-5th iPlanets Academy In-Home Hybrid Homeschool & Summertime Learning is with Mimi who is also homeschooling her s#Texas 75126.#https://lnkd.in/gXBdpxAn#THEME: DINOSAURS | FOSSILS#CARNIVORES (meat-eaters)#This Hybrid Homeschool Class is for Drop Off ONLY.#Membership enrollment must be paid and all enrollment paperwork must be filled out completely BEFORE you can attend a class.#Drop ins are $35.00 daily#subject to availability#and limited to 4 times on a trial basis.#Dedicated Hybrid Homeschool Classes:#3 days | Tues-Thurs | 10:00 AM-2:00 PM | $420.00 Monthly#4 days | Tues-Thurs | 10:00 AM-2:00 PM | Sat 10:00 AM-5:00 PM $560.00 Monthly#5 days | Tues-Fri 10:00 AM-2:00 PM | Sat 10:00 AM-5:00 PM | $700.00 Monthly#Monthly Supplies#Uniforms#Meals#and Educational Field Trips are not included. We accept dues by Cash#Paypal#CashApp#or ApplePay. NON-TRANSFERABLE/NO REFUNDS#NO EXCEPTIONS!#Enrolling now for our Fall/Winter session: Hybrid Homeschool Classes Sept 6#2022-May 27#2023 Registration is $100.00 Cash#Our Educational Space: https://lnkd.in/eRHUvTxP#Please Like and Share our page#and check out our parent reviews on Facebook and testimonials on our website. They love us as much as we love them! https://lnkd.in/diXBCYK#For more information#to see all of our guidelines
9 notes
·
View notes