#ageingintelligence
Explore tagged Tumblr posts
Text
Report from UN Science Summit 2024/ Reimagining urban futures: how cities can champion longevity and prevention using novel approaches, tools, and data.
On September 20th, 2024, at the United Nations Science Summit in New York, a distinguished panel of experts convened to discuss a vision that could revolutionise our urban landscapes for healthy longevity.
The session, titled "City of Longevity: Making Cities Champions of Prevention," marked the global premiere of NICA’s City of Longevity toolkit, a comprehensive and articulated program designed to transform evidence into actionable solutions, creating "healthy longevity formulas." This proprietary methodology and software can be used interactively with citizens or enhanced with AI support.

Frame from City of Longevity toolkit.
Drawing on this revolutionary foundation, the session brought together diverse perspectives from urban planning, gerontology, economics, and public health. As the moderator of this ground-breaking discussion, Prof. Nic Palmarini had the privilege of guiding a conversation that not only highlighted the challenges we face but also illuminated a brighter path forward for healthier, more resilient cities.

The Urgent Need for Urban Health Transformation
Our cities are at a crossroads. With rapidly ageing populations and increasing chronic disease burdens, urban centres worldwide are grappling with unsustainable healthcare costs and declining quality of life for many residents. Dr. Lars Hartenstein, co-founder of the McKinsey Health Institute, aptly summarized our current predicament: "We have a narrative and an action gap." We know what needs to be done, but translating that knowledge into concrete action remains a significant challenge. The City of Longevity approach provides a clear framework for real action.
The panel unanimously agreed that a paradigm shift is necessary. As Prof. Dr. med. Elisabeth Steinhagen-Thiessen from Charité – Universitätsmedizin Berlin emphasised: "We produce these chronically ill people. This is the story. Normally, we should heal the diseases. We don't do that." This stark assessment underscores the need to move from a reactive healthcare model to a proactive, preventative approach.
A Holistic Approach to Urban Health
Horacio Terraza, Urban Lead at the World Bank and the Inter-American Development Bank, stressed the importance of comprehensive urban planning. "We need to think city-integral," he stated, highlighting the interconnectedness of urban systems and their collective impact on health. This holistic view includes everything from transportation and housing to green spaces and social services.

Horacio Terraza, The World bank
Data-Driven Decision Making and Measurable Outcomes
Dr. Yochai Shavit, Director of Research at Stanford Centre on Longevity, emphasised the critical role of data and research in guiding longevity initiatives. "What we need to think about is where research is required to set benchmarks and establish clear goals for people to pursue," he noted. This call for measurable outcomes resonated throughout the discussion, with panellists agreeing that cities need concrete targets to become longevity champions.
The potential of artificial intelligence and big data analytics to accelerate this process was a recurring theme. These technologies offer unprecedented opportunities to identify health trends, predict risks, and tailor interventions to specific populations.

Yohcai Shavit, Stanford Centre on Longevity
Citizen Engagement: The Heart of Healthy Cities
One of the most powerful messages to emerge from the panel was the crucial role of citizen participation. Prof. Lynne Corner, Deputy Director at NICA and Co-Founder of the Edelman Longevity Lab, passionately advocated for this approach, stating, "Citizens as co-creators, co-designers of this journey of longevity are absolutely essential."
This sentiment was echoed by Dr. Joachim Rautter, Managing Director of the Berlin Innovation Centre for Ageing and Longevity, who shared insights from Berlin's grassroots movements. "What we are currently trying to do in Berlin is a bottom-up approach from the citizens' level," he explained, illustrating how community-driven initiatives can catalyse city-wide change.
The panel agreed that successful longevity initiatives must balance top-down policy approaches with grassroots citizen movements. By involving residents in the design and implementation of health initiatives, cities can ensure that interventions are culturally relevant, widely accepted, and effectively address local needs.

Lynne Corner, NICA+VOICE
Economic Implications and the "Business Model for Prevention"
The discussion also delved into the economic aspects of urban longevity initiatives. Prof. Dr. med. Elisabeth Steinhagen-Thiessen highlighted the workforce implications, noting, "When we have so many chronically ill elderly by the age of 55, we lose all these people. They could have worked; they could have been healthier."
This led to a critical insight: investing in prevention and longevity isn’t just about reducing healthcare costs—it’s about maintaining a productive, engaged workforce and fostering economic vitality. As Prof. Lynne Corner pointed out, "We have no business model for prevention, and that’s the opportunity to shift our thinking towards developing one. This must become the norm."
The panel explored how cities could incentivise businesses to invest in employee health, create age-friendly workplaces, and develop products and services that promote longevity. The potential for a "longevity economy" emerged as an exciting prospect, with opportunities for innovation and growth across various sectors, from health tech to urban design.
Cultural Relevance and Local Solutions
A key takeaway was the importance of tailoring longevity initiatives to local cultures and contexts. As I noted during the panel, "Don’t give people cherries if they like strawberries. You have to leverage cultural factors in cities." This was illustrated by Prof. Dr. med. Elisabeth Steinhagen-Thiessen's example of a successful strawberry trial in Rostock, Germany, which improved participants' health while fostering community engagement.
The panel agreed that while global knowledge-sharing is crucial, solutions must be adapted to fit local cultures, preferences, and resources. This approach ensures higher adoption rates and long-term sustainability of health initiatives.
Addressing Social Determinants of Health
Throughout the discussion, the importance of addressing social determinants of health was a recurring theme. As noted in the introductory remarks, individual behavior and social circumstances account for about 60% of health outcomes. This underscores the need for cities to look beyond traditional healthcare and consider factors such as housing, education, income inequality, and social cohesion in their longevity strategies.
Dr. Lars Hartenstein emphasised the need for targeted interventions, noting that different population segments may require distinct approaches. For instance, middle-income groups may face unique health challenges that demand specific attention.

The Role of Technology and Innovation
The potential of technology to accelerate progress in urban health was a topic of great interest. From AI-powered health risk assessments to smart city infrastructure that promotes physical activity, the panel explored various ways in which innovation could support longevity initiatives.
However, the experts cautioned against over-reliance on technology. As Dr. Joachim Rautter noted, "You need all the stakeholders in the field, including the big brands." This reminder emphasised the importance of human connections and community engagement alongside technological advancements.
Moving from Knowledge to Action
A consistent theme throughout the discussion was the urgent need to translate knowledge into concrete action. As Dr. Lars Hartenstein pointed out, "We already know so much. We could act comprehensively based on what we know today."
As the session concluded, one thing was clear: the path to longevity doesn’t just run through our hospitals or research labs; it weaves through our streets, schools, workplaces, and communities. The City of Longevity provides a blueprint and a practical solution for a healthier, happier future for all, based on:
A spirit of strengthened global solidarity;
Connecting different agendas because we are better together;
Breaking down silos to create practical solutions;
Sharing data-driven approaches;
Open, flexible, and updatable frameworks;
Building on what's working with "immediately actionable interventions" that focus on the most vulnerable and involve all stakeholders, from countries to communities.
Bridging the Implementation Gap
The panel explored various strategies for bridging the current implementation gap, including:
Creating cross-sector partnerships between government, business, academia, and community organisations;
Accelerating pilot projects to test and refine longevity initiatives locally before scaling them up;
Establishing knowledge-sharing "longevity formulas" between cities to accelerate the adoption of best practices;
Investing in public education and awareness campaigns to empower citizens to make healthier choices;
Advocating for policy changes that support preventative health measures and age-friendly urban design.

Conclusion: A Call to Action for Cities Worldwide
As our panel discussion drew to a close, one thing was abundantly clear: transforming our cities into champions of longevity and prevention is not just desirable—it’s urgent and imperative. The challenges we face, from aging populations to rising chronic disease rates, demand a fundamental reimagining of our urban environments.
But this transformation also represents an unprecedented opportunity. By investing in longevity, cities can improve the health and well-being of residents, drive economic growth, foster innovation, and create more resilient, sustainable environments and communities.
The path forward will require collaboration on an unprecedented scale. It will demand breaking down silos between sectors, engaging citizens as true partners, and reimagining long-standing systems and practices. The City of Longevity represents a practical step towards making this vision a reality.
As we concluded our session at the UN Science Summit, there was a palpable sense of optimism and determination among the panellists and the audience, who joined remotely from multiple global locations.
The City of Longevity is not just a distant ideal—it’s a practical blueprint for a healthier, happier urban future.
To all those reading this—whether you're a city official, a business leader, a healthcare professional, or a concerned citizen—we invite you to join us.
Together, we can transform our cities into beacons of health, vitality, and longevity for generations to come. The future of urban health is in our hands. Let’s build it together.

Yocahi Shavit, Lynne Corner, Horacio Terraza, Joachim Rautter, Lars Hartenstein with moderator, Nic Palmarini.
1 note
·
View note
Text
Innovation against isolation and loneliness and the role of cities.
Nic Palmarini, Director, UK's National Innovation Centre for Ageing.
The four horsemen vs. the wonder drug.
We know very well who are the Four Horsemen of the Apocalypse who - typically in late adulthood - come banging on the door of our lives and who amount to over 80% of deaths in people over 50 who do not smoke: Atherosclerotic disease (comprised of cardiovascular disease and cerebrovascular disease), Cancer, Neurodegenerative disease (Alzheimer's disease being the most common) "Foundational disease", a spectrum of everything hyperinsulinemia to insulin resistance to fatty liver disease to type 2 diabetes.
We know just as well that to counter them, besides the science on which the redeeming business model of cure is based, there is only one actual wonder drug: prevention. The literature is vast and consolidated on choices and virtuous behaviours: sleeping well, staying active, a balanced diet, keeping the mind engaged and sustained by a purpose, and a strong network of relationships.
On the first four aspects, much technology has made its fortune in recent years by exploiting the mobile + IoT boom boosted by increasingly effective and sophisticated machine learning systems thanks to the mass of data generated by us, with thousands of applications combined with sensors to measure performance, metabolism, stress or the level of attention, in other words, our quantified self. Much less, however, has been done to help us live 'with' and 'in' a society whose social and economic dynamics are prone to exacerbate phenomena such as isolation and loneliness. It must be admitted social connection - the structure, function, and quality of our relationships with others - is still an underappreciated contributor to individual and population health, community safety, resilience, and prosperity.
Technology-supported innovation solutions have mainly focused on care - formal or informal - led by the American trailblazers (the historic Papa and Honor, the now defunct Heroes, and the rising star CareYaya), which have inspired hundreds of start-ups all over the world that have literally copied their logic and services, and then declined some aspects of it until arriving at the various' grandchildren rental' we have in Italy. A mainly "care-like" approach, we were saying. Without forgetting the founding pillars of Apple, Meta, Google, and Amazon - the enablers of the digital dynamics of relationships - who invest in innovation to promote relationship, engagement, participation, and inclusion?
In fact, the first question would be: what kind of society finds itself renting grandchildren to make up for its lack of essential interaction? To answer - however superficially and without opening what would be a necessary chapter on the founding values of each culture - we are obliged to refer to an 'advanced Western society', even in its relational decline. It is no coincidence, in fact, that grandchildren rentals are the clone of what, eight years ago, it seems like a geological era, Chuck McCarthy observed in Los Angeles as a dramatic social phenomenon and - to that - responded with The People Walker [1].
Faced with the emergence of the isolation of men and women in the inner cities as well as in the suburbs of middle-class America, and well before the phenomenon was amplified by a devastating event such as the COVID-19 pandemic, McCarthy accompanied hundreds of strangers on foot for thousands of miles walking people who were isolated in their home and without anybody to have a walk with, to earn a few extra bucks and get himself out of the house more too.

"Twice a week for the past month, I've paid an underemployed actor $30 an hour to walk me through the hills of L.A. like a Labrador. Chuck McCarthy isn't a dog walker, though; he's a people walker."
Attesting to a cultural difference between the smooth social fabric of U.S. megacities where larger cities are basically two-tiered (a wealthy downtown professional class relies on inexpensive labourers who can't afford to live near their workplace or drive a car; who are forced into long commutes creating a sort of a social vacuum) and that of old Europe is as obvious as it is necessary.
Europe, particularly Italy, has a profoundly different urban context, population distribution and social fabric. Without going into the merits of factors such as population density per square kilometre or the role of the Church, one fact suffices: in Italy, among people aged 75 and over, 51% live no more than one kilometre from their nearest child and 20% live with them. Only 8.9% have no children and live alone, and only 0.9% have children far away abroad[1]. And yet, even though this figure is all in all an exceptional dimension, isolation is a phenomenon that - in the face of a society that is progressively older, urbanized and increasingly enveloped in the violent polarization of its digi-social loops - shows all its disturbing pervasiveness.
Isolation and loneliness are not the same thing.
Social isolation and loneliness are often cited as one Siamese brothers, inextricably linked. But they are not the same thing.
We have often associated old age with loneliness out of principle or narrative convenience because, all things considered, it is more effective and easier to narrate. Loneliness is a feeling that develops when there's a perceived difference between desired and actual levels of social interaction, meaning, and relationships. Loneliness is a subjective state and more easily strikes the imagination because it appeals to that feeling we all know well, that fear we all had as children when, for a second, we lost sight of the reassuring face of mum or dad. We felt lost, abandoned, and deprived of that need for care that accompanies puppies of all species like the whole life suddenly has no meaning. We felt lonely. Imagining an older man alone strikes at the heart because it strikes at our childhood self.
And so, we talk about the 'pandemic of loneliness', not distinguishing it from isolation, which instead refers to social relationships, social roles, group membership and the social interactions that ensue. Not only that, isolation relates to not only 'presence' but also to inclusion. Its form is, therefore, more insidious and more challenging to portray. People living alone can still feel content with their level of social activity, and people physically surrounded by others can still feel lonely and disconnected.
The relationship between isolation and loneliness is dynamic and interconnected, where one dimension contributes to triggering the other with often devastating consequences. But the triggering process seems straightforward. An observational Harvard study published in SSM–Population Health sought to find out if one problem might be more dangerous than the other. Researchers analysed the health data of almost 14,000 people (ages 50 or older) who were followed for four years. Both loneliness and isolation were associated with poor health outcomes. But, social isolation was a stronger predictor of physical decline and early death. Loneliness was more predictive of mental health issues, such as depression or feeling that life had no meaning[2].
In ancient times, humans relied on social bonding and communication with others for "mutual aid and protection"; becoming socially isolated was essentially a risk to one's survival and almost a sentence to death. Today, we have enough data to give dimension to the evidence that common sense has always suggested. The lack of social connection poses a significant risk to individual health and longevity. “Loneliness and social isolation increase the risk of premature death by 26% and 29%, respectively. More broadly, lacking social connection can increase the risk of premature death. In addition, poor or insufficient social connection is associated with an increased risk of disease, including a 29% increased risk of heart disease and a 32% increased risk of stroke. Furthermore, it is associated with an increased risk for anxiety, depression, and dementia. Additionally, the lack of social connection may increase susceptibility to viruses and respiratory illness”[3].
Although these data refer to late adulthood, which is the subject of our interest on this occasion, to think that loneliness and social isolation are phenomena of old age is a distortion, again, driven by common stereotypes such as thinking of young age as that of lightness, carefreeness, social relations and therefore free from the phenomena of disconnection and participation. We know very well that this is not the case, and recent data, in some worlds, suggested by the Pandemic, have indeed shown us the extent and seriousness of these phenomena for the younger generations with a particular risk of social isolation not only experienced but also simply perceived.
These include and are amplified by changes in peer development, autonomy development, identity exploration, cognitive maturation, social perspective development, and physical maturation. This is baggage whose weight then spills over throughout life with consequences that are still difficult to measure objectively longitudinally but which to ignore would be a colossal mistake both contextually and prospectively. It, therefore, becomes clear that in the face of this scenario, social isolation and the resulting risk of loneliness no longer represent a mere contextual dimension to the horsemen of the apocalypse: they are often its initiator and silent accelerator.
Innovation means fighting the root causes.
As we usually do, addicted to a pathology-centric and cure-centric model (the current medical and pharmacological business model), we focus on the effects with little interest in the causes. If we do not focus on the causes, in fact, not only do we content ourselves with promoting palliative forms whose efficacy is yet to be proven (least of all, in this case, the idea of a 'magic pill' that 'cures' isolation or loneliness makes sense) but we also actually limit the development of that innovation capable of suggesting system solutions instead of praesidium solutions.
In our analysis of root causes, 'Loss' appears to be the main trigger factor[4].
Loss of physical and mental ability: Health issues can limit one's ability to attend and participate in social activities with others;
Loss of family and friends: Social networks naturally shrink over time if not maintained, eventually leading to isolation;
Loss of professional identity: Many underestimate retirement's emotional impact from the sudden reduction of daily social interactions;
Loss of recognition in media and market: Aging stereotypes perpetuate older adult portrayals as dependent on others and non-contributing;
Loss of social status: The concept of ageing often becomes associated with loss of social status, recognition, and value;
Loss of a purpose in life: Difficulty in finding purpose after retirement can be an isolating experience that drives societal disconnect;
Therefore, if we want to stimulate system innovation, we must ensure that any solution designed to mitigate loneliness and isolation must target the underlying cause – loss. And like treating similar devastating physical ailments like heart disease and diabetes, the most effective solutions support identification and preventative action.
To prevent loss and keep older adults connected and engaged in their communities, we must re-think many aspects of society, from employment to education, transportation, housing and more. Researchers, advocacy groups, and public health workers need better tools to aggregate and mine data, identify at-risk people and communities, and deploy interventions more quickly. And when loss does occur, older adults need tools and support to build and enhance their social capital in the same way they might nurture financial capital. Serving older adults involves many stakeholders – family, caregivers, healthcare practitioners, and social workers – all of whom want to work in a more connected way but lack the underlying structure or tools to do so.
Currently, there's no effective or accurate way to screen for isolation or loneliness – no standard tool or protocols exist. Loneliness can often hide in plain sight as it often presents with other conditions such as poverty or depression. And in North America and northern Europe, cultures that can place a high value on independence and stoicism, there's a real stigma to admitting to loneliness and an unwillingness to seek help.
There is also a pervasive assumption that older adults are reluctant to use technology, but did we ask them? Did we provide a meaningful, usable, accessible technology for them?
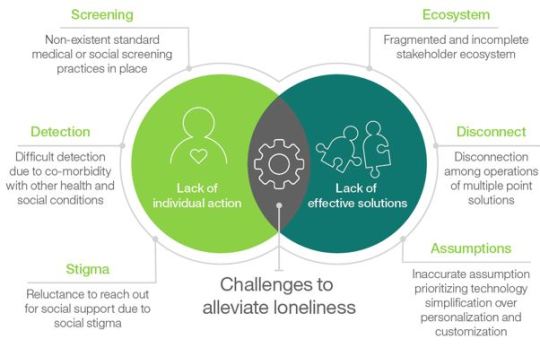
Abstract from Loneliness and aging: Navigating an enduring crisis [6]
As usual, where we see an issue related to ageing, we should also be open-minded enough to see the opportunity since - given the global economic system in which our society is rooted - the only way to reduce inequalities and scale solutions that can help a broader population is to identify the opportunities for the potential stakeholders. Which might not be "the usual suspects". There is enormous opportunity across multiple sectors, and no one industry or organisation will have a "magic button" for this issue – instead, the best solutions will cut across industry silos, from universities working with communities to create inter-generational housing for students and seniors, to telecom providers working with electronics vendors on virtual town-square projects, to self-driving vehicles – whose more enthusiastic audience may be older adults, because the reward to risk ratio is so high. The potential of cognitive and IoT technologies to deliver data integration, personalisation, natural language processing and scalability will be essential to support these solutions.
How do we create a new kind of village?
Three main questions can drive innovation:

Even if isolation and loneliness can happen in every context – a crowded condo, a school room, a dance hall, a public park in a village or a neighbourhood -it is also true that we are part of the global urbanization trend that suggests that the "new kind of village" described before resembles more and more to cities.
For the first time in human history, in 2008, most of the world's population was living in urban rather than rural contexts, and rapid global urbanization means cities are the dominant environment in which we will live not only as younger people but also into later life. Cities are the symbolic and physical representation of the intersection of our cognitive, affective, and behavioural components and the highest expression of the evolution of our intelligence and social systems we have created.
This – seems an unstoppable trend – makes cities more exposed to the consequences of age-related social and demographic changes, the different stages of individual human experience and social interaction. "With more complex social composition and variation in living standards, and the greater degree of human design and initiative that their functioning requires (for example, in terms of mobility, digital environment and built environment), they have the potential to help us accelerate the understanding of not only how we mitigate, adapt, or manage changes in society but also proactively influence it and transform from passive, adaptive, assisting containers, to being active tools for our through life well-being, health - our longevity. Cities have a fundamental role and clear opportunity to suggest forward proposals rather than reactive responses to living longer, better lives, with better social circumstances and sustainable, economic growth"[2].
Benjamin Barber and others have suggested that cities could succeed in various areas of public life where nation-states have struggled to make progress.
"The challenge of democracy in the modern world has been how to join participation, which is local, with power, which is central. The nation-state once did the job, but recently, it has become too large to allow meaningful participation even as it remains too small to address centralised global power… The solution stands before us… Let cities, the most networked and interconnected of all our political associations, defined above all by collaboration and pragmatism by creativity and multi-culture, do what states cannot."[9]
Furthermore, "City and local governments are in a prime position to tackle the social determinants of health because of the breadth of their responsibilities over a defined geographical area, with powers cutting across different areas of public policy. This ability to take a place-based approach is important because of the way that health needs and outcomes are distributed spatially. In most cities, the greatest levels of need are concentrated in neighbourhoods where poverty levels are highest and social outcomes are poorest. Improving health outcomes in these areas requires multi-sectoral action and leadership from those with an overarching responsibility for place"[4]. Most of the actions taken by city governments impact the health of citizens, and most of that is not about health care per se but about transport systems, urban design, planning and all the other functions and tools that city governments have at their disposal.
It is a mistake to think of the city as a unicum. There is a central government of the city, which is what we need to strategically direct policies. Still, the city is an aggregate of villages, of communities with such specific peculiarities that they have repercussions on the health and lives of citizens. Take London, for example. The highest life expectancy for both women is in Kensington and Chelsea, with 84.1 for men and 87.9 for women. The lowest life expectancy is found in Barking and Dagenham for both men (77.0 years) and women (81.7 years). This makes it a whole seven years less than in Kensington for male residents. The next lowest was Greenwich, Newham and Lewisham. Healthy life expectancy for women ranges from 57.8 years in Tower Hamlets to 70.1 years in Wandsworth. In contrast, for men, life expectancy ranges from 58.1 years in Barking and Dagenham to 70.2 in Richmond upon Thames[5]. It is clear that while London is narrated and imagined as the city we all know for the Big Ben or Piccadilly Circus, it is also evident that it is made by so many different nuances so well described by data on healthy life expectancy.
So, in these contexts, we must develop innovation policies to combat isolation and loneliness, but with a central government that identifies a common goal, which can only be the health-adjusted life expectancy of its citizens or HALE. In the recent past, for too long, we have focused on measuring life expectancy tout-court. Still, the transition we are experiencing from an ageing society to a longevity society requires us to imagine policies and services that aim to create not only a citizenry that lives long but does so healthily. I will not dwell on why this is a crucial step, as I would like to emphasize how this must become the pivotal' policy effectiveness' objective to be shared between city departments.
Every single initiative, from a more effective sewage system to the redesign of public transport to speed limits in city centres, must always and in any case be contextualized and measured against its corresponding 'Return in Healthy Longevity'. Suppose we establish this KPI as our focus. In that case, we can not only easily understand where to prioritize our interventions (perhaps Chelsea can be placed in the queue compared to Tower Hamlet) but also more quickly understand the drivers of the reasons for such a difference. Economic and social factors (per capita income and education) underlie these macro-differences but understanding "how" and "how much" these factors, along with all the other components that impact our health, influence isolation - which, as we have said, is probably the spark from which loneliness is amplified - is what can allow us to intervene quickly.
Historically, the moral thermostat of politics is fixed on a point somewhere between duty and prudence. Unhinging this dynamic is intrinsically complex, and perhaps the only way to do so is to unlock a basic principle, namely to formally acknowledge that, as we have said, no one industry or organization will have a 'silver bullet' for this issue, and therefore to involve each actor in a hybrid model not by offloading responsibility onto one another, but by coordinating interaction with one another and developing an ecosystem opposed to the current fragmented and partial one.
By leveraging data and technology to establish an absent shared screening and detection model. Who can tell if a person is isolated? How can we distinguish whether depression is caused by loneliness rather than by other factors? Who communicates the data with whom? Who cares to act? Just the usual charities or voluntary groups in the area? And even if so, can we systematize volunteering? Can we launch campaigns to combat the stigma associated with old age and the shared celebration of independence as a symbol of a healthy and progressive society? Are we sure that it is only up to the U.N. or a ministry to run such campaigns? Wouldn't it be more effective and pervasive if brands were the ones to convey this message?
Isolation and loneliness should be tackled with the same vigour we strive for a net-zero footprint. Where everyone is involved, where everyone offers joyful communications to keep our planet habitable. Where everyone sells an opportunity with a return on their investment, which is not merely social, it is economic. The opportunity for innovation is contextualized (mostly) in cities and concerns every business sector.
The city, the enabler of innovation.
It would seem, therefore, that the city bears most of the responsibility for the solutions and that it is up to central, local, and hyperlocal public administrations to find the investments and provide the tools to implement them. At least, this is how it should be in the welfare state that we have, perhaps at one point in history, idealised in an eternal debate between hyper-liberalism and the nanny state. This is a distorted representation. As Michael Lyons says: "The local government is not an agency responsible for delivering a specific set of statutory services. Rather, it is a government unit responsible for the well-being of a community and a place, and independent of, whilst also being connected to, the wider system of government".
In other words, it is up to local (and hyper-local) governments not to deliver the solutions but to build the ecosystem in which they can be born, proliferate and resolve. A function of knowledge, promotion of evidence, prioritisation, and coordination. In an economic and social context, it is radically different from when many of the policies that are still in place today were designed. A context plagued by new forms of isolation and loneliness exacerbated by new social dynamics, digital ones above all. A context in which solutions based on the intelligent interpretation of data are no longer a possibility but the baseline on which to build solutions. This is what local authorities should do: indicate the priorities and where they are most urgent and stimulate the market to innovate. One example above all.
In 2011, Michele Vianello, Deputy Mayor of Venice, argued that "building a WIFI network in a municipality is not dissimilar to building a nursery or kindergarten"[6]. Compared to Vianello as a universal right of citizenship, Broadband access explains well which axes it can and should evolve. It is not very different from public school children's right to healthy nutrition. More data will become available if the city increasingly moves its services to digital ones. This data can then be the basis for measures and effectiveness of our interventions.
Providing broadband access will be strategic and socially essential to provide access to services and receive feedback from citizens. Tel Aviv, Barcelona, Perth, Wellington, Osaka, Tallinn, Helsinki, Milan, or Leeds, Bradford, Oxford, Manchester, Salford, York, Edinburgh, Cardiff and Newport, all cities which have been equipped with free public Wi-Fi, are excellent examples. However, a lot more can be done from an infrastructural point of view (diffusion, and – moreover, speed and signal reliability), sharing with the public (access information) and usability (ease of access).
Since the risk is what Citizens Advice in the UK found: during the first lockdown, certain groups, including people with children, disabled people, people from Black, Asian or ethnic minority backgrounds, those who were shielding and young people were particularly struggling with their broadband bill. Towards the end of 2022, an estimated 2.3 million people had fallen behind on their broadband bill, according to the charity[7]. How can we suggest access to education, information, and data if we can't grant the bare access? How can we keep people connected? How can we prevent them from being at risk of total isolation (physically and digitally)? We know it might sound against any current market logic. Still, probably – following Vianello's provocation – it is time Telco provided free broadband access to people (at least those at risk? But, who are they? Is age the only KPI?) and develop services to sustain costs using data and technology to create low-cost systems for analysing isolation risk, or developing hybrid 'town squares' with increasingly customised community-based content, resources and services that can finally intelligently bring together the physical and digital, connecting places and people.
This is the innovation that the authorities should stimulate by involving all industries. From Electronics, Consumer Goods, & Retail to Target new markets with enhanced insight into consumer behaviour and preferences, to real estate providing novel inter-generational living solutions and empathic homes, to healthcare developing active screening for early signs of loneliness with integration to social services, to travel and transportation improving mobility with self-driving vehicles, offering new experiences with VR travel libraries or more intelligent shared services, to government and business redesigning retirement concepts and create new work and volunteer opportunities, to education offering new curriculum and skills training. These are just simple suggestions which are translated already into actions by companies like Getsetup, Rendever, Volunteroo, onHands, Virtual Leap, Start-Up for Seniors, Call and Check, CHC - Create Healthy Communities, Dorot, Civic Dollars, Informetis, VOICE, Centaur Robotics to name a few of dozens exploring alternative ways to engage older people in everyday life and combat isolation and loneliness as an ecosystem instead as a laser-focused solution.
However, it is not so much the output that interests us in this context as the city's role in becoming the epicentre of an ecosystem dedicated to sharing evidence and research, acting as an integrator and facilitating both the development of new solutions and their distribution to citizens. A striking example of how this flow has been implemented egregiously is that of New York State, where the director of the Office for the Aging, Greg Olsen, leads a task force that collaborates with accelerators, start-ups, federal offices and the National Institutes of Health (NIH) - whose mission is 'Turning Discovery Into Health' - to interpret citizens' needs, interests, life patterns and risk of isolation and decline.
It is enough to realise how the State of New York and the City of New York are working jointly to bring innovation into people's homes for free. The agreement with New York and ElliQ, a voice-operated care companion designed to alleviate loneliness, empower independence and support people in taking control of their social, cognitive and physical well-being, is an example of the central role of cities in fostering innovation. ElliQ, one of the few products specifically designed for older adults who are living alone or spend most of their day alone, was on the market for almost a decade and only found its profitable go to market when it signed framework agreements with the State and the City of NY which were offering the entire technology free of charge to citizens selected by precise criteria based on data from local operators.
The results? In 2023, NYSOFA issued a report[8] showing a 95% reduction in loneliness and a significant improvement in well-being among older adults using the platform. ElliQ users throughout New York have also consistently demonstrated exceptionally high levels of engagement over time, interacting with their ElliQ over 30 times daily, six days a week. More than 75% of these interactions are related to improving the older adults' social, physical and mental well-being, not to mention giving ElliQ a revenue 'pipeline' to convince other investors to invest in the company and thus give it a chance to develop more and more sophisticated technologies based on Machine Learning that will benefit more and more people. These results have allowed to serve from about a thousand homes to over twenty thousand planned in the coming months. All are funded with the New York State budget as part of a package of programmes through NYSOFA to address social isolation and provide support for caregivers.
So, will the solution to isolation and loneliness be a cognitive robot in our homes? Of course not. It will be more cohesive and inclusive communities, city neighbourhoods redesigned in the spirit of Barcelona's Superilles, more effective tools to manage volunteering, programmes to engage commuters to be part of the social fabric around their Office and not only where they reside, campaigns to promote interdependence instead of stigmatising it, solutions to learn how to recognise isolation and identify it, harnessing local touch points as catalysts for engagement and - of course - it will also be technologies capable of being there when it is unfortunately impossible to do so in person.
Involving and selecting innovation in all its forms - digital, process, financial - having the courage to experiment with it and support it, helping it to prove its effectiveness: this, too, is the role of cities and their administrators if we really want to imagine how to tackle and solve loneliness with the tools that our ingenuity makes available to us, every day.
Originally published in the “Silver Economy Meets Innovation: Aging Better, Together. Strategies and Startups to Tackle Loneliness” by AC75 Startup Accelerator.
[1] https://en.wikipedia.org/wiki/The_People_Walker [2]https://www.istat.it/it/files//2020/04/statisticatoday_ANZIANI.pdf [3]https://www.sciencedirect.com/science/article/pii/S2352827323001246 [4] Our Epidemic of Loneliness and Isolation: The U.S. Surgeon General’s Advisory on the Healing Effects of Social Connection and Community, 2023 [5] N. Palmarini, H.Fraser, S.Zinck et alter, “Loneliness and ageing: Navigating an enduring crisis”, Institute for Business Value Press, 2017-2020 [6] N. Palmarini, H.Fraser, S.Zinck et alter, “Loneliness and ageing: Navigating an enduring crisis”, Institute for Business Value Press, 2017-2020 [7] N. Palmarini, H.Fraser, S.Zinck et alter, “Loneliness and ageing: Navigating an enduring crisis”, Institute for Business Value Press, 2017-2020 [8] N.Palmarini, L.Corner, “City of longevity: a new paradigm for cities in a longevity society”, 2023, NICA. [9] B.Barber, “Strong Democracy: Participatory Politics for a New Age”, University of California Press, 2013 [10] C.Naylor, D.Buck, “The role of cities in improving population health”, the Kings Fund, 2018 [11] https://trustforlondon.org.uk/data/life-expectancy-borough/ [12] https://www.michelevianello.net/wifi-gratuito-diritto-universale-cittadinan¬za/ [13] https://www.citizensadvice.org.uk/about-us/about-us1/media/press-releases/more-than-one-in-six-struggling-to-afford-broadband/ [14] https://aging.ny.gov/system/files/documents/2023/08/nysofa-and-elliq-engagement-report-july-2023.pdf
0 notes
Text
Horizoning™ report - Adaptations to the Urban Environment in China.

We have recently published our latest Horizoning™ report - Adaptations to the Urban Environment in China.
As part of the UK-China Healthy Ageing Project, this report is the third instalment in a series exploring the rise of healthy longevity in China. It delves into emerging trends in urban environments and the associated opportunities.
With the rapid urbanisation in China and the need to accommodate an ageing population, we investigate how products and services can empower citizens to live confidently and enjoyably in urban settings.

The report is designed to provoke thought and guide the development of innovative solutions for urban adaptations, aiming to inspire and catalyse new approaches to healthy longevity and contribute to economic growth.
You can read the full report here.
0 notes
Text
Cities of Longevity: Making Cities the 'Champions of Prevention'
The UK’s National Innovation Centre for Ageing (NICA) is excited to announce a pivotal event at the Science Summit during the United Nations General Assembly 79 (UNGA79) in New York City on September 20th. This prestigious platform will spotlight the launch of the City of Longevity Toolkit, a groundbreaking initiative designed to help cities become champions of prevention and promote healthier living.

What is the City of Longevity Toolkit?
The City of Longevity Toolkit is not just a concept; it’s a practical, actionable guide that cities can use to make real changes. This toolkit offers evidence-based strategies and tools that cities can tailor to their unique needs, reflecting their history, demographics, current challenges and individual character.
Here’s how it works:
Tailored Solutions: The toolkit offers adaptable components that cities can select based on their specific health challenges and goals. Whether it’s improving air quality, enhancing access to healthy food, or promoting active lifestyles, cities can pick and choose the elements that best address their local needs.
Implementation Strategies: It includes step-by-step guides on how to integrate these solutions into city planning and daily operations. This isn’t about abstract ideas; it’s about actionable steps that city planners, policymakers, and community leaders can take immediately.
Data-Driven Insights: The toolkit is grounded in the latest research, providing cities with data and insights to measure the impact of their interventions. This ensures that efforts are not only well-informed but also effective and measurable.
Best Practices: It shares successful case studies and practical examples from other cities that have already made significant strides in promoting health and longevity. Cities can learn from these examples to avoid common pitfalls and adopt proven strategies.
Why Focus on Cities?
Urban environments play a pivotal role in shaping our health outcomes. Cities influence everything from air quality to food availability, and they can be powerful agents of change. The City of Longevity Programme aims to tap into this potential by equipping cities with practical tools to drive health improvements.
By focusing on how cities can actively support healthy living, we’re not just talking about potential benefits—we’re offering concrete methods for cities to make a tangible impact.
The toolkit enables cities to:
Promote Healthy Behaviors: Implement programs and policies that encourage residents to adopt healthier lifestyles.
Enhance Urban Infrastructure: Improve city design to make it easier for people to engage in physical activity and access nutritious food.
Engage the Community: Involve local residents in health initiatives to ensure they are relevant and effective.
Why UNGA79?
The Science Summit at UNGA79 is the ideal stage for launching this toolkit. It brings together global experts and innovators to discuss how we can address urgent challenges through collaboration and innovation. By presenting the City of Longevity Toolkit at this summit, NICA aligns with the UN’s mission to promote global progress and sustainability.
This summit is all about the importance of sharing practical solutions and shared knowledge in tackling global issues. The City of Longevity Toolkit represents this approach in action, offering cities the means to implement effective health strategies and make a real difference in their communities.
Join us as we launch the City of Longevity Toolkit and explore how cities can become proactive agents of health, driving meaningful change and fostering a healthier future for all.
Registration to the event is now open Science Summit UNGA79 – Science Summit at UN General Assembly
0 notes
Text
Transform Food Planning in Your Area Toolkit
Brought by Sustain, a powerful alliance of organisations and communities working together for a better system of food, farming, and fishing, and cultivating the movement for change, Transform Food Planning in Your Area is an online toolkit designed to help community organisations use the planning system to design better food policies for city neighbourhoods.
As the City of Longevity makes behavioural change one of its core purposes, this toolkit is a helpful resource to start planning change and engagement.
Check out the online toolkit here.

1 note
·
View note
Text
Cities, Longevity, and Economic Factors

What do the latest global consumption trends reveal about the cost of maintaining an affluent lifestyle? We know that economic wealth and the education associated with it (or generated by it) are key determinants of longevity.
Could we similarly glean from such studies what the crucial drivers are that could help us define new metrics for both inequalities and strategies to combat them?
Are we overlooking the analysis of the wealthiest cities as a means to build a more equitable society and provide policymakers with new tools to develop smarter policies that accelerate access to healthy longevity resources? How can the wealth of one neighbour benefit others?
Read the full Global Wealth and Lifestyle Report here.
1 note
·
View note
Text
City of Longevity invited to the Global Inequalities Forum

As part of the first global forum on inequalities we were invited to discuss how to address and mitigate inequalities through a proactive approach to longevity by cities.
This event is the prologue to the 24th Triennale Milano International Exhibition will take place from May to November 2025. With the title Inequalities, it is conceived as an important forum for reflecting on tendencies and contradictions of the present and on the urgency of the challenges currently facing our planet.
You can register for the event here.
0 notes
Text
NICA's City of Longevity on Marie Claire Italy July/August 2024 Issue
A massive coverage on Marie Claire Italy titled:
WHERE WE WILL LIVE:IN LONGEVITY CITIES
They are not magic places, but cities with serious prevention policies. Because: "We can no longer just take care of an ageing population any more, but we must help them (or better “us”) ageing better.'"




0 notes
Text
One Year of City of Longevity
For the celebration of our City of Longevity's first anniversary we’ve been reached by our Berlin stakeholder Joachim Rautter, co-founder of the Berlin Innovation Centre for Ageing and Longevity.

1 note
·
View note
Text
Frames from City of Longevity conference
1 note
·
View note
Text
#CITY OF LONGEVITY first global conference

Let's face it, it is unsustainable to keep treating people and then sending them back to the conditions that made them sick in the first place. It is time for a change. It is time to imagine - together, globally - new narratives, tools, and strategies to look at our future. We will host cities and delegates from around the world to discuss how to move from the current models centered on care/reaction to new models centred on prevention/proaction. On #intergenerational dialogue and engagement instead of developing sectoral policies. On leveraging existing touch points so decisive for our health. On leveraging data to give us answers and help us make better decisions. On leveraging vocations and territory to suggest how to improve our #lifestyles. #ageingintelligence #dispatchesfromCoL
0 notes
Text
Sensing the passion: the connected scarf

As Chintan Patel, Chief Technology Officer of Cisco UK & Ireland says, "Being a true passionate fan is physiological, it has nothing to do with how many games you attend or where you are in the world. It's what unites us as a collective. Now we’ve got the data to prove it".
How much care, love, and passion do we pour into our team? Going to the stadium on Sundays, watching the game with our friends, being together with others at the pub. Are these emotions measurable? What feelings make us feel good? And what do they bring to our well-being?
Citizen's exec says: "For more than 100 years, the scarf has been the ultimate symbol of football fandom. It’s seen the highs and the lows; and captures the blood, sweat and tears of fans, week in and week out".
Partnering with Cisco, they decided to measure it. Using an EmotiBit bio sensor sitting discreetly on the neck, The Connected Scarf captures the body’s bio-signals throughout the match and allows us to shape more curated, customized experiences in the future. The scarf records a range of physiological measures, including heart rate, body temperature, and emotional arousal – giving factual information to analyze how fans feel at different matches.
Is this the first step toward a new fan experience? We can't say yet.
2 notes
·
View notes
Text
The internet of senses: cognitive computing on the rise
The evolution of sensors and especially the ability to interpret collected data opens a new season to the possibilities offered by senses such as smell or taste for interpreting the world around us and how it pertains to our lives.
It is another step in our direction of developing solutions ever closer to who we are, what we need, and what makes us feel better. We have always followed Ericcson with great interest, and today we have one more reason to do so.
4 notes
·
View notes
Text
The power of a smile ...
Mastercard is trialling a biometric payment system that could see customers just use their face rather than contactless cards, smartphones or PINs. In this trial shoppers will smile at a scanner to pay for their shopping.
Ajay Bhalla, the president of cyber and intelligence at Mastercard, was quoted in the Telegraph as saying: “The way we pay needs to keep pace with the way we live, work and do business, offering choice to consumers with the highest levels of security.
Ajay also says “Our goal with this new programme is to make shopping a great experience for consumers and merchants alike, providing the best of both security and convenience.”
0 notes
Text
Accessible raised gardens
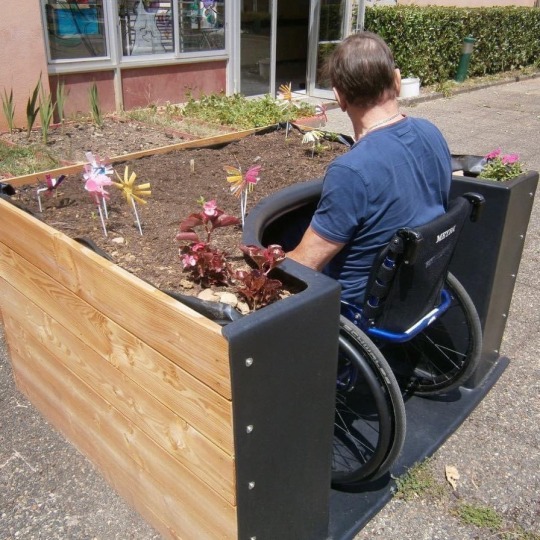

“These raised gardens, thought up by a group of French designers, make gardening accessible for seniors and people in wheelchairs!”
Home Junkie - Facebook
1 note
·
View note
Text
Did you miss working out whilst Pregnant?
Nike's new global maternity training program, featured in Femtech World, includes a prenatal and postpartum exercise plan with 24 workouts designed by qualified trainers and vetted by a panel of five pregnancy experts and an OB/GYN. The program covers early pregnancy, later pregnancy, and postpartum stages.
This app helps users stay healthy and continue working out through various stages of pregnancy, including during fertility treatment and while breastfeeding. It also offers a deep core and pelvic floor plan, addressing one of the two biggest reasons people stop doing sports.
0 notes