#VWAP support and resistance
Explore tagged Tumblr posts
Text
USDCHF on the 1-Hour Timeframe: Ninja Tactics to Outsmart the Market When Swiss Precision Meets Forex Chaos Picture this: You carefully analyze the USDCHF pair on the 1-hour timeframe, feeling like a Swiss watchmaker crafting the perfect timepiece. But seconds later, your trade plummets faster than your confidence after sending a risky text. Sound familiar? Welcome to the world of USDCHF—a pair that moves with surgical precision but loves throwing curveballs. The good news? Beneath the chaos lies a hidden blueprint for success, known only to seasoned pros. Let’s pull back the curtain on some ninja tactics and insider techniques to dominate USDCHF on the 1-hour timeframe. Why the USDCHF 1-Hour Timeframe Is a Hidden Goldmine The USDCHF pair is like that quiet student in class who aces every exam. It doesn’t grab headlines like EURUSD or GBPJPY, but smart traders know it offers: - Low Volatility with Sudden Bursts: It usually moves methodically, but when it strikes, it hits hard. - Clear Technical Patterns: On the 1-hour timeframe, USDCHF respects support and resistance levels like Swiss etiquette—polite, but firm. - Institutional Flow Clues: USDCHF often reflects risk sentiment and central bank moves, giving you a heads-up before other pairs. But here’s the twist: most retail traders misread this pair. They either chase fake breakouts or ignore subtle shifts in liquidity. Let’s avoid those pitfalls. The Sneaky Liquidity Grab Strategy Ever noticed USDCHF breaks a support level, lures in breakout traders, then viciously reverses? That’s a liquidity grab—market makers hunting for stop-losses. How to Profit: - Identify Key Levels: Mark strong support and resistance zones on the 1-hour timeframe. - Wait for the Fakeout: If USDCHF spikes below support but quickly reclaims the level, don’t panic. That’s your entry signal. - Enter with Confidence: Go long when the price re-enters the range, placing your stop just below the fakeout wick. - Ride the Reversal: Target the opposite resistance level, often achieving a 2:1 or 3:1 reward-to-risk ratio. Example: In December 2024, USDCHF dipped below 0.8720, triggering retail sell orders, only to reverse sharply to 0.8820 within hours. Traders using this strategy banked over 100 pips. The "Swiss Sniper" RSI Divergence Play RSI divergences on the 1-hour chart can be a game-changer—if you know where to look. Ninja Steps: - Monitor RSI (14): Look for price making a lower low while RSI forms a higher low. - Confirm at Key Levels: Divergence works best near strong support zones on USDCHF. - Enter on Candle Confirmation: A bullish engulfing or pin bar after divergence is your green light. - Set Your Target: Aim for the nearest resistance, or use the ATR (Average True Range) for realistic profit goals. Case Study: According to John Bollinger, creator of Bollinger Bands, combining RSI divergence with volatility bands can increase win rates by 20% (Source: BollingerBands.com). The Hidden Session Overlap Momentum Surge Ever wondered why USDCHF suddenly comes to life between 2 PM and 5 PM (GMT)? That’s the London-New York overlap, where liquidity surges. How to Capitalize: - Identify Pre-Session Ranges: Observe USDCHF’s range during the quieter Asian session. - Breakout Watch: Once the overlap begins, breakout moves are often more legitimate compared to fakeouts earlier in the day. - Volume Confirmation: Use the Volume Weighted Average Price (VWAP) to confirm breakout strength. - Ride the Session Flow: Capture quick 30-50 pip moves during this overlap. Pro Tip: Forex expert Kathy Lien emphasizes, “Session overlaps offer some of the most predictable trends due to volume convergence” (Source: BKForex). USDCHF's Secret Love Affair with the DXY Index USDCHF moves like a couple on a reality TV show—driven by drama in the US Dollar Index (DXY). Correlation Hack: - When DXY breaks key resistance, USDCHF often follows suit on the 1-hour timeframe. - Conversely, a DXY rejection from resistance can trigger USDCHF sell-offs. Quick Execution: - Track DXY Levels: Use TradingView for a live DXY chart. - Sync Entries: Align your USDCHF positions with DXY breakouts or reversals. - Stay Ahead: This gives you a 5-10 minute edge over traders solely focused on USDCHF charts. Insider Tools to Stay Ahead Serious traders need cutting-edge tools. Here’s what separates pros from amateurs: - Latest Economic Indicators: Stay updated on USD and CHF news at StarseedFX News. - Forex Education: Master strategies like liquidity grabs and divergence at StarseedFX Courses. - Smart Trading Tool: Automate your lot sizing and manage orders efficiently at StarseedFX Smart Tool. Key Takeaways: Elite USDCHF Tactics - Liquidity Grabs: Spot fakeouts, enter reversals, target 2:1 RR moves. - RSI Divergence: Combine with key levels and price action confirmation. - Session Overlap Momentum: Focus on London-New York overlap for clean breakouts. - DXY Correlation: Use DXY as a leading indicator to front-run USDCHF moves. Mastering USDCHF on the 1-hour timeframe isn’t about chasing every spike. It’s about precision, patience, and knowing the hidden rules most traders overlook. —————– Image Credits: Cover image at the top is AI-generated Read the full article
0 notes
Text
5 Key Indicators Every Trader Should Know: Essential Tools for Today's Market
The Trading Compass: Navigating India's Current Market
Hey there, fellow traders! 📈 Have you been feeling the market's unpredictability lately? You're not alone! I've been trading through this volatility too, and wanted to share some hard-earned wisdom about the technical indicators that have truly made a difference in my decision-making process.
India's market has been particularly turbulent recently, with everything from global economic shifts to domestic policy changes throwing curveballs our way. That's why having reliable tools to guide your trading decisions isn't just helpful—it's essential for survival in today's market environment.
Let me walk you through the five indicators I personally rely on every single day:
1. RSI: Your Market Mood Reader
Think of the Relative Strength Index as your market psychiatrist—it tells you when the market is getting too emotional in either direction. On a scale of 0-100, it measures whether an asset is potentially overvalued or undervalued.
I've found RSI incredibly reliable lately, especially when:
It pushes above 70, suggesting a stock might be running too hot (happening frequently in our tech sector right now)
It dips below 30, hinting at oversold conditions (I've found some great bargains in manufacturing this way)
2. MACD: Your Trend's Best Friend
Don't let the complicated name fool you! The Moving Average Convergence Divergence indicator simply helps you understand the momentum and direction of trends.
Here's how I personally use MACD in today's market:
When the MACD line crosses above the signal line, I pay attention—this bullish signal has been remarkably accurate in renewable energy stocks lately (helped me catch a 12% move just last week!)
I watch the histogram to see momentum building or fading—crucial for timing entries and exits
Zero-line crossings give me confidence about the overall trend direction—essential for my medium-term positions
3. Bollinger Bands: Your Volatility Visualizer
In times like these, understanding volatility is everything—and Bollinger Bands make it visual. They expand during chaotic periods and contract during calmer ones.
Three ways I apply Bollinger Bands in my daily trading:
Band width immediately shows me if volatility is increasing/decreasing—absolutely crucial as our markets navigate current transitions (saved me from several false breakouts recently)
I love finding mean reversion opportunities when prices touch band extremes—this strategy has been particularly profitable in FMCG stocks
After consolidation periods, decisive band breakouts often precede strong trends—I've seen this pattern repeatedly in banking stocks this year
4. VWAP: Your Institutional Edge
As algorithms dominate more trading, understanding where big money is active becomes critical. VWAP (Volume-Weighted Average Price) helps me see the true average price incorporating volume—essentially showing where institutions are likely active.
Here's how VWAP gives me an edge:
Major institutions use it for execution benchmarks, creating natural support/resistance levels
Trading above/below VWAP helps confirm my intraday bias—essential in today's quick-moving markets
I use it as an exit benchmark to improve my average performance
5. Fibonacci Retracement: Your Timeless Market Map
It amazes me that a mathematical sequence discovered centuries ago works so well in our digital markets today, but Fibonacci retracement levels consistently help identify potential turning points.
My three favorite Fibonacci applications:
The 38.2%, 50%, and 61.8% retracement levels provide amazing entry points in trends—I've used these successfully throughout this year's commodity cycles
Fibonacci extensions help me project realistic profit targets beyond previous highs/lows
When Fibonacci levels align with other indicators like RSI or MACD, the high-probability setups that emerge have dramatically improved my win rate
Bringing It All Together: The Integrated Approach
Here's what I've learned after years of trading: while each indicator offers valuable insights, the real magic happens when you combine them strategically. I don't make major trading decisions without confirmation from multiple indicators—it's like having several expert advisors all agreeing on the same trade. You can learn this strategies and how to effectively apply them by enrolling in the Stock Market Courses in Mumbai
I'd love to hear which indicators you find most helpful in your trading! Drop a comment below and let's learn from each other. Happy trading! 📊
1 note
·
View note
Text
Trading Mastery: Blending Intraday Strategies, Investment Wisdom, and Swing Analysis
Success in the stock market requires a blend of well-defined intraday trading strategies, solid investment tips, and effective swing trading indicators. By using a swing stock screener alongside technical analysis, traders can optimize their trade decisions, improve accuracy, and maximize returns.
Effective Intraday Trading Strategies
Intraday trading focuses on buying and selling stocks within the same trading day, requiring quick decision-making and precise strategies. The most successful traders use a combination of the following:
1. Scalping – Capturing Small Profits Repeatedly
Involves making multiple trades within minutes.
Uses technical indicators like VWAP and moving averages for quick entries.
2. Momentum Trading – Riding Strong Price Movements
Focuses on stocks with high trading volume and rapid price swings.
Uses MACD and Relative Strength Index (RSI) to confirm trends.
3. Breakout Trading – Entering at Key Price Levels
Identifies stocks breaking above resistance or below support.
Uses Bollinger Bands and stochastic oscillator for confirmation.
4. VWAP Strategy – Trading Around Volume-Weighted Prices
Uses VWAP (Volume Weighted Average Price) as a reference for entries and exits.
Top Stock Market Investment Tips
For long-term success, traders and investors must follow fundamental principles to minimize risk and maximize gains:
Risk Management – Never risk more than 2% of capital per trade.
Diversification – Invest in different sectors to reduce volatility.
Stay Updated – Follow economic news, earnings reports, and global trends.
Technical & Fundamental Analysis – Combine chart patterns with financial metrics.
Emotional Discipline – Avoid panic trading and stick to a trading plan.
Best Technical Indicators for Swing Trading
Swing trading involves holding stocks for days or weeks to capture medium-term price movements. The best technical indicators for this strategy include:
1. Moving Averages – Identifying Trends
The 50-day and 200-day moving averages help track long-term trends.
2. Relative Strength Index (RSI) – Spotting Overbought/Oversold Levels
Stocks above RSI 70 are overbought, below RSI 30 are oversold.
3. MACD – Measuring Momentum
MACD crossovers indicate trend changes.
4. Bollinger Bands – Tracking Volatility
Stocks touching upper bands may be overbought, lower bands may signal buying opportunities.
Using a Swing Stock Screener for Better Trades
A swing stock screener helps traders filter stocks based on specific criteria, saving time and improving accuracy.
Key Features of a Swing Stock Screener
Volume & Liquidity Filters – Ensures smooth trade execution.
Trend Identification – Screens stocks following moving averages.
RSI & MACD Filters – Identifies momentum shifts.
How to Combine a Swing Stock Screener with Indicators
Use a screener to find stocks with strong trends and volume.
Apply RSI, MACD, and moving averages for confirmation.
Set entry and exit points using support and resistance levels.
Conclusion
Mastering intraday trading strategies, following sound investment principles, and utilizing the best technical indicators ensures better market performance. A swing stock screener further refines stock selection, increasing precision and profitability. By combining these tools, traders can enhance their decision-making and achieve consistent results in the stock market.
0 notes
Text
Mastering Multiple Time Frame Analysis: A Day Trader's Guide to Futures Market Context
Ever stared at your charts feeling like you're trying to solve a Rubik's cube blindfolded? You're not alone. Technical analysis across multiple time frames can feel overwhelming, but I promise you – it's not rocket science. Let's break down this essential trading approach that'll help you stop trading like a caffeinated squirrel and start trading with real context.
Why Multiple Time Frame Analysis Matters
Remember that time you went all-in on a "perfect" 5-minute setup, only to get steamrolled by a daily trend? Yeah, we've all been there. Multiple time frame analysis in technical analysis helps you:
Avoid trading against major trends
Identify higher-probability setups
Understand market structure better
Manage risk more effectively
The Three-Timeframe Approach
Think of time frames like nesting dolls – each one fits inside the other. Here's how to structure your analysis:
Higher Timeframe (Trend)
Daily or 4-hour charts for context
Identifies primary trend direction
Shows major support/resistance levels
Intermediate Timeframe (Trigger)
1-hour or 30-minute charts
Confirms trend alignment
Spots potential entry zones
Lower Timeframe (Entry)
5-minute or 1-minute charts
Precise entry timing
Stop loss placement
Real-World Application: ES Futures Example
Let's put this technical analysis approach into practice using the E-mini S&P 500 futures (ES):
Higher Timeframe (Daily):
Identifying bullish trend above 20-day EMA
Major resistance at previous swing highs
Volume profile showing value areas
Intermediate Timeframe (1-hour):
Bull flag formation developing
RSI showing positive divergence
Volume increasing on pullbacks
Lower Timeframe (5-minute):
Looking for hammer candlesticks at support
VWAP bounces for entries
Clear stop loss below recent swing low
Common Pitfalls to Avoid
Analysis Paralysis Don't get stuck jumping between 20 different time frames like a kid in a candy store. Stick to your three chosen frames.
Timeframe Conflict When timeframes show conflicting signals, always defer to the higher timeframe. It's like arguing with your boss – technically you can, but should you?
Over-Trading Just because you see a setup on the 1-minute chart doesn't mean you need to take it. Wait for alignment across your chosen timeframes.
Pro Tips for Success
Start Wide, Go Narrow Always begin with the highest timeframe and work your way down. It's like using Google Maps – you start with the country view before zooming into street level.
Use Time-Appropriate Indicators
Higher timeframes: Slower indicators (200 MA, weekly pivots)
Lower timeframes: Faster indicators (9 EMA, RSI)
Practice Time Frame Alignment Create a checklist:
Higher timeframe trend direction ?
Intermediate timeframe confirmation ?
Lower timeframe entry trigger ?
Putting It All Together
The beauty of multiple time frame technical analysis is that it forces you to slow down and see the bigger picture. Think of it like planning a road trip:
Higher timeframe is your map view
Intermediate timeframe is your GPS
Lower timeframe is your actual driving
Remember, successful trading isn't about catching every move – it's about catching the right moves with proper context.
Conclusion
Multiple time frame analysis isn't just another fancy trading term to throw around at dinner parties (though it does sound impressive). It's a practical approach to understanding market context and making better trading decisions. Start with three timeframes, stick to your system, and watch how your trading perspective transforms.
Pro Tip: Don't forget to backtest your multiple time frame strategy on historical data. It's like practicing your dance moves before hitting the club – much better than learning the hard way!
Ready to level up your technical analysis game? Start by choosing your three timeframes and practice identifying alignment. Your future self (and trading account) will thank you.
Remember: The market will always be there tomorrow. Take your time to master this approach, and trade with confidence knowing you've done your homework across all relevant time frames.
#trading psychology#market analysis#trading strategy#futurestrading#market trends#marketindicators#tradingstrategy#trading education
1 note
·
View note
Text
Demystifying Indicators: Understanding Definitions and Examples in Technical Analysis
In the realm of financial markets, technical analysis stands as a cornerstone methodology for understanding price movements and making trading decisions. At the heart of this approach lie indicators, indispensable tools that provide insights into market trends, momentum, volatility, and potential reversals. This article aims to unravel the concept of indicators, offering a comprehensive definition and exploring various examples to illustrate their significance in technical analysis.
Defining Indicators:
Indicators in technical analysis refer to mathematical calculations applied to historical price and volume data to derive insights into market behavior. These calculations generate visual representations, typically in the form of charts, that assist traders and analysts in identifying trends, making predictions, and formulating trading strategies. Indicators are classified into different categories based on their functions, including trend-following, momentum, volatility, and volume indicators.
Types of Indicators:
Trend-Following Indicators: These indicators help traders identify the direction of the prevailing trend. Examples include Moving Averages, which smooth out price data to reveal underlying trends, and the Average Directional Index (ADX), which quantifies the strength of a trend.
Momentum Indicators: Momentum indicators measure the rate of change in price movements, providing insights into the speed and magnitude of price shifts. Examples include the Relative Strength Index (RSI), which compares the magnitude of recent gains to recent losses to determine overbought or oversold conditions, and the Moving Average Convergence Divergence (MACD), which analyzes the relationship between two moving averages to signal potential trend reversals.
Volatility Indicators: Volatility indicators quantify the degree of price fluctuations in the market, aiding traders in assessing risk and adjusting their trading strategies accordingly. The Bollinger Bands, for instance, depict volatility by plotting standard deviations around a moving average, while the Average True Range (ATR) measures the average range between high and low prices over a specified period.
Volume Indicators: Volume indicators analyze trading volume to gauge the strength or weakness of price movements. Examples include the On-Balance Volume (OBV), which accumulates volume based on whether prices close higher or lower than the previous close, and the Volume Weighted Average Price (VWAP), which calculates the average price weighted by volume traded.
Examples of Indicators in Technical Analysis:
1. Moving Average (MA):
The Moving Average is a trend-following indicator that smooths out price data by calculating the average price over a specified period. Traders use MAs to identify the direction of the trend and potential support or resistance levels. For example, a bullish signal occurs when the price moves above its MA, indicating upward momentum, while a bearish signal occurs when the price falls below its MA, signaling a potential downtrend.
2. Relative Strength Index (RSI):
The RSI is a momentum oscillator that measures the speed and change of price movements. It oscillates between 0 and 100 and is typically used to identify overbought or oversold conditions in the market. A reading above 70 suggests overbought conditions, signaling a potential reversal to the downside, while a reading below 30 indicates oversold conditions, signaling a potential reversal to the upside.
3. Bollinger Bands:
Bollinger Bands consist of a middle band, typically a 20-period moving average, and two outer bands that represent standard deviations from the middle band. These bands expand and contract based on market volatility. Traders use Bollinger Bands to identify overbought or oversold conditions and potential price breakouts. For example, when the price touches the upper band, it may indicate overbought conditions, while a touch of the lower band may signal oversold conditions.
4. Volume Profile:
Volume Profile displays the volume traded at each price level over a specified period, typically represented as a histogram on the price chart. It helps traders identify key support and resistance levels based on the concentration of trading activity. High-volume nodes indicate areas of significant buying or selling interest, while low-volume areas suggest potential price breakouts or reversals.
Conclusion:
Indicators play a pivotal role in technical analysis, offering traders valuable insights into market dynamics and guiding decision-making processes. From trend identification to momentum analysis and volatility assessment, indicators provide a multifaceted approach to understanding price movements and formulating trading strategies. However, it's essential to recognize that no single indicator can provide foolproof predictions, and traders should use indicators in conjunction with other analytical tools and risk management strategies. By mastering the art of interpreting indicators and integrating them into their trading arsenal, traders can enhance their ability to navigate the complexities of financial markets and achieve their investment objectives.
0 notes
Text
101 Stock Market Terms Every Good Trader & Investor Knows

Certainly! Here are 101 stock market terms that every good trader and investor should know:
If you want to learn more about trading then joinInvestingdaddy.com.

Stock: Ownership in a company represented by shares.
Share: A unit of ownership in a company.
Dividend: A portion of a company's profits distributed to shareholders.
Market Capitalization: The total value of a company's outstanding shares.
Index: A benchmark that tracks the performance of a group of stocks.
Bull Market: A period of rising stock prices.
Bear Market: A period of falling stock prices.
Volatility: The degree of variation of a stock's price.
Liquidity: How easily a stock can be bought or sold without significantly affecting its price.
Volume: The number of shares traded in a stock over a specific period.
Bid: The highest price a buyer is willing to pay for a stock.
Ask: The lowest price a seller is willing to accept for a stock.
Spread: The difference between the bid and ask prices.
Blue Chip Stocks: Large, well-established companies with a history of stable performance.
Penny Stocks: Stocks with low prices, often traded over-the-counter.
Initial Public Offering (IPO): The first sale of a company's stock to the public.
Market Order: An order to buy or sell a stock at the current market price.
Limit Order: An order to buy or sell a stock at a specified price.
Stop Order: An order to buy or sell a stock when it reaches a certain price.
Short Selling: Selling borrowed stock with the expectation of buying it back at a lower price.
Margin: Borrowed funds used to purchase stocks.
Margin Call: A demand by a broker for additional funds to cover potential losses.
Day Trader: A trader who buys and sells stocks within the same trading day.
Swing Trader: A trader who holds stocks for a few days to several weeks.
Long Position: Owning a stock with the expectation of its price rising.
Short Position: Selling a stock with the expectation of its price falling.
Resistance: A price level at which a stock tends to encounter selling pressure.
Support: A price level at which a stock tends to encounter buying pressure.
Moving Average: An average of a stock's price over a specific period, used to identify trends.
Candlestick: A type of chart that shows the open, high, low, and close prices of a stock over a specific period.
Volume Weighted Average Price (VWAP): The average price a stock has traded at throughout the trading day, weighted by volume.
Relative Strength Index (RSI): A momentum oscillator that measures the speed and change of price movements.
MACD (Moving Average Convergence Divergence): A trend-following momentum indicator that shows the relationship between two moving averages.
Beta: A measure of a stock's volatility relative to the market.
Alpha: A measure of an investment's performance relative to a benchmark.
Portfolio: A collection of investments held by an individual or institution.
Diversification: Spreading investments across different assets to reduce risk.
Asset Allocation: Allocating investments among different asset classes such as stocks, bonds, and cash.
Dividend Yield: The annual dividend income of a stock relative to its price.
Earnings Per Share (EPS): A company's net income divided by its number of outstanding shares.
Price-to-Earnings Ratio (P/E): A measure of a stock's valuation calculated by dividing its price by its earnings per share.
Return on Investment (ROI): The gain or loss generated on an investment relative to its cost.
Market Order: An order to buy or sell a stock at the best available price.
Limit Order: An order to buy or sell a stock at a specific price or better.
Stop Order: An order to buy or sell a stock once it reaches a certain price.
Trailing Stop: A stop order that adjusts automatically as the price of a stock moves.
Market Cap: The total market value of a company's outstanding shares.
Dividend Aristocrat: A company that has consistently increased its dividend for at least 25 consecutive years.
Dividend Reinvestment Plan (DRIP): A program that allows shareholders to automatically reinvest dividends to purchase additional shares.
Capital Gain: The profit made from selling an investment for more than its purchase price.
Capital Loss: The loss incurred from selling an investment for less than its purchase price.
Sector: A group of stocks that operate in the same industry.
Cyclical Stocks: Stocks that tend to rise and fall with the business cycle.
Defensive Stocks: Stocks that are less sensitive to economic cycles and provide stable returns.
Growth Stocks: Stocks of companies that are expected to grow at an above-average rate compared to the market.
One of the best way to start studying the stock market to Join India’s best comunity classes Investing daddy invented by Dr. Vinay prakash tiwari . The Governor of Rajasthan, the Honourable Sri Kalraj Mishra, presented Dr. Vinay Prakash Tiwari with an appreciation for creating the LTP Calculator.
LTP Calculator the best trading application in India

You can also downloadLTP Calculator app by clicking on download button.

Value Stocks: Stocks that are considered undervalued relative to their fundamentals.
Dividend Stocks: Stocks that pay regular dividends to shareholders.
Income Stocks: Stocks that provide consistent income through dividends.
**
0 notes
Text
How to Day Trade for a Living: A Beginner’s Guide to Trading is an excellent resource for novice traders who aspire to become successful day traders. In this book, Andrew Aziz, a Canadian trader and official Forbes Business Council member, succinctly describes the fundamentals of day trading and explains how it differs from other styles of trading and investment. The book is concise and easy to read, making it an ideal starting point for beginners who are interested in day trading. Although it provides readers with a comprehensive understanding of the fundamentals of day trading, Aziz acknowledges that simply reading the book will not make you a profitable trader. He emphasizes that profitability comes with practice, the right tools and software, ongoing education, and a serious approach to trading. For intermediate traders, the book offers an extensive overview of classic day trading strategies that most retail traders regularly use with proven success. Readers who believe they are beyond the novice stage may want to jump ahead and begin reading from Chapter 7 for a summary of the most important day trading strategies that are covered in the book. Each chapter provides a detailed explanation of various day trading strategies, including ABCD Pattern Trading, Bull Flag Momentum Trading, Top Reversal Trading, Bottom Reversal Trading, Moving Average Trend Trading, VWAP Trading, and Support and Resistance Trading. Aziz explains how to find the Stock in Play for trade, what indicators to use on the charts, when to enter and exit the trade, what the stop loss should be, and how to take profits. One of the book’s most useful features is how Aziz approaches day trading as a serious profession. He describes his daily morning routine, which includes waking up early, exercising, eating breakfast, and preparing his trading station before the markets open in New York. Aziz notes that whatever your routine may be, starting the morning in a similar fashion can greatly help your mental preparation for entering the market. How to Day Trade for a Living is a fun book to read, as Aziz successfully conveys his passion for trading throughout the text. He also shares his personal experiences, including a story about how he lost $10,000 in one day during his early trading career due to a lack of preparation and emotional control. This personal touch makes the book relatable and engaging, even for those who are not experienced traders. In summary, if you are interested in becoming a day trader, How to Day Trade for a Living is a great starting point. Aziz’s book provides a comprehensive overview of the fundamentals of day trading, including classic strategies that most retail traders regularly use with proven success. This book is not a get-rich-quick scheme, but rather a helpful guide that emphasizes the importance of professionalism, ongoing education, and a serious approach to trading. Don't miss out on this captivating read! Grab a copy of our book now or try it out on Audible with a FREE 30-day trial. Start the journey today and immerse yourself in a world of knowledge and inspiration. Click "Buy Now" or "Start My FREE Trial" to get started. Price: [price_with_discount] (as of [price_update_date] - Details)
0 notes
Text
According to Mikołaj Zakrzowski, a leading Web3 analyst at cryptocurrency analytics firm Cryptoquant, the current market conditions are leaning in favor of the bears. The analyst pointed to the fact that the sell volume from Bitcoin takers substantially overshadows the buy volume. This sort of market setup has previously proven unfavorable for the flagship digital currency. Image by @StackSmartly As of now, more market participants are looking to sell Bitcoin than buy it, creating a supply and demand imbalance. When there is more supply than demand, prices tend to drop. At the same time, Evai CEO Matthew Dixon emphasized concerns regarding the U.S. Dollar Index (DXY) breaking its resistance level. This breach suggests a stronger dollar outlook, which could potentially spell trouble for risk assets like Bitcoin and its altcoin peers. At press time, the world's largest cryptocurrency is priced at $26,000.22, with a 24-hour trading range between $25,574.72 and $26,183.10. Its market capitalization stands at over $506 billion. Despite the grim technical picture, there are still some signs of hope. Notably, the cryptocurrency's value remains above a crucial support benchmark of $25,157, which is the November 2022 volume weighted average price (VWAP). Some analysts have also pointed out bullish divergences that have formed on various Bitcoin charts, suggesting a potential upward price trajectory. Thus, while there are indications of possible headwinds for Bitcoin and other cryptocurrencies, some experts believe there is room for a bullish turnaround. Source
0 notes
Link

#Support and Resistance#Support level#Resistance Level#support and resistance levels#technical analysts#Adx#Vwap#Rsi
1 note
·
View note
Text
VWAP
Unlocking Trading Strategies with VWAP Indicator: A Comprehensive Guide Are you an aspiring trader looking to navigate the complex world of financial markets with precision and confidence? Or perhaps you’re a seasoned investor seeking to enhance your trading strategies with advanced tools? Whatever your level of expertise, understanding the VWAP (Volume Weighted Average Price) indicator can be…
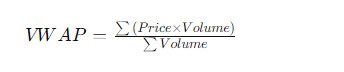
View On WordPress
#day trading#Financial Markets#learn technical analysis#Market Sentiment#stock markets#Support and Resistance#swing trading#technical analysis#Trading Strategies#trading tools#Trend Identification#Volume Weighted Average Price#VWAP#VWAP bands#VWAP crossovers#VWAP indicator
0 notes
Text
The Hidden Power Play: How Volume Weighted Average Price and Unemployment Rate Reveal Market Secrets Most Traders Miss Picture this: You’re juggling charts, sipping your third coffee, and suddenly the market plummets. Your trade nosedives faster than your gym motivation in January. You scream internally. Sound familiar? What if I told you two often-overlooked metrics—Volume Weighted Average Price (VWAP) and Unemployment Rate—could transform your trading game from tragic sitcom to financial thriller? Let’s uncover the underground tactics and ninja secrets hiding beneath these data points. Prepare for advanced insights, humor, and those elusive game-changing strategies. VWAP: The VIP Pass to Market Flow That Pros Guard Like Gold You know that feeling when you spot designer shoes on sale, but the last pair is snatched right in front of you? That’s what trading without VWAP feels like—always one step behind the pros. What Is VWAP? Volume Weighted Average Price is not just a fancy line on your chart. It’s the price at which most trading volume occurred during a session. Big players (a.k.a. the market whales) use it as their benchmark. If you’re not watching it, you might as well be trading blindfolded. Underground Tactic: VWAP as a Dynamic Support and Resistance Zone Forget rigid lines drawn in 2017. VWAP adapts to the market like your cat refusing to sit in the same spot twice. Price hovering around VWAP signals equilibrium—but when price breaks away with volume, that’s your cue for potential entries. Key Moves: - Entry Trigger: If price dips below VWAP and reclaims it with volume, consider a long position. Reverse for shorts. - Confirmation: Look for rejection patterns near VWAP (pin bars, wicks) backed by volume surges. Example: On March 8, 2024, GBP/AUD rebounded sharply after reclaiming VWAP post-unemployment data release—a textbook bounce seen by few. Unemployment Rate: The Silent Market Shaker You Ignore at Your Peril Traders treat economic calendars like laundry schedules—not checking until disaster strikes. But unemployment data? That’s where the real magic brews. Why It Matters More Than You Think: High unemployment = weaker currency expectations. Low unemployment = stronger currency confidence. But here’s the twist: It’s not the number that moves markets—it’s the surprise factor. Example: February 2024, U.S. Non-Farm Payrolls (NFP) stunned with 353,000 jobs vs. 185,000 expected. USD skyrocketed. Traders watching only price action missed the goldmine. Elite Insight: The VWAP + Unemployment Rate Combo Hack - Pre-News Setup: Track price relative to VWAP before major unemployment data. - Post-News Entry: After an unexpected release, check if price spikes away from VWAP with volume. This often leads to continuation moves as institutions adjust positions. The “Smart Trader” Routine: Mastering VWAP & Unemployment Together - Economic Calendar Prep: Use StarseedFX’s live updates Forex News Today to anticipate unemployment releases. - Pre-Event VWAP Scan: Identify if price is hugging, above, or below VWAP. - Reaction Watch: After data release, observe price behavior relative to VWAP within the first 5-15 minutes. - Volume Confirmation: Enter when price aligns with VWAP direction and volume backs the move. - Journal Everything: Use Free Trading Journal to track outcomes. Hidden Patterns: How VWAP Exposes False Breakouts False breakouts are like bad first dates—promising at first but leave you wondering where it all went wrong. VWAP helps you avoid these heartbreaks. Pro Technique: VWAP Reclaim Trap - Fakeout Spotting: If price breaks resistance but quickly falls below VWAP, it often signals a bull trap. - Short Setup: Enter short after price closes back under VWAP with volume decline. Example: EUR/USD, January 2024. Price broke 1.0900 but collapsed under VWAP within minutes. Smart traders shorted; others clung to hope. Expert Quotes: What the Pros Say John Carter, Author of Mastering the Trade, states: “VWAP is institutional traders’ north star—if you ignore it, you’re trading their leftovers.” Source Kathy Lien, Managing Director at BK Asset Management, emphasizes: “Economic data surprises often drive the biggest moves; understanding the context is key.” Source Real-World Success: When VWAP & Unemployment Aligned Perfectly January 2024: AUD/USD spiked after shock Australian employment data. Traders using VWAP noticed price hugging above it pre-release, confirming bullish momentum post-announcement. Those aligning VWAP with fundamentals rode the move for 85 pips. Why Most Traders Miss This (But You Won't) - They Overlook VWAP: Mistaking it as a day trader tool. Wrong. Swing traders can use daily, weekly, even monthly VWAP. - They Misread Unemployment: They see numbers, not the context. - They Ignore Volume: Price moves are whispers; volume is the megaphone. Your Next-Level Blueprint: - Master VWAP as a dynamic market compass. - Treat unemployment data as volatility fuel. - Fuse both metrics to exploit institutional footprints. - Automate your trading precision using the Smart Trading Tool. —————– Image Credits: Cover image at the top is AI-generated Read the full article
0 notes
Text
Trading Like a Pro: Winning Intraday Strategies & Smart Stock Market Investment Tips
Success in the stock market requires the right approach, whether you’re engaging in intraday trading or long-term investing. Intraday trading strategies focus on quick, short-term trades, while stock market investment tips help build sustainable wealth. This article explores effective intraday trading techniques, risk management principles, and key investment strategies to enhance profitability and trading efficiency.
Mastering Intraday Trading Strategies
Intraday trading, also known as day trading, involves buying and selling stocks within the same trading day. To maximize gains and minimize risks, traders rely on technical analysis, market trends, and disciplined strategies.
1. Scalping – Profiting from Small Price Movements
Traders execute multiple trades throughout the day, targeting small price changes.
Works best with high-volume stocks and minimal bid-ask spreads.
2. Momentum Trading – Capturing Strong Price Movements
Focuses on stocks with high volatility and significant price action.
Entry signals include breakouts above resistance levels and surging trading volume.
3. Breakout Trading – Entering Early on Strong Moves
Involves trading stocks that break key support or resistance levels.
Confirm breakouts with volume spikes to validate the trend.
4. VWAP Strategy – Trading Around Volume-Weighted Price
VWAP (Volume Weighted Average Price) acts as a reference point for institutional traders.
Buying below VWAP signals a bullish move, while selling above VWAP suggests weakness.
5. Reversal Trading – Spotting Trend Changes
Identifies potential trend reversals using RSI, MACD, and candlestick patterns.
Works well when price action shows clear divergence from technical indicators.
Essential Stock Market Investment Tips
Long-term market success requires a well-planned strategy. These stock market investment tips help traders and investors make informed decisions.
1. Diversify Your Portfolio to Minimize Risk
Invest in multiple sectors to reduce exposure to a single stock or industry.
A diversified portfolio balances losses and profits across different assets.
2. Follow Market Trends Before Making Decisions
Monitor broader market trends to align investments with prevailing momentum.
Stocks typically perform better when moving in the same direction as the overall market.
3. Use Risk Management Strategies
Always set a stop-loss to protect capital from unexpected downturns.
Never risk more than 2% of total capital on a single trade.
4. Stay Updated on News & Economic Events
Market-moving news, earnings reports, and global events impact stock prices.
Follow financial news sources to stay ahead of potential market shifts.
5. Avoid Emotional Trading & Stick to a Strategy
Fear and greed often lead to impulsive decisions that hurt profitability.
Develop a solid trading plan and execute trades based on analysis rather than emotions.
Combining Intraday Trading with Investment Strategies
A well-rounded approach includes both short-term intraday trading and long-term investments.
Use technical analysis for intraday trades and fundamental analysis for long-term investments.
Set realistic profit targets and maintain strict risk management in both trading styles.
Backtest strategies to analyze past performance before applying them to live markets.
Conclusion
A successful trading journey requires mastering intraday trading strategies while following smart stock market investment tips. Whether you aim for quick profits through scalping or long-term gains via diversification, a disciplined approach ensures consistent success. By implementing risk management, staying informed, and executing well-planned trades, traders can navigate market volatility effectively and enhance profitability.
0 notes
Photo

Took a trade at VWAP rejection. Then stock started creating support just below VWAP so exit with a small profit. As i just trade for 1st 2 hours so missed the next move... shorting at resistance when it got rejected
1 note
·
View note
Text
Unveiling VWAP: A Comprehensive Guide to Volume Weighted Average Price

In the realm of financial markets, traders rely on a multitude of tools and indicators to analyze price movements and make informed decisions. Among these tools, Volume Weighted Average Price (VWAP) stands out as a crucial metric used by traders, investors, and institutions to assess the average price at which a security has traded throughout the trading day, taking into account both price and volume. In this in-depth exploration, we uncover the intricacies of VWAP, its calculation, interpretation, and practical applications in trading strategies.
Understanding VWAP
Volume Weighted Average Price (VWAP) is a trading benchmark commonly used by institutional traders to evaluate the efficiency of their execution and assess the fair value of a security over a specific time period, typically one trading day. Unlike simple moving averages that only consider price data, VWAP incorporates both price and volume information, giving more weight to periods of high trading activity.
Calculating VWAP
The VWAP calculation involves two primary components: price and volume. It is computed by multiplying the price of each transaction by the corresponding volume, summing up these values, and then dividing by the total volume traded over the specified time frame. The formula for VWAP is as follows:
[ \text{VWAP} = \frac{\sum{(Price \times Volume)}}{\sum{Volume}} ]
Key Features of VWAP
Intraday Benchmark: VWAP is often used as a benchmark by institutional traders to evaluate their execution performance relative to the average price at which a security has traded throughout the trading day. Traders aim to execute orders at prices better than the VWAP to achieve optimal results.
Sensitivity to Volume: Unlike simple moving averages, VWAP gives more weight to periods of higher trading volume, reflecting the influence of market participants' activity levels on the average price. Therefore, VWAP is particularly sensitive to changes in trading volume throughout the day.
Intraday Trends Assessment: By comparing the current price of a security to its VWAP, traders can gauge whether the prevailing intraday trend is bullish or bearish. Prices trading above VWAP may indicate bullish sentiment, while prices trading below VWAP may suggest bearish sentiment.
Practical Applications of VWAP
Execution Strategies: Institutional traders often use VWAP as a benchmark for executing large orders over the course of the trading day. By breaking down orders into smaller chunks and executing them at prices close to or better than VWAP, traders aim to minimize market impact and achieve efficient execution.
Trend Confirmation: Traders and investors use VWAP as a tool for confirming the direction of intraday trends. When prices consistently trade above VWAP, it may signal bullish momentum, while prices consistently trading below VWAP may indicate bearish momentum.
Support and Resistance Levels: VWAP can also serve as a dynamic support or resistance level during intraday trading. Traders often observe how prices interact with VWAP to identify potential buying or selling opportunities and determine optimal entry and exit points.
Limitations of VWAP
Intraday Focus: VWAP is primarily suited for intraday trading and may not be as effective for longer-term analysis or investment decisions. Traders and investors should complement VWAP analysis with other tools and indicators for comprehensive market analysis.
Lack of Predictive Power: While VWAP provides valuable insights into intraday price trends and trading activity, it is not a predictive indicator and should be used in conjunction with other technical and fundamental analysis tools for decision-making.
Conclusion
Volume Weighted Average Price (VWAP) is a powerful tool that provides traders, investors, and institutions with valuable insights into intraday price trends, trading activity, and execution efficiency. By incorporating both price and volume data, VWAP offers a comprehensive view of market dynamics and serves as a benchmark for evaluating performance and identifying trading opportunities. While VWAP has its limitations, its practical applications in execution strategies, trend confirmation, and support/resistance analysis make it an indispensable tool in the toolkit of market participants. As with any trading tool or indicator, it's essential to understand VWAP's strengths and weaknesses and use it in conjunction with other analysis techniques for optimal results in navigating the complexities of financial markets.
0 notes
Text
Copper fell by ab out 1.6% and trades around $3.2910 a pound. The market found some selling around the day's upper DVAH
Copper fell by ab out 1.6% and trades around $3.2910 a pound. The market found some selling around the day’s upper DVAH
Copper fell by ab out 1.6% and trades around $3.2910 a pound. The market found some selling around the day’s upper DVAH which is cofluent with the weekly VWAP. DVAL may serving as supportive level while a move lower leading the path of least resistance towards the lower and prior VWAP close level.

View On WordPress
0 notes
Text
How to Day Trade for a Living: A Beginner’s Guide to Trading is an excellent resource for novice traders who aspire to become successful day traders. In this book, Andrew Aziz, a Canadian trader and official Forbes Business Council member, succinctly describes the fundamentals of day trading and explains how it differs from other styles of trading and investment. The book is concise and easy to read, making it an ideal starting point for beginners who are interested in day trading. Although it provides readers with a comprehensive understanding of the fundamentals of day trading, Aziz acknowledges that simply reading the book will not make you a profitable trader. He emphasizes that profitability comes with practice, the right tools and software, ongoing education, and a serious approach to trading. For intermediate traders, the book offers an extensive overview of classic day trading strategies that most retail traders regularly use with proven success. Readers who believe they are beyond the novice stage may want to jump ahead and begin reading from Chapter 7 for a summary of the most important day trading strategies that are covered in the book. Each chapter provides a detailed explanation of various day trading strategies, including ABCD Pattern Trading, Bull Flag Momentum Trading, Top Reversal Trading, Bottom Reversal Trading, Moving Average Trend Trading, VWAP Trading, and Support and Resistance Trading. Aziz explains how to find the Stock in Play for trade, what indicators to use on the charts, when to enter and exit the trade, what the stop loss should be, and how to take profits. One of the book’s most useful features is how Aziz approaches day trading as a serious profession. He describes his daily morning routine, which includes waking up early, exercising, eating breakfast, and preparing his trading station before the markets open in New York. Aziz notes that whatever your routine may be, starting the morning in a similar fashion can greatly help your mental preparation for entering the market. How to Day Trade for a Living is a fun book to read, as Aziz successfully conveys his passion for trading throughout the text. He also shares his personal experiences, including a story about how he lost $10,000 in one day during his early trading career due to a lack of preparation and emotional control. This personal touch makes the book relatable and engaging, even for those who are not experienced traders. In summary, if you are interested in becoming a day trader, How to Day Trade for a Living is a great starting point. Aziz’s book provides a comprehensive overview of the fundamentals of day trading, including classic strategies that most retail traders regularly use with proven success. This book is not a get-rich-quick scheme, but rather a helpful guide that emphasizes the importance of professionalism, ongoing education, and a serious approach to trading. Don't miss out on this captivating read! Grab a copy of our book now or try it out on Audible with a FREE 30-day trial. Start the journey today and immerse yourself in a world of knowledge and inspiration. Click "Buy Now" or "Start My FREE Trial" to get started. Price: [price_with_discount] (as of [price_update_date] - Details)
0 notes