#UV-Visible Spectrophotometer
Explore tagged Tumblr posts
Text

UV-Visible Spectrophotometer
UV-Visible Spectrophotometer is a double beam instrument with a computer simulation optimized optical base. The continuously adjustable spectral bandwidth ranges from 0.1 to 5nm, making it ideal for samples with sharp absorption peaks. Precision is improved across the UV-Vis spectrum, from 190nm to 900nm, due to the well-aligned PMT detector and high-quality deuterium, tungsten, and mercury lamps. The device includes an optional 8-position cell holder as well as a high throughput 100-position autosampler with an easy-to-use interface.
0 notes
Text

Double-beam UV-Visible Spectrophotometer
Double-beam UV-Visible Spectrophotometer is adopted with microcomputer technology and electronic control system, features holographic grating with 1200 lines/mm. Equipped with solid silicone photodiode detector and xenon lamp as light source, have 190 to 1100 nm of wavelength range. Designed with 7-inch TFT screen with sensitive buttons and large sample chamber, it also supports USB storage and different data formats.
#Double-beam UV-Visible Spectrophotometer manufacturerMeterin Georgia#Double-beam UV-Visible Spectrophotometer suppliers in Georgia#Double-beam UV-Visible Spectrophotometer manufacturer in Hawaii#Double-beam UV-Visible Spectrophotometer suppliers in Hawaii#Double-beam UV-Visible Spectrophotometer manufacturer in Indiana#Double-beam UV-Visible Spectrophotometer suppliers in Indiana#Double-beam UV-Visible Spectrophotometer manufacturer in Iowa#Double-beam UV-Visible Spectrophotometer suppliers in Iowa
0 notes
Text
Best Blood Bag Tube Sealer Supplier And Manufacturer In India — Lasany international
One of our standout products is the Best Blood Bag Tube Sealer, which has been widely acclaimed for its reliability and durability. As a trusted blood bag tube sealer supplier, we offer advanced sealing solutions that maintain the integrity of blood samples, preventing any contamination or leaks.
Lasany International, we are not only dedicated to manufacturing top-notch medical equipment but also committed to being a preferred blood collection monitor supplier. We cater to various healthcare institutions, hospitals, clinics, and medical facilities across India and beyond. Our focus on customer satisfaction and prompt service has earned us the trust of countless clients nationwide.
Contact us today to learn more about our products and services and experience the Lasany International difference!
If you are looking for top-tier medical equipment manufacturers and reliable blood collection monitor suppliers in India, Lasany International should be your ultimate destination. Their commitment to excellence, product quality, and customer satisfaction make them the trusted partner in the healthcare industry.
0 notes
Text
Understanding the Nanodrop Spectrophotometer: A Crucial Tool for Nucleic Acid and Protein Analysis

In the fields of molecular biology, genetics, and biochemistry, accuracy and efficiency are vital. One of the most widely used instruments that meets these demands is the Nanodrop spectrophotometer. Designed to measure the concentration and purity of nucleic acids and proteins in extremely small sample volumes, this compact and powerful tool has revolutionized laboratory workflows. If you’re working in a lab or planning to upgrade your analytical instruments, you can get precise and rapid readings using this remarkable device.
What is a Nanodrop Spectrophotometer?
A Nanodrop spectrophotometer is a micro-volume UV-Vis spectrophotometer that allows scientists to quantify DNA, RNA, and proteins with as little as 1-2 microliters of sample. Unlike traditional spectrophotometers, which often require cuvettes and larger volumes, the Nanodrop uses surface tension to hold a droplet of sample between two optical surfaces. This innovation makes it possible to analyze minute samples without wasting reagents or time.
The instrument works by passing ultraviolet and visible light through the sample. It measures how much light is absorbed at specific wavelengths to determine the concentration and purity of the sample. Its most common application is the measurement of nucleic acids at 260 nm and proteins at 280 nm.
How Does It Work?
The Nanodrop spectrophotometer employs a unique sample-retention system that uses optical fibers and a pedestal design. Here's a simplified breakdown of its operation:
Sample Placement: A tiny drop (typically 1-2 µL) of the sample is pipetted directly onto the lower measurement pedestal.
Optical Arm Movement: The upper optical arm lowers to create a liquid column.
Light Path Creation: A light beam travels through the sample and the absorbance is measured.
Software Analysis: The built-in software instantly calculates concentration, purity ratios (e.g., 260/280, 260/230), and displays results.
This procedure is not only quick—usually under 10 seconds—but also easy to repeat, reducing user error and improving reproducibility.
Key Features and Advantages
The popularity of the Nanodrop spectrophotometer is no accident. Here are some of the key benefits it offers:
Micro-Volume Capability: Perfect for precious or limited samples.
No Need for Cuvettes: Reduces plastic waste and lowers consumables cost.
Fast Analysis: Results are available in just seconds.
High Accuracy: Provides consistent and reliable results.
Integrated Software: User-friendly interface with data logging and export options.
Purity Assessment: Detects contamination in samples through purity ratios.
Whether you're working in genomics, proteomics, or clinical diagnostics, these features contribute to more efficient lab workflows.
Applications Across Fields
The Nanodrop spectrophotometer is widely used across several scientific disciplines:
1. Molecular Biology
Used to quantify DNA or RNA extracted from cells or tissues. Its fast and accurate measurement helps researchers prepare samples for downstream applications like PCR, qPCR, or sequencing.
2. Proteomics
The tool measures protein concentrations and can also analyze protein-ligand interactions when used with additional methods.
3. Clinical Diagnostics
In clinical labs, it supports the identification of pathogens or genetic mutations through sample analysis.
4. Pharmaceutical Research
Helps in drug development by analyzing proteins and nucleic acids critical to therapeutic targets.

Limitations and Considerations
While the Nanodrop spectrophotometer is a powerful tool, it does have limitations:
Lower Sensitivity for Diluted Samples: May not be ideal for extremely low-concentration samples.
No Fluorescence Detection: Cannot measure samples that require fluorescent tags.
Requires Careful Cleaning: Residual samples can interfere with results if not cleaned properly between uses.
To maximize performance, users must follow proper maintenance and calibration protocols.
Popular Models and Alternatives
Some of the most well-known models include:
NanoDrop One/OneC: Offers full-spectrum UV-Vis analysis and includes a cuvette option.
NanoDrop 2000: A classic model known for its reliability and broad wavelength range.
NanoDrop Lite: Budget-friendly option for essential quantification needs.
Alternatives include traditional spectrophotometers and fluorometers, though they may lack the same convenience and sample efficiency.
Why Choose a Nanodrop Spectrophotometer?
If you need accurate, fast, and efficient analysis of biomolecules in small sample volumes, the Nanodrop spectrophotometer is a top-tier choice. It eliminates the need for dilution, simplifies workflows, and delivers reproducible results—all of which are critical for modern scientific research.
For any laboratory looking to optimize its analysis process, especially when working with limited or precious samples, it’s time to get the reliability and performance that only a Nanodrop spectrophotometer can provide.
Conclusion
The Nanodrop spectrophotometer stands as a benchmark in micro-volume analysis, blending precision, speed, and ease of use into a single compact device. It supports a wide range of applications, from basic research to advanced diagnostics, making it indispensable in many labs worldwide. If your work demands high-quality molecular quantification without wasting resources or time, it's smart to get a Nanodrop spectrophotometer and streamline your workflow with confidence.
0 notes
Text
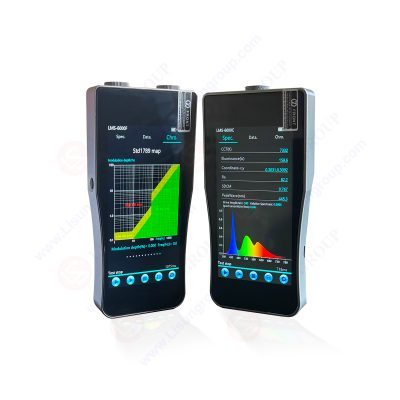
Introduction In the realm of analytical instrumentation, spectrophotometry stands as one of the most essential and widely used techniques for quantifying light absorption and transmission. By analyzing how a substance interacts with light at different wavelengths, spectrophotometers provide critical data across scientific research, industrial quality assurance, environmental monitoring, and medical diagnostics. Among the leading manufacturers in this field is Shanghai LISUN, a Shanghai-based company that has established itself as a trusted provider of high-precision optical measurement equipment. With over two decades of experience, Shanghai LISUN offers a diverse range of spectrophotometers designed to meet international standards while delivering outstanding performance, reliability, and user-friendliness. This article presents a comprehensive technical overview of Shanghai LISUN spectrophotometers, covering their working principles, hardware components, software capabilities, calibration procedures, application areas, and future development directions. Whether you are a researcher, lab technician, or industry professional, this guide will serve as an invaluable resource for understanding and utilizing Shanghai LISUN’s advanced spectrophotometric technology. LMS-6000 Portable CCD Spectroradiometer Fundamentals of Spectrophotometry What Is a Spectrophotometer? A spectrophotometer is an optical instrument used to measure the intensity of light as a function of its wavelength after it has passed through or been reflected by a sample. This technique enables users to determine the concentration of a substance in solution, identify unknown compounds, or assess the optical properties of materials such as glass, plastics, and coatings. Types of Spectrophotometers Spectrophotometers can be broadly categorized into several types based on their design and application: • UV-Vis Spectrophotometers: Operate in the ultraviolet and visible spectrum (typically 190–800 nm), ideal for biological and chemical analysis. • NIR Spectrophotometers: Work in the near-infrared range (700–2500 nm), often used for food, pharmaceutical, and polymer analysis. • FTIR Spectrophotometers: Fourier Transform Infrared instruments used for identifying functional groups in organic molecules. • Portable Spectrophotometers: Compact, battery-powered devices suitable for fieldwork and mobile labs. Shanghai LISUN primarily focuses on UV-Vis and portable models, offering both single-beam and double-beam configurations tailored to specific applications. Technical Overview of Shanghai LISUN Spectrophotometers Company Background Founded in 2003, Shanghai LISUN has grown into a globally recognized brand in lighting and optical testing equipment. Headquartered in Shanghai, China, Shanghai LISUN holds certifications including CE, RoHS, ISO 9001, and IEC standards. Its spectrophotometers are widely adopted in academic institutions, research laboratories, and industrial facilities around the world. Product Range Shanghai LISUN offers a comprehensive portfolio of spectrophotometers designed to suit various needs: Each model is built using precision-engineered optical components and robust mechanical structures to ensure long-term stability and repeatability. Key Components and Design Features • Light Source Shanghai LISUN spectrophotometers use either deuterium lamps (for UV range) or tungsten-halogen lamps (for visible range). Some models feature dual-lamp systems for seamless switching between UV and visible measurements. • Monochromator The monochromator employs holographic diffraction gratings to separate polychromatic light into individual wavelengths. This ensures minimal stray light and high spectral purity. • Detector Photomultiplier tubes (PMTs) or silicon photodiodes are used depending on the sensitivity requirements. These detectors convert light signals into electrical current with high linearity and low noise. • Cuvette Holder Standard cuvette holders accommodate 10mm path-length cells, with optional accessories for micro-volume samples, solid reflectance probes, and temperature-controlled chambers. • Software Interface Shanghai LISUN’s proprietary software provides a user-friendly graphical interface with features such as: • Real-time spectral scanning • Quantitative analysis via calibration curves • Kinetic measurements • Multi-wavelength analysis • Data export in CSV, Excel, PDF formats • Remote control via USB or Ethernet Calibration and Performance Verification Importance of Calibration Regular calibration is crucial to maintaining the accuracy and traceability of spectrophotometric measurements. Shanghai LISUN instruments come pre-calibrated from the factory but require periodic recalibration using certified reference materials (CRMs). Common calibration checks include • Wavelength Accuracy: Verified using holmium oxide filters or mercury lamps. • Absorbance Linearity: Checked using neutral density filters or potassium dichromate solutions. • Stray Light Test: Performed with sodium iodide or potassium chloride solutions. • Baseline Flatness: Ensured by measuring air or blank samples. Shanghai LISUN software includes built-in calibration wizards that guide users through each step, ensuring compliance with international standards such as ISO 6425 and ASTM E275. Applications Across Industries Life Sciences and Biotechnology In molecular biology and biochemistry labs, Shanghai LISUN spectrophotometers are extensively used for • Nucleic acid quantification (DNA/RNA at 260/280 nm) • Protein concentration determination (BCA, Bradford assays) • Enzyme kinetics studies • Cell viability assays For example, protein concentration can be estimated using the Beer-Lambert Law by measuring absorbance at 280 nm, where aromatic amino acids like tryptophan and tyrosine absorb strongly. Pharmaceutical Industry Pharmaceutical companies rely on spectrophotometric analysis during drug formulation, production, and quality control. Applications include: • Determining active pharmaceutical ingredient (API) content • Monitoring tablet dissolution rates • Analyzing impurities and degradation products • Verifying excipient compatibility Portable Shanghai LISUN models are particularly useful for on-site quality checks in production lines. Environmental Monitoring Environmental scientists use Shanghai LISUN spectrophotometers to analyze water, soil, and air samples for pollutants such as: • Heavy metals (lead, arsenic, mercury) • Nutrients (nitrates, phosphates) • Organic contaminants (pesticides, herbicides) • Microbial load indicators Education and Research Institutions Universities and research centers use Shanghai LISUN spectrophotometers for teaching and experimental work. Their intuitive interface makes them ideal for student training, while advanced models support detailed kinetic and spectral studies in fields like chemistry, physics, and materials science. Operational Workflow with Shanghai LISUN Spectrophotometers To demonstrate the practical usage of Shanghai LISUN spectrophotometers, here is a typical workflow Step 1: Sample Preparation • Prepare a series of standard solutions with known concentrations. • Dilute the test sample if necessary to bring absorbance within the linear range (usually between 0.1 and 1.0). Step 2: Instrument Setup • Turn on the instrument and allow the lamp to warm up. • Select the appropriate wavelength(s) based on the analyte’s absorption characteristics. • Set scan mode (single wavelength, multi-wavelength, or full spectrum). Step 3: Calibration • Measure the absorbance of each standard solution. • Plot a calibration curve using absorbance vs. concentration. Step 4: Sample Measurement • Place the test sample in the cuvette holder. • Record the absorbance value. • Use the calibration curve to calculate the concentration. Step 5: Data Analysis and Reporting • Export data to external software for further processing. • Generate reports with graphs and statistical summaries. • Save results for audit trails and documentation. Future Trends and Technological Innovations As optical measurement technology continues to evolve, Shanghai LISUN remains committed to staying at the forefront of innovation. Several key trends are shaping the next generation of spectrophotometers. • Miniaturization and Portability Advancements in micro-optics and sensor technology are enabling the development of compact, handheld spectrophotometers. Shanghai LISUN is exploring wearable and wireless models for real-time field analysis in agriculture, healthcare, and environmental science • Integration with Artificial Intelligence (AI) Machine learning algorithms are being applied to enhance data interpretation, automate calibration, and improve predictive analytics. Shanghai LISUN is researching AI-driven spectrophotometers that can learn from historical data and optimize measurement conditions autonomously. • Internet of Things (IoT) Connectivity Smart spectrophotometers with cloud connectivity allow for remote monitoring, real-time data sharing, and centralized management. Shanghai LISUN plans to integrate IoT capabilities into future models, enabling users to access data from anywhere via mobile apps or web portals. • Sustainability and Green Technology Shanghai LISUN is also focusing on sustainable manufacturing practices, including energy-efficient designs, recyclable materials, and reduced electronic waste. Future spectrophotometers may feature solar-powered options or eco-friendly packaging. Conclusion Shanghai LISUN spectrophotometers represent a significant advancement in the field of optical measurement. With cutting-edge technology, user-friendly interfaces, and broad application versatility, they serve as indispensable tools across academia, industry, and government sectors. Whether analyzing biomolecules in a life sciences lab, monitoring water quality in environmental testing, or ensuring product consistency in pharmaceutical manufacturing, Shanghai LISUN spectrophotometers deliver consistent performance and reliable results. Looking ahead, Shanghai LISUN will continue to innovate and expand its product portfolio, incorporating smart technologies and sustainable practices to meet the evolving needs of global users. As spectrophotometry becomes increasingly integrated with digital platforms and automation, Shanghai LISUN is well-positioned to lead the way in shaping the future of optical measurement. Read the full article
0 notes
Text
0 notes
Text
Multi-Cuvette Spectrophotometer Market Size Forecast Unlocking High-Throughput Analysis in Modern Laboratories
The Multi-Cuvette Spectrophotometer Market Size is witnessing significant momentum as demand for advanced analytical instruments grows across diverse scientific sectors. This sophisticated equipment has become indispensable in industries such as pharmaceuticals, environmental testing, food safety, and life sciences research. Offering high-throughput measurement, better accuracy, and enhanced automation capabilities, multi-cuvette spectrophotometers are increasingly favored for simultaneous analysis of multiple samples—delivering both operational efficiency and precision.
According to recent industry analysis, the Multi-Cuvette Spectrophotometer Market Size Size is poised for steady expansion through 2030, backed by technological advancements, greater R&D investments, and the global shift toward automated laboratory processes. From quantifying nucleic acids and proteins to monitoring industrial chemical reactions, this instrumentation is proving central to modern data-driven workflows.
Market Size Overview
The Multi-Cuvette Spectrophotometer Market Size stands at the intersection of automation and high-capacity testing. These instruments enable the analysis of multiple samples simultaneously, saving time and minimizing human error—critical factors in laboratory environments where accuracy and throughput are paramount.
While traditional single-cuvette devices require manual replacement for each test, the multi-cuvette variant dramatically improves speed and reproducibility. These devices are particularly relevant in high-volume settings like pharmaceutical QC labs and academic research institutions.
The Multi-Cuvette Spectrophotometer Market Size Growth is being further accelerated by growing interest in compact benchtop systems, integrated software solutions, and IoT-based remote access features.
Key Market Size Drivers
Several factors are fueling the widespread adoption of multi-cuvette spectrophotometers:
Rising demand for automation: Laboratories are integrating automated spectrophotometry to streamline workflows and reduce manual intervention.
Stringent quality and compliance standards: Regulatory frameworks in pharmaceuticals and food safety are driving the need for highly accurate optical instruments.
Growth in life sciences research: Increasing focus on DNA/RNA quantification, protein analysis, and cell-based assays is bolstering product usage.
Technological innovation: Advances in light source stability, detector sensitivity, and cuvette design continue to improve instrument performance.
Market Size Segmentation
By Technology
UV-Visible Spectrophotometers: The most widely adopted due to versatility across biochemistry and industrial applications.
Fluorescence Spectrophotometers: Gaining ground in advanced research due to their superior sensitivity.
Infrared Spectrophotometers: Used in organic compound analysis, particularly in chemical and materials research.
By Component
Optical Systems: Core to instrument accuracy.
Software Platforms: Essential for data management and real-time analytics.
Cuvettes & Holders: Customized for UV, visible, or IR range and crucial for sample stability.
By End-User
Pharmaceutical & Biotech Companies: Employing spectrophotometers for formulation, purity, and stability testing.
Environmental Testing Laboratories: Monitoring pollutants in water and air samples.
Academic & Research Institutions: Relying on the equipment for teaching and experimental consistency.
Food & Beverage Market Size: Using spectrophotometry for ingredient verification and contamination checks.
Trends in the Market Size
Integration with Laboratory Information Management Systems (LIMS): Enhances traceability and efficiency.
Energy-efficient and portable designs: Emerging models cater to mobile labs and field applications.
Cloud-based Data Access: Facilitates remote monitoring and compliance auditing.
Reusability and sustainability: Demand for eco-friendly cuvettes and low-energy instruments is rising.
Increased customization: Instruments tailored to specific assay needs are gaining popularity among niche users.
Regional Insights
North America leads in adoption, particularly in pharmaceutical R&D and government-funded environmental monitoring programs.
Europe is witnessing increased demand in academic and food testing sectors, with strict regulatory support.
Asia-Pacific emerges as the fastest-growing region, driven by expanding research investments in China, Japan, and India.
Latin America and the Middle East & Africa show steady growth, particularly in educational institutions and agricultural testing labs.
Key Opportunities
Expansion into developing regions with emerging biotech clusters.
Collaboration with research institutes for real-time application data.
Development of AI-integrated analysis software.
Modular, upgradeable systems for budget-conscious users.
Major Players in the Market Size
Key companies shaping the Multi-Cuvette Spectrophotometer Market Size Share include:
Thermo Fisher Scientific
Agilent Technologies
PerkinElmer Inc.
Shimadzu Corporation
Hitachi High-Tech Corporation
Eppendorf AG
Bio-Rad Laboratories
Beckman Coulter (Danaher Corporation)
These manufacturers are focusing on robust design, user-friendly interfaces, and software upgrades to gain a competitive edge.
Conclusion
The Multi-Cuvette Spectrophotometer Market Size is evolving into a vital segment of the global analytical instrumentation industry. Its growing presence in laboratories worldwide reflects not only technological progress but also a broader shift toward digitized, high-throughput scientific processes. As demand for precision diagnostics and efficient analytical workflows continues to rise, this market is expected to experience substantial growth through 2030 and beyond.
Trending Report Highlights
Explore other fast-growing technologies transforming the industrial and scientific sectors:
Proximity And Displacement Sensor Market Size
Sapphire Semiconductor Market Size
Scara Robot Market Size
Piezoelectric Hemisphere Market Size
Pin Fin Heat Sink For IGBT Market Size
Porous Silicon Substrate Market Size
Power Discrete And Module Market Size
Video Measuring System Market Size
Servo Drive Market Size
SIC On Insulator Substrate Market Size
Small Cell Antenna Market Size
Smart Demand Response Market Size
0 notes
Text
0 notes
Text
Unraveling the Principles of HPLC: Insights for Professionals in Zodiac Life Sciences
High-Performance Liquid Chromatography (HPLC) is a vital analytical technique widely used in various scientific fields, including pharmaceuticals, environmental testing, and biochemistry. The principle behind HPLC involves separating compounds in a mixture based on their interactions with a stationary phase and a mobile phase. In simple terms, the mobile phase, which is often a liquid solvent, carries the sample through a column filled with a solid material (the stationary phase). As the sample moves through the column, different components in the mixture interact differently with the stationary phase, leading to their separation.

At its core, HPLC operates on the premise of differential partitioning. Different substances will have varying affinities for the stationary phase, meaning that some will pass through the column faster than others. This separation occurs due to differences in size, polarity, and charge of the compounds involved. Once the compounds are separated, they can be detected and quantified by various detectors, such as UV-visible spectrophotometers, making HPLC an indispensable tool for analyzing complex mixtures.
Zodiac Life Sciences embraces the advantages of HPLC in its research and product development efforts. By utilizing this powerful technique, researchers can efficiently analyze the purity and composition of new pharmaceutical compounds, ensuring that their products are both effective and safe for consumers. Such precision is essential in the fast-paced world of drug development, where small changes can significantly impact a product's efficacy.
Moreover, HPLC is essential in quality control processes. With Zodiac Life Sciences committed to maintaining high standards, HPLC plays a crucial role in monitoring raw materials and finished products. The ability to quickly and accurately assess the substance composition allows the organization to adhere to regulatory guidelines and deliver reliable products to the market.
In summary, the principle of HPLC revolves around separating and analyzing components in a mixture through liquid chromatography. Organizations like Zodiac Life Sciences harness this technology to enhance their research, ensure product safety, and maintain quality control. As analytical techniques like HPLC continue to evolve, they will undoubtedly play a more significant role in advancing science and improving our quality of life.
0 notes
Text
Why fused silica is suitable as an important component for optical glass applications?
Quartz, especially fused silica, is widely used in optical applications because of its unique properties. But do you know why fused silica is suitable as an important component for optical glass applications? Some excellent properties of fused silica determine its importance.
Properties of Fused Silica
1.High transmittance
Fused silica transmits light from the UV to the IR spectrum. According to the wave band, quartz glass is divided into JGS1, JGS2, JGS3 (related to the OH group content in the material). JGS1 is UV grade quartz glass with high transmittance (about 93.5%) in the 180-2500nm wave band. JGS2 quartz glass is transparent in the 220-2500 nm wave band, with a transmittance of over 93.5%. JGS3 is an infrared grade quartz glass, which not only has a transmittance of more than 93.5% in the near-ultraviolet-visible light wave band (260-700nm), but also has a high transmittance in the 700-3500 nm wave band.
2.High heat resistance
Quartz glass has a very small thermal expansion coefficient and can withstand severe temperature changes. Quartz glass is heated to about 1100 ℃, and it will not burst into normal temperature water.
The softening point temperature of quartz glass is about 1730°C, it can be used for a long time at 1100°C, and the maximum use temperature in a short time can reach 1450°C.
3.Corrosion resistance
Except for hydrofluoric acid, quartz glass hardly reacts chemically with other acids, and its acid resistance is 30 times that of ceramics.
High chemical purity and excellent hardness.
Fused Silica Optical Applications:
Due to these excellent optical, mechanical and thermal properties, fused silica is widely used in all spectra.
1.UV Applications:
Laser Nuclear Technology, Microlithography, Spectroscopy, Signal Coupling
2.Infrared applications:
high-end infrared lenses, high-precision optoelectronic devices
3.Visible Light Applications:
Spectrophotometers
Hengshui Aohong Glass can manufacture all kinds of high-quality optical glass, if you are interested in optical glass products and quartz glass products, you can contact us.
0 notes
Text
0 notes
Text

Double Beam UV-Visible Spectrophotometer
Double Beam UV-Visible Spectrophotometer is a compact, tabletop, double beam and Czerny-Turner monochromator comprised Double Beam UV-Visible Spectrophotometer, comes with 20 mm of focal length and 1600 lines/mm of grating. With 190 to 1100 nm of wavelength range, features adjustable 5-speed bandwidth of 0.5 nm, 1 nm, 2 nm, 4 nm, and 5 nm with fast-medium-slow scanning speed. Designed with Silicon Photocell detector, deuterium and tungsten lamp as light source, and 8-inch color touch-screen, supports spectra printing, storage and data analysis. Incorporated with USB communication port, ARM chip control and data processing, and easy user interface, this spectrophotometer has automatic scanning of measured spectrum, multi-wavelength (1-3 λ) measurement, kinetic measurement, 1-3 curve fitting, and 1-4 derivative spectra.
#Double Beam UV-Visible Spectrophotometer manufacturer in Virginia#Double Beam UV-Visible Spectrophotometer suppliers in Virginia#Double Beam UV-Visible Spectrophotometer manufacturer in Washington#Double Beam UV-Visible Spectrophotometer suppliers in Washington#Double Beam UV-Visible Spectrophotometer manufacturer in Wyoming#Double Beam UV-Visible Spectrophotometer suppliers in Wyoming
0 notes
Text
1 note
·
View note
Text
Find The Best Scientific Laboratory in Mumbai – Advancing Research with Gravity Lab
Mumbai, the financial and technological hub of India, is home to numerous scientific institutions and laboratories that contribute significantly to the country's research and development efforts. Among these, Gravity Lab has emerged as a leading scientific laboratory in Mumbai, offering cutting-edge facilities, expert support, and a commitment to innovation that sets it apart from the rest.
Whether you're a researcher, student, entrepreneur, or part of a larger industrial project, finding a reliable scientific laboratory in Mumbai is crucial for accurate testing, data collection, and experimental success. Gravity Lab is designed to cater to all these needs and more.

Why Choose a Scientific Laboratory in Mumbai?
Mumbai’s strategic location and infrastructure make it an ideal base for scientific research. With proximity to major academic institutions, industries, and international logistics, Mumbai provides a conducive environment for innovation and scientific inquiry.
A scientific laboratory in Mumbai not only serves academic and industrial research but also plays a crucial role in public safety, environmental monitoring, pharmaceutical testing, and technological development. The availability of highly trained professionals, modern equipment, and strict quality standards ensures that scientific results generated in Mumbai-based labs are accurate, reliable, and widely accepted.
Introducing Gravity Lab – Your Scientific Partner
Gravity Lab is one of the top-rated scientific laboratories in Mumbai, offering a wide spectrum of laboratory services. It stands out not only for its technical capabilities but also for its client-centric approach and commitment to scientific excellence.
Core Services Offered by Gravity Lab
Gravity Lab provides a wide range of testing and analytical services to cater to various industries, including:
Chemical Analysis: High-precision testing of raw materials, chemicals, and industrial compounds using state-of-the-art instruments like GC-MS, HPLC, FTIR, and AAS.
Microbiological Testing: Comprehensive microbial analysis for food, pharmaceuticals, water, and environmental samples to ensure compliance with safety standards.
Environmental Testing: Air, water, and soil analysis to assess environmental pollutants and help companies meet environmental regulations.
Pharmaceutical Testing: Quality control and stability testing of pharmaceutical products in line with global standards such as ICH and WHO.
Food Testing: Nutritional analysis, shelf life studies, and contamination testing to support the food industry in ensuring product safety.
Research and Development Support: Customized experimental design, data analysis, and reporting for academic and industrial R&D projects.
State-of-the-Art Infrastructure
Gravity Lab is equipped with cutting-edge instruments and technology to ensure high levels of precision and accuracy in testing. The lab maintains ISO and NABL accreditations, demonstrating its commitment to quality and adherence to global standards.
Some of the advanced instruments available at Gravity Lab include:
Gas Chromatography-Mass Spectrometry (GC-MS)
High Performance Liquid Chromatography (HPLC)
Atomic Absorption Spectrophotometer (AAS)
UV-Visible Spectrophotometers
Incubators, autoclaves, laminar air flow units
Digital and analytical balances with microgram sensitivity
The laboratory is also equipped with controlled environments for microbiological work, including clean rooms, sterilization zones, and bio-safety cabinets.
Experienced and Qualified Team
What sets Gravity Lab apart is its team of seasoned scientists, microbiologists, chemists, and lab technicians. Each professional is trained in standard operating procedures (SOPs), safety protocols, and the latest scientific techniques to deliver accurate and timely results.
Moreover, Gravity Lab continually invests in staff training and development to stay ahead in a rapidly evolving scientific landscape. This ensures that every test, every analysis, and every report is conducted with the highest degree of professionalism and scientific rigor.
Tailored Solutions for Diverse Industries
Gravity Lab serves a broad spectrum of clients, from startups and research institutes to multinational corporations. No matter the scale or complexity of your needs, Gravity Lab can develop customized testing protocols and reporting formats to suit your objectives.
Industries served include:
Pharmaceuticals and healthcare
Food and beverage
Cosmetics and personal care
Environmental monitoring
Water treatment
Chemical manufacturing
Agriculture and biotechnology
Gravity Lab also provides consultancy services for regulatory compliance, helping clients meet Indian and international quality and safety standards.
Collaborations and Research Projects
As a leading scientific laboratory in Mumbai, Gravity Lab has partnered with various academic institutions and government agencies on research projects. These collaborations span topics such as antimicrobial resistance, climate change impacts, pharmaceutical innovation, and food safety.
Gravity Lab encourages partnerships with universities, offering laboratory support for thesis work, internships, and collaborative research. This bridges the gap between academia and industry, fostering a culture of innovation and discovery.
A Commitment to Quality and Ethics
Gravity Lab’s operations are grounded in integrity, transparency, and scientific ethics. The laboratory follows a stringent quality assurance program that includes internal audits, proficiency testing, and continuous improvement initiatives. All testing is documented and traceable, ensuring complete accountability and client trust.
Clients receive detailed, easy-to-understand reports accompanied by expert interpretations when needed. Gravity Lab believes in building long-term relationships based on reliability, responsiveness, and scientific excellence.
Visit or Contact Gravity Lab
If you're looking for a trusted scientific laboratory in Mumbai, Gravity Lab is your go-to destination. With world-class facilities, expert personnel, and a deep commitment to scientific advancement, Gravity Lab is equipped to meet your research and testing needs with precision and efficiency.
Contact Information
📍 Address:Gravity Lab Scientific Laboratory Mumbai, Maharashtra, India
📞 Phone: +91-9821198397 📧 Email: [email protected] 🌐 Website: https://gravitylab.in/
Whether you need one-time testing, ongoing research support, or expert scientific consultation, Gravity Lab is ready to help.
0 notes
Text
The Ultimate Guide to Cuvet Types, Materials, Sizes, and Best Practices
In the field of laboratory science, precision and accuracy are essential. Whether you're conducting routine chemical analysis or advanced spectrophotometric experiments, choosing the right tools is critical to achieving reliable results. One such essential tool is the cuvet. While it may seem like a simple container, the cuvet plays a vital role in a wide range of experiments, especially those involving light-based measurements. This comprehensive guide explores the different types of cuvets, their materials, sizes, and best practices to help laboratory technicians and researchers make informed decisions.
What is a Cuvet?
A cuvet is a small, tube-like container made from transparent material such as glass, plastic, or quartz. It is designed to hold samples for optical analysis in instruments like spectrophotometers and fluorometers. Light passes through the cuvet, and the instrument measures how much of that light is absorbed or transmitted by the sample inside. The accuracy of this measurement is highly dependent on the cuvet's quality, cleanliness, and size.
Types of Cuvets
Cuvets come in several forms, each suited to different laboratory applications. Understanding the types of cuvets available can help you select the best one for your specific needs.
1. Standard Cuvets
These are the most commonly used cuvets in laboratories. They are typically square or rectangular and have a standard path length of 10 mm. These cuvets are used for general spectrophotometric applications.
2. Micro Cuvets
Micro cuvets are designed for experiments that involve small sample volumes. They are especially useful when working with expensive or rare samples, as they require only 70–500 µL of liquid.
3. Flow Cuvets
Flow cuvets allow liquid samples to flow continuously through the chamber during measurement. They are ideal for kinetic studies and automated systems where continuous sample monitoring is required.
4. Disposable Cuvets
Made of plastic, disposable cuvets are convenient and cost-effective for single-use applications. They prevent cross-contamination and are ideal for high-throughput labs.
5. Cylindrical Cuvets
These round cuvets are often used in fluorometry applications. Their shape can offer better light distribution in certain optical systems.
Cuvet Materials
The material of the cuvet affects its performance and the types of experiments it can be used for. Each material has specific optical properties that influence its compatibility with various wavelengths of light.
1. Plastic Cuvets
Plastic cuvets are lightweight, affordable, and disposable. They are ideal for visible light applications but are not suitable for UV spectroscopy because they absorb UV light.
2. Glass Cuvets
Glass cuvets are suitable for visible light applications and are more durable than plastic ones. However, like plastic, they do not transmit UV light effectively.
3. Quartz Cuvets
Quartz cuvets are the most versatile and are transparent to both UV and visible light. They offer excellent clarity and chemical resistance, making them ideal for high-precision work.
Cuvet Sizes and Path Lengths
Cuvet size is one of the most important considerations in any experiment involving light transmission or absorbance. The size refers to both the path length (the distance the light travels through the sample) and the volume the cuvet can hold.
10 mm Path Length: This is the most commonly used cuvet size, suitable for standard spectrophotometric measurements.
Short Path Lengths (1–5 mm): Ideal for concentrated samples, as they reduce absorbance and prevent saturation.
Long Path Lengths (20 mm or more): Used for dilute samples that need more sensitivity.
Volume Capacity: Depending on the cuvet, volumes can range from 50 µL in micro cuvets to over 4 mL in macro cuvets.
Selecting the correct cuvet size ensures that your instrument provides accurate and consistent readings.
Best Practices for Using a Cuvet
Regardless of the cuvet type or material, following best practices in handling and maintenance is key to obtaining reliable data.
1. Handle with Care
Always hold the cuvet by the frosted or non-optical sides to avoid leaving fingerprints on the clear surfaces. Fingerprints and smudges can scatter light and interfere with readings.
2. Clean Properly
Cuvets must be cleaned thoroughly before and after each use. Use distilled water and, if necessary, appropriate solvents. Avoid abrasive materials that may scratch the optical surface.
3. Calibrate with a Blank
Before measuring your sample, calibrate your instrument using a blank cuvet filled with the solvent or buffer. This step ensures that any absorbance by the solvent is not mistaken for the sample's absorbance.
4. Use Matched Cuvets
For comparative experiments, use matched cuvets—those that have identical optical properties. This reduces variability and enhances measurement precision.
5. Store Safely
Store cuvets in a clean, dry container, preferably in a protective box. This helps avoid contamination and physical damage, especially for expensive quartz cuvets.
Choosing the Right Cuvet
Choosing the appropriate cuvet involves more than just selecting the correct size. You must also consider your sample type, the wavelength range required, and whether the cuvet will be reused or disposed of.
Here’s a quick guide:
Use plastic cuvets for quick, disposable, and visible-light-only applications.
Use glass cuvets for more durable, visible-range applications.
Use quartz cuvets for UV-visible experiments requiring high precision.
Use micro cuvets when sample volume is limited.
Use flow cuvets in kinetic or real-time studies.
Conclusion
Though often overlooked, the cuvet is a critical part of many laboratory experiments. Understanding its types, materials, and sizes can significantly improve the quality of your results. By selecting the right cuvet for your needs and following proper usage and care practices, you ensure more accurate and reproducible outcomes in your lab work. Whether you're a seasoned researcher or a laboratory technician, making informed decisions about your cuvets can make all the difference in experimental success.
0 notes
Text

UV-Vis Spectroscopy
UV-Vis Spectroscopy (Ultraviolet-Visible Spectroscopy) is a widely used analytical technique in chemistry and biochemistry for analyzing the absorbance and transmittance of light through a sample. This technique helps identify and quantify compounds based on their electronic transitions, particularly those involving π to π* or n to π* transitions. UV-Vis spectroscopy plays a crucial role in monitoring reaction progress, determining concentration via Beer-Lambert’s law, and analyzing structural features of organic and inorganic molecules. Its simplicity, speed, and non-destructive nature make it an essential tool across research, pharmaceutical, environmental, and industrial laboratories.
International Chemistry Scientist Awards
Website: chemistryscientists.org
Contact us: [email protected]
Nominate now: https://chemistryscientists.org/award-nomination/?ecategory=Awards&rcategory=Awardee
#sciencefather#researchawards#Professor,#Lecturer,#Scientist,#Scholar,#Researcher#UVVisSpectroscopy #Spectroscopy#AnalyticalChemistry#BeerLambertLaw#ChemistryTools#MolecularAbsorption#UVVisibleLight#OrganicAnalysis#InorganicChemistry#ChemicalAnalysis#Chromophores#ScienceExplained#LabTechniques#ResearchTools#Spectrophotometer#STEMEducation#MolecularSpectroscopy#QuantitativeAnalysis#Absorbance#VisibleSpectrum
👉 Don’t forget to like, share, and subscribe for more exciting content!
Get Connected Here: =============
Blogger :https://www.blogger.com/blog/post/edit/6961521080043227535/467226973388921229
Twitter : https://x.com/chemistryS79687
Pinterest : https://in.pinterest.com/chemistryaward/
Instagram: https://www.instagram.com/alishaaishu01/
Youtube : https://www.youtu
be.com/channel/UCAD_pDvz3ZHqv_3hf-N0taQ
0 notes