#USDA Rural Housing
Explore tagged Tumblr posts
Text
https://www.rd.usda.gov/programs-services/single-family-housing-programs
Not enough people know about the USDA rural housing programs, but I’ve known multiple people who have only been able to afford houses this way. What counts as rural might surprise you (it definitely surprised me!)
I should write a whole thing about it someday, I don’t have the energy to do it rn, but if you are below the median income level in your area then programs like this are worth looking into
#they have programs for both buying a home and renovating existing homes that are within ‘rural’ areas#still requires income of some kind and loan approval so it’s not the solution for everyone#usda#buying a house
5 notes
·
View notes
Text
Kentucky Mobile Home Buyers: USDA Loan
USDA Loans for Manufactured Homes in Kentucky USDA Loans for Manufactured Homes in Kentucky – 100% Financing Coming Soon! Are you looking for affordable home financing options for manufactured or mobile homes in Kentucky? Big news is here! Starting March 4, 2025, the USDA will officially offer 100% financing for manufactured homes. This exciting change will make homeownership more accessible…
#100 financing#doublewide home#kentucky usda loan#manfactured homes#mobile home#rural housing mobile home#singlwide home#usda loan mobile home
0 notes
Text
0 notes
Text
Tell me about your general region (continent or country) and living density (rural enough that your nearest neighbor is eight miles away, suburban where there's nothing but single-family housing as far as the eye can see, a city with tens of thousands of people per square mile, etc) in the tags!
Metric measurements rounded to the nearest half meter, then nearest tenth of a kilometer.
According to the USDA, a food desert is:
A tract with at least 500 people, or 33 percent of the population, living more than one-half mile (urban areas) or 10 miles (rural areas) from the nearest supermarket, supercenter, or large grocery store.
#polls#phoenix polls#food#food deserts#suburbia#rural#urban#anyway I live in suburban hell and my nearest grocery store is about 45 minutes away by foot. and it's too dangerous to bike. so.#always gotta drive
949 notes
·
View notes
Text
Things Biden and the Democrats did, this week #7
Feb 23-March 1 2024
The White House announced $1.7 Billion in new commitments from local governments, health care systems, charities, business and non-profits as part of the White House Challenge to End Hunger and Build Healthy Communities. The Challenge was launched with 8 billion dollars in 2022 with the goal of ending hunger in America by 2030. The Challenge also seeks to drastically reduce diet-related diseases (like type 2 diabetes). As part of the new commitments 16 city pledged to make plans to end hunger by 2030, the largest insurance company in North Carolina made nutrition coaching and a healthy food delivery program a standard benefit for members, and since the challenge launched the USDA's Summer EBT program has allowed 37 states to feed children over the summer, its expected 21 million low income kids will use the program this summer.
The US House passed a bill on Nuclear energy representing the first update in US nuclear energy policy in decades, it expands the Nuclear Regulatory Commission and reduces reducing licensing fees. Nuclear power represents America's single largest source of clean energy, with almost half of carbon-free electricity coming from it. This bill will boost the industry and make it easier to build new plants
Vice President Harris announced key changes to the Child Care & Development Block Grant (CCDBG) program. The CCDBG supports the families of a million American children every month to help afford child care. The new changes include capping the co-pay families pay to no more than 7% of their income. Studies show that high income families pay 6-8% of their income in childcare while low income families pay 31%. The cap will reduce or eliminate fees for 100,000 families saving them an average of over $200 a month. The changes also strength payments to childcare providers insuring prompt payment.
The House passed a bill making changes to the Small Business Administration’s 8(a) program. The 8(a) is an intensive 9 year program that offers wide ranging training and support to small business owners who are socially and economically disadvantaged, predominantly native owned businesses. Under the current structure once a business reaches over 6.8 million in assets they're kicked off the program, even though the SBA counts anything under $10 million as a small business, many companies try to limit growth to stay on the program. The House also passed a bill to create an Office of Native American Affairs at the SBA, in order to support Native-owned small businesses.
The White House and HUD announced steps to boost the housing supply and lower costs plans include making permanent the Federal Financing Bank Risk Sharing program, the program has created 12,000 affordable housing units since 2021 with $2 billion and plans 38,000 additional units over ten years. As well as support for HUD's HOME program which has spent $4.35 billion since 2021 to build affordable rental homes and make home ownership a reality for Americans. For the first time an administration is making funds available specifically for investments in manufactured housing, $225 million. 20 million Americans live in manufactured housing, the largest form of unsubsidized affordable housing in the country, particularly the rural poor and people in tribal communities.
The Department of Energy announced $336 million in investments in rural and remote communities to lower energy costs and improve reliability. The projects represent communities in 20 states and across 30 Native tribes. 21% of Navajo Nation homes and 35% of Hopi Indian Tribe homes remain unelectrified, one of the projects hopes to bring that number to 0. Another project supports replacing a hydroelectric dam in Alaska replacing all the Chignik Bay Tribal Council's diesel power with clear hydro power. The DoE also announced $18 million for Transformative Energy projects lead by tribal or local governments and $25 million for Tribal clean energy projects, this comes on top of $75 million in Tribal clean energy projects in 2023
Transportation Secretary Pete Buttigieg put forward new rules to ensure airline passengers who use wheelchairs can travel safely and with dignity. Under the planned rules mishandling a wheelchair would be a violation of the ACAA, airlines would be required to immediately notify the passenger of their rights. Airlines would be required to repair or replace the wheelchair at the preferred vendor of the passenger's choice as well as provide a loaner wheelchair that fits the passenger's needs/requirements
The EPA launched a $3 Billion dollar program to help ports become zero-emission. This investment in green tech and zero-emission will help important transportation hubs fight climate change and replace some of the largest concentrations of diesel powered heavy equipment in America.
the EPA announced $1 Billion dollars to help clean up toxic Superfund sites. This is the last of $3.5 billion the Biden administration has invested in cleaning up toxic waste sites known as Superfund sites. This investment will help finish clean up at 85 sites across the country as well as start clean up at 25 new sites. Many Superfund sites are contained and then left not cleaned for years even decades. Thanks to the Biden-Harris team's investment the EPA has been able to do more clean up of Superfund sites in the last 2 years than the 5 years before it. More than 25% of America's black and hispanic population live with-in 5 miles of a Superfund site.
Bonus: Sweden cleared the final major barrier to become NATO's 32nd member. The Swedish Foreign Minster is expected to fly to Washington to deposit the articles of accession at the US State Department. NATO membership for Sweden and its neighbor Finland (joined last year) has been a major foreign policy goal of President Biden in the face of Russian aggressive against Ukraine. Former President Trump has repeatedly attacked NATO and declared he wants to leave the 75 year old Alliance, even going so far as to tell Russia to "do whatever the hell they want" with European NATO allies
#Thanks Biden#Joe Biden#Politics#US politics#Democrats#Climate change#end hunger#hunger#proverty#disability#native Americans#tribal rights#clean energy#child care#housing#housing crisis
773 notes
·
View notes
Text
This is an open letter to rural Americans, if that's you or someone you know, read on. Fair warning, though, this is the kind of no-nonsense straight talk that you pride yourself in and won't be easy for you to hear.
Look, I hear your complaints about gay and transgender people and I hear your concerns about kids identifying as strange things like nonbinary. I even hear your, admittedly strange and not well supported, complaints about kids identifying as animals.
I know what you're worried about, you're worried about things changing around you, and you're right to be. The last half century or more has been absolutely devastating to people like you and communities like yours. I don't even need to know where you live, just about every rural town and rural county has seen their population cut in half since the end of the Second World War and the economy has suffered for that.
Farming and ranching, the cornerstones of the rural economy, have gotten harder. You've been squeezed by your suppliers and your customers to the point where it's difficult to make ends meet, much less a profit. Kids don't see a future in your community and they leave for somewhere else which only makes it harder for the ones who decide to stay and people increasingly turn to drugs and suicide because they don't see any other way.
Thirty years ago there was a hospital in easy reach, then it closed and the nearest one is now hours away. That means that things that didn't used to be fatal now kill people in your community, things that didn't used to be damaging now maim them because they just can't get to the doctor fast enough. And even if they're not suffering heart attacks, being bitten by animals, or being injured on the job or out in the country, the stress is building up day by day. It gnaws at the back of your mind, making it hard to focus on the things you need to do, and the adrenaline is slowly eating your body alive.
Fifty years ago you could have sold your farm to a young farmer in your old age and retired, now you're stuck working until you die because there's no one to pass your legacy on to and, when you do die, your land will get swallowed up by a huge factory farm that won't bring jobs or contribute to your community. Change has been terrible for you and I don't think you're insane for wanting it to stop.
But here's the thing, you're focusing on the wrong change. It's not your fault either, the people you trusted have betrayed you. Hear me out, because this is going to hurt, but you need to hear it.
What do the politicians in your area tell you? They tell you that you're tough, independent, no-nonsense people, right? You're not one to complain when life get's hard, not like those pampered city folk? They say that they're one of you, don't they? That they're just farmers and ranchers and they know you like those outsiders never could, am I still right? I know because that's what the politicians where I grew up used to say. Still do actually.
You need to look at them, though. The average Congressman or State Representative is a millionaire and your guys are no exceptions. They're not poor farmers breaking their backs trying to make ends meet, they're the owners of big businesses milking federal and state subsidies while putting on the theater that they actually have to go dig fence posts and clear brush instead of the reality that they have people to do that kind of thing for them when they're not trying to impress you.
And when they go to the state house or the capital, they're not advocating for you. They're taking millions of dollars from your suppliers and your distributors and making sure that their interests are heard. And you may say "oh, well that's fine, representing the agriculture industry is representing me too," but is it really? Let me ask you this; the agriculture business in the US is worth $1.5 trillion according to the USDA, how much of that are farming and ranching communities actually seeing?
If even 10% of that money was making it to rural communities it would revitalize the country. Can you imagine what $150 billion would do for all the rural towns and communities across this country? Agribusiness is doing fine, but you aren't. Stop to think about that for a minute.
The reason the politicians sell you the idea of tough independence is that they don't want you to notice how dependent you are on the outside world. That's not a bad thing, by the way, we live in a modern, interconnected world that can provide things our parents and grandparents couldn't have dreamed of. You've benefited from it too, from better technologies to increase yields and greater access to more customers all around the world.
What you haven't benefited from is the middle men. Remember when I talked about your suppliers and distributors squeezing you? Yeah, your suppliers don't actually make the things you buy and the distributors don't actually use the things you sell. These people stand between you and the people who actually do those things and take whatever money they can along the way.
And if there were lots of suppliers and lots of distributors that would be fine. You live far away from factories and cities, you need someone to bring things to you and take what you produce to your customers, and it's reasonable that those people make money too. But how many suppliers do you have? How many distributors? Like I said, I don't even need to know where you are to know that it's less than 5, probably less than 3, because it's like that everywhere.
Every business you buy from knows they have no competition, so they jack up their prices as high as they can while still making a sale and every business you sell to knows you have no other options so they offer you the lowest price they can, and both of them are pocketing the difference. When you wonder what happened to your communities and your downtowns, think about how everyone but you is making a decent amount of money off of agriculture in this country.
So yes, you're tough and you're independent, but you're still a part of the world economy. You still buy things that come from somewhere else and you sell things that go somewhere else and somewhere in the middle of that you need to make money. And the people you keep electing, the ones who tell you they're just like you and that you're tough and independent and no-nonsense, they're taking a ton of money from the people who actually are making it in order to make sure that nothing changes and nothing gets better.
At the end of the day, it's not gay people or trans people or atheists or immigrants or even furries that are destroying your communities and your livelihoods, it's the people who smile and tell you they're one of you. They're the ones making sure that your money goes to them instead of to the new field equipment that could help you expand your operation, they're the ones making sure that you don't make enough to rent another field and hopefully put in some extra crop next season, and they're the ones making sure that none of that money that comes from what you produce stays in your community where it could build wealth and income for the people who actually live there.
At this point you may be wondering whether I think you're a fool or an idiot. After all, I just described you getting taken for a ride by the people you trusted for most of your life. It sounds like I'm just another city person who thinks that anyone without a PhD is a moron who needs to be told what to do every minute of every day so they don't drown in the shower because they're that stupid.
But here's the thing, I don't think you're a fool or an idiot, far from it. I think you're proud.
You're proud of who you are and where you come from and there's a lot of good in that, but there's a reason the good book lists pride as one of the seven deadly sins.
Long ago you and your distributors and suppliers used to work hand in hand to produce more food and get it in the hands of hungry people. You got to know each other and trust each other, working together to make this country one of the most agriculturally productive on Earth. But sometime during the Cold War, things changed. The local distributors and suppliers you used to work with got bought out by big corporations. They kept the local faces they knew you trusted, but they had no real interest in you or your community and they used that trust to pull the rug out from under you.
It's decades later now and the results are undeniable. Whole towns depopulated, main streets crumbling, young people moving away, and necessary services like hospitals unable to make enough to stay open, but you still refuse to look the truth in the face because doing so would mean admitting that you've been had, and you're too proud for that. So instead you vote for politicians who pretend to be like you and tell you comforting slogans while selling you out and you blame people who had nothing to do with it, all because you're too proud.
Because the people destroying your community don't have purple hair or piercings. They don't want to use the wrong bathroom or lust after their own sex or deny God. Heck, they don't even wear fursuits and use litter boxes instead of toilets. The people destroying your community wear ties and suits. They keep their hair neat and trimmed and they don't decorate their bodies with tattoos or piercings. When they do actually come to your community, they trade the suit and tie for working clothes, but they're so clean it's clear they've never been used. They look like they fit in, but they don't, they may have owned a farm, but they've never actually had to work one before. They were born into wealth, not labor, and they're the ones paying millions to the people you elect.
They've told you for years that they're one of you, just more workers in the field of agriculture that you work in too, but they're not remotely the same. They're the ones that sit in offices and crunch numbers, they hire people like you and illegal immigrants for the real work. They've been doing this for as long as most people can remember, telling you that they're part of your community while sucking it dry.
If you're going to save your community and your way of life, you're going to need to overcome your pride. Look into the faces of your children, walk around your community, talk with God; do whatever you need to, but you need to realize that right now your pride is the biggest obstacle to saving everything you value. Pride in your home and community is one of the greatest things on Earth, but right now what your home and community need isn't your pride, it's your humility. You're going to need to dig deep and find that within yourself. Find the part of yourself that would give anything, even your life, to protect your family, and prepare for something that, for some of you, might be even harder.
Now, once you're in the right frame of mind, take a hard look at the questions I asked you earlier. You know the ones, the ones about how many distributors there are that you can actually sell to and how many suppliers you can actually buy from. You knew the answers to those, didn't you? Now I want you to look at the actions of the people you vote for. Not their words, their actions. Have they ever voted for anything that would give you more leverage to demand higher prices? Have they ever voted for anything that would give you more options and lower the price of the things you buy? I'm betting the answer is "no".
They'll tell you that they don't want to interfere in the free market, and fair enough, but look at what they do vote for. How many of those things give money to the big companies you buy from and sell to? How many times have they looked the other way at those companies hiring illegal immigrants while they tell you how much they're doing about the problem? Again, I don't need to know where in the country you live, I know the answers to those questions because they're all the same.
The truth is that they've been using your pride against you, the people you elect and the companies you do business with. Like a magician who keeps you watching his right hand while his left keeps pulling rabbits, they've kept you angry at a parade of things all while they pick your pocket year after year after year and, if you let them keep doing it, soon there won't be anything left.
So what can you do? Well, you remember those city folk? The ones with purple hair, piercings, tattoos, and transgender surgeries? The ones who celebrate gay people and reject God? The ones who don't know a hard days' work like you do? They're starting to feel what you've been feeling. The big companies they work for and buy from have started sucking their communities dry too and they've been noticing. You're never going to agree with them on values, but you're in the same fight now. The threat is growing and either both of your communities are going to survive or neither one is.
Remember what I said about putting aside your pride? This is going to be the hardest part of it, you're going to need to practice your humility. You're going to need to look past what your politicians say about immigrants and gay people and start looking at what they're promising to do for your business. Not more subsidies for farms, more handouts, real action to level the playing field so that you can sell your crops and livestock and buy your equipment at a fair price, and they're going to need to work with the people from that other community to do it because your community alone doesn't have the power to break up the big businesses that are dominating everything now.
The truth is that big companies haven't just gotten powerful by working the economy, they've gotten powerful by taking over the government and tilting the field in their favor. So many of the people you vote for are in their pocket that it's going to be hard for you to find someone who's not and, when you do find them, it's going to be hard for them to get their message out to people because the guy who does what the big companies want is going to have a lot more money to swamp your radio and TV stations with ads and to buy every billboard in the county.
But if you want to stop the slow death of your community, you're going to need to do something, because what you're doing now isn't working. It's going to take the hard work that you know how to do and the type of community spirit that you've built, but it's also going to take a lot more humility than you've had to show in your life. If you can do it, there's a chance you can reverse the decline and rebuild your community. If you can't, then the way of life that you know and love may become as much a part of the past as the flintlock and the tricorner hat; a symbol of the intrepid spirit that built this country that fell behind the times and only exists now in museums.
13 notes
·
View notes
Text
The Farm Bill is a critical piece of legislation that reauthorizes the country’s agricultural and nutrition programs about every five years—and the 2024 version is now on legislators’ desks, with some major changes.
Originally designed to support farmers, the Farm Bill has evolved over time to prioritize nutrition assistance, with the Supplemental Nutrition Assistance Program (SNAP) now comprising 76% of the budget—projected to increase to 84% in the current version. This shift underscores the growing emphasis on addressing food insecurity among low-income Americans, as SNAP currently serves over 42 million individuals, or about 12% of the population.
The 2024 Farm Bill will fund SNAP, agriculture subsidies, and crop insurance through 2029, at a projected cost of $1.5 trillion. However, as the first Farm Bill to exceed $1 trillion, it faces heightened scrutiny as both parties clash over the allocation of funding between SNAP, subsidies, and other key programs.
The current version of the bill, introduced by the Republican-led House Agriculture Committee, has sparked controversy by proposing a $30 billion cut to SNAP funding over the next decade. This reduction would be achieved by limiting adjustments to the Thrifty Food Plan (TFP)—a low-cost, standardized estimate of the minimum cost of a nutritious diet, used to determine SNAP benefit levels—to inflation rates only.
The TFP is reevaluated every five years to reflect current food costs. In 2021, the Biden administration reevaluated the TFP to respond to high food costs due to COVID-19 and supply chain issues in the global food industry, resulting in the largest-ever increase in SNAP benefits, totaling $256 billion. Now, Republicans are seeking to restrict future adjustments to reflect only inflation costs, marking the largest SNAP reduction in nearly three decades. But Democrats and researchers argue that such a restriction could have significant impacts on the 42 million SNAP recipients, including 17 million children, 6 million older adults, and 4 million people with disabilities.
Americans face rising food insecurity and barriers in accessing nutritious diets
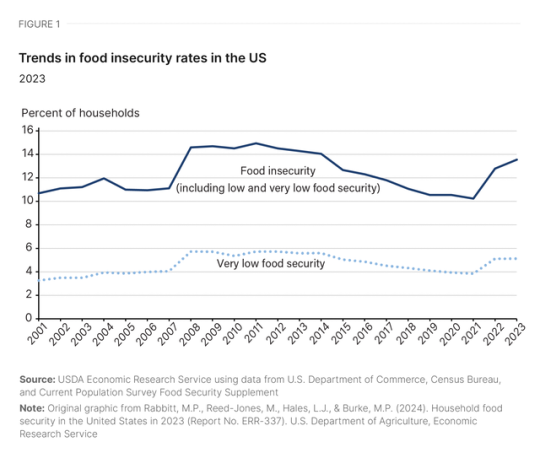
The proposed cuts, along with provisions to outsource program operations, could undermine SNAP’s ability to effectively combat food insecurity. This is especially concerning given that food insecurity rates rose to 13.5% of U.S. households in 2023, affecting 18 million families—a statistically significantly increase from 2022, according to the U.S. Department of Agriculture (USDA). Food insecurity rates are notably higher for single-parent, female-headed households; Black and Latino or Hispanic households; and households in principal cities and rural areas. In addition, voters are growing increasingly worried about inflation and high food costs, with 70% citing food prices as a major concern. This view is especially pronounced among younger voters, who have been hit hard by a 20% surge in food costs since 2020, as reported by the Bureau of Labor Statistics.
In addition to concerns surrounding food insecurity and rising costs, the TFP debate risks being a superficial fix that overlooks deeper, more critical challenges low-income families face in accessing nutritious diets. A USDA study found that 88% of SNAP participants encounter challenges in maintaining a healthy diet, with 61% citing the high cost of healthy foods as a key barrier. Other reasons include a lack of time to prepare meals at home and transportation difficulties in accessing healthy foods.
Access barriers—combined with broader economic factors such as regional variations in real food prices and other costs of living, shifts in food composition data, changing consumption patterns, and updated dietary guidance—significantly impact low-income households’ ability to maintain affordable, nutritious diets. Addressing such factors is crucial for creating a more sustainable and impactful SNAP program, yet they remain sidelined in favor of quick, inflation-focused approaches that do little to address systemic barriers to healthy food access for vulnerable families.

The proposed $30 billion cut to SNAP funding over the next decade by restricting the USDA’s authority to adjust the TFP beyond inflation rates will have serious and multidimensional challenges for these low-income, food-insecure households. In addition, the bill’s proposal to outsource core SNAP operations to private entities could create complications in the application process and eligibility criteria, while also increasing federal costs by $1 million.
Notably, the current version of the bill proposes to expand SNAP’s purpose to include the prevention of diet-related chronic diseases. Critics, such as the HEAL (Health, Environment, Agriculture, Labor) Food Alliance, argue that this risks diverting attention away from SNAP’s core mission of reducing food insecurity, and instead shifts the focus to diet-related concerns facing low-income populations. Yet these diet-related concerns are often a result of multifaceted challenges such as stress (or “bandwidth poverty”), food insecurity, and other factors such households face. The current version of the bill also proposes to cut climate-focused conservation efforts introduced by the Inflation Reduction Act.
Proposed changes to agricultural subsidies have sparked equity concerns
The proposed Farm Bill aims to reallocate funds by raising price floors for key agricultural commodities such as corn, wheat, and soybeans, while cutting SNAP funding. A large portion of the increased spending is directed toward farm programs and crop insurance—raising concerns about equity and the disproportionate benefits to large, wealthy farms.
A report from the American Enterprise Institute highlights this disparity, revealing that the top 10% of farms receive 56.4% of all crop insurance subsidies, with the top 5% receiving 36.4%. Since these subsidies are not means-tested—and the level of subsidies is directly proportional to an agri-business’s production levels—the wealthiest and largest businesses capture the most significant share of these benefits. Research from the Environmental Working Group confirms evidence on the concentration of these subsidies toward the wealthiest agri-business owners. They found that between 1995 and 2021, the top 1% of recipients received 27% of the total $478 billion in farm subsidies—underscoring the disproportionate benefits to large-scale, wealthy farmers. Moreover, these subsidies favor a narrow range of commodity crops such as corn, soybeans, wheat, and cotton, which accumulates benefits to white, wealthy farmers while farmers of color receive little support. This inequitable allocation of resources raises important questions about the Farm Bill’s broader social and economic implications.
The Government Accountability Office and Congressional Budget Office have proposed reforms to the current inequitable structure of these subsidies. Such reforms have the potential to reduce the fiscal deficit while protecting rights of farmers, ensuring food assistance to low-income populations, and maintaining price levels of key commodities. Reforms include implementing income limits on premium subsidies for wealthy farmers, adjusting compensation for insurance companies to reflect market rates, and reducing taxpayer reimbursements for administrative costs.
SNAP benefits aren’t keeping up with the true costs of a healthy diet
A critical aspect of SNAP that is often overlooked in fiscal policy debates is the economic adequacy of the program’s benefits. There is a growing body of research suggesting that SNAP benefits in their current form are insufficient to cover the “real” cost of a healthy diet.
In other words, the TFP might not truly reflect the real value of food costs low-income households face. The TFP was originally intended to represent the minimum food expenditure basket that would allow low-income households to avoid food insecurity. It is not necessarily based on the most recent scientific methodologies that factor in food prices, accessibility, and dietary needs.
Recent evaluations have shown that the TFP often underestimates the cost of a nutritious diet, particularly in areas with higher living costs. An Urban Institute study found that despite food price inflation moderating in 2023, SNAP benefits remained inadequate for covering food costs: By the end of 2023, the average modestly priced meal cost $3.37, which was 19% more than the average maximum SNAP benefit of $2.84. Families with zero net income faced a shortfall of $49.29 per month by the end of the year, with urban areas experiencing a 28% gap between meal costs and SNAP benefits, compared to 17% in rural areas. In the five counties with the largest gaps, the shortfall exceeded 70% throughout the year.
Recent economic research indicates that current SNAP benefits often fall short of covering the actual cost of a low-budget, healthy diet, with significant variations in benefit adequacy across U.S. regions. Researchers have found that these geographic variations in SNAP purchasing power significantly affect welfare outcomes such as child health and food insecurity. Despite deductions for housing and child care, many regions face much higher real costs of food, and SNAP dollars do not go far in such high-cost areas. To ensure equitable support, social scientists have put forth proposals to index SNAP benefits to local area food prices.
Therefore, the proposed cuts to SNAP funding risk exacerbating systemic and multidimensional challenges low-income populations already face. Concerns about food insecurity and diet-related chronic diseases are symptomatic of deeper systemic challenges related to health insurance access, stress and bandwidth poverty, access to healthy foods, the higher cost of healthy foods, and structural oligopolies in the American food industry. Research suggests that SNAP inadequacy is linked to worse health outcomes, such as increased risk of obesity, diabetes, and hypertension. Yet instead of focusing on deeper systemic issues, the current Farm Bill proposes a quick fix, Band-Aid solution by proposing to cut SNAP funding further.
Policy recommendations for a stronger Farm Bill
Despite proposing massive cuts to SNAP, increasing inequitable farm subsidies, and cutting climate funding for conservation efforts, the 2024 Farm Bill does lay out some positive measures. These include raising the income cutoff for SNAP eligibility (the Earned Income Deduction) from 20% to 22% of income, which will ensure more households just at the margin of earned income now have access to SNAP benefits. It proposes to give benefits access to individuals with drug-related convictions, who were previously excluded. Further, it proposes to extend the age limit for high school students on SNAP from 18 to 22 years, allowing students to work without disincentivizing income for eligibility. However, despite these positives, the proposed cuts and other changes could undermine the Farm Bill’s effectiveness in addressing food insecurity and equity concerns in agricultural subsidies.
The proposed cuts based on restricting SNAP increases to only reflect inflation diverge significantly from academic research underscoring that the TFP should be updated regularly to factor in food prices, consumption patterns, and nutritional guidelines. While this measure could save $29 billion between 2025 and 2033, it will further dampen SNAP’s purchasing power as food costs continue to rise and vary across regions.
The polarization of the Farm Bill reflects a broader ideological divide over the role of welfare in American society. Republicans have historically advocated for limited assistance and stricter work requirements for SNAP recipients. In contrast, Democrats have historically perceived welfare programs such as SNAP as essential tools for reducing poverty and inequality, and advocated for expanded benefits and more coverage.
Politicians need to look beyond this ideological gap and focus instead on creating a more equitable and effective Farm Bill that addresses society’s economic and welfare needs. A zero-sum approach that pits agricultural interests against the needs of food-insecure, low-income consumers is not proving to be effective.
What follows are key policy recommendations for crafting an inclusive and equitable Farm Bill that addresses the economic and welfare needs of vulnerable populations, including low-income households and underrepresented farmers.
Evidence-based SNAP adjustments: Use scientific methodologies to measure the TFP’s adequacy and issue frequent and regular updates to SNAP benefits. Factors that impact the TFP beyond inflation include other costs of living, regional variations in SNAP adequacy, food consumption patterns, and healthy diet guidelines.
Index benefits to reflect local economic conditions: Implement regional cost-of-living adjustments to SNAP benefits, which can address disparities in food costs and improve equity across geographic regions.
Expand access to healthy foods: Invest in initiatives that improve access to healthier food options, such as affordable farmers markets, community gardens, and incentives for retailers in underserved areas to improve food access and support local economies.
Rebalance agricultural subsidies: Impose income limits on farm subsidies and expand efforts to improve subsidy access for small-scale and BIPOC farmers.
Integrate climate goals: Allocate funding for climate-resilient agricultural practices and provide financial assistance and incentives to small-scale and BIPOC farmers to invest in such technologies.
Foster bipartisan collaboration: Encourage cooperation across party lines to create a Farm Bill that balances agricultural support with food assistance—recognizing their interdependence rather than treating them as competing interests.
Engage stakeholders: Involve farmers, nutrition advocates, and SNAP recipients in the legislative process to ensure policies reflect the needs and realities of those directly impacted.
The 2024 Farm Bill represents a critical opportunity for Congress to craft a more equitable and inclusive policy that addresses the dual needs of supporting agricultural production as well as nutrition assistance. However, as it currently stands, proposals such as the $30 billion cut to SNAP funding, the shift in focus toward preventing diet-related diseases, and the continued expansion of agricultural subsidies that disproportionately benefit white, wealthy farmers and a limited number of commodity crops risk undermining SNAP’s response to food insecurity and worsening inequality in the agriculture sector.
Policymakers must look beyond zero-sum dynamics that pit agricultural subsidies against nutrition assistance, when the fundamental issues farmers and low-income households face are symptomatic of deeper systemic inequalities in the economic and welfare structures of fiscal policy. Therefore, rather than continuing to concentrate support in the hands of wealthy, large-scale agricultural producers, the Farm Bill should prioritize uplifting smaller, diverse farmers and ensuring low-income households have the resources they need to access nutritious food. Encouraging small-scale and low-income BIPOC farmers to invest in green technology is also essential, as this would foster more sustainable agricultural practices while supporting communities’ economic growth. At the same time, Congress must ensure that commodity prices remain stable and affordable, preventing further economic burdens on consumers.
An equitable and welfare-focused Farm Bill would embrace a broader vision—one that balances the needs of both rural farming communities and urban, food-insecure families. By aligning agricultural subsidies with sustainable practices and expanding SNAP’s effectiveness, Congress can craft a policy that not only strengthens food security, but also builds a more just, resilient, and environmentally responsible food system for all Americans.
17 notes
·
View notes
Text
also btw i know most young people are like i can never afford a house blah blah blah and it's usually the down payment is the reason why
there are loans that do not require a down payment that's how i bought my house
my home loan is through the usda to support lower and middle class people in rural areas purchase homes there's also grant and assistance programs like do research you would be surprised
hopefully this is mean but you like need to do research and figure it out i think a lot of people just assume they won't ever be able to buy a house without any research into it
also a tough pill to swallow but most likely you won't be able to buy a house in the middle of whatever us major city you live in it's probably gonna be farther out but yeah do research you would be surprised 🤷♂️
#t#and like my house is not perfect it's less than a 1000 sq ft and over a 100 years old#but it's MINE#😎
11 notes
·
View notes
Text
Excerpt from this press release from the Department of the Interior:
Today, the Departments of the Interior, Agriculture, and Commerce released a report outlining recommendations to enhance community-led economic development by creating jobs in the sustainable forest product sector and outdoor recreation while supporting healthy, resilient forests. This report was developed in response to climate change impacts, workforce and housing shortages, and barriers to intergovernmental coordination in rural forest-dependent communities and builds on President Biden’s Executive Order on Strengthening the Nation’s Forests, Communities, and Local Economies (E.O. 14072), which he signed on Earth Day 2022.
The report’s release comes during Climate Week, as the Biden-Harris administration continues demonstrating its commitment to addressing the climate crisis.
America’s forests provide millions of jobs and underpin local economies, particularly in rural communities. The Biden-Harris administration is mobilizing historic resources to help these forests and communities thrive. Through the Bipartisan Infrastructure Law, Inflation Reduction Act, and Great American Outdoors Act—in addition to annual appropriations—the Administration is providing historic funding for wildfire risk reduction, innovative forest products that create jobs, restoration and forest management to help our forests better withstand extreme weather events, outdoor recreation investments such as campgrounds, and research and development programs. The Department of the Interior’s Bureau of Land Management’s 21st Century Blueprint for Outdoor Recreation, USDA Forest Service’s Reimagine Recreation initiative and Department of Commerce’s U.S. Economic Development Administration’s Travel, Tourism and Outdoor Recreation program are also advancing public lands management and the outdoor recreation and tourism industries, for the benefit of current and future rural communities.
Today’s report provides recommendations to further these efforts by encouraging greater collaboration among federal agencies to deliver the resources and services that rural, forest-dependent communities need and to foster economic resilience.
The report proposes fostering community resilience by better connecting communities with the many existing tools to navigate climate-based risks in a way that also builds sustainable economic development and healthy forest practices. In addition, coordination across the federal government and with partners can help communities tap into existing resources to pursue their economic development plans and address bottlenecks or barriers to delivering support.
The report also emphasizes how forests benefit underserved communities, including Tribes, which are disproportionately affected by climate impacts. For example, the Interior Department and Forest Service's Equity Action Plans seeks to enhance Tribal co-stewardship and promote equitable access to cultural and recreational opportunities for all communities.
5 notes
·
View notes
Text
Stuff on my mind lately…
See the thing is… our landlord hasn’t done maintenance on this house in any serious sense since we moved in when I was five or six. It’s been WELL over 20 years. My dad had to fix the leaky ceiling in the back room years ago when it became uninhabitable. There’s a giant hole in the living room ceiling cover by a tarp and it’s been there for years. We went almost a decade without a heater in the house - I’d see my breath in the mornings in the back room, because we couldn’t afford running room heaters in all the bedrooms all night. The kitchen laminate has never been updated or repairs so it has holes torn in it. The windows are not weatherproof. Both the front and back doors stick in the summer and let in cold from the seams in the winter. The carpet hasn’t been replaced the entire time either; there’s patches in the living room that are completely worn away of threads. The roof has leaks and they either don’t fix it at all or do the laziest and cheapest temporary fix possible. Both porch stairs are in rough shape; my dad’s replaced them over the years but even just today I watched one bend under my mom’s weight, and she’s not that heavy. She walks with a cane. It’s a risk for there to be weak stairs.
They upped our rent last fall due to “maintenance costs rising”.
What fucking maintenance?
So like. It’s very honest and an understatement to say either we need to pressure the landlord into doing the bare fucking minimum (unlikely, both on the landlord’s part and my folks being willing to make a fuss) or to move.
The issue is… we get this place dirt cheap for local rental costs.
And if we were gonna pay what a rental comparable to this place costs, well fuck, it’s almost cheaper in most cases to just fucking buy a place.
There’s a real nice home not far in a rural area that’s not bad for the current costs in this area, almost a steal tbh. It’s rural so it works for the usda rural home loan. None of us have owned a home before so we can get some aid as first time home buyers. Idk if it would actually work out but it’s not as much of a longshot as it could be.
But… I don’t want to stay here forever. I don’t want to live in this state, let alone this area, for many more years. I keep my eye out for jobs elsewhere so I can potentially find a chance to move, now that I’ve got 5+ years experience at my career, including running a branch, leading a committee/system-project, and cochairing a service group’s meetings. Yeah there’s still experiences I need to have to fully round out but I think they’re not complete deferents.
So… it’s like. Do we move sooner, or later? Do we pay to reflow at least the living room and my folks’ bedroom, where the carpet is worst worn and try to make living in this house a little less of a nightmare, or would that be a waste of money (it’s not like we’d be allowed to take it out of rent; flooring wear doesn’t count I believe for upkeep costs on the landlord’s part). I looked up how much it would cost to install laminate flooring that is waterproof and scratch resistant for an estimate of our house’s sqft and it’ll be several thousand easily. Only a bit more than it would cost to remove the fucking popcorn ceiling and repair the giant hole in it. Either of those repairs could make things better and easier on my folks. Easier to clean, no worries about the leaks in the rain, less dust-allergens-pet hair getting caught up in fibers and nooks and crannies.
I saw a house for rent at a VERY reasonable cost near my work. It only has one bathroom, so I don’t want to bring my parents in because I am SO tired of sharing a bathroom with them. I could afford it myself, and have my own space.
My mom would never get out of the house unless my dad drivs her, and he hates doing it even for a logical reason (like grocery shopping) and she hates going places with him anymore these days. She would be stuck, and that’s not fair to either of them to never get a break from each other. And frankly, I’m skeptical they could afford living here without my income helping.
Idk, it’s just a complicated knot of coin flips and luck and hoping for the best no matter what we decide to do. I’d prefer to own my own place, but do I do that now because you don’t know if you’ll ever get a job elsewhere any time soon? Or do I wait because you never know when you’ll find that golden opportunity and what the housing market might look like in the future?
#Jules rambles#it’s a potentially damned if I do damned if I don’t#why can’t things be very obvious for good and bad decisions?#instead I gotta sit here twisting my mind into gordian knots of stress and decision fatigue
2 notes
·
View notes
Text
2024 Kentucky USDA Loan Income Limits for Kentucky Counties Kentucky USDA loan income limits vary by location and household size
How to Qualify for a USDA Home Loan in Kentucky
#2024 KY USDA Rural Housing Income Limits for Kentucky Counties for the Guaranteed RHS Loan#First-time buyer#Kentucky#Mortgage loan#USDA and Conventional Home Loans#usda first time buyer Kentucky
0 notes
Text
i am buying a house, and (maybe) you can too!
so... you want to buy a house, but you don't make a lot of money and you have no way to save up the recommended 10% recommended downpayment on a mortgage, which means you're basically going to be stuck renting forever, right?
well... actually, maybe not!
this post is going to be very US-centric, so i cannot speak to the homebuying experience in other countries, but if you live in the united states... you might be able to buy a house for much less up front than you might think!
this is gonna get long, but the main things you'll need are:
a credit score in the low- to mid-600s. this can vary by program, but most down payment assistance programs require somewhere between a 620 and 660. (i might make a second post at some point about credit scores bc fixing my credit score was a long and arduous process.)
enough in savings to cover a few up-front expenses. there are a couple of things that the down payment assistance programs won't cover. for me, we ended up having to pay ~$1500 up front total, which - to put it in perspective - is less than the deposit and move-in fees were going to be at most apartments in our area.
that's basically it! if you can do those two things, you might be able to buy a house!
let's talk about the details.
programs vary by state, but most states have down payment assistance programs of one kind or another. there's also a federal USDA loan program which is $0 down as well, but is only available in rural areas.
these programs WILL usually require you to have a certain credit score, usually somewhere in the 600s. (the particular program my housemates and i are using requires a minimum 640, but some require a higher or lower credit score than that.)
usually your first step is speak to a mortgage lender. the mortgage lender i'm working with is only available in the state of tennessee and not all mortgage companies accept all down payment assistance options, so i would research options in your state and then check to see if the programs have a list of preferred lenders and/or loan officers.
this sounds scary, but my loan officer has been a life-saver during this process. generally your loan officer wants to help you succeed, particularly when they know you're a first time home owner. tell your loan officer that you're going to be a first time home owner and you're interested in a $0 down payment program. they can run the numbers and see if you qualify, and if so, how much you can qualify for.
you can have multiple people on the mortgage with you, but everyone on the mortgage has to meet the credit score requirement.
if you do qualify, also talk to your loan officer about how much you can pay per month for a mortgage, too, since this might also impact what price range you're shopping in.
you'll also want a real estate agent. (trust me on this. you want a real estate agent.) my loan officer recommended a real estate agent to me and we quite literally could not have done this without him. your real estate agent does a lot more than just help you find houses to look at. they will also point out things that you might not know to look for and will also help negotiate with the seller for you.
when you talk to your real estate agent, tell them you are using a down payment assistance program and that you will need the seller to cover your closing costs. closing costs, for reference, are a bunch of small expenses that are paid when you officially sign the mortgage. typically both the buyer and the seller have separate closing costs, but it's fairly normal for buyers to ask the seller to pay for their closing costs for them in the current market. your real estate agent can then negotiate for this for you.
if the seller covers your closing costs and you can get approved for down payment assistance, there are only three things you will probably have to pay for out of pocket:
"earnest money." this is a small sum of money you pay to hold the house after the seller accepts your bid. (in our case, we paid $500 for our earnest money.)
the home inspection. our home inspection was also about $500, though the price of this could vary based on where you live.
the home appraisal. for us this was also about $500, though again, this could vary based on where you live.
and that's basically it! obviously talk with your loan officer and real estate agent about the cost of these things bc they might not be the same cost for you as they were for me, but for us, this ended up actually being cheaper than moving into a new apartment!
#i might try to write up some tips on improving your credit at some point too?#obviously i'm not a professional and this is just information based on my experience#but also six months ago we had NO IDEA that buying a home was even an option#and we were looking at trying to rent a house#and honestly... the credit score requirement on the mortgage was about the same as the credit score requirement for most of the rentals her#i don't know what to tag this as lmao#briar.txt
5 notes
·
View notes
Text
If you want to be a home owner please look into local assistance for first time home buyers.
In the US there are special loans for first time home buyers as well as assistance if you want to live in a rural area ( FHA and USDA loans). Special loans are more flexible with minimum down payment and credit score minimums as well as don't have some requirements that Conventional Loans have.
Ie one thing that helped us is Conventional loans require you to work full time consistently in the same field for 2 years. FHA only requires 6 months of employment and a letter explaining your history and to have an income that can afford the loan. I didn't have the work history needed for a Convention Loan.
The Loans, Grants, and Assistance vary state to state and you may have other options if you live in a major city. (Our second grant was only for our area.)
There also may be government backed housing assistance agencies which will help you with going through the process for free or a low payment (our state requires you to do some education with them for the FHA loan, and it was free).
My partner and I recently bought a house with a FHA Loan/Grant and a First Homeowners Grant from our lender (which has the qualifications of being a low income area, low income, as well as first homeowners). We were able to forgo any down payment or closing costs and will be paying less monthly costs then the rentals we were considering month to month.
We still had to pay some things. We paid for inspection, appraisal, insurance upfront, refundable deposit and 1000 dollars at closing.
FHA loans also have the added cost of loan insurance for month to month costs, but overall is still cheaper then renting so 🤷 I am not complaining.
Another thing to expect as a lower income buyer is you likely will only be able to afford fixer uppers so expect to have a lot of initial repair costs as well as maintaining your home over time. There is assistance for those things as well but be careful of loan scams when looking for those.
If you do consider going this route, make sure to be thorough with inspections and negotiate with what you find. It is a lot of upfront costs for something you may not go with, but can save you thousands in the long run. We needed to change out knob and tube in our house and since we found it in the inspection we were able to negotiate 12k from the sellers to fix it rather than paying that out of our pockets later. We also saved over a thousand by getting them to service the neglected HVAC. You're not likely to get a seller to fix everything, but you can save a lot with negotiating.
More homeowners can stabilize communities and help rent to not skyrocket uncontrollably. Especially if the homeowners arent nimbys who only care about their property values and instead actually care about their renting neighbors. Homeowners also have more power in your local politics, so taking advantage of these programs and getting more power to disadvantaged people and communities is so important.
#new homeowner#my partner and o have been yapping about this to everyone who will listen because fuck landlords and our city is gentrifying at a terrifyin#pace and the more homeowners the better#low income homeowners#not rich ppl moving in and buying the shiny new luxury housing that was built on demolished 100 yr old rowhomes#i want my neighbors to be safe from eviction and have the equity for retirement#for full disclosure i make 15.50 and my partner makes 17 an hr in a major city#we have good credit but it took a bit of a hit when applying to rentals#i dont know abt this stuff internationally#but theres likely simular stuff
3 notes
·
View notes
Text
Soil: The Secret Weapon in the Fight Against Climate Change - EcoWatch
www.ecowatch.com
Soil: The Secret Weapon in the Fight Against Climate Change
EcoWatch
7 - 8 minutes
By Claire O’Connor
Agriculture is on the front lines of climate change. Whether it’s the a seven-year drought drying up fields in California, the devastating Midwest flooding in 2019, or hurricane after hurricane hitting the Eastern Shore, agriculture and rural communities are already feeling the effects of a changing climate. Scientists expect climate change to make these extreme weather events both more frequent and more intense in coming years.
Agriculture is also an important — in fact a necessary — partner in fighting climate change. The science is clear: We cannot stay beneath the most dangerous climate thresholds without sequestering a significant amount of carbon in our soils.
Agricultural soils have the potential to sequester, relatively inexpensively, 250 million metric tons of carbon dioxide-equivalent greenhouse gasses annually — equivalent to the annual emissions of 64 coal fired power plants, according to National Academy of Sciences.
But we can’t get there without engaging farmers, turning a source of emissions into a carbon sink. Here are just a few of the ways the Natural Resources Defense Council works to encourage climate-friendly farming:
Creating New Incentives for Cover Crops: Cover crops are planted in between growing seasons with the specific purpose of building soil health. Despite their multiple agronomic and environmental benefits, adoption is low — only about 7% of U.S. farmland uses cover crops. NRDC is working to scale up cover cropping through innovative incentives delivered through the largest federal farm subsidy: crop insurance. We’ve worked with partners in Iowa and Illinois to launch programs that give farmers who use cover crops /acre off of their crop insurance bill. And partners in Minnesota and Wisconsin are exploring similar options. While we’re delighted at the benefit this program has for farmers in those individual states, we’re even more excited about the potential to scale this program to the 350 million acres that utilize subsidized crop insurance nationwide. A recent study suggests that cover crops sequester an average of .79 tons of carbon per acre annually, making cover crops one of the pillars of climate-friendly farming systems.
Supporting Carbon as a New “Agricultural Product”: Championed by Senator Ron Wyden, the 2018 Farm Bill created a new program, the Soil Health Demonstration Trial, that encourages farmers to adopt practices that improve their soil health, and tracks and measures the outcomes. NRDC worked alongside our partners at E2 and a number of commodity groups, farmer organizations, and agribusinesses to secure passage of this provision. The Demonstration Trial will create a new, reliable income stream — farmers will get paid for the carbon they sequester regardless of how their crops turn out, and it builds the data needed for confidence in any future carbon markets. USDA recently announced the first round of awards under this new program, totaling over million in investments to improve soil health. Senator Cory Booker has since drafted legislation that would increase funding for the program nearly 10-fold to 0 million annually; Representative Deb Haaland released a companion bill in the House.
Scaling up Regenerative Agriculture: Regenerative agriculture is an approach to farming that looks to work with nature to rebuild the overall health of the system. Regenerative farmers use a variety of tactics, including reduced chemical inputs, diverse crop and livestock rotations, incorporating compost into their systems, and agroforestry, among others. Our team is in the midst of interviewing regenerative farmers and ranchers to learn more about what’s working for them and what challenges they’ve faced in their shift to a regenerative approach. We’re planning to analyze our interview results and combine them with a literature review to identify what role NRDC could potentially play in helping to scale up regenerative farming and ranching systems. We’ll also be sharing quotes and photos from our interviews on social media every Friday starting in January, so stay tuned for some inspiring farm footage!
Supporting Organic Farmers: Organic agriculture by design reduces greenhouse gas emissions, sequesters carbon in the soil, does not rely on energy-intensive chemical inputs, and builds resiliency within our food system. Practices integrated into organic production will become increasingly more important in the face of a changing climate. NRDC supports organic farmers through policy initiatives like the Organic Farm-to-School program that was introduced in the California legislature last year. In the coming year, we’ll continue to work to support organic farmers in California.
Reducing Food Waste: Food waste generates nearly 3% of anthropogenic greenhouse gas emissions in the U.S., and NRDC is working hard to reduce that number, and improve soil health in the process. Some of our policy proposals include securing passage of date labelling legislation to eliminate confusion about whether food is still good to eat, working with cities to reduce waste and increase rescue of surplus food, and supporting efforts at all levels to increase composting of food scraps. Adding compost to soils improves their ability to sequester carbon, store nutrients, and retain water. Composting food scraps also helps to “close the loop” on organic matter and nutrients by returning them to the agricultural production cycle, rather than sending that organic material to landfills, where it generates methane (a powerful climate pollutant).
Climate-friendly farming also offers a host of important co-benefits. For example, when farmers use complex crop rotations to break weed, pest, and disease cycles, they can reduce the amount of synthetic chemicals they need to use. When they use practices like cover crops, no-till, and adding compost to protect and restore the soil, they reduce the need for synthetic fertilizers that emit greenhouse gasses. And when farmers can reinvest the oppressive amount of money they had been previously spending on expensive, synthetic inputs into the additional labor required to carbon farm, they bring new jobs to economically-depressed rural areas.
Farmers understand better than many of us the harsh realities of climate change, regardless of their opinions about what’s causing those changes. And tight margins and trade wars make the potential of new value streams particularly attractive for farmers right now. By working alongside the farmers and farmworkers who tend the land, we can bring new allies into the fight against climate change, restore the health of our soil, and create a healthy, equitable, and resilient food system.
2 notes
·
View notes
Note
Hi, I've been following your housing issues and I just wondered if you'd looked into a USDA Rural Development loan? These mortgages are specifically designed for lower income people. All you have to do is fill out the application and they'll let you know if you are accepted and if so, what your budget will be when looking for a house. I couldn't find on your blog if you'd looked into yet. It might be a no go, but it's worth checking out!
I've had the USDA loan suggested to me many times but theres a couple reasons why I haven't done it yet.
The first is that it would require me to move out of the city, away from conveniences that would make it difficult for us as I am the only one with a working car. And country homes are harder to find right now because a lot of them were snatched up during covid. (I was told to look at houses in etna. Literally there are zero houses for sale in etna. It's that bad.)
The second is that most of these programs help with the down payment. I dont need the down payment. Down payment is covered. What I need is for my income to be enough.
It's more important for us to get out of the rental situation we're in now than it is to find a house.
31 notes
·
View notes
Text
For people wanting to own a house in country places, the USDA Home Loan program is like an awesome chance that only opens for them. It helps such folks reach their dream of becoming homeowners. This blog focuses on key aspects, benefits, and requirements for securing a USDA home loan, aiding home buyers in rural or small areas.
#property#real estate#united states#gustancho associates#gca mortgage#usa#va loans#fha loan#first time home buyer#bad credit score#usda loans#fha loans
2 notes
·
View notes