#TVresolution
Explore tagged Tumblr posts
Text
What TV resolution do we need?

As usual, CES 2020 clearly demonstrated the main focus areas of companies' efforts to improve TVs. In fact, they cover almost all aspects, including design, audio quality, enhanced functionality, etc. But, improving image quality remains one of the main directions. Today, companies solve this problem using a variety of methods, including: - increasing resolution; - increased efficiency of AI 8K Upscaling; - improving color rendering by improving the backlight; - automatic calibration. TCL demonstrated the 8th series with Mini LED backlight Technology and announced its next generation called Vidrian Mini LED.

Today, this Chinese company is confidently leading the way in improving FALD (full-array local dimming) technology. According to many experts, Mini LED backlight or, already, Vidrian Mini LED Technology will be able to closely approximate the color accuracy of LED TVs to OLED technology. In addition, this year, almost all companies introduced new auto-calibration modes. In particular, Sony developed Ambient Optimization, new Samsung TVs use Adaptive Picture, Adaptive Peak Brightness and Adaptive Tone Mapping, LG TVs have Dolby Vision IQ. But an unprecedented number of 8K models from almost all leading companies demonstrates the dominance of the trend of increasing TV resolution.
Introduction
Disputes over the avalanche spread of 4K are still ongoing, but almost all leading companies already offer 8K TVs. Basically, skeptics of this trend use two fairly convincing arguments. First, many have not forgotten the relatively recent history of 3D TVs. The rapid growth of its popularity began after a demonstration at CES and IFA in 2010. Many experts quite logically predicted its excellent prospects. Of course, the manufacturers adequately responded to demand, significantly improving and cheapening this technology in its models. Unfortunately, the high cost of producing 3D content has become an insurmountable obstacle to its further development. As a result, almost all companies abandoned 3D support in their TVs. Therefore, today experts quite reasonably express doubts regarding the prospects for the production of native 8K content, which today is practically absent. Probably for this reason, companies are actively improving 8K AI Upscaling technology. In the worst case, these TVs will be able to improve quality playback of lower resolution content.

Secondly, they quite reasonably ask about the advisability of increasing resolution in terms of eye capabilities. The screen resolution of smartphones confirms these doubts. As known, many modern smartphones already provide 400, 500 ppi and higher. But according to many ophthalmologists, 600 ppi is close to the limit of perception for our vision. Accordingly, a further increase in resolution does not make much sense. In the same time, many companies continue to increase it. Today, the absolute record belongs to the Sony Xperia Z5 with 806 ppi.

This value corresponds to 4K, but does not make sense due to the limited possibilities of our eye. But this argument has some additional aspects.
Vernier acuity (hyperacuity)
As know, standard measure of visual acuity using Snellen eyechart. The argument of skeptics is based on the limitation of visual acuity, which does not distinguish between 8K vs 4K due to too high pixel density. In particular, its lower limit does not exceed 20/20.

But the Japanese NHK broadcaster did some interesting research to find out the effect of resolution on perception. Of course, visual acuity remains a major factor, but it's not the only one. Brain and Vernier acuity (hyperacuity) also significantly affect image perception. For example, many people will be able to distinguish the difference between two pairs of lines, one of which contains perfectly parallel lines, and the second includes lines with an offset of only one pixel. In this case, Vernier acuity will take this displacement as a stepping stone.

But the spacing the pixels on the 8K screen is half vs 4K matrix. Accordingly, reducing the height of the step increases the smoothness of the lines and we perceive the 8K image as clearer. Moreover, the brain reinforces this difference by trying to create a more analog-like image, increasing its realism. Thus, the argument based on only traditional visual acuity is not convincing enough.
Experiment Results
Moreover, recent studies of Dr. YungKyong Park of Ewha Womans University in Seoul further supports this hypothesis. In this experiment, scientists installed side-by-side 65-inch TVs with 4K and 8K resolution, which were calibrated at 500 nits of peak luminance. Of course, all 120 participants in the experiment had the same 20/20 visual acuity and normal color vision. The experiment was conducted at a distance of 9 feet from the displays in a dark room. Content included the 16 images and 3 videos with visuals. As a result, almost all participants in the experiment noted the difference 8K vs 4K displays.

Interestingly, the participants in the experiment noted not increased sharpness or contrast of the image due to higher resolution. According to them, 8K images looked cooler, warmer, more delicious, heavier, etc, which corresponds to sensory perception. In addition, Dr. Kyoung-Min Lee of Seoul National University investigated 8K resolution in terms of its perception by the brain. As known, increasing resolution reduces information loss. Accordingly, the dynamic signal-to-noise ratio increases. As a result, the level of immersive effect also rises. Thus, the brain is less tired when perceiving 8K content. At the same time, watching provides richer emotions due to high realism of the perceived content.
Conclusions
1. In the absence of native 8K content, 8K TVs will be able to improve quality playback of lower resolution content with 8K AI Upscaling technology. 2. Today, the screen of 75" 8K TV provides up to 120 ppi. But according to ophthalmologists, the eye can perceive up to 600 ppi due to Vernier acuity (hyperacuity). In this case, the brain distinguishes images with different detailing even if they are not visualized. Therefore, increasing the TV resolution will be relevant in the coming years. In fact, increasing resolution reduces information loss. Accordingly, the dynamic signal-to-noise ratio increases. As a result, the process requires less brain effort to interpolate the lost data. In other words, the brain is less tired when perceiving content in high resolution. In addition, the level of immersive effect also rises due to high realism of the perceived content. Thus, higher detail reduces the load on the brain, while increasing the immersive effect. 3. Given these factors, increasing ppi of the TV screen by increasing the number of pixels has good prospects and to continue to be one of the main ways to improve image quality. This video demonstrates the capabilities of the 8K AI Upscaling in the Samsung Q950TS 8K at CES 2020. Read the full article
#8KAIUpscaling#8KTVs#hyperacuity#LGDolbyVisionIQ#SamsungAdaptivePicture#SonyAmbientOptimization#TVresolution#Vernieracuity#VidrianMiniLEDtechnology
0 notes
Link
0 notes
Link
https://www.enquirygate.com/Mi-TV-4X-125-7-cm-(50-Inches)-4K-Ultra-HD--LED-TV-p/1038
0 notes
Text
Resolution vs PPI in TV and phone

Traditionally, CES 2020 has demonstrated the main modern trends in improving TVs. Of course, the demonstration of 8K models from the leaders of this segment became one of the main events of this year. In addition, companies have demonstrated a huge number of innovative solutions in terms of design, color rendering, new features, audio playback, etc. For example, Samsung showed a very unconventional 43-inch 4K Sero Vertical TV, perfectly adapted for content from a smartphone.

The screen of this TV easily rotates 90 degrees. TCL announced the innovative Vidrian Mini LED on glass technology, which was the next generation of Mini-LEDs backlight.

In the case of its implementation, the color accuracy of LCD TVs can almost come close to the level of OLED technology.
8K resolution
But increasing the resolution remains one of the main directions of improving the image quality. As known, this aspect causes quite heated discussions among experts. First, many recall the relatively recent history of 3D technology. At the first stage, it won a huge number of fans among consumers and many experts quite reasonably predicted excellent prospects. Of course, the manufacturers adequately responded to demand, significantly improving and cheapening this technology in its models. Unfortunately, the high cost of producing 3D content has become an insurmountable obstacle to its further development. As a result, almost all companies abandoned 3D support in their TVs. Therefore, today experts quite reasonably express doubts regarding the prospects for the production of native 8K content. As known, today it's practically absent. Therefore, just in case, companies are actively improving 8K AI upscaling technology.

At a minimum, 8K TVs will provide better quality playback of lower resolution content. Secondly, many experts doubt the advisability of increasing the resolution in terms of the physiological characteristics of our vision. Indeed, visual acuity has a maximum limit.

Accordingly, at some stage, a further increase in resolution becomes meaningless. But the results of some recent studies open up new prospects for this trend.
Resolution vs PPI
As known, screen resolution is defined as the number of pixels per unit area. For these reasons, ppi (pixels per inch) most correctly characterizes the screen.

Today many smartphone manufacturers often indicate this value in specs as one of the main parameters of the screen. Basically, its value affects the image detail. Unfortunately, TVs manufacturers initially replaced it with the marketing concept of “screen resolution”. Today, companies use the terms HD Ready (720p), Full HD (1080p), 4K Ultra HD (2160p), or 8K Ultra HD (4320p). Accordingly, these abbreviations correspond to 1366 x 768 or 1280 x 720, 1920 x 1080, 3840 x 2160, or 7680 x 4320 pixels.

Maybe companies were trying to replace the not very clear "ppi" with simpler names. Indeed, today HD, UHD, 4K or 8K are more understandable for most consumers. In addition, it's very convenient from a marketing point of view, providing companies with additional opportunities for maneuver due to uncertainty. Obviously, the image clarity on the screen, in addition to the number of pixels, directly depends on the size of the screen and pixels. Therefore, the visualization of the difference between UHD and 4K resolutions begins to appear on screens from 55 inches and above.

Of course, companies are well aware that image quality does not depend on ambitious abbreviations, but on real ppi. Therefore, they increase the actual number of pixels (resolution) while increasing the diagonal of their models. But manufacturers can rarely resist the marketing temptation to write 4K Ultra HD on the box, instead of the more informative ppi.
Pixels Per Inch
The pixel density is calculated using a fairly simple formula: PPI = / d, where a and b - the number of pixels horizontally and vertically (resolution), d - inches of the screen. But today, the Internet offers many simple and convenient online calculators. For example, the ppi for the 49-inch LG 49UJ630V with a resolution of 3840 x 2160 is 89.91. Of course, this value is not very informative for most consumers. But there are quite a few recommended schemes for choosing a TV viewing distance in terms of optimal image clarity.
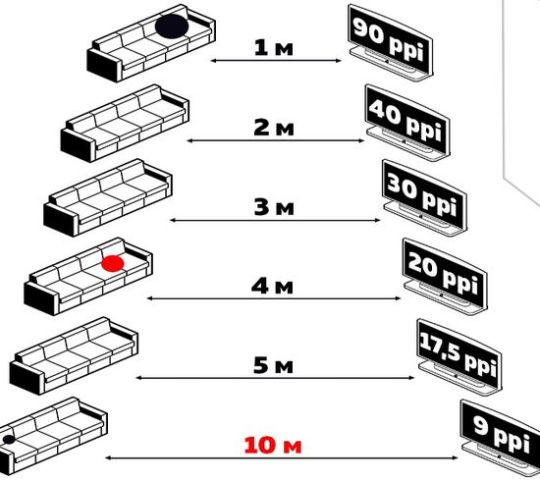
According to it, LG 49UJ630V provides a high image clarity at a distance of 1 meter or more. The situation with smartphones is significantly different. On the one hand, the screen size of a modern model usually does not exceed 7 inches. Accordingly, the size of its pixel is also significantly smaller compared to TV. But the distance between the eye and the screen rarely exceeds 12 inches. Therefore, high detail requires significantly more ppi compared to TVs. For example, many modern smartphones already provide 400 ppi and higher. According to many ophthalmologists, 600 ppi is close to the limit of perception for our vision. Accordingly, a further increase in resolution does not make much sense. Moreover, it increases the energy consumption of the screen matrix, significantly reducing the battery life of the smartphone. But many companies continue to increase it. Today, the absolute record belongs to the Sony Xperia Z5 with 806 ppi.

Similar to TV, this value corresponds to 4K. Of course, this trend is mainly due to marketing considerations.
Conclusions
Perhaps today we can assume that the resolution of the smartphone screens has reached a maximum and its further increase is meaningless due to the natural limitations of our vision. But with TVs, the situation is somewhat different. In fact, increasing the TV resolution allows the user to reduce the viewing distance without visualization of pixels. But this problem is hardly relevant at a distance of several meters or more. On the other hand, a closer location in front of the 65 or 75-inch screen is unlikely to be comfortable for most people with normal vision. For example, ppi of the 75" 8K TV is 117, and a 75" 4K model provides 59 ppi. Of course, even 59 ppi eliminates the visualization of pixels due to the large viewing distance. But there is an additional aspect. These values are significantly less than the vision limit. According to the results of some studies, the brain forms an image based on data obtained from the eyes, regardless of our sensations. In other words, the brain distinguishes between images with different detail, even when a person does not feel it visually. In particular, increasing resolution reduces information loss. Accordingly, the dynamic signal-to-noise ratio increases. As a result, the level of immersive effect also rises. Thus, the brain is less tired when perceiving content in high resolution. At the same time, such watching provides richer emotions due to high realism of the perceived content. Given these factors, increasing ppi TVs by increasing the number of pixels has good prospects and to continue to be one of the main ways to improve image quality. This video shows 8K vs 4K vs HD. Read the full article
#4KSeroVerticalTV#8KAIupscalingtechnology#8Kresolution#pixeldensity#pixels-per-inch#ppi#SonyXperiaZ5#TVresolution#VidrianMiniLEDonglasstechnology
0 notes
Link
0 notes