#Solar Vehicle Market Research
Explore tagged Tumblr posts
Text
#solar#solar system#solar energy#Solar vehicles#automotive#electric vehicles#transportation#market research#researchreports
0 notes
Text
Yesterday felt like an earthquake shook the foundations of our climate and environmental laws, followed by a hurricane that scattered the bits all over the place and a wildfire that burned those bits that weren't scattered. I didn't watch any part of yesterday's debauchery, either on TV or streaming or the alerts that pop up on my iPhone or iPad, or read anything (neither national, local or environmental or climate specialized media). I figured most of the crap he did yesterday will be the subject of strategic lawsuits, and much will be tossed out as contrary to legislation or regulation or unconstitutional. In other words, I'll pay attention to the reconstruction, not the destruction. But.......it was still a horse shit day.
This compilation from the Sabin Center for Climate Change Law (of the Columbia Law School/Columbia Climate School) is outstanding. Click/tap on the caption of this post and you'll be able to figure out what happened and sort things out as you want. Just click/tap on the caption and go for it. But if you don't want to do that, here's the compilation, abbreviated. Italicized/red fonts are my addition, either explanatory or editorial.
PUTTING AMERICA FIRST IN INTERNATIONAL ENVIRONMENTAL AGREEMENTS
Withdraw from Paris Climate Agreement
Withdraw from any other agreements made under UN Framework Convention on Climate Change (UNFCCC)
Revoke any financial commitments under UNFCCC
Revoke U.S. International Climate Finance Plan
DECLARING A NATIONAL ENERGY EMERGENCY
Declares national energy emergency, primarily based on high energy prices
Use any lawful emergency authorities “to facilitate the identification, leasing, siting, production, transportation, refining, and generation of domestic energy resources.”
Use Defense Production Act and federal eminent domain authorities
Issue emergency fuel waivers to allow year-round sale of E15 gasoline (E15 is ethanol/gasoline mix)
“Expedite the completion of all authorized and appropriated infrastructure, energy, environmental and natural resources projects”
Use emergency authorities and nationwide permits to grant approvals under Clean Water Act Sec. 404, Rivers and Harbors Act Sec. 10, and Marine Protection Research and Sanctuaries Act Sec. 103 for energy projects
Use emergency consultation processes under Endangered Species Act, and frequent convening of Endangered Species Act Committee, for energy projects
Use construction authority of Army Corps of Engineers
The term “energy” is defined to mean “crude oil, natural gas, lease condensates, natural gas liquids, refined petroleum products, uranium, coal, biofuels, geothermal heat, the kinetic movement of flowing water, and critical minerals” [not wind or solar] (excluding wind and solar is childish and just plain stupid)
UNLEASHING AMERICAN ENERGY
“eliminate the ‘electric vehicle (EV) mandate’ and promote true consumer choice … by terminating … state emissions waivers that function to limit sales of gasoline-powered automobiles; and by considering the elimination of unfair subsidies and other ill-conceived government-imposed market distortions that favor EVs” (the elon musk pacifier....i.e., Tesla)
“safeguard the American people’s freedom to choose from a variety of goods and appliances, including but not limited to lightbulbs, dishwashers, washing machines, gas stoves, water heaters, toilets, and shower heads”
Require all agency heads to review all existing regulations “that impose an undue burden on the identification, development, or use of domestic energy resources – with particular attention to oil, natural gas, coal, hydropower, biofuels, critical mineral, and nuclear energy resources”
Attorney General “shall consider whether pending litigation against illegal, dangerous, or harmful policies should be resolved through stays or other relief”
Revocation of many executive orders
Terminate the American Climate Corps
Council on Environmental Quality must propose rescinding its NEPA regulations (NEPA regulations are the core of our environmental laws)
CEQ to convene working group to expedite permitting approvals
“all agencies must prioritize efficiency and certainty over any other objectives, including those of activist groups that do not align with the policy goals”
“facilitate the permitting and construction of interstate energy transportation and other critical energy infrastructure, including … pipelines”
In NEPA and other permitting reviews, “agencies shall adhere to only the relevant legislated requirements for environmental considerations and any considerations beyond those requirements are eliminated”
Disband Interagency Working Group on the Social Cost of Greenhouse Gases; all of its guidance, recommendations, etc. are withdrawn
Consider eliminating the “social cost of carbon” calculation
EPA in collaboration with other agencies shall submit recommendations to OMB “on the legality and continuing applicability” of the greenhouse gas endangerment finding of 2009 (this is the core concept from the US Supreme Court case that provides the legal basis for greenhouse gas controls)
Immediately pause disbursement of funds appropriated through Inflation Reduction Act or Infrastructure Investment and Jobs Act; review processes for issuing grants, loans, contracts, or any other financial disbursement of appropriated funds
Secretary of Energy to restart reviews of applications for approvals of LNG export projects
Maritime Administration to review approvals for proposed deepwater ports for LNG export
“identify all agency actions that impose undue burdens on the domestic mining and processing of non-fuel minerals and undertake steps to revise or rescind such actions”
UNLEASHING ALASKA’S EXTRAORDINARY RESOURCE POTENTIAL
Expedite permitting and leasing of energy and natural resource projects in Alaska
Prioritize development of Alaska’s LNG potential
End restrictions on development of Arctic National Wildlife Refuge and certain other areas in Alaska
Numerous other actions to facilitate energy development in Alaska
TEMPORARY WITHDRAWAL OF ALL AREAS ON THE OUTER CONTINENTAL SHELF FROM OFFSHORE WIND LEASING AND REVIEW OF THE FEDERAL GOVERNMENT’S LEASING AND PERMITTING PRACTICES FOR WIND PROJECTS
Stop leasing of federal waters for offshore wind
Issue no new or renewed approvals, rights of way, loans for onshore or offshore wind projects
“consider the environmental impact of onshore and offshore wind projects upon wildlife, including, but limited to, birds and marine mammals”
PUTTING PEOPLE OVER FISH: STOPPING RADICAL ENVIRONMENTALISM TO PROVIDE WATER TO SOUTHERN CALIFORNIA
Restart work “to route more water from the Sacramento-San Joaquin Delta to other parts of the state for use by the people there who desperately need a reliable water supply”
“The recent deadly and historically destructive wildfires in Southern California underscore why the State of California needs a reliable water supply and sound vegetation management practices in order to provide water desperately needed there”
DELIVERING EMERGENCY PRICE RELIEF FOR AMERICAN FAMILIES AND DEFEATING THE COST-OF-LIVING CRISIS
Among many other actions, “eliminate counterproductive requirements that raise the costs of home appliances”
“Eliminate harmful, coercive ‘climate’ policies that increase the costs of food and fuel”
29 notes
·
View notes
Text

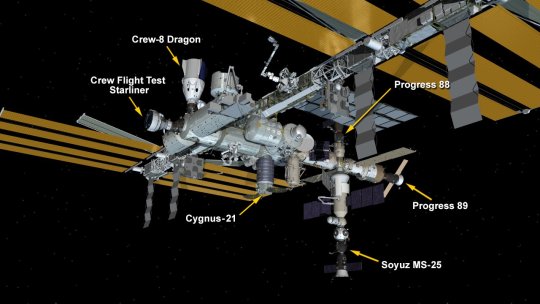
New SpaceTime out Monday
SpaceTime 20240826 Series 27 Episode 103
Starliner crew to return on Dragon
NASA has decided to return the stranded Starliner crew to Earth aboard rival SpaceX’ Dragon capsule because of ongoing concerns about the reliability of their Boeing spacecraft.


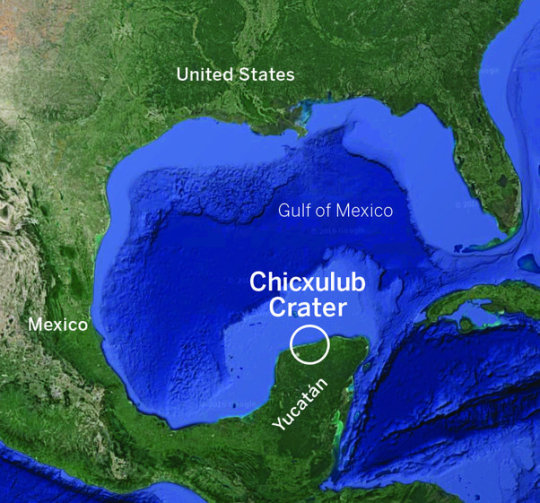
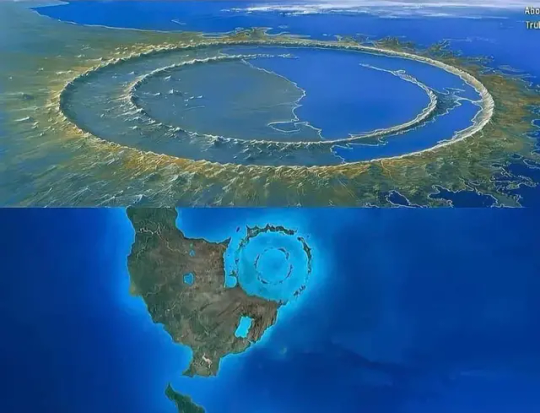
Tracking down the asteroid that killed the dinosaurs
A new study claims the asteroid which triggered the extinction of 75 percent of all life on Earth including all the non-avian dinosaurs 66 million years ago originated beyond the orbit of Jupiter during the early development of the solar system.


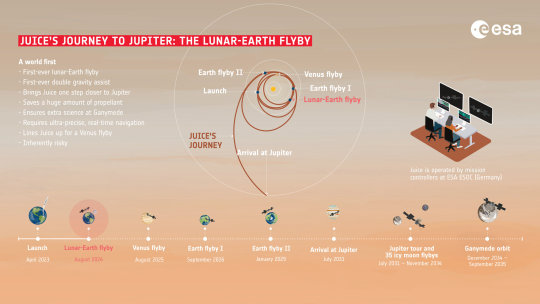
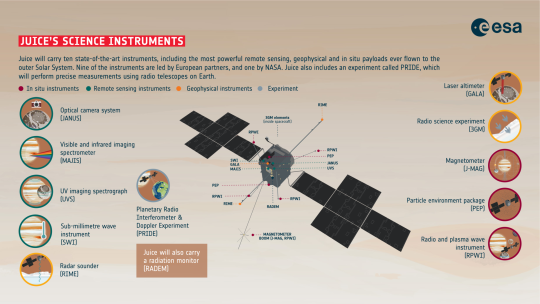
JUICE completes the first joint Lunar-Earth gravity assist flyby
The European Space Agency’s JUICE -- Jupiter Icy Moons Explorer – spacecraft has successfully completed the first ever joint Lunar-Earth gravity assist fly by flinging itself just as planned towards Venus.


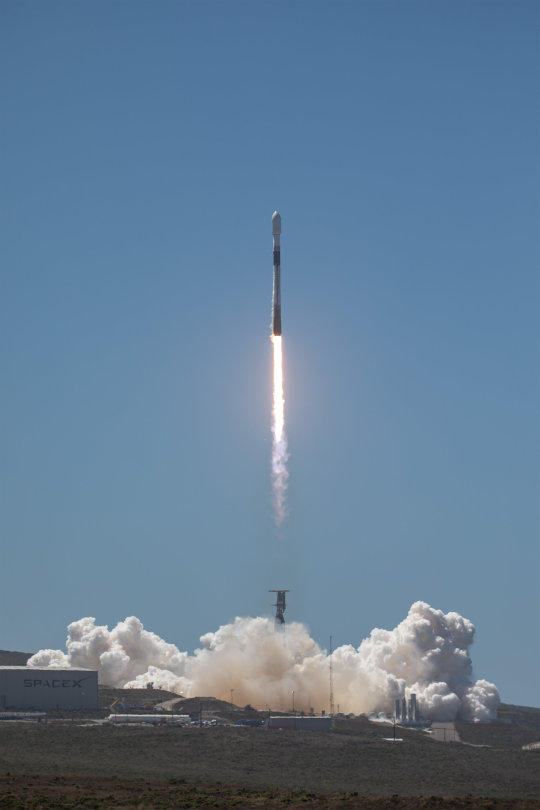
Three more Australian satellites sent into orbit
The latest trio flew up aboard SpaceX’s transporter 11 mission on a Falcon 9 rocket from Space Launch Complex 4E at Vandenberg Space Force Base in California. Transporter 11 is carrying 116 payloads, including CubeSats, microsats, and an orbital transfer vehicle carrying eight payloads.






The Science Report
Babies born to fathers of an older age more likely to have health complications at birth.
The bacteria that can produce rigid, heat stable plastics.
Tiny volcanic glass shards found in Tasmania came from a super-eruption in New Zealand.
Skeptics guide to body language
SpaceTime covers the latest news in astronomy & space sciences.
The show is available every Monday, Wednesday and Friday through Apple Podcasts (itunes), Stitcher, Google Podcast, Pocketcasts, SoundCloud, Bitez.com, YouTube, your favourite podcast download provider, and from www.spacetimewithstuartgary.com
SpaceTime is also broadcast through the National Science Foundation on Science Zone Radio and on both i-heart Radio and Tune-In Radio.
SpaceTime daily news blog: http://spacetimewithstuartgary.tumblr.com/
SpaceTime facebook: www.facebook.com/spacetimewithstuartgary
SpaceTime Instagram @spacetimewithstuartgary
SpaceTime twitter feed @stuartgary
SpaceTime YouTube: @SpaceTimewithStuartGary
SpaceTime -- A brief history
SpaceTime is Australia’s most popular and respected astronomy and space science news program – averaging over two million downloads every year. We’re also number five in the United States. The show reports on the latest stories and discoveries making news in astronomy, space flight, and science. SpaceTime features weekly interviews with leading Australian scientists about their research. The show began life in 1995 as ‘StarStuff’ on the Australian Broadcasting Corporation’s (ABC) NewsRadio network. Award winning investigative reporter Stuart Gary created the program during more than fifteen years as NewsRadio’s evening anchor and Science Editor. Gary’s always loved science. He studied astronomy at university and was invited to undertake a PHD in astrophysics, but instead focused on his career in journalism and radio broadcasting. Gary’s radio career stretches back some 34 years including 26 at the ABC. He worked as an announcer and music DJ in commercial radio, before becoming a journalist and eventually joining ABC News and Current Affairs. He was part of the team that set up ABC NewsRadio and became one of its first on air presenters. When asked to put his science background to use, Gary developed StarStuff which he wrote, produced and hosted, consistently achieving 9 per cent of the national Australian radio audience based on the ABC’s Nielsen ratings survey figures for the five major Australian metro markets: Sydney, Melbourne, Brisbane, Adelaide, and Perth. The StarStuff podcast was published on line by ABC Science -- achieving over 1.3 million downloads annually. However, after some 20 years, the show finally wrapped up in December 2015 following ABC funding cuts, and a redirection of available finances to increase sports and horse racing coverage. Rather than continue with the ABC, Gary resigned so that he could keep the show going independently. StarStuff was rebranded as “SpaceTime”, with the first episode being broadcast in February 2016. Over the years, SpaceTime has grown, more than doubling its former ABC audience numbers and expanding to include new segments such as the Science Report -- which provides a wrap of general science news, weekly skeptical science features, special reports looking at the latest computer and technology news, and Skywatch �� which provides a monthly guide to the night skies. The show is published three times weekly (every Monday, Wednesday and Friday) and available from the United States National Science Foundation on Science Zone Radio, and through both i-heart Radio and Tune-In Radio.
#science#space#astronomy#physics#news#nasa#astrophysics#esa#spacetimewithstuartgary#starstuff#spacetime#jwst#hubble space telescope#james webb space telescope
10 notes
·
View notes
Text
Emissions of two of the most potent greenhouse gases have substantially increased in China over the last decade, a study has found.
Perfluorocarbons are used in the manufacturing processes for flat-panel TVs and semiconductors, or as by-products from aluminium smelting. They are far more effective at trapping heat in the atmosphere than CO2, and can persist in the Earth’s atmosphere for thousands of years, unlike CO2 which can persist for up to 200 years.
A research team led by Minde An at Massachusetts Institute of Technology examined the emissions of two specific perfluorocarbons, tetrafluoromethane and hexafluoroethane, both with atmospheric lifetimes of 50,000 and 10,000 years respectively.
By analysing atmospheric observations in nine cities across China from 2011 to 2021, they found that both gases exhibited an increase of 78% in emissions in China and, by 2020, represented 64-66% of global emissions for tetrafluoromethane and hexafluoroethane. However, while levels of fluorocarbon emissions are increasing at an alarming rate, CO2 still accounts for about 76% of total greenhouse gas emissions.
The increase in emissions from China was sufficient to account for the global emission increases over that same period, suggesting that China is the dominant driver in tetrafluoromethane and hexafluoroethane release into the atmosphere globally.
The emissions were found to mainly originate from the less populated industrial zones in the western regions of China, and are thought to be due to the role of perfluorocarbons in the aluminium industry.
China is the world’s largest producer and exporter of aluminium, with the country’s production reaching a record-high output of 41.5m tonnes last year.
With the rapid expansion of China’s aluminium and semiconductor industries, these ongoing high levels of fluorocarbon emissions could pose a particular threat to China’s carbon neutrality goal and global climate mitigation. The country is aiming to achieve “peak carbon” emission by 2030 and become “carbon neutral” by 2060.
The authors suggest that with technological innovation and incorporation of the aluminium industry into the carbon market, or a national carbon trading scheme allowing emitters to buy or sell emission credits, it is possible that these rising levels could be reduced.
While being a significant source of CO2 emissions, aluminium production is also essential in the energy transition from fossil fuels to cleaner renewable energy sources by helping produce many low-carbon technologies such as solar panels, electric vehicles and wind turbines.
Organisations such as the World Economic Forum argue that the aluminium industry must act now to find a balance between ensuring efficient production alongside mitigating the industry’s negative impacts on the climate.
2 notes
·
View notes
Text
i really just can't take any bidenomics reflection about how certain initiatives failed to influence voters seriously if the reflection fails to acknowledge the information crisis and the relative stupidity of the average swing voter--and i give less credence to any political analysis that refuses to frame "democratic failure" as even a little bit the result of republican opposition/electoral wins--
but this article's brief "to be fair" section about the accomplishments of the biden administration's major legislative victories was a neat summation and also sort of shows how rolling back parts of the IRA may not be easy or all that motivating for an already fractious and narrow-majority republican house:
Still, the market-making bills that did pass were momentous. To give credit where due: Biden’s green industrial policy was a technocratic tour de force. Learning from Obama’s fiscal timidity, his staffers understood that lightly nudging markets would not suffice to meet the climate crisis. This is because of what economists call a market failure. Developing foundational technologies is often initially prohibitively expensive, because of low immediate consumer demand or lack of economies of scale. Private investment is unlikely to take the risk—and needs a helping shove (and often some security) from the state. Bidenomics was that shove. The clean energy strategists Lachlan Carey and Jun Ukita Shepard have described the relationship between its three bills in anatomical terms. The CHIPS Act is the “‘brains’ of the operation,” underwriting billions to foundational research in energy biofuels, advanced battery technology, and quantum computing. The Infrastructure Act is the backbone, supporting not only traditional roads, ports, and water infrastructure but also clean hydrogen, low and zero-emission transit buses, and EPA Superfund projects to clean up contaminated sites. The IRA is the financial heart of the machine, subsidizing both the production and consumption of green technology. The lions’ share of federal spending has been directed at foundational research and development and the initial scaling up of markets—the stage, as Carey and Shepard put it, “where private markets are less likely to invest in research, development, demonstration, and early commercialization.”
Bidenomics also aims to onshore entire supply chains. For instance, the Section 45X Advanced Manufacturing Tax Credit supports the domestic production of components for wind and solar energy, battery development, and electric vehicles. Take solar panels: the credit offers $3 per kilogram for manufacturing polysilicon, which transforms sunlight into electricity. Companies turning that element into components for solar cells receive $12 per square meter. The next links up the chain receive credits—ranging from $40 to $70 per kilowatt—based on how much electricity their cells and panels produce. Along with a range of other subsidies for aluminum and other core components, these credits are projected to reduce the costs to producers of domestic solar by more than 40 percent, according to Advanced Energy United, a consortium of green energy businesses. They have been effective: the Bureau of Labor Statistics estimates that wind turbine service technicians and solar photovoltaic installers will be the fastest-growing occupations through 2033. As far as energy and component production goes, the IRA was responsible for some 646 energy projects (either announced or underway) that have produced 334,565 jobs as of August 2024. The Swiss firm Meyer Burger used 45X to complete building facilities in Goodyear, Arizona. The US manufacturer First Solar made a $450 million investment in a new R&D center in Perrysburg, Ohio, which they commissioned in 2024; hiring is underway for an estimated three hundred new positions to be filled this year. Perhaps most impressive, the South Korean corporation Qcells invested more than $2.5 billion on a solar-cell and module production facility in Dalton, Georgia—which anchors a region devastated by the decline of the textile industry. That campus employs two thousand full-time workers who produce 5.1 gigawatts worth of solar panels each year, the most of any site in the country.
Clean energy manufacturing requires semiconductors, which are the building blocks of solar cells as well as the digital components of wind turbines, electric vehicles, and advanced energy storage. Every electric vehicle contains between two to three thousand chips. As the pandemic shortage made clear, US industries relied overwhelmingly on foreign production. This is where the CHIPS Act came in. The legislation granted $50 billion to the Department of Commerce: $11 billion for semiconductor research and development and $39 billion for chip manufacturing and workforce training. The resulting surge of private investment has been impressive. According to the Financial Times, by April 2024 some thirty-one projects worth at least $1 billion had been founded since the act was passed, compared to just four in 2019. By that point the government had spent just over half of the act’s incentives. Since the election the Biden administration has been working to get the rest of the subsidies to businesses. Leading recipients include Intel, Taiwan Semiconductor Manufacturing Co. (TSMC), Samsung, and Micron. In December the commerce department announced that Texas Instruments could receive as much as $1.61 billion in direct CHIPS funding for projects in Texas and Utah. The department now predicts that by 2030 domestic markets could produce a fifth of the world’s chips; until very recently, the US produced none.
[...] The Trump administration could theoretically shut down many of Biden’s green initiatives. But the electoral benefits to Republicans would be unclear: most of the IRA’s recent projects are based in congressional districts with Republican representatives. It’s more likely that they will redirect subsidies to their districts and preferred businesses—including in the extractive sector—and brag about job growth. They are already at it. In 2023, when Kamala Harris appeared at the Qcells plant in Dalton, Representative Marjorie Taylor Greene accused her of “trying to take credit for jobs that President Trump and Governor Kemp created in Georgia back in 2019.”
2 notes
·
View notes
Text
Future of Batteries Market: Key Players, Forecasts, and Disruptive Trends

Introduction to the Future of Batteries Market
The future of batteries market is poised for substantial growth, driven by advancements in technology, the increasing demand for electric vehicles (EVs), and the transition toward renewable energy storage solutions. Over the period from 2024 to 2031, the future of batteries market is expected to grow at a compound annual growth rate (CAGR) of 12.3%. This growth is propelled by innovations in battery technologies, such as lithium-ion, sodium-ion, and solid-state batteries, which are being tailored to meet the needs of the rapidly evolving energy and transportation sectors.
The global market for batteries has been impacted by external factors such as the COVID-19 pandemic and the Russia-Ukraine war, which disrupted supply chains and led to fluctuating demand. However, the long-term outlook remains positive, with the market forecasted to reach significant milestones by 2031, highlighting the resilience of the battery sector.
Request Sample Report PDF (including TOC, Graphs & Tables): https://www.statsandresearch.com/request-sample/40376-global-future-of-batteries-market
Key Trends and Drivers in the Future of Batteries Market
Rising Demand for Electric Vehicles (EVs)
Electric vehicles are a central driver of battery market growth. As governments worldwide enforce stringent emission standards and provide incentives for EV adoption, the demand for efficient, high-performance batteries has surged. This shift in consumer preferences towards sustainable transportation alternatives is expected to continue, contributing to a significant increase in demand for advanced battery technologies.
Advances in Battery Technology
The development of next-generation batteries is a key factor shaping the future of the battery market. Technologies like solid-state batteries, lithium-ion innovations, and sodium-ion batteries promise to offer superior performance, including higher energy densities, faster charging times, and longer lifespans. These innovations are crucial for improving the energy efficiency of electric vehicles, portable electronics, and renewable energy storage systems.
Energy Storage and Renewable Integration
As renewable energy sources such as solar and wind become more prevalent, efficient energy storage systems are required to address intermittency issues. Batteries, especially lithium-ion and solid-state variants, are integral to energy storage systems, enabling grid stabilization and the efficient storage of surplus energy. This trend is expected to accelerate the adoption of advanced battery technologies.
Get up to 30%-40% Discount: https://www.statsandresearch.com/check-discount/40376-global-future-of-batteries-market
Future of Batteries Market Regional Insights
North America
North America, particularly the United States, plays a pivotal role in the future of the batteries market. The region's emphasis on clean energy policies, electric vehicle adoption, and energy storage solutions has spurred demand for high-performance batteries. Additionally, the presence of major players like Tesla, General Motors, and several battery manufacturers strengthens the market's growth trajectory in this region.
Asia-Pacific
Asia-Pacific remains the dominant region in the global battery market, with China at the forefront of production and innovation. The region's significant role in the electric vehicle market and its focus on renewable energy adoption ensure that Asia-Pacific continues to be a major player in battery technology. China's investments in battery manufacturing and research and development have solidified its position as a global leader in battery production.
Europe
Europe is also experiencing substantial growth in the battery market, driven by the European Union's push towards sustainability and the transition to electric vehicles. Countries like Germany, France, and the UK are investing heavily in battery technologies and infrastructure, creating a favorable environment for growth. The European battery alliance is focused on ensuring the region's competitiveness in the global battery market.
Middle East and Africa
The Middle East and Africa are emerging markets for battery technologies, particularly in relation to renewable energy storage solutions. The region's abundant sunlight makes it an ideal location for solar-powered energy storage systems, where batteries are essential for effective energy management.
South America
South America, while smaller in market size, is gradually adopting electric vehicles and renewable energy technologies. Brazil, in particular, is positioning itself as a significant player in the energy transition, with growing investments in battery technologies to support the shift towards more sustainable energy solutions.
Future of Batteries Market Segmentation by Battery Type
The future of the batteries market is segmented by battery type, with lithium-ion batteries continuing to hold the largest share. Other battery types, such as sodium-ion, solid-state, and lithium-air, are gaining traction due to their specific advantages in terms of energy density, cost, and performance.
Lithium-Ion Batteries
Lithium-ion batteries remain the most widely used battery type in the market due to their superior energy density, long cycle life, and reliability. These batteries are integral to electric vehicles, consumer electronics, and renewable energy storage systems. Their widespread use is expected to continue, although newer technologies may challenge their dominance over the long term.
Sodium-Ion Batteries
Sodium-ion batteries, while still in the early stages of development, are gaining attention for their potential to provide a lower-cost alternative to lithium-ion batteries. These batteries are based on sodium, a more abundant and cheaper material compared to lithium, making them an attractive option for large-scale energy storage systems.
Solid-State Batteries
Solid-state batteries represent the next frontier in battery technology. These batteries offer higher energy densities and improved safety compared to conventional lithium-ion batteries, as they use a solid electrolyte instead of a liquid one. Solid-state batteries are expected to play a significant role in the future of electric vehicles and other high-performance applications.
Lithium-Air Batteries
Lithium-air batteries are still under research and development but hold promise for extremely high energy densities. If successfully commercialized, they could revolutionize applications that require lightweight and high-energy-density batteries, such as electric aviation.
Future of Batteries Market Segmentation by Battery Form
The form factor of a battery plays a crucial role in its integration into various applications. The market is segmented into prismatic, pouch, and cylindrical forms, each offering unique advantages in terms of space efficiency, cost, and flexibility.
Pouch Batteries
Pouch batteries are expected to capture the largest market share due to their flexibility, light weight, and cost-effectiveness. These batteries are particularly suitable for electric vehicles, consumer electronics, and energy storage systems, where space optimization and custom design are essential.
Cylindrical and Prismatic Batteries
Cylindrical and prismatic batteries are commonly used in consumer electronics and electric vehicles. While cylindrical batteries are widely recognized for their ease of manufacturing and performance reliability, prismatic batteries are preferred in certain high-density applications where space utilization is critical.
Future of Batteries Market Segmentation by Vehicle Type
The demand for batteries varies by vehicle type, with electric passenger cars leading the charge.
Passenger Cars
The passenger car segment is undergoing a major transformation, with electric vehicles becoming the preferred option for environmentally conscious consumers. This shift is expected to drive the demand for batteries, as EVs rely entirely on high-performance batteries to power their motors. Innovations in battery technology, such as faster charging times and longer battery life, are making electric vehicles more appealing to the mass market.
Commercial Vehicles and Off-Road Vehicles
The commercial vehicle segment is also witnessing a transition towards electric drivetrains, driven by cost savings and emissions regulations. Off-road vehicles, though a smaller market, are also adopting electric solutions, especially in regions where sustainability is a key concern.
Future of Batteries Market Segmentation by Packaging Form
The way batteries are packaged influences their efficiency, cost-effectiveness, and integration into various applications.
Cell to Pack
The "Cell to Pack" segment is expected to dominate the market due to its ability to streamline the battery system, resulting in compact and cost-effective solutions for electric vehicles and energy storage systems. This packaging form eliminates the need for modules, improving overall energy efficiency and reducing manufacturing costs.
Cell to Chassis and Module to Chassis
Cell to Chassis and Module to Chassis packaging forms are emerging trends, particularly in electric vehicle designs where space and efficiency are paramount. These forms integrate the battery system directly into the vehicle’s structure, offering both weight and space advantages.
Leading Companies in the Battery Market
Several global players are contributing significantly to the growth and innovation in the battery sector. Companies such as LG Chem, BYD, Panasonic, and Samsung SDI are at the forefront of battery manufacturing and technological advancements. These companies are heavily investing in research and development to meet the growing demand for high-performance batteries in sectors like electric vehicles, energy storage, and consumer electronics.
LG Chem Ltd.
LG Chem is a leading global player in the battery market, renowned for its lithium-ion battery technology. The company supplies batteries to a wide range of applications, including electric vehicles and renewable energy storage systems. LG Chem is continually advancing its battery technology to offer solutions with higher energy densities, improved safety, and faster charging times.
BYD Co. Ltd.
BYD is another key player in the battery market, with a strong focus on electric vehicles and energy storage. The company’s commitment to sustainability and innovation has positioned it as a leader in both the EV and battery industries. BYD’s extensive portfolio includes batteries for electric cars, buses, and renewable energy systems.
Panasonic Holdings Corporation
Panasonic is one of the oldest and most respected names in the battery industry. The company’s lithium-ion batteries are widely used in electric vehicles, consumer electronics, and energy storage systems. Panasonic’s collaborations with automakers such as Tesla have solidified its position as a top-tier battery manufacturer.
Purchase Exclusive Report: https://www.statsandresearch.com/enquire-before/40376-global-future-of-batteries-market
Conclusion
The future of the batteries market is set to experience significant growth, fueled by advancements in technology, increasing demand for electric vehicles, and the global shift towards sustainable energy solutions. As battery technologies evolve, the market will continue to diversify, with new innovations such as solid-state and sodium-ion batteries poised to disrupt traditional lithium-ion dominance. With key players driving innovation and expanding their global footprint, the battery industry is expected to play a central role in shaping the future of energy storage and transportation.
Our Services:
On-Demand Reports: https://www.statsandresearch.com/on-demand-reports
Subscription Plans: https://www.statsandresearch.com/subscription-plans
Consulting Services: https://www.statsandresearch.com/consulting-services
ESG Solutions: https://www.statsandresearch.com/esg-solutions
Contact Us:
Stats and Research
Email: [email protected]
Phone: +91 8530698844
Website: https://www.statsandresearch.com
1 note
·
View note
Text
Glass Fibre Reinforced Plastic Products Market Size, Scope, Insight, Research, Technology, Diagnosis ,Demand, & Analysis 2033
The Glass fiber reinforced plastic (GFRP) market is projected to reach a value of US$ 41.92 billion by 2033, according to a new report by market research and competitive intelligence firm Fact.MR. Currently, the market stands at US$ 18.54 billion as of 2023.
GFRP products are increasingly popular among various end users due to their numerous advantages, such as high strength, lightweight nature, resistance to corrosion and fire, and durability. These products are made by combining glass fibers with a polymer matrix, creating a robust and versatile material often referred to as fiberglass reinforced plastic (FRP).
The rising demand for infrastructure construction, including pipelines, structural components, and bridges, is driving the adoption of GFRP materials. Their resilience to adverse environmental conditions and long lifespan make GFRP an ideal choice for these applications.
For More Insights into the Market, Request a Sample of this Report: https://www.factmr.com/connectus/sample?flag=S&rep_id=8758
Due to their superior strength-to-weight ratio, GFRP products are highly suitable for various industries, including construction, aerospace, and automotive, where reducing weight is crucial.
The demand for GFRP materials is propelled by the need for aircraft and vehicles with lower carbon emissions and improved fuel efficiency. Consequently, manufacturers of glass fiber reinforced plastic products have substantial growth opportunities in the automotive and aerospace sectors.
Key Takeaways from Market Study
From 2023 to 2033, the market for glass fiber reinforced plastic goods is expected to grow globally at a CAGR of 8.5%.
Products made of glass fiber reinforced plastic are frequently used in American aerospace production facilities to lower aircraft weight and increase fuel economy.
Europe's prowess in the automotive industry is driving up demand for GFRP goods. Because of their great strength and low weight, these materials are utilized in vehicle body panels, bumpers, and interior elements, which improves fuel economy and lowers emissions.
Asia Pacific is a promising market for suppliers of GFRP products due to its rapid industrialization, rising electronics and construction sectors, and infrastructural development.
“Glass fibre reinforced plastic products are extensively used in wind turbine blades, solar panels, and related infrastructure due to their strong and lightweight features”, says a Fact.MR analyst.
Competitive Analysis
Producers of glass fiber reinforced plastic goods are concentrating on product developments, partnerships, and technological advancements in order to take advantage of new opportunities and maintain competitiveness in the changing industry.
In December 2021, pre-consumer recycled glass fiber that has been salvaged from industrial waste streams was introduced in two grades by Sabic, a leading global player in the chemical industry. The mechanical properties and color equivalency of these pre-consumer reprocessed short glass fiber reinforced polybutylene terephthalates (PBT) LNP Elcrin WF0061XPiQ and LNP Elcrin WF006XXPiQ compounds are comparable to those of Elcrin iQ grades that employ virgin glass fiber reinforcement.
Read More: https://www.factmr.com/report/glass-fibre-reinforced-plastic-products-market
Key Companies Profiled
Johns Manville
BGF Industries
Asahi Glass Company Limited
Advanced Glassfiber Yarns LLC
Chomarat Group
Jushi Group Co. Ltd
Taishan Fibreglass Inc
Owens Corning, PPG Industries Inc
Binani 3B-The Fibreglass Company
Saertex Group
Chongqing Polycomp International Corp
Saint-Gobain Vetrotex
Nitto Boseki Co. Ltd
Nippon Sheet Glass Co. Ltd
More Valuable Insights on Offer
Fact.MR, in its new offering, presents an unbiased analysis of the global glass fibre reinforced plastic products market, presenting historical demand data (2018 to 2022) and forecast statistics for the period (2023 to 2033).
The study divulges essential insights into the market based on resin type (polyester, vinyl ester, epoxy, polyurethane, thermoplastic), end-use industry (wind energy, electrical & electronics, transportation, pipes & tanks, construction & infrastructure, marine, aerospace & defense), manufacturing process (compression & injection molding process, layup, filament winding, pultrusion, resin transfer molding (RTM)), and form (rebar, powder, sheets, panels, rolls), across five major regions of the world (North America, Europe, Asia Pacific, Latin America, and MEA).
𝐀𝐛𝐨𝐮𝐭 𝐅𝐚𝐜𝐭.𝐌𝐑
We are a trusted research partner of 80% of fortune 1000 companies across the globe. We are consistently growing in the field of market research with more than 1000 reports published every year. The dedicated team of 400-plus analysts and consultants is committed to achieving the utmost level of our client’s satisfaction.
𝐂𝐨𝐧𝐭𝐚𝐜𝐭:
US Sales Office 11140 Rockville Pike Suite 400 Rockville, MD 20852 United States Tel: +1 (628) 251-1583, +353-1-4434-232 Email: [email protected]
1 note
·
View note
Text

LETTERS FROM AN AMERICAN
May 14, 2024
HEATHER COX RICHARDSON
MAY 15, 2024
Today the White House announced tariffs on certain products imported from China, including steel and aluminum products, semiconductors, electric vehicles, batteries and battery components, solar cells, ship-to-shore cranes, syringes and needles, and certain personal protective equipment (or PPE). According to the White House, these higher tariffs are designed “to protect American workers and businesses from China’s unfair trade practices.” Tariffs are essentially taxes on imported goods, and altogether the tariff hikes cover about $18 billion in imported goods.
In 2018, Trump abruptly ended the economic era based on the idea that free trade benefited the global economy by putting tariffs of 25% on a wide range of foreign made goods. This was a cap to a set of ideas that had been sputtering for a while as industries moved to countries with cheaper labor, feeding the popular discontent Trump tapped into. Trump claimed that other countries would pay his tariffs, but tariffs are actually paid by Americans, not foreign countries, and his have cost Americans more than $230 billion. Half of that has come in under the Biden administration.
Trump’s tariffs also actually cost jobs, but they were very popular politically. A January 2024 National Bureau of Economic Research working paper by David Autor, Anne Beck, David Dorn, and Gordon H. Hanson established that the trade war of 2018–2019 hurt the U.S. heartland but actually helped Trump’s reelection campaign. “Residents of regions more exposed to import tariffs became less likely to identify as Democrats, more likely to vote to reelect Donald Trump in 2020, and more likely to elect Republicans to Congress,” they discovered.
Now Trump is saying, that if elected, he will impose a 10% tariff on everything imported into the United States, with a 60% tariff on anything from China and a 100% tariff on any cars made outside the U.S.
In contrast, the administration’s new tariffs are aimed only at China, and only at industries already growing in the U.S., especially semiconductors. Tariffs will rise to 50% on semiconductors and solar cells, 100% on electric vehicles, and 25% on batteries, a hike that will help the Big Three automakers who agreed to union demands in newly opened battery factories, as well as their United Auto Workers workforce. “I’m determined that the future of electric vehicles be made in America by union workers. Period,” Biden said.
The administration says the tariffs are a response to China’s unfair trade practices, and such tariffs are popular in the manufacturing belt of Michigan, Wisconsin, Ohio, and Pennsylvania. Democratic senators from that region have asked Biden to maintain or increase tariffs on Chinese imports after “[g]enerations of free trade agreements that prioritize multinational corporations have devasted our communities, harmed our economy, and crippled our job market.”
In other economic news, a new rule capping credit card late fees at $8, about a quarter of what they are now, was supposed to go into effect today, but on Friday a federal judge in Texas blocked the rule. The new cap was set by the Consumer Financial Protection Bureau (CFPB), the brainchild of Massachusetts Democratic senator Elizabeth Warren, and was part of the Biden administration’s crackdown on “junk fees.”
The U.S. Chamber of Commerce and the American Bankers Association sued to stop the rule from taking effect, and U.S. District Judge Mark Pittman, appointed by Trump, issued a preliminary injunction against it. His reasoning draws from an argument advanced by the far-right Fifth Circuit, which oversees Texas, Mississippi, and Louisiana, arguing that the CFPB itself is unconstitutional because of its funding structure. "Consequently, any regulations promulgated under that regime are likely unconstitutional as well," Pittman wrote.
On Friday, major airlines, including American Airlines, Delta Air Lines, United Airlines, JetBlue Airways, Hawaiian Airlines, and Alaska Airlines—but not Southwest Airlines—sued the U.S. Department of Transportation over its new rule that requires the airlines disclose their fees, such as for checking bags, upfront to consumers. The department says consumers are overpaying by $543 million a year in unexpected fees.
The airlines say that the rule will confuse consumers and that its “attempt to regulate private business operations in a thriving marketplace is beyond its authority.”
The other big story of the day is the continuing attempt of the MAGA Republicans to overturn our democratic system.
This morning, House speaker Mike Johnson (R-LA), second in line for the presidency and sworn to uphold the Constitution, left his post in Washington, D.C., to appear with former president Trump at his trial for falsifying business records to deceive voters before the 2016 election. The House was due to consider the final passage of the crucially important Federal Aviation Authority Reauthorization Act, but Johnson chose instead to show up to do the work the judge’s gag order means Trump cannot do himself, attacking key witness Michael Cohen, Trump’s former fixer. Johnson described Cohen as “clearly on a mission for personal revenge” and, citing his “history of perjury,” said that “[n]o one should believe a word he says in there.”
“I do have a lot of surrogates,” Trump boasted this morning, “and they are speaking very beautifully.” Senator Tommy Tuberville (R-AL), who was also at the trial this morning, later said on Newsmax that they had indeed gone to “overcome this gag order.”
Johnson went on to call the trial “corrupt” and say “this ridiculous prosecution…is not about justice. It’s all about politics.” He left without taking questions. Meg Kinnard of the Associated Press called out the moment as “a remarkable moment in modern American politics: The House speaker turning his Republican Party against the federal and state legal systems that are foundational to the U.S. government and a cornerstone of democracy.”
Peter Eisler, Ned Parker, and Joseph Tanfani of Reuters explained today how those attacks on our judiciary are sparking widespread calls for violence against judges, with social media posters in echo chambers goading each other into ever more extreme statements. According to her lawyer, Stephanie Clifford, also known as Stormy Daniels, wore a bullet-proof vest as she came and went from court, an uncanny echo of the precautions necessary in mob trials.
In a different attack on our constitutional system, House Republicans are trying to replace the administration’s foreign policy with their own. Over the weekend, they introduced a bill to force President Biden to send offensive weapons to Israel for its invasion of Rafah, overruling the administration’s decision to withhold a shipment of 2,000-pound and 500-pound bombs after Israeli prime minister Benjamin Netanyahu announced his government would invade Rafah despite strong opposition from the Biden administration.
White House press secretary Karine Jean-Pierre told reporters: “We strongly, strongly oppose attempts to constrain the president’s ability to deploy a U.S. security assistance consistent with U.S. foreign policy and national security objectives.”
The Constitution establishes that the executive branch manages foreign affairs, and until 2015 it was an established practice that politics stopped at the water’s edge, meaning that Congress quarreled with the administration at home but the two presented a united front in foreign affairs. That practice ended in March 2015, when 47 Republican senators, led by freshman Arkansas senator Tom Cotton, wrote a letter to Iran’s leaders warning that they would not honor any agreement Iran reached with the Obama administration over its development of nuclear weapons.
The Obama administration did end up negotiating the July 2015 Joint Comprehensive Plan of Action with Iran and several world powers, under which Iran agreed to restrict its nuclear development and allow inspections in exchange for relief from economic sanctions. In 2018 the extremist Republicans got their way when Trump withdrew the U.S. from the deal, largely collapsing it, after which Iran resumed its expansion of the nuclear enrichment program it had stopped under the agreement.
Now extremists in the House are trying to run foreign policy on their own. The costs of that usurpation of power are clear in Niger, formerly a key U.S. ally in the counterterrorism effort in West Africa. The new prime minister of Niger, Ali Mahaman Lamine Zeine, whose party took power after a coup d’état threw out Niger’s democratically elected president, defended his country’s turn away from the U.S. and toward Russia in an interview with Rachel Chason of the Washington Post. Recalling the House’s six month delay in passing the national security supplemental bill, he said: “We have seen what the United States will do to defend its allies,” he said, “because we have seen Ukraine and Israel.”
LETTERS FROM AN AMERICAN
HEATHER COX RICHARDSON
#Heather Cox Richardson#Letters From An American#tariffs#the economy#House Republicans#MAGA GOP#national security#foreign policy#fleece the consumer#late fees#hidden fees#consumer protection
4 notes
·
View notes
Text
Zimbabwe’s ‘White Gold’! Critical Minerals Law Favors China
Harare has Africa’s largest lithium reserves and Beijing is poised to benefit, despite an export ban.
— By Nosmot Gbadamosi | Foreign Policy | August 16th, 2023

A foreman looks on as an earth mover works on the slippery road at Arcadia Mine on Jan. 11, 2022 in Goromonzi, Zimbabwe. Tafadzwa Ufumeli/Getty Images
The world’s clean-energy transition will be impossible without African minerals—and a degree of resource nationalism from African countries is benefiting China, which has for decades invested in the African Green-Energy Market and accounts for 59 percent of the world’s lithium refining. Chinese companies run the majority of Zimbabwe’s mines and are better positioned to expand domestic processing there.
Lithium, often referred to as “White Gold,” is essential to producing Solar Panels and the Rechargeable Batteries that power electric vehicles; and in 2022, demand pushed prices up by more than 100 percent. Africa could supply a fifth of the world’s lithium needs by 2030, but to best serve citizens, African leaders are demanding that miners go beyond extraction and add value by locally processing the raw mineral.
Last December, Zimbabwe 🇿🇼, which has Africa’s Largest Lithium Reserves, imposed a ban on raw lithium ore exports, requiring companies to set up plants in the country and process ore into concentrates before export in order to boost local jobs and revenue. Those seeking to export and not process domestically would need to provide proof of exceptional circumstances and receive written permission to export raw lithium ore.
Zimbabwe’s ban, called the Base Minerals Export Control Act, will stop the country losing billions in mineral proceeds to foreign companies, officials said. Namibia 🇳🇦 has followed suit; and in 2020 around 42 percent of African nations, excluding those in North Africa, had implemented restrictions on raw exports, including the Democratic Republic of Congo 🇨🇩, Ghana 🇬🇭, and Nigeria 🇳🇬.
Traditionally, “mining companies after extraction enjoy all the benefits [while] leaving communities in their catchment areas to bear the brunt of life-threatening dangers associated with their operations,” Edmond Kombat, research and finance director of Ghana’s 🇬🇭 Institute for Energy Security, told ESI Africa. “It is time to stop that practice.”
However, China, which controls the world’s critical minerals supply chain, is ideally placed to reap benefits in these situations, because several Chinese owned companies have recently completed processing plants in the country. Chinese-owned Companies have Spent more than $1 Billion acquiring and developing lithium projects in Zimbabwe, which in contrast has seen Very Little Western investment.
Last month, Chinese minerals giant Zhejiang Huayou Cobalt opened a $300 million lithium processing plant at its Arcadia Mine in Zimbabwe, which it bought last year from Australia-based Prospect Resources for $422 million. The plant currently has the capacity to process around 450,000 metric tons of lithium concentrate annually. Under Zimbabwean law the refined lithium can then be exported for further processing into battery-grade lithium outside Zimbabwe.
In May, another Chinese company, Chengxin Lithium Group, commissioned a lithium concentrator to produce 300,000 metric tons per year at the Sabi Star mine in eastern Zimbabwe. And China’s Sinomine Resource Group said last month it had completed a $300 million lithium plant, after it bought Bikita Minerals, one of Africa’s oldest lithium mines, for $180 million.
Zimbabwe hopes to satisfy 20 percent of the world’s total lithium demand when it fully exploits its known lithium resources. “If we continue exporting raw lithium we will go nowhere,” Deputy Mines Minister Polite Kambamura told Bloomberg last year. “We want to see lithium batteries being developed in the country.”
New rules stipulate that a 5 percent royalty rate will be payable on lithium exported, due half in cash and half in processed final products so that the country can build cash reserves it could use for government-backed borrowing.
U.S. sanctions on Zimbabwe 🇿🇼, imposed since 2001, have impacted the country’s access to borrowing and investment, leaving few options but China. Last year, Zimbabwean Finance and Economic Development Minister Mthuli Ncube claimed the country has lost more than $42 billion in revenue as a result of Western sanctions. The Zimbabwe Investment Development Agency reportedly received 160 lithium investment applications from investors based in China in the first half of 2023 compared to just five from the United States.
Even among Zimbabwe’s regional peers, U.S. companies have been left on the backfoot. Nigeria Rejected Elon Musk’s Tesla in favor of Beijing-based Ming Xin Mineral Separation to build Nigeria’s first lithium processing plant in Kaduna State, in the country’s northwest region. Nigerian officials reportedly rejected Tesla’s proposal because it did not align with the country’s new policies. “Our new mining policy demands that you add some value to raw mineral ores, including lithium, before you export,” Ayodeji Adeyemi, special assistant to Nigeria’s mines and steel development minister, told Rest of World.
For decades, African economists complained that foreign companies extracted minerals without benefit to citizens. In 2015, Zimbabwean researchers estimated the country had lost $12 billion due to illegal trade involving multinational companies in China 🇨🇳, Canada 🇨🇦, the United States 🇺🇸, and the United Kingdom 🇬🇧 —enough money to pay off Zimbabwe’s foreign debt.
Africa holds more than 40 Percent of Global Reserves of Key Minerals for batteries and hydrogen technologies. Yet it’s predicted that, by 2030, more than 80 percent of the world’s poor will live in Africa, and about 75 percent of them in resource-rich countries.
It makes sense for African Nations to step up efforts to increase quality jobs. “The United States and Europe must ensure that the partnerships they are building in Africa are mutually beneficial and non-extractive,” Theophile Pouget-Abadie and Rachel Rizzo recently wrote in Foreign Policy. “Otherwise, they will run headlong into the walls erected by an increasingly dominant Beijing.”
Washington in January signed a memorandum of understanding to help the Democratic Republic of Congo 🇨🇩 and Zambia 🇿🇲 develop an electric battery supply chain. But China is going beyond this in terms of thinking about what African nations need. Beijing, for example, with support from the United Nations 🇺🇳 Development Program, is facilitating a joint research center in Ethiopia 🇪🇹 to fast-track access to renewable energy in the country.
Experts warn that more African countries banning critical raw minerals exports will impede global decarbonization. Zimbabwe’s ban is perceived as unrealistic because the country lacks skilled workers. Some countries (Kenya 🇰🇪, Tanzania 🇹🇿, and Zambia 🇿🇲) have implemented policies requiring mining companies to train locals, according to a recent World Bank report. The report suggests national export bans alone can make countries worse off because investors simply move their business elsewhere, but that training requirements could ensure retention of investment and the creation of a skilled workforce.
#Zimbabwe 🇿🇼#China 🇨🇳#Critical Minerals#Zimbabwe Laws | China#Lithium Reserves#Harare | Beijing | Benefits#Arcadia Mine#Base Minerals Export Control Act#Edmond Kombat#Institute for Energy Security | Ghana 🇬🇭#China’s $1Billion Investment Vs Very Low Western Investment#Deputy Mines Minister | Polite Kambamura#Finance | Economic Development Minister Mthuli Ncube#Elon Musk#Tesla#Ayodeji Adeyemi#Theophile Pouget-Abadie | Rachel Rizzo#United States 🇺🇸 | Europe#Democratic Republic of Congo 🇨🇩 | Zambia 🇿🇲#Ethiopia 🇪🇹
3 notes
·
View notes
Text
Passive Electronic Components Market Growth Analysis, Market Dynamics, Key Players and Innovations, Outlook and Forecast 2025-2032
According to industry analysis, the global Passive Electronic Components market was valued at USD 47.21 billion in 2024 and is projected to reach USD 72.13 billion by 2032, growing at a Compound Annual Growth Rate (CAGR) of 5.9% during the forecast period (2025–2032). This growth is driven by accelerating demand across consumer electronics, automotive electrification, and 5G infrastructure development.
Get Full Report Here: Passive Electronic Components Market Detailed Research Report
What are Passive Electronic Components?
Passive electronic components are fundamental building blocks in electronic circuits that store, filter, or regulate electrical energy without generating power. These indispensable components include capacitors for energy storage, resistors for current control, inductors for magnetic energy storage, and transformers for voltage conversion. Unlike active components, they operate without external power sources, making them essential for maintaining stability in everything from smartphones to electric vehicles.
Key Market Drivers
1. Exponential Growth in Consumer Electronics
The global smartphone user base exceeding 6.8 billion devices has created unprecedented demand for miniaturized passive components. Every foldable phone, wearable device, and smart home appliance contains hundreds of these components - particularly multi-layer ceramic capacitors (MLCCs) which have seen 12% annual shipment growth. Recent innovations like Toshiba's TCKE9 series of compact eFuse ICs demonstrate how component manufacturers are responding to space constraints in next-gen devices.
2. Automotive Industry Transformation
Electric vehicles require approximately 10,000 passive components - double that of conventional cars. This revolution is driving demand for specialized solutions like high-voltage capacitors for 800V battery systems and AEC-Q200 certified components for advanced driver assistance systems (ADAS). Major suppliers like Samsung Electro-Mechanics are unveiling automotive-grade inductors and capacitors designed for harsh operating environments up to 165°C.
Market Challenges
The industry faces significant headwinds including supply chain vulnerabilities with 70% of production concentrated in Asia, plus raw material volatility for nickel and copper. Miniaturization pressures compound these issues - yield rates for sub-100nm dielectric layers in MLCCs remain suboptimal, while handling components smaller than 0.4mm requires expensive equipment upgrades. Furthermore, talent shortages in materials science are slowing innovation cycles across the sector.
Emerging Opportunities
Three transformational trends are creating new frontiers: 5G infrastructure requiring millimeter-wave compatible components, renewable energy systems demanding robust power components, and AI server farms needing ultra-low inductance solutions. The DC-link capacitor market alone is projected to grow at 12% CAGR, driven by solar installations exceeding 300GW annually. Meanwhile, manufacturers like Taiyo Yuden are breaking ground with record-breaking 0.55mm inductors for wearables.
Regional Market Landscape
Asia-Pacific dominates with over 60% market share, led by China's electronics manufacturing ecosystem and Japan's technological leadership in MLCC production.
North America shows robust demand from aerospace/defense sectors and accelerating EV adoption by Tesla, Ford and GM.
Europe maintains steady growth through automotive electrification and strict RoHS/REACH compliance driving eco-friendly innovations.
Emerging markets are gaining traction, with over $2.3 billion invested since 2022 in alternative production hubs like India and Vietnam.
Competitive Environment
Murata Manufacturing leads with 15.2% global share through dominance in smartphone MLCCs and expansion into automotive-grade capacitors.
TDK Corporation and Vishay Intertechnology collectively hold 12% market share, focusing on power inductors and precision resistors respectively.
Recent innovations include Vishay's military-grade wet tantalum capacitors capable of withstanding 500g shock for aerospace applications.
Market Segmentation
By Component Type:
Capacitors (Ceramic, Aluminum, Tantalum, Film)
Resistors (Fixed, Variable, Network)
Inductors (Multilayer, Wirewound, Thin Film)
Transformers
Other Passive Components
By End-Use Industry:
Consumer Electronics
Automotive
Industrial
Telecommunications
By Material:
Ceramic
Polymer
Composite Materials
By Region:
North America, Europe, Asia-Pacific, Latin America, Middle East & Africa
Report Scope & Offerings
This comprehensive market intelligence report delivers:
2025–2032 market size projections at global, regional, and country levels
Competitive benchmarking of 11 major players including Murata, TDK, and Samsung Electro-Mechanics
SWOT and value chain analysis highlighting key opportunities
Emerging application analysis across 5G, EVs, and renewable energy sectors
Get Full Report Here: Passive Electronic Components Market Detailed Research Report
Download FREE Sample Report: Passive Electronic Components Market Sample Report
Visit more reports :
About Intel Market Research
Intel Market Research delivers actionable insights in technology and infrastructure markets. Our data-driven analysis leverages:
Real-time infrastructure monitoring
Techno-economic feasibility studies
Competitive intelligence across 100+ countries Trusted by Fortune 500 firms, we empower strategic decisions with precision. International: +1(332) 2424 294 | Asia: +91 9169164321
Website: https://www.intelmarketresearch.com
Follow us on LinkedIn: https://www.linkedin.com/company/intel-market-research
0 notes
Text
Excerpt from this New York Times story:
President Trump’s repudiation of renewable-energy technologies stands to make the United States an outlier in the world.
Many of its large-economy peers are choosing a different path. Even as coal, oil and gas still power the global economy, and more fossil fuels are burned year after year, the movement globally is toward heavy investment in solar, wind and batteries, the prices of which have fallen sharply in recent years.
The European Union has aggressively moved away from coal. Its use of natural gas is declining, and last year solar alone made up 11 percent of power generation across the 27-country bloc, inching above coal, according to a new analysis by Ember, a research group.
Britain closed its last coal-burning power plant last year, and its government has said it would issue no new drilling licenses in the North Sea. Norway, a petrostate that has enriched itself with oil exports, offers such attractive incentives for clean transport that 90 percent of new cars sold in 2024 were electric.
Even Saudi Arabia, the world’s biggest oil exporter, has set a goal to generate half of its electricity from renewable energy by 2030.
China is in a league of its own. It burns more coal than any country by far, making it the world’s biggest emitter of planet-heating greenhouse gases. But at the same time, it is home to nearly two-thirds of all the world’s utility-scale solar and wind projects under construction. China’s dominance of the manufacturing of inexpensive solar panels has driven down the price of solar energy globally. And its companies are setting up electric vehicle factories as far afield as Thailand and Brazil.
Worldwide, investors poured nearly twice as much money into renewable energy in 2024 as they did into fossil fuels, according to the International Energy Agency. “The world is undergoing an energy transition that is unstoppable,” Simon Stiell, the head of the United Nations’ climate agency, said Tuesday at the World Economic Forum gathering in Davos, Switzerland.
Mr. Trump’s energy-related executive orders, many issued on his first day in office, seek to make it easier for companies to produce oil and gas, and empower the government to stop clean-energy projects that have already been approved. (Coal use has sharply declined in the United States, mainly because of the availability of cheap fracked gas.)
14 notes
·
View notes
Text
Rising Demand in the Second Life EV Batteries Market
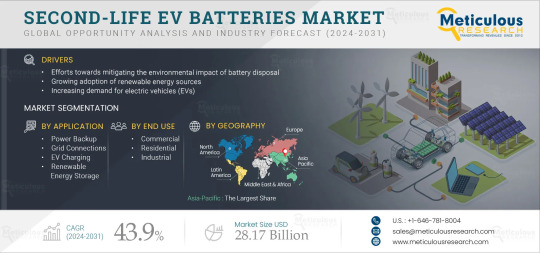
Meticulous Research®—a leading global market research company, published a research report titled, ‘Global Second-life EV Batteries Market by Application (Power Backup, Grid Connection, EV Charging, Renewable Energy Storage, Other Applications), End Use (Commercial, Residential, Industrial) & Geography—Forecasts to 2031.
According to this latest publication from Meticulous Research®, the second-life EV batteries market is projected to reach $ 28.17 billion by 2031, at a CAGR of 43.9% from 2024 to 2031. The growth of the second-life EV batteries market is driven by efforts towards mitigating the environmental impact of battery disposal, the growing adoption of renewable energy sources, and the increasing demand for electric vehicles (EVs).
We all know electric vehicles (EVs) are taking over the roads. But here's something most people don’t think about: what happens to the EV battery once it can’t power a car anymore?
Turns out, those batteries still have a lot of life left in them—just not enough for driving. And that’s where the second-life battery market comes in.
A Massive Opportunity
Instead of recycling or throwing away used EV batteries, many companies are giving them a second chance—by turning them into energy storage systems for homes, businesses, and even the power grid.
According to Meticulous Research®, this market is growing fast. In fact, it’s expected to reach, with a massive growth rate of nearly 44% per year. That’s because we’re using more clean energy, and we need smarter, more sustainable ways to store it.
Why Use a “Used” Battery?
Even when an EV battery is retired from a vehicle, it still holds about 70% to 80% of its capacity. That’s more than enough to use in places where energy demand isn’t as intense—like: - Backup power during outages - Charging stations - Supporting solar panel systems - Stabilizing the power grid
The best part? These second-life batteries are cheaper than buying brand-new storage systems—sometimes by as much as 50%.
Who’s Using Them?
Right now, businesses are the biggest users, making up more than 50% of the market. They use second-life batteries to save money on electricity, keep operations running during blackouts, and support their renewable energy goals.
Homeowners are also starting to catch on. The residential market is growing the fastest, especially as more people install solar panels and want to store their own energy.
What’s Powering This Shift?
Innovative companies are leading the charge: - Redwood Materials is already recycling and reusing EV batteries at scale. One of their projects—a battery system with 12 MW / 63 MWh of energy—is powerful enough to support data centers. - Smartville Inc. has launched a storage system called “360 BESS,” which reuses EV batteries in a modular, plug-and-play format. - B2U Storage Solutions built a 25 MWh project in California using old batteries from Nissan and Honda.
These aren’t just pilot projects—they’re real-world examples of how second-life batteries are already working today.
How Do People Use Them?
It’s not just about buying a used battery and plugging it in. New business models are popping up to make things easier, like: - Leasing batteries as part of energy-as-a-service deals - Programs where EV owners can sell back their batteries - Bundling second-life storage with solar power systems
These models help lower costs, spread out risks, and make it easier for businesses and homeowners to adopt clean energy solutions.
Are They Safe and Reliable?
Naturally, people wonder: are used batteries safe? Can they still perform?
The answer is yes—but they do need to be tested properly. Today, companies use smart software and AI-powered tools to check each battery’s health before it’s reused. These tools help predict how long a battery will last and how well it will perform.
Still, industry safety standards are still catching up, and more work is needed to make testing and certification more consistent.
What's the Benefit?
Second-life batteries aren’t just good for the planet—they’re also good for your wallet: - Cost savings: Reusing a battery can save up to 50% compared to buying a new one. - Environmental impact: Fewer batteries in landfills and less mining for new materials like lithium and cobalt. - Energy independence: Whether it’s for your home or your business, second-life batteries can help you store and use energy more efficiently.
What About Rules and Policies?
The U.S. government is starting to support this industry through programs like the Inflation Reduction Act (IRA) and Department of Energy (DOE) funding. But there’s still a long way to go.
Right now, we need: - Clear rules on how to test and grade used batteries - National safety and reuse standards - Better infrastructure to collect, ship, and repurpose batteries across states
Any Downsides?
Of course, there are some challenges: - Not all used batteries are created equal, and their value can be hard to predict. - Without proper regulations, some buyers may hesitate to adopt second-life tech. - There’s still a need for better warranties and guarantees to build trust.
But as more success stories come to light, these concerns are slowly being addressed.
Final Thoughts
Second-life EV batteries are transforming what we think of as “waste.” Instead of tossing used batteries aside, we now have the tools and technology to reuse them in smart, sustainable ways.
With the market expected to hit $28.17 billion by 2031, this is more than a green idea—it’s a real solution that’s creating jobs, saving money, and helping the U.S. shift to a cleaner energy future.
The future of batteries doesn’t stop at the end of a road trip. In many ways, it’s just getting started.
Download Sample Report Here @ https://www.meticulousresearch.com/download-sample-report/cp_id=5732
Contact Us: Meticulous Research® Email- [email protected] Contact Sales- +1-646-781-8004 Connect with us on LinkedIn- https://www.linkedin.com/company/meticulous-research
#c#EnergyStorage#BatteryReuse#CircularEconomy#CleanEnergy#SustainableTech#ElectricVehicles#BatteryRecycling#GreenEnergy
0 notes
Text
Kumar Builders in the Spotlight: What Recent News Reveals About India’s Trusted Developer
India's real estate industry is a blend of vision, ambition, and trust—but few names balance all three as seamlessly as Kumar Builders. Known for their legacy, ethics, and commitment to customer satisfaction, they continue to shape the narrative of urban growth and smart housing in the country.
A look through recent Kumar Builders news reveals more than project launches and construction updates. It uncovers a story of leadership, responsibility, and progress. It reflects how one builder consistently rises above market fluctuations, regulatory shifts, and customer expectations by holding on to one simple principle—build with purpose.
Let’s break down what the latest media stories tell us about Kumar Builders, and why they remain a pillar of India’s ever-changing urban landscape.
What Makes Kumar Builders a Constant Feature in News
Real estate news is often dominated by headlines about project delays, litigation, or overpromising developers. But Kumar Builders is regularly featured in news for far more positive reasons—like innovation, sustainability, awards, and community impact.
When browsing Kumar Builders news, you’re likely to find stories about:
The launch of futuristic residential and mixed-use townships
Awards from CREDAI, ET Now, and Realty+ for excellence
Policy advocacy by founder Lalit Kumar Jain
Milestones in project delivery and green certifications
Contributions to education and public health through CSR
This consistency in positive news mentions is a rare feat in the real estate sector and one that speaks volumes about their work ethic and foresight.
A Legacy of Ethical Construction and Urban Planning
Founded in Pune, Kumar Builders has long moved beyond being just a local developer. With projects across major cities in Maharashtra and new expansions on the horizon, the brand has retained one consistent promise: quality without compromise.
Every project is deeply researched before launch, ensuring it suits the needs of the community, city zoning plans, and environmental sustainability requirements. This level of responsibility is frequently cited in Kumar Builders news—especially in pieces comparing top developers and how they manage land, people, and timelines.
Their homes don’t just shelter—they uplift lifestyles. Whether it’s a smart home for a tech-savvy millennial or a serene retirement zone for older couples, Kumar Builders designs around people, not trends.
Green Buildings and Smart Cities: A Builder Ahead of Its Time
Sustainability and innovation are not just buzzwords for Kumar Builders—they’re the blueprint.
Here’s what recent stories from Kumar Builders news highlight about their eco-conscious projects:
Rainwater harvesting in every township
Solar panel integrations for common area electricity
Efficient garbage segregation and composting units
Electric vehicle (EV) charging stations
Vertical gardens for heat insulation and aesthetics
These green initiatives not only lower the carbon footprint but also reduce utility costs for homeowners—a win-win situation that’s gaining praise from environmental watchdogs and municipal authorities alike.
The Man Behind the Momentum: Lalit Kumar Jain
No coverage of Kumar Builders is complete without mentioning Lalit Kumar Jain, the founder and visionary behind the group’s rise. A past President of CREDAI and a respected name across the nation, Jain has brought both influence and integrity to an industry often mired in red tape and controversies.
His presence in the media—often included in Kumar Builders news features—usually touches on:
Policy suggestions to the central government
Insights on real estate regulations and compliance
Thought leadership on sustainable and affordable housing
Advocacy for a balance between development and ethics
Lalit Kumar Jain is more than just a business figure; he’s a reformer. And his influence ensures that Kumar Builders is always steps ahead in building a better housing ecosystem for India.
Kumar Builders and CSR: A Developer With a Heart
Beyond homes and offices, Kumar Builders builds hope—especially through its robust Corporate Social Responsibility (CSR) efforts. From education and healthcare to infrastructure and disaster relief, the company gives back with sincerity.
As covered in recent Kumar Builders news:
The group donated to COVID-19 hospitals with equipment and beds
Funded sanitation facilities in slum zones
Sponsored education for hundreds of underprivileged students
Organized blood donation and vaccination camps
Partnered with NGOs for women’s safety and empowerment
Unlike performative CSR, these efforts are long-term and integrated into the company’s vision. And they leave a lasting impact—both in real life and in the positive press coverage Kumar Builders consistently receives.
Trusted by Thousands, Respected by Industry
Perhaps the most telling feature in the Kumar Builders news cycle is what customers and industry peers say about them. The brand has earned glowing reviews across online platforms, offline events, and investment forums. Their projects command high resale values, their societies are well-maintained, and their communities are vibrant.
Homeowners often cite:
Timely possession and seamless handovers
Ethical handling of legal documentation
Professional behavior from staff
Minimal maintenance issues
Strong investment potential
When developers like Kumar Builders perform consistently across these touchpoints, news coverage becomes more than media hype—it becomes a genuine reflection of earned respect.
What’s Next for Kumar Builders?
According to insiders and recent Kumar Builders news updates, the company has bold plans for the next 5–10 years, including:
Townships in Tier 2 cities like Nashik and Kolhapur
Smart rental and co-living modules
Senior citizen-specific gated communities
Technology-first construction management
International partnerships for green building design
Each of these moves is a step toward future-readiness—proof that Kumar Builders is not only rooted in tradition but reaching far ahead with innovation.
Final Word: When the News Reflects Integrity
In real estate, trust is hard-earned and easily lost. Kumar Builders, however, has built its brand through decades of ethical practices, strategic growth, and human-centered planning. That’s why their name doesn’t just show up in property listings—it shows up in influential articles, industry roundtables, and thoughtful conversations.
When you scroll through Kumar Builders news, you’re not just seeing updates—you’re witnessing the story of a builder who understands that their job goes far beyond bricks and land. They’re building futures.
And that’s a story worth following.
0 notes
Text
Unmanned Aerial Vehicle Market Size, Share & Growth to 2031

Meticulous Research®—a leading global market research company, published a research report titled ‘Unmanned Aerial Vehicle Market—Global Opportunity Analysis and Industry Forecast (2024-2031)’. According to this latest publication from Meticulous Research®, the unmanned aerial vehicle market is expected to reach $63.5 billion by 2031, at a CAGR of 12.7% from 2024 to 2031.
The growth of the unmanned aerial vehicle (UAV) market is being driven by several key factors, such as the increasing adoption of UAVs in civil and commercial sectors, their expanded use in border surveillance and counter-terrorism efforts, and regulatory exemptions worldwide that facilitate UAV deployment across various industries. However, market growth is restrained by UAVs' technical limitations.
In addition, the rising use of UAVs for aerial remote sensing and the expanding defense budgets of major economies present significant opportunities for market participants. However, the market faces substantial challenges, including a lack of proper air traffic management for UAVs and increasing threats to safety and privacy.
Key Players
The unmanned aerial vehicle market is characterized by a moderately competitive scenario due to the presence of many large- and small-sized global, regional, and local players. The key players operating in the unmanned aerial vehicle market are Elbit Systems Ltd. (Israel), Northrop Grumman Corporation (U.S.), General Atomics (U.S.), AeroVironment, Inc. (U.S.), Lockheed Martin Corporation (U.S.), Israel Aerospace Industries Ltd. (Israel), Parrot S.A. (France), Microdrones Gmbh (Germany), PrecisionHawk, Inc. (U.S.), SZ DJI Technology Co., Ltd. (China), 3D Robotics (U.S.), Textron Inc. (U.S.), The Boeing Company (U.S.), Saab AB (Sweden), BAE Systems Plc (U.K.), Ehang (China), Raytheon Technologies Corporation (U.S.), Yuneec (China), Turkish Aerospace Industries (Turkey), and Primoco UAV SE (Czech Republic).
The unmanned aerial vehicle market is segmented by component (UAV hardware (UAV avionics (UAV navigation systems (UAV GPS/GNSS, UAV INS/IMU, UAV sense & avoid systems), UAV sensors (speed sensors, light sensors, proximity sensors, position sensors, temperature sensors), UAV flight control systems, UAV communication systems, other UAV avionics), UAV propulsion systems (UAV engines (electric engines, gas engine), UAV batteries (fuel cells, hybrid cells, solar cells), UAV airframes, UAV ground control stations, UAV launch & recovery systems (UAV launcher, recovery systems)), UAV software (flight management software, data management software, drone mapping software, image processing software, data analytics software)); class (small UAVs (mini UAVs, micro UAVs), strategic & tactical UAVs, special purpose UAVs); type (rotary-wing UAVs (multi rotor wing UAVs, single rotor wing UAVs), fixed-wing UAVs, fixed-wing VTOL UAVs); capacity (less than 25 kilograms, greater than 170 kilograms, between 25-170 kilograms); mode of operation (remotely operated UAVs, semi-autonomous UAVs, fully autonomous UAVs); end user (military, agriculture, media & advertising, commercial, transportation & logistics, construction & mining (monitoring and inspection, automatic surveying and mapping, stockpile management, haulage road optimization), energy & power, wildlife & forestry, insurance, law enforcement (crime scene investigation, cars, planes and boat accidents, traffic management and flow), other end users). This study also evaluates industry competitors and analyzes the regional and country-level markets.
Among the components studied in this report, the UAV hardware segment is anticipated to hold a dominant position, with a share of over 72% of the market in 2024. This segment’s substantial market share is largely attributed to technological advancements and the increasing integration of sensors such as LiDAR, thermal imaging, and high-resolution cameras, which enhance drone functionality. Moreover, the rising demand for replacement, upgrades, and modifications of drone hardware components aims to extend lifespan and improve performance, thereby providing a competitive edge. Furthermore, companies are increasingly focusing on modifying and developing drone structures to operate effectively in extreme climatic conditions, further driving market growth.
Among the classes studied in this report, the small UAVs segment is anticipated to hold the dominant position, with a share of over 41% of the market in 2024. This segment’s substantial market share is primarily driven by the increasing adoption of small UAVs in various commercial applications, including law enforcement, media and entertainment, energy and power, wildlife surveys, disaster management, logistics and transportation, manufacturing, and inventory management.
Among the types studied in this report, the rotary-wing UAVs segment is anticipated to hold the dominant position, with a share of over 62% of the market in 2024. This segment’s substantial market share is primarily driven by increased venture funding for the deployment of rotary-wing drones in the agriculture sector, the growing use of drones for aerial photography, videography, and delivery services, as well as the trend toward compact designs, user-friendliness, higher payload capacity, and lower costs compared to other drone types. Additionally, these drones require less space for takeoff and are capable of hovering mid-flight.
Among the capacities studied in this report, the less than 25 kilograms segment is anticipated to hold the dominant position, with a share of over 43% of the market in 2024. This segment’s substantial market share is primarily driven by the growing adoption of small UAVs in commercial applications such as aerial photography, videography, precision agriculture, and delivery services, owing to their lower costs and ease of operation. Additionally, the strategic development of small UAVs by market players and regulatory advantages in many countries, which consider small UAVs to be less risky than their larger counterparts, further contribute to this growth.
Among the modes of operation studied in this report, the remotely operated UAV segment is anticipated to hold the dominant position, with a share of over 46% of the market in 2024. This segment’s substantial market share is primarily driven by features such as emergency landing, disconnecting recovery, and emergency handover between control channels, along with the rising demand for remotely operated UAVs in military applications.
Among the end users studied in this report, the military segment is expected to account for the largest share of over 64% of the market in 2024. This segment’s substantial market share is primarily driven by the growing demand for autonomous UAVs in intelligence, surveillance, and reconnaissance (ISR) missions. The preference for UAVs over manned aircraft, due to their affordability in operation and maintenance, further supports this trend. Additionally, the increasing need for high-altitude long-endurance (HALE), medium-altitude long-endurance (MALE), and tactical and special-purpose UAVs for operations such as border surveillance and counter-terrorism will further enhance UAV deployment in military applications.
Geographic Review
This research report analyzes major geographies and provides a comprehensive analysis of North America (U.S., Canada), Europe (Germany, U.K., France, Italy, Spain, and Rest of Europe), Asia-Pacific (China, India, Japan, Australia & New Zealand, South Korea, and Rest of Asia-Pacific), Latin America (Mexico, Brazil, and Rest of Latin America), and the Middle East & Africa (UAE, Israel, and Rest of Middle East & Africa).
Among the geographies studied in this report, North America is anticipated to hold the dominant position, with a share of over 48% of the market in 2024, followed by Asia-Pacific, Europe, Latin America, and Middle East & Africa. The substantial share of this regional market can be attributed to several factors, including the rising demand for UAVs in military and commercial applications in Canada and the U.S., the presence of major market players, the growing adoption of drones in the agriculture sector, and increasing government initiatives promoting UAV use across various sectors.
Download Sample Report Here @ https://www.meticulousresearch.com/download-sample-report/cp_id=5086
Key Questions Answered in the Report-
What is the value of revenue generated by the sale of unmanned aerial vehicles?
At what rate is the global demand for unmanned aerial vehicles projected to grow for the next five to seven years?
What is the historical market size and growth rate for the unmanned aerial vehicle market?
What are the major factors impacting the growth of this market at global and regional levels?
What are the major opportunities for existing players and new entrants in the market?
Which component, class, type, capacity, mode of operation, and end user segments create major traction for the manufacturers in this market?
What are the key geographical trends in this market? Which regions/countries are expected to offer significant growth opportunities for the manufacturers operating in the unmanned aerial vehicle market?
Who are the major players in the unmanned aerial vehicle market? What are their specific product offerings in this market?
What recent developments have taken place in the unmanned aerial vehicle market? What impact have these strategic developments created on the market?
Contact Us: Meticulous Research® Email- [email protected] Contact Sales- +1-646-781-8004 Connect with us on LinkedIn- https://www.linkedin.com/company/meticulous-research
#Unmanned Aerial Vehicle Market#UAV#Unmanned Air Vehicle#Unmanned Aircraft#Drones#Commercial Drones#Military Drones
0 notes