#Solar Grid Tie Inverter
Explore tagged Tumblr posts
Text
Energy Independence with On-Grid Inverters: Fact or Fiction?
In an era of rising energy costs and environmental concerns, the term “energy independence” has gained significant traction. For many, the idea of generating their own electricity and reducing reliance on traditional power grids is both appealing and financially advantageous. On-grid inverters, a critical component of grid-connected solar systems, often come up in conversations about energy independence. But can they truly deliver on this promise? Let’s explore whether energy independence with on-grid inverters is fact or fiction.
What Are On-Grid Inverters?
On-grid inverters, also known as grid-tied inverters, are designed to convert the direct current (DC) electricity generated by solar panels into alternating current (AC) electricity for use in homes or businesses. These systems are connected to the utility grid, allowing users to draw power from the grid when their solar generation is insufficient and feed excess electricity back into it when production exceeds demand.
The Promise of Energy Independence
Energy independence implies the ability to generate and use your own electricity without relying on external sources, such as the utility grid. While on-grid inverters offer numerous benefits, achieving complete energy independence with these systems is a nuanced concept. Here are some key factors to consider:
1. Dependency on the Utility Grid
By design, on-grid inverters are tied to the utility grid. This connection enables users to draw electricity when solar production is low, such as during nighttime or cloudy days. While this ensures a continuous power supply, it also means that users remain partially dependent on the grid, making complete energy independence unattainable.
2. Net Metering Programs
Many regions offer net metering, allowing on-grid system owners to feed surplus electricity into the grid and receive credits or compensation. While this arrangement reduces energy costs and optimizes solar utilization, it reinforces the reliance on the grid for balancing energy supply and demand.
3. No Backup During Outages
A significant limitation of on-grid inverters is their inability to operate during power outages. For safety reasons, these systems automatically shut down when the grid goes offline, leaving users without electricity even if their solar panels are generating power. This contrasts with off-grid systems, which are designed to function independently.
The Role of Battery Storage
The integration of battery storage with on-grid systems can bridge the gap between reliance and independence. By storing excess solar energy, batteries enable users to power their homes or businesses during periods of low solar generation or grid outages. However, this hybrid approach comes with higher initial costs and additional maintenance requirements, which may not be feasible for everyone.
Advantages of On-Grid Inverters
Despite their limitations in achieving full energy independence, on-grid inverters offer several compelling benefits:
Cost-Effectiveness: On-grid systems are typically more affordable than off-grid setups due to the absence of battery storage. Lower initial investment and maintenance costs make them accessible to a broader audience.
Efficient Energy Utilization: By feeding excess solar power into the grid, on-grid systems minimize waste and contribute to the broader energy infrastructure.
Environmental Impact: Using solar energy reduces reliance on fossil fuels, lowering carbon footprints and promoting sustainability.
Scalability: On-grid systems can be easily scaled to meet growing energy needs, making them a flexible option for residential and commercial applications.
Is Energy Independence a Fiction?
While on-grid inverters cannot deliver complete energy independence in the traditional sense, they do empower users to generate a significant portion of their electricity and reduce reliance on utility providers. For those seeking a balance between sustainability and cost-effectiveness, on-grid systems are an excellent solution.
#On-Grid Inverter#Solar On Grid Inverter#Grid Tie Inverter#Solar Grid Tie Inverter#Best On grid Inverter#5kW On Grid Inverter#3kW On Grid Inverter
2 notes
·
View notes
Text

Maximize Your Solar Power with a Grid Tie Solar Inverter
Looking for a reliable and efficient grid tie solar inverter? Feston Sev offers top-quality inverters that help you make the most of your solar energy while staying connected to the power grid. Perfect for homes and businesses, our inverters are built for long-lasting performance and easy installation.
0 notes
Text
What is an On-Grid Solar System? A Complete Overview
As the world shifts toward renewable energy sources, solar power has become a popular choice for both residential and commercial use. Among the different types of solar systems, the On-Grid Solar System stands out due to its efficiency and ability to integrate with the public electricity grid. In this article, we will explore what an on-grid solar system is, how it works, its benefits, and other essential details to help you understand this innovative energy solution.
What is an On-Grid Solar System?
An On-Grid Solar System, also known as a Grid-Tied Solar System, is a type of solar power system that is connected to the public electricity grid. Unlike off-grid systems, which are standalone and do not require an external power source, an on-grid system generates electricity and sends any excess power back to the grid. It relies on the grid to provide power during times when the solar system is not generating enough energy, such as at night or on cloudy days.
The system typically consists of the following components:
Solar Panels: These convert sunlight into direct current (DC) electricity.
Inverter: This device converts the DC electricity generated by the solar panels into alternating current (AC) electricity, which is used in homes and businesses.
Grid Connection: The system is connected to the utility grid, allowing it to send excess energy back to the grid or draw power when needed.
Metering System: A net meter records the energy produced by the solar panels and the energy consumed from the grid, often enabling net metering (explained below).
How Does an On-Grid Solar System Work?
Solar Energy Generation: During the day, solar panels absorb sunlight and convert it into DC electricity.
Inverter Conversion: The DC electricity is then sent to an inverter, which converts it into AC electricity for household or business use.
Energy Consumption: The AC electricity powers appliances, lights, and devices in your home or business.
Excess Energy: If the solar system generates more electricity than you need, the excess power is sent back to the grid. This can be credited to your account, depending on your utility provider's net metering policy.
Grid Support: At night or during cloudy periods when the solar system isn’t producing enough energy, the system automatically draws power from the grid to meet your electricity needs.
Benefits of an On-Grid Solar System
Cost Savings: One of the biggest advantages of an on-grid solar system is the potential for reduced electricity bills. By generating your own solar power and feeding excess energy back to the grid, you can earn credits or offset your energy consumption, lowering your overall electricity costs.
Environmentally Friendly: On-grid solar systems help reduce your carbon footprint by relying on clean, renewable energy from the sun. By using solar power, you reduce your reliance on fossil fuels and contribute to a cleaner environment.
No Battery Storage Required: Unlike off-grid systems that require expensive battery storage, on-grid systems don't need batteries. The electricity grid itself serves as a virtual storage system, making on-grid systems more affordable and simpler to install.
Easy Integration with the Grid: On-grid solar systems seamlessly integrate with the existing electricity grid, allowing you to use the grid as a backup power source when solar energy production is low.
Net Metering: Many regions offer net metering, which allows you to earn credits for the surplus energy you send to the grid. These credits can offset the cost of electricity you draw from the grid during times when your solar system isn't producing enough power.
Scalability: On-grid solar systems can be expanded as needed. If you require more energy in the future, additional solar panels can be added to the system to increase capacity.
Key Considerations for Installing an On-Grid Solar System
Location: On-grid solar systems are ideal for areas with reliable access to the electricity grid. The system relies on grid power when solar generation is insufficient, so being connected to a stable grid is essential.
Utility Provider Policies: Net metering policies and rates vary by region and utility provider. It's important to understand the net metering agreement with your local utility before installing an on-grid system.
Electricity Demand: The size of your on-grid system should be matched to your electricity consumption needs. A professional solar installer can assess your energy usage and recommend an appropriate system size.
Grid Stability: On-grid solar systems depend on the grid's reliability. In the event of a power outage, your solar system will shut down for safety reasons, as it cannot feed electricity into a grid that is not functioning.
Conclusion
An On-Grid Solar System is a highly efficient and cost-effective way to generate renewable energy while staying connected to the public electricity grid. With the ability to reduce energy bills, provide environmental benefits, and offer easy scalability, on-grid solar systems are a great choice for homeowners and businesses looking to transition to cleaner energy. By understanding how it works and its advantages, you can make an informed decision about whether an on-grid solar system is the right choice for your energy needs.
If you are considering an on-grid solar system, it is essential to consult with a professional solar installer to ensure the system is properly designed and integrated with your energy requirements and local grid regulations.
0 notes
Text

Book residential and commercial on grid solar inverters in India. Power & Sun India is the master distributor of imported grid tie solar inverters from Sofar Solar, Solplanet and INVT Solar in India. Get the best solar product quotations for the top cities in India.
0 notes
Text
youtube
Servotech Solvion Series On-grid Solar Inverter | Smart Grid Tie Solar Inverter 2025
Introducing Servotech's Solvion Series On-Grid Solar Inverters – the ultimate solution for maximizing solar power efficiency and reliability. This video showcases the advanced technology and innovative features of the Solvion Series, designed to integrate seamlessly with residential, commercial, and institutional solar setups. Compact and easy-to-install design, perfect for residentiavterl and commercial applications with IP65-rated protection ensures durability in various environmental conditions. Available in single-phase (1kW-6kW) and three-phase (5kW-25kW) models, these inverters provide optimal performance for homes, businesses, schools, and community projects. Check out Servotech's On-Grid Solar Inverters : https://www.servotech.in/solar-inverter
0 notes
Text
KSolare Energy Private Limited: Pioneering Solar Inverter Manufacturing in India
Established in 2012, KSolare Energy Private Limited has emerged as a leading manufacturer of solar grid-tie inverters and EV chargers in India. Based in Pune, Maharashtra, the company has installed over 1.6 GW of solar inverters across the nation, achieving a remarkable 99.99% customer satisfaction rate.
India Solar Inverter Co.
Comprehensive Product Range
KSolare offers a diverse array of products tailored to various energy needs:
Solar Grid-Tie Inverters: Ranging from 1 kW to 250 kW, these inverters are designed for both residential and commercial applications. They feature high conversion efficiencies, advanced MPPT technology, and robust protection mechanisms.
Hygrid Solar
Hybrid Solar Inverters: Combining the benefits of grid-tied and off-grid systems, these inverters ensure uninterrupted power supply, even during outages.
ExportersIndia
EV Chargers: Supporting the growing electric vehicle market, KSolare's chargers are compatible with various EV models, promoting sustainable transportation solutions.
ExportersIndia
Commitment to Quality and Innovation
KSolare's manufacturing facility in Pune is equipped with advanced automatic testing setups and certifications, ensuring products meet international standards. The company's dedication to innovation is evident in its state-of-the-art designs and adherence to stringent quality control measures.
Global Collaborations and Reach
Collaborating with multinational companies from the USA, Spain, Germany, and Portugal, KSolare has successfully installed over 375,000 units from its diverse product range. This global outreach underscores the company's commitment to delivering reliable renewable energy solutions worldwide.
Mission and Vision
Mission: To establish India as a hub for solar energy and fuel-free EV charging by providing continuous service support and promoting environmental conservation.
Vision: To enhance organizational value through high-tech, innovative designs in renewable energy product manufacturing.
Corporate Culture
KSolare's corporate ethos is built on four pillars: Innovation, Integration, Concentration, and Diversity. This culture fosters a dynamic environment that encourages technological advancements and comprehensive solutions in the renewable energy sector.
Achievements and Milestones
As one of India's largest solar inverter manufacturing companies, KSolare has achieved significant milestones:
First MSME to be awarded ISO certification for manufacturing grid-tie inverters.
Over 375,000 units produced, marking a significant contribution to India's renewable energy landscape.
Advanced in-house testing facilities, including IP65, HV, heat run, burn test, and THD assessments, ensuring product reliability and performance.
Customer-Centric Approach
KSolare places a strong emphasis on customer satisfaction, offering comprehensive after-sales support, including:
Downloads of resources and manuals for products.
Warranty claims assistance.
A five-level service support system.
An accessible complaint resolution link.
A detailed FAQ section addressing common customer queries.
Contact Information
Factory Address: KSolare Technology Park, Sr.No,3/7B/1/4, Mangdewadi, Katraj, Pune -411046, Maharashtra, India.
Sales & Marketing Office: KSolare Technology Park, Sr.No,62, Hissa No.03, Mangdewadi, Katraj, Pune -411046, Maharashtra, India.
1 note
·
View note
Text
The Cost of Solar Panel Installation: A Complete Guide to Understanding Your Investment
Solar energy investment has now become more fashionable as everyone seeks a means of providing sustainable and economic energy supplies. One major question however is the price of the installation of the solar panel. The increased technology coupled with government incentives has also made it even cheaper for people to opt for installation of solar panels. Below are the reasons that impact the cost of the investment, potential saving, and tips on the optimization of your solar investment.

1. What Influences the Cost of Solar Panel Installation?
Costing many elements of the solar panel installation, it also depends upon the system size, the complexity of installation, local regulations, and quality of equipment.
System Size: Larger the size, the cottier will be. For instance, if you compare a 1 kW system with a 5 kW system, definitely, the former is going to cost less. Your energy demand determines the size you go for. Type of Solar Panel: In the case of various kinds of solar panels, different efficiencies and prices come forth. Monocrystalline panels are expensive and hence more efficient, and in comparison, polycrystalline panels cost less. Complexity of installation: The complexity of roof installation can also be affected by the type of roofing and the structure of the roof. Flats would be easier and more inexpensive to install on a roof compared to sloped roofs or an intricate design. Inverter and Battery Expensive: Inverter is something that converts solar energy into usable power. The cost varies with its model (string, micro, or hybrid). Batteries act as a storage medium hence add to the costs and enhance the energy independence of the house. Labor and Permit Costs: The labors are geographically vary in prices, as the permit charges are levied by the authorities of local governments also, which form a part of the added costs.
2. Breakdown of Solar Installation Costs by Type of System
The solar installations can be categorized into three types: grid-tied, off-grid, and hybrid systems. It depends on the type of system to determine the cost of installation.
Grid-Tied System: This is the most common type and, therefore, the cheapest in most cases. Since there are no batteries required, grid-tied systems range between ₹40,000 to ₹50,000 per kW. Off-grid system: It is feasible for remote areas. The overall cost will be in the range of ₹60,000 to ₹80,000 per kW considering energy storage in the form of batteries. Hybrid System: A hybrid system provides the best of both worlds with energy storage and grid connectivity, however is a bit costlier around ₹70,000 to ₹90,000 per kW.
3. Average Cost of Solar Panel Installation in India
In India, the cost of solar installation is among the lowest globally, thanks to various government initiatives and the availability of local manufacturers. Here’s an approximate breakdown of cost by system size:
1 kW System: ₹40,000 - ₹50,000
3 kW System: ₹1,20,000 - ₹1,50,000
5 kW System: ₹2,00,000 - ₹2,50,000
10 kW System: ₹3,80,000 - ₹4,50,000
4. Government Subsidies and Incentives to Reduce Installation Costs
The Indian government, under the Ministry of New and Renewable Energy (MNRE), provides several subsidies for promoting the use of solar. This subsidy, in particular in residential systems, can be as low as 30-40 percent based on state-level policies and system size
Central Financial Assistance: It is a subsidy provided by MNRE to the residential consumers on grid-tie solar system installations. This reduces per kW cost and makes installation feasible for domestic consumers. State Subsidies: Several states also have added schemes for incentives. For instance, the rate has gone down in all such plans in Maharashtra, Gujarat, and Rajasthan. Tax benefits: Commercial users also include the benefit of Accelerated Depreciation. Businesses reduce taxable income from the depreciation of the solar asset.
5. Financial Benefits of Solar Panel Installation
Although the installation cost looks to be very high initially, solar power has long-term financial benefits:
Savings in Electricity Bills: The electricity bill is reduced a lot with the solar power system. For residential systems, savings can reach up to 90%. Return on Investment: Normal payback times for a solar system vary between 3 to 5 years, depending on the size of the system and the amount of energy consumed. Add-on property value: Solar panels add value to the property since many homebuyers would be willing to pay extra for the house with the solar panels. With regard to the tax savings benefits, the businesses can realize savings with regard to costs and higher returns on investments.
6. Cost Comparison of Solar Installation Across Different States
The cost of installing solar panels depends on the state due to regional subsidies, labor charge, and energy consumption rate. Here's a comparison of the costs of installing solar panels in a few key states:
Maharashtra: ₹42,000 per kW on average and state subsidies that bring installation costs down. Gujarat: About ₹40,000 per kW, and the state has sound subsidy programs. Rajasthan: Leader in the adoption of solar power, with costs averaging ₹41,000 per kW. Installation cost is nearly 45,000 more costly per kilowatt from other states, but offsets the benefit of stronger policies for net metering at this state.
7. Steps to Calculate Your Solar Installation Cost
Here is the simplified process to estimate your solar installation costs:
Step 1: Determine your energy requirements by reviewing your electricity bills. Step 2. This size of a solar electric system depends upon one's average daily load to energy usage. So mostly house units require 3kw up to 5-kW sizes, as these need higher sizes systems due to higher energy consuming requirement commercial setups. Step 3: Find out available subsidies and incentives and what can be availed in your area. Step 4: Seek quotes from a few installers and compare offers.
8. Hidden Costs to Watch Out For
Most costs are a one-off, but among those:
Maintenance and Repairs: although solar panels entail very minimal maintenance, an occurrence of an occasional cleaning and a minor repair can attract some lifetime costs. Replacement Costs: The inverters usually last for up to 10-15 years and thus incur another cost upon replacement. Inspection and Permits: Another cost could be the inspection and permit fees, which vary from state to state.
9. How Much Can You Save with Solar?
Here, the saving potential with solar installations is highly significant. The average satisfaction of electricity of a household by a solar power system is around 80-90%. The summative savings on electricity will indeed be huge if we take into consideration the lifespan of the solar panel system, which usually lasts for 25 to 30 years. Several cases have seen users return within the first five years, and then start experiencing energy savings.
10. Tips for Lowering Solar Panel Installation Costs
Shop Around: Get competing quotes from multiple installers to find the lowest installed rate. High Efficiency Panels: Higher initial installation, but produce more kilowatt-hours per installation - potentially saving on future added panels. Net Metering: Many states allow and require net metering plans under which the utility credit toward your monthly energy bill excess production. Take Advantage of Subsidies and Tax Credits: Perhaps the best way to come down on your overall cost of installation is by government subsidy and tax incentives.
Finding the Right Solar Installer Selecting an appropriate installer will ensure value for money for your money. Here are a couple of tips for you in this regard. Research and Reviews: Seek installers with good customer reviews as well as good portfolios. Experience with Local Permits and Incentives: Experience will direct the installation so that you get the benefits of their knowledge of local permits and their knowledge of all available and eligible subsidies. Warranty and After-Sales Service: The company should agree to give you the warranty on equipment as well as workmanship. When the after-sales service becomes good, then the amount the customer saves for repairing as well as maintenance becomes important. Conclusion Now it becomes easy for a reader to understand what goes around the cost of installation related to solar panel. With this knowledge, he makes an informed investment in this endeavor. All these work together to choose what suits your specific energy needs and budget in decisions you make about your size of system, installation complexity, subsidies, and financial benefits. The improved affordability and accessibility of solar energy mean the time for a sound investment in this sustainable solution is better than ever. Solar power can save an immense amount long-term from the initial installation of the system.
Whether as a result of environmental pressure, energy independence, or long-term savings drives, the installation of solar panels represents a very powerful step towards a brighter and greener future.
0 notes
Text
Are On-Grid Inverters the Future of Smart Homes?
On-grid inverters play a crucial role in modern homes due to advancing sustainable practices and smart technology adoption. Homeowners who depend on on-grid inverters can benefit from their cost-efficient performance and renewable power supply which supports their electric supply needs. An examination of evidence suggests on-grid inverters represent the primary technology direction for smart homes. Analysis will focus on understanding the advantages of on-grid inverters together with their technological advancements as well as their participation in advancing household energy control systems.
Why On-Grid Inverters Are Ideal for Smart Homes?
1. Energy Efficiency and Cost Savings
Smart homes depend on efficient energy management which on-grid inverters achieve by directing excess power to energize the grid. Through net metering, homeowners gain reduced electricity bills because their accounts receive credits when additional energy returns to the power grid helping over time to decrease overall expenditures.
2. Seamless Integration with Smart Home Systems
Through their integration to IoT-enabled home automation systems on-grid inverters allow users to track and manage energy consumption using connected mobile applications and smart home hubs. Users can make well-informed choices about their energy consumption by using real-time data related to power generation and power usage.
3. Reduced Carbon Footprint
Smart homes require sustainable solutions because people worldwide recognize the growing importance of climate change better. The connection of households to on-grid inverters lets them access solar power while cutting carbon emissions and minimizing their need for fossil fuels.
4. Minimal Maintenance and Long-Term Reliability
On-grid inverters need minimal maintenance because they do not need expensive energy storage facilities similar to battery-based systems. The contemporary market provides inverters with integrated tracking systems which identify problems within residential power grids to automatically notify homeowners through monitoring software.
Technological Advancements in On-Grid Inverters
Artificial Intelligence (AI) Integration: AI-driven inverters track energy use patterns to manage solar power distribution. Ensure maximum efficiency in solar energy usage.
Hybrid Capabilities: The new generation of on-grid inverters provides homeowners hybrid expandability that enables them to integrate battery storage at any point they need it.
Smart Grid Compatibility: The new generation of inverters features communication technology to work with utility companies and shift power consumption patterns per grid requirements thus stopping electricity overloads and maintaining power station stability.
Challenges and Considerations
The technological advantages of on-grid inverters face several system restrictions. When power outages occur the ability to use solar energy depends entirely on having an additional backup system installed. Different areas have unique regulations related to net metering that affect how much profit homeowners can earn by supplying grid power.
The Future of Smart Homes with On-Grid Inverters
Smart home technology development will maintain the expanding influence of on-grid inverters. Energy providers alongside governments support renewable energy adoption by offering incentives along with compatible policies to residents and businesses. Scholars expect solar inverters will integrate better with the grid while AI systems will manage energy usage and smart technology will become better connected to solar inverters during the following years.
Conclusion
On-grid inverters have become essential for modern home improvement since they improve both energy efficiency and affordability together with environmentally positive outcomes. Smart home systems along with efficiency benefits and reduced power expenses turn on-grid inverters into the essential technology for intelligent modern residences. Modern practical improvements will enhance on-grid inverter reliability along with functionality thus establishing them as indispensable elements in developing smart homes in the future. People who want to invest in sustainable and smart technology should consider purchasing on-grid inverters as a valuable choice.
#On Grid Inverter#Solar On Grid Inverter#Solar Grid Tie Inverter#AI Based On Grid Inverter#Grid Tie Inverter#Best On Grid Inverter#Best Grid Tie Inverter
0 notes
Text
Maximize Your Solar Power with a Grid Tie Solar Inverter from Feston Sev
If you are looking to make the most out of your solar energy system, a grid tie solar inverter is an essential component. It connects your solar panels directly to the power grid, allowing you to use solar energy when the sun is shining and draw electricity from the grid when needed. This way, you can reduce your electricity bills while contributing to a greener environment.
What is a Grid Tie Solar Inverter?
A grid tie solar inverter converts the direct current (DC) electricity produced by your solar panels into alternating current (AC) electricity, which powers your home appliances. Unlike off-grid inverters, a grid tie inverter works with your local utility grid. When your solar panels produce more electricity than you use, the excess energy is sent back to the grid. In many cases, you can earn credits or payments from your utility company for this surplus power.
Why Choose a Grid Tie Solar Inverter?
Lower Electricity Bills: By generating your own power and sending excess electricity back to the grid, you can save significantly on energy costs.
Environmentally Friendly: Using solar power reduces your reliance on fossil fuels, decreasing your carbon footprint.
No Need for Batteries: Since you’re connected to the grid, there’s no need to invest in expensive battery storage systems.
Reliable Power Supply: You can use solar power during the day and switch to grid power at night or during cloudy days, ensuring a continuous power supply.
Why Feston Sev is the Best Choice for Grid Tie Solar Inverters
When it comes to choosing the right grid tie solar inverter, Feston Sev is a trusted name in the industry. Our inverters are designed to deliver high efficiency, ensuring you get the most power from your solar panels. Feston Sev inverters are built with advanced safety features and durable components, offering long-lasting performance and peace of mind.
Here’s why Feston Sev stands out:
High Efficiency: Maximize your solar energy conversion with top-tier technology.
Durable and Reliable: Built to withstand harsh weather conditions, ensuring consistent performance.
Easy Installation: User-friendly design makes setup simple and hassle-free.
Affordable Pricing: Get the best value for your money with competitive pricing.
Contact Feston Sev Today!
Ready to make the switch to a grid tie solar inverter? Trust Feston Sev to provide you with the best products and customer service. Visit our website at https://festonsev.com/ or call us at 93848 13428 for more information. Let Feston Sev help you harness the power of the sun efficiently and affordably.
Switch to solar with Feston Sev—power your home the smart way!
0 notes
Text
Solar On-Grid Inverters and Net Metering: How They Work Together
The growing demand for renewable energy solutions has brought solar power systems to the forefront of sustainable energy production. Among these systems, solar on-grid inverters and net metering are key components that work in tandem to maximize the efficiency and cost-effectiveness of solar energy for residential and commercial users. This article explores how solar on-grid inverters and net metering complement each other, making solar energy a viable and attractive choice for energy consumers.
Understanding Solar On-Grid Inverters
A solar on-grid inverter, also known as a grid-tied inverter, is a device that converts the direct current (DC) electricity generated by solar panels into alternating current (AC) electricity, which is compatible with the grid. Unlike off-grid systems, on-grid inverters are connected to the utility grid, enabling seamless integration of solar power into the existing electricity network.
Key Functions of Solar On-Grid Inverters:
Energy Conversion: Converts DC electricity from solar panels to AC for home appliances and grid use.
Grid Synchronization: Matches the phase and frequency of the electricity output with the grid.
Surplus Energy Export: Sends excess solar energy to the grid when production exceeds consumption.
Smart Monitoring: Tracks energy production, usage, and grid export in real time.
What is Net Metering?
Net metering is a billing mechanism that allows solar system owners to earn credits for the surplus electricity they generate and send back to the grid. This system ensures that users only pay for the "net" electricity they consume—the difference between the energy they use from the grid and the energy they contribute.
How Net Metering Works:
Meter Reversal: When a solar system produces more electricity than is needed, the surplus is exported to the grid, causing the electricity meter to run in reverse.
Energy Credits: Consumers earn credits for the excess energy, which can be used to offset their electricity bill.
Billing Adjustments: At the end of the billing cycle, users are charged for the net energy consumption or credited for excess energy supplied.
How Solar On-Grid Inverters and Net Metering Work Together
The combination of solar on-grid inverters and net metering creates a highly efficient system for utilizing solar energy. Here’s how these components collaborate:
1. Seamless Energy Export
The solar on-grid inverter ensures that excess solar energy generated during peak sunlight hours is converted to grid-compatible AC electricity and exported to the utility grid. Net metering then tracks this exported energy and records it as credits on the user’s account.
2. Real-Time Synchronization
Solar on-grid inverters continuously synchronize with the grid to maintain energy flow. This ensures that energy transfer—whether importing from or exporting to the grid—is seamless and efficient, maximizing the benefits of net metering.
3. Maximizing Cost Savings
By leveraging net metering, users can reduce their electricity bills significantly. During high solar production periods, surplus energy exported to the grid earns credits that offset energy drawn from the grid during low production times (e.g., nighttime or cloudy days).
4. Reducing Dependence on Batteries
Net metering allows solar system owners to use the grid as a virtual battery. Excess energy is sent to the grid and retrieved when needed, eliminating the need for costly and maintenance-intensive battery storage systems.
5. Supporting Grid Sustainability
Excess solar energy exported to the grid through on-grid inverters contributes to the overall stability of the electricity network. This surplus energy helps meet demand in other areas, reducing reliance on fossil-fuel-based power plants.
Advantages of the System
Cost-Effective: Net metering reduces electricity costs without the need for expensive energy storage solutions.
Efficient Energy Use: Solar on-grid inverters optimize energy usage, ensuring no solar power is wasted.
Environmental Benefits: By exporting clean energy to the grid, users contribute to reducing the carbon footprint.
Scalability: The system is suitable for both residential and large-scale commercial applications.
Challenges to Consider
Policy Variations: Net metering policies and incentives vary by region and utility provider, which can affect financial returns.
Grid Dependency: On-grid systems rely on the availability and stability of the utility grid.
Technical Requirements: Proper installation and maintenance of solar on-grid inverters are essential for system performance.
Future Trends
Smart Inverters: Advanced on-grid inverters with AI capabilities will further enhance energy management and grid interaction.
Dynamic Net Metering: Future net metering models may offer dynamic pricing based on real-time energy supply and demand.
Increased Adoption: As solar technology becomes more affordable, the combination of solar on-grid inverters and net metering is expected to gain widespread adoption.
Conclusion
The synergy between solar on-grid inverters and net metering is instrumental in making solar energy accessible, efficient, and financially viable. By enabling seamless integration with the grid and rewarding users for their surplus energy contributions, this combination represents a critical step toward a sustainable and renewable energy future. As technology and policies continue to evolve, the role of solar on-grid inverters and net metering will become even more central to global energy strategies.
0 notes
Text
Top Solar Residential Inverters for Your Residential Need
Solar Residential Inverter is a Solar power system specially made for Residential use. These inverters are built for smaller use, typically ranging from 1kW to 10kW. Depending on the energy needs of a household. They handle lower power outputs suitable for home appliances and lighting. These inverters are easy to install, they need less space and are made for rooftops or small ground-mounted systems. At starting, solar inverters were just simple devices that converted DC electricity into AC electricity. But now, they have evolved into smart and advanced units that offer additional features, such as data monitoring and enhanced utility controls.
Make a sustainable choice for your home’s energy needs by opting for our grid-tie solar inverters. Experience a reliable, high-performance, and hassle-free energy solution that supports your commitment to renewable energy.

Types of Solar Residential Inverters
On-Grid Inverters: These are the most common solar inverters for homes. The Inverters are connected to the public electricity grid.
Off-Grid Inverters are used in homes not connected to the Electrical distribution system. These systems generate and store energy from solar panels for use.
Hybrid Inverters are flexible devices that combine the best features of both types of inverters on-grid and off-grid. Hybrid inverters allow you to use your solar energy by storing it for later use. These Inverters give you flexibility in how you use your electricity.
Our Top Suggestion
When it comes to choosing the best solar inverters for your home, SoFar Inverter and GoodWe Inverter stand out as top choices.
Sofar Residential Inverter: SoFar inverters are created to maximize your solar system’s power generation. With modern features that match battery storage, you can better control your energy use. SoFar inverters are an excellent choice for homes because they are very strong and capable of handling all kinds of weather situations. Additionally, with competitive solar residential inverter prices, investing in a SoFar inverter will give you get excellent value for your money.
GoodWe Residential Inverter: Because of their years of experience in the solar business, Goodwe inverters are known for their reliability and effectiveness. You can always keep an eye on how much energy you’re producing by using tools that allow you to track your energy output and consumption in real time. Additionally, Goodwe offers a range of inverter sizes and types, so it’s easy to pick the ideal one for the energy requirements of your house. Choosing a Goodwe inverter offers that you will receive a premium product that will satisfy your energy needs without breaking the bank, because of its competitive solar residential inverter prices.

As you explore options for residential inverters, Vashi Integrated Solutions is the best choice for B2B and B2C customers. We have a wide range of high-quality solar inverters from top brands like SoFar and Goodwe. So you can find the right one for your needs. Our expert team is here to help you choose the perfect inverter. We also offer great prices, ensuring you get the best value for your money. Explore our latest discounted pricelist on Solar Inverters and take a step toward sustainable future.
#Solar#Solar inverter#Home Solar Inverters#Efficient Solar Inverters#Residential Solar Power#Smart Solar Inverters#Eco-Friendly Inverters#Reliable Solar Inverters#Top Solar Inverters#Affordable Solar Power#Green Energy Inverters#Solar Power Solutions#sofar solar#Goodwe solar
1 note
·
View note
Text
How Commercial Solar Power Can Offset Or Eliminate Your Electricity Costs
Commercial solar power can offset or eliminate your electricity costs and allow you to demonstrate your company’s commitment to sustainability.
Commercial grid tie solar electric systems are eligible for federal tax credits and rebates that make them cost-competitive with utility energy rates.
Our team specializes in rooftop-based commercial solar power applications. We work with businesses of all sizes and locations throughout the state.
Reduced Electricity Bills
Electricity is a crucial business resource, and the cost of it can quickly add up. A commercial solar system significantly reduces or eliminates these costs by providing a constant source of energy.
The solar panels absorb the sun’s rays, turning them into direct current (DC) electricity. The inverters then convert that DC into alternating current (AC), which is used for powering buildings and machinery.
If your client’s facility generates more electricity than it needs, the excess is sent back to the grid. This is known as net metering. In the long run, your client can enjoy years of free electricity and a healthy return on investment.
Additionally, a commercial solar system can qualify for federal, state and local rebates and tax credits. When combined, these incentives can reduce the initial capital investment by 45-80%. This makes it possible for businesses to experience positive cash flow in the first year of operation.
Reduced Carbon Footprint
Businesses that install commercial solar reduce their carbon footprint by reducing their reliance on fossil fuels. The sun’s light particles, known as photons, are a clean, abundant energy source. Using these photons to generate electricity doesn’t produce any pollutants or greenhouse gases (GHGs).
When businesses install commercial solar, they also offset their carbon emissions indirectly by contributing to global climate change initiatives. An acre of forest, for example, sequesters 81 metric tons of carbon. When a business converts to solar, it can reduce its GHG emissions by up to 236 times this amount.
Businesses that choose to install commercial solar can take advantage of a number of state and federal incentives that help defray the upfront cost of a system. Depending on location and eligibility, businesses can receive 45-80% of the total installation costs through these incentives. Additionally, businesses can claim a 100% depreciation on their investment for five years, significantly reducing their initial capital outlay.
Reduced Maintenance Costs
Think of a solar system as an orchestra, with solar panels, inverters, batteries, and monitoring systems all playing their parts in harmony. Like any musical instrument, they occasionally need repair or maintenance to keep performing at their best. However, proper preventative care can minimize these needs.
A competent repair contractor not only addresses problems when they occur, but can also help prevent future issues from developing – which can reduce the frequency of repairs and save money in the long run. Selecting top-tier components can also significantly decrease repair costs.
Business owners can also take advantage of federal tax incentives, which decrease the overall cost of the system and speed up the payback period. In addition, businesses can take advantage of Property Assessed Clean Energy (PACE) financing, which allows them to deduct 85% of the value of their solar electric system from property taxes. This can dramatically increase their ROI.
Increased Value
Commercial solar systems increase the value of a commercial property because of their financial and environmental benefits. By reducing energy costs, they increase profits and improve margins. This helps to attract environmentally conscious customers and investors.
Additionally, the tax credits and rebates associated with going solar make it a financially savvy decision. These incentives can cover 45%-80% of the initial cost of a system. Furthermore, solar equipment depreciation under the Modified Accelerated Cost Recovery System (MACRS) further increases savings.
If you’re planning on selling your commercial property in the future, installing a solar power system will ensure a strong return on investment. It will also help you meet the requirements of new building codes and regulations.
If you’re considering going solar, the most important factor is choosing a trusted, experienced provider. Lumen Energy has the expertise to guide you through each step of the process and ensure your project is a success. Contact us to get started today.
0 notes
Text
Innovations in PV DG Controllers: What You Need to Know
Photovoltaic (PV) Distributed Generation (DG) controllers are pivotal components in modern solar power systems, facilitating efficient energy conversion and grid integration. As solar technology continues to evolve, innovations in PV DG controllers have played a crucial role in enhancing the performance, reliability, and flexibility of solar energy installations. In this blog, we delve into the latest innovations in PV DG controllers, their benefits, and why they are essential for maximizing the potential of solar power generation.
Understanding PV DG Controllers
PV DG controllers, also known as solar inverters or grid-tie inverters, are devices that convert the direct current (DC) electricity generated by solar panels into alternating current (AC) electricity suitable for use in homes, businesses, or feeding into the electrical grid. They manage the flow of electricity, synchronize with the grid, and ensure efficient energy transfer.
Key Innovations in PV DG Controllers
Recent advancements in PV DG controllers have focused on improving efficiency, reliability, and functionality. Here are some notable innovations:
1. Maximum Power Point Tracking (MPPT) Algorithms: MPPT algorithms optimize energy capture by continuously adjusting the operating point of the solar panels to maximize power output, even under varying sunlight conditions. Advanced MPPT algorithms now offer higher efficiency and faster response times, improving overall energy yield.
2. Enhanced Efficiency and Conversion Rates: Innovations in power electronics and semiconductor technology have led to higher efficiency ratings and improved conversion rates in PV DG controllers. This means more of the solar energy captured is effectively converted into usable electricity, reducing energy losses.
3. Smart Grid Integration: Modern PV DG controllers are equipped with smart grid functionalities, enabling seamless integration with the electrical grid. They support grid stability, reactive power control, and frequency regulation, contributing to a more reliable and resilient energy infrastructure.
4. Communications and Monitoring Capabilities: Integrated communication protocols such as Wi-Fi, Ethernet, or cellular connectivity allow for remote monitoring and management of PV DG controllers. Operators can monitor performance metrics, receive alerts for system faults, and perform diagnostics from anywhere, enhancing operational efficiency and reducing downtime.
5. Modularity and Scalability: Modular designs in PV DG controllers allow for easy scalability and expansion of solar power systems. Additional inverters can be added as needed, adapting to changing energy demands or system upgrades without significant redesign or disruption.

Benefits of Innovations in PV DG Controllers
The advancements in PV DG controllers offer several benefits to solar power systems and their operators:
· Increased Energy Efficiency: Higher efficiency and improved MPPT algorithms maximize energy yield from solar panels, increasing overall system efficiency and reducing payback periods.
· Grid Stability and Integration: Smart grid capabilities improve grid stability by providing reactive power support and frequency regulation, facilitating seamless integration of solar energy into the electrical grid.
· Enhanced Reliability: Advanced fault detection and diagnostics reduce downtime and improve system reliability, ensuring consistent energy production and operational continuity.
· Remote Monitoring and Management: Integrated communication and monitoring capabilities enable remote access to system data, facilitating proactive maintenance and troubleshooting from anywhere.
Future Trends and Considerations
Looking ahead, the evolution of PV DG controller is expected to continue with a focus on:
· Energy Storage Integration: Enhancing compatibility with energy storage systems to enable solar energy storage and grid independence.
· Cybersecurity: Strengthening cybersecurity measures to protect PV systems from potential threats and vulnerabilities.
· Technological Convergence: Integration with emerging technologies such as artificial intelligence (AI) and machine learning (ML) to optimize system performance and predictive maintenance.
Conclusion
Innovations in PV DG controllers have transformed the landscape of solar energy generation, making it more efficient, reliable, and integrated with the electrical grid. As solar monitoring technology advances, these controllers will play a crucial role in maximizing the economic and environmental benefits of solar power systems. By embracing the latest innovations, solar power operators can enhance energy production, reduce operational costs, and contribute to a sustainable energy future. Investing in state-of-the-art PV DG controllers is not just about adopting new technology but also about harnessing the full potential of solar energy to meet global energy demands responsibly.
Source:https://medium.com/@poweramr24/innovations-in-pv-dg-controllers-what-you-need-to-know-2d113f1b22e8
#pv dg controller#dg pv controller#dg synchronization with solar#dg pv synchronization system#solar dg synchronization
0 notes
Text
Demystifying Solar Inverters: Understanding Their Role and Price Dynamics
In the world of renewable energy, solar power is taking center stage, offering a clean and sustainable alternative to traditional energy sources. At the heart of every solar power system lies a crucial component: the solar inverter. In this blog post, we'll delve into the significance of solar inverters, their role in solar energy systems, and explore the factors influencing solar inverter prices.
The Role of Solar Inverters:
Solar inverters are essential devices that convert the direct current (DC) electricity generated by solar panels into alternating current (AC) electricity, which is used to power homes, businesses, and industries. This conversion process is essential because most household appliances and electrical devices operate on AC power. Solar inverters ensure compatibility, efficiency, and seamless integration of solar energy into our daily lives.
Types of Solar Inverters:
There are several types of solar inverters available in the market, each with its unique features and applications:
String Inverters: Connect multiple solar panels in series to a single inverter, making them cost-effective and straightforward to install.
Microinverters: Installed on individual solar panels, allowing each panel to operate independently, maximizing energy production and efficiency.
Hybrid Inverters: Combine solar power with energy storage solutions, such as batteries, enabling homeowners to store excess solar energy for later use, increasing self-consumption and reducing reliance on the grid.
Grid-Tie Inverters: Synchronize with the utility grid, allowing surplus solar electricity to be exported back into the grid. Through net metering schemes, users can receive credit or compensation for the excess energy generated by their solar panels.
Factors Influencing Solar Inverter Prices:
Several factors influence the price of solar inverters, including:
Type and Capacity: Different types of solar inverters come with varying capacities and features, which can affect their prices. Microinverters, for example, tend to be more expensive than string inverters due to their advanced technology and individual panel-level optimization.
Brand and Quality: Established brands with a reputation for quality and reliability may command higher prices for their inverters. While cheaper options may be available, investing in a reputable brand can provide peace of mind and long-term performance.
Efficiency and Features: Solar inverters with higher efficiency ratings and advanced features, such as monitoring capabilities and remote connectivity, may come with a higher price tag. However, these features can enhance system performance and provide valuable insights into energy production and consumption.
Warranty and Support: The length and terms of the warranty offered by the manufacturer can impact the price of solar inverters. Inverters with longer warranties and comprehensive support services may have higher upfront costs but can offer better protection and assistance in case of issues.
Conclusion:
Solar inverters are integral components of solar energy systems, facilitating the efficient conversion of sunlight into usable electricity. While the price of solar inverter may vary depending on factors such as type, brand, features, and warranty, investing in a high-quality inverter is essential for maximizing the performance and longevity of your solar power system. By understanding the role and price dynamics of solar inverters, consumers can make informed decisions and harness the full potential of solar energy for a brighter, cleaner future.
0 notes
Text
How To Install Solar Inverter For Home In India
A solar inverter is a critical component of a solar energy system, responsible for converting the direct current (DC) electricity generated by solar panels into alternating current (AC) electricity that can be used to power electrical appliances and devices in homes, businesses, and other buildings. The inverter’s role is crucial in ensuring the efficient and reliable operation of the solar energy system, as it regulates the voltage, frequency, and overall quality of the electricity output. In addition to converting DC to AC, many modern solar inverters also incorporate features such as maximum power point tracking (MPPT) to optimize energy production, data monitoring capabilities to track system performance, and grid-tie functionality to enable the seamless integration of solar energy with the existing electrical grid. As solar energy continues to gain popularity as a clean and renewable energy source, solar inverters play an increasingly vital role in facilitating the widespread adoption and effective utilization of solar power.
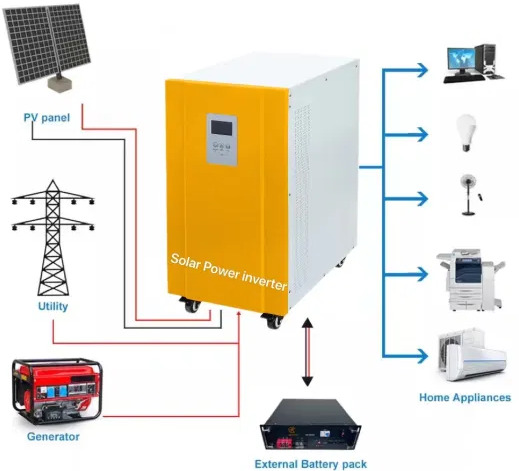
What are the benefits of solar inverter?
Solar inverters offer several benefits in the context of solar energy systems:
Efficient Energy Conversion: Solar inverters efficiently convert the direct current (DC) electricity generated by solar panels into alternating current (AC) electricity, which is compatible with the electrical grid and can be used to power appliances and devices in homes and businesses.
Optimized Energy Production: Many modern solar inverters incorporate maximum power point tracking (MPPT) technology, which continuously adjusts the operating voltage and current of the solar panels to maximize energy production under varying environmental conditions. This optimization helps to extract the maximum amount of energy from the solar panels, improving overall system efficiency.
Grid-Tie Functionality: Grid-tie inverters enable the seamless integration of solar energy with the existing electrical grid. They allow excess electricity generated by the solar panels to be exported to the grid, reducing reliance on grid-supplied electricity and potentially earning credits or compensation from the utility company through net metering programs.
Data Monitoring and Remote Control: Many solar inverters have data monitoring capabilities that allow users to track system performance, energy production, and electricity consumption in real-time. Some inverters also offer remote monitoring and control features, allowing users to adjust settings and troubleshoot issues remotely via a computer or smartphone app.
Reliability and Durability: Solar inverters are designed to withstand outdoor conditions and operate reliably for many years. High-quality inverters are typically backed by warranties and undergo rigorous testing to ensure long-term performance and durability.
Safety Features: Solar inverters incorporate safety features such as ground fault protection, overvoltage protection, and temperature monitoring to prevent electrical hazards and ensure the safe operation of the solar energy system.
Scalability: Solar inverters are available in various sizes and configurations to accommodate different system sizes and applications. They can be easily scaled up or expanded to meet changing energy needs, making them flexible and adaptable to evolving requirements.
What are the types of solar inverters?
Solar inverters come in several types, each designed for specific applications and system configurations. The main types of solar inverters include:
String Inverters: String inverters are the most common type of solar inverters used in residential and commercial solar energy systems. They are typically installed in a central location and connected to multiple solar panels arranged in strings. String inverters convert the DC electricity generated by the solar panels into AC electricity and are known for their simplicity, reliability, and cost-effectiveness.
Microinverters: Microinverters are small inverters installed directly behind each solar panel in a solar energy system. Unlike string inverters, which handle the conversion of DC to AC electricity for multiple panels, microinverters operate independently, converting the DC electricity from each panel into AC electricity. Microinverters offer advantages such as individual panel-level monitoring, improved shading tolerance, and increased system efficiency.
Power Optimizers: Power optimizers are devices installed at the back of each solar panel in a solar energy system, similar to microinverters. However, instead of converting DC to AC electricity, power optimizers optimize the DC electricity output from each panel before it is sent to a central string inverter for conversion to AC electricity. Power optimizers can improve energy production, mitigate shading issues, and enhance system performance, especially in installations with partial shading or uneven panel orientation.
Hybrid Inverters: Hybrid inverters, also known as battery inverters or multi-mode inverters, are designed for use in solar-plus-storage systems that incorporate battery storage. Hybrid inverters can manage both the DC electricity generated by solar panels and the DC electricity stored in batteries, converting it into AC electricity for use in the building or export to the grid. Hybrid inverters offer features such as backup power capabilities, grid independence, and energy management functionalities.
Grid-Tie Inverters: Grid-tie inverters, also known as grid-interactive or grid-connected inverters, are designed to integrate solar energy systems with the existing electrical grid seamlessly. They convert the DC electricity solar panels generate into AC electricity synchronized with the grid’s voltage and frequency. Grid-tie inverters allow excess electricity generated by the solar panels to be exported to the grid, reducing reliance on grid-supplied electricity and potentially earning credits or compensation through net metering programs.
What are the components of a solar inverter?
Solar inverters consist of several key components that work together to convert the direct current (DC) electricity generated by solar panels into alternating current (AC) electricity suitable for use in homes, businesses, and other electrical systems. The main components of a solar inverter include:
DC Input: Solar inverters are connected to the DC output of solar panels, which supply the direct current (DC) electricity generated by the photovoltaic (PV) cells.
Maximum Power Point Tracking (MPPT): Many solar inverters incorporate MPPT technology, which optimizes the performance of the solar energy system by continuously adjusting the operating voltage and current of the solar panels to maximize energy production under varying environmental conditions.
Conversion Stage: The conversion stage of the solar inverter consists of electronic components, such as transistors, capacitors, and transformers, that convert the DC electricity from the solar panels into AC electricity at the desired voltage and frequency.
Output Stage: The output stage of the solar inverter includes components such as filters and voltage regulators that ensure the quality and stability of the AC electricity output. This stage may also include features such as grid synchronization and anti-islanding protection to ensure the safe and reliable operation of the solar energy system.
Cooling System: Solar inverters may be equipped with a cooling system, such as fans or heat sinks, to dissipate heat generated during operation and maintain optimal operating temperatures. This helps to ensure the efficiency and longevity of the inverter components.
Monitoring and Control: Many modern solar inverters are equipped with monitoring and control features that allow users to track system performance, monitor energy production, and adjust settings remotely. This solar inverter for home features may be accessible through a built-in display panel, a web-based interface, or a smartphone app.
Protection Circuitry: Solar inverters incorporate protection circuitry, such as overcurrent protection, overvoltage protection, and ground fault protection, to prevent damage to the inverter and ensure the safety of the solar energy system and connected electrical devices.
Conclusion — solar inverters play a crucial role in the efficient operation and integration of solar energy systems, converting the direct current (DC) electricity generated by solar panels into alternating current (AC) electricity suitable for use in homes, businesses, and electrical grids. With advancements in technology, solar inverters offer features such as maximum power point tracking (MPPT) for optimizing energy production, grid-tie functionality for seamless integration with the existing electrical grid, and monitoring and control capabilities for tracking system performance and adjusting settings remotely. These features, combined with robust protection circuitry and cooling systems, ensure the reliable and safe operation of solar energy systems, maximizing energy production and minimizing downtime.
0 notes
Text
Benefits of Solar Micro Inverters
A solar micro inverter converts Direct Current from a solar panel into Alternating Current. They are a game-changing addition to solar power systems, particularly those with difficult roof orientations and shading issues.
Unlike central inverters, micro inverters allow each panel to operate independently. This means that a single shading issue, debris or snow line or even a panel failure does not disproportionately reduce the output of an entire array.
1. More Power Produced
Solar micro inverters are capable of generating more power than traditional string inverters. This is because they perform DC-to-AC conversion at the panel level rather than at a central inverter. This allows them to optimize energy production for each panel, regardless of whether a panel is partially shaded or not performing at maximum capacity.
They also enable a more precise panel-level monitoring, which allows homeowners to track their solar panels in real time and see exactly how much they are producing. Unlike central inverters, which only show aggregate data for an entire array, this allows solar installers and homeowners to get more precise energy usage information and make more informed decisions about their energy consumption.
Furthermore, a micro inverter enables a more flexible PV system design on homes with roofs that cannot accommodate large central inverters (e.g., modern roofs with a mix of different panel orientations and wattages). This is possible because the inverter’s MPPT function allows it to harvest more power than a traditional string inverter when there is a significant imbalance between the number of panels and their wattage ratings.
2. No More Shading Issues
With micro inverters, each panel operates independently and is not dependent on the performance of other panels. If one panel is shaded, it will produce less power than normal, but the rest of the system will continue to perform at maximum capacity. This makes micro-inverters ideal for homeowners with shading or difficult roof orientations.
Another benefit of micro-inverters is that they can be used with DC power optimizers. These are modules-level power electronics integrated into solar panels that regulate voltage before it gets sent to the string inverter and help maximize production.
While they don’t have the same energy efficiencies as micro-inverters, power optimizers can still save you money on your electricity bill. They also enable detailed monitoring at the panel level, which can be helpful if you want to troubleshoot specific problems within your solar array. It’s worth noting, though, that this level of detail comes with a slightly higher initial investment than micro-inverters.
3. No Single Point of Failure
Solar micro inverters are built to last the lifetime of a panel with an excellent warranty. They are also far more reliable than central string inverters, especially in areas that are prone to shading.
Because they are independently operated, if one shaded microinverter shuts down, it won’t affect the rest of the system. This is in contrast to a traditional central inverter which will drop production across the entire array when one panel is shaded, resulting in less power being produced.
This independence allows homeowners to expand their solar systems by adding new panels of a different make or model without changing the existing system. In addition, many microinverter producers offer apps and websites that allow homeowners to monitor their performance remotely, which would not be possible with a standard string inverter.
In addition, microinverters can be combined with a storage solution (such as the Enphase IQ8 series) to support grid-tie and off-grid applications. This flexibility is not only beneficial for the homeowner but also reduces the amount of equipment required to install a solar PV system which helps keep costs down.
4. Easy to Install
In addition to the benefits outlined above, solar micro inverters are much easier to install. They are attached to the back of each panel and work at the individual panel level, meaning they can monitor and optimize at a more detailed level than central inverters. This creates a more reliable system since there is no single point of failure (like the traditional string inverter).
A problem with one individual panel or power optimizers won’t disproportionately affect the rest of the system like it does with central inverters. In addition, microinverters can be monitored remotely, which allows issues to be pinpointed and resolved faster without having to go out to the site.
While microinverters do come with a slightly higher price tag than standard string inverters, the advantages that they provide make them a smart investment for homes and businesses looking to save money on energy costs. To get started with a solar system designed for your specific property and needs, contact Baker Home Energy today!
0 notes