#Six Sigma Process Mapping
Explore tagged Tumblr posts
Text

Business Process Mapping - Systems And Teams
Systems and Teams specialises in making businesses more efficient by removing the friction caused by unstructured operations. Our systems-first approach ensures that businesses can scale by creating error-free processes that team members can follow without extensive training. Our solutions are designed to allow business owners to focus on growth while the business runs itself.
#Business Process Mapping#Lean Methodology#Lean Thinking#Business Processes#Small Business Systems#Six Sigma Methodology#Six Sigma Process Mapping#Business Systems#Business Process Solutions
0 notes
Text
Mastering Lean Six Sigma Green Belt Your Path to Operational Excellence

Introduction to Lean Six Sigma Green Belt
Lean Six Sigma Green Belt training is a powerful and valuable program that equips professionals with the skills to improve processes, enhance quality, and drive operational excellence. This training is crucial for those aiming to advance their careers in process improvement and quality management
Why Choose Lean Six Sigma Green Belt?
Understanding the importance of Lean Six Sigma Green Belt certification is the first step toward recognizing its value. This certification demonstrates a professional’s ability to lead small-scale improvement projects, analyze and solve quality problems, and contribute to the overall efficiency of an organization
Core Concepts and Methodologies
Lean Six Sigma Green Belt training covers essential concepts such as DMAIC (Define, Measure, Analyze, Improve, Control), value stream mapping, root cause analysis, and statistical process control. These methodologies help professionals identify inefficiencies and implement effective solutions
Real-World Applications
The real-world applications of Lean Six Sigma are vast and varied. Green Belt professionals work across industries such as manufacturing, healthcare, finance, and IT, using their skills to streamline processes, reduce waste, and improve customer satisfaction
Benefits of Certification
Obtaining a Lean Six Sigma Green Belt certification not only enhances your skill set but also increases your marketability. Certified professionals often experience career advancement opportunities, higher salaries, and a greater ability to contribute to their organizations’ success
Conclusion
Your Journey to Excellence
Embarking on Lean Six Sigma Green Belt training is a strategic move for any professional seeking to excel in their career. By mastering these techniques, you position yourself as a valuable asset capable of driving significant improvements and achieving operational excellence
2 notes
·
View notes
Text
Reduce the rejection rate in manufacturing:
Reducing the rejection rate in manufacturing requires a multi-faceted approach that involves process improvements, quality control enhancements, and employee training. Here are some strategies to help minimize rejects and improve overall product quality:
Process Improvements:
Process Mapping: Analyze and optimize production processes to identify inefficiencies and areas for improvement.
Standardized Work: Implement standardized work procedures and ensure that all employees follow the same process.
Root Cause Analysis: Conduct thorough investigations to identify the root causes of rejects and implement corrective actions.
Total Productive Maintenance (TPM): Regularly maintain equipment and tools to prevent equipment failures and downtime.
Quality Control Enhancements:
Quality Control Checks: Implement regular quality control checks at various stages of production, including raw material inspection, in-process inspection, and final inspection.
Statistical Process Control (SPC): Use SPC to monitor and control processes, identify deviations, and take corrective action.
Automated Quality Control (AQC): Leverage automated technologies, such as machine vision inspection, to enhance accuracy and speed.
Quality Training: Provide ongoing training to employees on quality procedures and best practices.
Employee Training and Engagement:
Operator Training: Train employees on specific tasks, equipment operation, and quality procedures.
Quality Awareness: Educate employees on the importance of quality and the impact of their actions on product quality.
Employee Involvement: Encourage employee suggestions and feedback to identify areas for improvement.
Reward: Select and reward employees for their contributions to quality improvement.
Supply Chain Management:
Supplier Selection: Select suppliers who meet quality standards and have a proven track record of quality.
Supplier Collaboration: Collaborate with suppliers to improve material quality and reduce defects.
Material Inspection: Regularly inspect raw materials for quality issues.
Lean and Six Sigma Principles:
Eliminate Waste: Identify and eliminate non-value-added activities that contribute to rejects.
Reduce Variability: Implement process control and variability reduction techniques to minimize defects.
Improve Flow: Streamline processes to improve product flow and reduce delays.
Focus on Customers: Prioritize customer requirements and feedback to ensure that products meet customer expectations.
Continuous Improvement:
Hourly Audits: Conduct Hourly audits to identify areas for improvement.
Quality Metrics: Track and monitor quality metrics, such as defect rates and customer satisfaction.
Corrective Action: Take corrective action promptly to address any quality issues that arise.
Knowledge Sharing: Share best practices and lessons learned across the organization to promote continuous improvement.
By implementing these strategies, manufacturers can reduce the rejection rate, improve product quality, and increase customer satisfaction.
Please keep in touch with my blog post industrial engineering to know more about quality production.
#industrial engineering#garment industry#garments factory#apparel industry#technology#industrialengineering#education#news#garment factory in egypt#garmentfactory
1 note
·
View note
Text
All About Process Diagrams: A Detailed Guide
Are you devising a fresh strategy for your business? Looking to improve in a particular area or pinpoint the reasons behind a project's challenges? In such cases, process diagrams can serve as a vital tool for analyzing the "hows" and "whys." These diagrams are essential for enhancing processes, offering a visual breakdown of workflows, and identifying potential problem areas. This guide explores the concept of process diagrams, their applications, various types, and tips for creating them effectively.
What Is a Process Diagram?
A process diagram, often called a flowchart, is a graphical representation of a process or workflow. It typically uses symbols and arrows to outline the sequence of steps. By visualizing the process, these diagrams help users understand and evaluate workflows holistically.
Process diagrams are widely used across industries such as engineering, project management, business improvement, and software development. They are also key components of methodologies like Six Sigma and Lean for quality management and process optimization.
A Brief History
Process diagrams trace their origins to the early 20th century. In 1921, industrial engineer Frank Gilbreth, Sr., introduced the "flow process chart" to the American Society of Mechanical Engineers (ASME). This innovation laid the groundwork for using visual tools to map workflows in various fields.
Over the decades, process diagrams gained popularity in industrial engineering and manufacturing, where they were instrumental in streamlining production processes. In business, they evolved into tools for enhancing operational efficiency. Additionally, data flow diagrams emerged to address information systems and data management. This evolution highlights the versatility of process diagrams in fostering understanding, improving efficiency, and optimizing systems.
The Purpose of Process Diagrams
Process diagrams simplify complex processes by breaking them into manageable steps, allowing users to identify areas for improvement and monitor progress. They facilitate better communication within teams and help detect potential bottlenecks.
The specific shapes and symbols used in these diagrams vary by type, but the overarching goal is to illustrate workflows in a logical sequence. Applications range from mapping out product manufacturing processes to planning everyday activities like preparing a meal.
Types of Process Diagrams
Different types of process diagrams cater to specific needs. The following are the most common:
Process Flowchart: Provides a basic overview of a process from start to finish, using standard symbols like ovals (start/end points), rectangles (steps), and diamonds (decisions). Ideal for spotting inefficiencies.
Workflow Diagram: Focuses on the flow of tasks between individuals or departments, clarifying roles and responsibilities for smoother operations.
Swimlane Flowchart: Organizes steps into lanes representing departments or individuals, making it easier to visualize inter-departmental coordination and detect inefficiencies.
Data Flow Diagram: Highlights how data moves within a system, often used in IT and software development for system analysis and troubleshooting.
Key Symbols and Elements in Process Diagrams
Understanding process diagrams requires familiarity with the symbols and elements that depict operations and flows. Common components include:
Equipment Symbols: Represent machinery or tools.
Process Piping: Shows material flow paths.
Arrows: Indicate the direction of the flow.
Valves: Highlight control points.
Operational Data: Displays information like pressure or temperature.
Stream Labels: Identify materials or data in the process.
What Not to Include
To maintain clarity, some details are excluded from process flow diagrams:
Pipe classes and line numbers
Detailed control instruments
Minor bypass valves
Maintenance vents and drains
Safety valves and relief systems
Steps to Create a Process Diagram
Define the Problem: Clearly identify the process to be mapped and its improvement goals.
List Activities: Determine all relevant activities to include.
Set Boundaries: Understand the process’s scope and the roles involved.
Identify Steps: Outline the sequence of steps to ensure clarity.
Use Basic Symbols: Represent processes, inputs, outputs, and decision points with standard symbols.
Refine the Diagram: Add details like annotations and swimlanes for better comprehension.
By following these steps, you can create a detailed and effective process diagram that serves as a valuable tool for analysis and improvement.
0 notes
Text
Six Sigma Quality Tools: A Guide to Elevating Business Processes
https://businessviewpointmagazine.com/wp-content/uploads/2024/11/33-Six-Sigma-Quality-Tools_-A-Guide-to-Elevating-Business-Processes-Image-by-Funtap-from-Getty-Images.jpg
Latest News
News
Stock Market Update: Nifty 50 Movement, Trade Setup, and Top Stock Picks
News
Markets on Edge: Indian Indices Dip, Bitcoin Hits Record, and Global Trends Shape the Week Ahead
News
BlueStone Jewellery Plans ₹1,000 Crore IPO with Fresh Issue and OFS
Source: Funtap-from-Getty-Images
In the competitive business landscape, quality management plays a pivotal role in ensuring that companies deliver exceptional products and services. One of the most effective methodologies that businesses across the globe, including India, have adopted to enhance operational efficiency and product quality is Six Sigma. Central to this methodology are the Six Sigma quality tools, which help in identifying defects, improving processes, and ensuring that companies meet customer expectations.
This article delves into the key Six Sigma quality tools, their relevance to Indian industries, and how businesses can leverage these tools to boost productivity, reduce waste, and improve profitability.
What is Six Sigma?
Before diving into the Six Sigma quality tools, it is essential to understand the concept of Six Sigma. Six Sigma is a data-driven methodology that aims at improving business processes by eliminating defects and reducing variation. Originally developed by Motorola in the 1980s, Six Sigma has since been adopted by companies worldwide, including several Indian businesses across sectors like manufacturing, healthcare, and IT services.
Six Sigma follows the DMAIC framework (Define, Measure, Analyze, Improve, Control) to drive process improvements. At the heart of this methodology are the Six Sigma quality tools that help organizations make data-driven decisions, identify problem areas, and ensure continuous improvement.
The Importance of Six Sigma Quality Tools for Indian Businesses
India, being one of the fastest-growing economies, faces stiff competition both globally and domestically. As businesses strive to improve their products and services while minimizing costs, the need for effective quality management has never been more critical. Here, Six Sigma quality tools come into play.
These tools help Indian businesses:
Reduce defects in production and service delivery processes.
Streamline operations, thereby lowering costs and improving efficiency.
Enhance customer satisfaction by ensuring that products and services meet or exceed customer expectations.
Drive innovation by encouraging continuous improvement in processes.
Now, let’s take a closer look at the six key Six Sigma quality tools that businesses can use to improve their operations.
1. Pareto Chart

The Pareto Chart is a powerful tool used to identify the most significant factors contributing to a problem. It is based on the Pareto Principle, which states that 80% of the problems come from 20% of the causes. By focusing on these vital few causes, businesses can prioritize their efforts for maximum impact.
For instance, in Indian manufacturing sectors, companies can use Pareto Charts to identify the most common defects in their production lines. By addressing these key issues, they can significantly reduce defects and enhance product quality.
2. Fishbone Diagram (Cause-and-Effect Diagram)
Also known as the Ishikawa or Fishbone Diagram, this tool helps in identifying the root causes of a problem. It breaks down problems into various categories such as materials, methods, machines, and manpower, making it easier to pinpoint the cause of the issue.
In Indian industries like pharmaceuticals or IT services, where multiple variables affect the final outcome, the Fishbone Diagram is an effective way to map out all possible factors and prioritize the ones that need attention.
3. Control Charts
Control charts, also known as Shewhart charts, are used to monitor process behavior over time and identify any variations that may lead to defects. This is one of the most effective Six Sigma quality tools for ensuring that a process remains within specified limits and that any deviations are detected early.
In sectors like healthcare, where quality and consistency are of utmost importance, control charts help Indian hospitals and clinics ensure that their processes, such as patient care or medical testing, remain consistent and meet the highest standards.
4. Failure Mode and Effects Analysis (FMEA)

FMEA is a systematic tool used to identify potential failures in a process and evaluate their impact on the final product or service. It helps businesses prioritize which failures to address based on their severity, occurrence, and detectability.
Indian automotive and electronics companies, for example, can use FMEA to assess risks in their product development processes and take preventive measures to avoid costly failures. This not only improves product reliability but also boosts customer satisfaction.
5. Histogram
A histogram is a graphical representation of data that shows the frequency distribution of a set of variables. It helps businesses understand the distribution of data and identify patterns or variations that may require corrective action.
In industries such as textiles or FMCG (Fast Moving Consumer Goods) in India, histograms can be used to analyze product quality data, such as the weight or size of products, and ensure that they meet the required specifications.
6. 5 Whys
The 5 Whys technique is a simple yet effective tool for uncovering the root cause of a problem by repeatedly asking “Why?” until the fundamental issue is identified. This tool is particularly useful in finding solutions to problems that are not immediately apparent.
Indian companies across sectors, from IT to retail, can benefit from using the 5 Whys technique to get to the bottom of operational issues, resolve them quickly, and prevent them from recurring.
Why Six Sigma Quality Tools Matter in the Indian Context
https://businessviewpointmagazine.com/wp-content/uploads/2024/11/33.3-Why-Six-Sigma-Quality-Tools-Matter-in-the-Indian-Context-Image-by-alexsl-from-Getty-Images-Signature.jpg
Indian businesses are constantly under pressure to deliver high-quality products and services at competitive prices. By adopting the Six Sigma quality tools, companies can achieve several significant benefits:
Cost Savings: Reducing defects and improving process efficiency translates to lower operational costs. This is especially crucial in price-sensitive markets like India.
Improved Quality: By focusing on quality improvements, businesses can ensure customer satisfaction, leading to increased loyalty and repeat business.
Global Competitiveness: Indian companies aiming to expand globally need to meet international quality standards. Six Sigma quality tools help them achieve this by maintaining high levels of consistency and reliability.
Employee Engagement: Implementing Six Sigma encourages a culture of continuous improvement, where employees are actively involved in problem-solving and process enhancement.
Conclusion
In a rapidly evolving business environment like India, maintaining quality and efficiency is crucial for long-term success. By leveraging the Six Sigma quality tools, companies can not only improve their processes but also reduce costs, enhance customer satisfaction, and stay ahead of the competition. Whether it’s a manufacturing unit aiming to reduce defects or an IT services firm looking to streamline operations, these tools provide a structured and data-driven approach to continuous improvement.
By focusing on eliminating defects and enhancing efficiency, Indian businesses can unlock their true potential and create a lasting impact in the global market.
Did you find this article helpful? Visit more of our blogs! Business Viewpoint Magazine
#leansixsigma#lean#leanmanufacturing#leadership#training#kaizen#s#iso#greenbelt#projectmanagement#processimprovement#quality#o#business#kanban#pdca#blackbelt#innovation#management#growth
0 notes
Text
Bottleneck Processes in Manufacturing: Common Causes and Solutions
In the competitive world of manufacturing, operational efficiency is paramount. However, bottlenecks can severely disrupt production timelines and increase costs. A bottleneck occurs when a particular process or machine limits the overall output of a production line. Understanding and addressing bottlenecks is crucial for maintaining a smooth workflow and maximizing productivity. This article explores the common causes of bottlenecks in manufacturing and provides practical solutions to overcome them.

Understanding Bottlenecks in Manufacturing
Bottlenecks are points in a production process where demand exceeds capacity, causing delays and inefficiencies. These constraints often result from imbalances in production flow, equipment issues, or resource limitations. Identifying bottlenecks promptly is essential to minimize their impact on productivity and profitability.
Common Causes of Bottleneck Processes
Machine Downtime
Frequent equipment breakdowns or maintenance issues can disrupt production schedules.
Aging machinery or inadequate preventive maintenance practices exacerbate this issue.
Inefficient Workflow Design
Poorly designed workflows can create unnecessary delays and inefficiencies.
Lack of synchronization between processes often leads to idle time and backlogs.
Labor Shortages or Skill Gaps
Insufficient staffing or a lack of skilled workers can slow down production.
Employee fatigue or errors due to overwork can further compound delays.
Supply Chain Disruptions
Delays in the delivery of raw materials or components create bottlenecks.
Unreliable suppliers or inadequate inventory management often lead to production halts.
Overproduction or Underutilization
Overproduction in one area of the line can overwhelm downstream processes.
Underutilization of resources results in inefficiencies and wasted capacity.
Effective Solutions to Address Bottlenecks
Conduct a Workflow Analysis
Map out the entire production process to identify bottleneck points.
Use tools like value stream mapping or process flow diagrams for better visualization.
Implement Preventive Maintenance
Schedule regular maintenance to reduce unexpected machine downtimes.
Invest in modern equipment with higher reliability and efficiency.
Optimize Resource Allocation
Reallocate labor or machinery to underperforming areas to balance workloads.
Train employees to enhance skills and improve productivity.
Adopt Automation and Technology
Use automated systems to streamline repetitive or time-consuming tasks.
Implement manufacturing execution systems (MES) to monitor and optimize production in real time.
Enhance Supply Chain Management
Establish strong relationships with reliable suppliers to minimize disruptions.
Adopt just-in-time (JIT) inventory systems to ensure smooth material flow.
Implement Lean Manufacturing Practices
Use lean principles to eliminate waste and improve process efficiency.
Employ techniques like Six Sigma to identify and resolve inefficiencies systematically.
Case Study: Bottleneck Resolution in Action
A medium-sized manufacturing company experienced delays due to an outdated bottleneck machine in its assembly line. After conducting a workflow analysis, they identified the root cause and invested in a modern, automated machine. This upgrade reduced downtime by 30% and increased production capacity by 20%, leading to significant cost savings and improved customer satisfaction.'
youtube
Final Thoughts
Bottlenecks in manufacturing are inevitable but manageable with the right strategies. By identifying common causes and implementing targeted solutions, businesses can streamline their production processes, reduce delays, and improve overall operational efficiency.
Investing in modern technology, training, and lean practices not only resolves current bottlenecks but also prevents future issues, ensuring sustained productivity and competitiveness in the market.
SITES WE SUPPORT
Software Processes - Wix
SOCIAL LINKS Facebook Twitter LinkedIn
0 notes
Text
Unlocking the Potential of Business Analysis
Unlocking the potential of business analysis involves understanding its core principles, tools, and techniques, as well as recognizing how it can bring value to an organization. Here’s how you can approach it effectively:
1. Grasp the Foundations
Definition: Business analysis is the practice of enabling change within an organization by identifying needs and recommending solutions that deliver value to stakeholders.
Key Objectives:
Understand business goals.
Bridge the gap between business needs and technical solutions.
Deliver actionable insights.
2. Master the Core Skills
To excel in business analysis, focus on the following skill sets:
Analytical Thinking: Break down complex problems into manageable components.
Communication Skills: Engage stakeholders and articulate findings clearly.
Problem-Solving: Identify root causes and propose practical solutions.
Technical Proficiency: Understand tools and systems used for analysis, like SQL, Excel, or specialized business analysis software.
3. Learn the Key Techniques
Some common techniques include:
SWOT Analysis: Evaluate Strengths, Weaknesses, Opportunities, and Threats.
Business Process Modeling: Visualize workflows to identify inefficiencies.
Requirement Gathering: Engage stakeholders through interviews, workshops, or surveys.
Gap Analysis: Compare current vs. desired performance or states.
4. Leverage Tools
Modeling Tools: Use tools like Visio, Lucidchart, or Bizagi for process mapping.
Data Analysis Tools: Familiarize yourself with Power BI, Tableau, or Excel for data-driven insights.
Project Management Tools: Collaborate using Jira, Trello, or Asana.
5. Align with Frameworks and Standards
Understanding industry-recognized frameworks ensures consistency and credibility:
BABOK® (Business Analysis Body of Knowledge): A guide by IIBA for best practices.
Agile Methodologies: Learn to adapt to iterative processes using Scrum or Kanban.
Lean Six Sigma: Focus on efficiency and quality in business processes.
6. Focus on Stakeholder Engagement
Build relationships with stakeholders at all levels.
Practice active listening to gather diverse perspectives.
Use storytelling and visualization to convey findings effectively.
7. Gain Certification
Certifications can boost credibility and demonstrate expertise:
Certified Business Analysis Professional (CBAP®): Advanced certification by IIBA.
PMI-PBA®: Focused on project management-oriented business analysis.
Agile Business Analyst Certification: Tailored for Agile environments.
8. Apply Business Analysis to Drive Value
Improve operational efficiency by optimizing processes.
Drive strategic initiatives by aligning solutions with organizational goals.
Enhance decision-making by providing actionable insights through data analysis.
By investing in these areas, you can unlock the full potential of business analysis, positioning yourself as a key player in driving organizational success. Let me know if you'd like resources or tailored guidance on any of these steps!
0 notes
Text
Process Improvement: The Secret to Boosting Efficiency and Success
In today's fast-paced world, businesses are constantly looking for ways to enhance their operations, improve productivity, and stay ahead of the competition. Enter Process Improvement, a game-changing approach to refining workflows, reducing waste, and achieving better outcomes. Whether you're a startup, a small business, or a global corporation, this concept has something to offer.
If you're new to the term, don't worry! We're here to break it down into simple, relatable terms that will leave you confident about how it can help transform your work and life.
What is Process Improvement?
At its core, Process Improvement is the practice of analyzing and enhancing existing processes to make them more efficient, cost-effective, and reliable. It’s all about identifying pain points, bottlenecks, or unnecessary steps in a workflow and finding better ways to tackle them.
Think of it this way: Imagine you’re baking a cake. The first time you try, you follow the recipe but take a lot of time measuring ingredients, preheating the oven, and cleaning up afterward. Over time, you find ways to streamline the process—pre-measuring ingredients, using tools to speed up mixing, and cleaning as you go. That’s Process Improvement in action!
Why is Process Improvement Important?
Businesses and individuals alike benefit from refining their processes. Here are some key reasons why it matters:
1. Saves Time
Time is money, right? Improving processes means tasks take less time to complete, freeing you to focus on what truly matters.
2. Reduces Costs
By eliminating inefficiencies, you can save resources like materials, labor, and energy. For businesses, this means higher profits.
3. Boosts Productivity
Streamlined workflows enable teams to accomplish more in less time, leading to happier employees and better results.
4. Enhances Quality
Consistently improving processes ensures fewer errors, better products, and more satisfied customers.
5. Encourages Innovation
When you actively look for better ways of doing things, you create a culture of creativity and continuous improvement.
Popular Process Improvement Techniques
There are several tried-and-true methods to improve processes. Here are some of the most commonly used ones:
1. Lean Methodology
Lean focuses on eliminating waste in processes. Waste can be anything that doesn’t add value to the final product or service. For example, reducing overproduction, unnecessary transportation, or excess inventory can significantly cut costs.
2. Six Sigma
Six Sigma aims to minimize errors and variability in processes. It uses data-driven techniques and statistical analysis to achieve near-perfect quality levels.
3. Agile
Though primarily used in software development, Agile principles can be applied to almost any field. Agile emphasizes adaptability and breaking work into smaller, manageable tasks.
4. Kaizen
Kaizen, a Japanese term meaning "continuous improvement," focuses on making small, incremental changes over time that add up to significant results.
5. Business Process Reengineering (BPR)
This technique involves rethinking and redesigning processes from scratch to achieve dramatic improvements in performance.
Steps to Implement Process Improvement
If you’re ready to embrace Process Improvement, here’s a simple step-by-step guide to get started:
Step 1: Identify the Process
Choose a specific process that needs improvement. It could be anything from how customer inquiries are handled to how invoices are processed.
Step 2: Analyze the Current State
Take a close look at how things are currently done. Map out the workflow, gather data, and identify bottlenecks or areas of waste.
Step 3: Set Clear Goals
Define what you want to achieve. Are you looking to save time? Reduce errors? Cut costs? Having a clear goal will guide your efforts.
Step 4: Brainstorm Solutions
Involve your team in brainstorming sessions to come up with potential improvements. Encourage creative thinking and open discussions.
Step 5: Implement Changes
Test the proposed solutions on a small scale before rolling them out company-wide. Monitor the results and make adjustments as needed.
Step 6: Measure Success
Use key performance indicators (KPIs) to evaluate the success of your improvements. Celebrate wins and document lessons learned.
Examples of Process Improvement in Action
Here are some real-life scenarios where Process Improvement can make a huge difference:
1. Customer Service
A company noticed long wait times for customer support. By implementing a chatbot for common inquiries, they reduced response times and freed up agents to handle complex issues.
2. Inventory Management
A retail store struggled with overstocked shelves. By adopting a just-in-time inventory system, they minimized waste and improved cash flow.
3. Team Collaboration
A marketing team used multiple tools for project management, leading to confusion. Switching to an all-in-one platform streamlined communication and boosted productivity.
Common Challenges in Process Improvement
While the benefits are clear, Process Improvement isn’t without its challenges. Here’s how to tackle some common obstacles:
1. Resistance to Change
Not everyone loves change. Involve employees early in the process, communicate the benefits, and provide training to ease the transition.
2. Lack of Resources
Improving processes can require time and money upfront. Prioritize high-impact changes that provide the quickest return on investment.
3. Poor Communication
Clear communication is key. Make sure everyone understands the changes and their role in the process.
Tools to Simplify Process Improvement
In today’s digital age, tools can make implementing Process Improvement much easier. Here are some popular ones:
1. Project Management Tools
Platforms like Trello, Asana, and Monday.com help teams manage tasks, deadlines, and communication.
2. Data Analysis Tools
Google Analytics, Tableau, and Power BI provide insights to make data-driven decisions.
3. Workflow Automation
Zapier and Automate.io connect apps and automate repetitive tasks, saving you time.
Final Thoughts
Process Improvement isn’t just a buzzword; it’s a powerful approach that can revolutionize how you work. By identifying inefficiencies, streamlining workflows, and fostering a culture of continuous improvement, you can unlock new levels of success and satisfaction.
0 notes
Text
Mastering Quality: The Comprehensive Guide to Ensuring Manufacturing Excellence

In the complex world of manufacturing, quality isn't just a buzzword—it's the lifeline of successful production. As someone who has spent years working closely with manufacturers across various industries, I've witnessed firsthand how strategic quality management can transform a good product into an exceptional one.
The Critical Importance of Quality Management
Manufacturing quality management goes far beyond simple inspection processes. It's a holistic approach that encompasses every stage of production, from initial design to final delivery. Think of it like conducting an orchestra—each instrument (or in this case, each production stage) must play in perfect harmony to create a masterpiece.
Understanding the Core Components of Quality Management
Effective quality management rests on several fundamental pillars:
Proactive Prevention: Instead of catching errors after they occur, successful manufacturers anticipate potential issues before they happen.
Continuous Improvement: Quality is not a destination but a continuous journey of refinement and optimization.
Data-Driven Decision Making: Leveraging accurate metrics and insights to drive strategic improvements.
Product Quality Optimization: A Strategic Approach
Optimizing product quality requires a multifaceted strategy. Here are key considerations that can significantly elevate your manufacturing processes:
1. Comprehensive Process Mapping
Before you can improve something, you must understand it completely. Process mapping allows manufacturers to:
Identify potential bottlenecks
Streamline workflow
Eliminate unnecessary steps
Reduce waste and inefficiencies
2. Advanced Quality Control Techniques
Modern manufacturing demands sophisticated quality control methods:
Statistical Process Control (SPC)
Six Sigma methodologies
Advanced measurement technologies
Real-time monitoring systems
3. Employee Training and Engagement
Technology alone cannot guarantee quality. Your workforce plays a crucial role:
Regular skill development programs
Creating a culture of quality consciousness
Encouraging employee feedback and suggestions
Implementing reward systems for quality improvements
The Role of Third-Party Inspections in Manufacturing Excellence
While internal quality checks are essential, third-party inspections provide an unbiased, external perspective. These inspections offer:
Objective assessment of manufacturing processes
Validation of quality standards
Identification of potential blind spots
Credibility with international clients
Factory Audits: Your Quality Assurance Roadmap
A comprehensive factory audit goes beyond surface-level assessments. It involves:
Examining production workflows
Evaluating equipment maintenance
Reviewing quality management systems
Analyzing workforce capabilities
Ensuring compliance with international standards
Developing Manufacturing Excellence Strategies
Creating a robust strategy for manufacturing excellence involves:
Technological Integration
Implementing IoT in quality monitoring
Using AI and machine learning for predictive quality control
Investing in advanced measurement and tracking technologies
Supply Chain Quality Management
Extending quality standards to suppliers
Creating collaborative quality improvement networks
Developing transparent communication channels
Certification and Continuous Learning
Pursuing quality assurance certificates
Participating in industry workshops
Staying updated with global manufacturing trends
Practical Implementation: From Strategy to Success
Transforming these strategies from theoretical concepts to practical realities requires:
Leadership commitment
Substantial investment in training
Patience during implementation
Willingness to adapt and evolve
Conclusion: Quality as a Competitive Advantage
In today's global market, quality is not just about meeting standards—it's about exceeding expectations. Manufacturers who embrace comprehensive quality management don't just produce products; they create experiences that build lasting customer trust.
Remember, manufacturing excellence is a continuous journey of learning, improving, and innovating. Your commitment to quality can be the defining factor that sets you apart in a competitive marketplace.
#china product inspection services#supplier quality audit#consumer product testing company#service supply chain management#quality inspection service in china#china inspection company#third party inspection company#inspection services in china#quality control china
0 notes
Text
Is the Six Sigma Yellow Belt certification worth it?
Absolutely, yes! For people who desire to get a simple introduction to the Six Sigma concept as well as DMAD structuring, Six Sigma Yellow Belt is recommended.
This certification will be an entry level and will provide an overview of Lean and Six Sigma.
Problem solving, process mapping and basic statistics are part of the content of this certification. It is designed to meet the needs of newcomers who want to get an initial overview of the main body of knowledge before learning how to become a Green or Black Belt.
0 notes
Text
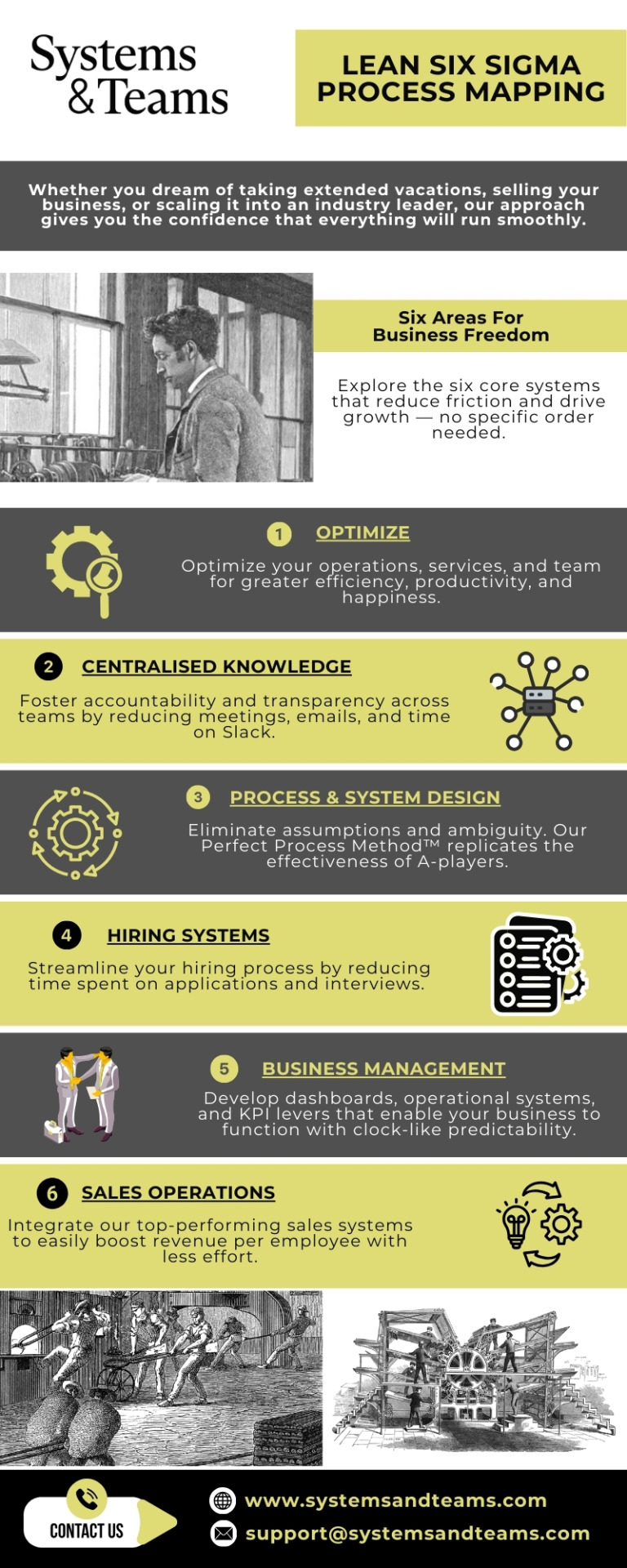
Six Sigma Process Mapping - Systems And Teams
#Six Sigma Methodology#Six Sigma Process Mapping#Small Business Systems#Business Processes#Lean Thinking#Lean Methodology#Business Process Management System#Business Process Operations#Succession Planning#Business Process Management#Business Process Mapping Consultants
1 note
·
View note
Text
Six Sigma vs Lean Six Sigma: Understanding the Key Differences

Source: kpifire.com
In this world of business and manufacturing where competition is high in the market. Organizations are trying to enhance their quality and reduce expenses and also seeking out methods to help achieve these goals. For better outcomes and to complete their goal, Organisations have turned towards two methodologies – Six Sigma and Lean Six Sigma. They have been proved to be very resourceful, and though they may seem similar it is important to study the differences and unique applications to make your Organisation successful and improve operations. In this article, we will understand the concept of Six Sigma vs Lean Six Sigma, which in turn helps you grow your business.
What is Six Sigma?
Six Sigma is a data-driven methodology that focuses on minimizing process variation and improving quality. Originating from Motorola in the 1980s, Six Sigma uses statistical tools and techniques to identify and eliminate defects in a process. The goal is to achieve a level of quality where the probability of defects is no more than 3.4 per million opportunities.
The Six Sigma methodology is built around the DMAIC framework:
Define: Identify the problem or improvement opportunity.
Measure: Collect and analyze data to understand the current performance.
Analyze: Identify root causes of defects or inefficiencies.
Improve: Implement solutions to address the root causes.
Control: Monitor the improved process to ensure long-term success.
By focusing on reducing defects and variability, Six Sigma enables organizations to deliver consistent, high-quality products and services.
What is Lean Six Sigma?
https://enterprisewired.com/wp-content/uploads/2024/11/1.1-What-is-Lean-Six-Sigma_-Source-academy.smu_.edu_.sg_.jpg
Lean Six Sigma is a hybrid methodology that combines the principles of Six Sigma with Lean manufacturing. Lean focuses on eliminating waste, improving flow, and optimizing efficiency. When merged with Six Sigma’s emphasis on reducing process variation, the result is a comprehensive approach to process improvement.
The Lean component emphasizes the eight types of waste (commonly known as TIMWOODS):
Transportation
Inventory
Motion
Waiting
Overproduction
Overprocessing
Defects
Skills (underutilization)
Lean Six Sigma incorporates the DMAIC framework but expands its scope to focus on both quality and speed. The methodology ensures that processes are not only defect-free but also efficient and cost-effective.
Six Sigma vs Lean Six Sigma: Key Differences
To understand Six Sigma vs Lean Six Sigma, it’s essential to recognize their unique focuses and benefits. While both aim to improve processes and deliver better outcomes, their approaches differ significantly.
1. Core Focus
Six Sigma: Prioritizes quality improvement by reducing process variation and defects.
Lean Six Sigma: Focuses on both eliminating waste and reducing defects for overall process efficiency.
2. Tools and Techniques
Six Sigma: Utilizes statistical tools such as hypothesis testing, regression analysis, and control charts.
Lean Six Sigma: Incorporates Lean tools like value stream mapping, 5S, and Kaizen along with Six Sigma techniques.
3. Scope of Application
Six Sigma: Best suited for processes where quality and precision are critical, such as manufacturing and healthcare.
Lean Six Sigma: Ideal for broader organizational applications, including supply chain management, logistics, and service industries.
4. Implementation Time
Six Sigma: Typically requires more time due to its in-depth data analysis and structured approach.
Lean Six Sigma: Offers faster results by addressing waste and inefficiencies alongside defect reduction.
5. Team Structure
Both methodologies use a hierarchical team structure with roles such as Green Belts, Black Belts, and Master Black Belts. However, Lean Six Sigma teams often include Lean specialists to address waste-specific challenges.
Benefits of Six Sigma
Improved Quality: Helps organizations deliver products and services with minimal defects.
Data-Driven Decisions: Relies on statistical analysis for accurate decision-making.
Customer Satisfaction: Enhances customer experience by meeting or exceeding quality expectations.
Cost Savings: Reduces costs by eliminating defects and rework.
Benefits of Lean Six Sigma
https://enterprisewired.com/wp-content/uploads/2024/11/1.2-Benefits-of-Lean-Six-Sigma-Source-simplilearn.com_.jpg
Increased Efficiency: Reduces cycle times and improves process flow.
Waste Reduction: Addresses all forms of waste to maximize resource utilization.
Scalability: Adaptable to various industries, from manufacturing to services.
Faster Results: Combines quick wins with long-term quality improvements.
Choosing Between Six Sigma and Lean Six Sigma
The choice between Six Sigma vs Lean Six Sigma depends on your organization’s goals and challenges. If your primary objective is to improve quality and reduce defects, Six Sigma may be the better choice. However, if you also aim to eliminate waste and enhance overall efficiency, Lean Six Sigma offers a more comprehensive solution.
Here are some scenarios to help guide your decision:
Choose Six Sigma if:
Your processes face significant variability and defects.
Quality improvement is your top priority.
You have the resources and time for an in-depth data-driven approach.
Choose Lean Six Sigma if:
You need to address inefficiencies and waste alongside quality issues.
Speed and efficiency are crucial for your operations.
You require a more holistic approach to process improvement.
Implementation Challenges
https://enterprisewired.com/wp-content/uploads/2024/11/1.3-Implementation-Challenges-Image-by-FatCamera-from-Getty-Images-Signature.jpg
Training and Expertise: Successful implementation requires trained personnel with expertise in the chosen methodology.
Cultural Resistance: Employees may resist changes to established processes.
Resource Allocation: Dedicated time, tools, and resources are essential for success.
Sustainability: Maintaining improvements over the long term can be challenging without proper monitoring and control systems.
Six Sigma vs Lean Six Sigma: Conclusion
While comparing Six Sigma vs Lean Six Sigma, it’s understood that both methods have offered tools to help improve the operations. Six Sigma contributes to deducting any defects and improving the quality. Whereas Lean Six Sigma offers a stable method after addressing waste and inefficiencies. Finally, which methods to use depends on the organization’s needs and goals. By studying the advantages and disadvantages of these methodologies, you can choose the approach that seems to be lining up with your business objectives and brings effective outcomes. Whichever organization aims to improve and grow their business, embracing either of these methodologies or a combination of both can help them pave the way towards a better and improved future of the organization.
0 notes
Text
Lean Six Sigma Certification Courses in Australia

Lean Six Sigma Certification courses in Australia provide professionals with the expertise to drive operational excellence and optimize business processes. Combining Lean methodologies, which focus on waste reduction, with Six Sigma's data-driven approach to reducing variation, Lean Six Sigma certification equips participants with a comprehensive toolkit for process improvement. Offered by numerous accredited institutions across Australia, these courses are ideal for professionals in diverse sectors—including manufacturing, healthcare, finance, and IT—seeking to enhance productivity, reduce costs, and achieve measurable outcomes.
The certification process in Australia follows a structured path, with different levels of expertise: Yellow Belt, Green Belt, Black Belt, and Master Black Belt. Each level progressively builds on the tools and strategies necessary for addressing more complex problems within organizations. Yellow and Green Belt certifications cover foundational and intermediate concepts, respectively, focusing on team-based problem-solving and process mapping. Black Belt and Master Black Belt certifications, on the other hand, prepare participants for leadership roles in process improvement, teaching advanced statistical analysis and project management techniques for implementing enterprise-wide changes.
Professionals who obtain Lean Six Sigma certification in Australia are well-positioned to drive efficiency and quality within their organizations, a skill set increasingly in demand across industries. Certification provides a competitive advantage, opening doors to roles in process improvement, quality management, and operational leadership. With organizations in Australia prioritizing continuous improvement to stay competitive, Lean Six Sigma-certified professionals are equipped to lead strategic projects that improve customer satisfaction, reduce waste, and enhance business outcomes.
0 notes
Text
The Importance of Continuous Improvement in Quality Assurance Consulting
Introduction In today’s fast-paced software development environment, the need for continuous improvement is paramount. Quality assurance consulting services play a crucial role in fostering a culture of ongoing enhancement within organizations. This article delves into the significance of continuous improvement in QA practices, exploring methodologies, strategies, and the impact on overall product quality.

Understanding Continuous Improvement
Continuous improvement refers to an ongoing effort to enhance products, services, or processes over time. In the context of quality assurance, it involves regularly assessing and refining QA practices to ensure they remain effective and aligned with organizational goals. The benefits of continuous improvement include:
Increased Efficiency: Streamlining processes reduces waste and optimizes resource utilization.
Enhanced Product Quality: Ongoing assessments lead to early detection of defects and improved product reliability.
Adaptability: Organizations can quickly respond to changing market demands and customer expectations.
Methodologies Promoting Continuous ImprovementSeveral methodologies promote continuous improvement within quality assurance consulting services:
Agile Practices: Agile methodologies emphasize iterative development and frequent feedback loops. By incorporating QA into each sprint, teams can identify issues early and make necessary adjustments before moving forward.
Scrum Framework: In Scrum, QA consultants work closely with development teams during sprint planning and reviews. This collaboration ensures that quality considerations are integrated into the development process from the outset.
Lean Principles: Lean focuses on minimizing waste while maximizing productivity. QA consultants can help organizations identify non-value-added activities within their testing processes and eliminate them.
Value Stream Mapping: This technique visualizes the flow of information and materials through a process, allowing teams to identify bottlenecks and areas for improvement.
Six Sigma: Six Sigma is a data-driven approach aimed at reducing defects and variability in processes. QA consultants can implement Six Sigma methodologies to analyze data, identify root causes of defects, and develop solutions.
DMAIC Framework: The Define, Measure, Analyze, Improve, Control (DMAIC) framework provides a structured approach for continuous improvement projects focused on quality enhancement.
Total Quality Management (TQM): TQM is an organization-wide approach that emphasizes customer satisfaction through continuous improvement in all aspects of operations. QA consultants can help organizations adopt TQM principles by fostering a culture of quality at every level.
Employee Involvement: Engaging employees in quality initiatives encourages ownership and accountability for quality outcomes.
Implementing Continuous Improvement StrategiesTo effectively implement continuous improvement strategies within QA consulting services, organizations should consider the following steps:
Regular Audits and Assessments: Conducting periodic audits of QA processes helps identify strengths and weaknesses. These assessments should focus on evaluating testing methodologies, tools used, and overall effectiveness in meeting quality objectives.
Feedback Mechanisms: Establishing channels for gathering feedback from team members, stakeholders, and end-users is essential. Regularly soliciting input allows organizations to make informed decisions about necessary improvements.
Training and Development Programs: Investing in training programs for QA teams ensures they stay updated on industry best practices and emerging technologies. Continuous learning fosters a culture of improvement where team members are empowered to contribute ideas for enhancing processes.
Setting Measurable Goals: Establishing clear metrics for evaluating the effectiveness of QA practices provides a benchmark for measuring progress over time. Goals should be specific, measurable, achievable, relevant, and time-bound (SMART).
Recognition and Rewards: Acknowledging team members’ contributions to continuous improvement initiatives fosters motivation and engagement. Celebrating successes reinforces the importance of quality as a shared responsibility within the organization.
Iterative Process Refinement: Continuous improvement is an ongoing journey rather than a one-time effort. Organizations should regularly revisit their processes to identify new opportunities for enhancement based on changing needs or emerging trends.
Case Examples of Continuous Improvement SuccessOrganizations that have embraced continuous improvement within their QA practices have reported significant benefits:
A software company that adopted Agile methodologies saw a 30% reduction in defect rates after implementing regular retrospectives where teams reflected on their performance and identified areas for improvement.
A financial institution that implemented Six Sigma methodologies reduced its processing errors by 50% within six months by analyzing data to identify root causes of defects in its transaction processing system.
These examples demonstrate how continuous improvement initiatives can lead to tangible results in terms of product quality and operational efficiency.
Conclusion Continuous improvement is essential for organizations striving to maintain high-quality standards in today’s competitive landscape. Quality assurance consulting services play a pivotal role in fostering this culture by implementing effective methodologies, strategies, and practices that drive ongoing enhancement efforts. By prioritizing continuous improvement within their QA processes, organizations position themselves for long-term success—delivering high-quality products that meet customer expectations while adapting swiftly to changing market dynamics!
#qa software testing services#software testing and quality assurance#software quality assurance companies#quality assurance services#quality assurance services company#qa consulting companies#qa software testing company
0 notes
Text
Building Successful Operations Support Analyst Career
How to Build a Successful Career as an Operations Support Analyst
Introduction
Building a successful career as an Operations Support Analyst involves a blend of education, skills development, relevant experience, and continuous professional growth. This role is pivotal in ensuring operational efficiency, supporting decision-making, and improving overall performance. The following guide outlines the key steps and strategies to thrive in this dynamic field.
Understanding the Role of an Operations Support Analyst
An Operations Support Analyst plays a crucial role in analyzing and improving business processes. Responsibilities typically include data analysis, process documentation, reporting, and providing actionable insights to management. The position requires a strong analytical mindset, attention to detail, and the ability to communicate effectively with various stakeholders.
1. Educational Foundation
a. Obtain Relevant Education
Most Operations Support Analyst positions require at least a bachelor’s degree. Relevant fields of study include:
Business Administration: Provides a broad understanding of business principles and practices.
Information Technology: Offers technical skills essential for analyzing operational processes.
Statistics or Mathematics: Develops analytical skills crucial for data interpretation and reporting.
b. Pursue Certifications
Consider obtaining certifications that enhance your qualifications, such as:
Lean Six Sigma: Focuses on process improvement and efficiency.
Project Management Professional (PMP): Demonstrates proficiency in project management principles.
Data Analysis Certifications: Platforms like Coursera or Udacity offer courses on data analysis tools (e.g., SQL, Excel, Python).
2. Develop Key Skills
a. Analytical Skills
The ability to analyze data and interpret results is vital. Develop skills in:
Data Analysis: Learn to use analytical tools like Excel, Tableau, or Power BI.
Problem-Solving: Cultivate a structured approach to identifying issues and proposing solutions.
b. Communication Skills
Effective communication is essential for conveying insights and collaborating with teams. Focus on:
Written Communication: Improve your ability to create clear reports and documentation.
Verbal Communication: Practice presenting findings to stakeholders and facilitating discussions.
c. Technical Proficiency
Familiarity with software and tools used in operations is important. Key areas to explore include:
Database Management: Understand SQL for querying databases.
Project Management Tools: Get comfortable with tools like Trello, Asana, or JIRA.
Process Mapping Software: Learn to use tools like Visio for documenting processes.
3. Gain Relevant Experience
a. Entry-Level Positions
Start in entry-level roles that offer exposure to operations, such as:
Data Entry Clerk: Provides experience with data handling and accuracy.
Administrative Assistant: Offers insights into organizational processes and team dynamics.
b. Internships
Seek internships or co-op programs that focus on operations support. These opportunities allow you to:
Work on real projects.
Network with professionals in the field.
Gain hands-on experience with data analysis and reporting.
c. Volunteer Opportunities
Look for volunteer roles that involve operations or data analysis, such as:
Assisting with non-profit organizations' data management.
Participating in community service projects requiring process improvement.
4. Networking and Professional Growth
a. Build a Professional Network
Networking can lead to job opportunities and mentorship. Consider:
Attending industry conferences and workshops.
Joining professional organizations, such as the Institute for Operations Research and the Management Sciences (INFORMS).
Engaging with peers on platforms like LinkedIn to share insights and opportunities.
b. Seek Mentorship
Find a mentor within your organization or industry who can guide you. A mentor can:
Provide valuable insights into career progression.
Share experiences and advice on navigating challenges in the field.
5. Continuous Learning and Development
a. Stay Updated on Industry Trends
The field of operations is constantly evolving. Stay informed by:
Following industry publications and blogs.
Participating in webinars and online courses related to operational excellence.
b. Pursue Advanced Education
Consider pursuing advanced degrees, such as a Master’s in Business Administration (MBA) or a Master’s in Operations Management, to enhance your career prospects.
c. Seek Professional Development Opportunities
Many organizations offer training programs. Take advantage of:
Workshops focused on advanced analytics.
Leadership development programs to prepare for managerial roles.
6. Pathways for Advancement
a. Identify Career Pathways
As an Operations Support Analyst, various advancement opportunities are available, including:
Operations Manager: Overseeing teams and improving operational efficiency.
Business Analyst: Focusing on specific business units and their operational needs.
Quality Assurance Analyst: Ensuring the quality of processes and outputs.
b. Showcase Your Achievements
Document your accomplishments and contributions in your role. This can include:
Successfully completed projects that improved efficiency.
Data-driven insights that led to informed decision-making.
Conclusion
Building a successful career as an Operations Support Analyst requires a proactive approach to education, skill development, and networking. By continuously seeking improvement and embracing new opportunities, you can position yourself for success in this dynamic field. The path may be challenging, but with dedication and the right strategies, you can achieve a rewarding career in operations support.
Call to Action
Are you ready to build your career as an Operations Support Analyst? Take the next step now! Explore opportunities on our career page and kickstart your journey to success at ReachLocal India! Your future in operations awaits.
0 notes
Text
Understanding Process-Smart: Enhancing Efficiency in Modern Workflows
In today’s fast-paced business environment, efficiency and adaptability are crucial for success. One approach that has gained traction is the concept of being "process-smart." This article explores what it means to be process-smart, its benefits, and how organizations can implement it to optimize their workflows.

What Does It Mean to Be Process-Smart?
Being process-smart involves understanding and improving the processes within an organization to enhance productivity and reduce waste. It goes beyond mere automation; it encompasses a strategic approach to how tasks are performed and how resources are allocated.
Key Characteristics of Process-Smart Organizations
Data-Driven Decision Making: Process-smart organizations utilize data analytics to evaluate their processes. By measuring key performance indicators (KPIs), they can identify bottlenecks and areas for improvement.
Continuous Improvement: A process-smart approach embraces the idea of continuous improvement, often through methodologies like Lean and Six Sigma. Organizations consistently seek feedback and make adjustments to enhance efficiency.
Collaboration and Communication: Effective collaboration across departments is essential. Process-smart organizations foster open communication to ensure that all team members are aligned and aware of the processes in place.
Benefits of Being Process-Smart
Adopting a process-smart approach offers numerous benefits that can significantly impact an organization’s bottom line.
Increased Efficiency
By streamlining workflows and eliminating unnecessary steps, organizations can complete tasks more quickly. This increased efficiency not only saves time but also allows employees to focus on higher-value activities.
Cost Reduction
With improved processes, organizations often see a reduction in operational costs. By identifying and removing waste, companies can allocate their resources more effectively, leading to significant savings.
Enhanced Employee Satisfaction
A well-defined process can lead to clearer roles and responsibilities, reducing confusion among team members. This clarity contributes to higher job satisfaction and employee morale, as team members feel more empowered to perform their tasks efficiently.
Improved Customer Satisfaction
Ultimately, a process-smart organization can deliver better products and services to its customers. By optimizing internal processes, companies can respond to customer needs more quickly and effectively, leading to enhanced customer loyalty and satisfaction.
Implementing a Process-Smart Strategy
To become process-smart, organizations can follow a systematic approach.
Step 1: Map Existing Processes
The first step is to document existing workflows. Process mapping helps visualize how tasks are performed, making it easier to identify inefficiencies.
Step 2: Analyze and Identify Bottlenecks
Using data analytics, organizations can assess the performance of their processes. Identifying bottlenecks is crucial for understanding where improvements can be made.
Step 3: Engage Employees
Involving employees in the improvement process is vital. They often have valuable insights into how processes can be optimized, as they are the ones working within them daily.
Step 4: Implement Changes and Monitor Results
Once changes are made, it’s essential to monitor the outcomes. Regularly reviewing processes ensures that improvements are sustained and that any new issues are addressed promptly.
Step 5: Foster a Culture of Continuous Improvement
Finally, organizations should cultivate a culture that encourages ongoing assessment and refinement of processes. Regular training and workshops can help maintain this focus on improvement.
Summary
In a world where efficiency is paramount, being process-smart is no longer optional—it's a necessity. By understanding and improving their workflows, organizations can enhance productivity, reduce costs, and ultimately deliver better value to their customers. Embracing a process-smart mindset paves the way for sustainable success in today’s competitive landscape.
0 notes