#Simple Moving Average (SMA)
Explore tagged Tumblr posts
Text
Types of Technical Indicators in Trading
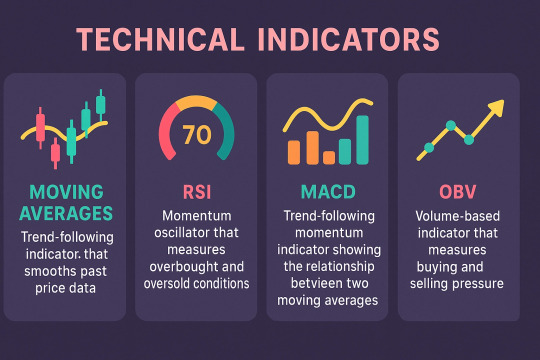
Technical indicators are essential tools used by traders to analyze market trends and make informed decisions. Among the many available, some of the most widely used types include Moving Averages, Relative Strength Index (RSI), MACD, and On-Balance Volume (OBV).
Moving Averages smooth out price data to identify trend direction over a specific period. Common types include the Simple Moving Average (SMA) and Exponential Moving Average (EMA), which help traders determine support and resistance levels and potential entry or exit points.
The Relative Strength Index (RSI) is a momentum oscillator that measures the speed and change of price movements. RSI values range from 0 to 100 and are typically used to identify overbought (above 70) or oversold (below 30) conditions, signaling potential reversals.
MACD (Moving Average Convergence Divergence) is a trend-following momentum indicator that shows the relationship between two EMAs. It helps traders identify changes in trend strength, direction, and momentum.
On-Balance Volume (OBV) uses volume flow to predict price movements. A rising OBV indicates accumulation, while a falling OBV suggests distribution, providing insights into the strength of a trend.
Using these indicators together can improve trading accuracy and help develop a solid, data-driven strategy.
Explore, all the Technical Indicators in Trading.
#Types of Technical Indicators in Trading#Technical Indicators in Trading#Indicators in Trading#trading indicators#indicators in trading
2 notes
·
View notes
Text
What tools or indicators can be used with Forex charts?
Here's a comprehensive and detailed breakdown of tools and indicators used in Forex trading, structured to span around 3,500 words. This document includes technical analysis tools, charting platforms, indicators (leading and lagging), and practical strategies for application.

Tools and Indicators Used with Forex Charts
Introduction
The foreign exchange (Forex) market is the largest and most liquid financial market globally, with trillions of dollars traded daily. To navigate this vast marketplace effectively, traders utilize a variety of tools and indicators to analyze price movements, identify trends, and execute strategic trades.
Understanding these tools and indicators is essential for any Forex trader—whether novice or experienced—as they form the foundation of technical analysis, one of the most widely used approaches in the financial markets.
This article explores the essential tools and indicators used in Forex charting, categorized into several groups for clarity and practical application.
1. Charting Platforms and Tools
1.1. Charting Software
To analyze Forex charts, traders need reliable charting platforms that provide real-time data, customizable indicators, and drawing tools.
Popular charting platforms:
MetaTrader 4 (MT4) and MetaTrader 5 (MT5): Industry standards offering robust technical analysis tools.
TradingView: A web-based platform with advanced charting features and social integration.
cTrader: Offers intuitive UI, depth of market (DOM) functionality, and automation options.
NinjaTrader: Used by more advanced traders for both Forex and futures markets.
1.2. Chart Types
Understanding different chart types helps traders select the most appropriate visualization method.
Line Chart: Plots closing prices; useful for identifying trends.
Bar Chart (OHLC): Shows open, high, low, and close prices; more data-rich.
Candlestick Chart: Most popular; visually intuitive and informative, ideal for pattern recognition.
Renko Charts: Focus on price movement, ignoring time.
Heiken Ashi: Smooths price action to better identify trends.
2. Categories of Forex Indicators
Forex indicators are generally categorized based on their function and timing:
Trend-following indicators (lagging)
Momentum indicators (leading)
Volatility indicators
Volume indicators
Support and resistance tools
Overlay indicators vs. oscillator indicators
3. Trend-Following (Lagging) Indicators
These indicators help identify the direction of the market trend.
3.1. Moving Averages (MA)
Simple Moving Average (SMA) and Exponential Moving Average (EMA) are essential tools.
SMA calculates the average of a selected range of prices.
EMA gives more weight to recent prices.
Usage:
Determine trend direction.
Create signals with crossovers (e.g., 50 EMA crossing 200 EMA = Golden Cross/Death Cross).
3.2. Moving Average Convergence Divergence (MACD)
Composed of two EMAs (MACD line and signal line) and a histogram.
Usage:
Crossover strategy for buy/sell signals.
Divergence from price to signal potential reversals.
3.3. Average Directional Index (ADX)
Measures trend strength, not direction.
Usage:
ADX above 25 = strong trend.
ADX below 20 = weak trend or range-bound market.
3.4. Ichimoku Kinko Hyo
A comprehensive indicator showing trend, momentum, and support/resistance.
Components:
Tenkan-sen (conversion line)
Kijun-sen (base line)
Senkou Span A and B (cloud)
Chikou Span (lagging line)
Usage:
Cloud (Kumo) provides dynamic support and resistance.
Crossovers and breakouts from the cloud indicate signals.
4. Leading Indicators (Momentum)
Leading indicators aim to forecast future price movements.
4.1. Relative Strength Index (RSI)
An oscillator ranging from 0 to 100.
Usage:
RSI > 70 = overbought.
RSI < 30 = oversold.
Divergence with price indicates reversals.
4.2. Stochastic Oscillator
Compares a specific closing price to a range over time.
Usage:
%K and %D lines; crossovers suggest entries/exits.
Overbought/oversold levels are typically 80/20.
4.3. Commodity Channel Index (CCI)
Shows when a currency is overbought/oversold relative to its average price.
Usage:
Readings above +100 or below -100 suggest overbought/oversold conditions.
4.4. Rate of Change (ROC)
Measures the speed of price change.
Usage:
Increasing ROC suggests growing momentum.
Often used with trend indicators to confirm movement.
5. Volatility Indicators
These indicators measure how much price fluctuates.
5.1. Bollinger Bands
Consists of a SMA and two bands (±2 standard deviations).
Usage:
Price touching the upper band = potential overbought.
Price touching the lower band = potential oversold.
Bollinger Band squeeze indicates potential breakout.
5.2. Average True Range (ATR)
Shows average price volatility over a specific time.
Usage:
Not a directional indicator.
Useful for setting stop-loss and target levels.
5.3. Keltner Channels
Similar to Bollinger Bands but use ATR instead of standard deviation.
Usage:
Identify breakouts and trend continuations.
6. Volume-Based Indicators
Forex is decentralized, so volume is often broker-based. However, tick volume can still be useful.
6.1. On-Balance Volume (OBV)
Cumulative volume indicator.
Usage:
Confirms trends.
Divergence from price may signal reversal.
6.2. Volume Weighted Average Price (VWAP)
The average price weighted by volume.
Usage:
Commonly used for intraday analysis.
Helps institutions judge fair value zones.
7. Support and Resistance Tools
7.1. Pivot Points
Calculated from previous period’s high, low, and close.
Types:
Standard
Fibonacci
Woodie
Camarilla
Usage:
Identify potential support/resistance levels.
Useful for intraday and swing trading.
7.2. Fibonacci Retracement
Identifies potential pullback levels.
Common levels: 23.6%, 38.2%, 50%, 61.8%, 78.6%
Usage:
Entry during retracements in trending markets.
Combine with trendlines for confirmation.
7.3. Trendlines and Channels
Drawn manually to connect swing highs/lows.
Usage:
Visualize trend direction and strength.
Breakouts signal potential reversals or continuations.
8. Custom Indicators and Tools
Many platforms allow traders to create or install custom indicators.
Examples:
Harmonic pattern indicators (Gartley, Bat, Crab)
Custom divergence indicators
Multi-timeframe RSI or MACD
Sentiment indicators
9. Chart Patterns and Price Action Tools
While not strictly indicators, chart patterns play a crucial role in technical analysis.
9.1. Classic Chart Patterns
Head and Shoulders
Double Top/Bottom
Triangles (Ascending, Descending, Symmetrical)
Flags and Pennants
Rectangles
Usage:
Reversal and continuation signals.
9.2. Candlestick Patterns
Doji
Hammer
Engulfing
Morning Star/Evening Star
Shooting Star
Usage:
Signal potential turning points.
Combine with support/resistance or trend indicators.
9.3. Price Action Tools
Swing Highs/Lows
Order Blocks
Break of Structure (BoS)
Liquidity Zones
Usage:
Used for precision entries and institutional trading style (Smart Money Concepts - SMC).
10. Combining Indicators for Strategy Building
10.1. The Problem of Indicator Overload
Using too many indicators can lead to conflicting signals and analysis paralysis.
Best Practice:
Combine indicators with different functions.
Example setup:
Trend: 200 EMA
Momentum: RSI
Volatility: Bollinger Bands
10.2. Confluence Trading
Confluence occurs when multiple indicators or tools point to the same conclusion.
Example:
Price hits a Fibonacci level + RSI is oversold + bullish engulfing candlestick.
This increases the probability of success.
11. Trading Strategy Examples
11.1. Moving Average Crossover Strategy
Indicators:
50 EMA and 200 EMA Entry:
Buy when 50 EMA crosses above 200 EMA. Exit:
Opposite crossover or stop-loss under support.
11.2. RSI Divergence Strategy
Indicators:
RSI Entry:
Look for bullish/bearish divergence. Exit:
Take profit at key support/resistance.
11.3. Bollinger Band Breakout
Indicators:
Bollinger Bands Entry:
Enter when price breaks out of a tight band range. Exit:
Use ATR or fixed pip target.
11.4. Ichimoku Cloud Trend Strategy
Indicators:
Ichimoku Kinko Hyo Entry:
Buy when price is above the cloud and Tenkan-sen crosses Kijun-sen upward. Exit:
Close when price enters the cloud or crossover occurs downward.
12. Risk Management Tools on Charts
Besides entry and exit signals, charts also support tools for risk management:
Stop-loss placement using ATR
Take-profit based on recent swing highs/lows
Position size calculator indicators
Trade simulators and replay tools
13. Psychological and Sentiment Indicators
Though not always on the chart, these tools influence market moves.
Commitment of Traders (COT) Report
Retail Sentiment Indicators (from brokers like IG or OANDA)
News sentiment tools
Economic calendars embedded in platforms
Conclusion
Forex charting is both an art and a science. With the right tools and indicators, traders can gain deep insights into market movements, enhance precision, and improve risk-to-reward ratios. However, no single tool guarantees success.
The key is to develop a strategy that suits your trading style—whether scalping, day trading, or swing trading—and consistently use a combination of indicators that complement each other rather than duplicate signals.
To summarize:
Use trend indicators to determine direction.
Use momentum indicators for timing entries.
Use volatility indicators to understand price fluctuations.
Use support/resistance tools to define high-probability zones.
Combine tools intelligently to build robust strategies.
Would you like this content formatted as a downloadable PDF or with visual examples for each indicator?
#forex robot#forex trend indicator#forexsignals#stock market#currency forex online trading#youtube#forextrader#forex market#forextrading#forex
1 note
·
View note
Text
Weighted Moving Average (WMA): Forex Trading Indicator Explained
In the dynamic world of Forex trading, the Weighted Moving Average (WMA) stands out as a crucial tool for traders. Unlike the Simple Moving Average (SMA), the WMA assigns more significance to recent data points, providing a clearer and more accurate reflection of market trends. Understanding how to use the WMA effectively can significantly enhance your trading strategy. What is a Weighted Moving…
#Financial Markets#Forex Trading#Market Analysis#Moving Averages#Technical Analysis#Trading Indicators#Trading Strategies#Trend Identification#Weighted Moving Average#WMA
2 notes
·
View notes
Text
what are the best indicators for forex trading
Introduction
https://secretindicator.com/product/non-repaint-m1-m5-scalping-indicator-for-mt4/
Telegram Channel
Forex trading is a high-potential yet high-risk financial endeavor. Every day, over $7 trillion is traded across global currency markets. But despite the market’s vast opportunities, most traders lose money—not because the market is unpredictable, but because they fail to use the right tools.
Among these tools, indicators play a central role. Forex indicators are essential for analyzing market trends, identifying potential trade setups, and minimizing risk. But with hundreds of indicators available, which ones are the best?
In this comprehensive guide, you’ll learn:
What forex indicators are
The top 10 best indicators used by professionals
How to combine indicators
When and how to use them for best results
Let’s get started.
What Are Forex Indicators?
Forex indicators are mathematical calculations based on historical price, volume, or open interest data. They’re used in technical analysis to forecast potential market movements and improve decision-making.
There are four major types of forex indicators:
Trend indicators – Show the direction of the market
Momentum indicators – Show the speed or strength of the movement
Volatility indicators – Measure price fluctuation
Volume indicators – Show trading activity
Why Are Indicators Important in Forex?
Trading without indicators is like driving blindfolded. While price action alone provides a lot of insight, indicators offer data-driven clarity. They help:
Identify high-probability trade entries and exits
Confirm price action signals
Avoid false breakouts
Maintain discipline and consistency
Professional traders use indicators to reduce emotional decisions and create rules-based strategies.
Top 10 Best Indicators for Forex Trading
1. Moving Averages (MA)
Type: Trend Best for: Identifying overall direction
Simple Moving Average (SMA) and Exponential Moving Average (EMA) are the most common. EMA is preferred by intraday traders because it reacts more quickly to price changes.
Popular Settings:
50 EMA – medium-term trend
200 EMA – long-term trend
20 EMA – short-term trend
Common Strategy:
Buy when 50 EMA > 200 EMA (golden cross)
Sell when 50 EMA < 200 EMA (death cross)
2. Relative Strength Index (RSI)
Type: Momentum Best for: Spotting overbought/oversold conditions
RSI oscillates between 0 and 100:
Above 70 = Overbought
Below 30 = Oversold
Key Advantage: It highlights potential reversals and momentum divergences.
Example Strategy:
Buy when RSI < 30 and price hits key support
Sell when RSI > 70 and price hits resistance
3. MACD (Moving Average Convergence Divergence)
Type: Trend + Momentum Best for: Entry confirmation
MACD uses:
A fast EMA (usually 12)
A slow EMA (usually 26)
A signal line (9 EMA of MACD)
When the MACD line crosses the signal line, it signals a shift in momentum.
Pro Strategy:
Look for MACD crossover + divergence for trend reversals
4. Bollinger Bands
Type: Volatility Best for: Identifying breakouts and price extremes
Bollinger Bands consist of:
A middle band (20-period SMA)
Upper and lower bands at ±2 standard deviations
Key Insight:
Price tends to return to the middle band
Breakouts beyond the bands suggest volatility spikes
Example Use Case:
Buy when price touches the lower band + RSI < 30
Sell when price touches upper band + RSI > 70
5. Stochastic Oscillator
Type: Momentum Best for: Short-term reversal trades
The stochastic oscillator compares the current price to its range over a set period (usually 14).
Values:
Above 80 = Overbought
Below 20 = Oversold
Why It’s Popular:
Great for scalping and intraday trades
Helps time entries in ranging markets
6. Fibonacci Retracement Tool
Type: Support/Resistance Best for: Pullback and reversal zones
Fibonacci levels (38.2%, 50%, 61.8%) are used to identify key areas where price may reverse or continue.
How to Use:
In an uptrend, draw from swing low to high
In a downtrend, draw from swing high to low
Look for trade setups at the 61.8% or 50% retracement levels with confluence (RSI, MACD, etc.)
7. Average True Range (ATR)
Type: Volatility Best for: Setting stop-loss and take-profit levels
ATR shows the average range of price movement over a set number of periods (typically 14).
Benefits:
Helps you avoid setting stop-loss too tight
Adapts to market volatility
Strategy Example:
Set stop-loss at 1.5x ATR below entry in buy trades
8. Ichimoku Cloud
Type: All-in-One Best for: Multi-faceted trend analysis
This powerful indicator shows:
Trend direction
Momentum
Support and resistance
Potential reversals
Cloud (Kumo) areas show support/resistance zones. When price is above the cloud = uptrend, below = downtrend.
Advanced Tool, but highly reliable once mastered.
9. Volume Indicator
Type: Volume Best for: Confirming breakouts
Volume isn’t always easy to interpret in forex (as it’s decentralized), but tick volume indicators can provide insight.
Key Rule:
Breakouts with high volume = strong move
Breakouts with low volume = possible fakeout
Use volume in combination with price action for better confirmation.
10. ADX (Average Directional Index)
Type: Trend Strength Best for: Avoiding weak trends
ADX values:
Below 20 = weak trend
Above 25 = strong trend
Benefits:
Helps filter out sideways markets
Useful for identifying when to trend trade or range trade
Combine ADX with RSI or MACD for high-probability setups.
Best Indicator Combinations for Forex Trading
No single indicator is 100% accurate. Smart traders use indicator combinations for confirmation.
Combo 1: Trend + Momentum
EMA + RSI
EMA shows trend direction
RSI helps time entry on pullbacks
Combo 2: Volatility + Momentum
Bollinger Bands + Stochastic
Great for range-bound trading and scalping
Combo 3: Trend + Volume
MACD + Volume
Confirms momentum and strength behind breakouts
Combo 4: Trend Strength + Reversal
ADX + Fibonacci + RSI
For swing and position traders to catch precise entries
Best Indicators for Different Trading Styles
Trading StyleBest IndicatorsWhyScalping (M1–M5)Stochastic, RSI, Bollinger BandsQuick signals, small reversalsDay Trading (M15–H1)EMA, MACD, RSIBalance of trend and momentumSwing Trading (H4–D1)Fibonacci, RSI, ADX, MACDCapture larger movesTrend TradingEMA, Ichimoku Cloud, ADXIdentify and ride trendsRange TradingBollinger Bands, Stochastic, RSIOverbought/Oversold zones
Tips for Using Forex Indicators Successfully
Don’t Overload Your Chart Use 2–3 complementary indicators. Too many = confusion.
Use Confluence Combine indicators with price action, support/resistance, and chart patterns.
Understand the Math Behind the Indicator Know what your indicator measures so you understand why it gives certain signals.
Backtest and Forward Test Always test your strategy on historical data before going live.
Avoid Repainting Indicators Use non-repaint indicators for consistent and reliable trading results.
https://secretindicator.com/product/non-repaint-m1-m5-scalping-indicator-for-mt4/
#forex market#forex online trading#forex factory#forex news#forex broker#forex ea#forex education#forex#forex indicators#crypto
0 notes
Text

Bollinger bands a powerful indicator for traders of all types
Bollinger Bands consist of three lines -
Middle Band: 20-period simple moving average (SMA)
Upper Band: 2 standard deviations above the middle band
Lower Band: 2 standard deviations below the middle band
0 notes
Text
Bitcoin Finds Support Above 50-Day SMA, But Next Direction Remains Uncertain
Bitcoin is holding steady above its 50-day Simple Moving Average (SMA), showing signs of underlying strength despite a lack of clear directional momentum. With rising trading volume and mixed technical indicators, the next move could swing either way, keeping the market on edge. RSI Holds Neutral As Bitcoin Awaits A Clearer Signal According to Shaco AI, in a recent update on X, Bitcoin is…
View On WordPress
0 notes
Text

Bitcoin Price Prediction: Trader Says $229K Is Next – Here’s the “Golden Cross” Indicator to Watch
Bitcoin is once again at the center of bold predictions as technical indicators flash signs of a potential breakout. Trader Tardigrade, a widely followed analyst on X, has identified a classic “golden cross” formation on the BTC daily chart, a bullish crossover where the 50-day simple moving average (SMA) rises above the 200-day SMA. Historically, this pattern signals the beginning of major uptrends.
This is the fourth golden cross Bitcoin has posted since 2023. The previous three saw price gains of 49%, 125%, and 68%. Applying these historical averages, Tardigrade projects a conservative upside target of $152,000, about 44% higher than today’s price of $106,802.
Under stronger market conditions, however, the analyst sees Bitcoin potentially soaring to $229,000, a move that would represent a 118% rally.
These predictions are rooted in more than just chart patterns. Bitcoin is already up roughly 47% from its April lows and has rallied 656% since the current market cycle began in late 2022. For traders watching closely, the golden cross is not just a pattern; it’s a potential roadmap.
Bitcoin (BTC/USD) Technical Resistance Near $107K Remains Key
As of now, Bitcoin price prediction remains neutral as BTC is trading near a critical resistance zone at $107,270. This level has acted as a ceiling multiple times over the past two weeks, and a breakout of this level can turn the price forecast bullish.
The current 1-hour chart shows a symmetrical triangle formation, with price compressing between rising support and declining resistance lines.
The 50-period EMA at $105,853 has turned upward, confirming short-term bullish momentum. MACD readings support this thesis as the indicator line crosses above the signal, though there’s no aggressive divergence. A recent green candle with a long upper wick suggests sellers are active just above current levels, meaning a breakout will require volume and conviction.
1 note
·
View note
Text
Smarter Decisions with Simple Moving Averages
Let’s dive into a technical analysis tool that’s helped countless investors and business leaders make smarter decisions. This isn’t just for Wall Street traders—anyone leveraging data trends in their professional life can benefit from understanding the Simple Moving Average (SMA). Whether you’re charting stock prices or analyzing customer behavior, the SMA breaks through noise to reveal clarity.…
0 notes
Text
Dogecoin Price Retests 100 SMA Again – Here’s What It Means For Price
After a turbulent price action over the weekend that saw Dogecoin briefly dip below $0.15, the meme-inspired cryptocurrency is now back again to testing an important technical level. Particularly, DOGE is now revisiting the 100-week Simple Moving Average (SMA), which has served as a strong support line for more than a year on the weekly candlestick timeframe, raising questions about what might
Read More: You won't believe what happens next... Click here!
1 note
·
View note
Text
Dogecoin Price Retests 100 SMA Again – Here’s What It Means For Price
Trusted Editorial content, reviewed by leading industry experts and seasoned editors. Ad Disclosure After a turbulent price action over the weekend that saw Dogecoin briefly dip below $0.15, the meme-inspired cryptocurrency is now back again to testing an important technical level. Particularly, DOGE is now revisiting the 100-week Simple Moving Average (SMA), which has served as a strong support…
0 notes
Text
Bitcoin Price Prediction: Trader Says $229K Is Next – Here’s the “Golden Cross” Indicator to Watch
Bitcoin is once again at the center of bold predictions as technical indicators flash signs of a potential breakout. Trader Tardigrade, a widely followed analyst on X, has identified a classic “golden cross” formation on the BTC daily chart, a bullish crossover where the 50-day simple moving average (SMA) rises above the 200-day SMA. Historically, this pattern signals the beginning of major…
0 notes
Text
what is the best indicator in forex
Understanding Forex Indicators
Telegram Channel
https://secretindicator.com/product/non-repaint-m1-m5-scalping-indicator-for-mt4/

Before we dive into which indicator is the best, it's crucial to understand what forex indicators are.
Forex indicators are statistical tools used in technical analysis to forecast future price movements by analyzing past data, primarily price and volume. They help traders:
Identify market trends
Determine entry and exit points
Gauge momentum
Confirm reversal or continuation patterns
There are four main types of indicators:
Trend-following indicators
Momentum indicators
Volatility indicators
Volume-based indicators
The best indicator for you will depend on your trading style, time frame, and risk appetite.
Top Forex Indicators Used by Professional Traders
Let’s explore some of the most widely-used forex indicators. These tools have stood the test of time and are commonly included in professional trading strategies.
1. Moving Average (MA) – Best for Trend Identification
Type: Trend-Following Popular Variants: Simple Moving Average (SMA), Exponential Moving Average (EMA)
A moving average smooths out price data to identify the direction of the trend over a specified period.
SMA gives equal weight to all data points.
EMA gives more importance to recent price action, making it more responsive.
Why It’s One of the Best:
Simple to use
Ideal for identifying bullish or bearish trends
Helps avoid false signals during sideways markets
Popular Strategy: Use crossovers of the 50 EMA and 200 EMA. When the 50 EMA crosses above the 200 EMA, it's a buy signal (golden cross). When it crosses below, it's a sell signal (death cross).
2. Relative Strength Index (RSI) – Best for Measuring Momentum
Type: Momentum Range: 0–100
The RSI is a momentum oscillator that measures the speed and change of price movements.
Above 70 = overbought (potential reversal down)
Below 30 = oversold (potential reversal up)
Why It’s One of the Best:
Helps avoid entering trades at extreme levels
Easy to interpret
Great for confirming other indicators
Pro Tip: Use RSI divergence with price action to catch early trend reversals.
3. MACD (Moving Average Convergence Divergence) – Best All-Rounder
Type: Momentum/Trend-Following
MACD uses two moving averages and a histogram to show the relationship between short-term and long-term momentum.
MACD Line = 12 EMA – 26 EMA
Signal Line = 9 EMA of MACD Line
Histogram = Difference between MACD and Signal Line
Why It’s One of the Best:
Combines trend and momentum analysis
Powerful when used with price action
Works well in multiple time frames
Strategy Example: When MACD crosses above the Signal Line, it’s a bullish signal. When it crosses below, it’s a bearish signal.
4. Bollinger Bands – Best for Volatility Measurement
Type: Volatility
Bollinger Bands consist of:
A 20-period SMA (middle band)
An upper band (SMA + 2 std dev)
A lower band (SMA - 2 std dev)
Why It’s One of the Best:
Shows volatility visually
Helps identify overbought/oversold zones
Useful for breakout trading
Popular Strategy: Buy when price touches the lower band and RSI confirms oversold; sell when price touches the upper band and RSI confirms overbought.
5. Fibonacci Retracement – Best for Support & Resistance
Type: Tool-Based Indicator (not mathematical)
The Fibonacci tool plots horizontal lines at key Fibonacci levels (23.6%, 38.2%, 50%, 61.8%, 78.6%) based on the recent price swing. These levels act as potential support or resistance.
Why It’s One of the Best:
Excellent for identifying reversal points
Works on all timeframes
Combines well with candlestick patterns and trendlines
Strategy Tip: Wait for a bounce off a key Fibonacci level with confirmation from RSI or MACD.
6. Stochastic Oscillator – Best for Timing Entries
Type: Momentum
This oscillator compares a particular closing price to a range of prices over a period.
Readings above 80 = overbought
Below 20 = oversold
Why It’s One of the Best:
Great for spotting short-term reversals
Ideal for scalping and short trades
High accuracy when combined with trend direction
Which Is the Best Forex Indicator?
Short Answer:
There is no single best indicator that fits all situations.
However, if we had to choose one all-rounder, it would be the MACD, due to its ability to combine trend, momentum, and signal clarity.
But let’s break it down by strategy: Trading StyleBest IndicatorWhyScalping (M1, M5)RSI + StochasticFast signals, momentum clarityDay Trading (M15–H1)EMA + MACDTrend + entry/exit precisionSwing Trading (H4–D1)MA + Fibonacci + RSILong-term direction + retracement levelsTrend TradingEMA (50 & 200)Identifies strong trendsRange TradingBollinger Bands + RSIOverbought/Oversold zones
Best Indicator Combinations
Many traders combine indicators to get more reliable signals. Here are a few powerful combos:
1. RSI + MACD
RSI identifies entry zones
MACD confirms momentum
Great for trend and reversal trades
2. EMA + Bollinger Bands
EMA shows trend direction
Bollinger helps you catch breakouts or bounces
3. Stochastic + Support/Resistance
Use stochastic to time entries at horizontal S/R zones
High win-rate in sideways markets
Mistakes to Avoid When Using Indicators
Overloading the Chart: Using too many indicators leads to confusion. Stick to 2–3 complementary tools.
Ignoring Price Action: Indicators should assist—not replace—candlestick analysis and market structure.
Using the Same Type Together: For example, don’t use RSI + Stochastic + CCI all together. They all measure momentum.
No Backtesting: Always test your indicator-based strategy on historical data.
Non-Repaint vs Repaint Indicators
Some indicators “repaint” past signals to make them look more accurate. Avoid these unless you're aware of how they behave.
Non-repaint indicators give fixed signals once a candle closes.
These are preferred for backtesting and real trading.
Examples of Non-Repaint Indicators:
MACD
RSI
EMA
Bollinger Bands
Should You Rely Only on Indicators?
No. Indicators are tools—not holy grails.
The best traders combine:
Technical indicators
Price action
Fundamental analysis
Risk management
Use indicators to enhance your trading, not as a crutch.
Best Indicators for MT4 and MT5
MetaTrader 4 and 5 are the most popular trading platforms. Most of the above indicators are pre-installed. However, for more advanced trading, consider downloading custom indicators like:
TDI (Traders Dynamic Index)
Ichimoku Cloud
Non-repaint scalping indicators
Trend Reversal Dashboard
Supertrend Indicator
Conclusion: What Is the Best Indicator in Forex?
There is no single best indicator for every situation. The key lies in understanding how each indicator works and how to combine them effectively for your trading style.
However, if we rank them based on popularity and versatility:
MACD – Best all-rounder
RSI – Best for spotting momentum shifts
EMA – Best for trend-following
Bollinger Bands – Best for volatility and breakouts
Fibonacci Retracement – Best for entries during pullbacks
https://secretindicator.com/product/non-repaint-m1-m5-scalping-indicator-for-mt4/
#forex market#forex factory#forex online trading#forex education#forex broker#crypto#forex news#forex#forex indicators#bitcoin#stablecoins#cryptonews#blockchain#forex ea
0 notes
Text
How to Read Stock Charts for Beginners?

If you’re new to investing, learning how to read stock charts for beginners can feel like deciphering a foreign language. But don’t worry—it’s easier than it looks. Stock charts are powerful tools that help you understand market trends, spot opportunities, and make smarter investment decisions. Whether you're a casual trader or planning long-term investments, mastering the basics of stock charts is the first step toward building confidence and growing your portfolio.
How to Read Stock Charts for Beginners – Understanding the Basics
Stock charts visually show a stock's price over time. They allow investors to track price movements, trading volume, and patterns that can help predict future performance.
The most common types of stock charts include:
Line charts – Simple and clean, showing the closing prices over a set period.
Bar charts – Display opening, closing, high, and low prices for each time unit.
Candlestick charts – Popular among traders, offering visual cues with color-coded bars.
Key Components of a Stock Chart
1. Price and Time Axes
Stock charts usually have time on the horizontal (X) axis and price on the vertical (Y) axis. This setup shows how the stock's price changes over days, weeks, or months.
2. Volume Bars
Volume bars appear at the bottom of most charts. They show how many shares were traded during a specific period. High volume often means strong interest or big news.
3. Moving Averages
Moving averages smooth out price data over a certain period, helping you spot trends.
Simple Moving Average (SMA): The average price over a defined time (e.g., 50-day SMA).
Exponential Moving Average (EMA): Gives more weight to recent prices.
Reading Candlestick Charts
Candlestick charts are ideal for beginners who want more detail in a visual format. Each candlestick represents one period (like a day) and shows:
Open and Close: The “body” of the candle.
High and Low: The “wicks” or “shadows” above and below the body.
Color: Green means the stock closed higher than it opened; red means it closed lower.
Recognizing common candlestick patterns—like dojis, hammers, and engulfing candles—can help forecast market behavior.
Identifying Trends and Patterns
Understanding trends can help you determine when to buy or sell.
Types of Market Trends
Uptrend: A series of higher highs and higher lows.
Downtrend: A series of lower highs and lower lows.
Sideways/Flat: Little movement in either direction.
Common Chart Patterns
Head and Shoulders: Indicates potential trend reversal.
Double Top/Bottom: Suggests strong support or resistance.
Flags and Pennants: Short-term continuation patterns.
Practical Tips for Beginners
Keep It Simple
Start with line or candlestick charts and focus on one stock at a time.
Combine Charts with Research
Charts are helpful, but always consider news, earnings reports, and broader market conditions.
Use Reliable Tools
Many platforms offer beginner-friendly charting tools. For a helpful resource on getting started, check out this complete beginner’s guide on how to read stock charts.
📊 Final Thoughts + CTA
Learning how to read stock charts for beginners doesn’t have to be overwhelming. By focusing on basic chart types, understanding key components, and recognizing simple patterns, you’ll gain the confidence to analyze stocks like a pro.
1 note
·
View note
Text
52 Week High Breakout Stocks Explained for Beginners

52 Week High Breakout Stocks: A Beginner’s Guide to Smart Trading
Have you ever noticed how some stocks suddenly catch fire and skyrocket in price? Often, these stocks are hitting what's called a 52-week high—the highest price they've reached in the past year. It's like watching a sprinter break their own record, and investors everywhere take notice.
But what does this really mean for you? And how can you use this strategy to your advantage—even if you're just starting out?
In this article, we’ll explore 52 week high breakout stocks in simple, everyday language. We'll unpack how they work, why traders care about them, and how trading courses or a course for trading can guide you to profit smartly and safely.
Discover 52 week high stocks and learn how to trade them smartly. Includes insights on trading courses and the right course for trading.
What Are 52 Week High Stocks?
52 week high stocks are shares of companies that have hit their highest price in the last 12 months. Think of it like an athlete breaking a personal best—it draws attention and signals strong performance.
When a stock breaks this level, it's often seen as a sign of momentum. Traders watch these closely because the stock may keep climbing higher.
Why Do Traders Love 52 Week High Breakouts?
Because breakouts often come with volume and velocity. Picture a dam breaking—once the water flows, it gushes. A breakout means demand is high, and price surges as buyers rush in.
Momentum: Prices can continue rising as more investors pile in.
Clear Entry Point: The breakout level gives a simple buy signal.
Potential for Quick Gains: These setups often lead to short-term profits.
The Psychology Behind Breakouts
Trading isn’t just numbers—it's emotion. When a stock breaks its 52-week high, it gets people excited. Why?
Fear of Missing Out (FOMO): Traders jump in, pushing the price higher.
Confidence: Investors see strength and believe in further growth.
It’s like a crowd cheering louder as the team scores again—it builds momentum.
How to Identify 52 Week High Stocks
You don’t need to dig through piles of data. Most trading platforms highlight 52-week highs in a separate section or filter.
Tips to spot them:
Use stock screeners with the “52 Week High” filter
Focus on high volume breakouts
Look at recent news for the stock
Technical Indicators That Help
To boost your confidence in a breakout, pair it with technical analysis. Here are tools that work:
Volume Spike: Confirms strong interest.
Moving Averages (50/200 SMA): If the breakout is above these, even better.
Relative Strength Index (RSI): Shows if a stock is overbought.
MACD: Helps validate momentum.
Risks Involved with Breakout Trading
Of course, no strategy is foolproof. Breakouts can fail, trapping traders who buy late.
Common risks:
False Breakouts: Stock crosses the level but reverses quickly.
High Volatility: Big price swings can shake out weak hands.
Emotional Trading: Chasing too late can lead to losses.
Always use stop-loss orders to protect yourself.
Real-Life Example of a Breakout Stock
Let’s take Tata Motors as an example.
In 2023, Tata Motors hit a 52-week high after a strong earnings report. The breakout came with high volume and media buzz. Traders who entered early rode the wave for a solid 15-20% return in a few weeks.
Moral? When price, volume, and news align—magic can happen.
Common Mistakes to Avoid
Here’s what to not do:
Jumping in without confirmation
Ignoring volume
Buying after a huge spike
Skipping risk management
Remember: The goal is consistent gains, not gambling.
How to Build a Breakout Watchlist
Smart traders keep a list of potential breakout candidates.
What to include:
Stocks near 52-week highs
Stocks with upcoming earnings or news
High relative volume movers
Use a spreadsheet or app like TradingView to track these daily.
How Much Capital Should You Start With?
You don’t need a fortune.
Many traders begin with ₹10,000–₹50,000, especially for short-term plays.
Rule of thumb: Never risk more than 1–2% of your capital on a single trade. It's like learning to swim in a pool before diving into the ocean.
Role of News and Sentiment in Breakouts
Never ignore the news. It acts like fuel for a breakout.
Earnings Reports
Mergers & Acquisitions
Government Policy Changes
Sector Boom (like EV or AI)
Use news apps or Twitter to stay in the loop.
Intraday vs. Swing Trading on Breakouts
Both styles work, but they’re different.
Intraday Trading: Quick in-and-out trades, perfect for volatile breakouts.
Swing Trading: Hold for days/weeks to catch extended runs.
Choose based on your schedule and risk tolerance.
Choosing the Right Course for Trading
Want to level up your skills? A course for trading can be a game-changer.
What to look for:
Practical strategies, not just theory
Real-life examples
Live sessions or community support
Affordable pricing
Make sure it includes modules on 52 week high stocks and breakout strategies.
How Trading Courses Can Boost Your Success
Think of a trading course as a shortcut through the maze.
Structured Learning: Saves years of trial and error
Guidance from Pros: Learn from those who’ve been there
Confidence Boost: You’ll know why you’re entering or exiting trades
Good trading courses bridge the gap between beginner and consistent profits.
Final Thoughts on Riding the Breakout Wave
52 week high breakout stocks offer exciting opportunities—but they’re not magic beans.
With the right mindset, proper risk control, and maybe a good trading course, you can trade them with clarity and confidence. Remember, the market rewards preparation—not luck.
So why wait? Start small, stay sharp, and trade smart.
FAQs
What are 52 week high breakout stocks? These are stocks that have crossed their highest price in the past 52 weeks, often seen as a bullish signal by traders.
Are 52 week high stocks good for beginners? Yes, especially if you pair them with technical indicators and proper risk management. Start with paper trading to practice.
Can I make quick profits with breakout trading? You can, but it comes with risks. Use stop-losses and only trade with money you can afford to lose.
Do I need a trading course to trade breakouts? While not mandatory, a course for trading can drastically improve your understanding and results by teaching tested strategies.
How do I know if a breakout is real or fake? Look for high volume, confirmation from indicators like RSI and MACD, and avoid entering trades based solely on price spikes.
0 notes
Text
Data Indicates A Bullish Market Outlook For Bitcoin
Bitcoin's 50-day simple moving average reached a record high, indicating a bullish market outlook.
However, the narrowing spread between bitcoin's price and the 50-day SMA suggests a potential price correction.
Recent data shows increased profit-taking by holders, aligning with the caution indicated by the price-to-SMA spread.
0 notes
Text
Whales Are Back: Is Uniswap About to Explode?
Uniswap (UNI) is currently trading at $6.3020, down by 0.53% in the past hour and 5.64% over the last 24 hours. Despite this short-term dip, growing whale activity and new ecosystem developments suggest bullish undercurrents, supporting a positive Uniswap price prediction in the near term.Aa

UNI’s price sits above the 50-day Simple Moving Average (SMA) of $5.9265, but still well below the 200-day SMA at $9.3644—signaling a market in transition. The current circulating supply of UNI stands at 628.7 million tokens, and trading volume over the past 24 hours exceeds $372 million, reflecting strong market participation.

A major catalyst is the launch of Spark on Unichain, Uniswap's Layer-2 network built using Optimism’s OP Stack. This new feature introduces native stablecoin yields on USDC, offering Uniswap users the ability to earn passive income directly on the platform.
Spark Finance is also now live on Optimism, extending yield opportunities through sUSDS—another stablecoin issued by Sky. These yields can be utilized across DEXs and DeFi lending platforms, deepening Uniswap’s integration within the broader DeFi ecosystem.
Also Read: Bittensor Price Prediction 2025, 2026 – 2030

Moreover, recent data from IntoTheBlock reveals a sharp uptick in large UNI transactions (over $100,000). This spike points to renewed whale interest. Such activity during a consolidation phase is often interpreted as accumulation, a pattern that historically precedes bullish breakouts.
While UNI faces near-term selling pressure, the combination of protocol innovations and institutional-sized transactions offers a promising outlook. Investors should monitor both price trends and on-chain activity, as these developments may be signaling the early stages of a trend reversal.
With yield opportunities increasing and whale interest rising, Uniswap may be positioning itself for a stronger performance in the weeks ahead.
0 notes