#Scope of Commodity Plastics industry
Explore tagged Tumblr posts
Text

VIII. Emancipation of Credit
Having shown that the voluntary organization of mutual credit is fully practicable; that the medium of exchange would thus be shorn of the difficulties which prevent labor from freely capitalizing products; that the various “banks” thus organized, private or associative, to exercise social functions, by a system of mutual clearance would indefinitely extend credit; that all the difficulties now so easy to conjecture would be solved as they were respectively recognized : – we may now proceed to claim for it the following beneficent results:
1. LABOR THE STANDARD OF VALUE. In demonetizing gold and silver, thus depriving them of the royalty they now exercise among commodities, it would destroy their use as standards of value and leave labor expended, the cost of production, the regulator of value. Value being determined by the proportional relation between products, this relation would no longer be sought in a fluctuating standard but measured by the extent and degree of labor expended and thus establish equity in exchange. Nor need there be a conventional standard agreed upon, for free competition would itself lead to equitable relations by and through experience and equality of opportunities, establishing a just rate measured by the intensity and skill of the exertion and degree of repugnance overcome. The agreement being voluntary, every banking company would find their own interest enhanced through competition in finding and acting upon what might be called this natural value. Prices, like everything else following the line of least resistance, in the absence of artificial conduits would naturally flow into equitable relation with cost of labor, thus giving to exertion its full reward. Inflation of credit could not be greater than the increase of surplus wealth deemed acceptable as security, and no such increase of circulating medium, therefore, could affect prices disastrously, or otherwise, below the standard of labor value, for it would measure it as the thermometer does heat. Nor could contraction raise prices, for in currency as in everything else under freedom supply would follow demand.
2. CESSATION OF INTEREST. It would remove the cause for usury without destroying incentive to production. In taking from capital its ill-gotten usufruct of labor the impetus to the production of wealth, in which all classes would be equally benefited and with no artificial limit to its scope and development, would remain because individual initiative would have greater freedom and fuller opportunities. But under our present boasted “incentives” we find individuality narcotized by divorcing capital from labor, accompanied with exhibitions of paternal care. And this would naturally result without calling in authority to accomplish what it, from its very essence, has always been averse to entertain – liberty. The necessity for exertion remaining, opportunity open to gratify wants and means to capitalize wealth, or even day’s labor, together with increased leisure and the more perfect development of individual aptitudes, is sufficient ground for the firm conviction that the extension of freedom into economic relations would not cause mankind to deteriorate into barbarism as our economic apologists for militancy affect to believe. To thus except Economics from the universally beneficent effect of greater freedom is to impugn evolution itself.
All wealth would in a just sense be available as capital when desired; and freedom prevailing no more could receive acceptance as security than would guarantee such. Every portion of this wealth converted by credit to reproductive purpose would be employed without exploiting one of those who give to products their real value, for labor and capital would be united, the reverse sides of the came exertion.
3. EMANCIPATION OF LABOR. The industrial type of social life could then realize its ideal, wherein plasticity excludes rigidity and order be founded on progress; than [sic] only would industrial emancipation become a fact. The producer would no longer be repressed by the fluctuating demand of a speculative market, nor beguiled by twilight schemes of occupancy of land without access to means for use, but be benefited by every new appliance which tended to reduce the exhaustiveness of toil. The opportunities for labor would increase as its wealth-producing qualities became more equitably shared, and ability to increase it receive no damper from fear that the fruits of exertion would be swallowed up by some device of privilege. In the incentive given to production emulation would be incited, ambition aroused, higher desires created and every element of individuality called into healthful exercise rather than repressed. Economics would no longer assert with Roscher that
“The condition of workmen can be continued good or materially improved only on condition that their number increase less rapidly than the capital destined for its wages.”
Nor follow it with the remark:
“Much especially depends upon their foresight and self-control as regards bringing children into the world. Without this latter virtue even the favorable circumstances would be soon trifled away!”
On the contrary, the toiler instead of remaining a hireling in the industrial forces, would not only have every manly faculty aroused, but every opportunity given through increased demand and fuller reward to rise to independence. While free land has been posited as the first element, because land is the source of all wealth, it is now evident that access to vacant land alone would not emancipate labor. As in the realm of biology the higher we rise in the scale of being the more complex functions become, so in Economics we find social functions much more complex in exchange than in land tenure. Waiving discussion whether abolition should precede from the simple to the complex to facilitate normal growth, it may be easily shown, if not already seen, that the monopoly of exchange involving the whole domain of distribution has a much more depressing influence upon the realization of the industrial type than land monopoly. Monopoly of credit carries with it privileged capital, extortion of interest, the struggle for profits, the greater part of the necessity for taxation and the prime cause for labor exploitation. With abolition of privilege here the desire to monopolize land would be curtailed. Bonanza estates are valueless to their holders save as restriction of access to capital drives needy labor to sell itself thereon. Even if emancipation here had no reflex action upon land holding, inability now possessed by capital to exploit would render land held for other than useful purposes a most undesirable investment. The difference is as great as between broad daylight and hazy twilight.
Social wealth and prosperity would then be attained, and by the only way it ever can be, by the wealth and prosperity of the individuals who together constitute society. The “Dismal Science” would no longer compute averages to show that in the prosperity of some an average well-being results, but in the incentive given to exertion, in the ever-widening circle of wants that freedom can alone call forth, betake itself to computations on the possibilities of a civilization founded on “ the greatest good to” ALL, instead of being the philosophy of speculation upon human misfortune and misery, and the art of expounding existing temporary relations as natural laws.
Finally, in the words of Col. Greene:
“The existing bank reproduces the aristocratic organizations; it has its Spartan element of privileged stockholders, its Laconian element of obsequious speculators, etc., on the outside a multitude of Helots who are excluded from its advantages. Answer us, reader: If we were able at this time to bring forward the existing banking system as a new thing, and should recommend its adoption, would you not laugh in our face and characterize our proposition ridiculous? Yet the existing system has an actual and practical being in spite of all its imperfections; nay, more, it is the ruling element of the present civilization of the Christian world; it has substituted itself, or is now substituting itself, in the place of monarchies and nobilities. Who is the noble of the present day, if not a man who lends on interest? Who is the emperor if not Rothschild? Now, if the present system of banking is capable of existence, how much more capable of actual existence is the system of mutual banking? Mutual banking combines all the good elements of the method now in operation, and is capable of securing a thousand benefits which the present method cannot compass, and is, moreover, free from its disadvantages! ”
#economics#history#industry#labor#money#sociology#work#anarchism#anarchy#anarchist society#practical anarchy#practical anarchism#resistance#autonomy#revolution#communism#anti capitalist#anti capitalism#late stage capitalism#daily posts#libraries#leftism#social issues#anarchy works#anarchist library#survival#freedom
2 notes
·
View notes
Text
Cellulose Ethers Market is estimated to grow at a CAGR of 6.1% during the forecast period 2024-2031
What Are Cellulose Ethers?
Cellulose ethers are modified forms of cellulose—a natural polymer derived from plant cell walls—where hydroxyl groups are replaced by ether groups such as methyl, ethyl, hydroxypropyl, hydroxyethyl, or carboxymethyl. These derivatives are water-soluble or swellable, imparting unique properties such as thickening, binding, emulsifying, film-forming, and stabilizing. Widely used in construction, pharmaceuticals, food, personal care, paints, adhesives, and oil drilling, cellulose ethers enhance viscosity, texture, moisture retention, and stability across diverse applications.
Global Market Overview
The cellulose ethers market is estimated at around USD 2.3–2.8 billion in 2024. It is projected to grow steadily to between USD 3.8 billion and USD 4.5 billion by 2030, representing a compound annual growth rate (CAGR) of 6.1%. Sustained demand in construction, especially for tile adhesives and cement mortars, along with rising needs in pharmaceuticals and food-grade applications, are driving this growth.
To buy the sample report, click on https://www.datamintelligence.com/buy-now-page?report=cellulose-ethers-market
Key influencing factors include:
Construction investment in emerging markets
Pharmaceutical demand for controlled-release formulations
Consumer interest in clean‑label food and personal care products
Expansion of oilfield services and industrial adhesivesTo get sample report, cilck on https://www.datamintelligence.com/download-sample/cellulose-ethers-market
Market Drivers & Growth Opportunities
1. Construction & Building Solutions
Cellulose ethers—particularly hydroxyethyl and hydroxypropyl methylcellulose—are essential in tile adhesives, concrete repair mortars, and self-leveling screeds. They provide improved workability, water retention, adhesion, and freeze–thaw stability. Rapid urbanization, renovation needs in mature markets, and infrastructure development in Asia-Pacific contribute strongly to market demand.
2. Pharmaceutical & Personal Care Demand
In pharma, cellulose ethers serve as binders, controlled-release agents, and tablet coatings. They also act as stabilizers in suspensions and emulsions. In personal care, they enhance emulsification, consistency, and moisturizing; products like shampoos, creams, and lotions frequently rely on cellulose ethers for smooth texture and stability.
3. Food & Nutrition Applications
Cellulose ethers are prized for thickening, stabilizing emulsions, and replicating fat texture in sauces, dressings, ready meals, dairy alternatives, and bakery items. With consumers seeking clean-label ingredients, plant-based, non-GMO cellulose derivatives are gaining prominence.
4. Painting, Coatings & Adhesives Industry
These derivatives improve binding, rheology, sag resistance, and film formation in paints, coatings, adhesives, and sealants. Water‑based formulations and low-VOC standards increase demand for cellulose-based additives compatible with sustainable coatings.
5. Oil & Gas Drilling Fluids
Used as viscosity enhancers and fluid loss control agents in drilling and fracturing fluids, cellulose ethers meet the needs of mature oilfields focused on stable and efficient operations.
6. Commodity & Sustainability Pressure
Global regulatory efforts to reduce plastic micro‑pollutants favor bio-based cellulose ethers over synthetic polymers, especially in Europe and North America.
7. Formulation & Processing Innovation
Trends toward nano-particle stabilization, combination with biopolymers like guar or xanthan, and custom grades for 3D printing or high-performance coatings point to expanded application scope.
To get the unlimited market intelligence, subscribe to https://www.datamintelligence.com/reports-subscription.
U.S. Market Trends
The U.S. cellulose ethers market is well-established, accounting for approximately 25–30% of global demand. Key growth segments include:
Construction & Infrastructure: Renovation and green building projects are stimulating use in cementitious materials and energy-efficient roofing.
Pharmaceuticals: Rising demand for extended-release tablets and controlled oral delivery systems is fueling new applications.
Food & Consumer Goods: Ethylcellulose and methylcellulose are gaining traction in plant-based food items, gluten-free bakery, and clean-label formulations.
Research & Development: Collaborations between additive manufacturers and universities focus on controlled-release systems, 3D printed biocompatible gels, and sustainable adhesives.
Major U.S. players supplement domestic production with imports, catering to high purity and food-grade industry standards.
Japan & Asia‑Pacific Market Trends
Japan plays a pivotal role in specialty cellulose ethers, with strong manufacturing activity and ongoing innovation:
Pharma and Cosmetics: Japan’s high-performance pharmaceutical and beauty sectors drive demand for premium-grade hydroxypropyl methylcellulose and ethylcellulose.
Eco-conscious Construction: Use in self-leveling mortars and indoor finishing products aligns with local environmental regulations.
Domestic R&D: University-industry partnerships focus on sustained-release drug delivery, edible coatings, and bio-inspired adhesives.
Export-Driven Production: Japanese manufacturers are supplying high-end cellulose ether grades to regional markets.
Across Asia-Pacific, rising urbanization, e-commerce growth, and infrastructure projects are fueling broader demand, especially in China, India, and Southeast Asia.
European & Global Sustainability Trends
In Europe, regulations like REACH and green-building mandates are accelerating the move to bio-based, non-toxic additives—favoring cellulose ethers.
Global coating and adhesives industries are shifting toward water-based systems and reduced VOC emissions, enhancing opportunities for cellulose ether integration.
Clean-label food trends reinforce acceptance of cellulose ethers in plant-based and gluten-free categories.
Eco-certifications and consumer preferences for plant-derived ingredients further bolster global adoption.
Competitive Landscape
Prominent players in the cellulose ethers market include Ashland, Dow, DuPont, Shin-Etsu, Nippon Soda, SE Tylose, Celanese, CP Kelco, and Dai-ichi Kogyo Seiyaku. Competitive strategies include:
Investment in high-purity, food/pharma-grade production
Collaboration with OEMs across coatings and 3D printing industries
Development of novel grades such as ultra-low temperature gelling or high-viscosity film formers
Regional expansion to serve construction and consumer markets
Challenges and Market Considerations
Raw Material Cost Volatility: Cellulose and chemical feedstock price fluctuations affect margins.
Applications Diversification: As standard uses mature, companies seek new application areas like functional foods, battery gels, and filtration membranes.
Regulatory Compliance: Injection into pharma, food, or environmentally sensitive products requires high regulatory and purity standards.
Market Consolidation: Price competition and global capacity growth may put pressure on margins.
Strategic Recommendations
Prioritize Specialty Grades Focus on high-margin, niche segments like pharma, cosmetics, and clean-label food applications.
Expand Coatings & Adhesives Portfolio Align new product lines with global low-VOC and waterborne material mandates.
Scale Sustainable Solutions Invest in biodegradable and FSC-certified cellulose sources for eco-conscious positioning.
Capitalize on Pharma Growth Partner with drug developers to create targeted-release drug delivery formulations.
Expand in Emerging Markets Establish local service and supply chains to meet the needs of booming construction and consumer packaging sectors.
Conclusion
The cellulose ethers market stands at a pivotal growth juncture, fueled by enduring demand from construction, pharmaceuticals, food, personal care, and coatings sectors. Technical innovation, sustainable material preferences, and geographic expansion—in both developed and emerging markets—present a multifaceted landscape for businesses to capitalize on.
Manufacturers and stakeholders who focus on specialty, high-purity grades, sustainability, regulatory excellence, and emerging applications stand to lead the next wave of growth in this dynamic and essential industry.
About Us
DataM Intelligence is a global market research and consulting firm dedicated to delivering strategic insights across high-growth industries such as chemicals and clean technology. Our comprehensive reports offer market sizing, competitive analysis, segmentation, and actionable forecasts—empowering clients to identify opportunities and manage risk confidently.
Contact Us
DataM Intelligence
Email: [email protected]
Phone: +1 877 441 4866
0 notes
Text
The Future of Oil and Gas Construction in UAE: Trends and Opportunities
UAE has become the backbone of the Global Oil and Gas sector for a long time due to its wealth and location. The energy landscape is changing globally as countries transition to greener sources of energy, and the UAE is responding by adopting technologies and strategies that will allow it to maintain an oil and gas industry. In this blog we will discuss the future of oil and gas construction in UAE with the top trends and opportunities impacting the industry.

Embracing Technological Advancements
Within the oil and gas construction in UAE, technology has become a certain key for innovation. This is the reason why more and more companies are investing in advanced technologies like artificial intelligence (AI), machine learning, and the Internet of Things (IoT) to optimize their operations and become more productive. AI-based analytics are predicting equipment failure, minimizing downtime as well and maintenance costs. Simultaneously, IoT devices are delivering immediate information about the integrity of pipelines and the performance of equipment, assuring safety and reliability.
Focus on Sustainability
As global concerns about environmental impact continue to rise, one of the main focuses of the UAE oil and gas industry is sustainability. From carbon capture and storage (CCS) and enhanced oil recovery (EOR) techniques, companies are making green moves to reduce carbon emissions. The incorporation of renewable energy assets — both solar and wind — into traditional oil and gas operations is also increasing, lowering the industry’s carbon footprint.
Further Development of Offshore Projects
The UAE is developing offshore oil and gas projects to unlock undeveloped reserves. Offshore drilling is an immense opportunity, and improvements in drilling technologies are making it more promising and cheaper. As they expand, specialized construction services are needed for rig construction, subsea infrastructure, etc. This presents an enormous opportunity, particularly for companies that can provide innovative capabilities for offshore construction tasks.
Infrastructure Development Investment
The UAE government is investing heavily in infrastructure construction to support oil and gas sector development. New pipelines, storage facilities, and refineries are added to increase capacity and efficiency. International investments and collaboration between local and international companies are being sparked by the establishment of industrial zones and Free Trade Zones, including the Abu Dhabi National Oil Company's (ADNOC) Ruwais complex.
Strategies for Coping with UAE Oil Industry Trends
UAE oil industry trends: The changing tides of 2023 Add value, petrochemicals and refining be able to spelunking g benefits to their companies. Producing high-value commodities, like plastics and fertilizers is a strategic step toward reducing dependence on volatile oil markets. The UAE is also looking to produce hydrogen as a clean energy path in line with global decarbonization strategies.
Opportunities for Growth
The scope for oil and gas construction in UAE is indeed flourishing and in fact offers ample opportunities for growth and development. Those companies that can swiftly adjust to changing industry dynamics and embrace innovation will be successful. Some key growth opportunities in the sector include:
Partnering and Internationalism: Partnering with foreign firms and technology providers can drive the sharing of innovative technologies and proven best practices, which improves competitiveness.
Talent Development: As our capabilities expand, so must our workforce. High levels of demand will be experienced by professionals with AI, data analytics, and sustainable practices.
Local Content and ICV: Developing local content and in-country value strategies to align with the UAE government policies can help build long-term businesses.
Diversifying and Integrating: Expanding into petrochemicals and refining operations can add value and, through enhanced downstream access, reduce dependency on crude oil exports.
Final Thoughts
With innovation and sustainability as its core values, the construction sector is pivotal in UAE's oil and gas industry on going evolution. This is also complemented by technological innovations, sustainability measures, efficient supply chains, new players, and investment opportunities. In this ever-changing and competitive landscape, companies achieve success by staying in touch with trends and capitalizing on opportunities in the oil industry of UAE. So, welcome to the transformative realm of oil and gas construction in UAE, where innovation reigns, resilience thrives, and opportunities are ripe for the taking.
Tekzone: Your Reliable Partner in Oil and Gas Construction
Tekzone is innovative in the UAE oil and gas construction. We are ready for your toughest projects, with a mission and focus on excellence, sustainability, and smart technology. From offshore construction to sustainable practices and advanced technologies, Tekzone is the partner you can trust. Find out more now about how we can help you through the path towards oil and gas construction of the future. Contact us to set up a consultation with our specialists or visit TEKZONE for more information.
0 notes
Text
The Future of Elastomers: Why TPVs Are Gaining Market Traction
The global thermoplastic vulcanizates market size is expected to reach USD 2,921.80 million by 2030, registering a CAGR of 8.7% during the forecast period, according to a new report by Grand View Research, Inc. Growing demand for the lightweight, high-performance materials from the automotive industry is expected to drive the global thermoplastic vulcanizates (TPV) market.
Increasing government intervention in fuel efficiency has led to the use of high-performance engineering plastics, including TPV, spurring demand. The growth of the consumer goods industry in the BRIC countries is also expected to have a positive impact on the global market. Price volatility for the key commodities is expected to remain a major concern for the market participants during the forecast period.
In addition, the growing demand for bio-based thermoplastics is expected to positively influence the overall market growth in the coming years. The continuing scarcity of fossil resources and the rise in crude oil prices have forced the world to look for new solutions regarding the development of TPV from renewable raw materials. Growing concerns about toxic problems associated with petrochemicals, as well as the depletion of crude oil reserves, have spurred the development of bio-based TPVs.
Government regulations restricting the consumption of petrochemical-based TPVs in certain areas such as consumer goods and medical devices are expected to further stimulate bio-based products in the thermoplastic vulcanizates market.
In the field of thermoplastic elastomers, the development of bio-based TPVs is in its early stage. However, it has a huge scope in the future as an alternative to its petrochemical counterparts. Furthermore, bio-based TPVs have the potential to substitute petrochemical-based TPVs in the existing markets as well as open up new perspectives, which is expected to create lucrative growth opportunities for bio-based thermoplastic vulcanizates in the coming years.
Depending on the application, the market is divided into automotive, liquid, consumer, medical, footwear, and others. Among them, medical applications are expected to show the fastest growth during the forecast period. High demand for advanced medical services due to the presence of increasing aging of the population, well-developed healthcare infrastructure, and increasing incidences of cardiovascular diseases worldwide is expected to drive the demand for medical devices, which in turn will positively affect the demand for TPV in medical applications.
Thermoplastic Vulcanizates Market Report Highlights
The global thermoplastic vulcanizates (TPV) market was valued at USD 1.65 billion in 2023 and is estimated to expand at a CAGR of 8.7% from 2022 to 2030
The automotive segment led the market and accounted for more than 58.0% share of the global revenue in 2023
The significant demand is attributed to the rising demand for lightweight and high-performance materials in the automotive industry
The thermoplastic vulcanizates market in Asia Pacific is expected to be one of the fastest-growing markets over the forecast period.
India thermoplastics vulcanizates market to witness a growth of 9.5% during the forecast period
Curious about the Thermoplastic Vulcanizates Market? Get a FREE sample copy of the full report and gain valuable insights.
Thermoplastic Vulcanizates Market Segmentation
Grand View Research has segmented the global thermoplastic vulcanizates market report based on the grade, processing method, application and region:
Thermoplastic Vulcanizates Grade Outlook (Volume, Tons; Revenue, USD Million, 2018 - 2030)
Natural
Standard Black
Pre-Colored
Others
Thermoplastic Vulcanizates Processing Method Outlook (Volume, Tons; Revenue, USD Million, 2018 - 2030)
Injection Molding
Extrusion Molding
Blow Molding
Thermoplastic Vulcanizates Application Outlook (Volume, Tons; Revenue, USD Million, 2018 - 2030)
Automotive
Exteriors
Interiors
Construction & Architecture
Consumer goods
Electric & Electronics
Medical & Healthcare
Others
Thermoplastic Vulcanizates Regional Outlook (Volume, Tons; Revenue, USD Million, 2018 - 2030)
North America
US
Canada
Mexico
Europe
Germany
UK
France
Italy
Spain
Netherlands
Eastern Europe
Russia
Poland
Hungary
Czech Republic
Belarus
Bulgaria
Romania
Slovakia
Asia Pacific
Japan
China
India
Australia
South Korea
Central & South America
Middle East & Africa
Key Players in the Thermoplastic Vulcanizates Market
Dawn Polymer
Ravago Manufacturing.
RTP Company
DuPont de Nemours, Inc.
Mitsui Chemicals Inc.
Celanese Corp.
LyondellBasell Industries Holdings B.V.
Mitsubishi Chemical Corp.
KRAIBURG TPE GmbH & Co. KG
Teknor Apex Company, Inc.
Trinseo
Hexpol AB
JSR Corporation
Zeon Corporation
Order a free sample PDF of the Thermoplastic Vulcanizates Market Intelligence Study, published by Grand View Research.
0 notes
Text
Analyzing the Engineered Plastics Market: Trends and Growth Potential
Engineered plastics, also known as engineering plastics market, are a group of plastic materials that have enhanced mechanical and thermal properties, making them suitable for more demanding applications than standard plastics. These materials are used in a wide range of industries, including automotive, aerospace, electronics, and healthcare. This article explores the current trends, driving forces, challenges, and future prospects of the engineered plastics market.
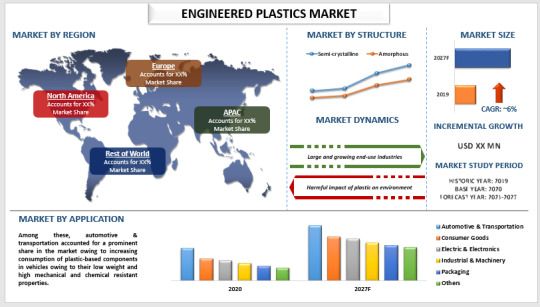
Understanding Engineered Plastics
Engineered plastics are polymers that exhibit superior strength, heat resistance, and durability compared to commodity plastics. Common types of engineered plastics include polycarbonate (PC), acrylonitrile butadiene styrene (ABS), polyamide (PA or nylon), polyoxymethylene (POM or acetal), and polyphenylene oxide (PPO). These materials are used in applications that require high performance and reliability.
Key Market Drivers
Growth in End-Use Industries: The expansion of industries such as automotive, aerospace, electronics, and healthcare is a major driver for the engineered plastics market. These industries demand materials that can withstand harsh environments, offer high precision, and contribute to lightweighting and energy efficiency.
Technological Advancements: Innovations in polymer science and manufacturing processes are enhancing the properties of engineered plastics. Advances such as reinforced composites, biodegradable polymers, and 3D printing materials are broadening the application scope of engineered plastics.
Environmental Regulations and Sustainability: Stringent environmental regulations and the growing emphasis on sustainability are driving the demand for engineered plastics. These materials are often recyclable, contribute to energy savings through lightweighting, and can replace metal parts, reducing the overall environmental impact.
Market Segmentation
The engineered plastics market can be segmented based on type, application, and region.
By Type:
Polycarbonate (PC): Known for its high impact resistance and transparency, used in automotive parts, electronics, and medical devices.
Acrylonitrile Butadiene Styrene (ABS): Offers good toughness and rigidity, used in automotive components, consumer electronics, and toys.
Polyamide (PA or Nylon): Known for its strength and wear resistance, used in automotive parts, textiles, and industrial applications.
Polyoxymethylene (POM or Acetal): Provides high stiffness and dimensional stability, used in precision parts like gears and bearings.
Polyphenylene Oxide (PPO): Offers high thermal stability and electrical insulation, used in electrical and electronic components.
By Application:
Automotive: Engineered plastics are used for components like fuel systems, interior and exterior parts, and under-the-hood applications.
Aerospace: These materials are used in lightweight structural components, interior parts, and insulation.
Electronics: Used in housings, connectors, and circuit boards.
Healthcare: Employed in medical devices, surgical instruments, and diagnostic equipment.
Industrial: Used in machinery parts, gears, bearings, and conveyor systems.
By Region:
North America: Driven by advancements in technology and the presence of key end-use industries.
Europe: Emphasis on sustainability and high-performance materials.
Asia-Pacific: Rapid industrialization and growth in automotive and electronics industries.
Latin America and Middle East & Africa: Emerging markets with increasing demand for high-performance materials.
Challenges in the Market
Despite the positive growth outlook, the engineered plastics market faces several challenges:
High Costs: The production and raw material costs for engineered plastics are higher than for commodity plastics, which can limit their adoption in cost-sensitive applications.
Regulatory Compliance: Meeting stringent environmental and safety regulations requires continuous innovation and investment in research and development.
Market Competition: The market is highly competitive, with numerous players offering a wide range of products. Differentiating based on quality, performance, and sustainability is crucial for gaining a competitive edge.
Request for a sample of the report browse through- https://univdatos.com/get-a-free-sample-form-php/?product_id=23691
Future Prospects
The future of the engineered plastics market is promising, with several growth opportunities on the horizon:
Advancements in Composite Materials: The development of reinforced composites and hybrid materials will enhance the performance characteristics of engineered plastics, expanding their application range.
Growth in Emerging Markets: Emerging economies in Asia-Pacific, Latin America, and Africa present significant growth opportunities. Increasing industrialization and infrastructure development in these regions will drive the demand for engineered plastics.
Sustainability Initiatives: The push for sustainability will continue to drive innovations in biodegradable and recyclable engineered plastics. These materials will play a crucial role in reducing the environmental impact of various industries.
Conclusion
The engineered plastics market is set for robust growth, driven by the expansion of end-use industries, technological advancements, and sustainability trends. While challenges such as high costs and regulatory compliance persist, innovations in composite materials and the growth of emerging markets offer substantial opportunities. As industries evolve, engineered plastics will continue to play a vital role in delivering high-performance, durable, and sustainable solutions.
Contact Us:
UnivDatos Market Insights
Email - [email protected]
Contact Number - +1 9782263411
Website -www.univdatos.com
0 notes
Text
Common Questions: The Mechanism for Adjusting the Carbon Border (CBAM)
To support you in your role as CBAM in Agile Advisors, A price will be applied to various carbon-intensive items imported into the EU under the recently implemented Carbon Border Adjustment Mechanism, a carbon pricing scheme by the EU.EU importers will have to acquire carbon certificates equal to the carbon price they would have paid if the imported goods had been produced under the EU's Emission Trading System (ETS) and disclose the upstream emissions in some imported items under the CBAM regulations. The equivalent cost may be subtracted from the EU importer's CBAM payment obligation if a non-EU manufacturer can show that they have already paid for the carbon used to manufacture the imported goods in a third nation.

We are Agile Advisors' CBAM regulations, there is a chance for "carbon leakage" as the EU steps up its efforts to combat climate change while non-EU nations continue to have laxer climate laws. Carbon leakage occurs when EU producers shift their carbon-intensive production operations to countries with laxer climate regulations or when carbon-intensive imports of equal value replace EU-made goods. The purpose of the CBAM is to maintain competitiveness between the EU and its trading partners and achieve carbon cost parity between domestically produced and imported goods. The following are the CBAM's goals: to stop the leakage of carbon by deterring businesses from moving to nations with laxer environmental laws. The following stakeholders will be most impacted by CBAM in the medium term.
Serving as an Agile Advisors Carbon Border Adjustment Mechanism, EU Importers businesses in the EU that bring in products covered by CBAM. EU importers will have to buy carbon certificates equal to the carbon price they would have paid if the imported items had been produced under the EU's ETS and disclose the upstream emissions for the relevant imported goods. Non-EU Operators: Manufacturers ("operators") who manufacture goods covered by CBAM outside of the EU and sell them to EU consumers. The obligation to track and report embedded emissions of goods manufactured and intended for export to the EU rests with non-EU operators. EU Consumers: Businesses operating in the EU that use commodities covered by CBAM as product or process inputs but do not import those goods themselves.
In our opinion as CBAM, Carbon monitoring and reporting regulations will help these organizations, but the carbon price on imported items might raise the cost of their raw materials. Established in 2005, the ETS places a yearly cap on greenhouse gas (GHG) emissions for businesses operating in specific industries. This cap will progressively drop over time to lower carbon emissions and promote decarbonization efforts. Emission allowances are given to in-scope firms for free or purchased up to the cap amount. In addition to the ETS, CBAM levies fees on the embedded carbon of imports that fall under its purview. The CBAM fee is the same as the fee levied under the ETS on non-imported commodities; however, it may be adjusted in accordance with any mandated carbon prices in the non-EU country of origin.
As an expert CBAM regulations, CBAM guarantees that imports (via CBAM) pay the same carbon price as comparable products coming from the EU (through ETS). To reduce overall carbon emissions, EU producers' ETS-free allowances will be gradually phased out, while EU importers will eventually be subject to CBAM responsibilities. CBAM covers imports into the EU of iron, steel, aluminum, electricity, cement, hydrogen, and some fertilizers. To safeguard EU businesses who have made investments in environmentally friendly technologies. By 2026, the European Parliament intends to broaden the scope to encompass plastics and chemicals, and by 2030, all industries will be covered by the EU ETS.
0 notes
Text
Acroleic Acid Production Cost, Manufacturing Process, Raw Materials Requirements, Costs and Key Process Information
The latest report titled Acroleic Acid Production Cost by Procurement Resource, a global procurement research and consulting firm, provides an in-depth cost analysis of the manufacturing process of Acrylic Acid.
Procurement Resource study is based on the latest prices and other economic data available. It also offers additional analysis of the report with detailed breakdown of all cost components (capital investment details, manufacturing cost details, economics for another plant location, dynamic cost model). In addition, the report incorporates the manufacturing process with detailed process and material flow, capital investment, operating costs along with financial expenses and depreciation charges.
Request Free Sample – https://www.procurementresource.com/production-cost-report-store/acrylic-acid/request-sample
Procurement Resource’s detailed report describes the stepwise consumption of material and utilities along with a detailed process flow diagram. Furthermore, the study assesses the latest developments within the industry, including Acrylic Acid manufacturing process, that might influence Acrylic Acid manufacturing cost, looking into capacity expansions, plant turnarounds, mergers, acquisitions, and investments.
Product Definition:
Acrylic Acid or Acroleic Acid (C3H4O2) is an alpha, beta-unsaturated monocarboxylic acid in which ethene is substituted by a carboxy group. The organic compound looks colourless with a tart/acrid odour and has the role of a metabolite and the conjugate acid of an acrylate. It is soluble in water and extremely corrosive to metals and tissue. Its respective melting, boiling, and flash point is 141.0°C, 14.0°C and 68°C. Its molecular mass is 72.06 g/mol, and its density is 1.0511 at 20°C.
Market Drivers:
The Acrylic Acid market is being driven by the growing usage of the acid for producing an extensive product range. It is used to make acrylic esters and resins, which are employed further to make adhesives and coatings, which boost the market growth further. In addition, it is used in oil and water treatment chemicals, water-absorbent polyacrylic acid polymers, and detergent intermediates. Owing to its ability to polymerize upon being heated, it is employed in the production of polyacrylates and as works as a monomer for polyacrylic and polymethacrylic acids. Also, it finds use in the production of plastics, flocculants, tackifiers, water-soluble resins and salts, etc., which in turn boosts the market expansion.
Looking for an exhaustive and personalised report that could significantly substantiate your business?
Although Procurement Resource leaves no page unfurled in terms of the rigorous research for the commodities that make the heftiest base of your business, we incline more towards tailoring the reports per your specificities. All you need is one-to-one consulting with our seasoned consultants to comprehend the prime parameters you are looking to pin your research on.
Some of the common requests we receive from our clients include:
Adapting the report to the country/region where you intend to establish your plant.
Adjusting the manufacturing capacity of the plant according to your needs.
Customizing machinery suppliers and costs to meet your requirements.
Providing additional information to the existing scope based on your needs.
Contact Us
Company Name: Procurement Resource Contact Person: Leo Frank Email: [email protected] Toll-Free Number: USA & Canada - Phone no: +1 307 363 1045 | UK - Phone no: +44 7537 132103 | Asia-Pacific (APAC) - Phone no: +91 1203185500 Address: 30 North Gould Street, Sheridan, WY 82801, USA
0 notes
Text
From Steel to Aluminum: Analyzing the Transformation in the Automotive Aluminum Market

Automotive aluminum is lightweight and high-strength metal increasingly being preferred for automobile manufacturing. It offers significant advantages of weight reduction and corrosion resistance for automotive structures and components like engine block, wheels, suspension parts and exterior body panels. The growing demand for fuel-efficient and emission compliant vehicles has accelerated the adoption of aluminum instead of conventional steel.
The global automotive aluminum market is estimated to be valued at US$ 58.33 Billion in 2024 and is expected to exhibit a CAGR of 12% over the forecast period 2024 to 2031, as highlighted in a new report published by Coherent Market Insights. Market Opportunity: Lightweighting for Better Fuel Economy has immense scope of growth over the forecast period. Automakers are under regulatory pressure to reduce the average weight of new vehicles to meet stringent corporate average fuel economy (CAFE) standards. Aluminum is around 30% lighter than steel, thereby helping automakers comply with these norms. A 10% reduction in vehicle weight can improve fuel economy by 6-8%. With aluminum, automakers can reduce vehicle weight by 100-250 lbs which translates to fuel savings for consumers. This presents a major growth opportunity for increased aluminum consumption in the coming years as automakers aggressively pursue lightweighting targets. Porter’s Analysis
Threat of new entrants: Low barriers allows more players to enter the market. However, the industry requires huge capital investments and R&D efforts to develop lightweight automobile components using aluminum. This poses risks for new players.
Bargaining power of buyers: Global automotive OEMs have significant bargaining power given their large procurement volumes. They can negotiate prices downwards and demand better quality and delivery.
Bargaining power of suppliers: Few big aluminum producers like Alcoa and Rio Tinto dominate global primary aluminum supply. This gives them bargaining leverage over automakers. Threat of new substitutes: Other lightweight materials like composites and plastics pose threats. But aluminum enjoys widespread acceptance in auto industry due to its advantages.
Competitive rivalry: Intense competition exists among established aluminum producers. They compete on technology, price and marketing to automotive clients. SWOT Analysis
Strengths: Lightweight and corrosion resistant properties make aluminum suitable for fuel-efficient vehicles. Rising environmental regulations favor its usage.
Weaknesses: Price fluctuations in aluminum commodities market impacts profits. Heavy dependence on automotive industry increases vulnerabilities.
Opportunities: Growing electric vehicles segment and demand for exterior body panels present new avenues. Developing nations are boosting automobile production.
Threats: Stagnant sales can hurt during economic slowdowns. Trade barriers and geopolitical tensions affect raw material supply. Key Takeaways The global automotive aluminum market is expected to witness high growth over the forecast period of 2024 to 2031.Rising environmental regulations regarding vehicular emissions are pushing automakers to use lightweight aluminum components that enhance fuel-efficiency. The global automotive aluminum market is estimated to be valued at US$ 58.33 Billion in 2024 and is expected to exhibit a CAGR of 12% over the forecast period 2024 to 2031.
Regional analysis indicates that Asia Pacific dominates the global automotive aluminum market currently. China, India, Japan and South Korea are major automobile manufacturing hubs in the region driving huge aluminum demand. Additionally, these countries are investing strongly in electric mobility which will further spur aluminum usage. North America and Europe are other key traditional markets while demand is rising fast in developing nations. Key players operating in the automotive aluminum market are Alcoa Inc., Arconic Inc., UACJ Corporation, CHALCO, AMG Advanced Metallurgical Group, Norsk Hydro ASA, Constellium N.V., Novelis Inc., and Rio Tinto. These leading aluminum producers are making significant investments in R&D and capacity expansions to cater to the growing demand from global automotive industry.
0 notes
Text
Medical Plastics Market is Estimated To Witness High Growth Owing To Increased Demand in Healthcare Packaging and Medical Devices
Medical plastics include flexible and rigid plastics used in healthcare applications like medical devices, packaging, components and consumables. The key advantages of medical plastics include lightweight, are chemically inert, biocompatible, high impact & shatter resistance and easy to sterilize properties. Medical plastics have wide applications from surgery instruments, medical tubing & catheters to diagnostic devices, drug delivery systems and healthcare packaging. The Medical Plastics Market is estimated to be valued at US$ 16,458.83 Mn in 2023 and is expected to exhibit a CAGR of 6.6% over the forecast period 2023 to 2030, as highlighted in a new report published by Coherent Market Insights
Market key trends: Increased demand for medical devices and healthcare packaging applications is driving the medical plastics market growth. The key factors influencing this demand include rising healthcare expenditure, higher disease incidence and aging population. Moreover, the COVID-19 pandemic has further accelerated the demand for medical devices and packaging like syringes, vials and bags. Additionally, technological advancements in polymers are enabling development of innovative long-lasting, durable and lightweight medical plastics solutions. continued R&D is also helping manufacturers develop recyclable solutions to address concerns regarding plastic waste disposal. Porter's Analysis Threat of new entrants: The medical plastics industry requires high capital investment and stringent regulatory approvals which pose high barriers for new entrants. However, scope of customization provides opportunity. Bargaining power of buyers: Large healthcare institutions and providers can negotiate prices down due to consolidation. However, complexity of products limits extensive bargaining. Bargaining power of suppliers: Key raw material suppliers such as petrochemical companies have significant influence over pricing due to limited substitutes and supplier concentration. Threat of new substitutes: While new biomaterial-based substitutes are emerging, regulatory compliance and performance compatibility make plastic materials difficult to replace in the short-term. Competitive rivalry: The medical plastics industry has prominent global players with strong brand identity and differentiation through innovation. However, commodity products face high competition. SWOT Analysis Strength: Wide applicability in medical devices & equipment due to desirable properties like sterilizability, biocompatibility and durability. Strong R&D focus on customized solutions has enhanced product portfolio. Weakness: Fluctuating raw material costs and regulatory compliance requirements increase production expenses. Dependence on limited suppliers for key materials. Opportunity: Rising healthcare investments and demand for minimally invasive procedures are driving the need for advanced medical plastics in emerging economies. Growing usage of 3D printing offers new opportunities. Threats: Implementation of stringent regulations around product approvals and biocompatibility testing delay market entry. Concerns around plastic waste management abilities. Key Takeaways The global medical plastics market is expected to witness high growth, exhibiting CAGR of 6.6% over the forecast period, due to increasing prevalence of chronic diseases and demand for improved healthcare infrastructure across major economies. Regional analysis: North America represents the largest and fastest growing regional market for medical plastics and is expected to dominate over the forecast period supported by well-established healthcare systems, major players presence and significant R&D investments in the region. Asia Pacific is anticipated to exhibit the highest growth rate owing to rising medical tourism, growing healthcare expenditure and expansion of healthcare facilities in countries such as China and India. Key players operating in the medical plastics market are Arkema S.A., BASF SE, Celanese Corporation, Covestro AG, Royal DSM, DowDuPont Inc., Solvay SA, Exxon Mobil Corporation, Trinseo S.A., Trelleborg AB, The Lubrizol Corporation, Saint-Gobain S.A., Tekni-Plex, Inc., and Röchling SE & Co. KG. These players are primarily focused on new product development, mergers & acquisitions and capacity expansions to strengthen their market position and diversify product portfolios to tap high growth areas through technologically advanced solutions.
0 notes
Text
Commodity Plastics Market to Exhibit Fastest Growth in Future Scope 2022-2032 | ExxonMobil Corporation, LG Chem, Sumitomo Chemical Co. Ltd
Commodity Plastics Market to Exhibit Fastest Growth in Future Scope 2022-2032 | ExxonMobil Corporation, LG Chem, Sumitomo Chemical Co. Ltd
This report estimates the growth rate and the market value based on industry dynamics and growth driving factors. While preparing this Global Commodity Plastics market research report, a few of the attributes that have been adopted include updated domain performance. The report offers wide-ranging statistical analysis of the market’s continuous developments, capacity, production, production…

View On WordPress
#Commodity Plastics#Commodity Plastics manufacturing Vendors#Commodity Plastics market#Commodity Plastics market share#Commodity Plastics market size#Commodity Plastics market SWOT analysis#Future Trends of Commodity Plastics industry#Scope of Commodity Plastics industry
0 notes
Text
most of the UK reviews i’ve read of martin eden have been a disappointment, tbh. i don’t know if this is because critics have been busy with cannes or because outlets here just don’t have the space, or because it’s kind of seen as old news. i have seen no real engagement with the politics or form beyond a couple of cursory lines, and it’s a shame because... i think it’s really rich wrt those elements?
so i am looking again at the (wonderful) review from film comment last year and it’s such a shame that it’s not available freely online. so i thought i’d post it here behind a cut. it’s long but worth it imo (and also engages really interestingly with marcello’s other films). it’s by phoebe chen.
COLLECTIVE CONSCIOUSNESS Jan 3, 2020 BY PHOEBE CHEN
EARLY IN JACK LONDON’S 1909 NOVEL MARTIN EDEN, there is a scattering of references to technical ephemera that the 20th century will promptly leave behind: “chromos and lithographs,” those early attempts at large-scale reproduction; “a vast camera obscura,” by then a centuries-old relic; a bullfight so fervid it’s like “gazing into a kinetoscope,” that proto-cinematic spectacle of cloistered motion. These objects now seem like archaic curios, not much more than the flotsam of culture from the moment it shifted gears to mass production. It’s a change in scale that also ensnares the novel’s title character, a hardy young sailor and autodidact-turned-writer-célèbre, famously an avatar of London’s own hollowing transmutation into a figure for mass consumption. But, lucky him—he remains eminent now on the other side of a century; chance still leaves a world of names and faces to gather dust. Easily the most arresting aspect of Pietro Marcello’s new adaptation is its spotlight on the peripheral: from start to end, London’s linear Künstlerroman is intercut with a dizzying range of archival footage, from a decaying nitrate strip of anarchist Errico Malatesta at a workers’ rally to home video–style super 16mm of kids jiving by an arcade game. In these ghostly interludes, Marcello reanimates the visual detritus of industrial production as a kind of archival unconscious.
This temporal remixing is central to Marcello’s work, mostly experimental documentaries that skew auto-ethnographic and use elusive, essayistic editing to constellate place and memory, but always with a clear eye to the present. Marcello’s first feature, Crossing the Line (2007), gathers footage of domestic migrant workers and the nocturnal trains that barrel them to jobs across the country, laying down a recurring fascination with infrastructure. By his second feature, The Mouth of the Wolf (2009), there is already the sense of an artist in riveting negotiation with the scope of his story and setting. Commissioned by a Jesuit foundation during Marcello’s yearlong residency in the port city of Genoa, the film ebbs between a city-symphonic array and a singular focus on the story of a trans sex worker and her formerly incarcerated lover, still together after 20-odd years and spells of separation. Their lives are bound up with a poetic figuration of the city’s making, from the mythic horizon of ancient travails, recalled in bluer-than-blue shots of the Ligurian Sea at dawn, to new-millennium enterprise in the docklands, filled with shipping crates and bulldozers busy with destruction.
Marcello brings a similar approach to Martin Eden, though its emphasis is inverted: it’s the individual narrative that telescopes a broader history of 20th-century Italy. In this pivotal move, Marcello and co-writer Maurizio Braucci shift London’s Oakland-set story to Naples, switching the cold expanse of the North Pacific for the Mediterranean and its well-traversed waters. The young century, too, is switched out for an indeterminate period with jumbled signifiers: initial clues point to a time just shy of World War II, though a television set in a working-class household soon suggests the late ’50s, and then a plastic helicopter figurine loosely yokes us to the ’70s. Even the score delights in anachronism, marked by a heavy synth bass that perforates the sacral reverb of a cappella and organ song, like a discotheque in a cathedral. And—why not?—’70s and ’80s Europop throwbacks lend archival sequences a further sense of epochal collapse. While Marcello worked with researcher Alessia Petitto for the film’s analog trove, much of its vintage stock is feigned by hand-tinting and distressing original 16mm footage. Sometimes a medium-change jolts with sudden incongruity, as in a cut to dockworkers filmed in black and white, their faces and hands painted in uncanny approximations of living complexions. Other transitions are so precisely matched to color and texture that they seem extensions of a dream.
Martin’s writer’s optimism is built on a faith in language as the site of communication and mutual recognition. So follows his tragedy.
Patchworked from the scraps of a long century, this composite view seems to bristle against a story of individual formation. It feels like a strange time for an artist’s coming-of-age tale adapted with such sincerity, especially when that central emphasis on becoming—and becoming a writer, no less—is upended by geopolitical and ecological hostility. At first, our young Martin strides on screen with all the endearing curiosity of an archetypal naïf, played by Luca Marinelli with a cannonballing force that still makes room for the gentler affects of embarrassment and first love. Like the novel, the film begins with a dockside rescue: early one morning, Martin saves a young aristocrat from a beating, for which he is rewarded with lunch at the family estate. On its storied grounds, Martin meets the stranger’s luminous sister, Elena Orsini (Jessica Cressy), a blonde-haloed and silk-bloused conduit for his twinned desires of knowledge and class transgression. In rooms of ornate stucco and gilded everything, the Orsinis parade their enthusiasm for education in a contrived show of open-mindedness, a familiar posture of well-meaning liberals who love to trumpet a certain model of education as global panacea. University-educated Elena can recite Baudelaire in French; Martin trips over simple conjugations in his mother tongue. “You need money to study,” he protests, after Elena prescribes him a back-to-school stint. “I’m sure that your family would not ignore such an important objective,” she insists (to an orphan, who first set sail at age 11).
Anyone who has ever been thrilled into critical pursuit by a single moment of understanding knows the first beat of this story. Bolting through book after book, Martin is fired by the ever-shifting measure of his knowledge. In these limitless stretches of facts to come, there’s the promised glow of sheer comprehension, the way it clarifies the world as it intoxicates: “All hidden things were laying their secrets bare. He was drunk with comprehension,” writes London. Marcello is just as attentive to how Martin understands, a process anchored to the past experiences of his working body. From his years of manual labor, he comes to knowledge in a distinctly embodied way, charming by being so literal. At lunch with the Orsinis, he offers a bread roll as a metaphor for education and gestures at the sauce on his plate as “poverty,” tearing off a piece of education and mopping up the remnants with relish. Later, in a letter to Elena, he recounts his adventures in literacy: “I note down new words, I turn them into my friends.” In these early moments, his expressions are as playful as they are trenchant, enlivened by newfound ways of articulating experience. His writer’s optimism is built on a faith in language as the site of communication and mutual recognition. So follows his tragedy.
One of Marcello’s major structural decisions admittedly makes for some final-act whiplash, when a cut elides the loaded years of Martin’s incremental success, stratospheric fame, and present fall into jaded torpor. By now, he is a bottle-blonde chain-smoker with his own palazzo and entourage, set to leave on a U.S. press tour even though he hasn’t written a thing in years. His ideas have been amplified to unprecedented reach by mass media, and his words circulate as abstract commodities for a vulturine audience. For all its emphasis on formation, Martin Eden is less a story of ebullient self-discovery than one of inhibiting self-consciousness. There is no real sense that Martin’s baseline character has changed, because it hasn’t. Even his now best-selling writing is the stuff of countless prior rejected manuscripts. From that first day at the Orsini estate, when his roughness sticks out to him as a fact, he learns about the gulf between a hardier self-image and the surface self that’s eyed by others.
WITH SUCH A DEEPLY INHABITED PERFORMANCE by Marinelli, it’s intuitive to read the film as a character study, but the lyrical interiority of London’s novel never feels like the point of Marcello’s adaptation. Archival clips—aged by time, or a colorist’s hand—often seem to illustrate episodes from Martin’s past, punctuating the visual specificity of individual memory: a tense encounter with his sister cuts to two children dancing with joyous frenzy; his failed grammar-school entrance exam finds its way to sepia-stained shots of a crippled, shoeless boy. These insertions are more affective echoes than literal ones, the store of a single life drawn from a pool of collective happening.
But, that catch: writing in the hopes of being read, as Martin does (as most do), means feeding some construct of a distinctive self. While the spotlight of celebrity singles out the destructive irony of Martin’s aggressive individualism, Marcello draws from Italy’s roiling history of anarchist and workerist movements to complicate the film’s political critique, taking an itinerant path through factions and waves from anarcho-communism in the early 1900s to the pro-strike years of autonomist Marxism in the late ’70s. In place of crystalline messaging is a structure that parallels Martin’s own desultory politics, traced in both film and novel through his commitment to liberal theorist Herbert Spencer. Early on, Martin has an epiphanic encounter with Spencer’s First Principles (a detail informed by London’s own discovery of the text as a teen), which lays out a systematic philosophy of natural laws, and offers evolution as a structuring principle for the universe—a “master-key,” London offers. Soon, Martin bellows diatribes shaped by Spencer’s more divisive, social Darwinist ideas of evolutionary justice, as though progress is only possible through cruel ambivalence. Late in the film, an image of a drunk and passed-out Martin cuts to yellowed footage of a young boy penciling his name—“Martin Eden”—over and over in an exercise book, a dream of becoming turned memory.
In Marcello’s previous feature, Lost and Beautiful (2015), memory is more explicitly staged as an attachment to landscape. Like Alice Rohrwacher’s Happy as Lazzaro, Lost and Beautiful plays as a pastoral elegy but lays out the bureaucratic inefficiency that hastens heritage loss through neglect. Rolling fields make occasional appearances in Martin Eden, but its Neapolitan surroundings evoke a different history. Far from the two oceans that inspired a North American tradition of maritime literature, the Mediterranean guards its own idiosyncrasies of promise and catastrophe. Of the Sea’s fraught function as a regional crossroads, Marcello has noted, in The Mouth of the Wolf, a braiding of fate and agency: “They are men who transmigrate,” the opening voiceover intones. “We don’t know their stories. We know they chose, found this place, not others.” Mare Nostrum—“Our Sea”—is the Roman epithet for the Mediterranean, a possessive projection that abides in current vernacular. Like so many cities that cup the sea, Naples is a site of immigrant crossing, a fact slyly addressed in Martin Eden with a fleeting long shot of black workers barreling hay in a field of slanted sun, and, at the end, a group of immigrants sitting on a beach at dusk. Brief, but enough to mark the changing conditions of a new century.
Not much is really new, however: not the perils of migration, nor the proselytizing individualists, nor the media circus, nor the classist distortions of taste, nor, blessedly, the kind of learning for learning’s sake that stokes and sustains an interest in the world. Toward the end of the film, there is a shot of our tired once-hero, slumped in the back seat of a car, that cuts to sepia stock of children laughing and running to reach the camera-as-car-window, as if peering through glass and time. It recalls a scene from Wim Wenders’s Wings of Desire, which leaps backward through a similar gaze, when the weary angel Cassiel looks out of a car window at the vista of ’80s Berlin and sees, instead, grainy footage of postwar streets strewn with rubble in fresh ruin. Where human perception is shackled to linearity, these wool-coated and scarfed seraphs—a materialization of Walter Benjamin’s “angel of history”—see all of time in a simultaneous sweep, as they wander Berlin with their palliative touch. Marcello’s Martin Eden mosaics a view less pointedly omniscient, but just as filled with a humanist commitment to the turning world, even as Martin slides into disillusion. All its faces plucked from history remind me of a line from a Pasolini poem: “Everything on that street / was human, and the people all clung / to it tightly.”
Phoebe Chen is a writer and graduate student living in New York.
14 notes
·
View notes
Text
Hydraulic Press Machine Market 2021-2027 Global Industry Analysis Covid-19 Impact
This Hydraulic Press Machine market report provides the best business insight and understanding to help key players stay ahead of the competition. It also detects emerging trends and forecasts future market numbers, trends, and characteristics. This Hydraulic Press Machine market report offers the most effective action strategies for dealing with the current market situation and establishing a marketplace. It also helps to improve and enhance the company’s position. This Hydraulic Press Machine market report allows industries to easily assess and compare their results to that of others. This Hydraulic Press Machine market report provides a straightforward view of market tactics, which can assist companies in achieving massive profits. It also offers a good picture of trade restraints, product releases, business penetration in new areas, and technical developments and advancements.
With the evolution of new materials such as structural plastics and fiber, manufacturing industries now have several options available to design their products. These new materials can offer performance advantages over traditional materials including aluminum, steel and concrete. Overall, material substitution has been only a minor factor affecting the demand for these metals in the past decade. However, the importance of substitution by alternative materials is likely to increase in near future. Surge in demand for these materials over metals is a major factor slowing down the growth of the global hydraulic press machine market.The performance of any manufacturing industry largely depends on the growth of its end-user industries. Automotive industry is considered as one of the largest end-user markets for manufacturing technology products. Anticipated growth in the automotive industry over the next few years is likely to help the manufacturing market to expand across the globe. In the automotive industry, stamping is an extensive manufacturing mechanism that is used to produce body parts for automobiles, for which hydraulic press machines are deployed.APAC accounted for the maximum market share during 2016 and will continue to dominate the market in the forthcoming years. One of the major factors responsible for the market’s growth in the region is the growing demand for automobiles, general machinery, and electronic goods.
Press machine is a type of machine, which is crucial to industrial manufacturing processes. Presses provide energy by exerting a force, which acts over a stroke. Hydraulic press machines are widely used in the metal forging industry to perform blanking, stamping, coining and embossing. Press machines are also used in the metal fabrication and metal extrusion processes. There are four main types of press machines as shown below.
Get Sample Copy of Hydraulic Press Machine Market Report at: https://www.globalmarketmonitor.com/request.php?type=1&rid=658545
Industries will come to know huge opportunities available in the market through this detailed Hydraulic Press Machine Market analysis report. This market report is classified into different unique ad significant segments to provide market analysis precisely. Every single segment depicts information about industry aspects. This report can be used as a perfect tool by players to get the viable edge over competitors. It also ensures lasting success to industries. In addition, trustworthy sources are used here to validate and revalidate the information mentioned here. Industry-based and unique research is performed by analysts to give thorough information about market development.
Major enterprises in the global market of Hydraulic Press Machine include: Hare Press Greenerd Beckwood Press Schuler
Market Segments by Application: Automotive Military Electrical and Electronics Ceramic and Abrasives Food and Beverages Others
On the basis of products, the various types include: H-Frame C-Frame Others
Table of Content 1 Report Overview 1.1 Product Definition and Scope 1.2 PEST (Political, Economic, Social and Technological) Analysis of Hydraulic Press Machine Market … 2 Market Trends and Competitive Landscape 3 Segmentation of Hydraulic Press Machine Market by Types 4 Segmentation of Hydraulic Press Machine Market by End-Users 5 Market Analysis by Major Regions 6 Product Commodity of Hydraulic Press Machine Market in Major Countries 7 North America Hydraulic Press Machine Landscape Analysis 8 Europe Hydraulic Press Machine Landscape Analysis 9 Asia Pacific Hydraulic Press Machine Landscape Analysis 10 Latin America, Middle East & Africa Hydraulic Press Machine Landscape Analysis 11 Major Players Profile …
Ask for a Report Sample at: https://www.globalmarketmonitor.com/request.php?type=3&rid=658545
Exhaustive geographical analysis is performed on the Hydraulic Press Machine market report along with covering few major regions such as Europe, China, North America, Japan, India, and South America. Moreover, this report sheds light on some crucial key points that will impel the financial flow of the global market. It further focuses on several crucial sources to apply in the business to accomplish the best outcomes and gains. It also covers some crucial approaches to explore global opportunities in the market and to expand the business. With the help of this comprehensive market analysis, key players can easily make a prominent place in the market. It also captures the global impacts of the Corona Virus on different segments and countries.
In-depth Hydraulic Press Machine Market Report: Intended Audience Hydraulic Press Machine manufacturers Downstream vendors and end-users Traders, distributors, and resellers of Hydraulic Press Machine Hydraulic Press Machine industry associations and research organizations Product managers, Hydraulic Press Machine industry administrator, C-level executives of the industries Market Research and consulting firms
Along with depicting real market condition, it also captures COVID-19 effect on market growth. This Hydraulic Press Machine Market analysis covers specific data about overall market to help key players in making informed decision. This market report serves as the model report for the new entrants as it provides principal data about growth size, segments of the industry and emerging developments. Key players can generate huge profits by doing the right investment in the market as this market report shares efficient market strategy. It becomes easy to target the specific products and generate huge revenues in the market as this report depicts constantly changing requirements of the customers in various regions.
About Global Market Monitor Global Market Monitor is a professional modern consulting company, engaged in three major business categories such as market research services, business advisory, technology consulting. We always maintain the win-win spirit, reliable quality and the vision of keeping pace with The Times, to help enterprises achieve revenue growth, cost reduction, and efficiency improvement, and significantly avoid operational risks, to achieve lean growth. Global Market Monitor has provided professional market research, investment consulting, and competitive intelligence services to thousands of organizations, including start-ups, government agencies, banks, research institutes, industry associations, consulting firms, and investment firms. Contact Global Market Monitor One Pierrepont Plaza, 300 Cadman Plaza W, Brooklyn,NY 11201, USA Name: Rebecca Hall Phone: + 1 (347) 467 7721 Email: [email protected] Web Site: https://www.globalmarketmonitor.com
1 note
·
View note
Text
Automotive NVH Materials: Boosting Vehicle Quality and Passenger Experience
Automotive NVH Materials Industry Overview
The global automotive noise, vibration & harshness (NVH) materials market size is expected to reach USD 15.16 billion by 2030, registering at a CAGR of 5.6% from 2023 to 2030, according to a new report by Grand View Research, Inc. Globally increasing automobile production has been a major factor driving market growth. The use of noise & vibration-absorbing and damping products in automobiles helps improve the overall ride quality, comfort, performance, and safety of the vehicle.
The growth in population and urbanization have resulted in increased demand for passenger cars and commercial vehicles thereby increasing the pressure on the automotive sector worldwide. The increasing demand for comfort and NVH reduction in vehicles are expected to drive market growth during the forecast period.
Growing awareness regarding the advantages of NVH reduction and acoustic management in vehicles has also led to the increased utilization of NVH materials in automobiles. In addition, the shifting consumer preferences towards comfort, and ride experience in passenger cars is expected to propel the demand for the product over the coming years.
Gather more insights about the market drivers, restrains and growth of the Automotive Nvh Materials Market
Foam laminates were the largest product category in 2022 and are expected to maintain a relatively high growth rate over the forecast period. The molded foam product category is expected to witness relatively low growth of 4.4% over the coming years, owing to its limited application scope in vehicles.
NVH materials in HCVs are expected to observe the fastest growth over the next coming years at an estimated CAGR of over 7.2% from 2023 to 2030. The increasing use of heavy-duty trucks in the logistics & transportation industry, for the transportation of heavy commodities over medium and long distances, propels the demand for HCVs. In addition, the presence of stringent regulations concerning vehicle safety, in terms of vehicle weight and safety standards, is expected to boost the demand for lightweight products in HCVs over the forecast period.
Browse through Grand View Research's Advanced Interior Materials Industry Research Reports.
The global silicon carbide fibers market size was valued at USD 1.20 billion in 2024 and is projected to grow at a CAGR of 28.1% from 2025 to 2030.
The global aluminum composite panel market size was estimated at USD 6.47 billion in 2024 and is expected to grow at a CAGR of 7.0% from 2025 to 2030.
Automotive NVH Materials Market Segmentation
Grand View Research has segmented the global automotive noise, vibration & harshness materials market based on product, application, end-use, and region:
Automotive NVH Materials Product Outlook (Revenue, USD Million, 2018 - 2030)
Molded Rubber
Metal Laminates
Foam Laminates
Film Laminates
Molded Foam
Engineering resins
Automotive NVH Materials Application Outlook (Revenue, USD Million, 2018 - 2030)
Absorption
Damping
Automotive NVH Materials End-Use Outlook (Revenue, USD Million, 2018 - 2030)
Cars
LCVs
HCVs
Automotive NVH Materials Regional Outlook (Revenue, USD Million, 2018 - 2030)
North America
US
Europe
Germany
UK
Asia Pacific
China
India
Japan
Central & South America
Brazil
Rest of the World
Key Companies profiled:
Creative Foam Corporation
BRC Rubber & Plastics Inc.
Wolverine Advanced Materials
ElringKlinger AG
Hoosier Gasket Corporation
Industry Products Co.
Interface Performance Materials
Hematite
Plastomer Corporation
Rogers Foam Corporation
Swift Components Corp
Unique Fabricating Inc.
Avery Dennison
KKT Holding GmbH
Nicholson Sealing Technologies Ltd.
KOPP GmbH & Co. KG
Janesville Acoustics
Order a free sample PDF of the Automotive NVH Materials Market Intelligence Study, published by Grand View Research.
0 notes
Text
Global Light Commercial Truck Market To 2027 Historical, Current, And Projected Size Of The Market

Global Light Commercial Truck Market, By Vehicle Type (Pick-Up Truck, Vans, Bus, Crossovers and SUV), Product Type (Plastic Fuel Tank, Metal Fuel Tank), Drive Type (IC Engine, Electric/Hybrid), End User (Commercial Fleet, Government Fleet), Country (U.S., Canada, Mexico, Brazil, Argentina, Rest of South America, Germany, Italy, U.K., France, Spain, Netherlands, Belgium, Switzerland, Turkey, Russia, Rest of Europe, Japan, China, India, South Korea, Australia, Singapore, Malaysia, Thailand, Indonesia, Philippines, Rest of Asia-Pacific, Saudi Arabia, U.A.E, South Africa, Egypt, Israel, Rest of Middle East and Africa) Industry Trends and Forecast to 2027
Market Analysis and Insights: Global Light Commercial Truck Market
Light commercial truck market is expected to witness market growth at a rate of 52.90% in the forecast period of 2020 to 2027. Data Bridge Market Research report on light commercial truck market provides analysis and insights regarding the various factors expected to be prevalent throughout the forecasted period while providing their impacts on the market’s growth.
Know More - https://www.databridgemarketresearch.com/reports/global-light-commercial-truck-market
The augmentation of the logistic division in emerging nations is foreseen to stimulate the increment of the business in the projection space. Developing architecture and e-commerce enterprises to generate possibilities. The digital emergence has an influential impression on the automobile enterprise, with developing online trade plentiful commercial transportation is being acquired to ship and transportation assets from storehouses to the consumer. Professionals are funding in commodity expansion to promote and augment the determination of the consumer by extending world-class merchandise. Nevertheless, the risks of rising geopolitical pressures owed to constantly protectionist commerce divisions restrain the growth of the market.
This light commercial truck market report provides details of new recent developments, trade regulations, import export analysis, production analysis, value chain optimization, market share, impact of domestic and localised market players, analyses opportunities in terms of emerging revenue pockets, changes in market regulations, strategic market growth analysis, market size, category market growths, application niches and dominance, product approvals, product launches, geographic expansions, technological innovations in the market. To gain more info on Data Bridge Market Research light commercial truck market contact us for an Analyst Brief, our team will help you take an informed market decision to achieve market growth.
Global Light Commercial Truck Market Scope and Market Size
Light commercial truck market is segmented on the basis of vehicle type, product type, drive type, and end user. The growth among segments helps you analyse niche pockets of growth and strategies to approach the market and determine your core application areas and the difference in your target markets.
On the basis of vehicle type, the light commercial truck market is segmented into pick-up truck, vans, bus, crossovers and SUV.
On the basis of product type, the light commercial truck market is segmented into plastic fuel tank, and metal fuel tank.
On the basis of drive type, the light commercial truck market is segmented into IC engine, and electric or hybrid.
On the basis of end user, the light commercial truck market is segmented into commercial fleet, and government fleet.
Planning To Lay Down Future Strategy? Request Sample https://www.databridgemarketresearch.com/request-a-sample/?dbmr=global-light-commercial-truck-market
Light Commercial Truck Market Country Level Analysis
Light commercial truck market is analysed and market size, volume information is provided by country, vehicle type, product type, drive type, and end user as referenced above.
The countries covered in the market report are the U.S., Canada and Mexico in North America, Brazil, Argentina and Rest of South America as part of South America, Germany, Italy, U.K., France, Spain, Netherlands, Belgium, Switzerland, Turkey, Russia, Rest of Europe in Europe, Japan, China, India, South Korea, Australia, Singapore, Malaysia, Thailand, Indonesia, Philippines, Rest of Asia-Pacific (APAC) in the Asia-Pacific (APAC), Saudi Arabia, U.A.E, South Africa, Egypt, Israel, Rest of Middle East and Africa (MEA) as a part of Middle East and Africa (MEA).
The requirement for vans crosswise Europe has been developing in the long run. They are utilized for an extensive variety of commercial ventures, such as building, mail and messenger duties, ambulance assistance, controlling and rescue services, and commuter transport.
The country section of the report also provides individual market impacting factors and changes in regulation in the market domestically that impacts the current and future trends of the market. Data points like down-stream and upstream value chain analysis, technical trends and porter's five forces analysis, case studies are some of the pointers used to forecast the market scenario for individual countries. Also, the presence and availability of global brands and their challenges faced due to large or scarce competition from local and domestic brands, impact of domestic tariffs and trade routes are considered while providing forecast analysis of the country data.
Request For ToC - https://www.databridgemarketresearch.com/toc/?dbmr=Light Commercial Truck
Competitive Landscape and Light Commercial Truck Market Share Analysis
Light commercial truck market competitive landscape provides details by competitor. Details included are company overview, company financials, revenue generated, market potential, investment in research and development, new market initiatives, regional presence, company strengths and weaknesses, product launch, product width and breadth, application dominance. The above data points provided are only related to the companies’ focus related to light commercial truck market.
The major players covered in the light commercial truck market report are Toyota Motor Corporation, Volkswagen AG, HYUNDAI MOTOR GROUP, Fiat Chrysler Automobiles, Honda Motor Co., Ltd., Groupe Renault, Nissan, Groupe PSA, Zhejiang Geely Holding Group, ASHOK LEYLAND, suzuki motor corporation, Tata Motors and MITSUBISHI MOTORS CORPORATION among other domestic and global players. Market share data is available for global, North America, Europe, Asia-Pacific (APAC), Middle East and Africa (MEA) and South America separately. DBMR analysts understand competitive strengths and provide competitive analysis for each competitor separately.
Customization Available: Global Light Commercial Truck Market
Data Bridge Market Research is a leader in consulting and advanced formative research. We take pride in servicing our existing and new customers with data and analysis that match and suits their goal. The report can be customised to include production cost analysis, trade route analysis, price trend analysis of target brands understanding the market for additional countries (ask for the list of countries), import export and grey area results data, literature review, consumer analysis and product base analysis. Market analysis of target competitors can be analysed from technology-based analysis to market portfolio strategies. We can add as many competitors that you require data about in the format and data style you are looking for. Our team of analysts can also provide you data in crude raw excel files pivot tables (Factbook) or can assist you in creating presentations from the data sets available in the report.
About Us: Data Bridge Market Research set forth itself as an unconventional and neoteric Market research and consulting firm with unparalleled level of resilience and integrated approaches. We are determined to unearth the best market opportunities and foster efficient information for your business to thrive in the market. Data Bridge Market Research provides appropriate solutions to the complex business challenges and initiates an effortless decision-making process.
Contact: Data Bridge Market Research Tel: +1–888–387–2818 Email: [email protected]
1 note
·
View note
Text
Brief description of the Mechanism for Adjusting the Carbon Border (CBAM)
In Agile Advisors as a Carbon Border Adjustment Mechanism, As proposed by the European Commission, a Carbon Border Adjustment Mechanism (CBAM) would help reach climate neutrality by 2050. It would respond to the dangers of "carbon leakage" brought on by the EU's higher climate commitment in concert with the other policy instruments in the "Fit for 55" package. The hypothetical scenario known as "carbon leakage" refers to European producers competing in global markets, shifting their output and emissions to nations with laxer or no climate regulations to reduce the cost of compliance. With time, carbon leakage mitigation strategies such as the EU Emissions Trading System's free emission allowance distribution will give way to CBAM. For a limited number of items, it guarantees a carbon price equal to domestic and imported production. It would also incentivize trading partners to lower their emissions in this way.

As Agile Advisors' Carbon Border Adjustment Mechanism, to import products made outside of the EU into the EU, businesses must buy certificates that reflect the number of emissions those products produce. The price of CBAM certificates will be determined by the European Commission using the average weekly price of ETS auctions as a guide. This implies that the ETS will be the basis for CBAM certificates. This will maintain the system's manageability for the administrative authorities while guaranteeing that the cost of CBAM certificates is as close as feasible to the cost of ETS allowances. Businesses that import products into the EU must get CBAM certificates and turn over the necessary cash each year to pay the associated emissions. An importer is not prohibited from acquiring an unlimited quantity of CBAM certificates to prevent trade restrictions’ certificates, in contrast to ETS allowances, are neither bankable nor tradeable, guaranteeing that they consistently reflect the evolution of the ETS price.
Our role as an Agile Advisors Carbon Border Adjustment Mechanism, any divergence could result in price differences that are so great as to reduce the incentives for decarbonizing local and imported commodities. On CBAM certificates, the only "transaction" permitted is repurchasing. Up to one-third of the total certifications acquired the previous year may be resold by an importer to the appropriate body. This should maintain flexibility and allow importers to maximize their profit margins without lowering prices or creating a speculative environment. CBAM will first include the direct emissions (scope 1) of the following industries: electricity, cement, aluminum, iron and steel, and fertilizers. The greenhouse gas emissions that the CBAM regulates are the same as those that are included in Annex I of the EU ETS, which provides for carbon dioxide (CO2) and, if applicable, nitrous oxide (N2O) and perfluorocarbons (PFCs).
To help you as Carbon Border Adjustment Mechanism, Scope 2 emissions, or indirect emissions, will not be included in the first phase but may be added after the transition period and following additional evaluation by the European Commission (details below). The industries chosen are an excellent place to start, but to have the most significant influence on the climate, certain additions would be helpful. The CBAM should strive to achieve the most critical emissions reductions as a tool for climate policy. Fertilizers have been added, which is excellent, but other bulk chemicals—like plastics—are not and ought to be covered by a CBAM. One of the leading and most polluting aspects of the plastics industry is bulk chemical manufacturing. Over the past ten years, emissions from this industry have stayed stubbornly high.
We believe as a Carbon Border Adjustment Mechanism, A CBAM would provide financial incentives to move to greener manufacturing methods and discover other, more ecologically friendly solutions instead of free allocation. Another significant omission in the current proposal is the exclusion of indirect emissions. The emissions produced during the manufacturing process of the electricity utilized in creating commodities, like in the aluminum industry, are referred to as indirect emissions. Their inclusion in the CBAM would encourage importers to develop renewable energy sources to power them and cleaner production techniques, which would have a more significant overall positive impact on the environment. Indirect emissions would also more accurately represent European industry's carbon cost, given that the electricity sector is subject to the EU ETS and must buy all of its emission allowances through auctions.
0 notes
Text
Reimagining the human
An essay by Eileen Crist in Science
Earth is in the throes of a mass extinction event and climate change upheaval, risking a planetary shift into conditions that will be extremely challenging, if not catastrophic, for complex life (1). Although responsibility for the present trajectory is unevenly distributed, the overarching drivers are rapid increases in (i) human population, (ii) consumption of food, water, energy, and materials, and (iii) infrastructural incursions into the natural world. As the “trends of more” on all these fronts continue to swell, the ecological crisis is intensifying (2–4). Given that human expansionism is causing mass extinction of nonhuman life and threatening both ecological and societal stability, why is humanity not steering toward limiting and reversing its expansionism?
The rational response to the present-day ecological emergency would be to pursue actions that will downscale the human factor and contract our presence in the realm of nature. Yet in mainstream institutional arenas, economic, demographic, and infrastructural growth are framed as inevitable, while technological and management solutions to adverse impacts are pursued single-mindedly. Although pursuing such solutions is important, it is also clear that reducing humanity's scale and scope in the ecosphere is the surest approach to arresting the extinction crisis, moderating climate change, decreasing pollution, and providing sorely needed leeway to tackle problems of poverty, food insecurity, and forced migration (5). The question that arises is why the approach of contracting the human enterprise tends to be ignored.
The answer lies in the deeper cause of the ecological crisis: a pervasive worldview that imbues the trends of more with a cachet of inevitability and legitimacy. This worldview esteems the human as a distinguished entity that is superior to all other life forms and is entitled to use them and the places they live. The belief system of superiority and entitlement—or human supremacy—manifests in a range of anthropocentric commonplace assumptions, linguistic constructs, institutional regimes, and everyday actions of individual, group, nation-state, and corporate actors (6). For example, the human is invested with powers of life and death over all other beings and with the prerogative to control and manage all geographical space. The all-encompassing manifestation of the belief system of human supremacy is precisely what constitutes it as a worldview.
This worldview is not necessarily an explicitly articulated narrative. Rather, it forms the tacit postulate from which people source meaning and justification to disregard virtually any limitation of action or way of life in the ecosphere and toward nonhumans. Human supremacy is the underlying big story that normalizes the trends of more, and the consequent displacements and exterminations of nonhumans—as well as of humans who oppose that worldview (7, 8). In this context, it is crucial to recognize that human supremacy is neither culturally nor individually universal, nor is it derived in any straightforward way from human nature. However, western civilization has elaborated its most forceful, long-standing expression, and through the West's ascendancy the influence of this worldview has spread across the globe (9).
Blind to the Wisdom of Limitations
The planetwide sense of entitlement bequeathed by a supremacist worldview blinds the human collective to the wisdom of limitations in several ways, thereby hindering efforts to address the ecological crisis by downscaling the human enterprise and withdrawing it from large portions of land and sea.
First, because the worldview demotes the nonhuman in favor of the human, it blocks the human mind from recognizing the intrinsic existence and value of nonhumans and their habitats. Nonhumans are rendered as resources and considered dispensable or killable; it is assumed that natural areas can be taken over and converted at will.
Second, a worldview founded on the elevation of the human impairs the experience of awe for this living planet, inducing instead the perception that viewing the ecosphere as a container of natural resources, raw materials, and goods and services makes sense. If humanity inhabited Earth with a profound sense of awe, news of an impending mass extinction would galvanize the world into action. Instead, what we find is that the response to anthropogenic mass extinction is muted in mainstream media and other social arenas.
Third, based on the conviction of the special distinction of the human, the worldview fosters the belief that humans are resourceful, intelligent, and resilient enough to face any challenges that may come. This tacit missive bolsters societal torpor and political inaction, because it is widely assumed that technological innovations and interventions will overcome problems.
Fourth, the worldview impedes humans from recoiling from, or even seeing, the violence of an expansionism that fuels extinctions, population plunges, mass mortality events, and starvations of nonhumans. Because these experiences are happening to “the merely living,” they are nonissues for mainstream media and the political sphere, which are focused almost exclusively on human affairs. For example, humanity's impact has become so pervasive that migratory animal species are in decline and the very phenomenon of migration is disappearing around the world. Yet neither the loss of animal migrations nor the suffering of the animals involved seem to be matters of concern in public arenas.
Lastly, the supremacist worldview insinuates that embracing limitations is unbefitting of human distinction. Whether openly or implicitly, limitations are resisted as oppressive and unworthy of humanity's stature.
By operating on all these levels, the worldview of human distinction-and-prerogative obstructs the capacity to question human hegemony for the sake of Earth's inherent splendor and in the service of a high-quality human life within a downsized, equitable global civilization nested in an all-species commonwealth. Instead, the trends of more—on the population, consumption, and infrastructure fronts—are left to persist their course seemingly unassailable.
Toward Scaling Down and Pulling Back
The reigning human-nature hierarchical worldview thus hinders the recognition that scaling down and pulling back is the most farsighted path forward. Scaling down involves reducing the overall amount of food, water, energy, and materials that humanity consumes and making certain shifts in what food, energy, and materials are used. This quantitative and qualitative change can be achieved by actions that can lower the global population within a human-rights framework, shrink animal agriculture, phase out fossil fuels, and transform an extractionist, overproducing, throwaway, and polluting economy into a recycling, less busy, thrifty, more ecologically benign economy (10–12). These shifts must align with a new ethos in civil society toward shared norms of mindfulness around dietary choices, avoidance of waste, conservation of energy, and reuse and recycling of materials.
Scaling down can be complemented with substantially pulling back our presence from the natural world. Achieving continental-scale protection of terrestrial and marine habitats will enable sharing Earth generously with all its life forms (13). Recent research reveals that large-scale nature conservation is also a powerful counter to climate change by absorbing a sizable portion of the carbon dioxide of the industrial age and preventing additional carbon (stored in the ecosphere) from being released (14, 15). Vastly expanding marine protected areas will support the resurgence of marine life. Ambitious forest, grasslands, freshwater ecologies, and wetlands protection and restoration will prevent extinctions and preempt an anthropogenic mass extinction event. A robust global network of green and blue protected areas will save wildlife populations and animal migrations from their current downward spirals. Preserving the night sky in extensive swathes of wild nature will keep an open portal into the cosmos we inhabit.
Many of the global approaches called for in this pivotal moment may lack the glamor of technological and engineering breakthroughs, but they promise far-reaching strides in resolving the ecological crisis and preventing human and nonhuman suffering. Paramount examples include state-of-the-art family planning services for all (including modern contraceptive technologies), universal education from the age of 4 to 17 or 18, substantial reduction of animal-product consumption, adoption of the reduce-reuse-recycle paradigm as an everyday norm, massive protection of wild nature, and adoption of sustainable and ethical food production practices on land and sea.
Beyond Human Dominance
The dominant framework of technofixes, technological schemes, and fine-tuning efficiencies is by itself no match for the tidal wave of human expansionism expected in this century. Looming before us is the imminent escalation of food, energy, materials, and commodities production, and resulting increases in wildlands destruction, species extinctions, wildlife extirpations, freshwater appropriation, ocean degradation, extractionist operations, and the production of industrial, pesticide, nitrogen, manure, plastic, and other waste—all unfolding amid climate-change ordeals.
In the face of this juggernaut, a singular focus on a techno-managerial portfolio seems fueled by a source other than pragmatism alone. That portfolio—which would include such initiatives as climate geoengineering, desalination, de-extinction, and off-planet colonization—is in keeping with the social rubric of human distinction. The prevalent corpus resonates with a Promethean impulse to sustain human hegemony while avoiding the most expeditious approach to the ecological predicament—contracting humanity's scale and scope by means that will simultaneously strengthen human rights, facilitate the abolition of poverty, elevate our quality of life, counter the dangers of climate change, and preserve Earth's magnificent biodiversity.
To pursue scaling down and pulling back the human factor requires us to reimagine the human in a register that no longer identifies human greatness with dominance within the ecosphere and domination over nonhumans. The present historical time invites opening our imagination toward a new vision of humanity no longer obstructed by the worldview of human supremacy. Learning to inhabit Earth with care, grace, and proper measure promises material and spiritual abundance for all.
66 notes
·
View notes