#SQLi
Explore tagged Tumblr posts
Text
Cosmic Cyberlocution: Unraveling the Meta-Vulnerable Mazes of SQL Injection and the Dawn of Database Origami
SQL injection is a form of cybernetic locution where a syntax-disrupting injection molecule, or SQLI (SQL-yielding iconograph), sees a digital opportunity to extract logic-streaks by abusing macrosemic dilations that keep the integrity of a database system. The communication platforms in their most innocent form just want to move data back and forth, unassumingly creating a tunnel sphere wherein an SQLI can metamorphose into a mutable SQL worm.

Upon initiating a cabalistic interrogation, this spitfire worm deceptively mutters invocations: SELECT, INSERT, DELETE, or UPDATE; it dynamically forges new paths, unlocking chunks of cherished data as if these were open source caveats. Like a parasitic virtual predator inflation-depreciating misapplied coded queries, the SQL injection concurrently engenders a wormhole in this ostensibly invulnerable info-sphere.
Trans-culturally multiverse in application, SQLI transcends the commonly known mundane application layer in the OSI (Onion Skin Ideation). It dangerously dinner-jackets into engulfed Mare Nostrums, barrelling through Davis-matrix ethical firewalls by exploiting a netizen's IF and ELSE constructs. Flicking the digital switches of these database TRIGGERS an SQL injection, potentially extrapolating whole terabytes of vulnerable data.
Yet, software network security gurus can counter this invisible cyber sword with delightful robust-and-rogue defenses such as formless form validation, parameterized quarrying, and sweet-natured stored proceedings. These stellar, fortress-like broadswords of data protection can infinitely out-radiate the shadowy cross world attacks of SQLI. In stringent conformity with these arcane meta-protocols, it is plausible to wheel a rampart so immaculate virtually nullifying the SQL injections.
Thus, shaped by eleventh-dimensional axes of high abstractions, this meta-vulnerable loophole in a spontaneously ordered network lets the seemingly innocuous data-lite masquerade disrupt, disorient, and deconstruct, ultimately leading to the discovery of an information goldmine in the interstices of unsuspecting crypto-crannies. Its pure lunacy to let the truth tables turn oblique by these sentient, cyberlocutionary semantics. But in its twilight, it awakens an array of diasporic countermeasures crinkled onto the database origami to repudiate the SQL worm onslaught.
#ko-fi#kofi#geeknik#nostr#art#blog#writing#twitter#sql injection#cybersecurity#infosec#hacking#hackers#information security#security#networking#mysql#sql#sqli
1 note
·
View note
Text
for everyone who maintains 1 or more servers
my observability stack is now betterstack; prometheus+grafana and wazuh. pretty cool stuff. Used to main Netdata but i stepped off that bus when they started pushing their cloud shit
14 notes
·
View notes
Text
SQLi simulation using a virtual machine
Demonstration/simulation of SQL Injection attacks (In-band, Union-based, Blind SQLi) using a Kali Linux virtual machine and a Damn Vulnerable Web Application (DVWA) on a low difficulty level
Blind SQL provided in the video can be used also for gaining other sensitive information: length of the name of the database, database name itself etc.
the common attacks are shown and described shortly in the video, but of course for better learning you can try it yourself.
more resources where you can try out exploiting SQLi vulnerability:
- Try Hack Me SQLi Lab
- W3Schools SQL Injection
- Hacksplaining SQL Injection
more advanced pokemons can try:
- Try Hack Me SQli Advanced Lab
and of course DVWA is a great tool!
5 notes
·
View notes
Text
SQL Injection in RESTful APIs: Identify and Prevent Vulnerabilities
SQL Injection (SQLi) in RESTful APIs: What You Need to Know
RESTful APIs are crucial for modern applications, enabling seamless communication between systems. However, this convenience comes with risks, one of the most common being SQL Injection (SQLi). In this blog, we’ll explore what SQLi is, its impact on APIs, and how to prevent it, complete with a practical coding example to bolster your understanding.

What Is SQL Injection?
SQL Injection is a cyberattack where an attacker injects malicious SQL statements into input fields, exploiting vulnerabilities in an application's database query execution. When it comes to RESTful APIs, SQLi typically targets endpoints that interact with databases.
How Does SQL Injection Affect RESTful APIs?
RESTful APIs are often exposed to public networks, making them prime targets. Attackers exploit insecure endpoints to:
Access or manipulate sensitive data.
Delete or corrupt databases.
Bypass authentication mechanisms.
Example of a Vulnerable API Endpoint
Consider an API endpoint for retrieving user details based on their ID:
from flask import Flask, request import sqlite3
app = Flask(name)
@app.route('/user', methods=['GET']) def get_user(): user_id = request.args.get('id') conn = sqlite3.connect('database.db') cursor = conn.cursor() query = f"SELECT * FROM users WHERE id = {user_id}" # Vulnerable to SQLi cursor.execute(query) result = cursor.fetchone() return {'user': result}, 200
if name == 'main': app.run(debug=True)
Here, the endpoint directly embeds user input (user_id) into the SQL query without validation, making it vulnerable to SQL Injection.
Secure API Endpoint Against SQLi
To prevent SQLi, always use parameterized queries:
@app.route('/user', methods=['GET']) def get_user(): user_id = request.args.get('id') conn = sqlite3.connect('database.db') cursor = conn.cursor() query = "SELECT * FROM users WHERE id = ?" cursor.execute(query, (user_id,)) result = cursor.fetchone() return {'user': result}, 200
In this approach, the user input is sanitized, eliminating the risk of malicious SQL execution.
How Our Free Tool Can Help
Our free Website Security Checker your web application for vulnerabilities, including SQL Injection risks. Below is a screenshot of the tool's homepage:
Upload your website details to receive a comprehensive vulnerability assessment report, as shown below:
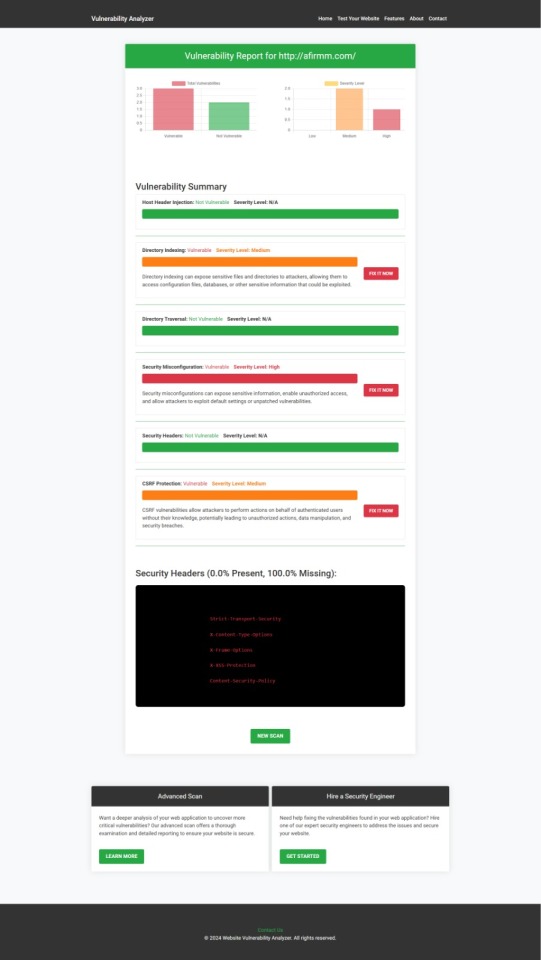
These tools help identify potential weaknesses in your APIs and provide actionable insights to secure your system.
Preventing SQLi in RESTful APIs
Here are some tips to secure your APIs:
Use Prepared Statements: Always parameterize your queries.
Implement Input Validation: Sanitize and validate user input.
Regularly Test Your APIs: Use tools like ours to detect vulnerabilities.
Least Privilege Principle: Restrict database permissions to minimize potential damage.
Final Thoughts
SQL Injection is a pervasive threat, especially in RESTful APIs. By understanding the vulnerabilities and implementing best practices, you can significantly reduce the risks. Leverage tools like our free Website Security Checker to stay ahead of potential threats and secure your systems effectively.
Explore our tool now for a quick Website Security Check.
#cyber security#cybersecurity#data security#pentesting#security#sql#the security breach show#sqlserver#rest api
2 notes
·
View notes
Text
Fortinet Warns of Severe SQLi Vulnerability in FortiClientEMS Software

Source: https://thehackernews.com/2024/03/fortinet-warns-of-severe-sqli.html
More info: https://fortiguard.fortinet.com/psirt/FG-IR-24-007
5 notes
·
View notes
Text
Functional Analyst E-commerce Shopify
https://tinyurl.com/26dnnvp3 Artia13 - Offres d'Emploi Functional Analyst E-commerce Shopify Emploi Belgique Titre du poste : Functional Analyst E-commerce Shopify Entreprise : SQLI Description du poste : ...
0 notes
Video
youtube
Customer Event 2025 in Amsterdam | SQLI Netherlands
0 notes
Photo

Освойте этичный веб-хакинг в реальном мире - XSS и SQLi - Udemy (2024)
Освойте этичный веб-хакинг в реальном мире - XSS и SQLi
Udemy
Изучите практические методы этического взлома для эксплуатации XSS и SQLi в реальных условиях Bug Bounty Hunting
Чему вы научитесь:
• Сценарии из реального мира
• Стратегии Bug bounty для получения максимального вознаграждения за обнаружение веб-уязвимостей.
• Выявление XSS-уязвимостей в реальных приложениях.
• Обход WAF
• Эксплуатация атак SQL Injection для обхода аутентификации и...
Читать далее
Подробнее на https://eground.org/threads/osvojte-ehtichnyj-veb-xaking-v-realnom-mire-xss-i-sqli-udemy-2024.145148/
0 notes
Text
Ingénieur Data
Job title: Ingénieur Data Company: SQLI Job description: passionnés du digital. Site web : Description du poste Nous recherchons un ingénieur Data sénior pour rejoindre nos équipes… et Azure Databricks, en garantissant la qualité et la fiabilité des données. Optimiser les performances des traitements… Expected salary: Location: Rabat Job date: Fri, 08 Nov 2024 03:22:50 GMT Apply for the job now!
0 notes
Text
Statistics
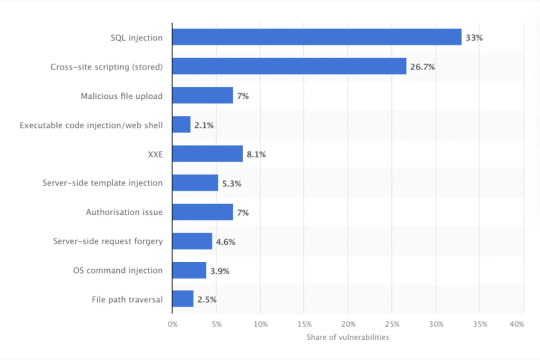
source: statista 2022 In 2023, SQL injection attacks were responsible for 23% of web application critical vulnerabilities discovered globally compared to 2022, where they were 33%. They remain one of the most prevalent security risks for web applications, despite a decline in its share of critical vulnerabilities from 33% in 2022 to 23% in 2023. This decrease indicates an improvement in secure coding practices and database security, but SQLi still poses a significant risk. ! this is why it it so important to share awareness and mitigation/defense measures on injection attacks
3 notes
·
View notes
Text
The Critical Truth About Security in Laravel Applications
Introduction
It is no big secret that more businesses are now building web solutions. Laravel is favored by developers worldwide for its elegant ease of use and robust functionalities. However, the harsh truth is that no framework, not even Laravel, is inherently secure without implementing effective Security in Laravel Applications protocols.

Many assume that using a robust framework or language will ensure that all security concerns are eliminated. Unfortunately, this belief often leads to overlooked vulnerabilities, leaving Security in Laravel Applications at risk. This is true for all technologies including Laravel.
Laravel is one of the most popular PHP frameworks, offering powerful tools and built-in security features to safeguard applications. While Laravel provides built-in security features, relying solely on the framework without a strategic approach to Security in Laravel Applications leaves applications exposed to attacks.
In fact, with the increasing sophistication of cyber threats, no application is immune to security vulnerabilities. It would be smart to trust a professional software development outsourcing company.
In this article, we will dive deep into the harsh realities of Laravel application security. It also explains the need for one to be more proactive when securing Laravel applicators; especially since the threats are getting more sophisticated.
Common Security Vulnerabilities in Web Applications

Understanding and addressing security vulnerabilities is crucial to building and maintaining secure web applications. By adopting a security-first mindset, performing regular audits, and following best practices, organizations can significantly reduce the risk of attacks and ensure the safety of their user’s data.
A well-established Laravel development company will have the expertise to help steer your project clear of such vulnerabilities. Here are some of the common security vulnerabilities:
SQL Injection (SQLi):
SQL Injection occurs when malicious input is passed into an SQL query, allowing attackers to manipulate the database.
Impact: This can lead to unauthorized access, data leakage, or even complete system compromise. Some of the other implications include data breach, data modification, or full database control.
Mitigation: Applications that do not properly sanitize user inputs are particularly vulnerable to this attack. Use prepared statements, parameterized queries, and ORM libraries that inherently protect against SQL injection.
Cross-Site Scripting (XSS):
XSS attacks happen when an attacker injects malicious scripts into web pages viewed by other users.
Impact: Stealing user credentials, spreading malware, or altering page content. This can result in data theft, session hijacking, or defacement of the website. XSS is typically found in web applications that improperly escape or filter user-generated content.
Mitigation: Sanitize and encode user inputs, use frameworks with built-in XSS protection, and implement Content Security Policy (CSP) headers.
Cross-Site Request Forgery (CSRF):
CSRF exploits the trust a web application has in a user's browser. An attacker tricks an authenticated user into executing unwanted actions, such as changing account details or making transactions, by sending a forged request from their session.
Impact: Unauthorized actions performed on behalf of a user.
Mitigation: Use anti-CSRF tokens, enforce SameSite cookie attributes, and verify the origin of requests.
Broken Authentication and Session Management:
Weak authentication and session management can lead to unauthorized access.
Impact: Account hijacking and privilege escalation. Issues such as weak passwords, poor session expiration policies, and improper session handling can allow attackers to take over user accounts.
Mitigation: Use secure session IDs, implement strong password policies, enable multi-factor authentication (MFA), and securely store credentials using industry-standard hashing algorithms.
Insecure Direct Object References (IDOR):
IDOR occurs when internal objects (such as database entries) are exposed without proper access controls.
Impact: An attacker can manipulate object identifiers (e.g., IDs in URLs) to gain unauthorized access to data they shouldn’t have access to. Access to sensitive data or modification of data.
Mitigation: Implement proper authorization checks, use indirect references, and validate user permissions before granting access.
Security Misconfiguration:
Misconfigured web servers, databases, or application frameworks can expose sensitive information or provide entry points for attackers. Examples include leaving default configurations intact, exposing unnecessary services, or using verbose error messages.
Impact: Information leakage, unauthorized access, and full system compromise.
Mitigation: Regularly review configurations, disable unused features, and enforce security best practices for server and application configurations.
Sensitive Data Exposure:
This occurs when sensitive data (e.g., financial, personal, or health information) is not adequately protected.
Impact: Insufficient encryption, improper storage practices, or insecure data transmission can lead to exposure: data theft, identity theft, or financial loss.
Mitigation: Use strong data storage and transmission encryption, enforce HTTPS, and secure API endpoints.
Broken Access Control:
Poorly implemented access control allows users to act beyond their intended privileges.
Impact: Unauthorized access to sensitive data or restricted features. This includes bypassing access restrictions, privilege escalation, or accessing restricted resources.
Mitigation: Implement role-based access controls (RBAC), enforce least privilege, and conduct regular access control audits.
Insufficient Logging and Monitoring:
Lack of proper logging and monitoring makes detecting and responding to security incidents difficult.
Impact: Increased time to detect breaches, lack of incident response. Without adequate visibility into application activities, suspicious behavior can go unnoticed until it's too late.
Mitigation: Implement comprehensive logging, monitor for anomalies, and set up alerting mechanisms for suspicious activities.
Insecure Deserialization:
Insecure deserialization happens when an application deserializes untrusted data, which can result in remote code execution or other malicious actions.
Impact: Remote code execution, denial of service, or privilege escalation. Attackers can exploit deserialization flaws to tamper with serialized objects and alter application logic.
Mitigation: Avoid deserialization of untrusted data, use formats like JSON instead of native serialization, and enforce strict input validation.
Using Components with Known Vulnerabilities:
Modern web applications rely on third-party libraries and frameworks.
Impact: Exploitation of known vulnerabilities, leading to data breaches or application compromise. Using outdated or vulnerable components can introduce security flaws into your application, making it susceptible to attacks.
Mitigation: Regularly update components, use dependency management tools, and monitor for security patches.
Unvalidated Redirects and Forwards:
This vulnerability occurs when an application accepts untrusted input that could alter the URL to which a user is redirected.
Impact: Phishing, redirecting to malicious sites. Attackers can use this to direct users to malicious sites, tricking them into providing sensitive information.
Mitigation: Avoid dynamic redirects, validate and sanitize all URLs, and implement a whitelist for redirects.
The assumption that a well-known framework automatically guarantees security is a big mistake. This assumption is particularly dangerous because it encourages complacency. Laravel, while offering a range of built-in security features, cannot cover every potential vulnerability that may arise from poor coding practices or weak configurations.
Understanding the Security Risks In Laravel

Laravel applications are often targeted by hackers due to their popularity and the potential for exploitation. The onus of securing an application lies not with the framework but with the developer. A secure framework provides tools and guidelines, but it is up to the developer to implement them effectively. Relying solely on the out-of-the-box features without understanding their limitations leaves room for exploitation.
Here are some of the common security risks in Laravel:
Authentication and Authorization:
Authentication and authorization form the backbone of any secure web application. While Laravel offers built-in authentication mechanisms, these systems are not foolproof. Developers need to implement additional layers of security, such as MFA and stringent password requirements, to protect user accounts from being compromised.
Session Hijacking and Insecure Cookies:
Session hijacking, where an attacker takes over a user’s session and impersonates them, is a significant security concern. Laravel provides mechanisms like CSRF protection tokens to prevent session hijacking, but developers must ensure that they are leveraging these tools correctly. Failure to enable secure cookie flags or regenerate session IDs after login can leave sessions vulnerable to attacks.
Laravel's CSRF Protection:
Cross-Site Request Forgery (CSRF) is an attack where a malicious website tricks a user into performing an action on another website without their consent. Laravel's built-in CSRF protection is only adequate if developers diligently ensure that every form includes a valid CSRF token. Periodically reviewing third-party libraries and integrations will also ensure that CSRF protection is not bypassed or omitted in those areas.
Regular Security Audits:
One of the most overlooked aspects of Laravel application security is the need for regular security audits. Regular security audits and code reviews are essential to identify potential vulnerabilities before attackers can exploit them. Developers must continuously monitor their applications, apply security patches, and review their code for possible weaknesses.
Laravel and Data Encryption:
Laravel provides robust encryption capabilities that are out of the box, allowing developers to encrypt sensitive data before storing it in the database. Developers must ensure that sensitive data, such as user credentials, financial information, and personal identifiers, are encrypted both at rest and in transit. Additionally, using robust encryption algorithms and securing encryption keys are crucial to preventing data breaches.
File Upload Vulnerabilities:
File uploads are a common feature in web applications, but they also pose significant security risks if not handled correctly. Improperly validated or sanitized file uploads can allow attackers to upload malicious files, such as executable scripts, and compromise the application’s server. Relying solely on the basic checks is insufficient. Attackers can still bypass these protections by manipulating file headers or using obscure file types. Implement strict file validation, sanitize file names, and store uploaded files in secure directories.
The Need for Effective Laravel Security Protocols
Securing a Laravel application is not a one-time task but a continuous process. It involves regular updates, vigilant coding practices, and the implementation of adequate security protocols. Keeping the Laravel framework and its dependencies updated is crucial, as this ensures that known vulnerabilities are patched.
Implementing comprehensive security protocols is essential to mitigate the risk of breaches and protect your Laravel application. Take advantage of the Laravel development services offered by experienced firms like Acquaint Softtech. We have the skills and resources to help you with your requirements.
There are several reasons why it is vital to implement effective security protocols. Here are some of the main reasons:
Prevent Data Breaches and Information Theft:
One of the most severe consequences of poor security is unauthorized access to sensitive information. This includes user credentials, financial details, and personal data. Attackers can exploit vulnerabilities to gain access to databases and steal confidential information. This can lead to legal consequences and business & financial loss.
Avoiding Website Defacement or Service Disruption:
Insecure Laravel applications are prone to attacks that result in unauthorized changes to the site content, known as website defacement. Attackers can exploit these weaknesses to modify website visuals, inject malicious content, or display defamatory messages. They can also initiate Denial-of-Service (DoS) attacks.
Prevent Remote Code Execution (RCE):
Laravel applications without robust security protocols are vulnerable to remote code execution attacks. In these attacks, attackers gain control over the server and execute arbitrary code, allowing them to take full control of the application and server environment.
Avoid Session Hijacking and Account Takeover:
Ineffective session management or weak authentication mechanisms can result in attackers hijacking active user sessions, leading to account takeovers. This can have serious repercussions, such as unauthorized access to sensitive user areas, modification of user data, and abuse of elevated privileges.
Avoid Reputation Damage:
A Laravel application that suffers from frequent security incidents can face irreversible reputational damage. This can lead to negative media coverage and bad publicity, impacting the brand image. It can also lead to loss of business partnerships and a tarnished reputation within the industry.
Prevent Code Integrity and Trust Issues:
If the application is found to have security vulnerabilities, specially in open-source projects or client applications, it can lead to loss of trust and affect other dependent applications.
Avoid Business Impact and Downtime:
Ultimately, ineffective security protocols can disrupt business operations, causing unplanned downtime or complete shutdowns. This results in revenue loss, operational setbacks, and loss of competitive advantage.
Here are some relevant statistics:
There were over 2365 cyberattacks in 2023, with over 343,338,964 victims.
The average cost of a data breach in 2024 is $4.88 Million.
The source for 35% of malware attacks in 2023 was email.
88% of cybersecurity breaches have a human error to blame.
97% of organizations are facing an increase in cyber threats since the war between Russia and Ukraine began in 2022.
Advantages Of Laravel Development
Laravel is one of the best web frameworks, and the fact that it is highly secure has a lot to do with it. There are many advantages to using Laravel. It is simple and easy to use, which makes it easy to build high-performing applications. It is highly flexible, and integrating third-party packages is easy.
Thus, businesses can benefit from their decision to hire Laravel developers. However, one of the most significant benefits is that it has several features dedicated to security. In fact, the latest Laravel, version 11 has many more features dedicated to make your application more secure.
Hire remote developers from a processional firm like Acquaint Softtech to gain the upper edge. The skilled developers here have the expertise and experience to build top-notch applications. The fact that we are an official Laravel Partner ensures we always deliver high-quality applications.
Conclusion
Security is an ongoing process that requires vigilance, expertise, and adherence to best practices. For Laravel applications, relying solely on default security features is not enough. Implementing a robust security strategy, conducting regular audits, and staying informed about emerging threats is essential to protecting both the application and its users from the consequences of ineffective security protocols.
The reality is that Laravel, while robust, cannot guarantee security on its own. Developers must stay proactive by combining Laravel's built-in features with industry-standard security protocols and best practices. A secure Laravel application is not just about using the right tools, it's about cultivating a security-first mindset and continuously evolving to stay ahead of potential threats.
#Security in Laravel Applications#Laravel Application Security#Secure Laravel Application#Hire Laravel Developers
0 notes
Text
Implementing a WAF for Protecting APIs from SQL Injection
Implementing a WAF for Protecting APIs from SQL Injection Introduction In today’s world of web application security, protecting APIs from SQL injection attacks is crucial. SQL injection (SQLi) is a common web application vulnerability where an attacker injects malicious SQL code to access sensitive data, alter database schema, or even take control of the database. In this article, we’ll explore…
0 notes
Text
SQL Injection in Drupal: How to Identify & Prevent Attacks
SQL Injection (SQLi) in Drupal: Identifying and Securing Your Website
Drupal is known for its flexibility and powerful content management capabilities. However, like any platform, it can be susceptible to security threats, particularly SQL Injection (SQLi) attacks. This blog will guide you on SQLi, the risks it poses to Drupal websites, and steps to detect vulnerabilities using our free Website Security Checker Tool. By the end, you'll have a clear understanding of how to protect your Drupal site.

What is SQL Injection (SQLi)?
SQL Injection is a common web security vulnerability that allows attackers to manipulate an application's database through input fields by injecting malicious SQL code. This can lead to unauthorized access, data theft, or even full control of the web application’s database.
Understanding SQLi in Drupal
Drupal is a popular CMS, and due to its database-driven nature, it's essential to ensure input fields are secure. Without proper validation, an attacker could exploit Drupal’s SQL-based functions, potentially leaking sensitive information.
Identifying SQLi Vulnerabilities in Drupal with a Free Tool
Detecting SQLi vulnerabilities is crucial for Drupal site security. Our free Website Security Checker Tool simplifies the process by scanning your website for various vulnerabilities, including SQLi risks. This tool generates a detailed report with steps to address any security issues it detects.

Using our tool, simply enter your Drupal website URL, and within seconds, you’ll receive a vulnerability assessment report. This report highlights potential SQLi risks and offers remediation tips, making it an essential tool for website administrators and developers.
Example: SQL Injection Vulnerability Code
Here’s a simple SQL Injection example that can affect Drupal or similar CMS platforms.
php
// Example code vulnerable to SQL Injection $userInput = $_GET['id']; $query = "SELECT * FROM users WHERE id = '$userInput'"; $result = db_query($query);
In this code snippet, $userInput is directly embedded in the SQL query without validation, allowing attackers to input malicious SQL code. For instance, an attacker could enter ' OR '1'='1 in place of id, which would bypass authentication.
Secure Code Solution To prevent SQL Injection, use parameterized queries or prepared statements:
php
// Secure code example $userInput = $_GET['id']; $query = "SELECT * FROM users WHERE id = :id"; $result = db_query($query, array(':id' => $userInput));
This method ensures any input is treated as data, not SQL commands, preventing SQL Injection.
Reviewing Your Vulnerability Report
After scanning your site with the tool, review the generated report, which details any SQLi vulnerabilities detected on your website. This report provides actionable steps for securing your website.

Regularly running vulnerability scans helps maintain security as your Drupal site evolves. Monitoring vulnerabilities and keeping your software up-to-date ensures a secure environment for your users.
How to Prevent SQL Injection in Drupal
To minimize SQL Injection risks, follow these tips:
Use Parameterized Queries - As shown above, parameterized queries prevent malicious code execution.
Update Regularly - Ensure Drupal core and modules are updated to the latest version.
Limit Database Privileges - Restrict database permissions to only what’s necessary.
Input Validation - Validate and sanitize all user inputs before processing them.
Conclusion
Securing your Drupal website from SQL Injection is essential for protecting user data and maintaining trust. Take advantage of our Website Security Checker Tool to detect and mitigate vulnerabilities effectively. Regular scans and proactive security practices will keep your website safe from SQLi and other potential threats.
#cyber security#cybersecurity#data security#pentesting#security#sql#sqlserver#the security breach show#drupal
0 notes
Text
SQLMutant: Advanced Tool for SQL Injection | #Pentesting #RedTeam #SQLInjection #SQLi #SQLMutant #Hacking
0 notes
Text
0 notes