#RFID readers
Explore tagged Tumblr posts
Text

Best Handheld RFID Readers
Boost your asset tracking and inventory management with UHF Handheld RFID Readers. Designed for portability and efficiency, these readers offer exceptional read range and accuracy. Perfect for various industries, they streamline operations and enhance productivity. Discover our range of UHF Handheld RFID Readers today!
1 note
·
View note
Text
Choosing the Right RFID Tag: A Breakdown of Different Types and Their Uses

Introduction to RFID Tags and Their Functionality
An RFID tag is composed of two fundamental components: an antenna for transmitting and receiving signals, and an RFID chip (or integrated circuit, IC) that stores the tag's ID and other relevant information.
RFID tags use radio waves to transmit data about an item to the antenna/reader combination. These tags typically do not have a battery, unless specified as Active or BAP tags. "They" refers to passive RFID tags, which do not have their own power source. Instead, they receive the energy required to operate from the radio waves generated by the RFID reader. When the tag receives the transmission from the antenna/reader, the energy flows through the internal antenna to the tag’s chip. This energy activates the chip, which then modulates the energy with the desired information and transmits a signal back to the antenna/reader.
On each chip, there are four memory banks – EPC, TID, User, and Reserved. Each of these memory banks contains information about the item that is tagged or the tag itself, depending on the bank and its specifications. Two of the memory banks, EPC and User, can store unique identifying information. The TID bank cannot be updated because it contains information about the tag itself and the unique tag identifier. The tag’s Reserved memory bank is used for special tag operations, such as locking the tag or expanding its available EPC memory. Different types of tags exist, including read-only tags that allow reading of stored data but not changing it, read/write tags that allow alteration or rewriting of stored data, and a combination of both, where some data is permanently stored while the remaining memory is left accessible for future encoding and updates.
RFID Tag Types and Operational Modes
Hundreds of different RFID tags are available in various shapes and sizes, each with features and options specific to certain environments, surface materials, and applications. Choosing the ideal tag for a specific application, environment, and item material is crucial for optimal tag performance.
An RFID Tag can be categorized into passive, semi-passive, or active.
Passive tags, the more common variant, do not require direct line-of-sight to a reader, making them versatile but with a shorter read range. They are compact and lightweight, activated by the energy from an RFID reader. This tag has a limited range of 0-15 meters, which makes it suitable for short-range applications only. The reading range is constrained by the power required to activate the chip. Given their size and cost, passive tags are the most common and can be inlaid like labels or take the form of hard tags made from materials such as plastic or metal. Ideal for applications requiring close-range identification, such as inventory management, access control, and retail item tracking.
Active RFID tags, featuring a battery that requires replacement every 3-5 years, excel in live tracking applications, offering an extended read range compared to passive tags. They have a higher reading range (up to 100 meters) than passive tags. These tags are more expensive due to the cost of their battery and transmitter. Despite the higher cost, they are suited for real-time tracking of high-value assets, vehicle tracking, and monitoring large-scale operations like shipping and logistics.
Semi-Passive Tags, very rarely used, function somewhere between active and passive tags. These tags are battery-powered, helping extend the communication range. Find applications in environments where a longer communication range is needed but where the continuous transmission of active tags may not be necessary, such as environmental monitoring and equipment maintenance tracking.
To Get More Information Visit our Website: https://www.idsolutionsindia.com/product/rfid-tags/
#RFID tags#RFID readers#RFID solutions#RFID technology#RFID tags cost#Active RFID tags#RFID tags manufacturers#RFID clothing tags#RFID laundry tags#Inventory Management System#Animal warehouse management
0 notes
Text
RFID Tags: The Future of Smart Inventory Management
An RFID tag, at its core, consists of two components – an antenna for transmitting and receiving signals, and an RFID chip (or integrated circuit, IC) storing the tag’s ID and other data. These tags are attached to items, facilitating their tracking using an RFID reader and antenna. Efficiency is paramount in inventory management. Saving time with increased accuracy poses an ongoing challenge for inventory managers across industries. Utilizing RFID Technology in inventory management, where each item is equipped with an RFID Tag and strategically placed readers or handheld RFID readers are used for rapid inventory, is rapidly gaining traction. This trend is driven by complexities arising from the sheer volume of inventory items, the rapid technological advancements, and the ever-expanding retail sector.
Moreover, current inventory management methods rely on manual counting processes or manual barcode scanning, both of which are time-consuming and not always accurate, resulting in potential sales losses or poor customer experiences.

Selecting the right RFID Tag for your inventory management system is crucial for its success. Below are some key considerations when choosing the appropriate RFID Tag:
Size & Form Factor: The size of the tag directly impacts its read range. Choosing the size based on the form factor of the RFID tags, such as wet inlays, labels, hard tags, or high-temperature tags, is essential.
Read Range: The appropriate read range, determined by the chip and RFID reader, should align with the application requirements, typically ranging from 3 feet to 12 feet.
Attachment Method: Various attachment options, including adhesive, magnet, screw, riveting, stitching, or hot stamping, are available and can also be customized.
Mounting Surface: Selecting the right tag for the existing mounting surface is crucial for optimal RFID performance. Metal surfaces, for instance, require specific Mount on metal tags rather than standard labels or tags.
Hundreds of RFID tags are available in diverse shapes and sizes, offering options tailored to specific environments, surface materials, and applications. Choosing the ideal tag for the application, environment, and item material is vital for optimal performance.
A successful inventory management system provides a clear, accurate view of inventory always. It offers item-level visibility and maintains historical records, enabling a chain of custody for each product. Users can track a specific product's journey from arrival to sale, allowing for detailed reports on product trends, replenishment information, and product visibility and display success.
#RFID tags#RFID tag manufacturers#RFID laundry tags#RFID clothing tags#RFID technology#RFID solutions#Active RFID tags#RFID readers#RFID chips
0 notes
Text
RFID readers are pivotal components within access control systems, utilizing Radio-Frequency Identification (RFID) technology to identify and track tagged objects or individuals. Employed in diverse sectors from retail to logistics, these readers wirelessly communicate with RFID tags, retrieving stored information such as product details or user credentials.
Functioning across various frequencies, they offer flexibility in range and application, from short-range proximity readers to long-range readers for logistics and asset tracking. With their seamless integration into access control systems, RFID readers enhance security and streamline processes, facilitating efficient and automated identification, authentication, and authorization protocols.
1 note
·
View note
Text
Are RFID Reader-Writers Compatible with All Types of RFID Tags?
In the realm of RFID technology, the compatibility between RFID reader-writers and RFID tags is a crucial aspect that directly impacts the efficiency and effectiveness of RFID systems. This article aims to explore the intricate relationship between RFID reader-writers and RFID tags, deciphering whether they are universally compatible.

Introduction to RFID Reader-Writers and RFID Tags
RFID Reader-Writers
RFID reader-writers are sophisticated devices designed to interact with RFID tags, enabling the reading, writing, and manipulation of data stored on these tags. They serve as the bridge between the physical world and digital databases, facilitating seamless data exchange in various applications.
RFID Tags
RFID tags are small electronic devices equipped with an antenna and a microchip that store unique identifiers and other relevant data. These tags come in various forms, including passive, active, and semi-passive, each catering to specific requirements and use cases.
Exploring Compatibility
Understanding Compatibility Factors
The compatibility between RFID reader-writers and RFID tags depends on several key factors, including frequency, protocol, and encoding standards. These factors dictate the communication protocols and data exchange mechanisms supported by both the reader-writer and the tag.
Frequency Compatibility
RFID systems operate at different frequencies, such as low frequency (LF), high frequency (HF), and ultra-high frequency (UHF). It is essential to ensure that the RFID reader-writer and the RFID tags operate at the same frequency for seamless communication.
Protocol Compatibility
RFID systems utilize various protocols, such as EPC Gen2, ISO 14443, and ISO 15693, to govern communication between the reader-writer and the tag. Ensuring protocol compatibility is crucial to enabling interoperability and data exchange between different RFID devices.
Encoding Standards
RFID tags may use different encoding standards, such as ASCII, Binary, or proprietary formats, to store and transmit data. Compatibility with these encoding standards ensures that the reader-writer can effectively interpret and manipulate data stored on the RFID tags.

Applications and Use Cases
Inventory Management
In the context of inventory management, RFID reader-writers must be compatible with a wide range of RFID tags to track and monitor inventory items accurately. Compatibility ensures seamless integration with existing systems and workflows, enabling efficient inventory management operations.
Access Control
For access control systems, RFID readers must be compatible with RFID tags used for personnel identification and authentication. Compatibility ensures reliable access control and security, allowing authorized personnel to access restricted areas seamlessly.
Challenges and Considerations
Vendor Lock-In
Some RFID systems may suffer from vendor lock-in, where proprietary technologies and protocols restrict interoperability with third-party devices. Overcoming vendor lock-in requires careful consideration of open standards and interoperable solutions.
Interference and Read Range
RFID systems may experience interference from environmental factors such as metal surfaces, liquids, and electromagnetic interference. Ensuring compatibility with RFID tags designed to withstand such challenges is essential for reliable operation and read range.
Conclusion
In conclusion, the compatibility between RFID reader-writers and RFID tags is a critical factor that influences the effectiveness and reliability of RFID systems. By understanding the compatibility factors and addressing potential challenges, organizations can ensure seamless integration and optimal performance of RFID technology across various applications.
#rfid readers#rfid reader writer#rfid scanner#rfid card reader#rfid scanner device#rfid reader and writer
0 notes
Text
Identifying The Importance Of RFID Readers In Asset Tracking Solutions
Radio Frequency Identification (RFID) has become an essential technology for asset tracking in various industries. At its core, an RFID system relies on RFID readers to capture data from RFID tags attached to objects. These readers emit radio waves that activate the tags, enabling them to transmit information like identification numbers, location, and condition. This captured data is then used to track and manage assets efficiently.
Enhanced Visibility and Control:
RFID readers play a crucial role in enhancing visibility and control over assets. They provide real-time data on the location and status of tagged items, allowing for:
Improved inventory accuracy: Real-time tracking eliminates manual counting and reduces errors, leading to more accurate inventory levels.
Streamlined logistics: Tracking assets throughout the supply chain optimizes delivery routes, reduces shrinkage, and improves overall efficiency.
Enhanced security: Access control systems can leverage RFID readers to restrict entry to unauthorized personnel or areas, safeguarding valuable assets.
Optimizing Operations and Maintenance:
RFID readers go beyond simple tracking by enabling:
Predictive maintenance: Sensor-equipped tags can transmit data on temperature, vibration, or other parameters, allowing for preventive maintenance before failures occur.
Automated workflows: RFID-based triggers can automate tasks like asset checkout or replenishment, streamlining operations and reducing manual intervention.
Data-driven decision making: The rich data collected by RFID readers can be analyzed to identify trends, optimize resource allocation, and make informed business decisions.
Choosing the Right RFID Reader:
Selecting the right RFID reader is crucial for successful asset tracking. Factors to consider include:
Frequency: Different frequencies offer varying read ranges and suit specific applications. UHF tags provide long-range tracking, while HF tags are better suited for smaller items or dense environments.
Read range: The required read range depends on the application. For example, tracking assets within a warehouse might require shorter-range readers than tracking pallets across a yard.
Environmental factors: Consider factors like temperature, humidity, and potential interference to ensure optimal reader performance.
iDTRONIC: A Leading Provider of RFID Solutions
iDTRONIC is a renowned manufacturer of high-quality RFID products, including a wide range of RFID readers. Their readers are known for their durability, reliability, and long read ranges. They offer various reader models to cater to diverse application needs, from compact handheld readers to high-performance fixed readers for industrial settings.
In conclusion, RFID readers are the backbone of effective asset tracking solutions. By providing real-time data and enabling automation, they offer significant benefits in terms of visibility, control, operational efficiency, and maintenance optimization. Choosing the right reader and partnering with a reliable provider like iDTRONIC is essential for maximizing the value of RFID technology in asset tracking applications.
0 notes
Text

RFID Readers and Smart Cities: Transforming Urban Living
As our cities grow at an unprecedented rate, they face numerous challenges in terms of infrastructure, sustainability, and quality of life. In this dynamic urban landscape, technology plays a pivotal role in addressing these challenges, and Radio-Frequency Identification (RFID) readers are emerging as a key enabler in the development of smart cities.
What Are Smart Cities?
Smart cities leverage technology and data to improve the quality of life for their residents while optimizing resource use, reducing waste, and enhancing overall efficiency. RFID readers are integral to this transformation.
**1. Efficient Transportation:
Traffic congestion and inefficient public transportation systems are common urban issues. RFID readers are used in smart city initiatives to monitor traffic flow, manage parking, and improve public transportation. RFID-enabled cards or tags can be used for contactless payment on buses and trains, reducing the need for physical tickets and queues.
**2. Waste Management:
Smart cities are turning to RFID technology to optimize waste collection. RFID tags on waste bins enable real-time monitoring, ensuring bins are only collected when full. This not only reduces unnecessary fuel consumption but also cuts down on emissions.
**3. Sustainable Energy:
RFID readers are used in smart meters to monitor and manage energy consumption. They enable residents to track their energy usage in real-time and make informed decisions to reduce their carbon footprint.
**4. Public Safety:
Enhancing public safety is a top priority for smart cities. RFID readers can be deployed in access control systems to secure public facilities, transportation hubs, and critical infrastructure. In emergency situations, RFID-enabled ID cards can be used for efficient evacuation management.
**5. Healthcare:
RFID readers play a crucial role in healthcare within smart cities. Patient records and medication can be tracked seamlessly, ensuring the right treatment at the right time. Additionally, RFID-enabled devices can assist in monitoring patients in real-time, even outside the hospital.
**6. Urban Planning:
For urban planners, RFID readers provide valuable data for optimizing city layouts and infrastructure. They can monitor the flow of people and vehicles, helping to design efficient road networks, public spaces, and buildings.
**7. Retail and Commerce:
Smart cities are reimagining retail. RFID readers are used for inventory management, reducing stockouts and overstock situations. In retail environments, RFID-enabled shopping experiences offer customers faster, more convenient checkouts.
**8. Environmental Conservation:
Many smart cities are embracing eco-friendly practices. RFID readers can be deployed in parks and nature reserves to monitor wildlife, track environmental changes, and prevent illegal activities such as poaching.
In conclusion
RFID readers are a foundational technology in the development of smart cities. They enable efficient transportation, sustainable energy use, enhanced public safety, and much more. As urban populations continue to rise, the integration of RFID technology will be key in creating cities that are not only smart but also sustainable, livable, and enjoyable for all residents. With ongoing innovation, we can expect even more exciting applications of RFID readers in the smart cities of the future.
0 notes
Text
Exploring the Role of RFID Readers in Asset Tracking Solutions
Radio Frequency Identification (RFID) technology has revolutionized the way businesses keep track of their assets. With the help of RFID readers, organizations can quickly and accurately monitor their inventory in real-time, enhancing the efficiency of their operations. The technology, which is rapidly gaining popularity among businesses of different sizes, is used to track objects, products, and equipment. RFID readers offer a robust and reliable solution that is easy to use, scalable, and cost-effective. In this blog post, we will explore the role of RFID readers in asset tracking solutions and how iDTRONIC Professional RFID is helping businesses to optimize their operations using this innovative technology.
iDTRONIC Professional RFID is a leading manufacturer of RFID readers that have been widely used in a variety of asset tracking solutions. These RFID readers have revolutionized the way organizations and businesses track their assets and manage their inventory. They offer a cost-effective, reliable and user-friendly solution that helps businesses to track their assets in real-time. The advanced features of iDTRONIC Professional RFID readers deliver high accuracy, instant read times and long read distances, which provides enhanced efficiency and higher productivity. Furthermore, the readers can be seamlessly integrated with existing asset management software, making it easier to manage assets across multiple locations. With the increasing need for better asset tracking solutions, iDTRONIC's RFID readers offer a scalable and flexible system that can fulfill businesses' needs.
iDTRONIC Professional RFID offers a wide range of RFID readers that are perfect for asset tracking solutions. With the increasing need for companies to manage their assets effectively, RFID technology is becoming more popular. RFID readers play an essential role in this technology since they read and interpret the data that's transmitted from RFID tags. One important factor to consider when choosing an RFID reader is the RFID frequencies that it supports. Most RFID readers operate at low, high or ultra-high frequencies. Companies must ensure that the RFID reader they choose supports the appropriate frequency for their RFID tags. The correct frequency ensures that data is transmitted efficiently, thereby providing accurate location and tracking information for assets. At iDTRONIC, we offer RFID readers that support various RFID frequencies, including Low Frequency, High Frequency, Ultra-High Frequency, and Active RFID. With this range of RFID reader choices, we can help our clients find the most appropriate readers to optimize their asset tracking solutions.
In conclusion, selecting the appropriate frequency for RFID tags is crucial to ensure efficient transmission of data and accurate asset tracking. At iDTRONIC, we understand the importance of choosing the right RFID reader that supports the appropriate frequency. Our range of RFID readers, including Low Frequency, High Frequency, Ultra-High Frequency, and Active RFID, ensures that our clients have the right tools to optimize their asset tracking solutions. With our expertise and diverse range of products, we are committed to providing innovative solutions that exceed our clients' expectations.
For more information about modern RFID Readers, visit our website https://idtronic-rfid.com/en/rfid-readers/
0 notes
Text

Tripod Turnstile Overview Tripod Turnstile, Swing Turnstile, as well as Flap Turnstile( RS Security Co., Ltd: www.szrssecurity.com) are modern-day control devices for pedestrian flows. They are made use of in position where the entrance and also departure of individuals need to be controlled, such as smart neighborhoods, canteens, resorts, galleries, gyms, clubs, subways, terminals, docks, and so on location. Making use of Tripod Turnstile, Swing Turnstile, as well as Flap Turnstile can make the flow of individuals orderly. Tripod Turnstile, Swing Turnstile, Flap Turnstile are made use of in combination with smart cards, finger prints, barcodes and also other identification system equipment to create an intelligent gain access to control channel control system; they are used in mix with computer systems, access control, participation, billing monitoring, ticket systems as well as other software program to develop a The smart Turnstile Gate thorough monitoring system can realize functions such as access control, attendance, consumption, ticketing, and current limiting. This Turnstile Gate administration system belongs to the "all-in-one card" as well as is mounted at flows such as neighborhoods, factories, wise buildings, canteens, etc. It can complete different management functions such as worker card traveling control, attendance at get off job as well as meals, and dining. Tripod Turnstile system attributes Fast and also practical: review the card in and out with one swipe. Utilize the authorized IC card and wave it before the wise Tripod Turnstile visitor to complete the Tripod Turnstile gate opening and also charge recording job. The card analysis is non-directional and the analysis as well as composing time is 0.1 seconds, which is quick and also practical. Protection and also confidentiality: Use history or local confirmation, authorized issuance, as well as unique identification, that is, the card can just be used in this system, and also it is confidential and also risk-free. Reliability: Card radio frequency induction, trustworthy and also steady, with the capacity to judge and also assume. Flexibility: The system can flexibly set entry as well as departure control workers consents, amount of time control, cardholder credibility as well as blacklist loss coverage, including cards as well as various other features. Versatility: Through authorization, the individual card can be utilized for "one-card" management such as parking, participation, access control, patrol, intake, and so on, making it very easy to understand numerous uses of one card. Simpleness: Easy to set up, basic to attach, the software application has a Chinese user interface as well as is very easy to operate. Tripod Turnstile, Swing Turnstile, and also Flap Turnstile( RS Security Co., Ltd: www.szrssecurity.com) are modern-day control tools for pedestrian passages. The usage of Tripod Turnstile, Swing Turnstile, and Flap Turnstile can make the flow of people orderly. Use the accredited IC card and also wave it in front of the clever Tripod Turnstile visitor to complete the Tripod Turnstile gate opening as well as fee recording work.
#Waist Height Turnstile#Flap Gate#Surveil Camera#Dead Bolt Locks#Gates Turnstiles#Turnstile Gate Nfc#Alcohol Breath Test#Uhf Rfid Reader Usb#Fingerprint Door Lock#Terra Quantum Bollard
9 notes
·
View notes
Text

Zebra FX9600 Fixed Mount RFID Reader
Looking for the best RFID reader in India? Look no further! Check out the Zebra FX9600 Fixed Mount RFID Reader, available at the best price in India. With its cutting-edge features and reliable performance, this RFID reader is ideal for various applications.
Key Features:
Frequency: UHF (865 - 928 MHz)
Mounting: Fixed/Wall Mount
Antenna Ports: 4 Ports
IP Rating: IP53
Experience seamless inventory tracking and management, streamline supply chain operations, and enhance efficiency in healthcare asset management and manufacturing automation with the Zebra FX9600 RFID reader.
Don't miss out! Ensure you have the latest technology to drive your business forward. Call us now at +91-8130501143 or visit us at https://www.encstore.com to get the Zebra FX9600 Fixed Mount RFID Reader today!
Applications:
Inventory tracking and management
Supply chain management and logistics
Healthcare asset management
Manufacturing and production automation
Ensure your business stays ahead of the curve with the best RFID reader available in India.
2 notes
·
View notes
Text
Active RFID Reader For Real-Time Monitoring and Control
Active RFID Reader is designed to detect indicators from active RFID tags, which have their personal strength supply. These readers are used in applications requiring long-variety monitoring, consisting of automobile monitoring, asset control, and personnel monitoring. They provide real-time information, prolonged range, and excessive accuracy in disturbing environments.
0 notes
Text

UHF Fixed RFID Readers
Enhance your inventory management with UHF Fixed RFID Readers. These devices provide reliable, high-speed reading of RFID tags, ideal for industrial and retail environments. Improve efficiency and accuracy in asset tracking with our top-notch UHF Fixed RFID Readers. Explore our selection today and optimize your operations!
1 note
·
View note
Text
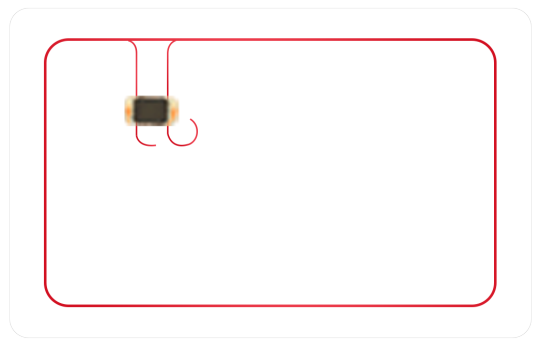
How To Make a Blank RFID Card?
How To Make a Blank RFID Card?
RFID card generation steps in detail: From design to production.
RFID card as a smart card, is widely used in access control, logistics, payment, and other fields. In this article, we will teach you step by step from design to production how to produce high-quality RFID cards to ensure the reliability and stability of the product. The following are the detailed generation steps.
1. Design the Appearance and Function of the RFID Card
First of all, before designing an RFID card, you need to clarify your needs and target users. According to different application scenarios and needs, you can determine the appearance and function of the RFID card. For example, you can choose the shape, size and material of the card as well as the design elements such as logo and text on the card.
At the same time, you also need to determine the function of the RFID card, such as access control card, public transportation card, membership card and so on. RFID cards with different functions may need to integrate different chips and modules for realizing the corresponding functions.
2. Select the Right RFID Chip
RFID chip, as the core component of RFID card, plays the role of storing and transmitting data. When choosing an RFID chip, you need to consider the following factors: chip type, operating frequency, read/write distance, storage capacity and security.
The common types of RFID chips on the market today are EM4100, MIFARE Classic, NTAG213, and so on. You can choose the appropriate chip type according to the demand.
3. Carry Out the Production of RFID Card
Before making an RFID card, you need to prepare an RFID chip, card substrate, card printing equipment, label application equipment, and other tools and materials.
First, the RFID chip will be pasted on the card substrate, and ensure that the connection between the chip and the card substrate is solid. Next, use the card printing equipment to print the card, you can add LOGO, text, and other elements on the card.
Finally, use the tag application equipment to encapsulate the card to ensure the quality and reliability of the card.
4. Conduct RFID Card Testing and Quality Control
After the production is completed, the RFID card to carry out the necessary testing and quality control. Tests can include read-and-write tests, communication stability tests, etc., to ensure that the RFID card can be used normally. At the same time, quality control, check the appearance of the card, printing quality, packaging quality, etc., to ensure that the quality of each RFID card meets the standards.
5. Mass Production and Issuance of RFID Cards
Finally, mass production and distribution of RFID cards is carried out. Determine the production quantity according to the demand and choose the appropriate production method. You can choose to produce by yourself, or you can choose to entrust the production to professional manufacturers.
0 notes
Text


The CRUISE2 Industrial-Grade Mobile Terminal, powered by SureTrack by SureSolutions, is a rugged handheld device designed for seamless RFID tracking and inventory management. It runs on Android 14 and features Wi-Fi 6, an octa-core processor, fingerprint recognition, and AI + OCR technology for precise data capture. With IP68 protection and 1.5m drop resistance, it ensures durability in demanding environments. SureTrack by SureSolutions provides this cutting-edge device for fresh produce management, warehousing, and retail operations. Available in long-range (10m), Wi-Fi 6, and standard models, it enhances operational efficiency with real-time tracking and streamlined workflows. https://www.suresolutions.in/category/rfid/
#rfid#rfid technology#rfid solutions#rfid tags#rfid reader#rfid supply chain#rfid antenna#rfid technology solutions#rfid-tags-technology#SureTrack
0 notes
Text
How to Install & Optimize Your RFID Tag Reader System
Introduction
Radio Frequency Identification (RFID) technology has revolutionized asset tracking, inventory management, and supply chain operations. However, the efficiency of an RFID tag reader system depends on proper installation and optimization. In this comprehensive guide, we will walk you through the best practices for setting up and enhancing your RFID reader system to ensure maximum efficiency and accuracy.
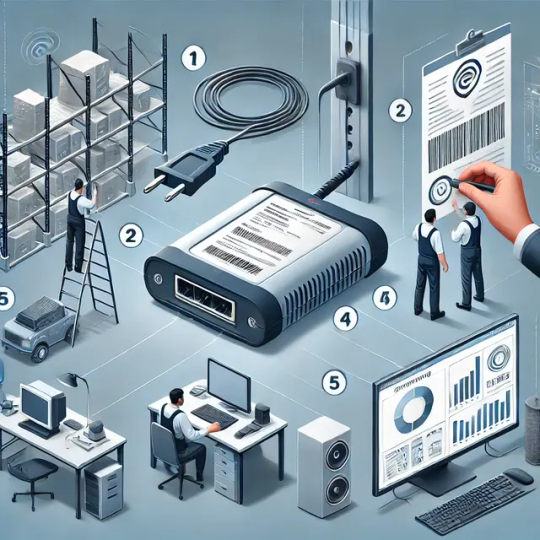

Step 1: Understanding RFID Components
Before installation, it’s crucial to understand the essential components of an RFID system:
RFID Tags: These contain embedded microchips and antennas that store data.
RFID Readers: Devices that emit radio waves to communicate with RFID tags.
Antennas: Transmit signals between the tags and the reader.
Middleware & Software: Process and interpret RFID data for integration with business systems.
Step 2: Selecting the Right RFID System
Choosing the right RFID system is critical for achieving optimal results. Consider the following factors:
Frequency Range: RFID operates in different frequency bands: Low Frequency (LF), High Frequency (HF), and Ultra High Frequency (UHF). Choose one based on your operational needs.
Read Range Requirements: Determine whether you need short-range or long-range reading capabilities.
Environmental Conditions: Harsh environments may require ruggedized RFID tags and readers.
Data Storage & Integration: Ensure the system can seamlessly integrate with your ERP or inventory management system.
Step 3: Planning RFID Reader Placement
Proper placement of RFID readers is crucial for ensuring accurate tag detection. Consider these best practices:
Minimize Interference: Avoid placing readers near metallic surfaces, electronic equipment, or sources of radio noise.
Optimize Read Zones: Position antennas strategically to maximize coverage and minimize blind spots.
Test Placement: Conduct a site survey to identify optimal reader locations before final installation.
Consider Orientation: The angle and distance between tags and readers affect read accuracy.
Step 4: Installing RFID Hardware
1. Setting Up RFID Readers & Antennas
Mount readers securely in designated locations.
Connect antennas to readers using RF coaxial cables.
Ensure antennas are aligned properly for maximum signal strength.
2. Deploying RFID Tags
Select Appropriate Tags: Choose tags based on application needs (passive, active, or semi-passive).
Ensure Proper Tag Placement: Place tags where they are easily scannable and not obstructed by materials that can interfere with radio signals.
Test Tag Readability: Before full deployment, test tags under real-world conditions to ensure they are readable from different angles and distances.
3. Connecting to the Network
Connect readers to the local network via Ethernet, Wi-Fi, or Bluetooth.
Configure IP addresses and establish communication with the central server.
Ensure adequate power supply to all components.
Step 5: Configuring & Optimizing the RFID System
After installation, fine-tuning the system ensures optimal performance.
1. Configuring RFID Reader Settings
Adjust read power settings to avoid interference and improve accuracy.
Set up data filtering to eliminate duplicate or incorrect tag reads.
Define read zones to control where and when tags are read.
2. Software Integration
Connect the RFID system to inventory management, asset tracking, or ERP software.
Implement automated data logging and reporting for streamlined operations.
Ensure real-time data synchronization with enterprise systems.
3. Conducting Performance Testing
Run benchmark tests to measure read rates and system efficiency.
Identify and troubleshoot weak signal areas or interference zones.
Conduct stress tests to determine system reliability under high workloads.
Step 6: Maintaining & Troubleshooting Your RFID System
Regular maintenance is essential to prevent downtime and performance issues.
1. Routine Inspections
Check for loose connections, damaged antennas, or misplaced readers.
Ensure RFID tags are intact and not obstructed by environmental factors.
2. System Performance Monitoring
Use RFID analytics tools to monitor tag reads and identify irregularities.
Regularly update firmware and software to keep the system up-to-date.
3. Troubleshooting Common Issues
Interference Problems: Reposition readers and reduce external RF noise sources.
Tag Read Failures: Adjust reader power settings and verify tag placement.
Connectivity Issues: Restart network connections and check system logs for errors.
Conclusion
Installing and optimizing an RFID tag reader system requires careful planning, proper hardware setup, and continuous performance monitoring. By following these best practices, businesses can achieve enhanced tracking efficiency, improved accuracy, and seamless data integration. Implementing these steps will ensure your RFID system operates at peak performance, leading to increased operational efficiency and cost savings.
0 notes
Text

ID Tech Solution's Trusted RFID Products for Indian Businesses
Trust ID Tech Solution to redefine reliability in RFID readers writers for Indian businesses. Our range of trusted RFID products assures unparalleled performance and durability, meeting the diverse needs of various industries. With a focus on innovation and quality, we provide solutions that set benchmarks for reliability and functionality in India's evolving market landscape.
0 notes