#Queen of France (c.1575)
Explore tagged Tumblr posts
Text

Unknown - Portrait of Louise of Lorraine, Queen of France (c.1575)
#art#paintings#museum#art pieces#tumblr art#Unknown - Portrait of Louise of Lorraine#Queen of France (c.1575)
119 notes
·
View notes
Text

4 notes
·
View notes
Text

Louise de Lorraine
Artist: Manner of François Clouet (French, c. 1516–1572)
Date: c. 1575
Medium: Oil on canvas
Collection: Museum of Fine Arts, Houston, TX, United States
Louise of Lorraine
Louise of Lorraine (French: Louise de Lorraine-Vaudémont; 30 April 1553 – 29 January 1601) was Queen of France as the wife of King Henry III from their marriage on 15 February 1575 until his death on 2 August 1589. During the first three months of their marriage, she was also Queen of Poland and Grand Duchess of Lithuania. As a dowager queen, Louise held the title of Duchess of Berry.
#portrait#louise of lorraine#francois clouet#french painter#queen of france#french history#costume#embroidery#handkerchief#coif#french art
9 notes
·
View notes
Text
The King & Queen of the Bean
“The custom of electing a King and Queen of the Bean on Twelfth Day is still kept up all over the north of France. A miniature porcelain figure of a child is sometimes substituted for the bean in the cake. If the lot, whether bean or doll, falls to a boy he becomes King and chooses his Queen; if it falls to a girl she becomes Queen and chooses her King.”
—J. G. Frazer, The Scapegoat (The Golden Bough, vol. IX, 1913, p. 315)
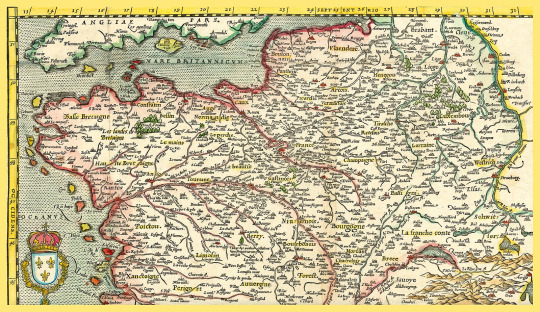
Map of Northern France, c. 1575, by the XVIème cent. French historian François de Belleforest.
(Source: François de Belleforest, Public domain, via Wikimedia Commons)
#jg frazer#the golden bough#the golden bough vol ix#queen of the bean#king of the bean#twelfth day#epiphany#northern france#france#folk customs#king cake#beans
0 notes
Photo

Louise of Lorraine, Queen of France, 1575
56 notes
·
View notes
Photo

María de’ Medici, by Frans Pourbus, c. 1606
Maria de' Medici (26 April 1575 – 3 July 1642) was Queen of France as the second wife of King Henry IV of France, of the House of Bourbon. She was a member of the wealthy and powerful House of Medici. Following the assassination of her husband in 1610, which occurred the day after her coronation, she acted as regent for her son, King Louis XIII of France, until 1617, when he came of age. She was noted for her ceaseless political intrigues at the French court and extensive artistic patronage.
7 notes
·
View notes
Text
Events 1.25
41 – After a night of negotiation, Claudius is accepted as Roman emperor by the Senate. 750 – In the Battle of the Zab, the Abbasid rebels defeat the Umayyad Caliphate, leading to the overthrow of the dynasty. 1348 – A strong earthquake strikes the South Alpine region of Friuli in modern Italy, causing considerable damage to buildings as far away as Rome. 1494 – Alfonso II becomes King of Naples. 1515 – Coronation of Francis I of France takes place at Reims Cathedral, where the new monarch is anointed with the oil of Clovis and girt with the sword of Charlemagne. 1533 – Henry VIII of England secretly marries his second wife Anne Boleyn. 1554 – São Paulo, Brazil, is founded by Jesuit priests. 1573 – Battle of Mikatagahara: In Japan, Takeda Shingen defeats Tokugawa Ieyasu. 1575 – Luanda, the capital of Angola, is founded by the Portuguese navigator Paulo Dias de Novais. 1585 – Walter Raleigh is knighted, shortly after renaming North America region "Virginia", in honor of Elizabeth I, Queen of England, sometimes referred to as the "Virgin Queen". 1704 – The Battle of Ayubale results in the destruction of most of the Spanish missions in Florida. 1755 – Moscow University is established on Tatiana Day. 1765 – Port Egmont, the first British settlement in the Falkland Islands near the southern tip of South America, is founded. 1787 – Shays's Rebellion: The rebellion's largest confrontation, outside the Springfield Armory, results in the killing of four rebels and the wounding of twenty. 1791 – The British Parliament passes the Constitutional Act of 1791 and splits the old Province of Quebec into Upper Canada and Lower Canada. 1792 – The London Corresponding Society is founded. 1819 – University of Virginia chartered by Commonwealth of Virginia, with Thomas Jefferson one of its founders. 1858 – The Wedding March by Felix Mendelssohn is played at the marriage of Queen Victoria's daughter, Victoria, and Friedrich of Prussia, and becomes a popular wedding processional. 1879 – The Bulgarian National Bank is founded. 1881 – Thomas Edison and Alexander Graham Bell form the Oriental Telephone Company. 1890 – Nellie Bly completes her round-the-world journey in 72 days. 1909 – Richard Strauss's opera Elektra receives its debut performance at the Dresden State Opera. 1915 – Alexander Graham Bell inaugurates U.S. transcontinental telephone service, speaking from New York to Thomas Watson in San Francisco. 1917 – Sinking of the SS Laurentic after hitting two German mines off the coast of Northern Ireland. 1918 – The Ukrainian People's Republic declares independence from Soviet Russia. 1918 – The Finnish Defence Forces (The White Guards) are established as the official army of independent Finland, and Baron C. G. E. Mannerheim is appointed its Commander-in-Chief. 1924 – The 1924 Winter Olympics opens in Chamonix, in the French Alps, inaugurating the Winter Olympic Games. 1932 – Second Sino-Japanese War: The Chinese National Revolutionary Army begins the defense of Harbin. 1937 – The Guiding Light debuts on NBC radio from Chicago. In 1952 it moves to CBS television, where it remains until September 18, 2009. 1941 – Pope Pius XII elevates the Apostolic Vicariate of the Hawaiian Islands to the dignity of a diocese. It becomes the Roman Catholic Diocese of Honolulu. 1942 – World War II: Thailand declares war on the United States and United Kingdom. 1945 – World War II: The Battle of the Bulge ends. 1946 – The United Mine Workers rejoins the American Federation of Labor. 1946 – United Nations Security Council Resolution 1 relating to Military Staff Committee is adopted. 1947 – Thomas Goldsmith Jr. files a patent for a "Cathode Ray Tube Amusement Device", the first ever electronic game. 1949 – The first Emmy Awards are presented in the United States; the venue is the Hollywood Athletic Club. 1960 – The National Association of Broadcasters in the United States reacts to the "payola" scandal by threatening fines for any disc jockeys who accept money for playing particular records. 1961 – In Washington, D.C., US President John F. Kennedy delivers the first live presidential television news conference. 1964 – Blue Ribbon Sports, which would later become Nike, is founded by University of Oregon track and field athletes. 1967 – South Vietnamese junta leader and Prime Minister Nguyen Cao Ky fires rival, Deputy Prime Minister and Defence Minister Nguyen Huu Co, while the latter is overseas on a diplomatic visit. 1969 – Brazilian Army captain Carlos Lamarca deserts in order to fight against the military dictatorship, taking with him ten machine guns and 63 rifles. 1971 – Charles Manson and four "Family" members (three of them female) are found guilty of the 1969 Tate–LaBianca murders. 1971 – Idi Amin leads a coup deposing Milton Obote and becomes Uganda's president. 1979 – Pope John Paul II starts his first official papal visits outside Italy to The Bahamas, Dominican Republic, and Mexico. 1980 – Mother Teresa is honored with India's highest civilian award, the Bharat Ratna. 1986 – The National Resistance Movement topples the government of Tito Okello in Uganda. 1990 – Avianca Flight 52 crashes in Cove Neck, New York, killing 73. 1993 – Five people are shot outside the CIA Headquarters in Langley, Virginia. Two are killed and three wounded. 1994 – The spacecraft Clementine by BMDO and NASA is launched. 1995 – The Norwegian rocket incident: Russia almost launches a nuclear attack after it mistakes Black Brant XII, a Norwegian research rocket, for a US Trident missile. 1996 – Billy Bailey becomes the last person to be hanged in the United States. 1998 – During a historic visit to Cuba, Pope John Paul II demands political reforms and the release of political prisoners while condemning US attempts to isolate the country. 1998 – A suicide attack by the Liberation Tigers of Tamil Eelam on Sri Lanka's Temple of the Tooth kills eight and injures 25 others. 1999 – A 6.0 magnitude earthquake hits western Colombia killing at least 1,000. 2003 – Invasion of Iraq: A group of people leave London, England, for Baghdad, Iraq, to serve as human shields, intending to prevent the U.S.-led coalition troops from bombing certain locations. 2005 – A stampede at the Mandhradevi temple in Maharashtra, India kills at least 258. 2006 – Mexican professional wrestler Juana Barraza is arrested in connection with the serial killing of at least ten elderly women. 2010 – Ethiopian Airlines Flight 409 crashes into the Mediterranean Sea off the coast of Na'ameh, Lebanon, killing 90. 2011 – The first wave of the Egyptian revolution begins throughout the country, marked by street demonstrations, rallies, acts of civil disobedience, riots, labour strikes, and violent clashes. 2013 – At least 50 people are killed and 120 people are injured in a prison riot in Barquisimeto, Venezuela. 2015 – A clash in Mamasapano, Maguindanao in the Philippines kills 44 members of Special Action Force (SAF), at least 18 from the Moro Islamic Liberation Front and five from the Bangsamoro Islamic Freedom Fighters. 2019 – A mining company's dam collapses in Brumadinho, Brazil, a south-eastern city, killing at least seven people and leaving 200 missing.
0 notes
Text
Summarized Chinese History by Tiarra De Soto
Trust me, I’m a History major. Here to spread my love for history.
Chinese dynasties:
1. Xia (2205-1575 BC)
-not considered as the 1st dynasty by most people because there was no system of record and writing
- believed as an urban legend
2. Shang (1570 - 1045 BC) -Beijing city
-ruled areas in the Yellow River (Huang Ho)
-Bronze Age (honoured bronze higher than silver
-barbaric sacrifices
-addicted to hunting and warfare
3. Zhou (1045- 256 BC) -Xian City
-longest ruling dynasty
-1st used the Mandate of Heaven to justify their rule {what the Chinese believed gave their rulers right to be emperor}
-Confucianism
-developed new weapons
-psychological warfare
-feudal system based on Confucius
-7 states battled for supremacy
-Jade represented their noble ranks
4. Qin (221-206BC)
-Shi Huangdi became emperor (1st emperor of China; died in 210 BC)
-beginning of the Great Wall of China
-roads and canals were built (most resourceful)
-feudal system was eliminated
-created the monetary system
-history and poems were destroyed (because Shi Huangdi wanted to recreate China in his reign)
-destroyed 2/3 of enemy's population
-Terracotta Warriors
4.1.1 The Great Wall of China
-thousands of men exposed to fatigue
-monument of dynastic might
-warning to the outside that China is united
-6000ft.
* 15 years of chaos after Shi Huangdi's death
5. Han (206 - 220 AD)
-Wu Di (5th emperor)
-established the civil service to create a strong and organized government
-papers and porcelain were invented
-embraced Confucianism, poetry, and literature
- Silk was the choice of fashion (imported silk to other nations like Persia, Baghdad, and Rome)
6. Six Dynasties (222-581 AD)
-China wasn't united under one ruler
7. Sui (5890618 AD)
-united China under one rule
-expanded the Great Wall and built Grand Canal
8. Tang (618-907 AD)
-peace and prosperity
-Golden Age
-Capital: Chang'an
9. Five Dynasties (907-960 AD)
-peasant rebellion takes down Tang
10. Song (960-1279 AD)
-reunited under the dynasty
-China became world leader in science and tech., including inventions: gunpowder and compass
11. Yuan (1279-1368)
-After Mongols defeated the Song, Kublai Khan, a Mongol leader, established this power
12. Ming (1368-1644)
-finished the Great Wall and the Forbidden City
-came to power by overthrowing the Mongols
13. Qing/ Manchu (1644-1912)
-last dynasty
-period of prosperity
-middle of this era, there were natural disasters, rebellions, invasions, and inept ruling courts
-Henry Pu Yi was the last emperor of China
The Advent of Europeans
1. Portuguese
-spread the knowledge of Western sciences among Chinese scholars
-Confucian scholars began to oppose the spread of Christianity
2. Spaniards
-Canton Trade
3. Dutch
-settled in Taiwan in1660s
-improve their relations with the Manchu government which came to power subsequently
4. British
-made an attempt to trade with the Chinese at Canton but failed
-led to the Opium War
-1685, Chinese opened port of Canton for trade and issued the necessary licence to European trading & British East India Co.
-Hoppo (Chinese Imperial Commissioner at Canton) allowed British to set up a permanent factory at Canton
5. French
-came in the Opium War 2
-Emperor Napoleon Bonaparte saw an opportunity to declare war in China
-Anglo-French Expedition
Opium War I
Causes:
-emperor of China banned the import of opium because Chinese were addicted
-Lin Tse-hsu (Hoppo) sent a mail to Queen Victoria (Britain) to declare that import of opium is no longer valid
-Britain did not follow; still continued to import
-British Captain Elliot was forced to surrender 20,000 chests of opium
-Lin dumped these chests of opium into the sea
Results:
-British fleet approached Canton in June 1840 and demanded from the Chinese gov't compensation for loss of opium and the necessary cost of the expedition
-British fleet blockaded Canton. 2000 troops sent from India occupied it.
-battled
-British won, China lost
=TREATY OF NANKING (August 29,1842)
a.) protection of the British subjects in China
b.) their trade in 4 important ports: Amoy, Foochow, Ningpo, and Shanghai were to be supervised by consular authorites
c.) cession of island of Hong Kong in perpetuity
d.) compensation of $21,000,000 to be paid in 4 instalments ($6,000,000 for the loss of opium, $12,000,000 for the cost of the war, and $3,000,000 for the debts owed by the Chinese authorities)
e.) the Cohong stood abolished
f.) easy communications through diplomatic channels
g.) tariff regulation regulating foreign trade
Opium War II
Cause: (Britain)
-Chinese vessel, Lorcha Arrow, flying a British flag was seized by a Chinese police patrol at Canton on charges of smuggling and piracy
-The British captain protested and the vessel was returned, though not the crew
-Britain asked for an apology, which China didn't give
Cause: (France)
-French missionary, Abbe Chapdelaine, trespassed. China found this act guilty. Was sentenced to death
-France saw this as "judicial murder"
-Napoleon Bonaparte saw this as an alibi to declare war
Results:
-Anglo-French Expedition
-China lost yet again
=TREATY OF TIENTSIN (June 26, 1858)
a.) diplomatic relations on the footing of equality were to be established between Britain and China with the former's minister residing at Peking
b.) China agreed to open 10 more ports for British trade
c.) British were to enjoy freedom of travel and conduct missionary activity
d.) extra-territoriality
e.) British vessels were to have access to all treaty ports
f.) Indemnity of 4,000,000 silver dollars was to be paid to the British Lord Elgin
Taiping Rebellion (1850-1862)
-means "great peace"
-ironically characterized by great violence
-rebels controlled half of China, mainly the valley of Yang Tse
Leader of the rebellion: Hung Hsiu-Chuan (from peasant community, Hakka)
Reasons of the movement:
-to bring collapse of the corrupt Manchu government
-establish a society based on justice
Hung Hsiu-Chuan:
-Christian fanatic
-set up a secret society called "Society of God" with friend Feng Yun-shan
* movement began by breaking of the Buddhist and Taoist idols
Shang Ti Hui movement
-got support of members of the White Lotus Society
-organized to launch an attack against Manchu Army
New dynasty was ushered
-Taiping Tien Kuo
-Hung as heavenly prince
-idea of universal brotherhood was spread
-movement is popular among millions of peasants
Supporters of Taiping:
-peasants
-artisans
Movement:
-increased population
-mismanagement of economy
-tax was calculated in terms of silver but paid in copper
-Chinese troops forced charcoal workers from society of God to give contributions, but they refused.
quarrel & rioting
-Emperor sent 2 commissioners to quell the riots
-Hung got mad and declared revolt "Exterminate the Manchus!"
-Hung built a powerful military force. Commanded by great generals to defend the movement
Results:
-25,000,000 were killed
-He and his soldiers wasted too much time indulging in all kinds of pleasures
-Hung did not give lands to peasants like he promised
-Hung committed suicide and his followers were defeated.
-This great rebellion was crushed.
Significance of the rebellion:
-Hung made a blueprint for China to have a society based on social and economic justice
Tung Chih Restoration
-means Union for Order
-engineered by Empress Dowager
-to revive China's dynastic leadership (because they always lose at wars, hence The Years of Humiliation)
People:
1. Tseng Kuo Fan
-spread of western education and influences
2. Feng Kuei Fan
-combination of Western education and Confucian teachings
3. Wang Tao
-Father of Journalism
-advocated Chinese writing into Western
4. Yen Fu
-urged the Chinese to lower their sense of superiority
5. Kang Yu Wei
-Hundred Days Reform (from feudal system to a modern industrialized state)
Chinese response to the Christian missions
-they were deeply disturbed
-Confucian Chinese envious of Christian converted Chinese because of special protection from the church
Result:
TIENTSIN MASSACRE
-killed Christian Chinese and foreign missionaries
-burnt the French Consulate
-Chinese government were to apologize to French government
-China had a bad reputation
The French conquered Indo-China
-France planed to make spiritual and political conquests over China's vassal states like Vietnam
-France conquered Vietnam, Cambodia, and Laos
-led to the Sino-French War
Sino-French War
-China was provoked with France conquering her vassal states
-battled
-China lost.....again
-China was bitter because this was the 1st MODERN war they've lost
Significance:
-rise of nationalism
Boxer Rebellion
-used their fists for battle, hence the title
-"Overthrow the Qing! Destroy the foreigners!"
-goal was to destroy the foreigners IN China and the converted Christian Chinese
-Chinese officials supported this rebellion
-Western powers helped suppress this movement
Result:
The Boxer Protocol
a.) China were to apologize to Japan and Germany for killing their minister and chancellor
b.) punish the Chinese officials that supported this rebellion
c.) suspend official examinations in 45 Chinese cities where violent outbreaks took place
d.) agree to expand foreign legations in Peking
e.) destroy Taku forts and allow the occupation of foreigners at 13 places to ensure free access to Peking
f.) raise import duties to 5% and pay $333,000,000 as war indemnity
Sino-Japanese War
-Tonhak rebellion in Korea (severe poverty)
-Korea asked China to suppress the war
-officer notified Japan, Japan got mad
then...
China VS Japan
-Japan crashed Chinese forces: land and water
Results:
-CHINA LOST AGAIN!!! :(
-open to South-West ports for trade for the Japanese
-Treaty of Shimonoseki
-China gave up Korea
-Taiwan and Pescadores islands ceded to Japan
-war indemnity
-Japan gained most favored nation of China
.....then after years and years of humiliation.....
The Open Door Policy
-United States advocated this to China
-dispatchment of European powers
-China were to be open to trade on equal basis
-originally Britain's initiation, but did not meet with adequate response from other European powers
The Outbreak of Chinese Revolution of 1911
-The Wuchang Uprising: the mishandling of railway protection movement
-Sun Yat Sen established the Kuomintang Party (Nationalist Party)
Sun Yat Sen's plan of actions:
1. Nationalism: People's rule
2. Democracy: People's authority
3. Socialism: People's livelihood
Sun Yat Sen VS Yuan Shi Kai
Nationalist VS Dictatorship
-Nationaists won= Sun Yat Sen was the 1st president of Republican China
-Soviet Union supported Sun Yat Sen
-Sino-Soviet Relations
-Sun Yat Sen sent his follower, Chiang Kai Shek to Russia to acquire military training
-Chiang Kai Shek reigned as the president of the nationalist party and China
Rise of Communism
led by: Mao Zedong/ Mao Tse Tung
-in rivalry with the Kuomintang Party
-did more than the Kuomintang party= sparked an envy
-Japan were to invade China= Kuomintang and Communists joined forces, called the United Front
-United Front defeated Japan. China won at last!
-Kuomintang became corrupt
-people in favor of Communism
-Civil war = Communism won
-Chiang Kai Shek fled to Taiwan
Mao's Communist China
-did a lot for China's economy
-elimination of feudal elements
-Mao Zedong was a follower of Marxism-Leninism
-make China industrialized
-women enjoyed equal rights
-schools and colleges increased greatly by 1956
Reforms:
The Great Leap Forward
-radical strategy for rapid economic growth development of the country. Strategy to increase agricultural output
Commune System
-land owning peasants worked in the communes.
Cultural Revolution (1965)
-re-educating the intellectuals and upper class in China
-called on young people to attack pragmatic leaders
-created a generation of lost youth known as the Red Guard
-economic development
*reforms were not successful
Deng Xiaoping
-Mao Zedong's successor
-took power of China following the 4 modernizations: Agriculture, Industry, Science, and Technology and Military
0 notes
Text
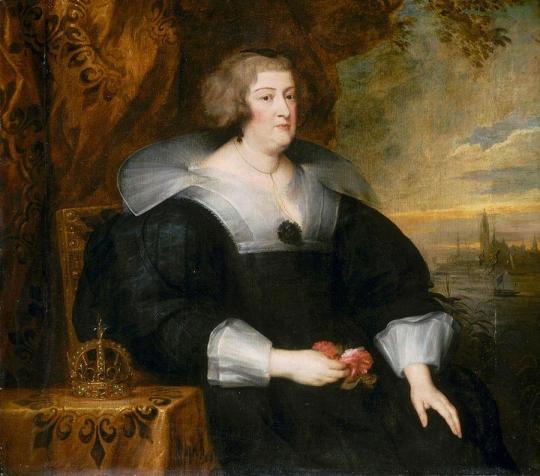

The Exiled Queen Marie de Medici with Coronet Overlooking Cologne
Artist: Anthony van Dyck (Flemish, 1599–1641)
Date: c. 1631
Medium: Oil on canvas
Collection: Palais des Beaux-Arts de Lille, France
Marie de' Medici
Marie de' Medici (French: Marie de Médicis; Italian: Maria de' Medici; 26 April 1575 – 3 July 1642) was Queen of France and Navarre as the second wife of King Henry IV. Marie served as regent of France between 1610 and 1617 during the minority of her son Louis XIII. Her mandate as regent legally expired in 1614, when her son reached the age of majority, but she refused to resign and continued as regent until she was removed by a coup in 1617.
Marie was a member of the powerful House of Medici in the branch of the grand dukes of Tuscany. Her family's wealth inspired Henry IV to choose Marie as his second wife after his divorce from his previous wife, Margaret of Valois. The assassination of her husband in 1610, which occurred the day after her coronation, caused her to act as regent for her son, Louis XIII, until 1614, when he officially attained his legal majority, but as the head of the Conseil du Roi, she retained the power.
Noted for her ceaseless political intrigues at the French court, her extensive artistic patronage and her favourites (the most famous being Concino Concini and Leonora Dori), she ended up being banished from the country by her son and dying in the city of Cologne, in the Holy Roman Empire.
#portrait#marie de' medici#queen of france#seated#costume#crown#table#house of medici#tuscany#cologne#coronet#woman#european#french history#oil painting#anthony van dyck#flemish painter#baroque style#artwork#european art#17th century painting
8 notes
·
View notes
Text
Events 1.25
41 – After a night of negotiation, Claudius is accepted as Roman emperor by the Senate. 750 – In the Battle of the Zab, the Abbasid rebels defeat the Umayyad Caliphate, leading to the overthrow of the dynasty. 1348 – A strong earthquake strikes the South Alpine region of Friuli in modern Italy, causing considerable damage to buildings as far away as Rome. 1494 – Alfonso II becomes King of Naples. 1515 – Coronation of Francis I of France takes place at Reims Cathedral, where the new monarch is anointed with the oil of Clovis and girt with the sword of Charlemagne. 1533 – Henry VIII of England secretly marries his second wife Anne Boleyn. 1554 – São Paulo, Brazil, is founded by Jesuit priests. 1573 – Battle of Mikatagahara: In Japan, Takeda Shingen defeats Tokugawa Ieyasu. 1575 – Luanda, the capital of Angola, is founded by the Portuguese navigator Paulo Dias de Novais. 1585 – Walter Raleigh is knighted, shortly after renaming North America region "Virginia", in honor of Elizabeth I, Queen of England, sometimes referred to as the "Virgin Queen". 1704 – The Battle of Ayubale results in the destruction of most of the Spanish missions in Florida. 1755 – Moscow University is established on Tatiana Day. 1765 – Port Egmont, the first British settlement in the Falkland Islands near the southern tip of South America, is founded. 1787 – Shays's Rebellion: The rebellion's largest confrontation, outside the Springfield Armory, results in the killing of four rebels and the wounding of twenty. 1791 – The British Parliament passes the Constitutional Act of 1791 and splits the old Province of Quebec into Upper Canada and Lower Canada. 1792 – The London Corresponding Society is founded. 1819 – University of Virginia chartered by Commonwealth of Virginia, with Thomas Jefferson one of its founders. 1858 – The Wedding March by Felix Mendelssohn is played at the marriage of Queen Victoria's daughter, Victoria, and Friedrich of Prussia, and becomes a popular wedding processional. 1879 – The Bulgarian National Bank is founded. 1881 – Thomas Edison and Alexander Graham Bell form the Oriental Telephone Company. 1890 – Nellie Bly completes her round-the-world journey in 72 days. 1909 – Richard Strauss's opera Elektra receives its debut performance at the Dresden State Opera. 1915 – Alexander Graham Bell inaugurates U.S. transcontinental telephone service, speaking from New York to Thomas Watson in San Francisco. 1917 – Sinking of the SS Laurentic after hitting two German mines off the coast of Northern Ireland. 1918 – The Ukrainian People's Republic declares independence from Soviet Russia. 1918 – The Finnish Defence Forces (The White Guards) are established as the official army of independent Finland, and Baron C. G. E. Mannerheim is appointed its Commander-in-Chief. 1924 – The 1924 Winter Olympics opens in Chamonix, in the French Alps, inaugurating the Winter Olympic Games. 1932 – Second Sino-Japanese War: The Chinese National Revolutionary Army begins the defense of Harbin. 1937 – The Guiding Light debuts on NBC radio from Chicago. In 1952 it moves to CBS television, where it remains until September 18, 2009. 1941 – Pope Pius XII elevates the Apostolic Vicariate of the Hawaiian Islands to the dignity of a diocese. It becomes the Roman Catholic Diocese of Honolulu. 1942 – World War II: Thailand declares war on the United States and United Kingdom. 1945 – World War II: The Battle of the Bulge ends. 1946 – The United Mine Workers rejoins the American Federation of Labor. 1946 – United Nations Security Council Resolution 1 relating to Military Staff Committee is adopted. 1947 – Thomas Goldsmith Jr. files a patent for a "Cathode Ray Tube Amusement Device", the first ever electronic game. 1949 – The first Emmy Awards are presented in the United States; the venue is the Hollywood Athletic Club. 1960 – The National Association of Broadcasters in the United States reacts to the "payola" scandal by threatening fines for any disc jockeys who accept money for playing particular records. 1961 – In Washington, D.C., US President John F. Kennedy delivers the first live presidential television news conference. 1964 – Blue Ribbon Sports, which would later become Nike, is founded by University of Oregon track and field athletes. 1967 – South Vietnamese junta leader and Prime Minister Nguyen Cao Ky fires rival, Deputy Prime Minister and Defence Minister Nguyen Huu Co, while the latter is overseas on a diplomatic visit. 1969 – Brazilian Army captain Carlos Lamarca deserts in order to fight against the military dictatorship, taking with him ten machine guns and 63 rifles. 1971 – Charles Manson and four "Family" members (three of them female) are found guilty of the 1969 Tate–LaBianca murders. 1971 – Idi Amin leads a coup deposing Milton Obote and becomes Uganda's president. 1979 – Pope John Paul II starts his first official papal visits outside Italy to The Bahamas, Dominican Republic, and Mexico. 1980 – Mother Teresa is honored with India's highest civilian award, the Bharat Ratna. 1986 – The National Resistance Movement topples the government of Tito Okello in Uganda. 1990 – Avianca Flight 52 crashes in Cove Neck, New York, killing 73. 1993 – Five people are shot outside the CIA Headquarters in Langley, Virginia. Two are killed and three wounded. 1994 – The spacecraft Clementine by BMDO and NASA is launched. 1995 – The Norwegian rocket incident: Russia almost launches a nuclear attack after it mistakes Black Brant XII, a Norwegian research rocket, for a US Trident missile. 1996 – Billy Bailey becomes the last person to be hanged in the United States. 1998 – During a historic visit to Cuba, Pope John Paul II demands political reforms and the release of political prisoners while condemning US attempts to isolate the country. 1998 – A suicide attack by the Liberation Tigers of Tamil Eelam on Sri Lanka's Temple of the Tooth kills eight and injures 25 others. 1999 – A 6.0 magnitude earthquake hits western Colombia killing at least 1,000. 2003 – Invasion of Iraq: A group of people leave London, England, for Baghdad, Iraq, to serve as human shields, intending to prevent the U.S.-led coalition troops from bombing certain locations. 2005 – A stampede at the Mandhradevi temple in Maharashtra, India kills at least 258. 2006 – Mexican professional wrestler Juana Barraza is arrested in connection with the serial killing of at least ten elderly women. 2010 – Ethiopian Airlines Flight 409 crashes into the Mediterranean Sea off the coast of Na'ameh, Lebanon, killing 90. 2011 – The first wave of the Egyptian revolution begins throughout the country, marked by street demonstrations, rallies, acts of civil disobedience, riots, labour strikes, and violent clashes. 2013 – At least 50 people are killed and 120 people are injured in a prison riot in Barquisimeto, Venezuela. 2015 – A clash in Mamasapano, Maguindanao in the Philippines kills 44 members of Special Action Force (SAF), at least 18 from the Moro Islamic Liberation Front and five from the Bangsamoro Islamic Freedom Fighters. 2019 – A mining company's dam collapses in Brumadinho, Brazil, a south-eastern city, killing at least 7 people and leaving 200 missing.
0 notes