#Pharmacological
Explore tagged Tumblr posts
Text








The Encyclopedia of Psychoactive Drugs Series (various editions)
#drugblr#drug blog#drugs#tw drugs#literature#vintage books#books#70s#60s#trippy art#psychedelic art#60s psychedelia#botany#pharmacology#vintage aesthetic#chaotic academia#book cover#pharmacy#hippy#surrealism
1K notes
·
View notes
Text
Chromatography-mass spectrometry for the in vivo metabolite analysis of saponins

Saponins are one of the main active ingredients of many herbal medicines such as ginseng, Polygala tenuifolia, Platycodon grandiflorum, licorice, rhizoma anemarrhenae, and radix bupleurum. Pharmacological studies have shown that saponins have biological activities such as antibacterial, antitumor, modulation of body metabolism and immunity, and treatment of cardiovascular diseases and diabetes mellitus. The in vivo metabolites of saponins were analyzed by chromatography-mass spectrometry to provide favorable evidence for the elucidation of the therapeutic mechanism of Chinese medicine.
Liquid chromatography-mass spectrometry (LC/MS) is a bioanalytical technique that combines the high separation performance of high-performance liquid chromatography HPLC with the high sensitivity and specificity of tandem mass spectrometry. It does not require complete chromatographic separation between analytes, and its multi-window detection capability allows the quantitative analysis of multiple components simultaneously.
Medicilon’s Bioanalysis Department boasts a professional, scientific research team with analysis laboratories equipped with advanced instruments. In the context of information management, our experiments and researches are compliant with the standards of FDA/NMPA GLP and involve pharmacokinetics, toxicokinetics, pharmacodynamics, immunogenicity, and bioequivalence, to provide our clients with services, including selection and development, preclinical and clinical researches of micromolecule drugs, biological preparations, vaccines, and biomarkers.
Chinese herbal medicines and their prescriptions are complex in composition. HPLC coupled with UV or DAD detectors can only provide signals such as retention time and UV absorption for individual peaks, while the structural information available for unknown components is quite limited. The identification of chromatographic peaks must have controls, which are difficult to obtain for most of the chemical elements of TCM, and for the in vivo drug analysis of TCM, the general detection techniques are challenging to meet the requirements for the determination of blood concentration after drug administration.
The application of HPLC/MS can combine the advantages of the high separation efficiency of HPLC and the high sensitivity and specificity of tandem mass spectrometry and give the molecular weight information of the measured components. The structural information of the measured substances can also be derived through multi-stage tandem mass spectrometry analysis.
1,Liquid chromatography-tandem mass spectrometry for the analysis of pseudo ginsenoside metabolites in human blood
To establish a liquid chromatography-tandem mass spectrometry method for determining pseudo ginsenoside GQ concentration in human plasma. An appropriate amount of internal standard was added to the plasma samples, extracted with ethyl acetate, and then analyzed by Waters Xevo TQS LC-MS/MS. A Poroshell 120 EC C8 column (2.1 mm×50 mm, 2.7 μm) was used at 40 ℃ with methanol-10 mmol-L-1 ammonium acetate aqueous solution (80:20) as the mobile phase at a flow rate of 0.3 m L-min-1. The determination was performed in the negative ionization mode using multiple reaction ion monitoring (MRM) in scanning mode with an electrospray ionization source (ESI).
The linear range of the method was 2.500~5 000 ng-m L-1, the minimum limit of quantification was 2.500 ng-m L-1, the intra-day, and inter-day precision was less than 15%, the accuracy was between 85% and 115%, the extraction recovery was about 9%~11%, the matrix effect was about 66%~73%, and the stability investigation results were good. The pharmacokinetic tests showed that the peak time was two h, and the half-life was approximately ten h after static injection of pseudo ginsenoside GQ 120 mg-sub-1 once daily for 5 d. The main pharmacokinetic parameters were the same at d 1 and d 5 of the trial, and the calculated accumulation coefficients were RC max=0.964±0.099 and RAUC=0.965±0.181, both of which were close to 1, respectively.
This method applies to the human pharmacokinetic study of pseudo ginsenoside GQ. Under this dosing regimen, there was no significant accumulation of pseudo ginsenoside GQ in humans, and continuous dosing did not affect the human pharmacokinetic process of pseudo ginsenoside GQ.
2,LC-MS/MS for the analysis of metabolites of yarrow saponin in rat blood
High-performance liquid-phase tandem mass spectrometry (LC-MS/MS) was used to determine the content of maidenhair saponin G in rat plasma and to study its pharmacokinetic characteristics in rats. Methods A Phenomenex Luna C18 column (150 mm×2 mm, three μm) was used with acetonitrile-water (containing 0.1% formic acid) as the mobile phase at a flow rate of 0.2 mL-min~(-1), and ginsenoside Rg3 was used as the internal standard; rats were injected with maidenhair saponin G 0.25, 0.5 and 1 mg-kg-1 in the tail vein, and blood was collected at different time points after drug administration.
The blood was collected at other time points after drug administration, and the blood concentrations were determined by LC-MS/MS method as described above. The pharmacokinetic parameters were fitted by DAS 3.0 software and a non-atrial model.
The results showed good linearity between 0.01~1.0 μg-m L-1 yari saponin G and peak area, and the methodological investigations all followed the requirements; the plasma pharmacokinetic parameters of rats after intravenous administration were: t1/2=3.447±0.898 h, MRT0-∞=4.568±1.075 h, CL=0.858±0.171 L-h-1-kg, and the AUC and Cmax increased equivalently with the increase of the administered dose. The AUC and Cmax increased equiproportionally with increasing amounts, which was consistent with linear pharmacokinetics. This method is simple, sensitive, and accurate and is suitable for determining yarrow saponin G in rat plasma and its pharmacokinetic study.
Some researchers have also used HPLC-ESI-MS/MS for the qualitative and quantitative analysis of saponins in blood saponin injection. Other researchers used pressurized solution extraction (PLE) with the HPLC-DAD-MS technique to determine nine saponins and two poly ethynyl alcohols in ginseng leaves and ginseng, a rapid method for the detection of herbal medicines and help control the quality of ginseng.
Establishing a reliable analytical method is a precursor to performing in vivo metabolite analysis of drugs. With the development of modern chromatographic coupling techniques, separating and identifying multiple trace metabolites in vivo has become a continuous process. In particular, LC-MS sample pretreatment is simple and generally does not require hydrolysis or derivatization treatment. LC-MS technology avoids the complicated and tedious work of separating and purifying metabolites and allows the separation and identification of difficult-to-identify in vivo trace metabolites.
0 notes
Text

𝓜𝓻. 𝓑𝓻𝓲𝓬𝓴 𝓦𝓪𝓵𝓵
Pairing: Bakugou x reader. All characters are aged up 18+. MDNI. ﹏﹏﹏﹏﹏﹏﹏﹏﹏﹏﹏﹏﹏﹏﹏﹏Summary: Maybe you should have looked up what your boss looked like...


Thinking about foreign!reader who comes to Japan as a support tech engineer and having an eventful first meeting with Bakugou
Bakugou hates airports, especially around this time of the year, too crowded, too loud, bustling with people. If he had a choice he wouldn't have come, send in a driver and cozied up in his bed but, his mom had different plans, she had called him the night before, specifically told him to pick her up from the airport. So, here he was, waiting for her plane to land, 3:45 am in the morning, a rapidly cooling coffee in his hand.
He was growing agitated at the whispering around him, it's easy for him to get recognised, blond hair and striking red eyes not easily forgettable. He sharply turns to leave the waiting room, not necessarily paying attention when his hand, the one that was holding cold coffee slams into someone and boom now he is staring at the aftermath.
You are staring start ahead, breathing deeply, you turn your head towards the jerk that slipped coffee all over you. Cold seeped through your shirt, the chill almost chilling your bones. You could feel the coffee seeping into your shirt, then inner wear and then your bra.
"Are you going to apologise or what?" You scowl at him, the coffee seeping through your shirt, the wet cloth irritating you further.
Bakugou continues to stare at you, anger evident on your features, he assumes you aren't Japanese from the lack of accent in your english. Before he could apologise you speak again.
"At least have the courtesy to apologise, asshole" you spit out at him, before throwing him the nastiest little glare.
Bakugou is surprised that you don't him, maybe it's his ego but again he is the top hero maybe not his rankings but he is famous and infamous for reasons. Everyone knows him, even people outside of Japan.
"Do you not know who I am?" He finally speaks, not the smartest response but a response nonetheless.
"Am I supposed to know you?" You look at him incredulously, anger subsiding and confusion settling in.
"you know what, don't answer that, i don't care and I am tired, all I know is you are a jerk and I really wish to never run into you again!" You semi-yell at him and leave the waiting room.
He almost chased after you but he phone started ringing, his mother's contact displayed on the screen, informing him of her arrival.
He looked back at the direction you had gone, but you already disappeared. Sighing he left to pick his mother from the arrival gate. And he leaves, slightly bummed that he didn't get to apologise.
-------
"-nd like he walked straight into me and didn't bother apologising." You waved your hands around, trying to emphasize your impromptu collision with Mr. Brick wall, to your new housemate and colleague.
Not necessarily a good think, shit talking on first day of work, but you had to kinda explain why you were doing laundry in the middle of the night.
"That's rude, could've at least apologised.". Mari agreed, both of you walked down the hallway as she was showing you around the agency building.
"Well, hopefully no further mishaps occur." She had stopped in front of a large laboratory, you could already spot your stuff on one of the tables.
"Yeah, hopefully." You mumbled mindlessly, eyes admiring the lab, it was the largest you had seen, with more advanced equipments as well. Mari left you alone at your destination, already going back to her work.
You also got to work, looking into boxes of broken and damaged support equipments, you had already read about them, their functions and materials used to build.
It was an easy job to repair the items, folding your sleeves you got to work, one by one you repaired majority of the items the only thing left where, chunky, hefty, gauntlets.
You knew the belonged to Pro-Hero Dynamight, read about him in passing, already aware of the architecture of the Gauntlets, it didn't take long for you to fix them up, even being generous enough to replace parts with your tech.
Assuming your work was done you called Mari.
"You still need to see if the function alright." She paused before looking at her laptop screen," Pro hero Dynamight is already in the building, you should give him the equipment and see if it works properly."
Even tho, you were slightly peeved, cause of course it works, you just fixed it, you still took the hefty box to 12th floor of the building.
You entered the office without knocking, hands busy holding the box, barely even looking at the people standings there you deposit the box on the table next to the couch.
"Here, it's for Dynamight, fixed it, they should work top notch." You gasp out, breath slightly rapid due to carrying all that weight.
You turn around and spot 2 people in the room, one was Pro-Hero Red Riot, whom you recognised because he has least amount of support equipments listed and the other was Mr. Brick wall.
"You little shit, what are you doing here?" You blurt out without thinking, finger accusingly pointing at him. Not yet aware that the Pro-Hero you were looking for is right there, at the end of your accusatory finger.
Kirishima stared at you in amusement, before speaking," You must be the new tech, Welcome to the agency, I am Kirishima Eijirou." He stood up and extended his hand for a shake, you politely took his hand and uttered your name. Before looking over his shoulder at Bakugou.
"Don't mind me, but what did lil' shit over there do?" Kirishima semi-whispered in your ear, thumb pointing back, at where Bakugou stood.
"I spilled coffee on me, and then stared at me like it was my fault." You stated, arms folded, glaring at him, Bakugou stared back at you, hands shoved in his pocket as he leaned against the table.
"It was an accident, you scurried away before I could apologise." He finally spoke, Kirishima nodded his head, like accepting the explanation.
"NO, I waited and Mr. Brick Wall didn't apologise." You yelled, looking at Kirishima to back you up.
"That's not cool," Kirishima looked at you, shit eating grin on his face, you grinned back, feeling confident that Pro hero Red Riot was on your side, he continued,"You should apologise, Dynamight."
The gratification of getting the apology didn't last long when you registered his last word.
"Dyna-dynamight??" You spluttered," As in Pro Hero?" You looked dumbfounded between the two heros, face flushing in embarrassment, before you turned to Bakugou, who was looking at you bemused.
"I didn't kno- I am sorry, it was my fault." You uttered desperately, the fear of getting fired on your first day making you forget your past grudges. You haphazardness making Kirishima giggle, and Bakugou sigh.
"Oi, it was my fault, should have seen where I was going" Bakugou said calmly, moving to smack the back of Kirishima's head, who promptly shit up.
"You don't have t-." Bakugou shushes you before you could speak," The mistake was mine, me being a hero doesn't change that."
You stared at him, hoping for him to dismiss you soon, so you could sob in the corner of your big, beautiful lab.
"How about this, I get you a coffee, as an apology." He asked, Kirishima let out a snort, before Bakugou glared at him.
"You don't have to, it's not an issue anymore, Mr. Bri-Dynamight." You looked sheepishly at him, hoping he didn't change on the nickname you had given him.
"Let me, I'll get you a coffee, you'll need it after working here for a while."
"Fine then, we can get it sometimes." You accept his proposal (?),before looking at him, awkwardly trying to gesture at the door.
Bakugou furrowed his eyebrows, watching you flare your arms towards the door, before Kirishima spoke," You can leave now, I am sure the gauntlets would work just fine."
At the dismissal you scurried out the door, running zig zag avoiding the few people present in the hallway.
"So, that's the 'fireworks' you were talking about, Mr. Brick wall." Kirishima queried, head resting against his palm, as a smug expression formed on his face.
"Don't fucking push it." Bakugou gritted out, trying to think of how he could fix his image in your eyes.
"Whatever you say, Mr. Brick wall." Kirishima chimed.


#so i have pharmacology exam tomorrow and here i am back again#apart from that this was an idea i have had for a while#although i feel like the fic turned out kinda shit#bnha#mha#bnha x reader#mha x reader#bnha smut#mha smut#bnha fluff#mha fluff#bakugou katsuki#bakugou x reader#bnha bakugou#katsuki bakugo x reader#bakugou katsuki x reader#bakugou#bakugou fluff#bakugou smut#bakugou x reader fluff#boss!bakugou#bakugou katsuki fluff#bakugou katsuki x you#bakugou katsuki smut#bnha bakugou katsuki
278 notes
·
View notes
Text

547 notes
·
View notes
Text





Jeff and Britta + we dated btw
based on this twitter thread
#joel mchale#jeff winger#gillian jacobs#britta perry#jeffbritta#community#community nbc#redstreet#pb#celebrity pharmacology#intro to knots#5x07#basic email security#grifting 101#tumblr hides my post when i include the name of the episode the third gif is from#but it's 5x07
400 notes
·
View notes
Text
Imagine studying at the same college with Mhin
modern AU

⋆.˚✮✮˚.⋆
⟢ Coming across each other only during breaks because you both study at different faculties. Mhin once thought about transferring into your group, and they would gladly do that but unfortunately your professions differ drastically.
⟢ Noticing each other from far corners of the hall and nodding; some kind of succinct gesture, bearing the meaning of mutual greeting and silent way of conveying “sure, we are tired but fuck it, we ball”.
⟢ Marking the way their frown and discontent on their face is gradually replaced by a soft smile as they approach you.
⟢ Quickly reaching the nearest coffee shop during said breaks, but only for your sake. Mhin is not a big fan of take-outs, but they won’t cease the opportunity to spare you a moment while waiting for your order and briefly talking about everything that happened over the period of your short “parting”, caused by curriculum and different class/lecture-rooms.
⟢ Suggesting that you both take aesthetically pleasing notes to add some colours to your routine; writing out ornate letters with brush pens, decorating pages with cute stickers and vivid patterns. But failing the attempt as Mhin prefers comfort and practicality (the most they can do is using pens of different colours and highlighting topics from time to time). They are convinced that all this ✨study aesthetic✨ doesn’t suit them at all and there are two reasons why – firstly, the nature of their specialisation, and secondly, the insane amount of shortened words and strikethroughs in their notes (also add here the margins of their notebooks filled with neurotic scribbles, little crosses that are outlined numerous times, doodles and tiny rough sketches). As they say, usage of cute stationery won’t help them at all, let alone enhancing their notes. “It will eventually cause even more mess”.
⟢ Constantly checking each other’s class schedule and receiving messages from them like “are you done yet”, “where are you”, “should i wait for you” as well sending those to them yourself (but knowing that you’ll both wait until one of you finishes classes no matter how long it takes).
⟢ Hastily walking under streetlights, barely hearing each other over the noise of the street and crowd, and agreeing on “these people are so weird and stupid, thanks god we are normal”. Listening to their complaints and subconsciously adorning the way snow flickers on their silver hair, bleached strands sticking out from the hood. And how amusing are their attempts to hide themselves from biting cold when they bury their lips and nose in the collar of their jacket.
⟢ Standing in a crowded bus and exchanging meaningful looks with them, discussing the environment solely with glances – driver’s rudeness, someone’s pungent cologne, a deliberately loud conversation, contents of a stranger’s phone—“damn, we shouldn’t have looked at his screen, gross!”
⟢ Helping each other with homework by mere presence; finishing your own tasks while lying on their bed and listening to the rustle of pages as Mhin sits at the desk and thoughtfully writes something. Heavy darkness of a late evening changes the bluish hues, and radiance from a table lamp, blanketing Mhin’s silhouette and reflecting in the window, feels undeniably warm and cozy.
⟢ Getting advice from them on how to cope with exam stress along with a list of light herbal sedatives which can help in dealing with anxiety. Definitely will explain their effects in detail and respond to your “professional deformation, huh?” with a sarcastic chuckle.
⟢ Trying to get to know them better; it is genuinely hard to lure anything out of them—though if you listen to them carefully, you may effortlessly catch some trivias about them or their interests. So in brief moments of silence—or when they read something attentively on the laptop, biting their lips—you look around their room and its sparse decor. Remember, Mhin advocates for practicality, it’s only natural that their books are placed in perfect order on the table and shelves, no posters on the walls (if you don’t count prints from anatomical atlases as ones), and there is a cute cat-shaped lamp on their nightstand, illuminating soft glow.
⟢ Accepting their offer to walk you home when it gets too late and dark. Hugging them goodbye when you get to your place and watching them till they disappear into the darkness of the winter night. Tomorrow awaits another day and new attempts to get closer to this whimsical lil’ fella, who is seemingly the only one worth knowing in the asylum you have to call your college.
#yes i think that in modern au they bleach and dye their hair silver what are you gonna do to me#at first didn’t really like them but now dare i say that i understand leander#and his adoration for mhin#especially when they are grumpy#mhin as medicine or pharmacology student agenda do we all agree chat#touchstarved game#touchstarved mhin#touchstarved headcanons#mhin x reader#mhin
51 notes
·
View notes
Text
It's increasingly clear that microplastics are everywhere, but scientists are still learning about how bad the health implications could be. Now a new study in mice shows these tiny bits of plastic can be passed from a mother into their unborn offspring, where they persist beyond birth. Previous studies have shown that micro and nanoplastics (MNPs), smaller than grains of sand, can pass into the placenta. This latest research finds the tiny plastic fragments can remain in the growing mouse pup for at least two weeks after birth, according to this data.
Continue Reading.
77 notes
·
View notes
Text

Cocaine
“Cocaine hydrochloride for medicinal use. This is a CII controlled substance in the United States.” - via Wikimedia Commons
#cocaine hydrochloride#pharmacy#pharmacology#pharmcore#pharmacycore#pharmacologycore#wikipedia#wikipedia pictures#medicine#medcore#medicalcore#medicore#medical#drugs#pharmaceutical#cocaine#roxane laboratories
92 notes
·
View notes
Text


Pierce deserves death by hanging on this episode but at least we got Troy in a bee costume out of it
(Edit: If you noticed the drawing changed, no you didn’t)
#troy barnes#celebrity pharmacology#nbc community#community tv#community#community fanart#art#doodles#alan art stuff
116 notes
·
View notes
Text
older adults are astounding i tell them my POTS means i need to consume more salt and ill send multiple sources and everyone over 40 is like “nooo bc salt bad” just go fight the doctor directly at this point
#like I took med terminology human diseases and pharmacology for FUN I’ll educate you if you want but you have to like listen#POTS#postural orthostatic tachycardia syndrome#chronic illness#dysautonomia#handmadeorganicpost
877 notes
·
View notes
Text
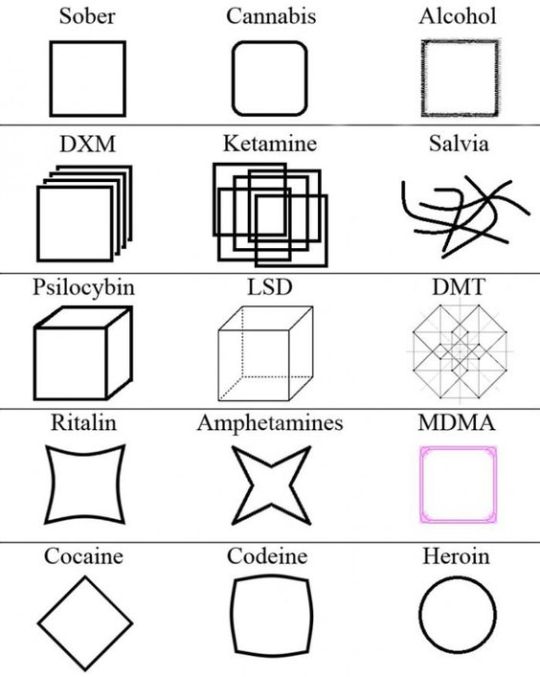
various substances and their effects on perception
#psychedelic art#drugs#drug blog#drugblr#pharmacy#surrealism#artwork#guides#mdma#cannabis#tw drugs#infographic#pharmacology#psilocybin
1K notes
·
View notes
Text


Exams coming up!
#studyblr#studying#inspiration#university#studyspo#aesthetic#med school#medical school#pharmacology#microbiology#medizinstudium#desksetup#my desk#med student
862 notes
·
View notes
Text
*manoeuvres the Host to stay under my tongue so that the Body of Christ is absorbed into my systemic circulation more quickly and with less liver metabolization*
#my post#the type of thing I think about during st Rita votive Mass I’m afraid#kitcatia remember me when you take pharmacology 🙏🙏
53 notes
·
View notes
Text
Illiterate pharmacist who can only tell medications apart by crushing them up and tasting the molecules
#r/196#196#r/196archive#/r/196#rule#meme#memes#shitpost#shitposting#pharmacy#med student#med school#medicine#pharmacology#pharma#big pharma
68 notes
·
View notes
Text
Pharmacologists really have the audacity to sit you down in your first lecture of their module and say okay so examples of extravascular include subcutaneously and then there’s obviously massive impacts on bioavailability because of this, and also because of tissue binding but you all know that, now imagine that the body is a cylinder containing an unknown volume of water so now you know that drug conc = dose/C0, now imagine there are two cylinders and one is the body and one is the plasma and they’re connected by a tube, okay now go back to your original body cylinder and imagine that there’s a filter getting rid of the drugs out of the water now you know that CLtotal = CLrenal + CLhepatic and that means that CL = rate of drug elimination/C,so the ester of elimination = k x A -> CL = k x A/C -> CL = k x v x c/c -> CL = k x v so with all that in mind it’s easy to derive that the equation you need is obviously CL = 0.693 x V / t1/2 and then look you in the eye and say the words “very simple”
I do not sense greatness for myself in this module
#biomed student#biomedicine#biology#pharmacology#biomedical science#biomed#university#I’m one lecture deep and I’m already tired you guys#dk rambles about random stuff
44 notes
·
View notes
Text


That's one of the grossest jokes that I've ever gotten into a show and I'm very proud of it. - Hilary Winston
#abed nadir#troy barnes#community#community nbc#celebrity pharmacology#danny pudi#donald glover#trobed#pb
90 notes
·
View notes