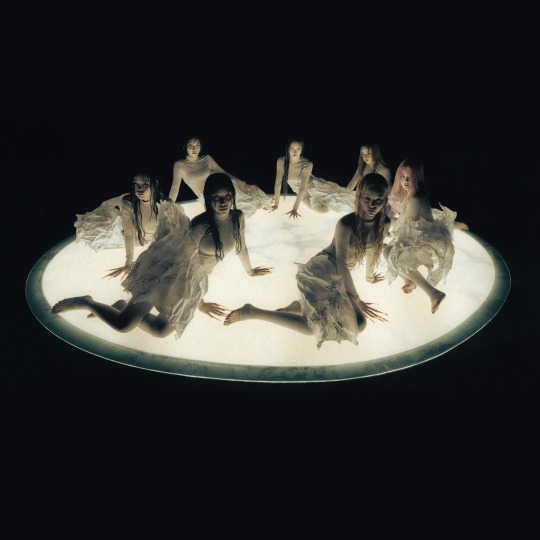
#NEW DNA
Explore tagged Tumblr posts
Text










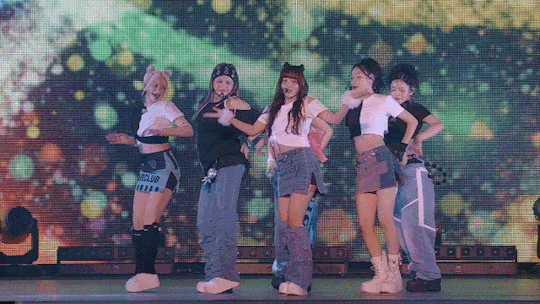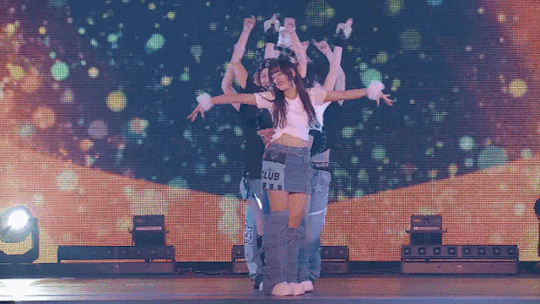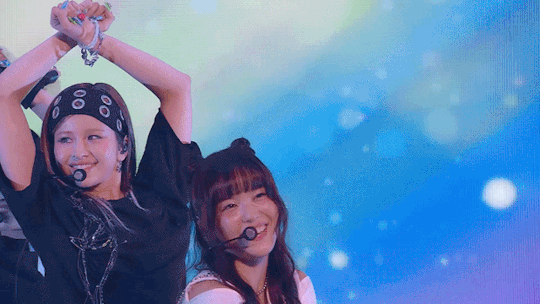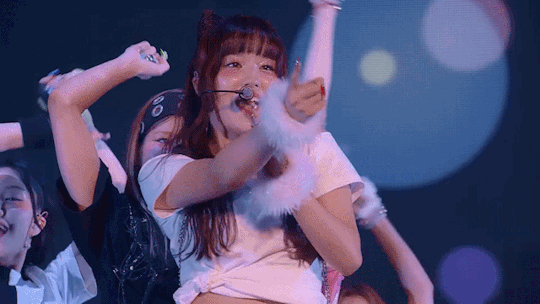






SHOOTING STAR - XG NEW DNA SHOWCASE
#like if saved#feel free to use#xg#xgalx#xg gif#new dna#shooting star#xgalx gif#xg jurin#xg chisa#xg hinata#xg harvey#xg juria#xg maya#xg cocona
67 notes
·
View notes
Text



⊹₊ ⋆ ⋆。𖦹°‧ just learned a new dance ⊹₊ ⋆ ⋆。𖦹°‧



⊹₊ ⋆ ⋆。𖦹°‧ ᡣ𐭩 ⊹₊ ⋆ ⋆。𖦹°‧
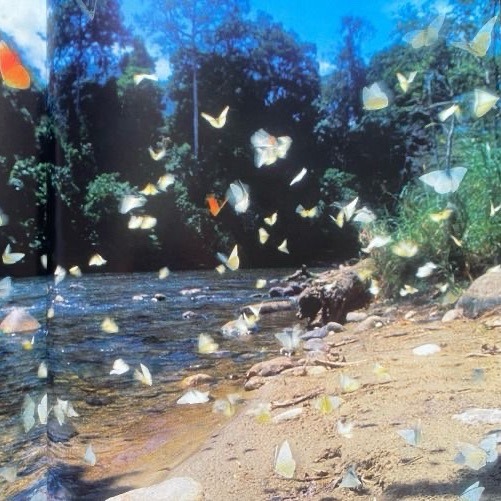
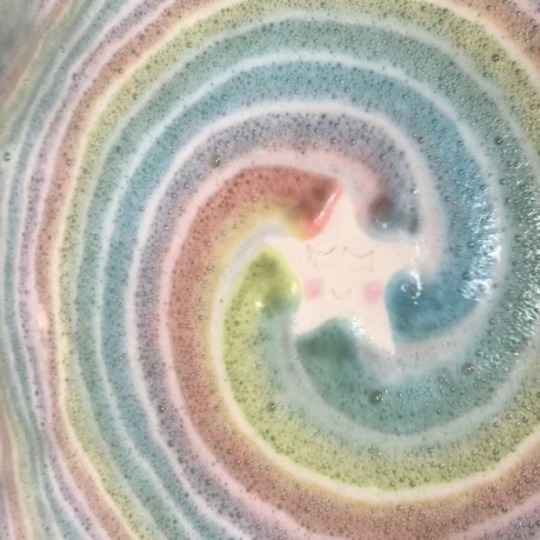
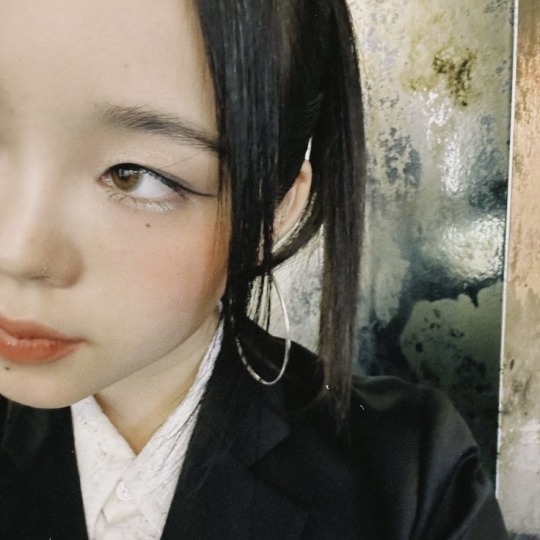



#cocona#xg#xg cocona#xgalx#xtraordinary girls#akiyama cocona#xg icons#cocona icons#cocona moodboard#xg moodboard#kpop#kpop aesthetic#kpop moodboard#jpop#jpop icons#jpop girl group#alphaz#cocona xg#kpop icons#woke up#new dna#this is xg#wolf#STREAM WOKE UP#C to the O-C-O#YOUNG QUEEN BUT ACT LIKE AN UNNIE
31 notes
·
View notes
Text
Exploring the Marvels of Biological Macromolecules: The Molecular Machinery of Life (Part 3)
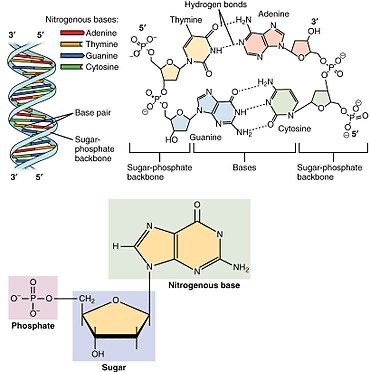
Nucleotide Structure: The Building Blocks
Nucleotides, the monomers of nucleic acids, consist of three fundamental components:
1. Phosphate Group (PO4): Provides a negatively charged backbone for the nucleic acid strand.
2. Pentose Sugar: In DNA, it's deoxyribose; in RNA, it's ribose. The sugar moiety forms the framework of the nucleotide.
3. Nitrogenous Base: Adenine (A), Guanine (G), Cytosine (C), Thymine (T) in DNA, and Uracil (U) in RNA. These bases are responsible for the genetic code.
DNA (Deoxyribonucleic Acid): The Repository of Genes
DNA is a double-stranded helical molecule, with each strand composed of a linear sequence of nucleotides. It encodes the genetic information necessary for an organism's development, growth, and functioning. The Watson-Crick base pairing rules—A with T and C with G
DNA (Deoxyribonucleic Acid): The Repository of Genes
DNA is a double-stranded helical molecule, with each strand composed of a linear sequence of nucleotides. It encodes the genetic information necessary for an organism's development, growth, and functioning. The Watson-Crick base pairing rules—A with T and G with C—ensure DNA's complementary and faithful replication.
RNA (Ribonucleic Acid): From DNA's Blueprint to Protein Synthesis
RNA plays diverse roles in the cell, including serving as a messenger (mRNA) for protein synthesis, a structural component of ribosomes (rRNA), and an adapter molecule (tRNA) that brings amino acids to the ribosome during translation. Unlike DNA, RNA is often single-stranded and contains uracil (U) instead of thymine (T).
Genome Organization and Chromosomes
Genomic DNA is organized into chromosomes within the cell nucleus. These structures enable efficient storage, replication, and transmission of genetic information during cell division and reproduction.
Replication and Transcription
DNA replication ensures the faithful duplication of genetic material during cell division, while transcription converts DNA into RNA, providing a template for protein synthesis.
Translation
The cellular machinery, composed of ribosomes and tRNA, reads the mRNA code and assembles amino acids into polypeptides during translation, ultimately forming functional proteins.
Genetic Code
The genetic code, a triplet code of nucleotide sequences (codons), dictates a protein's sequence of amino acids. It is nearly universal, with only minor variations across species.
Epigenetics
Epigenetic modifications, such as DNA methylation and histone modifications, regulate gene expression without altering the underlying DNA sequence, pivotal in development and cell differentiation.
Macromolecular interactions are the essence of cellular life. Within the complex microcosm of a cell, countless molecules engage in precise and choreographed dances, forming intricate networks that govern every facet of biology. These interactions, governed by the principles of biochemistry, are the foundation upon which life's processes are built.
Amino Acids: The Building Blocks
Proteins are composed of amino acids organic molecules that contain an amino group (-NH2), a carboxyl group (-COOH), a hydrogen atom, and a distinctive side chain (R group). There are 20 different amino acids, each with a unique side chain that confers specific properties to the amino acid.
Primary Structure: Amino Acid Sequence
The primary structure of a protein refers to the linear sequence of amino acids in the polypeptide chain. The genetic information in DNA encodes the precise arrangement of amino acids.
Secondary Structure: Folding Patterns
Proteins don't remain linear; they fold into specific three-dimensional shapes. Secondary structures, such as α-helices and β-sheets, result from hydrogen bonding between nearby amino acids along the polypeptide chain.
Tertiary Structure: Spatial Arrangement
The tertiary structure is the overall three-dimensional shape of a protein, determined by interactions between amino acid side chains. These interactions include hydrogen bonds, disulfide bridges, ionic bonds, and hydrophobic interactions.
Quaternary Structure: Multiple Polypeptide Chains
Some proteins, known as quaternary structures, comprise multiple polypeptide chains. These subunits come together to form a functional protein complex. Hemoglobin, with its four subunits, is an example.
Protein Functions: Diverse and Essential
Proteins are involved in an astounding array of functions:
1. Enzymes: Proteins catalyze chemical reactions, increasing the speed at which reactions occur.
2. Structural Proteins: Proteins like collagen provide structural support to tissues and cells.
3. Transport Proteins: Hemoglobin transports oxygen in red blood cells, and membrane transport proteins move molecules across cell membranes.
4. Hormones: Hormonal proteins, such as insulin, regulate various physiological processes.
5. Immune Function: Antibodies are proteins that play a crucial role in the immune system's defense against pathogens.
6. Signaling: Proteins are critical in cell signaling pathways, transmitting information within cells.
Protein Denaturation and Folding
Protein Diversity: The vast diversity of proteins arises from the combinatorial possibilities of amino acid sequences, secondary structure arrangements, and three-dimensional conformations.
Nucleic acids, the remarkable macromolecules that govern all living organisms' genetic information, are life's quintessential molecules. These complex polymers of nucleotides play an unparalleled role in the storage, replication, and expression of genetic information, shaping the development, characteristics, and functions of every living entity on Earth. Let's embark on an exploration of the intricate world of nucleic acids.
Nucleotide Structure: The Building Blocks
Nucleotides, the monomers of nucleic acids, consist of three fundamental components:
1. Phosphate Group (PO4): Provides a negatively charged backbone for the nucleic acid strand.
2. Pentose Sugar: In DNA, it's deoxyribose; in RNA, it's ribose. The sugar moiety forms the framework of the nucleotide.
3. Nitrogenous Base: Adenine (A), Guanine (G), Cytosine (C), Thymine (T) in DNA, and Uracil (U) in RNA. These bases are responsible for the genetic code.
DNA (Deoxyribonucleic Acid): The Repository of Genes
DNA is a double-stranded helical molecule, with each strand composed of a linear sequence of nucleotides. It encodes the genetic information necessary for an organism's development, growth, and functioning. The Watson-Crick base pairing rules—A with T and G with C—ensure DNA's complementary and faithful replication.
RNA (Ribonucleic Acid): From DNA's Blueprint to Protein Synthesis
RNA plays diverse roles in the cell, including serving as a messenger (mRNA) for protein synthesis, a structural component of ribosomes (rRNA), and an adapter molecule (tRNA) that brings amino acids to the ribosome during translation. Unlike DNA, RNA is often single-stranded and contains uracil (U) instead of thymine (T).
Genome Organization and Chromosomes:
Replication and Transcription: DNA replication ensures the faithful duplication of genetic material during cell division, while transcription converts DNA into RNA, providing a template for protein synthesis.
Translation: The cellular machinery, composed of ribosomes and tRNA, reads the mRNA code and assembles amino acids into polypeptides during translation, ultimately forming functional proteins.
Genetic Code: The genetic code, a triplet code of nucleotide sequences (codons), dictates the sequence of amino acids in a protein. It is nearly universal, with only minor variations across species.
Epigenetics: Epigenetic modifications, such as DNA methylation and histone modifications, regulate gene expression without altering the underlying DNA sequence, pivotal in development and cell differentiation.
Macromolecular interactions are the essence of cellular life. Within the complex microcosm of a cell, countless molecules engage in precise and choreographed dances, forming intricate networks that govern every facet of biology. These interactions, governed by the principles of biochemistry, are the foundation upon which life's processes are built.
#science#biology#college#education#school#student#medicine#doctors#health#healthcare#genetics#genetic engineering#science nerds#dna activation#new dna
24 notes
·
View notes
Text
T-G-I-F!!!
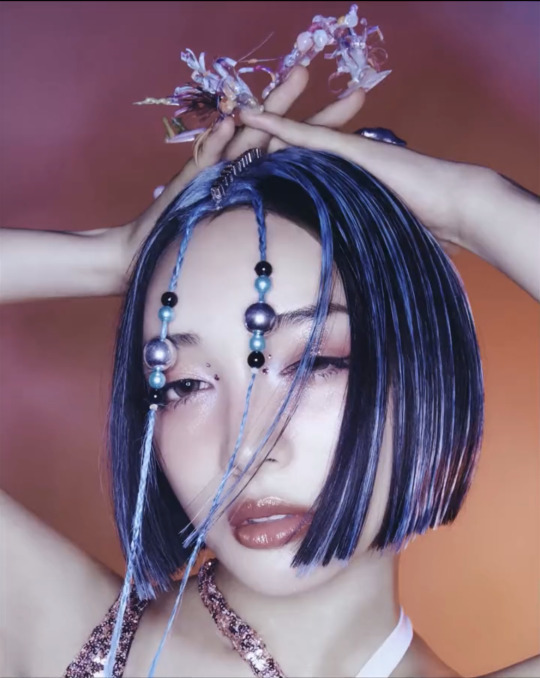
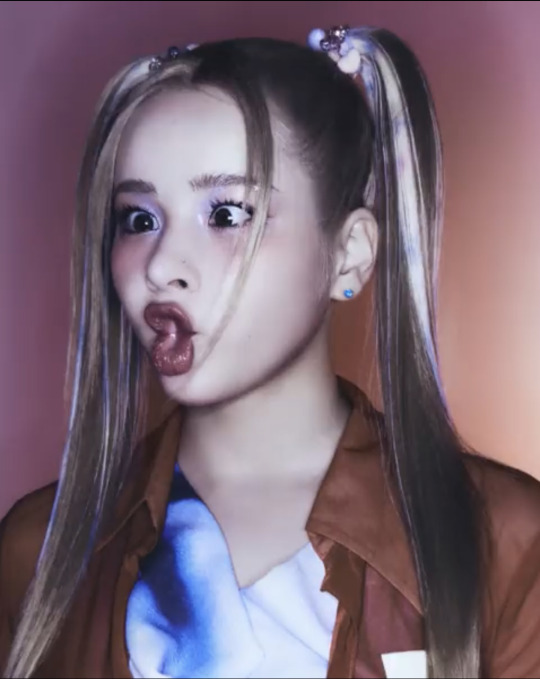
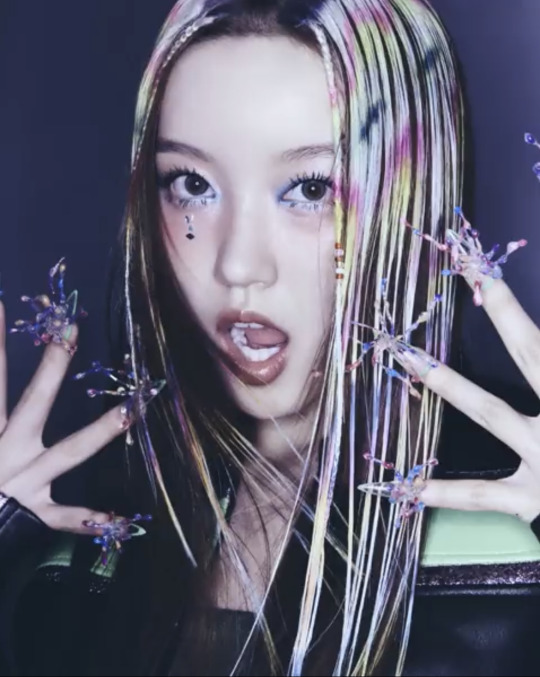
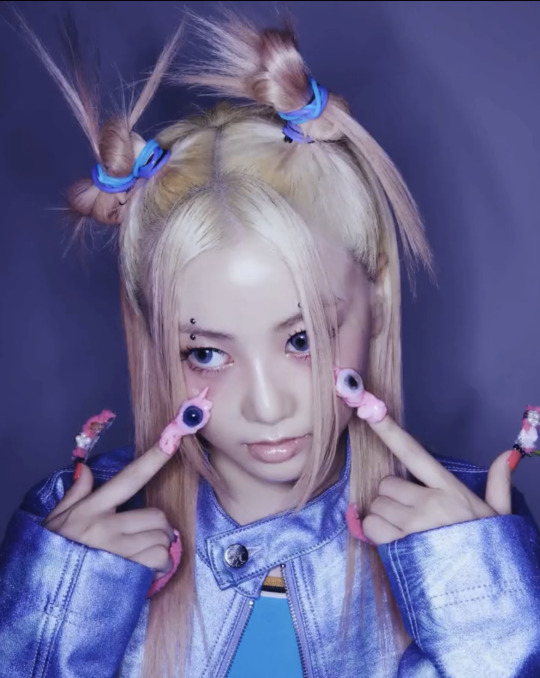
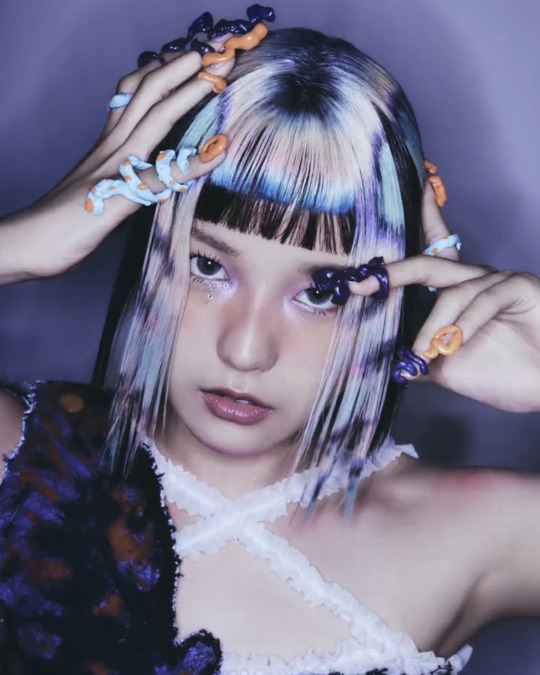
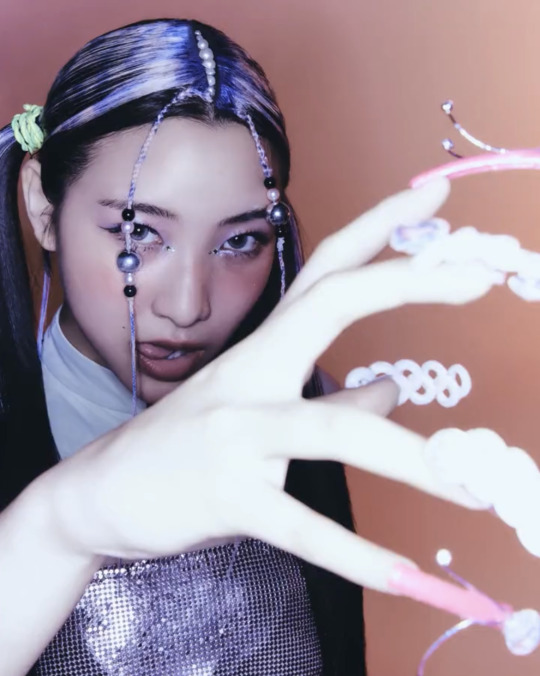
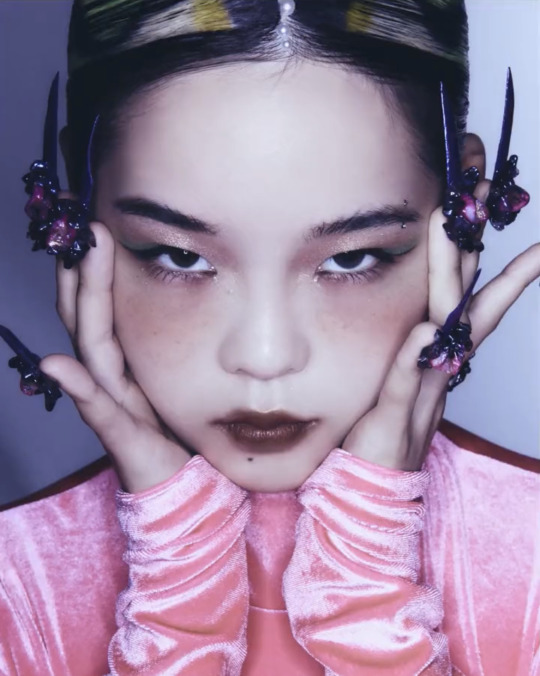







XG TGIF concept video photos
#xgalx#XG#xtraordinary girls#xg icons#NEW DNA#HESONOO#jurin#chisa#harvey#cocona#Maya#Hinata#Juria#grl gvng#tgif
45 notes
·
View notes
Text
Obsessed with this song
12 notes
·
View notes
Text
XG "New Dance" era wallpapers
Using Adobe Firefly, the end result is pretty amazing (You can still see the generated parts if you look close enough, so it's not perfect).
Finally I decided to share it here because I think this wallpaper looks really cool.
Even though it is easy to make, please give credit to me when you share it elsewhere. Don't steal it ok 😎👍
Anyway,
I JUST LEARNED A NEW DANCE, NEW DANCE, NEW DANCE 🕺🕺🕺
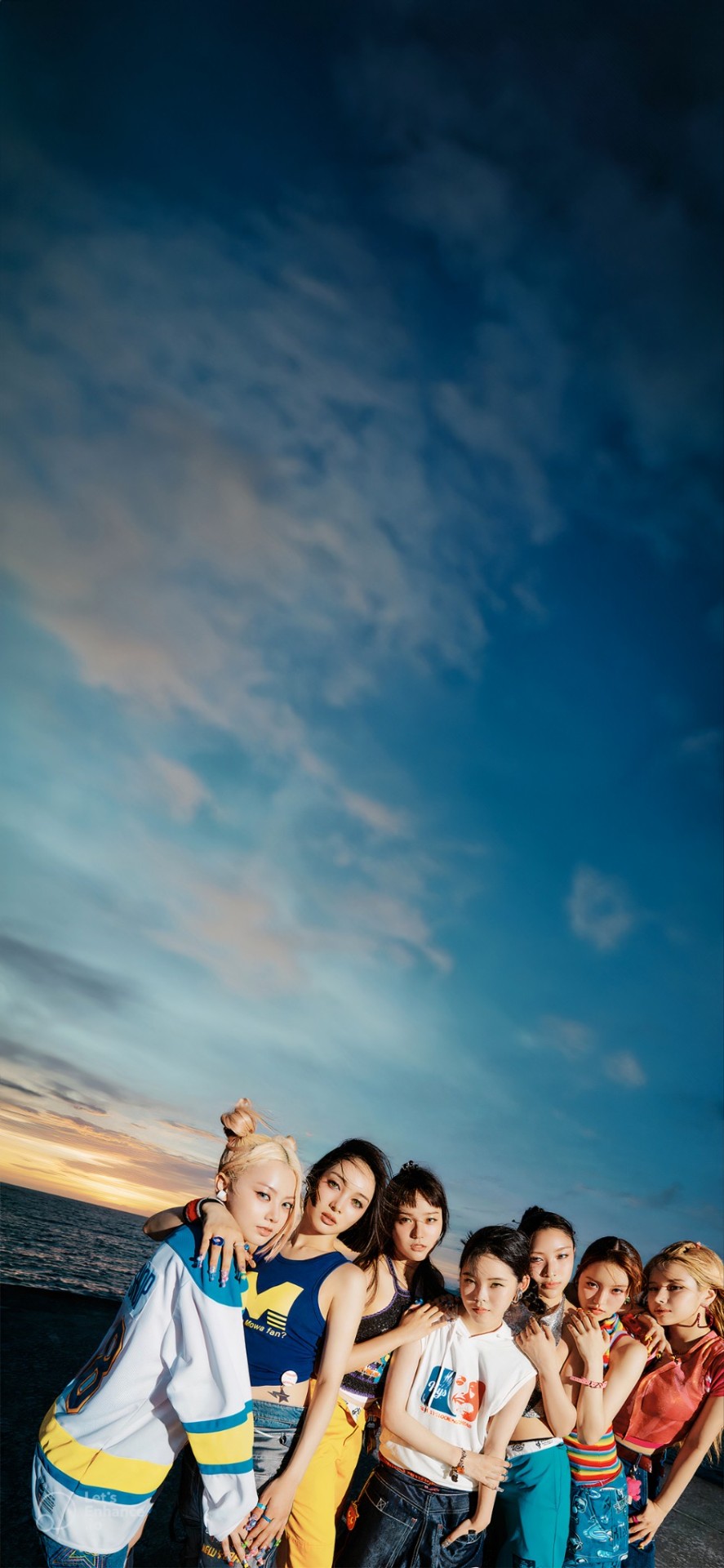


#xg#xg wallpapers#new dance#asaya jurin#kondou chisa#sohara hinata#amy harvey#ueda juria#kawachi maya#akiyama kokona#xtraordinary girls#xgalx#xg edits#new dna#kpop#jpop#xpop#girl group#xg lockscreens#xg alphaz#alphaz#fandom#Spotify
13 notes
·
View notes
Text



new dance, XG
photobooth
#kpop moodboard#femaleidols#girlgroupnetwork#xg#xgalx#xg alphaz#new dance#xg jurin#xg juria#xg hinata#xg harvey#xg chisa#xg maya#xg cocona#its been days and my brain keeps screaming#SLIDE WITH MY GIRLS TO THE PARTY#new dna
12 notes
·
View notes
Text





11 notes
·
View notes
Text
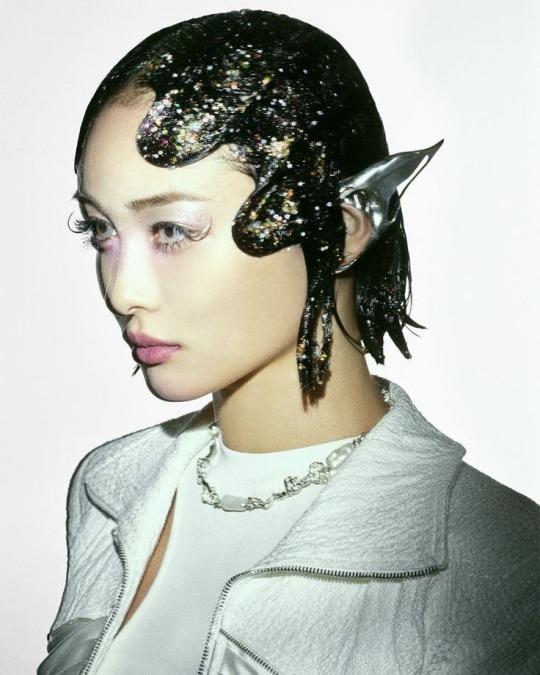

#obsessed#XG#Jurin#New DNA#photoshoot#concept#styling#girl groups#ggs#ethereal#makeup#cool#stunning#women#looks
3 notes
·
View notes
Text
youtube
XG - NEW DANCE (Official Music Video)
2 notes
·
View notes
Text
Boy, just follow my flow, don't matter where we go (Oh, ah)
Oh, the only direction I know
Want your body swervin' left, right, left, right
I want your body movin' left, right, left, right
You keep me up, my heart is beatin' up and down
Spinnin' 'round and 'round ('Round and 'round)
Just like my Pirellis burnin' on the ground
If you're down with me, then let's ride, let's ride
Can't nobody stop it, that's right, that's right
And my adrenaline is racin' up and down
Spinnin' 'round and 'round ('Round and 'round)
Hit the pedal to the ground, listen to the sound
Listen to the sound
2 notes
·
View notes
Text
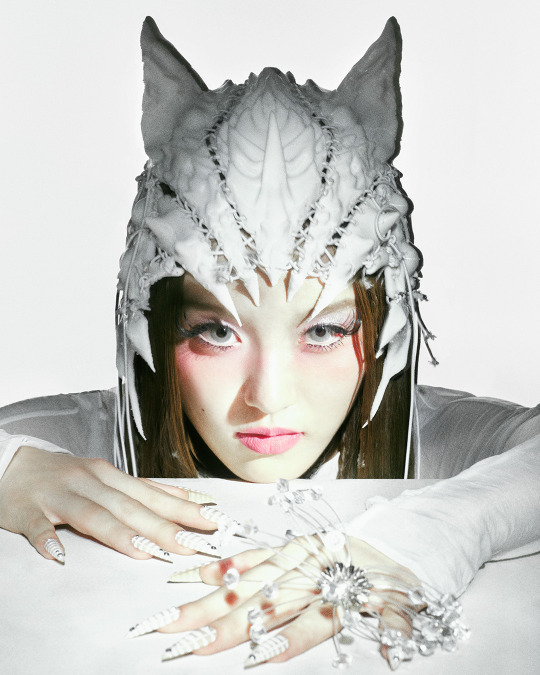
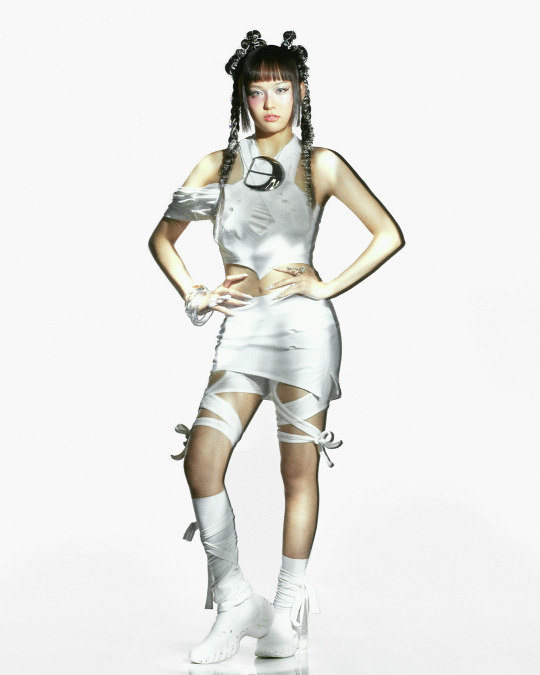
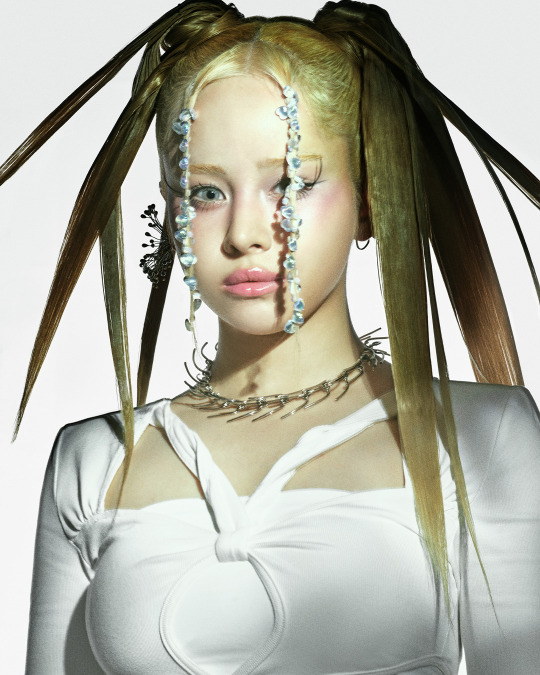
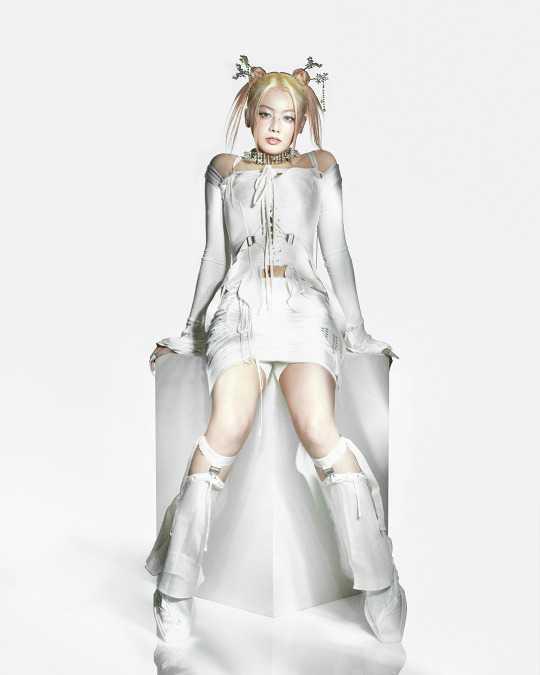
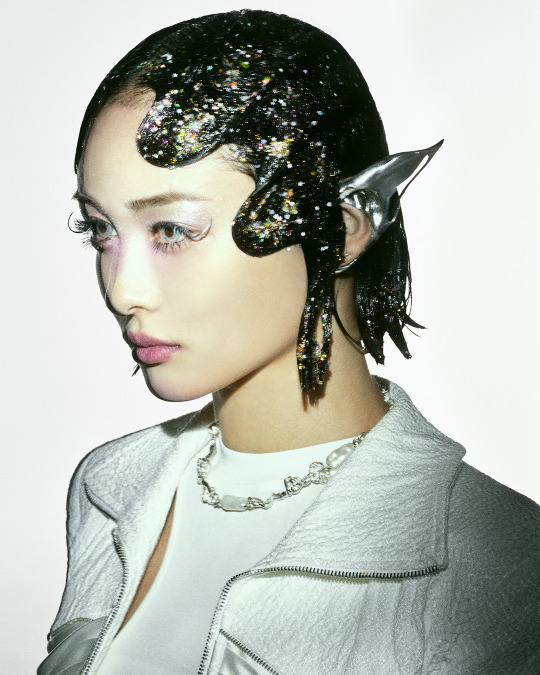
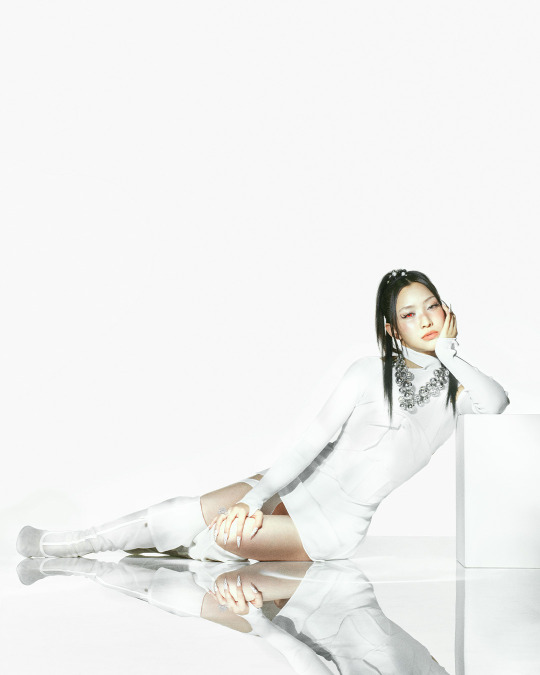
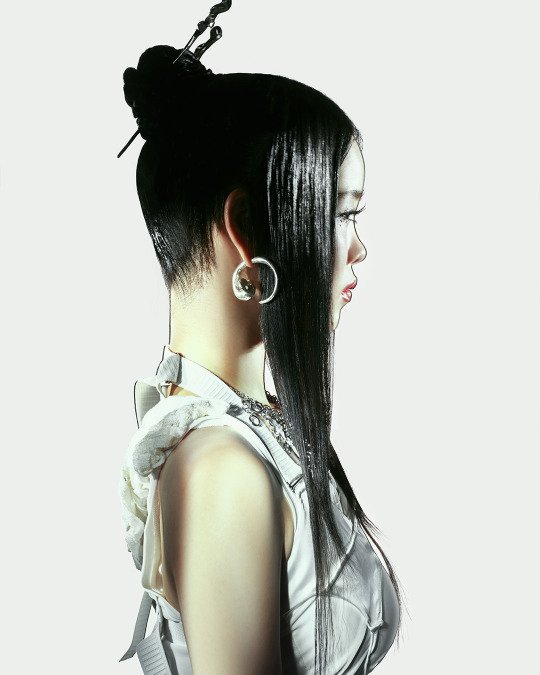
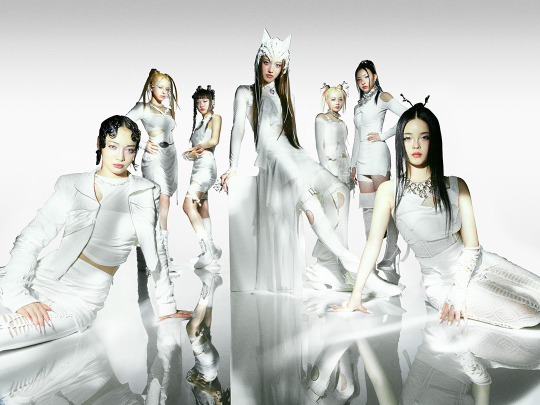









XG for Puppet Show
#XG for PUPPET SHOW#xg#xgalx#xg icons#juria#hinata#harvey#xg chisa#cocona#jurin#maya#xg alphaz#xg harvey#chisa#xg juria#alphaz#xtraordinary girls#new dna#hesonoo#grl gvng#new dance#xg grl gvng#xg tgif#xg new dance#XG puppet show#Puppet show
30 notes
·
View notes
Text

Thank God I'm Fly
2 notes
·
View notes








