#Military Tank Containers Market research
Explore tagged Tumblr posts
Text
Vetronics Market | Global Trends & Military Opportunities

Technology has significantly advanced, playing a crucial role in several industries. The paradigm for R&D in the defense sector has evolved investments in vetronics. This is a result of the growing trend across different defense forces to equip military vehicles with technologically sophisticated electronic systems.
According to our experts, the global vetronics market was valued at $3668.33 million in 2021 and is expected to reach $5372.01 million by 2028, with a CAGR of 5.62% during the forecast period 2022-2028.
Vetronics, also known as vehicle electronics, enables military units to implement and integrate systems such as communication, command and control, vehicle warfare, navigation, vehicle protection, and surveillance. Over the years, its relevance has increased as defense departments seek to make their armed forces lighter, faster, and more deployable.
Integration of Digitalization in Battlefield Operations
The digitization of domains such as communication and surveillance is critical in the integrated operations of the modern battlefield. Electronic warfare has already been adopted as a sub-domain by the majority of advanced nations. They actively engage in advanced capability research to equip their forces and gain a tactical advantage over their competitors.
For example, the US Army is testing the Electronic Warfare Tactical Vehicle (EWTV), containing an unspecified specification of radio jamming equipment. It can detect and disrupt a wide range of signals, from cellphones to enemy UAV control links.
Factors such as ease of deployment and a broad range of sensing and disruption are key features incorporated in modern armored vehicle-mounted jamming systems that increase their utility. The rapid adoption of such technology is expected to drive the studied market during the forecast period.
Additionally, the ongoing military modernization programs in respective armies worldwide have increased the number of land-based vehicles. Our study suggests tanks are the fastest growing land-based fleet type segment, with a CAGR of 5.82% during the forecast period. The development is due to the interconnection systems of the new tanks. The technological update enables tanks to integrate with wheeled armored vehicles outfitted with standard vetronics to collect and transform battlefield sensor data into high-value security and combat services.
Impact of Competitors’ Strategic Initiatives
The global vetronics market is highly fragmented, with key players controlling significant market shares. Major companies like Thales Group, Lockheed Martin Corporation, and L3Harris Technologies continue to invest in the R&D of military robotics and related subsystems. Such measures have enabled them to expand the spectrum of applications for their distinctive and exclusive product line of vetronics.
The market participants’ operations focus on designing, engineering, and manufacturing high-performance vetronics for the world’s armed forces’ terrestrial assets. Furthermore, because a contract for armored vehicles necessitates high technological expertise, the companies are merging to enhance their current portfolio.
Some of the examples are listed below-
Collins Aerospace Military Global Positioning System (GPS) division was successfully acquired by BAE Systems, bringing decades of experience, cutting-edge technology, and a sizable installed base of products.
With the purchase of Gemalto by Thales for €4.8 billion, the acquisition will cover every step of the important decision-making process in the digital age, from sensor-generated data to real-time decision support.
Curtiss-Wright Corporation announced on July 5, 2022, that it had successfully acquired the Safran Aerosystems Arresting Company (SAA) for $240 million in cash. The acquisition of Safran’s arresting systems division solidifies Curtiss-position Wright as the world’s leading recovery and arresting systems provider for fixed-wing aircraft. Curtiss-Naval Wright’s & Power division will include the company.
Key Challenges & Regional Opportunities
Although cuts in the defense budget and the rising cost of raw materials can challenge the vetronics market, it is continuously expanding due to breakthrough technology in military vehicles.
The current fiscal condition worldwide is the key barrier to the market’s expansion. Many emergent breakthroughs offer considerable long-term benefits but need significant investments in deploying new technologies and platforms.
Based on the global scenario, the North America vetronics market held the largest share in 2021 and is expected to maintain its stronghold throughout the forecasting period. The region is witnessing considerable growth, owing to its military and government efforts to modernize its army and fleet.
Additionally, the United States is the key contributor to the regional market, accounting for 96.93% of the share in 2021. The country’s large market share is due to the rapid development of venture capital markets. For instance, American Rheinmetall Systems has received a multi-million-dollar investment to offer cutting-edge combat vehicle mission systems technologies to support the modernization of US Army combat vehicles.
FAQ
Ques 1: Which segments are studied in the Vetronics Market?
Land-based fleet type, component and vertical are the segments studied in vetronics market.
Ques 2: What are the key component of vetronics market?
Electronic Warfare & C4 Systems, Navigation Systems, Power Systems, and Vehicle Protection Systems are the key component of vetronics market.
0 notes
Text
Aircraft Crashworthy Fuel Tank Market Outlook Report 2024-2031: Trends, Strategic Insights, and Growth Opportunities | GQ Research
The Aircraft Crashworthy Fuel Tank market is set to witness remarkable growth, as indicated by recent market analysis conducted by GQ Research. In 2023, the global Aircraft Crashworthy Fuel Tank market showcased a significant presence, boasting a valuation of US$ 300 million. This underscores the substantial demand for Aircraft Crashworthy Fuel Tank technology and its widespread adoption across various industries.
Get Sample of this Report at: https://gqresearch.com/request-sample/global-aircraft-crashworthy-fuel-tank-market/

Projected Growth: Projections suggest that the Aircraft Crashworthy Fuel Tank market will continue its upward trajectory, with a projected value of US$ 520 million by 2031. This growth is expected to be driven by technological advancements, increasing consumer demand, and expanding application areas.
Compound Annual Growth Rate (CAGR): The forecast period anticipates a Compound Annual Growth Rate (CAGR) of 1.2%, reflecting a steady and robust growth rate for the Aircraft Crashworthy Fuel Tank market over the coming years.
Technology Adoption
In the aircraft crashworthy fuel tank market, technology adoption is driven by the need for enhanced safety and compliance with stringent regulatory standards. Manufacturers are increasingly integrating advanced materials and innovative design techniques to improve the crashworthiness of fuel tanks. These advancements include the use of composite materials, such as carbon fiber reinforced polymers, and novel manufacturing processes like 3D printing, which allow for more resilient and lightweight fuel tank structures. Additionally, the adoption of smart technologies, such as sensors and monitoring systems, is becoming prevalent, enabling real-time data collection and predictive maintenance, thereby enhancing overall safety and efficiency.
Application Diversity
The application of crashworthy fuel tanks spans various sectors within the aviation industry. These tanks are not only crucial for military aircraft, where survivability and protection against ballistic threats are paramount, but they are also increasingly used in commercial aviation, general aviation, and rotorcraft. In military applications, the focus is on enhancing the ability of aircraft to withstand combat conditions, while in commercial aviation, the emphasis is on passenger safety and compliance with aviation safety regulations. The diverse applications highlight the versatility and importance of crashworthy fuel tanks across different types of aircraft and operational requirements.
Consumer Preferences
Consumer preferences in the aircraft industry are heavily influenced by safety, reliability, and cost-effectiveness. Airlines and military operators prioritize fuel tanks that offer superior crash protection, reduced risk of post-crash fires, and long service life. Additionally, there is a growing demand for fuel tanks that are lighter and more fuel-efficient, contributing to overall aircraft performance and operational cost savings. Environmental sustainability is also becoming a significant factor, with consumers preferring solutions that minimize environmental impact through the use of eco-friendly materials and manufacturing processes.
Technological Advancements
Technological advancements are at the forefront of the crashworthy fuel tank market. Innovations in material science, such as the development of high-strength, lightweight composites, and self-sealing materials, are critical. These materials not only enhance the structural integrity of fuel tanks but also improve their ability to withstand and contain fuel in the event of a crash. Additionally, advancements in manufacturing technologies, including additive manufacturing and precision engineering, allow for more complex and optimized designs. The integration of smart sensors and data analytics further enhances the performance and maintenance of these fuel systems, providing real-time monitoring and predictive capabilities.
Market Competition
The market for aircraft crashworthy fuel tanks is highly competitive, with several key players striving to develop superior products. Companies are investing heavily in research and development to innovate and differentiate their offerings. Strategic partnerships and collaborations are common, as firms seek to combine expertise and resources to advance their technological capabilities. Market competition also drives continuous improvement in manufacturing processes, cost efficiency, and product quality. Regulatory compliance and certification are critical factors that influence competitive positioning, as companies must ensure their products meet stringent aviation safety standards.
Environmental Considerations
Environmental considerations are increasingly shaping the aircraft crashworthy fuel tank market. The industry is under pressure to reduce its environmental footprint, leading to the adoption of sustainable materials and eco-friendly manufacturing processes. The use of recyclable and biodegradable materials in the production of fuel tanks is becoming more prevalent. Additionally, innovations aimed at improving fuel efficiency and reducing emissions are gaining traction. Companies are also exploring the potential of alternative fuels and hybrid propulsion systems, which require specialized fuel tank solutions to accommodate different fuel properties and storage requirements. Environmental regulations and standards play a crucial role in guiding these developments, ensuring that the industry moves towards more sustainable practices.
Regional Dynamics: Different regions may exhibit varying growth rates and adoption patterns influenced by factors such as consumer preferences, technological infrastructure and regulatory frameworks.
Key players in the industry include:
General Dynamics
Meggit PLC
Zodiac Aerospace
ContiTech AG
Aero Tec Laboratories Inc.
Amfuel
GKN Aerospace
Plascore Inc.
UTC Aerospace Systems and BAE Systems.
The research report provides a comprehensive analysis of the Aircraft Crashworthy Fuel Tank market, offering insights into current trends, market dynamics and future prospects. It explores key factors driving growth, challenges faced by the industry, and potential opportunities for market players.
For more information and to access a complimentary sample report, visit Link to Sample Report: https://gqresearch.com/request-sample/global-aircraft-crashworthy-fuel-tank-market/
About GQ Research:
GQ Research is a company that is creating cutting edge, futuristic and informative reports in many different areas. Some of the most common areas where we generate reports are industry reports, country reports, company reports and everything in between.
Contact:
Jessica Joyal
+1 (614) 602 2897 | +919284395731
Website - https://gqresearch.com/
0 notes
Text
Water-based Fire Extinguisher Market Market Analysis: Understanding Trends and Dynamics by 2032
New Research Report on “Water-based Fire Extinguisher Market Market” provide insightful data on the main market segments, dynamics, growth potentials and future prospects of industry. The study covers complete analysis on changing market trends for industry. The report shows the year-on-year growth of each segment and touches upon the different factors that are likely to impact the growth of each market segment. Each segment has analyzed completely on the basis of its production, consumption as well as revenue. And also offers Water-based Fire Extinguisher Market market size and share of each separate segment in the industry.
Get a Sample Copy of the Report at - https://www.proficientmarketinsights.com/enquiry/request-sample/1250
The global Water-based Fire Extinguisher Market size was USD 10631.87 million in 2024 and the market is projected to touch USD 13947.41 million by 2031, exhibiting a CAGR of 3.9% during the forecast period.
Top Key Players in the Water-based Fire Extinguisher Market Market:
Safe Pro Fire (India)
Nanjing Yimiao Fire Engineering Co., Ltd. (China)
Relish Fire Private Limited (RFPL)(India)
PSI-SAFETY(U.S.)
CheckFire (U.K.)
Safety Plus Industrials Co., Ltd (Taiwan)
Varsha Fire Engineers (India)
Login Eye (India)
Vimal Fire Controls Pvt. Ltd. (India)
Naffco (U.A.E)
Gielle Industries (Italy)
Request Sample for Covid-19 Impact Analysis - https://www.proficientmarketinsights.com/enquiry/request-covid19/1250
The Water-based Fire Extinguisher Market market research report presents a comprehensive assessment of the market and contains thoughtful insights, facts, historical data, and statistically supported and industry-validated market data. It also contains projections using a suitable set of assumptions and methodologies. The research report provides analysis and information according to market segments such as geographies, application, and industry.
Market split by Type, can be divided into:
Water Fire Extinguisher
Foam Fire Extinguisher
Water Mist fire Extinguisher
Market split by Application, can be divided into:
Offshore Installations
Tank Farms
Military Facilities
Airport
Others
Report presents a detailed picture of the market by the way of study, synthesis, and summation of data from multiple sources by an analysis of key parameters. Our Water-based Fire Extinguisher Market market covers the following areas:
Water-based Fire Extinguisher Market market sizing
Water-based Fire Extinguisher Market market forecast
Water-based Fire Extinguisher Market market industry analysis
Inquire or Share Your Questions If Any Before the Purchasing This Report -https://www.proficientmarketinsights.com/enquiry/pre-order-enquiry/1250
What Global Water-based Fire Extinguisher Market Market Report Offers?
Provides strategic profiling of key players in the Water-based Fire Extinguisher Market market.
Drawing a competitive landscape for the world Water-based Fire Extinguisher Market industry.
Describes insights about factors affecting the Water-based Fire Extinguisher Market market growth.
Analyze the Water-based Fire Extinguisher Market industry share based on various factors- price analysis, supply chain analysis etc.
Extensive analysis of the industry structure along with Water-based Fire Extinguisher Market market forecast 2020-2024.
Granular Analysis with respect to the current Water-based Fire Extinguisher Market industry size and future perspective.
Regions Covered in Water-based Fire Extinguisher Market Market Report:
North America (United States, Canada and Mexico)
Europe (Germany, UK, France, Italy, Russia and Turkey etc.)
Asia-Pacific (China, Japan, Korea, India, Australia, Indonesia, Thailand, Philippines, Malaysia and Vietnam)
South America (Brazil etc.)
Middle East and Africa (Egypt and GCC Countries)
Purchase this Report (Price 2900 USD for a Single-User License) - https://www.proficientmarketinsights.com/purchase/1250
0 notes
Text
Collapsible Fuel Tanks, Global Market Size Forecast, Top 10 Players Rank and Market Share
Collapsible Fuel Tanks Market Summary
According to the new market research report “Global Collapsible Fuel Tanks Market Report 2023-2029”, published by QYResearch, the global Collapsible Fuel Tanks market size is projected to reach USD 813.2 million by 2029, at a CAGR of 6.1% during the forecast period.

Figure. Global Collapsible Fuel Tanks Market Size (US$ Million), 2018-2029

Based on or includes research from QYResearch: Global Collapsible Fuel Tanks Market Report 2023-2029.
Market Drivers:
Increasing remote military training, weapon testing, surveillance, and defense activities are to augment the sales of collapsible fuel tanks in the market.
Collapsible fuel tanks are gaining huge popularity across the various industries such as oil & gas, mining, agriculture, and industries among others, owing to their favorable attributes such as easy install, bulk storage, high durability, resistance to temperature fluctuation & moisture, others.
In addition to this, collapsible fuel tanks are also finding numerous applications for disaster relief fuel supply purposes, owing to their high portability and ease of installation for fuel storage purposes. Hence, increasing floods, landslides, forest fires, earthquakes, and others worldwide is expected to create lucrative opportunities for growth in the global market.
Restraint:
Inability to install on irregular surfaces, high risk of puncture, and safety issues associated with the collapsible fuel tanks are the factor hampering the growth in the global market.
Growing concerns about environmental issues have led to stricter material requirements for these temporary storage tanks.
Opportunity:
Increasing demand for temporary storage solutions across rising on-shore mining and oil & gas exploration activities across the world is projected to accelerate the sales of collapsible fuel tanks in the global market.
The Russian-Ukrainian war and the game between China and the United States have increased instability in some regions, and frequent military activities will drive market demand in the short term.
Increasing floods, landslides, forest fires, earthquakes, and others worldwide is expected to create lucrative opportunities for growth in the global market.
Figure. Collapsible Fuel Tanks, Global Market Size, The Top 10 Players Hold 70% of Overall Market

Based on or includes research from QYResearch: Global Collapsible Fuel Tanks Market Report 2023-2029.
This report profiles key players of Collapsible Fuel Tanks such as Continental, MPC Containment, Safran.
In 2022, the global top five Collapsible Fuel Tanks players account for 52% of market share in terms of revenue. Above figure shows the key players ranked by revenue in Collapsible Fuel Tanks.
Figure. Collapsible Fuel Tanks, Global Market Size, Split by Product Segment

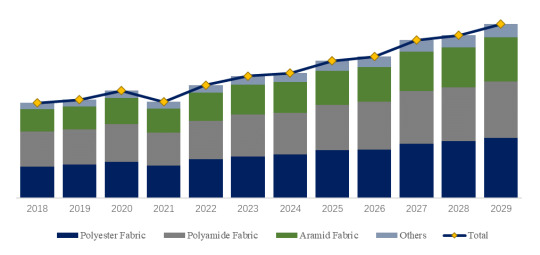
Based on or includes research from QYResearch: Global Collapsible Fuel Tanks Market Report 2023-2029.
In terms of product type, Polyester Fabric is the largest segment, hold a share of 34%.
Figure. Collapsible Fuel Tanks, Global Market Size, Split by Application Segment


Based on or includes research from QYResearch: Global Collapsible Fuel Tanks Market Report 2023-2029.
In terms of product application, Commercial is the largest application, hold a share of 55.7%.
Figure. Collapsible Fuel Tanks, Global Market Size, Split by Region


Based on or includes research from QYResearch: Global Collapsible Fuel Tanks Market Report 2023-2029.
About The Authors
Wangzhuang - Lead Author
Email: [email protected]
John is a technology & market senior analyst specializing in semiconductor devices, materials, and equipment. Wang has 3 years’ experience in semiconductor and focuses on Chemicals, consumer goods, food and beverages, machinery and equipment, software and business services, etc. He is engaged in the development of technology and market reports and is also involved in custom projects.
About QYResearch
QYResearch founded in California, USA in 2007.It is a leading global market research and consulting company. With over 16 years’ experience and professional research team in various cities over the world QY Research focuses on management consulting, database and seminar services, IPO consulting, industry chain research and customized research to help our clients in providing non-linear revenue model and make them successful. We are globally recognized for our expansive portfolio of services, good corporate citizenship, and our strong commitment to sustainability. Up to now, we have cooperated with more than 60,000 clients across five continents. Let’s work closely with you and build a bold and better future.
QYResearch is a world-renowned large-scale consulting company. The industry covers various high-tech industry chain market segments, spanning the semiconductor industry chain (semiconductor equipment and parts, semiconductor materials, ICs, Foundry, packaging and testing, discrete devices, sensors, optoelectronic devices), photovoltaic industry chain (equipment, cells, modules, auxiliary material brackets, inverters, power station terminals), new energy automobile industry chain (batteries and materials, auto parts, batteries, motors, electronic control, automotive semiconductors, etc.), communication industry chain (communication system equipment, terminal equipment, electronic components, RF front-end, optical modules, 4G/5G/6G, broadband, IoT, digital economy, AI), advanced materials industry Chain (metal materials, polymer materials, ceramic materials, nano materials, etc.), machinery manufacturing industry chain (CNC machine tools, construction machinery, electrical machinery, 3C automation, industrial robots, lasers, industrial control, drones), food, beverages and pharmaceuticals, medical equipment, agriculture, etc.
0 notes
Text
Aircraft Fuel Tanks Market May Set New Growth Story

Advance Market Analytics published a new research publication on "Aircraft Fuel Tanks Market Insights, to 2028" with 232 pages and enriched with self-explained Tables and charts in presentable format. In the Study you will find new evolving Trends, Drivers, Restraints, Opportunities generated by targeting market associated stakeholders. The growth of the Aircraft Fuel Tanks market was mainly driven by the increasing R&D spending across the world.
Get Free Exclusive PDF Sample Copy of This Research @ https://www.advancemarketanalytics.com/sample-report/69228-global-aircraft-fuel-tanks-market-1 The Aircraft Fuel Tanks Market report covers extensive analysis of the key market players, along with their business overview, expansion plans, and strategies. The key players studied in the report include: Lockheed Martin Corporation (United States), GKN Aerospace (United Kingdom), ContiTech (Germany), Cobham (United Kingdom), TAG Aviation (Switzerland), Boeing (United States), UTC Aerospace Systems (United States), Meggitt (United Kingdom), PFW Aerospace (Germany), General Dynamics (United States), Zodiac Aerospace (France). Definition: Aircraft Fuel tanks refer to a major component which manages fuel distribution between tanks on the aircraft. These tanks come in a variety of types and sizes and can be located almost anywhere in the aircraft such as near wings, fuselage, and tail. A fuel tank contains a different component which includes pumps, piping, gauges, valves, filters and inserting systems for performing the desired action. In Aircraft Fuel tanks, the safety aspect is one of the major concern, which needs to be examined during the investigation and manufacturers are focusing on developing lightweight fuel tanks to increase the overall efficiency of aircraft. Rising in the number of aircraft delivery is expected to drive the market for aircraft fuel tanks in the forecasted period. The following fragment talks about the Aircraft Fuel Tanks market types, applications, End-Users, Deployment model etc. A thorough analysis of Aircraft Fuel Tanks Market Segmentation: by Type (Internal Tanks (Integral Tank, Rigid Removable Tanks, Bladder Tanks and Tip Tanks), External Tanks (Conformal Fuel Tank and Drop Tank)), Aviation Type (Commercial Aviation, Military Aviation, Private Jet), Capacity (<30 L Aircraft Fuel Tank, 30 L to 50 L Aircraft Fuel Tank, 51 L to 70 L Aircraft Fuel Tank, More than 70 L Aircraft Fuel Tank), Aircraft type (Narrow Body Aircraft, Wide Body Aircraft, Regional Jet, Turboprop, Rotary-wing Aircraft, Military Transport Aircraft, Fighter Jets), Material (Aluminum Aircraft Fuel Tank, HDPE Aircraft Fuel Tank, Steel Aircraft Fuel Tank) Aircraft Fuel Tanks Market Drivers:
Rising Global Air Traffic Owing to Influx of Air Passenger Led to Increase in Demand of Aircraft
Growing Aircraft Production for Military Applications
Aircraft Fuel Tanks Market Trends:
Use of Automation Techniques Such as Robotics For Aircraft Fuel Tank Designing
Growing Focus Towards Designing Low Weight Aircraft Fuel Tanks
Aircraft Fuel Tanks Market Growth Opportunities:
Rise in Aircraft Fuel Tank Deliveries Across The Countries
Heavy Investment in Research and Development of Aircraft Technologies
As the Aircraft Fuel Tanks market is becoming increasingly competitive, it has become imperative for businesses to keep a constant watch on their competitor strategies and other changing trends in the Aircraft Fuel Tanks market. Scope of Aircraft Fuel Tanks market intelligence has proliferated to include comprehensive analysis and analytics that can help revamp business models and projections to suit current business requirements. We help our customers settle on more intelligent choices to accomplish quick business development. Our strength lies in the unbeaten diversity of our global market research teams, innovative research methodologies, and unique perspective that merge seamlessly to offer customized solutions for your every business requirement. Have Any Questions Regarding Global Aircraft Fuel Tanks Market Report, Ask Our Experts@ https://www.advancemarketanalytics.com/enquiry-before-buy/69228-global-aircraft-fuel-tanks-market-1 Strategic Points Covered in Table of Content of Global Aircraft Fuel Tanks Market:
Chapter 1: Introduction, market driving force product Objective of Study and Research Scope the Aircraft Fuel Tanks market
Chapter 2: Exclusive Summary and the basic information of the Aircraft Fuel Tanks Market.
Chapter 3: Displaying the Market Dynamics- Drivers, Trends and Challenges & Opportunities of the Aircraft Fuel Tanks
Chapter 4: Presenting the Aircraft Fuel Tanks Market Factor Analysis, Porters Five Forces, Supply/Value Chain, PESTEL analysis, Market Entropy, Patent/Trademark Analysis.
Chapter 5: Displaying the by Type, End User and Region/Country 2018-2022
Chapter 6: Evaluating the leading manufacturers of the Aircraft Fuel Tanks market which consists of its Competitive Landscape, Peer Group Analysis, BCG Matrix & Company Profile
Chapter 7: To evaluate the market by segments, by countries and by Manufacturers/Company with revenue share and sales by key countries in these various regions (2023-2028)
Chapter 8 & 9: Displaying the Appendix, Methodology and Data Source
Finally, Aircraft Fuel Tanks Market is a valuable source of guidance for individuals and companies. Read Detailed Index of full Research Study at @ https://www.advancemarketanalytics.com/reports/69228-global-aircraft-fuel-tanks-market-1 What benefits does AMA research study is going to provide?
Latest industry influencing trends and development scenario
Open up New Markets
To Seize powerful market opportunities
Key decision in planning and to further expand market share
Identify Key Business Segments, Market proposition & Gap Analysis
Assisting in allocating marketing investments
Thanks for reading this article; you can also get individual chapter wise section or region wise report version like North America, Middle East, Africa, Europe or LATAM, Southeast Asia. Contact US : Craig Francis (PR & Marketing Manager) AMA Research & Media LLP Unit No. 429, Parsonage Road Edison, NJ New Jersey USA – 08837 Phone: +1 201 565 3262, +44 161 818 8166 [email protected]
#Global Aircraft Fuel Tanks Market#Aircraft Fuel Tanks Market Demand#Aircraft Fuel Tanks Market Trends#Aircraft Fuel Tanks Market Analysis#Aircraft Fuel Tanks Market Growth#Aircraft Fuel Tanks Market Share#Aircraft Fuel Tanks Market Forecast#Aircraft Fuel Tanks Market Challenges
0 notes
Text
United States Styrene Butadiene Rubber (SBR) Market Industry Trends, Share, Forecast 2022-2029
BlueWeave Consulting, a leading strategic consulting and market research firm, in its recent study, estimated the United States styrene butadiene rubber (SBR) market size at USD 1.41 billion in 2022. During the forecast period between 2023 and 2029, BlueWeave expects United States styrene butadiene rubber (SBR) market size to grow at a significant CAGR of 6.45% reaching a value of USD 2.06 billion by 2029. Major growth drivers for the United States styrene butadiene rubber (SBR) market include an increasing interlinking of polymer chains brought on by oxidation. Unlike natural rubber, which tends to harden with time, SBR retains its softness due to this cross-linking, rendering it a favorable material for manufacturing tires. This distinctive property underscores SBR's prominence as a preferred option within the market. The demand for SBR is particularly significant in the tire industry due to these attributes. Also, as the population grows, leading to higher vehicle demand and subsequently increased tire production, the demand for SBR is expected to rise in the USA. Also, its non-slip attributes make SBR suitable for producing footwear soles and heels, contributing notably to market expansion. It is projected that the USA's styrene butadiene rubber (SBR) market will likely reach a volume of 1500 thousand tons throughout the forecast period. However, fluctuations in prices of raw materials and limited supplies of natural rubber are anticipated to restrain the overall market growth during the forecast period.
United States Styrene butadiene rubber (SBR) Market – Overview
Styrene butadiene rubber (SBR) is a synthetic rubber derived from the copolymerization of styrene and butadiene. The predominant method for its production is emulsion polymerization. SBR boasts exceptional mechanical attributes, including high heat resistance, strong tensile strength, resistance to cracking and tearing, and notable resilience. Consequently, it finds widespread application, notably in tire manufacturing. Often combined with natural rubber for enhanced resilience, SBR is employed in various industries, such as tire production, conveyor belts, foam articles, adhesives, sealants, domestic mats, footwear soles, chewy candy, food container adhesives, car mats, brake pads, tubing, V-belts, floor coverings, military tank pads, and rubberized battery box cases.
Sample Request @ https://www.blueweaveconsulting.com/report/united-states-styrene-butadiene-rubber-market/report-sample
Impact of COVID-19 on United States Styrene butadiene rubber (SBR) Market
COVID-19 pandemic adversely affected the United States styrene butadiene rubber (SBR) market. It led to disruptions in supply chains, reduced manufacturing capacities, and shifts in consumer demand. Lockdown measures and reduced economic activity during the pandemic's peak resulted in decreased demand for automotive and industrial products, influencing SBR utilization. While the gradual recovery in economic activities led to a rebound in demand, challenges remained due to supply chain bottlenecks and labor shortages. The pandemic emphasized the need for resilient supply chains and adaptive production strategies to navigate uncertainties and ensure the United States SBR market's sustained growth amidst such unprecedented challenges.
United States Styrene butadiene rubber (SBR) Market – By Application
Based on application, the United States styrene butadiene rubber (SBR) market is divided into Tires, Industrial, Footwear, Polymer Modification, and Adhesives segments. The tires segment held the highest share in the United States styrene butadiene rubber (SBR) market by application. SBR's unique blend of mechanical properties, such as durability, abrasion resistance, and high tensile strength, make it a preferred material for tire production. As the automotive sector continues to grow, the demand for high-quality, long-lasting tires has surged. SBR's ability to enhance tire performance and safety while meeting stringent industry standards has propelled its widespread adoption. This strong alignment between SBR's properties and tire manufacturing requirements underscores its dominant position in the United States SBR market within the tires application segment.
Competitive Landscape
Major players operating in the United States styrene butadiene rubber (SBR) market include Goodyear Tire and Rubber, LANXESS AG, Lion Elastomers, Bridgestone Corporation, Trinseo, Zeon Chemical, Dow Chemical, INEOS Styrolution, Chevron Phillips Chemical Company, and Sinopec. To further enhance their market share, these companies employ various strategies, including mergers and acquisitions, partnerships, joint ventures, license agreements, and new product launches.
Contact Us:
BlueWeave Consulting & Research Pvt. Ltd
+1 866 658 6826 | +1 425 320 4776 | +44 1865 60 0662
0 notes
Text
0 notes
Text
Military Sensors Market Trends, Technological Advancement, And Driving Factors
The global military sensors market is set to gain impetus from the emergence of the Wireless Sensor Network (WSN) technology. It is mainly designed for recording and monitoring various conditions at different locations. This information is given by Fortune Business Insights™ in a new report, titled, “Military Sensors Market Size, Share & COVID-19 Impact Analysis, By Platform (Ground, Airborne, Naval, Space), By Component (Hardware, Software), By Application (Navigation & Communication, Intelligence & Reconnaissance, Electronic Warfare, Command & Control, Monitoring & Surveillance, Target Recognition), and Regional Forecast, 2020-2027.” The report further states that the market size was USD 25.94 billion in 2019 and is projected to reach USD 34.58 billion by 2027, exhibiting a CAGR of 6.91% during the forecast period.
How Did We Create This Report?
As customer expectations are changing, the aspirations of dealers are also transforming rapidly. Distribution channels are becoming complex. To provide our clients with detailed information, we have conducted extensive primary and secondary research. We have thoroughly investigated each opportunity qualitatively and quantitatively so that our clients get a complete picture of both emerging and existing opportunities. We have also conducted a techno-economic study.
Browse Complete Report Summary:
Drivers & Restraints-
Increasing Development of MEMS-based Sensors to Accelerate Growth
The development of military sensors depends more on optical microelectromechanical systems (MEMS) and RF MEMS devices. These are capable of meeting special military requirements. MEMS have multiple beneficial properties. They have high reliability, low power consumption, and compact sizes. Hence, they are mainly used to develop sensors for unmanned aerial vehicles (UAVs), missiles, battlefield tanks, drone electronics, and surveillance.
At the same time, nanotechnology-based and MEMS-based military sensors are extensively utilized in monitoring the weapon's health and battlefield environment. However, these sensors have complex designs, which, in turn, may obstruct the military sensors market growth in the near future.
Segment-
Airborne Segment to Grow Rapidly Backed by Surging Usage of Military Helicopters & UAVs
Based on the platform, the airborne segment generated 27.03% in terms of the military sensors market share in 2019. It is expected to show the highest CAGR throughout the forthcoming years because of the rising usage of UAVs, fighter jets, and military helicopters in India, China, and the U.S.
Regional Insights-
Rising Modernization Programs to Boost Growth in North America
In 2019, North America procured USD 10.05 billion in terms of revenue and is set to dominate in the coming years. The rising initiatives by governments to conduct modernization programs, as well as the procurement of 3D expeditionary long-range radar in the region, would aid growth.
Europe, on the other hand, is set to grow substantially on account of the rising usage of EOIR military sensors by the U.K. Defense Ministry. In Asia Pacific, the increasing territorial disputes between India and Pakistan, as well as the geopolitical tensions between China and India, would contribute to growth.
Competitive Landscape-
Key Players Focus on Gaining New Contracts to Compete with Their Rivals
The market contains numerous prominent companies that are persistently striving to gain a competitive edge by procuring new contracts from government agencies. They are doing so to deliver their in-house military sensors. Below are two of the latest industry developments:
November 2020: BAE Systems won a contract worth USD 94 million from the U.S. Navy to deliver the latter with advanced technology. It will be used to develop several unmanned aerial systems.
May 2020: FLIR Systems received a second contract from the Army to provide unmanned aerial systems for the Soldier Borne Sensor program. The program is capable of offering real-time visual sector scanning.
0 notes
Text
Vetronics Market | Global Trends & Military Opportunities
Aerospace and Defense
29, September 2022
Technology has significantly advanced, playing a crucial role in several industries. The paradigm for R&D in the defense sector has evolved investments in vetronics. This is a result of the growing trend across different defense forces to equip military vehicles with technologically sophisticated electronic systems.
According to our experts, the global vetronics market was valued at $3668.33 million in 2021 and is expected to reach $5372.01 million by 2028, with a CAGR of 5.62% during the forecast period 2022-2028.

Vetronics, also known as vehicle electronics, enables military units to implement and integrate systems such as communication, command and control, vehicle warfare, navigation, vehicle protection, and surveillance. Over the years, its relevance has increased as defense departments seek to make their armed forces lighter, faster, and more deployable.
Integration of Digitalization in Battlefield Operations
The digitization of domains such as communication and surveillance is critical in the integrated operations of the modern battlefield. Electronic warfare has already been adopted as a sub-domain by the majority of advanced nations. They actively engage in advanced capability research to equip their forces and gain a tactical advantage over their competitors.
For example, the US Army is testing the Electronic Warfare Tactical Vehicle (EWTV), containing an unspecified specification of radio jamming equipment. It can detect and disrupt a wide range of signals, from cellphones to enemy UAV control links.
Factors such as ease of deployment and a broad range of sensing and disruption are key features incorporated in modern armored vehicle-mounted jamming systems that increase their utility. The rapid adoption of such technology is expected to drive the studied market during the forecast period.
Additionally, the ongoing military modernization programs in respective armies worldwide have increased the number of land-based vehicles. Our study suggests tanks are the fastest growing land-based fleet type segment, with a CAGR of 5.82% during the forecast period. The development is due to the interconnection systems of the new tanks. The technological update enables tanks to integrate with wheeled armored vehicles outfitted with standard vetronics to collect and transform battlefield sensor data into high-value security and combat services.
Impact of Competitors’ Strategic Initiatives
The global vetronics market is highly fragmented, with key players controlling significant market shares. Major companies like Thales Group, Lockheed Martin Corporation, and L3Harris Technologies continue to invest in the R&D of military robotics and related subsystems. Such measures have enabled them to expand the spectrum of applications for their distinctive and exclusive product line of vetronics.
The market participants’ operations focus on designing, engineering, and manufacturing high-performance vetronics for the world’s armed forces’ terrestrial assets. Furthermore, because a contract for armored vehicles necessitates high technological expertise, the companies are merging to enhance their current portfolio.
Some of the examples are listed below-
Collins Aerospace Military Global Positioning System (GPS) division was successfully acquired by BAE Systems, bringing decades of experience, cutting-edge technology, and a sizable installed base of products.
With the purchase of Gemalto by Thales for €4.8 billion, the acquisition will cover every step of the important decision-making process in the digital age, from sensor-generated data to real-time decision support.
Curtiss-Wright Corporation announced on July 5, 2022, that it had successfully acquired the Safran Aerosystems Arresting Company (SAA) for $240 million in cash. The acquisition of Safran’s arresting systems division solidifies Curtiss-position Wright as the world’s leading recovery and arresting systems provider for fixed-wing aircraft. Curtiss-Naval Wright’s & Power division will include the company.
Key Challenges & Regional Opportunities
Although cuts in the defense budget and the rising cost of raw materials can challenge the vetronics market, it is continuously expanding due to breakthrough technology in military vehicles.
The current fiscal condition worldwide is the key barrier to the market’s expansion. Many emergent breakthroughs offer considerable long-term benefits but need significant investments in deploying new technologies and platforms.
Based on the global scenario, the North America vetronics market held the largest share in 2021 and is expected to maintain its stronghold throughout the forecasting period. The region is witnessing considerable growth, owing to its military and government efforts to modernize its army and fleet.
Additionally, the United States is the key contributor to the regional market, accounting for 96.93% of the share in 2021. The country’s large market share is due to the rapid development of venture capital markets. For instance, American Rheinmetall Systems has received a multi-million-dollar investment to offer cutting-edge combat vehicle mission systems technologies to support the modernization of US Army combat vehicles.
FAQ
Ques 1: Which segments are studied in the Vetronics Market?
Land-based fleet type, component and vertical are the segments studied in vetronics market.
Ques 2: What are the key component of vetronics market?
Electronic Warfare & C4 Systems, Navigation Systems, Power Systems, and Vehicle Protection Systems are the key component of vetronics market.
#vetronics market#vetronics#aerospace and defense industry#triton market research#market research reprots
0 notes
Text
Vetronics Market | Global Trends & Military Opportunities
Technology has significantly advanced, playing a crucial role in several industries. The paradigm for R&D in the defense sector has evolved investments in vetronics. This is a result of the growing trend across different defense forces to equip military vehicles with technologically sophisticated electronic systems.
According to our experts, the global vetronics market was valued at $3668.33 million in 2021 and is expected to reach $5372.01 million by 2028, with a CAGR of 5.62% during the forecast period 2022-2028.
Vetronics, also known as vehicle electronics, enables military units to implement and integrate systems such as communication, command and control, vehicle warfare, navigation, vehicle protection, and surveillance. Over the years, its relevance has increased as defense departments seek to make their armed forces lighter, faster, and more deployable.

Integration of Digitalization in Battlefield Operations
The digitization of domains such as communication and surveillance is critical in the integrated operations of the modern battlefield. Electronic warfare has already been adopted as a sub-domain by the majority of advanced nations. They actively engage in advanced capability research to equip their forces and gain a tactical advantage over their competitors.
For example, the US Army is testing the Electronic Warfare Tactical Vehicle (EWTV), containing an unspecified specification of radio jamming equipment. It can detect and disrupt a wide range of signals, from cellphones to enemy UAV control links.
Factors such as ease of deployment and a broad range of sensing and disruption are key features incorporated in modern armored vehicle-mounted jamming systems that increase their utility. The rapid adoption of such technology is expected to drive the studied market during the forecast period.
Additionally, the ongoing military modernization programs in respective armies worldwide have increased the number of land-based vehicles. Our study suggests tanks are the fastest growing land-based fleet type segment, with a CAGR of 5.82% during the forecast period. The development is due to the interconnection systems of the new tanks. The technological update enables tanks to integrate with wheeled armored vehicles outfitted with standard vetronics to collect and transform battlefield sensor data into high-value security and combat services.
Impact of Competitors’ Strategic Initiatives
The global vetronics market is highly fragmented, with key players controlling significant market shares. Major companies like Thales Group, Lockheed Martin Corporation, and L3Harris Technologies continue to invest in the R&D of military robotics and related subsystems. Such measures have enabled them to expand the spectrum of applications for their distinctive and exclusive product line of vetronics.
The market participants’ operations focus on designing, engineering, and manufacturing high-performance vetronics for the world’s armed forces’ terrestrial assets. Furthermore, because a contract for armored vehicles necessitates high technological expertise, the companies are merging to enhance their current portfolio.
Some of the examples are listed below-
Collins Aerospace Military Global Positioning System (GPS) division was successfully acquired by BAE Systems, bringing decades of experience, cutting-edge technology, and a sizable installed base of products.
With the purchase of Gemalto by Thales for €4.8 billion, the acquisition will cover every step of the important decision-making process in the digital age, from sensor-generated data to real-time decision support.
Curtiss-Wright Corporation announced on July 5, 2022, that it had successfully acquired the Safran Aerosystems Arresting Company (SAA) for $240 million in cash. The acquisition of Safran’s arresting systems division solidifies Curtiss-position Wright as the world’s leading recovery and arresting systems provider for fixed-wing aircraft. Curtiss-Naval Wright’s & Power division will include the company.
Key Challenges & Regional Opportunities
Although cuts in the defense budget and the rising cost of raw materials can challenge the vetronics market, it is continuously expanding due to breakthrough technology in military vehicles.
The current fiscal condition worldwide is the key barrier to the market’s expansion. Many emergent breakthroughs offer considerable long-term benefits but need significant investments in deploying new technologies and platforms.
Based on the global scenario, the North America vetronics market held the largest share in 2021 and is expected to maintain its stronghold throughout the forecasting period. The region is witnessing considerable growth, owing to its military and government efforts to modernize its army and fleet.
Additionally, the United States is the key contributor to the regional market, accounting for 96.93% of the share in 2021. The country’s large market share is due to the rapid development of venture capital markets. For instance, American Rheinmetall Systems has received a multi-million-dollar investment to offer cutting-edge combat vehicle mission systems technologies to support the modernization of US Army combat vehicles.
#Vetronics Market#Vetronics#Defense industry#defense#market research#market research reports#triton market research
0 notes
Text
Protests Unite Myanmar’s Ethnic Groups Against Common Foe
Myanmar’s military, known as the Tatmadaw, has killed at least 510 people and detained more than 2,500 others since it took power on Feb. 1. Now terrorized by the military themselves, many people from the Bamar ethnic majority are developing a sense of solidarity with the country’s numerous minority groups. Public apologies for years of indifference and denial of minority people’s experiences have proliferated. “We have learned day by day, and our point of view has changed. We feel really sorry,” said Yin Yin, a Bamar youth who worked as a hotelier in Yangon before the coup.
Many Bamar people also seem to be shifting their political objectives. Early in the protests, a split emerged between groups led by an older generation of protesters from the 1988 student uprisings who called for the release of democratic leader Aung San Suu Kyi and elected officials and a return to the previous system of governance and a diverse group of protesters who united under the General Strike Committee of Nationalities (GSCN) with more ambitious demands. The GSCN advocates for the abolition of the military-drafted 2008 constitution and the establishment of a new one based on federalism. These calls have rapidly gained momentum, especially among a young generation eager to make amends for past injustices and build a more equitable society.
Before the coup, military violence and government oppression of ethnic minorities evoked only weak responses from the Bamar public. Mass denial followed the 2017 campaign against the Rohingya, and only a few activists spoke out. When the Tatmadaw launched airstrikes in Kachin state in 2018 and the government blocked displaced people from safe passage or access to humanitarian assistance, there was little outcry beyond activist circles. The same was true when the government shut down the internet in Rakhine state and parts of Chin state for more than a year.
But the shared experience of suffering under military violence has contributed to shifting views among Bamar demonstrators. “Since the coup started, we all faced the same thing, the same tragic incidents all over the country,” Yin Yin said. “It doesn’t matter if we are Burmese, Kachin, Chin, or any ethnic group. As long as we are living in Myanmar, we have the same rights and we need the same freedom, so federal democracy is a must.”
Myanmar's ethnic rebels isolate junta ahead of Armed Forces Day
Since then, these insurgent groups from the Karen, the Shan, and the Kachin have become emboldened in their anti-junta positions. The armed wing of the Karen National Union recently cut the food supply lines to feed soldiers deployed near the Thai-Myanmar border, according to media reports. Elsewhere, according to local sources, the armed wing of the Kachin, active close to the Myanmar-China border, launched fresh strikes against military positions this month. Last Sunday, a battalion of the Kachin Independence Army mounted dawn attacks on three Tatamadaw-held bases.
"The KNU has already condemned the coup, and no longer recognizes the Tatmadaw as a legitimate actor," said Jason Tower, a researcher working on conflict issues in Myanmar for the United States Institute of Peace, a think tank supported by the U.S. Congress. "The Tatmadaw will have to address growing push back from the ethnic armed groups."
He said the military's grip on Myanmar will be loosened as the rebel groups become emboldened by the chaos caused by the coup. "The Tatmadaw will be strategically weakened if it has to face conflict with ethnic armed groups on many fronts," he said. "This can worsen as the rebel armies strategically align themselves with the CDM."
A Tuesday statement by the Arakan Army -- a powerful rebel force that battled the Tatmadaw in 2019 and 2020 in the state of Rakhine -- was the latest warning shot to the junta about the shifting political alliances. It declared that it was closing ranks with the other armed ethnic groups in condemning the coup and subsequent crackdown. The move comes after the militant group had agreed on a ceasefire with the Tatmadaw last year, suggesting that the two adversaries were headed for peace.
But that is not all. The military's resources are also being stretched as China pressures the junta to protect its economic assets after 32 Chinese-owned factories in Yangon were torched this month. The investments were part of China's multibillion-dollar stake in Myanmar, spanning an oil-and-gas pipeline and large infrastructure projects as part of Beijing's Belt and Road infrastructure initiative.
"Threats to Chinese property and lives will be taken very seriously and, as has already been seen, diplomats will want to show an immediate response," said a senior analyst at a Yangon-based think tank, who spoke on condition of anonymity. "But [Chinese] officials also know that relations will have to be maintained with all sides in the current impasse, including the military government, NLD and ethnic nationality movements because it is too early to know who will ultimately succeed."
China’s rare earth supplies disrupted by Myanmar tumult
Chinese companies started complaining about delays in shipments of the minerals since mid-March, reportedly due to the deteriorating political and economic situation, which Chinese media reports say have had an impact on logistics.
Rare earth metals are used in aerospace, advanced military equipment, mobile phones and electric vehicles, among other tech products. Myanmar is a major supplier of rare earth ores, which are exported to China for extraction and processing, and then either used in local production or shipped on to global markets.
Hiccups in Myanmar’s supply of rare earths are the latest indicator that the audacious military coup, launched by Senior General Min Aung Hlaing, and subsequent national chaos is starting to seriously disrupt Myanmar’s economy and businesses.
The impact on rare earth shipments is the latest sign the coup is adversely impacting China, which earlier expressed concern about the security of its twin oil and gas pipelines that run through Myanmar into southern China and other commercial interests amid a public backlash against Beijing for its perceived support of the country’s ruling generals.
The geopolitics of Myanmar’s black swan coup
India is being wooed by the United States as a member of a military proto-alliance aimed at containing China, known as the Quad.
Yet the normative foundations of this arrangement were exposed as frail because India, which was also present at the parade, can’t afford to put democratic values before its interest in securing its eastern border, for which it needs close ties with the Myanmar military.
China is also in a quandary. The coup undermined all the hard work Beijing put in to building a solid relationship with a transitional democratic government led by Aung San Suu Kyi.
Beijing’s client is now under arrest and its strategic investment projects linking China to the sea along the so-called China-Myanmar Economic Corridor are exposed to risk by an army that is at best ambivalent about close ties with China.
There was therefore no hesitation on Beijing’s part to lend support to coup leader Senior General Min Aung Hlaing at the Army Day Parade. China is key to the Myanmar military junta’s survival and while the surge in instability on its border may not be ideal, all in all this probably suits Beijing just fine.
Neighboring countries Bangladesh, Laos and Thailand were also present at the parade, highlighting their own narrow security interests, but also how divided the region is over the coup.
ASEAN member states have struggled to forge a consensus of concern and agreed action to de-escalate the situation. Indonesia has pushed for action, supported by Brunei, Malaysia and Singapore, but mainland states such a Thailand and Vietnam have dragged their feet, arguing that the coup is an internal affair – despite the rising risk of a mass outflow of refugees.
This regional divide has upset Washington’s geopolitical calculus. The new Biden administration is trying to corral ASEAN into a more effective bulwark against China. The Myanmar coup has been a distraction to that drive.
Washington’s priority is to solidify alliances with larger powers India, Japan and South Korea. In mid-March US Secretary of State Antony Blinken and Defense Secretary Lloyd Austin paid an inaugural visit to Tokyo and Seoul. Blinken finished the trip in a testy meeting with Chinese counterparts in Alaska, while Austin went onto Delhi.
Missing from their itinerary was anywhere near Myanmar in Southeast Asia; nor was there a hoped-for joint statement on Myanmar in US talks with the Chinese, an omission that was noticed in the region.
35 notes
·
View notes
Text
The mission was, on paper, simple.
Find the HEV. Bring back samples of the carbon underlayer (rumored to be an energized, programmable carbon fiber nanotube arrangement) and the protective plating (rumored to be a cutting-edge 3D-printed polymer lattice kiln-fired to a tough, durable, radiation-shielding semi-crystalline state) and, if possible, a copy of the integrated programming (rumored to be an advanced biometric/medical suite capable of autonomous diagnostics and treatment.)
Simple.
Black Mesa was allegedly raking in billions in military and private sector contracts for their advanced metamaterials, everything from new forms of tank plating to new forms of rocket fuel, but the stuff the HEV was made of wasn’t hitting their usual contract markets. If it existed, really physically existed outside a PowerPoint presentation in an R&D pipe-dream, they were keeping it awfully close to the chest.
And that begged the question, the question Horizon Labs was willing to pay him six figures to answer: why?
Why pour millions or more, and years of research and development, into a product you aren’t selling?
Because the product doesn’t exist, went the popular train of thought.
Because the product is just an asset to the production of something more valuable, went an entirely different train of thought.
Either way, Horizon had an itch that would be nicely scratched by a little “inspiration” from Black Mesa’s polymer laboratories.
Johnson wasn’t new to the game.
He’d wandered the halls of two universities as an adjunct professor and collected up the combined research of a slew of brilliant young doctoral candidates (not like the universities would ever let students patent or publish.) He’d stolen blueprints for a quantum supercomputer from a quasi-military installation in Florida (they’d stolen them from a Japanese tech lab first, and Johnson was just leveling the playing field by selling them to a Nigerian royal. A real one who paid in gold.) He’d walked out of a medical research facility in Russia with samples of artificial bone grown on a hand-carved calcite lattice and embedded with the recipient’s own DNA (four hospitals in India had pooled their resources to buy that job.) And he still had, under the skin above his left elbow, a microchip containing the formula for the world’s most efficient organic rocket fuel, developed in UAE fishponds. He had a buyer waiting for him in Jerusalem.
But he’d gotten a tip that someone on the far side had an idea who he was, and then Horizon had contacted him about this job. The combination of being literally underground and also making a paycheck was rather appealing at the moment.
Black Mesa was a little deeper underground than he’d anticipated, he thought, as he looked up at the raw red stone ceiling arching three stories above his head.
He wasn’t new to the game, but Black Mesa was another kind of player altogether.
Old, twisting, dangerous. Its guards were a hand-wave to convention; the real danger was the facility itself and, as his belt Geiger counter pinged a warning, the decades of research they’d already abandoned here.
He’d never heard of anyone successfully stealing intellectual property from Black Mesa before, but that didn’t mean it hadn’t been tried. He’d heard of lots of tries.
The tram line turned a corner; below, the pooled nuclear coolant shimmered radium green.
#Ardeas Original Stuff#not tagging this in the fandom because it's like 47 steps to the left of cannon#Johnson Goes to Work
8 notes
·
View notes
Note
Hi! :-) I'm pretty bad at reading between the lines and understanding subtext, especially since English isn't my first language, so I thought it'd be easier to ask: when did The Big One happen? Was the world previous to that 'normal' (similar to ours)? What exactly did they do to MC at the farm? What, exactly, is a regene? Sorry for so many Q's, lol. I really love Fallen Hero but I feel like I'm missing a lot of information, or maybe not all of it has been published yet. Gr8 work! 🖤
The world before that was not entirely like ours, it diverged around 1900 or so. If our world focused a lot on the space race, atomic power, atomic bombs, getting to the moon, flight, satellites and things like that, the FH world focused a lot more on medical tech and what we would call cyborg tech. It’s behind on things like cellphones and the internet (think mid nineties for that) and we never went to the moon. Putting the new and updated timeline below.
A ReGene is a vat-grown body implanted with an artificial intelligence mind. They tend to be boosted in various ways, and subject to intense modifications since they have no rights, they tend to be used for experimental new technologies. If they die, they just grow more.
What the MC did at the Farm is spoilers.
History of the Fallen Hero world.
1945: World War II ends, but the technological arms race continues. The United States and the Soviet Union both 'recruit' available German and Japanese scientists, taking full advantage of what they learned from the more unconscionable experiments during the war.
1951: The Korean War very nearly turns nuclear when the first Chinese Type 52 bipedal tanks help push the UN forces out of the mountains and nearly out of the country. Though clumsy and slow, they prove to be useful in the mountainous terrain, leading to an upswing in the power armor industry.
1955: The Soviet Union announces that it has successfully created the first functional, cybernetic limb replacement. This is widely considered the start of the Cyber Race.
1957: The Soviet Union manages to successfully interface man and machine, leading to a quantum leap in power armor technology as bipedal movement patterns become a lot more organic.
1960's: The US repeatedly releases new versions of its power armor suits as the Vietnam war rages, the lighter, more maneuverable armors being more suitable for the terrain. Various upgrades for soldiers are becoming more and more common, and the nickname 'Mods' is coined for those changed by the cybernetic implants.
1968: The first so-called 'Masked Heroes' appear in public, Modded veterans from the Vietnam war angered by their treatment at the hands of the government and the public. Very soon afterwards, new villains also take to the stage, and the police find it increasingly difficult to deal with disturbed people who have military training and equipment.
1971: A metabolic diet pill launched without proper product testing turns out to have uncommon and dangerous side effects. Though most users die or are crippled, a certain lucky few develop powers hitherto unseen in humans. The pill is quickly nicknamed the 'Hero Drug' and though it is pulled off the market, use and research continues. People who have gained powers are nicknamed 'Boosts' in the media.
1976: The Hero Drug is declared an illegal narcotic, banned after causing the deaths of untold thousands of people. Still, the lure is too strong, and research moves underground and behind securely-locked corporate doors.
1979: Wei Chen, who will later be known to the public as Marshal Steel, is born.
1980: The Year of Hell. The Big One hits the West Coast, and the San Andreas fault causes a massive earthquake to strike Los Angeles, which triggers the Cascadia subduction zone a few days later. The massive earthquake and resulting tsunami throws the whole West Coast into disarray with more than 150,000 estimated dead and missing. As if this was not enough, three months later the Mammoth Lake volcanic system reawakens, and the resulting eruption destroys any hope of quickly salvaging the west.
1980-1990: Aftershocks ravage the West Coast, halting any rebuilding effort. Little by little rebuilding turns to evacuation, all efforts being put into getting the Midwest back on its feet to regain a stable food supply. Food riots are common and several armed uprisings against the increasingly-authoritarian government are struck down by the military.
1981: The US government is nearly paralyzed by refugees as well as the rain of ash covering most of the Midwest. President Clark declares martial law.
1982: ${ortega_name} Ortega, also known as Charge, is born.
1984: Los Angeles is renamed 'Los Diablos' in 'The Angels of Los Diablos,' a famous documentary about the rescue efforts.
1986: The GeniTech corporation patents the creation of lab-grown stem cell organs, revolutionizing the transplant industry.
Late 80s: Estimated birth of ${name} ${surname}, later known as Sidestep.
Early 90s: Fed up with the suffocating yoke of the federal government and martial law, more and more people start moving back into the ruins of the west, starting the recolonization. A disproportionate amount of these people are Enhanced heroes and villains, both Mods and Boosts fleeing government control.
1992: In an effort to increase private industry investments, the West Coast is declared a free economic zone, where there will only be the bare minimum of federal government oversight. No taxes. No regulations.
1992: The GeniTech corporation patents whole-body stem cell clones, allowing for large-scale harvesting of replacement organs. Following a tumultuous debate about the ethics involved, GeniTech is one of the first companies to move their corporate headquarters to Los Diablos to escape regulation.
1993: The Re-Gene project is first revealed in a New York Times article, claiming it dates back to the seventies with the goal of making androids for use in war. The author, Tim Mazetti, was killed in a traffic accident soon afterwards. The future Ranger, Lady Argent, is born.
1996: Los Diablos is up and running: the first Mayor is elected, and it is starting to look more and more like a functional city. With the huge changes to the coastline, large tracts of the South Bay are abandoned and the city shuffles inland. The future Ranger, Herald, is born. Chen drops out of high school.
1997: Appalled at the lack of law and order in the free economic zone, or the FEZ as people call it, the newly-elected President Ross creates the Marshal system. Recruiting some of the most famous masked heroes of the region, he funds the 'Rangers' initiative in order to stem the worst excesses of the Enhanced populace. Chen joins the army, gets a boyfriend. Mount Hood is one of the founding members of the Los Diablos Rangers, as is Sentinel.
1998: Chen is deployed overseas, SE Asia. Sentinel joins the Rangers.
1999: A breakthrough in energy technology leads to the first plasma reactors, leading to ever more compact cybernetics. Hollow Ground self-declares as the kingpin of Los Diablos. Chen's boyfriend is killed. Chen has an accident with an IED and loses his hands. His body proves to handle mods well, so apart from his hands the army invests in an access port for armor interface as well. Ortega has their accident and is used as a test subject for their cutting edge electrical mods and spinal column. Chen and Ortega meet in the hospital during rehab. Mount Hood becomes Marshal Hood of the Rangers.
2000: Intent on regaining lost influence, the US flexes its muscles in the Middle East. This leads to a series of proxy wars with the ailing Soviet Union. Chen gets deployed there, now piloting an armored suit instead of a helicopter. The first known sighting of a Re-Gene on the battlefield. Chen sees Re-Genes on the battlefield. Ortega debuts as Charge, sponsored by a military subcontractor because they want to see how the mods perform.
2001: Steel is sick of the army and what they are doing abroad. He has racked up enough commendations that he's considered a suitable candidate for the Rangers, equipped with a new, shiny armor. Meets up with Ortega again when they are both in for surgery upgrades, and Chen talks him into signing up for the Rangers. Ortega's father dies.
2002: Ortega joins the Rangers. Sentinel officially starts to transition, there's a lot of controversy that Hood shuts down. Sentinel is not fired.
2004: A huge scandal rocks the Re-Gene project after its operatives are suspected of human rights abuses in another proxy war in Panama. It is never brought to court as the Re-Genes themselves are androids with artificial minds, but the scandal moves the project back underground where it has remained ever since.
2005: The Special Directive is formed, rumored to be a black-ops strike team of Re-Genes, deployed against anyone deemed dangerous enough by the government.
2006: Anathema joins the Rangers. The Rangers team up with the Special Directive for a mission. It does not go frictionless.
2007: Ortega is promoted to Marshal after the death of Marshal Hood at the hands of Hollow Ground. Sunstream joins the Rangers.
2008: Sidestep debuts as a vigilante. Charge and Sidestep meet for the first time.
2009: Psychopathor is the villain headliner of that year until finally put to a stop by the Rangers and Sidestep. Dr. Mortum and the Vitruvian are active as villains, but not high key threats enough to be a target for the Rangers.
2010: The Catastrofiend goes on a year long rampage, tearing through the Marshal before disappearing again, a pattern that will be repeated over the years. Ashfall works closely with the Rangers, becoming another associate.
2011: Los Diablos is hit by the Nanosurge, a runaway nano-weapon devouring all flesh before it is contained by an alliance of heroes led by the Rangers. Sidestep plays a vital part in its defeat. Herald takes the hero drug and survives the boosting process. Psychopathor escapes. Sunstream quits the Rangers and disappears soon afterwards.
2012: The Void is looking to expand their Santa Ana territory into Los Diablos, and the Rangers strike back, leading to a final showdown in the southeast deserts. Herald moves to Los Diablos. Dr. Mortum retires from active villain life, focusing on research.
2013: The Heartbreak incident occurs. Sidestep and Anathema are believed to be killed in action. Ortega retires as Marshal and hero, replaced by Steel. Sentinel and Herald meet.
2014: Ortega returns from retirement, joining the Rangers once more as Charge. Steel loses both his legs when he's nearly crushed under a building in the battle against the Catastrofiend that has resurfaced. The Catastrofiend gets securely locked up. Herald gets his first sponsorship (and name) as a corporate hero. Herald debits as a vigilante under a different name.
2015: Lady Argent debuts as a vigilante in San Francisco. Herald gets hired as a corporate hero, and gets his hero name.
2016: Lady Argent joins the Rangers. Steel nearly gets assassinated, losing an arm in the process. Sentinel retires. The Catastrofiend escapes, but disappears after a mercifully short rampage.
2017: The MC returns to Los Diablos under an assumed identity.
2018: Herald joins the Rangers.
2020: The events of Rebirth.
2021: The events of Retribution (the next book)
129 notes
·
View notes
Text
Character Guide – What Your Character Experiences While Leaving the Military
As I blundered through yet another wave of revisions for my sci-fi/fantasy WIP, I had an epiphany which, reasonably, should’ve come when the project first began. But didn’t, as all glaring plot holes don’t.
Here I have a soldier-esque character, whose background and experience affects huge swashes of the plot. I’ve nailed down what happens while they’re with the military; I’ve nailed down what happens several years after they’re out. But what about that transitional phase? What did they do there? What would they feel? For that matter, rent exists even in a rundown sci-fi/fantasy – am I looking forward to a played-for-laughs convenience store job, or could my character arguably rocket into a steady position somewhere they like?
Good question.
The answer to those question(s) – and yours, if you’re asking them – took some research, and finally resulted in reading “Leaving the Military: Life After Resettlement; How to Get a Job That Doesn’t Suck,” by Chris Hitchens. What makes it a great resource? Unlike many an article I read and books I checked out at the library, it doesn’t just dive into “hut hut hut get a job here we go!” It takes time to evaluate what may motivate servicemen and women to leave the military, what they might experience in response from their peers, and what an emotional experience it really can be.
In this article, I’ll walk you through the main questions and considerations this book brought to my attention and then answered… so you can write better military characters, figure out that transitional phase and weave it into the plot, or hey – learn what your or a loved one’s options are for exiting the military!
Let’s dive in.
The Five Stages of Grief Apply
My MC doesn’t care much for her military-esque group, especially not at the end of their service. So I always assumed she’d bounce back pretty quickly, and move on to the next stage. However, it’s important to consider that – whether or not you liked something, if it took a huge place in your life, you will feel its absence. Either your character LOVED the military and misses the camaraderie, the structure, the sense of doing good, or any number of things… or they hated the military, but they miss the routine, the sense of direction (even if they disagreed with the direction), or the security of that career. You can’t spend 24 hours a day, 7 days a week at something and not feel a gap when it’s vanished.
So your character will sense that pit, a pit which is grief in some small or great capacity. Do they fill it up with something, like a distraction? How fast do they go through the stages? Do they skip some stages? Do they go back to the career for a time, draw out the ‘quitting’ process, or do they cut it entirely? No matter what they feel – they will feel something. Nail down what that is!
Civilian Jobs ARE Different From Military Jobs
This is what I’ve heard from most ex-military I’ve spoken to, and this book emphasized it again – officially making it earn a place in my ‘transitional notes for MC’ category. Civvies don’t act like the military, and neither do their jobs. Not only is there less of a strict hierarchy and a lot more (what will be perceived by your character as) disorder, but their values will be different. The military is very goal-oriented, with a task at hand that needs completion. However, a civilian company may be sales- and profit-oriented, motivating them to cut corners or bend quality to achieve that.
No matter what job your character takes up, there will be differences in the company culture as well as the general structure of their new job. The important thing is to identify what your character could and couldn’t tolerate. How does your character feel about this? Do they do something to improve or worsen this? Would it cause them to adapt, or rebel? How important is the job to them? Are they invested in this new team?
Military Skills Do Translate, But Not (Always) Directly
Your character may not create an organizational chart of their strengths and weaknesses, but I recommend that you do. What did they enjoy about their previous career, and what did they hate? What were they good and bad at? This is what narrows military talents into civvy talents like ‘team building’ or ‘unsupervised discipline.’ If your character was a fantastic pilot, then maybe a civilian flying career would be a great choice; or maybe all that skill at multitasking will make them incredible at running a tech company.
This sort of thing can also serve as an excellent way to disguise your characters’ past. Who would suspect an accountant of being an ace tank mechanic? Well, their photographic memory always came in handy.
It’s important to remember your character has real talents – but they haven’t been labeled in the way civilians categorize talents. Marksmanship doesn’t look as typical on a resume as an English degree, but can still be useful. They could be an instructor, could be excellent at sports, could work with the parks department – any number of choices.
The Lingo is Different
Even if your character finds their way into a secure civilian job, there will still be differences to overcome, mainly in the language. The Army, Air Force, Navy – you name it – operate through a series of shorthand and code words, some not as fancy as you’d imagine, while others downright unintelligible. As Hitchens outlined, even ordering a drink can result in a language barrier, since “Tea, Standard NATO” doesn’t mean “Tea, white, two sugars” to most people.
That doesn’t mean your character runs around shouting “ALPHA DELTA NINER” like a loon, but think of it like this; how often do you translate “Big Mood” to “I feel the same way” when around your grandma? The military has their own ‘meme speak.’ Keep that in mind, and you’re on the right path.
Your character will feel ostracized in the little ways and forced to adjust, which may further their feelings of grief (however intense those may be). Do they adjust quickly? Do they make a conscious effort or let it happen naturally? What do they feel after several months of immersion when they run into a fellow ex-military who knows the lingo? What happens if they’re trying to disguise their past, but keep sliding distinct terms into their speech by accident? Does it hurt their productivity at their job or social life at all?
A Quick and Successful Leap Requires Preparation
Most of us sail out of high school and into the job market, where we flail for a period of time. But that’s expected, because we’re new, right? If your character is fresh from the military, they’re likely past that newbie age group, but are still faced with the same problems. Very little (if any) civilian job experience, an outdated (or nonexistent) CV, and rusty skills (at best) for job interviews. Now, this can be the set-up for a played-for-laughs job at the local grocery store, should you character be the kind who takes things slowly or instinctually.
However, if you want to skip your character to the higher end of the career spectrum – or if they themselves wouldn’t be content with taking it slow – then it’s important to be aware of one thing: making that happen takes preparation. More than probably anyone else leverages to get a job. They’re behind the eight-ball and need to make it up fast. So, this means using some of that military know-how and putting it to good work.
What is the opposition? How to best take it down? Does this mean highlighter pens and a list of keywords from the job description to tailor your CV? Does this mean rehearsing job interview questions? Does this mean thoroughly researching positions online (or cornering other employees under the guise of a drink, should your character be the cunning and over dedicated type)? Keep in mind that, during this transition period, either they will take it slow and adjust gingerly, as most do when they first enter the job market. …Or, if they wouldn’t be content with minimum wage, they will need to actively raise themselves above this – abnormally fast.
All in All
Leaving the military and taking up a civilian life isn’t as simple as ‘sign your name here, you’re a civilian, good luck’ and then immediately diving into a regular life. The transitional phase exists either in a large and dramatic way, or a smaller but still influential manner. Allowing your character to experience this can help round out their personality and create ties from their past to their present in subtle, crafty ways. Even more-so, keeping this in mind can allow you to portray a character of their nature and situation more realistically, so they resonate as human beings.
I touched the high points, but be sure to read the official “Leaving the Military” by Chris Hitchens for a more thorough look. Support a fellow self-published author and give a read! It’s an introduction to the namesake experience, and one of an ongoing series. I’d recommend it as a great resource for a military character – or hey, for an actual member of the armed forces, if you know someone who’s bringing their career to a close. It’s short, funny, and contains actionable tips
Happy writing!
#leaving the military#military characters#character development#military#army#resettlement#writer refere#writer resourc#chris hitchens
2K notes
·
View notes
Photo

Hodeidah, Yemen (CNN) – Saudi Arabia and its coalition partners have transferred American-made weapons to al Qaeda-linked fighters, hardline Salafi militias, and other factions waging war in Yemen, in violation of their agreements with the United States, a CNN investigation has found.
The weapons have also made their way into the hands of Iranian-backed rebels battling the coalition for control of the country, exposing some of America's sensitive military technology to Tehran and potentially endangering the lives of US troops in other conflict zones.
Saudi Arabia and the United Arab Emirates, its main partner in the war, have used the US-manufactured weapons as a form of currency to buy the loyalties of militias or tribes, bolster chosen armed actors, and influence the complex political landscape, according to local commanders on the ground and analysts who spoke to CNN.
By handing off this military equipment to third parties, the Saudi-led coalition is breaking the terms of its arms sales with the US, according to the Department of Defense. After CNN presented its findings, a US defense official confirmed there was an ongoing investigation into the issue.
The revelations raise fresh questions about whether the US has lost control over a key ally presiding over one of the most horrific wars of the past decade, and whether Saudi Arabia is responsible enough to be allowed to continue buying the sophisticated arms and fighting hardware. Previous CNN investigations established that US-made weapons were used in a series of deadly Saudi coalition attacks that killed dozens of civilians, many of them children.
The developments also come as Congress, outraged with Riyadh over the murder of journalist Jamal Khashoggi last year, considers whether to force an end to the Trump administration's support for the Saudi coalition, which relies on American weapons to conduct its war.
In 2015, Riyadh launched a coalition to oust Iranian-supported Houthi rebels from the country's capital and reinstate the internationally recognized government of President Abdu Rabu Mansour Hadi. The war split the country in two, and with it came the weapons -- not just guns, but anti-tank missiles, armored vehicles, heat-seeking lasers and artillery -- all flooding into an unruly and complex state.
Since then, some of America's "beautiful military equipment," as US President Donald Trump once called it, has been passed on, sold, stolen or abandoned in Yemen's state of chaos, where murky alliances and fractured politics mean little hope for any system of accountability or tracking.
Some terror groups have gained from the influx of US arms, with the barrier of entry to advanced weaponry now lowered by the laws of supply and demand. Militia leaders have had ample opportunity to obtain military hardware in exchange for the manpower to fight the Houthi militias. Arms dealers have flourished, with traders offering to buy or sell anything, from a US-manufactured rifle to a tank, to the highest bidder.
And Iran's proxies have captured American weapons they can exploit for vulnerabilities or reverse-engineer for native production.
'Do you have American guns here?'
In the narrow, ramshackle streets of Taiz's historic district, weapons shops lie tucked between women's clothing stores.
Arms markets are illegal in Yemen, but that doesn't stop them operating openly in this large, mountainous city in the country's southwest.
To one side hang veils, abayas and colorful dresses for sale; to the other are pistols, hand grenades, and US assault rifles available on special order.
In one arms market, sweets were displayed among the ammunition. "Do you have American guns here?" CNN asked. "The American guns are expensive and sought after," the weapons trader replied, in an exchange captured by undercover CNN cameras.
In another of the city's markets, a very young-looking boy handled weapons like an expert. Men joked and chewed khat, a commonly used drug, and the atmosphere was casual. But these shops don't just take individual orders, they can supply militias -- and it's this not-so-hidden black market that in part is driving the demand for hi-tech American weapons and perpetuating the cycle of violence in Yemen.
Once the intellectual heart of the country, Taiz is now a tinder box that set off a war within a war last year, when the various militias backed by the Saudi-led coalition turned their guns on each other.
Amid the chaos of the broader war, al Qaeda in the Arabian Peninsula (AQAP) made its way to the frontlines in Taiz in 2015, forging advantageous alliances with the pro-Saudi militias they fought alongside.
One of those militias linked to AQAP, the Abu Abbas brigade, now possesses US-made Oshkosh armored vehicles, paraded in a 2015 show of force through the city.
Abu Abbas, the founder, was declared a terrorist by the US in 2017, but the group still enjoys support from the Saudi coalition and was absorbed into the coalition-supported 35th Brigade of the Yemeni army.
“Oshkosh Defense strictly follows all US laws and regulations relating to export control," the firm told CNN.

And there are deadlier forms of weaponry that have made their way into the city. In October 2015, military forces loyal to the government boasted on Saudi- and UAE-backed media that the Saudis had airdropped American-made TOW anti-tank missiles on the same frontline where AQAP had been known to operate at the time.
Local officials confirmed that the airdrop happened, but CNN's attempts to conduct further interviews were blocked and the team was intimidated by the local government. A local activist joked that the weapons had probably been sold on.
Graveyard of US military hardware
At a graveyard of discarded US-made military hardware near the flashpoint port city of Hodeidah, it becomes clear that the Alwiyat al Amalqa -- the Giants Brigade, a predominantly Salafi, or ultra-conservative Sunni, militia -- is a favored faction.
Nearly half a dozen Mine-Resistant Ambush Protected (MRAP) vehicles sit side by side, most bearing stickers with the insignia of the Giants Brigade.
One even has the export label on it showing it was sent from Beaumont, Texas to Abu Dhabi, in the UAE, before ending up in the hands of the militia. The serial number of another MRAP reveals it was manufactured by Navistar, the largest provider of armored vehicles for the US military.

The armored all-terrain vehicles are built to withstand ballistic arms fire, mine blasts and improvised explosive devices (IEDs). “It’s the vehicle that every crew wants when they’re out in the field,” Navistar’s website says. The firm declined to comment on this report.
Recipients of US weaponry are legally obligated to adhere to end-use requirements which prohibit the transferring of any equipment to third parties without prior authorization from the US government. That authorization was never obtained.
The Saudi coalition did not respond to multiple requests for comment. A senior UAE official denied “in no uncertain terms that we are in violation of end-user agreements in any manner.”
The Giants Brigade is a “part of Yemeni forces,” the official told CNN, adding that the group was under the direct supervision of the UAE and, therefore, the equipment was in the “collective possession” of the coalition.
The US Department of Defense, when asked specifically about the Giants Brigades, said it had not given Saudi Arabia or the UAE permission to hand over US weaponry to other factions on the ground.
"The United States has not authorized the Kingdom of Saudi Arabia or the United Arab Emirates to re-transfer any equipment to parties inside Yemen," Pentagon spokesman Johnny Michael told CNN. "The US government cannot comment on any pending investigations of claims of end-use violations of defense articles and services transferred to our allies and partners."
Iran is ‘assessing US military technology closely’
Because a majority of American troop deaths in Afghanistan and Iraq are caused by IEDs, it is critical that knowledge of MRAP vulnerabilities does not fall into enemy hands.
But it's already too late.
In September 2017, a Houthi-run TV channel broadcast images of Mohammed Ali al-Houthi, the de facto rebel leader, proudly sitting behind the wheel of a captured US-made MRAP in the capital Sanaa, as a crowd chanted "death to America" in the background.
CNN obtained an image showing the serial numbers of a second American MRAP in the hands of another senior Houthi official last year in Hodeidah.
The vehicle was part of a $2.5 billion sale to the UAE in 2014. The sale document, seen by CNN, certifies that "a determination has been made that the recipient country can provide the same degree of protection for the sensitive technology" as the United States.
MRAPs like these, captured on the battlefield, have been probed by Iranian intelligence, according to a member of a secret Houthi unit backed by Iran known as the Preventative Security Force. The unit oversees the transfer of military technology to and from Tehran.
The member of the force, speaking to CNN anonymously out of fear for his safety, revealed that Iranian and Hezbollah advisers have already gotten their hands on the armored vehicles and other US military hardware.
"Iranian intelligence are assessing US military technology very closely," the source said in an audio interview done from Sanaa. "Listen, there isn't a single American weapon that they don't try to find out its details, what it's made of, how it works."

IEDs are now mass-produced in Yemen by Houthi forces on a scale only previously achieved by ISIS, according to a report published by Conflict Armament Research.
The group tracks weapons and their supply chains in conflict zones, and has found IEDs containing Iranian components in Yemen.
Hiram Al Assad, a member of the Houthi Political Council, confirmed to CNN that the MRAPs were still in Houthi hands but denied the existence of the Preventative Security Force.
Iran has not responded to a CNN request for comment.
Human cost of conflict
The flood of US weaponry is fueling a conflict that has killed tens of thousands -- among them children on school buses and families fleeing violence -- and pushed millions more to the brink of famine.
Two-year-old Rehab is so severely malnourished that her chest has collapsed into a deep dent at the center of her tiny body.

There are an estimated 200 cases of malnutrition like hers in the village of Tohta, a frontline area surrounded by artillery and mortar positions on the Red Sea coast near Hodeidah.
A few months ago, the local clinic was shut down due to political disagreements over funding. But Dr. Fatma Ibrahim won’t give up.
She conducts house-to-house visits every week, and as soon as she steps into the street, worried parents flock to her.
“Look, look,” one father demands as he shows the doctor his skeletal 14-month-old girl, Roula. Ibrahim gently examines her, but soon it's time to move on to the next baby.
For a young man, joining a fighting faction is one of the few means of finding employment in a poor country with little infrastructure and a barely functioning economy.
At the same time, too many powerful political figures and key armed actors in the region have been prospering greatly from the conflict and, as a result, they lack the incentives to agree to a peace process that would threaten their financial gain.
The US is by far the biggest supplier of arms to both Saudi Arabia and the United Arab Emirates, and its support is crucial to the Saudi-led coalition’s continuing war in Yemen.
US lawmakers are trying to pass a resolution ending the Trump administration’s support for the coalition. But there is scant evidence that the White House wants to listen, despite evidence that the actions of a key US ally may be making Americans less safe.
In the wake of the murder of Jamal Khashoggi murder last year, Trump said it would be foolish for the US to cancel multi-billion dollar arms deals with the Saudis. "I don't want to lose all of that investment being made into our country," he said.
9 notes
·
View notes
Text
Vetronics Market | Global Trends & Military Opportunities
Technology has significantly advanced, playing a crucial role in several industries. The paradigm for R&D in the defense sector has evolved investments in vetronics. This is a result of the growing trend across different defense forces to equip military vehicles with technologically sophisticated electronic systems.
According to our experts, the global vetronics market was valued at $3668.33 million in 2021 and is expected to reach $5372.01 million by 2028, with a CAGR of 5.62% during the forecast period 2022-2028.
Vetronics, also known as vehicle electronics, enables military units to implement and integrate systems such as communication, command and control, vehicle warfare, navigation, vehicle protection, and surveillance. Over the years, its relevance has increased as defense departments seek to make their armed forces lighter, faster, and more deployable.

Integration of Digitalization in Battlefield Operations
The digitization of domains such as communication and surveillance is critical in the integrated operations of the modern battlefield. Electronic warfare has already been adopted as a sub-domain by the majority of advanced nations. They actively engage in advanced capability research to equip their forces and gain a tactical advantage over their competitors.
For example, the US Army is testing the Electronic Warfare Tactical Vehicle (EWTV), containing an unspecified specification of radio jamming equipment. It can detect and disrupt a wide range of signals, from cellphones to enemy UAV control links.
Factors such as ease of deployment and a broad range of sensing and disruption are key features incorporated in modern armored vehicle-mounted jamming systems that increase their utility. The rapid adoption of such technology is expected to drive the studied market during the forecast period.
Additionally, the ongoing military modernization programs in respective armies worldwide have increased the number of land-based vehicles. Our study suggests tanks are the fastest growing land-based fleet type segment, with a CAGR of 5.82% during the forecast period. The development is due to the interconnection systems of the new tanks. The technological update enables tanks to integrate with wheeled armored vehicles outfitted with standard vetronics to collect and transform battlefield sensor data into high-value security and combat services.
Impact of Competitors’ Strategic Initiatives
The global vetronics market is highly fragmented, with key players controlling significant market shares. Major companies like Thales Group, Lockheed Martin Corporation, and L3Harris Technologies continue to invest in the R&D of military robotics and related subsystems. Such measures have enabled them to expand the spectrum of applications for their distinctive and exclusive product line of vetronics.
The market participants’ operations focus on designing, engineering, and manufacturing high-performance vetronics for the world’s armed forces’ terrestrial assets. Furthermore, because a contract for armored vehicles necessitates high technological expertise, the companies are merging to enhance their current portfolio. Some of the examples are listed below-
Collins Aerospace Military Global Positioning System (GPS) division was successfully acquired by BAE Systems, bringing decades of experience, cutting-edge technology, and a sizable installed base of products.
With the purchase of Gemalto by Thales for €4.8 billion, the acquisition will cover every step of the important decision-making process in the digital age, from sensor-generated data to real-time decision support.
Curtiss-Wright Corporation announced on July 5, 2022, that it had successfully acquired the Safran Aerosystems Arresting Company (SAA) for $240 million in cash. The acquisition of Safran’s arresting systems division solidifies Curtiss-position Wright as the world’s leading recovery and arresting systems provider for fixed-wing aircraft. Curtiss-Naval Wright’s & Power division will include the company.
Key Challenges & Regional Opportunities
Although cuts in the defense budget and the rising cost of raw materials can challenge the vetronics market, it is continuously expanding due to breakthrough technology in military vehicles.
The current fiscal condition worldwide is the key barrier to the market’s expansion. Many emergent breakthroughs offer considerable long-term benefits but need significant investments in deploying new technologies and platforms.
Based on the global scenario, the North America vetronics market held the largest share in 2021 and is expected to maintain its stronghold throughout the forecasting period. The region is witnessing considerable growth, owing to its military and government efforts to modernize its army and fleet.
Additionally, the United States is the key contributor to the regional market, accounting for 96.93% of the share in 2021. The country’s large market share is due to the rapid development of venture capital markets. For instance, American Rheinmetall Systems has received a multi-million-dollar investment to offer cutting-edge combat vehicle mission systems technologies to support the modernization of US Army combat vehicles.
0 notes