#Main Engine Cylinder Liner
Explore tagged Tumblr posts
Text
youtube
RA Power Solutions is the largest Allen cylinder manufacturer and producer. We have the manufacturing drawings available for most of the models of the popular engines. We also manufacture the cylinder liners as per the drawing and chemical composition of a cylinder liner provided by the clients. The liners can also be developed and manufactured as per the sample. For more details on cylinder liner manufacture and supplies, cast iron cylinder liner, and cast steel cylinder liner manufacturer email [email protected], and call +91 9810012383 or tel. +91-124-4251615.
#Allen cylinder manufacturer#cylinder liner manufacture and supplies#cast steel cylinder liner manufacturer#Cast Iron Cylinder Liner Manufacturer#Marine Engine Cylinder Liners#Cylinder Liner For Forging Press#Main Engine Cylinder Liner#Cylinder Liner Installation#Cast Iron Engine Cylinder Liner#Youtube
0 notes
Text
youtube
We manufacture cylinder liners and cylinder sleeves for all prominent marine and industrial diesel engine makes and models, including Daihatsu, Yanmar, Bergen, Niigata, Mirrlees, Alco, ABC, Crepelle, Nohab, and Allen. We follow OEM specifications while manufacturing cylinder sleeves and liners. The design or sample is used to create and produce cylinder liners.
Small quantities are also appropriate. Please email us at [email protected], or visit this link for additional information about cylinder liner manufacturers: https://turbineshaft.in/cylinder-liners-cylinder-sleeves.html
#cylinder liners#cylinder liners exporter#cylinder liner manufacturer#Cylinder Liner Installation#Diesel Engine Cylinder Liner Supplier#Cast Iron Engine Cylinder Liner#Main Engine Cylinder Liner#Aluminium Cylinder Liner Manufacturer#Compressor Cylinder Liner Producer#Cylinder Head Liner#Cylinder Liner Sleeve Manufacturer#Cylinder Liner And Sleeves#Youtube
1 note
·
View note
Text
For more details on repair of engine blocks, metal surgery, and MAN engine cylinder liners please email us at [email protected], or [email protected], or call us at +91 9582647131 or +91 9810012383.
#Crack Repair of Cylinder Liners#Crack Repair of Cylinder Liners By Metal Locking#cylinder liners crack repair#Main Engine Cylinder Liner#main engine cylinder liner repair#MPI Test Of Cylinder Liner#Crack Liner Repair By Metal Stitching#MAN engine cylinder liners#metal surgery
0 notes
Text
Main Engine Parts Supplier and Exporter in USA, Spain, India
Exporter of Main Engine Parts - Cylinder cover, Cylinder Liner, and Piston offered by Megatech Marine Services, in India, USA, Togo, Greece, and Germany.
[email protected] 9925206887
0 notes
Text
Premium Cylinder Liners for Enhanced Engine Performance

Essential parts of an engine's construction and cylinder liners greatly affect engine performance and lifetime. Often called engine sleeves, these liners offer a protective layer inside the engine's cylinders where combustion takes place. Maintaining ideal engine performance depends on heat dissipation, which the liners aid with, as well as from less friction and wear and strain. Premium-quality cylinder liners guarantee that the engine operates smoothly, effectively, and for a longer amount of time, whether the vehicle is commercial, industrial equipment, or personal car. One cannot emphasize their importance in improving general engine conditions.
Material Quality and Manufacturing Accuracy
The materials used and the manufacturing precision determine most of the lifetime and performance of cylinder liners. Usually formed from high-grade cast iron or alloyed steel, premium cylinder liners have excellent resistance to wear, heat, and corrosion, which makes these materials desirable. Including honing and precision polishing, the manufacturing process guarantees that the liners preserve an exact fit and excellent roundness. This accuracy reduces friction between the piston and the liner, producing smoother engine performance. Avoiding expensive repairs and guaranteeing long-term dependability depend on investments in premium cylinder liners.
Improved heat dissipation for best performance
Their capacity to improve heat dissipation is among the main benefits of premium cylinder liners. During combustion, engines produce a lot of heat; if this heat is not well controlled, overheating and damage may result. Premium liners improve engine performance by effectively transferring heat away from the combustion chamber, therefore preventing overheating. These liners lower component failure risk and enable the engine to function more effectively by preserving a balanced temperature. This is crucial for high-performance engines running under specific demanding conditions.
Reducing Wear and Tear in Highly Stressful Conditions
Particularly in commercial and industrial uses, engines bear great stress. This strain, over time, can cause internal components—especially the cylinder walls—to degrade. A protective barrier and premium cylinder liners help to lower engine wear and tear. Their new manufacturing methods and better materials guarantee that they may survive in high-stress conditions without sacrificing their structural integrity. Lowering the frequency of maintenance and replacements increases engine lifetime. Furthermore, by reducing wear, these liners preserve engine performance and fuel economy, thus saving long-term costs.
Long-Term Benefits and Cost-Effectiveness
Although premium cylinder liners would seem to be a major outlay, their long-term advantages much exceed their original cost. Over time, these liners save a great deal by shielding the engine from too much wear, enhancing fuel economy, and avoiding expensive repairs. Furthermore, premium liners are a great option for both personal and business automobiles because of their higher dependability and performance. Their longevity guarantees fewer replacements, which reduces maintenance expenses. Any engine owner would be wise to invest in these liners, given their low cost and improved engine performance they produce.
Conclusion
Enhancement in engine performance, heat dissipation, and wear reduction in high-stress environments all depend on premium cylinder liners. Their premium components and exact production guarantees better fuel economy and a longer lifetime for your engine. Although the initial cost could be more than that of regular liners, their long-term advantages—fewer repairs and reduced maintenance costs—make them wise investments. Consider premium cylinder liners from thepartsxperts.com, where quality meets innovation for the best engine solutions if you want to improve the performance and lifetime of your engine.
For More Info:
cylinder liners
0 notes
Text
John-Deere 3029, 4039, 4045, 6059, 6068 Engines (Saran)-499999CD Disassembly
This article describes the disassembly of John-Deere 3029, 4039, 4045, 6059, 6068 Engines (Saran)-499999CD
John Deere Service Advisor Electronic Data Link EDL2 Diagnostic Adapter High Quality

ENGINE DISASSEMBLY SEQUENCE
The following sequence is suggested when complete
disassembly for overhaul is required. Refer to the
appropriate repair group when removing individual
engine components.
1. Drain all coolant and engine oil. Check engine oilfor metal contaminates (see Groups 25 and 30).
2. Remove fan belts, fan, and alternator (seeGroup 30).
3. Remove turbocharger (if equipped) and exhaust manifold (see Group 35).
4. Remove rocker arm cover with vent tube. On engines having an Option Code label on rocker arm cover, be careful not to damage label (see Group 05).
5. Remove water manifold with thermostats (see Group 30).
6. Remove oil cooler piping and water pump (seeGroups 25 and 30).(Continued on next page)
7. Remove dipstick, oil filter, and engine oil cooler.
Discard standard-flow oil cooler if oil contained metal
particles (see Group 25).
8. Remove oil pressure regulating valve assembly(see Group 25).
9. Remove fuel filter, fuel transfer pump, and fuel lines (see Group 40).
10. Remove injection lines, injection pump, andinjection nozzles (see Group 40).
11. Remove starting motor.
12. Remove rocker arm assembly and push rods.Keep rods in sequence (see Group 05). Check forbent push rods and condition of wear pad contactsurfaces on rockers.
13. Remove cylinder head. Check piston protrusion.Verify piston height selection (see Groups 05 and10).
14. Remove cam followers. Keep in same sequence as removed (see Group 20).
03.2024 John Deere Service Advisor 5.3.235 AG/CF Diagnostic Software
15. Remove oil pan (see Group 25).
16. Remove flywheel and flywheel housing (see Group 15).
17. Remove crankshaft pulley (see Group 15).
18. Remove timing gear cover (see Group 20).
19. Remove oil pump drive gear, outlet tube (and its O-ring in block) and pump body (see Group 25).
20. Remove oil slinger, timing gears and camshaft.Perform wear checks (see roup 20).
21. Remove balancer shafts (4-cylinder only, if equipped), see Group 20.
22. Remove engine front plate (see Group 20).
23. Remove lube oil system by-pass valve (see Group 25).
24. Stamp cylinder number on rod (if required). Remove pistons and rods. Perform wear checks with “PLASTIGAGE”. On 4 and 6-cylinder engines, remove two at a time (see Group 10).
25. Remove main bearings and crankshaft. Perform wear checks with PLASTIGAGE” (see Group 15).
26. Remove cylinder liners and mark each one with cylinder number from which removed (see Group 10).
27. Remove piston cooling orifices (see Groups 10 and 15).
28. Remove balancer shaft and camshaft bushings (if equipped), see Group 20.
29. Remove cylinder block plugs and serial number plate (as required) when block is to be put in a “hot tank” (see Group 10).
30. Clean out liner bores (upper and lower areas) with nylon brush (see Group 10).
31. Measure cylinder block (see Groups 10, 15, and 20)
02.2024 John Deere Parts ADVISOR EPC(CF& AG& CCE)
0 notes
Text
Engine (part 1)
Powers the motorcycle.
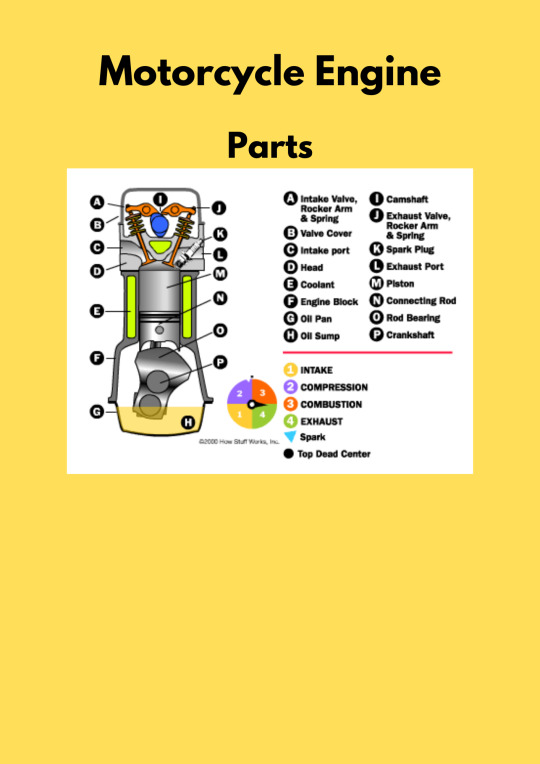


Functions :
Cylinder Head :
Combustion chamber of the engine.
Location for installing spark plugs.
Site for distributing lubricating oil.
Place for valve mechanisms.
Intake and exhaust passages.
Location for circulating coolant.
Region for the water jacket flow.
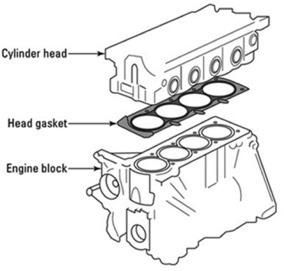
Head Gasket :
Oil leak prevention and seal maintenance from cylinder block to head.
Compression support for combustion.
Pressure containment to prevent spreading from cylinder block to head.
Heat management from cylinder block to head.
Cylinder Block :
It gives a cozy home for the piston to move up and down smoothly.
Directs the power made during combustion to push the piston.
Helps the crankshaft (a part that turns motion into rotation) do its job.
Acts like a highway for coolant, keeping things cool.
Creates a path for oil to keep the engine running smoothly.
Acts as the main hub for engine parts to chill together.
Keeps the engine's ID (serial number) in a safe place.
Provides a space for fuel to ignite and power up the engine.
Supports important parts like cylinder liners, cylinder head, and flywheel, making the engine work like a charm.
--
Valve Mechanisms
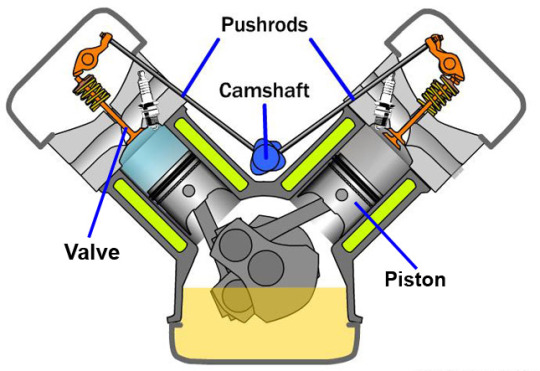
2 Types of Valves :
Intake Valve :
Location : Top of the cylinder.
Function : Controls the air and fuel going into the engine.
Importance : Makes sure clean air and fuel get inside the engine.
Exhaust Valve :
Location : Side or bottom of the cylinder.
Function : Manages the exit of used gases from the engine.
Importance : Helps get rid of the stuff the engine doesn't need anymore.
Functions of Valves :
Managing the Fuel-Air Mix : The intake valve controls how the air and fuel blend enters the cylinders, kicking off the combustion process. This shapes the motorcycle's power and overall performance.
Clearing Used-up Gases : The exhaust valve directs the removal of burnt gases from the cylinders, preventing the build-up of exhaust gases inside the engine and improving how efficiently the motorcycle runs.
Types of Valves :
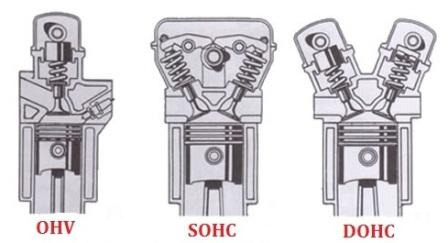
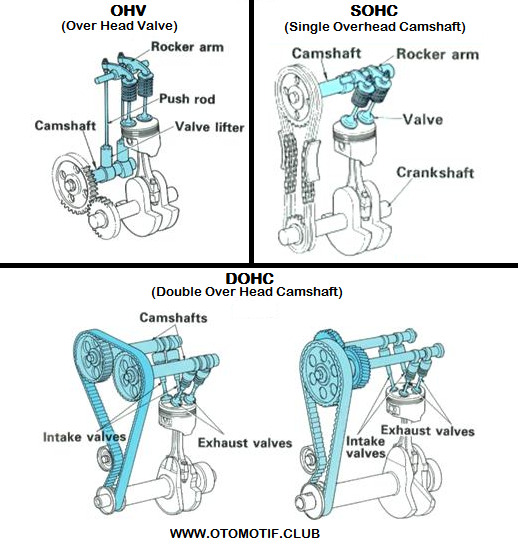
source : rangkumanmesinotomotif.blogspot.com source : Facebook - Otomotif.Club
OHV (Over Head Valve) :
Characteristics : 1. Simple design with the camshaft located near the crankshaft. 2. Uses push rods to operate the valves. 3. Often found in smaller engines like lawnmowers and some older vehicle designs. Pros : 1. Cost-effective to manufacture. 2. Compact design, suitable for smaller engines. 3. Generally, reliable and durable. Cons : 1. Limited in high-performance applications. 2. Less precise valve control compared to DOHC. 3. Typically, not as fuel-efficient as more modern designs.
SOHC (Single Overhead Camshaft) :
Characteristics : 1. Uses a single camshaft placed in the engine head. 2. The camshaft controls both intake and exhaust valves through rocker arms or similar mechanisms. 3. Commonly used in a variety of vehicles. Pros : 1. More efficient than OHV in terms of valve control. 2. Provides a good balance between performance and cost. 3. Suitable for everyday use and a wide range of applications. Cons : 1. Generally less powerful than DOHC engines. 2. Limited in high-performance applications. 3. May not offer as precise valve timing as DOHC.
DOHC (Double Overhead Camshaft):
Characteristics : 1. Uses two camshafts, one for intake valves and one for exhaust valves. 2. Camshafts are typically located in the engine head. 3. Allows for precise valve timing and control. Pros : 1. Excellent valve control, leading to better performance. 2. Suitable for high-performance vehicles. 3. Can achieve higher engine speeds and power output. Cons : 1. More complex and expensive to manufacture. 2. Requires more maintenance. 3. Generally not as fuel-efficient at lower speeds compared to SOHC.
--
Types :

Note : There are more than 8 types. These eight are the most common engines.
Single Engine :
Description : A single-cylinder engine has only one cylinder. Pros : Simple design, lightweight, and cost-effective. Cons : Vibrations, less power compared to multi-cylinder engines.
Function : Simple, lightweight design suitable for basic transportation. Motorbike Example : Honda CRF230F.
Parallel-Twin Engine :
Description : Two cylinders arranged parallel to each other. Pros : Compact size, good torque at lower RPMs. Cons : Moderate vibrations, less smooth than inline-four.
Function : Balanced performance with good torque, suitable for various riding styles. Motorbike Example : Yamaha MT-07.
Inline-Three Engine :
Description : Three cylinders arranged in a line. Pros : Balance of power and fuel efficiency, smoother than a single. Cons : Slightly more complex than a twin, but less than a four.
Function : Balances power and fuel efficiency, providing a smooth ride. Motorbike Example : Triumph Street Triple.
Inline-Four Engine :
Description : Four cylinders in a line. Pros : High power, smooth performance, well-balanced. Cons : Larger size, complexity, and potential for more weight.
Function : High power and smooth performance, ideal for sport and touring bikes. Motorbike Example : Kawasaki Ninja ZX-6R.
V-Twin Engine :
Description : Two cylinders arranged in a V-shape. Pros : Strong torque, unique sound, compact. Cons : Can have uneven power delivery, may produce more heat.
Function : Strong torque, distinctive sound, suitable for cruisers and custom bikes. Motorbike Example : Harley-Davidson Sportster.
L-Twin Engine :
Description : Similar to a V-twin but with one cylinder vertical and the other horizontal. Pros : Good torque, unique configuration. Cons : Some uneven power delivery, more complex than a V-twin.
Function : Good torque with a unique configuration, often found in sport and touring bikes. Motorbike Example : Ducati Panigale V2.
V4 Engine :
Description : Four cylinders arranged in a V-shape. Pros : Good power and balance, smooth performance. Cons : Can be larger, more complex and costly to manufacture.
Function : Balances power and smoothness, suitable for sport and touring motorcycles. Motorbike Example : Honda VFR1200F.
Flat Twins (Boxer Engine) :
Description : Two cylinders arranged horizontally. Pros : Low center of gravity, smooth operation. Cons : Wider, potentially more complex design.
Function : Low center of gravity, smooth operation, often used in touring bikes. Motorbike Example : BMW R1250GS.
--
Cylinders
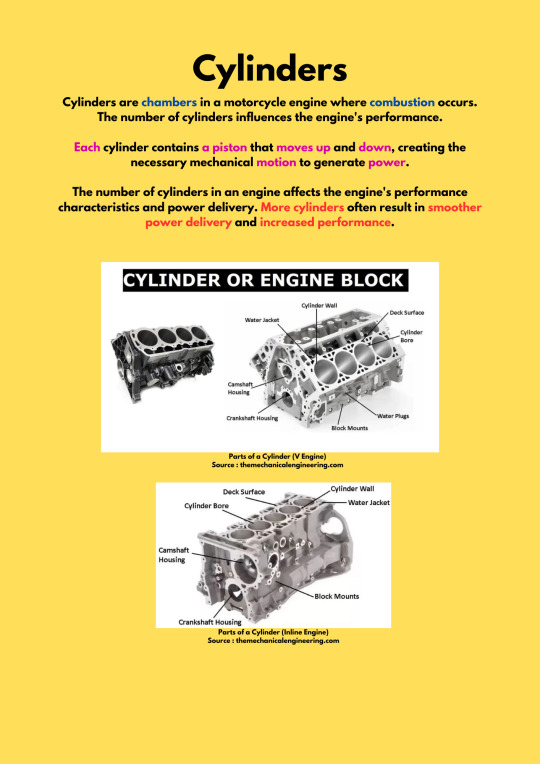
Engines & The Number of Cylinders :
Single CC Range : 50cc - 500cc
Twin : CC Range : 250cc - 2000cc Straight-Twin V-Twin Flat-Twin Tandem-Twin
Triple : CC Range : 600cc - 1200cc Inline-Three
Four : CC Range : 600cc - 2000cc Inline-Four Flat Four V4 Square Four
Five : CC Range : 1500cc+ V5
Six : CC Range : 1200cc - 1800cc Inline-Six Flat Six V8
--
Strokes
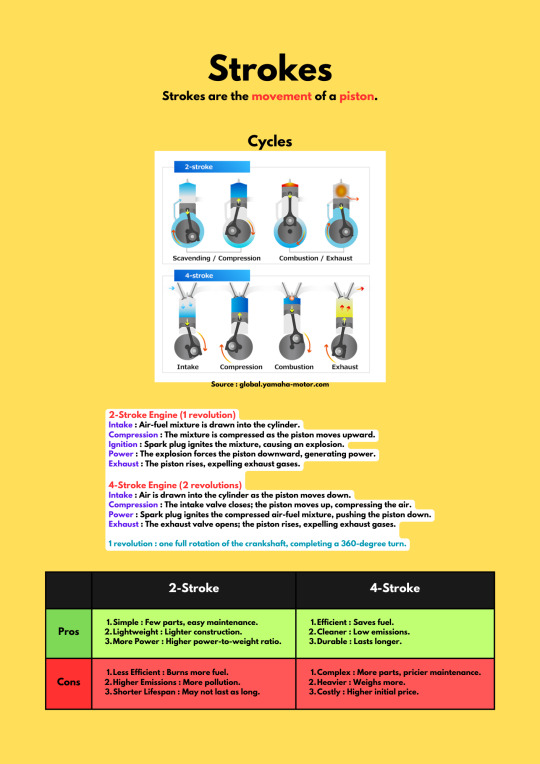
--
Engine Displacement

--
Fuel System
Fuel Delivery
Fuel delivery is the process of supplying fuel to the engine for combustion. It involves mechanisms like fuel injection or carburetion, ensuring the right fuel-air mixture for engine performance.
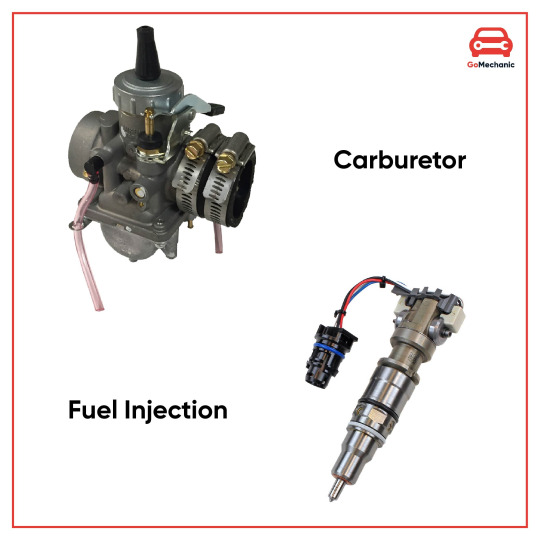
source : gomechanic.in
Types of Fuel Delivery :
1. Fuel Injection : What it is : Modern way of delivering fuel to the engine. How it works : Sprays precise amounts of fuel directly into the engine. Location : Fuel injectors near the intake manifold or in the engine; throttle body near the engine. Pros : More efficient, better control, usually cleaner emissions. Cons : Can be more complex and expensive. 2. Carburetion : What it is : Traditional method of mixing air and fuel. How it works : Uses a carburetor to blend air and fuel before entering the engine. Location : Carburetor usually on the side or top of the engine, connected to the intake manifold. Pros : Simplicity, lower cost. Cons : Generally less precise, potentially lower efficiency.
Throttle System
Controls the amount of air and fuel entering the engine, ultimately regulating the engine's power and speed.

source : sanemotionmoto.com
Mechanical Throttle (by-Cable)
Operation : Utilises a physical cable to connect the throttle grip on the handlebar to the throttle valve in the carburetor or throttle body. Characteristics : Direct mechanical linkage. Responsive but may require periodic adjustments. Common in older motorcycles and some traditional or simpler models. Pros : Simplicity. Familiarity for riders accustomed to older bikes. Cons : May require more frequent adjustments. Limited integration with advanced electronic features.

source : sanemotionmoto.com
Electronic Throttle (by-Wire)
Operation : Replaces the physical cable with electronic sensors and actuators that send signals to control the throttle valve. Characteristics : Offers more precise control. Integrates with advanced engine management systems. Can include additional features like cruise control and traction control. Pros : Enhanced control and responsiveness. Enables integration with modern electronic systems. Potential for additional functionalities. Cons : Complex electronic systems may be more challenging to troubleshoot or repair. Initial cost may be higher.
0 notes
Text
The main advantage of auto sleeves in Nissan engines is that they provide ease of maintenance.
0 notes
Text
Marine Engine Cylinder Liner | RA Power Solutions
RA Power Solutions specializes in the manufacture of marine engine cylinder liner, a crucial component ensuring smooth ship operations. RA Power Solutions' liners are crafted with precision, using high-quality materials that enhance durability. They play a vital role in maintaining optimal engine performance, preventing overheating, and reducing friction. With a commitment to excellence, we ensure their marine engine cylinder liners meet industry standards, contributing to the reliability and efficiency of marine engines. Trust in RA Power for top-notch solutions that keep your marine engines running seamlessly on the high seas. To get further details regarding main engine cylinder liner, and compressor cylinder liner producer, contact us at [email protected], 0124-425-1615, or +91-9810012383. YouTube: https://youtu.be/d1oU4vmGqec?feature=shared
#engine cylinder liner#cylinder liners#engine cylinder liner manufacturer#cylinder liner manufacturer#cylinder liner manufacturer and supplier
0 notes
Text
JAC T6 Bakkie Gets More Power
JAC Motors South Africa has beefed up its T6 one-tonne range by adding a 2,8-litre TDI double-cab variant, consequently from customer input locally and from neighbouring countries.
The 2,8-litre four-cylinder common-rail inter-cooled turbo-charged diesel engine develops 68 kW at 3 600 r/min and 210 Nm torque between 1 800 r/min and 2 000 r/min. The powerplant connects to a five-speed manual transmission in the 4×2 and a six-speed manual transmission in the 4×4 derivative.
The T6 2.8L TDI offers a claimed fuel consumption of 7,9 l/100 km, and the 4×4 achieves 10,5 l/100 km on average.
“Over the past five years, customer feedback played an important role in our brand’s local growth. We believe the market’s need for a reliable and fuel-economical 2,8-litre turbo-diesel engine is one of those examples where we can respond with tried and tested products,” says Karl-Heinz Göbel, CEO of JAC Motors South Africa.
The new engine came as a response to requests from customers from neighbouring countries and remote parts of South Africa, with its core focus on affordability, reliability, and ease of maintenance.
The T6 2.8L TDI engine earned its workhorse credentials globally and ticked off all the boxes in terms of what the local market wants, including excellent retail price points of less than R350 000 for the 4×2 and R400 000 for the 4×4 derivative.
Fuel consumption of the engine under normal and extreme working conditions is one of its main selling points. Add to that its track record of reliability and easy and low-cost maintenance, and the car caters for big fleet owners and regular customers.
The JAC T6 has a ladder frame suspension and a double-wishbone independent front suspension with coil springs, while the 245/65 R17 tyre size of the T6 2.8L TDI improves loading performance and reduces understeer.
It has a turning radius of 6,2 metres with a ground clearance of 197 mm and a 900 kg payload, also supporting a maximum Towing Mass (Braked) of 2,000 kg.
The double-skinned load box measures 1 520 mm × 1 520 mm × 470 mm with an anti-scratch and corrosion-resistant truck bed liner.
“Our T6 bakkies are reliable all-rounders with excellent gravel-road ability, comfortable cabs, and big load boxes. The addition of the 2.8L TDI derivative, with its reliable and durable drivetrain and low maintenance cost, now offers potential customers a choice of an economical workhorse at a much lower purchase price than its double-cab competitors,” says Göbel.
Standard features include fog lamps, electrically adjustable mirrors with integrated indicator lights, running boards, alloy wheels and a style bar.
The T6 2.8L TDI features two crash bags, anti-lock braking and EBD (Electronic Brake-force Distribution). A high-mounted brake light, reverse camera, rear parking sensors and speed-sensing auto door locks are standard equipment for added safety and convenience.
Interior trimmings include power steering, a height-adjustable leather-trimmed multi-function steering wheel, air-conditioning, leather seats and power windows.
The T6 2.8L TDI 4×4 features an electronically controlled four-wheel-drive system with an approach angle of 29,6 degrees, a break-over angle of 23,5 degrees and a departure angle of 22,4 degrees.
The official retail prices of the T6 range include the company’s standard five-year/150 000 km manufacturer’s warranty and five-year/60 000 km service plan.
.
.
.
.
Shared from https://www.carshop.co.za/news/
0 notes
Text
CNG cylinder

Type 1 CNG CYLINDERS
Type 1 CNG Cylinders for LIGHT-DUTY VEHICLES, MEDIUM AND HEAVY-DUTY VEHICLES Type 1 CNG cylinders are made of steel. Available Capacity (L), 30, 35, 40, 50, 60, 70, 80, 90. DSW CNG cylinders are manufactured conforming to specific country national standards or International standards like ISO: 11439, ECER 110, GB17258, ISO: 11120 Compressed Natural Gas cylinders (CNG cylinders) are a popular alternative with truck, transit, and refuse fleets.
Category: cng cylinders for vehicleTags: CNG Gas Cylinder, Compressed Gas Cylinder
Description
ISO11439 Type 1 CNG CYLINDERS
Type 1 CNG cylinders are used regularly in science and engineering buildings, machine shops, and retail and campus dining. Researchers, staff, and contractors store and use various compressed gases for different reasons. Compressed natural gas (CNG) is a fuel gas mainly composed of methane (CH4), compressed to less than 1% of the volume it occupies at standard atmospheric pressure.
CNG TANK SIZES


what is a Type 1 gas cylinder?
Type 1 CNG gas cylinders: Type 1 cylinders feature an all-steel shell construction, featuring no composite materials in their design.
Type 1 CNG Cylinder, which can store natural gas under pressure 20MPa or 25MPa made of 4130X seamless steel tube with ISO9809-1/ISO9809-3/EN/DOT approval. which are explosive pressure vessels containing flammable and explosive gases. The storage pressure for automotive cylinders is 20MPa.
Suitable applications include: Scuba Modified atmosphere packaging (MAP) Laboratory Onsite industrial/manufacturing
There are four categories available in CNG gas cylinders. The first category is seamless alloy steel cylinders (CNG-1). CNG-2 is a composite gas cylinder with steel or aluminum lining and a barrel reinforced with long fibers impregnated with “hoop winding” resin. The third category is composite gas cylinders with aluminum liner plus carbon fiber fully wound and glass fiber ring wound reinforcement (CNG-3). The fourth category is the composite gas cylinder with plastic liner plus carbon fiber full winding and glass fiber ring winding reinforcement (CNG-4).
Each of these Compressed Gas cylinders has its advantages and disadvantages, and it depends.
The main cylinders used worldwide are steel cylinders, generally made from high-quality chromium-molybdenum steel, and the ISO 11439 and ECE R110 standards can meet the requirements of most countries.
A complete automotive CNG cylinder has a cap, a valve, and a safety relief device. The cap protects the valve, and the safety relief device on the valve should be of the rupture disc-fusible plug combination type.
0 notes
Text
Crack Repair By Metal Stitching And Metal Locking
RA Power Solutions Pvt Ltd is the only company in the world, that can undertake repair of damaged, cast components and crack repair onsite, even while sailing of the vessel. The video shows successful repair of the main engine block and cylinder liners which developed cracks. Our expert technicians specialize in repairing badly damaged castings or cracks. For more details, please email us at [email protected], or [email protected], or call us at +91 9582647131 or +91 9810012383.
#white metal babbitt bearings#crack repairs of damage casting#onsite crackrepair#damaged engine block repair
0 notes
Text
Mega Marine | Ship Machinery Parts
We are supplier for marine engine parts & its spares, machinery, automation and general items.
We supply and export below items on regular basis of original maker products:
· Main engine parts & spares for B&W SULZER MAN MITSUBISHI AKASAKA MAK series and all other makers.
· Auxiliary engine parts & spares for YANMAR/DAIHATSU/WARTSILA/SULZER/ALLAN/VOLVO/CAT/GM and all other makers.
· Turbo chargers & spares for MITSUBISHI/ABB/MAN and other makers.
· Complete Engine & D.G. Set, Crankshaft, Engine Frame, Cylinder Cove, Cylinder Liner, Piston, Connecting Rod, Piston Rod, Exhaust Valve and Seat, Fuel Pump, Camshaft, Water & Oil Pump
· Oil purifiers, Air compressors, chilling compressor, Oily water separator & its filters/ PPM Monitors, Bilge pump, Hydraulic pump & Hyd. Items Any type of makers and it types.
· Injector tester or fuel valve test bench for any of the engine. (IOP MARINE OBEL-P PRODUCTS Denmark, HANMI MARINE Korea, L’orange, Nagano Japan, WooAm Korea, Diesel KIKI, ZEXEL, Bosch, akasaka, Mitsubishi)
· High Pressure Hydraulic Pumps (IOP Marine, Goltens, Fujikin japan, Nagano Japan, SKF)
· Helping tools, Engine indicator, Feeler gauge, Peak pressure gauge all makers available. Brands: Leutert, Lemag, Viggo A. Kjaer, etc. All types of pressure gauges, Temperature, Rpm meter, etc.
· Lashing material: For Container vessel : GERMAN LASHING, MacGregor, SEC Breman
· Life boat its equipment & spare parts.
· Governor, Governor motors & spares.
· Oil Content Monitor [bilge alarm] ppm monitor & sensors.
· Wildon pumps/helping tools items.
· Wire Rope for crane
We are largest stockiest of filters for crane/ Hyd. filters /M/E filters /Generator filters /OWS filters & other machinery filters for vessel, we have more than 1 lakh filters in ready stock .
Feel free to contact us for any questions or any kind of marine related requirements.
We do export worldwide at competitive & reasonable prices.
https://ship-machinery-parts.blogspot.com/
https://shipmachineryparts.business.site
https://www.shipmachineryparts.com/
#Mega marine#Ship machinery parts#Shipmachineryparts.com#Ship Automation#Machinery#fuel valve tester#Injector
0 notes
Text
For more details regarding crack repair of aluminium and cast iron by metal lock & metal stitching, please email us at [email protected], or [email protected], or call us at +91 9582647131 or +91 9810012383.
#Bronze and Cast Iron Component By Metal Lock#Metal Lock & Metal Stitching#crack repair of aluminium#Crack Repair By Metal Stitching#Metal Stitching of Cylinder Liner#Crack In Main Engine Liner
0 notes
Text
Main Engine Parts Supplier and Exporter in USA, Spain, India
Exporter of Main Engine Parts - Cylinder cover, Cylinder Liner, and Piston offered by Megatech Marine Services, in India, USA, Togo, Greece, and Germany.
https://www.megatechmarine.com/main-engine.php
[email protected] 9925206887
0 notes
Text
John Deere PowerTech 9.0 Engine Disassembly Sequence for Overhaul
John Deere PowerTech 9.0 Engine Disassembly Sequence for Overhaul.The following sequence is suggested when complete disassembly for overhaul is required.
John Deere Related Contents:
2023 John Deere Service Advisor 5.3.235 AG+CF
John Deere EDL V2 Adapter
John Deere Parts Advisor EPC 2023
Instructions: 1. Drain all coolant and engine oil. Check engine oil for metal contaminates. 2. Remove turbocharger oil inlet line and oil return line. Remove turbocharger and air pipe to EGR cooler assembly. 3. Remove fan pulley and thermostat housing assembly. 4. Remove coolant pump assembly from timing gear cover. NOTE: DO NOT damage option code label (if equipped),when removing rocker arm cover. NOTE: The vent hose should be disconnected from the vent elbow. The vent elbow should not be removed from the rocker arm cover unless the intent is to replace the elbow assembly. 5. Remove breather hose from rocker arm cover. Remove rocker arm cover. 6. Remove electronic injector wiring harness. 7. Remove rocker arm assembly and push rods. Identify parts for reassembly. 8. Remove front crankshaft pulley and damper assembly. 9. Remove fuel injection lines, fuel connectors, and injection nozzles. 10. Remove engine oil filter, filter base, and valve housing 11. Remove fuel filter and mounting base. Remove high pressure fuel pump gear cover and remove injection pump. 12. Remove high pressure common rail. 13. Remove engine oil cooler assembly 14. Remove front and rear exhaust manifolds and EGR cooler and valve assembly. 15. Remove air intake manifold. NOTE: ALWAYS bolt down liners when rotating engine flywheel with cylinder head removed. 16. Remove cylinder head with assembly. Remove head gasket. 17. Revolve engine on repair stand and remove engine oil pump assembly. 18. Remove front timing gear cover. 19. Revolve engine to vertical position. Remove pistons and connecting rods. Identify for reassembly. Perform bearing-to-journal wear checks with PLASTIGAGE®. 20. On SAE No. 3 flywheel housings, remove flywheel housing and then remove flywheel. 21. On SAE No. 1 and 2 flywheel housings, remove flywheel and then remove flywheel housing. 22. Remove main bearing caps and remove crankshaft.Perform bearing-to-journal wear checks with PLASTIGAGE®. 23. Remove camshaft and cam followers. Identify for reassembly. 24. Revolve engine to horizontal position, remove liners, O-rings, and packings. Mark liners for reassembly in same bore from which removed. 25. Remove piston cooling orifices from cylinder block. 26. Remove any sensors/gauges, cylinder block plugs and engine serial number plate, if block is to be put in a “hot tank
John Deere Service Advisor 5.3.235 AG+CF 2023 2020 2018 Free Download
0 notes