#MTP harness assemblies
Explore tagged Tumblr posts
Text
MTP/MPO Fiber Optic Cable: Types and Their Applications
With ever-greater bandwidths and network connections to deal with in data centers, traditional duplex fiber patch cords like LC fiber patch cords no longer meet the demands. To solve this issue, MTP/MPO fiber optic cable that houses more fibers in a multi-fiber MTP/MPO connector was introduced in the market as a practical solution for 40G/100G/400G high-density cabling in data centers. This article will introduce different MTP/MPO cable types and their applications.

What is MTP/MPO Cable?
MPO (multi-fiber push-on) is the first generation of clip-clamping multi-core fiber optic connectors. MTP is an advanced version of MPO with the better mechanical and optical performance. They look similar and are fully compatible and interchangeable.

MTP/MPO cable consists of MTP/MPO connector and optical fiber. MTP/MPO connector has a female type (without pins) or a male type (with pins). MTP/MPO connector increases the fiber optic cable density and saves circuit card and rack space, which is well suited for current data center cabling and future network speed upgrades.
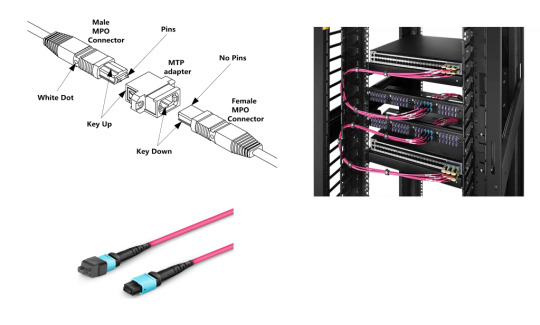
MTP/MPO Cable Types
MTP/MPO cable types are classified based on function, polarity, fiber count, fiber mode, and jacket rating.
By Function
Based on function, MPO/MTP cable type is divided into MTP/MPO trunk cable, MTP/MPO breakout cable, and MTP/MPO conversion cable.
MTP/MPO Trunk Cable
MTP/MPO trunk cable is terminated with an MTP/MPO connector (female/male) on both ends, which is available in 8-144 fiber counts for users’ choices. Typically, MTP/MPO trunk cable is ideal for creating a structured cabling system, including backbone and horizontal interconnections such as 40G-40G and 100G-100G direct connections.

2.MTP/MPO Breakout Cable
MTP/MPO breakout cable (aka. harness cable or fanout cable) is terminated with a female/male MTP/MPO connector on one end and 4/6/8/12 duplex LC/FC/SC/ST connectors on the other end, such as 8-fiber MTP/MPO to 4 LC harness cables and 12-fiber MTP/MPO to 6 LC harness cables. Typically, MTP/MPO breakout cable is ideal for short-range 10G-40G and 25G-100G direct connections or for connecting backbone assemblies to a rack system in the high-density backbone cabling.
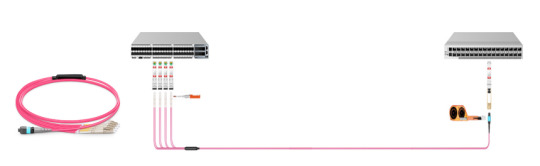
3.MTP/MPO Conversion Cable
MTP/MPO conversion cable has the same fanout design as MTP/MPO breakout cable but is different in fiber counts and types. MTP/MPO conversion cable is terminated with MTP/MPO connectors on both ends. MTP/MPO conversion cable is available in 24-fiber to 2×12-fiber, 24-fiber to 3×8-fiber, and 2×12-fiber to 3×8-fiber types, and is ideal for 10G-40G, 40G-40G, 40G-100G, and 40G-120G connections, which eliminate fiber wasting and largely increase the flexibility of the MTP/MPO cabling system.
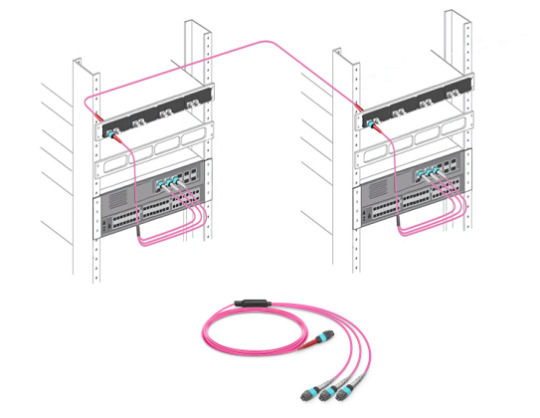
By Polarity
Polarity refers to the difference between the optical transmitters and receivers at both ends of the fiber link. Due to the special design of MTP/MPO connectors, polarity issues must be addressed in high-density MTP/MPO cabling systems. To guarantee the correct polarity of the optical path, the TIA 568 standard defines three connection methods, called Type A, Type B, and Type C. The cables of the three MTP/MPO connector types have different structures.
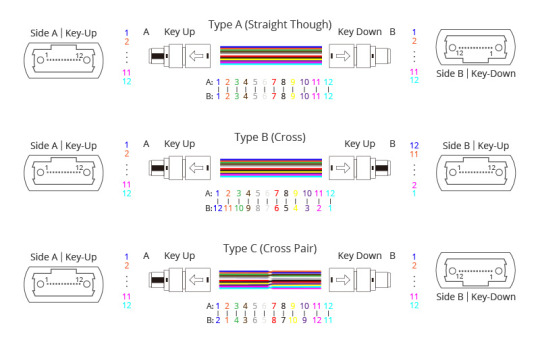
By Fiber Count
Based on fiber count, MTP/MPO cable type is divided into 8/12/16/24 fiber. The 8-fiber MTP/MPO cable can transmit the same data rate as 12-fiber, but with lower cost and insertion loss, making it a more cost-effective solution. 12-fiber MTP/MPO cable is the earliest developed and most commonly used solution in 10G-40G and 40G-100G connections. If it is used in 40G QSFP+ or 100G QSFP28 transceivers, 4 fibers will be idle, resulting in low fiber utilization.16-fiber MTP/MPO is designed for 800G QSFP-DD/OSFP DR8 and 800G OSFP XDR8 optics direct connection and supporting 800G transmission for hyperscale data center. 24-fiber fiber MTP/MPO cable is used to establish a 100GBASE-SR10 connection or 400G connection between CFP and CFP transceivers.

By Fiber Mode
Based on fiber mode, MTP/MPO cable includes single-mode (SM) and multi-mode (MM). SM MTP/MPO cable is suitable for long-distance transmissions, such as in metropolitan area networks (MANs) and passive optical networks PONs (PONs), with less modal dispersion, and it is available in OS2 type. While MM MTP/MPO cable is suitable for short-distance transmission, allowing 40 Git/s maximum transmission distance of 100m or 150m, and it is available in OM3/OM4 types.

By Jacket Rating
According to different fire rating requirements, the jackets of MTP/MPO cable types are divided into low smoke zero halogen (LSZH), optical fiber non-conductive plenum (OFNP), communications multipurpose cable plenum (CMP), etc. LSZH MTP/MPO cable is free of halogenated materials (toxic and corrosive during combustion), provides better protection for personnel and equipment in a fire, and is suitable for closed places. OFNP MTP/MPO cable contains no electrically conductive elements and is designed with the highest fire rating, which can be installed in ducts, plenums, and other spaces for building airflow. CMP MTP/MPO cable can restrict flame propagation and smoke exhaust rate during a fire, which is suitable for plenum spaces, where air circulation for heating and air conditioning systems are facilitated.
Conclusion
MTP/MPO cables provide stable transmission, high performance, high-density cabling for various environments, and prevent network bottlenecks, reduce network latency, and expand bandwidth and scalability for future network expansion. Sun Telecom provides total and customized solutions of fiber optic products to the global market. Contact us if you have any needs.
2 notes
·
View notes
Text
https://www.china-tscom.com/products/mpo-mtp-cable-assembly/
MTP/MPO cable assembly use MPO or MTP® multi-fiber connectors. MTP®/MPO Fiber Patch Cord greatly saves space and is very convenient to use. Based on single ferrule MT technology, the MPO Fiber Patch Cord assemblies provide up to 72 fiber connections in a single point, reducing the physical space and labor requirement, while providing the same bandwidth capacity of a multi-fiber cable with individual fiber connector terminations per cable.
Typically with MT series like MTP®/MPO fiber connectors, these MTP®/MPO Patch Cord features multi-fiber connections in the same single-core fiber optic patch cord. Except for Standard MTP/MPO cable assemblies including MTP®/MTP® harness cable, shuffle cable, hydra cable and trunk cable, we also provide other types like IP68 MTP®/MPO fiber cable, MTP®/MPO loopback adapter and so on for different applications
MTP® MPO Fiber Cable Assembly Types
T & S MTP® / MPO cable assemblies meet the requirements of IEC61754, IEC61755, TIA568, GR1435 and other standards, and adopts a push-pull locking structure with male and female heads to ensure butt tightness and low loss. Single head loss of SM product: conventional product IL ≤ 0.75db, RL ≥ 60dB; elite product IL ≤ 0.35db, RL ≥ 60dB. Single head loss of MM product: conventional product IL ≤ 0.60db, RL ≥ 20dB; elite product IL ≤ 0.35db, RL ≥ 20dB. The optical fiber channel is used for termination and supports high bandwidth applications. It is specially designed to save cable management time and high-density fiber distribution area. The outer diameter of the optical cable can match the pre-termination of Ø 2.0 ~ 5.5mm, and the spring elasticity of 9.8N and 20n can be matched; mm supports 10g, 40g, 100g and 400g applications.
MPO To MPO Fiber Cable Assemblies
MPO cable assemblies are also referred to multi-fiber push-on cable assemblies, which are fiber connectors with multiple optical fibers. It is also acknowledged as an array connector with more than 2 fibers. Generally, in the common data center uses, MPO Connectors are typically available with 8, 12 or 24 fibers. Most MPO fiber optic cable assemblies have 12 fibers arranged along the center of a rectangular ferrule. They are paired in the same way as the traditional LC, SC, and ST connectors, except that the MPO connector needs a male connector to connect to a female connector.

0 notes
Text
Brief Introduction to Ribbon Optical Cable
In order to meet the increasing system bandwidth needs, local area network (LAN) campus and building backbones, as well as data center backbones, are migrating to higher cabled fiber counts. Ribbon optical cables can offer the highest fiber density relative to cable size, maximize utilization of pathway and spaces and facilitate ease of termination, which makes them an ideal solution for the need. This post mainly focuses on the benefits and applications of ribbon optical cable.
Ribbon Optical Cable Design
Ribbon optical cable is a type of cable widely deployed in campus, building and data center backbone applications where high fiber counts are required. There are 8 fibers, 12 fibers, 24 fibers and other higher fiber counts available on the market. At present the 12-fiber ribbons are readily accessible and identifiable with ribbon identification numbers and TIA-598 compliant fiber color coding, which make it prevalent in today’s networks. Usually there are two kinds of outer jacket of ribbon optical cables: non-flame-retardant and formulated flame-retardant. The former is often used in outside plant applications, while the latter is typically used for indoor applications. Here is an example of ribbon optical cable construction.
Benefits of Ribbon Optical Cable
As we all know, stranded loose-tube and ribbon optical cable are staples of the outside plant applications. Both of them perform well in harsh outdoor environments, and both are available in a multitude of configurations, including: all-dielectric, armored, aerial self-supporting, etc. However, when compared to stranded loose-tube cable designs, the ribbon design offers robust performance equivalent to the stranded loose-tube cable, and provides the maximum fiber density relative to cable diameter. The chief distinction between these cables is the manner in which the individual fibers themselves are packaged and managed within the cable. A ribbon cable has the individual fibers precisely bonded together in a matrix that might encompass as few as four or as many as 24 fibers. In contrast, a loose-tube cable has between 2 to 24 individual fibers housed in multiple buffer tubes with each fiber detached from the other.
It’s the special ribbon design that makes ribbon optical cable offer more advantages over loose-tube designs in many applications.
Ribbon optical cable can be prepped and spliced much more rapidly than loose tube cables. That’s means less installation time, less installation labor cost and significantly less emergency restoration time.
Ribbon optical cables enable a smaller footprint in splice closures and telecommunications room fiber management.
Ribbon cables offer greater packing density in higher fiber counts which enables more efficient use of limited duct space.
Ribbon cables are typically very cost competitive in counts above 96 fibers.
Ribbon Optical Cable Application
Although there are various fiber counts available with ribbon optical cable, the 12-fiber ribbon cables are the most commonly used ones. With the introduction of innovations such as ribbon splitting tools and field-installable 12-fiber array connectors, 12-fiber ribbons are easily terminated with simplex and duplex connectors such as LC or SC connectors or with the MTP connector. The MTP connector is a 12-fiber push/pull optical connector with a footprint similar to the common simplex connector. Many users like to apply MTP connectors to ensure the highest quality connector insertion loss and return loss performance and to expedite the cable installation.
In order to illustrate how ribbon optical cables are deployed, here take the termination of MTP connectorized ribbon cable with patch panel as an example.
The termination is normally used in an interconnect application where a harness assembly is used on the front of the patch panel. We know the MTP harness assemblies have 12-fiber MTP connector on one end of the cable and simplex or duplex style connectors on the other end. Just like the picture below shows.
Except for the application noted above, ribbon optical cables also can be used in both interconnect and cross-connect applications where an MTP connector module cassette is used. And they can be applied to pathways and spaces.
Conclusion
Ribbon optical cables deliver high fiber density in the most compact cable package possible. And they also maximize the number of fibers that can be deployed in a limited space while streamlining fiber termination. At the same time they can save time and money with easy mass fusion splicing. Ribbon cable is now easily obtained using traditional simplex or duplex connectors as well as MTP Connectors, which make them suitable for various applications.
Sources:http://www.fiber-optic-components.com/brief-introduction-to-ribbon-optical-cable.html
0 notes
Text
MPO - MTP ASSEMBLIES - THE GAME CHANGER OF DATA CENTER CABLING
MPO / MTP Fanout & Trunk Cables that can be custom built for any application. All cables come factory terminated and pre-tested, ensuring top performance and ease of installation. Fanout assemblies can be built with any single fiber connector and any major fiber type. These cables are designed to work in conjunction with MPO Fiber Distribution products.
High-Density MPO Fiber Distribution Cassettes offer unsurpassed fiber density and are designed to be used in conjunction with High Density Panels. Each cassette contains a fanout assembly that transitions from a MPO 12 fiber connector to 6 LC duplex pairs. Cassettes are designed to be installed with LC Uniboot assemblies for the highest density available. Panel and cassette combination is capable of supporting 144 fibers in 1RU, 288 fibers in 2RU and 576 fiber in 4RU. MTP / MPO harness cables are available with 8-, 12-, 24-, 36-, 48-, 72-, 96- and 144-fiber options. Read More.
https://www.gbic-shop.de/blog/en/98-mpo-mtp-solutions/278-mpo-mtp-assemblies-the-game-changer-of-data-center-cabling.html
0 notes
Text
MTP Fiber Patch Cables Overview
by www.fiber-mart.com
MTP stands for multi-fiber termination push-on connector and is designed by US Conec and built around the MT ferrule.
MTP fiber patch cable
takes its name from the MTP connector, which allows high-density connections between network equipment in telecommunication rooms. The following text will thoroughly cover types, advantages and applications of MTP fiber patch cords, and solution provided by fiber-mart.com. Types of MTP Fiber Patch Cords There are different types of MTP fiber patch cords based on various criteria. According to the core of the fiber, MTP fiber patch cords are categorized into MTP single mode fiber patch cords and MTP multi-mode fiber patch cords. According to the connectors on both ends, there are mainly two configurations for MTP fiber patch cables. One is the MTP connector to MTP connector, which is often called MTP trunk cable. The other is MTP connector to standard LC/FC/SC/ST/MTRJ connectors (generally MTP to LC), which is often called the MTP harness cable, or MTP fan-out cable. The picture shows a MTP trunk cable and a MTP harness cable. Advantages of MTP Fiber Patch Cords The MTP fiber system is a truly innovative group of products which moves fiber optic networks into the new millennium. MTP connector, as a kind of multi-fiber connector, is most commonly used for 12 or 24 fibers. It has about the same size of a SC connector and provides up to 12 or 24 times the density, thereby offering savings in circuit card and rack space. Using MTP trunk cables, a complete fiber optic backbone can be installed without any field termination being required. Moreover, MTP connector is designed as a high-performance version of the multi-fiber push on (MPO) and will interconnect with MPO connectors, so it is compatible with VZ TPR.9431, IEC-61754-7 and EIA/TIA-604-5. It uses a simple push-pull latching mechanism for easy and intuitive insertion and removal. MTP jumpers utilizes precision ferrules, precise housing dimension and metal guide pins to ensure fiber positioning when mating and give excellent performance. And the easy installation of them saves time and money. They can optimize network performance and maximize lifespan. MTP multi-fiber jumpers deliver the performance and reliability needed in today's demanding high-speed broadband and data networks. They are designed to cater for up-scaling needs and future technologies growth. Applications of MTP Fiber Patch Cords The MTP fiber patch cord is the choice for a wide variety of applications. MTP fiber patch cords can be used for backbones, disaster recovery, building fiber optic distribution, quick setup of new wiring hubs, warehouses, direct termination of ribbon cables, repair of plug and play universal system solutions, and parallel optical interconnects between servers. Besides these general applications above, MTP trunk cable and MTP harness cable, two commonly used MTP fiber patch cords, have their respective special uses. MTP trunk cables are available in 12-144 count. These high count MTP assemblies are ideal for backbone and data center applications that require a high fiber count in a limited space. MTP fan-out assemblies provide connection to equipment or panels that are terminated with ST, SC, FDDI, or ESCON connectors and meet a variety of fiber cabling requirements. Such assemblies are pre-wired available for patch panels and wall enclosures. fiber-mart.com MTP Fiber Patch Cables Solution fiber-mart.com offers single mode and multi-mode MTP assemblies, such as MTP-LC, MTP-ST, MTP-FC, MTP-MU, MTP-MT-RJ, MTP-E2000, simplex and duplex. Also we provide UPC MTP assemblies and APC MTP cables. All fiber counts are available in plenum, riser, or outdoor ratings to suit different kinds of environment. Our high quality factory pre-termination eliminates the need for costly field termination and testing.
0 notes
Photo

MTP to LC SM/MM Fan-out/Breakout Staggered Harness cable assembly is mainly used for 10G/40G/100G, The LC fanout cable with 2.0mm/3.0mm branch cable, the LC side could adopts uniboot/single boot Duplex LC or dual boot duplex LC connector. The Harness MTP cable supports polarity suport both type A and type B.
0 notes
Text
OM3 And OM4 Fiber for 10G/40G/100G Network
Multimode fiber has been highly favored by Ethernet users and gained the widest acceptance in network backbones where it has offered users the opportunity to extend link distances, increase network reliability, and lower costs by centralizing electronics. OM3 fiber emerges just at the right time. The predominance of OM3 fiber is that utilizes laser-optimized fiber, which is the highest-capacity medium for short-wave 10G optical transmission. OM4 fiber just joined multimode fiber family after OM3 fiber in order to meet the requirement of longer range applications. This passage would give a brief introduction to OM3 and OM4 fiber, give a further analysis on their differences and selection guide, as well as list their applications.
Introduction to OM3 & OM4 Fiber
Both OM3 and OM4 fiber meet the ISO 11801 standard. The standard specifies that OM3 fibers are capable of 10 Gb/s performance over distances of up to 300m. Like being mentioned, the laser optimized 50/125 mm multimode OM3 fiber is of predominance, which provides sufficient bandwidth to support 10 GbE and beyond with cable lengths up to 550 meters. OM4 fiber is a further improvement to OM3 fiber. It also uses a 50µm core but it supports 10 Gigabit Ethernet at lengths up 550 meters and it supports 100 Gigabit Ethernet at lengths up to 150 meters.
Main Difference Between OM3 And OM4 Fiber
—Optical attenuation
Attenuation is caused by losses in light through the passive components, such as cables, cable splices, and connectors. Attenuation is the reduction in power of the light signal as it is transmitted (dB). The maximum attenuation of OM3 and OM4 fiber allowed at 850nm: OM3<3.5 dB/Km; OM4 <3.0 dB/Km. So it is obvious that OM4 fiber causes lower losses due to different construction.
—Modal dispersion
As is known to most people, modal dispersion attaches great importance to bandwidth. The lower the modal dispersion, the higher the modal bandwidth and the greater the amount of information that can be transmitted. The minimum OM3 and OM4 fiber cable bandwidth at 850nm: OM3 2000 MHz·km; OM4 4700 MHz· km. The higher bandwidth available in OM4 means a smaller modal dispersion and thus allows the cable links to be longer or allows for higher losses through more mated connectors.
OM3 And OM4 Fiber 10G/40G/100G Transmission Distance
The maximum transmission distance of OM4 fiber is 400-550m (depending on module capability) while OM3 fiber can only be up to 300m. And thus, OM4 can tolerate a higher level of loss at distances between 200-300m as it is designed to operate at longer distances than OM3 fiber. It may be a more flexible option for network managers to install OM4 fiber within these instances. You can check difference between OM3 and OM4 in transmission distance in the following table.
OM3 And OM4 Fiber Price
In comparison to OM3 fiber, the cost for OM4 is higher due to the manufacture process and market fluctuations. In a large extent, cost depends on the construction type of the cable (loose tube, tight buffered, etc.). OM4 fiber cable is about twice as expensive as OM3 fiber cable. This means that the cost difference of lots of fiber products such as standard fiber patch panels, MTP cassette modules, fiber patch cords is very small (as the volume of cable is small).
OM3 And OM4 Fiber Selection Guide
Fifty micron OM3 fiber is designed to accommodate 10 Gigabit Ethernet up to 300 meters, and OM4 can accommodate it up to 550 meters. Therefore, many users are now choosing OM3 and OM4 over the other glass types. In fact, nearly 80% of 50 micron fiber sold is OM3 or OM4. If you require higher data rates or plan on upgrading your network in the near future, laser optimized 50 micron (OM3 or OM4) would be the logical choice. Compared to OM4, OM3 fiber is more future proofing for most applications, which allows speeds of 10 GB/s up to 100 GB/s. OM4 fiber provides users a transmission solution over longer distances and leaves more wiggle room in optical budgets.
OM3 and OM4 fiber cables are typically used in data center structured cabling environments running high speeds of 10G or even 40 or 100 Gigabit Ethernet, SAN (Storage Area Networking), Fiber Channel, FCOE (Fiber Channel Over Ethernet) with such manufacturers as Cisco, Brocade, EMC and others. Typical applications could be virtualized or internal cloud core data center applications. For 40G and 100G fiber cable applications, MTP/MPO cable would also be a great choice. MTP cabling assemblies (MTP/MPO trunk cable, MTP/MPO harness cable, MTP/MPO conversion cable, etc), with their overwhelming advantages, providing a fast, simple and economical upgrade path from 10 Gigabit to 40 or 100 Gigabit applications.
Conclusion
In this article, we mainly discussed OM3 fiber, OM4 fiber, their main differences, transmission guide and applications for 10G/40G/100G network. We put emphasis on OM3 and OM4 fiber 10G/40G/100G transmission distance and selection guide. OM3 and OM4 multimode fiber provide a cost effective solution for inside buildings or corporate campuses. Hope this article would be helpful for you to understand OM3 and OM4 fiber and to select right fiber cable for yourself.
0 notes
Text
100% Fiber Utilization with 2x3 MTP Conversion Cable
When faced with eight-fiber parallel applications, such as 40GBase-SR4 40 Gigabit Ethernet and 100GBase-SR4 100 Gigabit Ethernet, technicians who use conventional 12-fiber MTP cable will waste a third of the fibers in the cable plant (four fibers for transmitting and four fibers for receiving, leaving the middle four unused). To overcome this inefficiency, new 2x3 MTP conversion harness is introduced. 2x3 MTP conversion cable terminated with three 8-fiber MTP connectors on one end and two 12-fiber MTP connectors on the other end can convert the signal from three four-channel transceivers to two 12-fiber trunks, which means 100% utilization of a 12-fiber network. The following text will mainly talk about how 2x3 MTP conversion cable uses all the fibers in 10G to 40G and 40G to 40G connection.
10G to 40G Connection With 2x3 MTP Conversion Cable
Although upgrading from 10G to 40G Ethernet becomes common in most data centers, it is still impossible to replace all the 10G devices with 40G devices for more cost consumption. There are many solutions that we have introduced in the previous articles used to connect 10G to 40G equipment. 2x3 MTP conversion cable is a cost-effective one. The scenario can be clearly see from the following image. The three 8-fiber MTP connectors terminated at the 2x3 MTP conversion cable are directly plugged into the three 40GBase-SR4 modules(100% fiber utilization), then all cable assemblies will be plugged into the QSFP+ interfaced switch. The conversion from 40G to 10G is the most important step in this connectivity. Here we may use MTP or MPO LC cassette (2x12MTP-12xLC cassette) to connect two 12-fiber MTP connectors at the other end of the conversion cable to twelve duplex LC patch cables. Then all the LC cable assemblies with 10GBase-SR modules will be directly plugged into the SFP+ port switch. The whole connection do not waste any fiber.
IdentifierFS.COM ProductsDescriptionAS5850-48S6Q48x 10GbE SFP+ with 6x 40GbE QSFP+ SwitchBQSFP-SR4-40G QSFP+ SR4 optics; 150m @ OM4 MMF, 100m@ OM3 MMFC2x3 MTP Conversion Cable2xMTP to 3xMTP; 50/125μm MM (OM3)D2x12MTP-12xLC cassetteMTP-12 to LC UPC Duplex 24 Fibers MPO/MTP Cassette, 10G OM3, Polarity AEDuplex LC Patch CableDuplex LC; OM3FSFP-10G-SRSFP SR optics; 300m over OM3 MMFGS3800-24F4S20x 100/1000Base SFP with 4x 1GE Combo and 4x 10GE SFP+ Switch
40G to 40G Connection With 2x3 MTP Conversion Cable
In this scenario, the three 8-fiber MTP connectors at the end of the conversion cable are directly plugged into the 40G module, then into 40G switch. In order to make sure all the fibers can be used in this 40G to 40G connectivity, we may use a adapter panel to connect the two 12-fiber MTP connectors of the conversion cable to the two 12-fiber MTP connectors attached at the end of the other 2x3 MTP conversion cable. Then the three 8-fiber MTP harness end with 40G modules will be plugged into the QSFP+ port switch. If you feel confused with my sentences, more clear description is shown in the image below.
IdentifierFS.COM ProductsDescriptionAS5850-48S6Q48x 10GbE SFP+ with 6x 40GbE QSFP+ SwitchBQSFP-SR4-40G QSFP+ SR4 optics; 150m @ OM4 MMF, 100m@ OM3 MMFC2x3 MTP Conversion Cable2xMTP to 3xMTP; 50/125μm MM (OM3)DMTP Adapter PanelFiber Adapter Panel with 4 MTP(12/24F) Key-up/Key-down AdaptersE2x3 MTP Conversion Cable2xMTP to 3xMTP; 50/125μm MM (OM3)FQSFP-SR4-40GQSFP+ SR4 optics; 150m @ OM4 MMF, 100m@ OM3 MMFGS5850-48S6Q48x 10GbE SFP+ with 6x 40GbE QSFP+ Switch
Conclusion
You can gain great value to deploy 2x3 MTP conversion cable, which does not add any connectivity to the link and it allows 100 percent fiber utilization and constitute the most commonly deployed method. However, you have to notice that the use of the 2x3 MTP conversion cable assembly at the core spine switch is not desirable, because patching across blades and chassis is a common practice.
0 notes
Text
Three Types of 40G QSFP+ Transceivers for Long Distance Transmission
Nowadays, people have access to data at all times and at everywhere, which gives rise to the rapid development of big data technology. During the application of big data technology, transceiver has become an indispensable component, which can help executives to get their data in real-time. Recently, 40GbE network has replaced 10G Ethernet network and has been used worldwide. For 40GbE network deployment, high-density cabling is the basic requirement. Also, optical components for high-speed data transmission are necessary. This article aims to introduce three types of 40G QSFP+ transceivers for long distance transmission—QSFP-4X10GE-IR, QSFP-40G-PLRL4 and QSFP-4X10G-LR-S.
QSFP-4X10GE-IR Transceiver
Designed with MTP interface, the parallel QSFP-4X10GE-IR transceiver offers 4 independent transmit and receive channels, each capable of 10Gbps operation. It utilizes 12-ribbon single-mode fiber cable with female MTP/MPO connector to realize 40Gbps data link with transmission distances up to 1 km.
QSFP-40G-PLRL4 Transceiver
The QSFP-40G-PLRL4 transceiver uses 12-fiber MTP interface to achieve 40Gbps parallel transmission, supporting maximum data link lengths up to 1.4 km. The cable type required for QSFP-40G-PLRL4 transceiver is an APC (angle polished connector) single-mode 12-fiber MTP cable. APC is the only available type for single-mode MTP-12 fiber.
QSFP-4X10G-LR-S Transceiver
The QSFP-4X10G-LR-S transceiver is a parallel 40Gbps QSFP+ optical module. It supports link lengths of up to 10 km on G.652 single-mode fiber. It enables high-bandwidth 40G optical links over 12-fiber parallel fiber terminated with MPO/MTP female connector. It can also be used in a 4x10G mode for interoperability with 10GBASE-LR interfaces up to 10 km.
When reading this, you may find that all these three types of 40G transceivers are designed with MTP interface and use parallel transmission. In parallel transmission, data signals are sent sequentially on the same channel. In addition, they all use 1310nm wavelength and can transfer data signals up to at least 1 km. What’s more, they are compatible with the Small Form Factor Pluggable Multi-Sourcing Agreement (MSA) and they support Digital optical monitoring (DOM).
Working Principle
Because the structures of these three types of 40G transceivers are similar, their working principles are similar, too. The single-mode cable terminated with 12-fiber MTP connector plugged into the 40G transceiver carries the 40G signal over only 8 of the 12 fibers, remaining 4 fibers unused. The 8 used fibers are mapped as 4x10G Tx and Rx pairs. We can easily understand the working principle of these three types of 40G QSFP+ transceivers from the figure below. In the transmit side, the transmitter converts parallel electrical input signals into parallel optical signals through the use of a laser array. Then the parallel optical signals are transmitted parallelly through the single-mode fiber ribbon terminated with MTP/MPO connector. While in the receive side, the receiver converts parallel optical input signals via a photo detector array into parallel electrical output signals.
Application
Many data centers are in the process of 10G to 40G migration. To make migration path smooth, we can use 40G transceivers together with MTP cable. Take QSFP-40G-PLRL4 transceiver for example, we can simply use MTP-LC harness cable to connect one QSFP-40G-PLRL4 transceiver and four 10GBASE-LR SFP+ transceivers. Here is a figure for you to have a better understanding of the connectivity. In addition, for 40 connectivity, we can use MTP trunk cable to connect two QSFP-40G-PLRL4 transceivers to make the optical links. Using 40G QSFP+ transceiver for high-speed long distance transmission over single-mode fiber is a cost-effective solution.
Conclusion
With special structures, MTP components are popular with data center managers for fast installation, high density and high performance cabling. QSFP-4X10GE-IR, QSFP-40G-PLRL4 and QSFP-4X10G-LR-S these three 40G QSFP+ transceivers have special interface designs which can be compatible with single-mode MTP connector and support long distance transmission. During the deployment of 40G QSFP+ module, selecting proper MTP assemblies are also essential to successfully accomplish the link.
Originally published at http://www.fiber-optic-cable-sale.com/some-thoughts-required-before-mtp-cabling.html
0 notes
Text
MTP Specifications and Deployment for 40GBASE-PLRL4 QSFP+
Commonly, QSFP+ transceiver designed with LC interface works with single-mode fiber for long distance application, while QSFP+ transceiver with MTP/MPO interface is used over multimode fiber for short distance transmission. For instance, 40GBASE-ER4 QSFP+ is designed with LC duplex interface, and it supports maximum transmission length of 40 km over single-mode LC duplex fiber; 40GBASE-SR4 QSFP+ with MTP/MPO interface supports a transmission distance no more than 150m over multimode fiber. However, in order to meet user’s diverse needs in real applications, some 40G transceivers are designed not following this rule, like 40GBASE-PLRL4 (parallel LR4 Lite). This transceiver is with MTP/MPO interface design but is used over single-mode fiber for long distance transmission. This article will introduce the MTP/MPO specifications for this transceiver and its deployment cases.

MTP Specifications for 40GBASE-PLRL4 QSFP+
QSFP-40G-PLRL4 transceiver uses MTP-12 interface to achieve parallel transmission, supporting maximum data links up to 1.4 km. The cable type required for 40GBASE-PLRL4 is an APC (angle polished connector) single-mode MTP-12 cable. The cable is similar to the 40G-SR MTP or MPO, with the only change being the use of single-mode fiber. UPC (ultra polished connector) is another type of connector for MTP-12 cables, but it is not suited for single-mode fiber in market. APC is the only available type for single-mode MTP-12 fiber. The MTP-12 connector plugged into the QSFP-40G-PLRL4 transceiver carries the 40G signal over only 8 of the 12 fibers, remaining four fibers unused, and these four can optionally be not presented in the cable for economic reason. The used 8 fibers are mapped as 4x10G Tx and Rx pairs. In addition, the MTP cables connected to QSFP-40G-PLRL4 transceiver can be either MTP trunk cables or MTP splitter cables.
Deployment of 40GBASE-PLRL4 QSFP+
The QSFP-40G-PLRL4 is optimized to guarantee interoperability with any IEEE 40GBASE-LR4 and 10GBASE-LR. So when the link for 40G network and 10G to 40G migration is less than 1.4 km, it will be very appropriate to use 40GBASE-PLRL4 QSFP+ transceiver with single-mode MTP cables.
In the first case, you can choose a MTP trunk cable together with the 40GBASE-PLRL4 QSFP+ module for direct 40G connection. The following picture shows two 40GBASE-PLRL4 QSFP+ transceivers connected by a single-mode 12-fiber MTP trunk cable.

In the second case, you can simply use an 8-fiber MTP to 4xLC duplex harness cablewith one 40GBASE-PLRL4 QSFP+ and four 10GBASE-LR SFP+ to achieve 10G to 40G.

You can see in the above two cases, MTP cable plays an important role and due to the special requirements of 40GBASE-PLRL4 for single-mode MTP APC fiber, it is necessary to choose the right MTP products connected to this 40G QSFP+.
Conclusion
40GBASE-PLRL4 QSFP+ module has special interface design which can be only compatible with single-mode MTP connector. During the deployment of 40GBASE-PLRL4 QSFP+ module, selecting proper MTP assemblies are essential to successfully accomplish the link. FS.COM is a professional fiber optic transceiver vendor and MTP product manufacturer, supplying compatible 40GBASE-PLRL4 QSFP+ transceiver of different brands, such as Cisco, Arista, Brocade, Huawei, etc. Also other customized compatible brands are available for your requirements. MTP cables and assemblies are available for same-day shipping at low prices. You will be surprised to see how many kinds of network devices FS.COM can offer and you will get more than cost-effective products but also impressive service.
Originally posted on: https://goo.gl/70Q5fl
#10GBASE-LR#40GBASE-PLRL4#MTP adapter panel#MTP harness cable#MTP Trunk Cable#QSFP-40G-PLRL4#SFP-10G-LR
0 notes
Text
https://www.china-tscom.com/products/mpo-harness-cable/
MTP®/MPO harness cables are a kind of MTP®/MPO fanout harness cable or breakout cable assembly with one MTP®/MPO connector on one end and multiple single-fiber connectors (LC, SC, FC, etc.) on the other end, designed for data distribution and routing to patch panels. It is used to transition from trunk backbone assemblies to fiber rack systems. The MTP® harness cable is fully configurable, available with a variety of cable and connector combinations. For the hardware and equipment in the same cabinet, the longer MPO cord can provide flexibility at any location, and the branch MTP®/MPO cable can be winded into the vertical cable organizer.
MTP®/MPO Harness Cable Features
Our MPO/MTP harness cable is with low loss performance.
MPO / MTP in 8/12/16/24/32 fibers interfaces for choices.
This MTP/MPO fanout harness cable is available in OS1, OS2, G.657A2, OM3, OM4 Fiber Grades – OM1 and OM2 available upon request.
Option for LSZH, OFNP or OFNR cable jacket.
100% factory terminated and tested.
Pulling eyes are provided as an option to protect the fiber ends during installation.
Save installation and reconfiguration time.
MTP®/MPO Harness Cord Applications
MPO-LC harness cables are dedicated for direct connection between MPO trunk cables and equipment with SFP+ ports via an MPO adapter. Available in polarity A, B or C, these MPO-LC harness cables as well enable connection to SFP+ ports in adjacent racks.
MPO-LC harness cables are compatible with all other MPO module cassette-based systems without any loss of optical performance.
MPO-LC harness cable is typically constructed with a mini cable that features by small diameter, low weight, and low bend radius. In a typical scenario, it’s used to make connections within the same rack or go-between adjacent racks via overhead cabling trays, slots or open ducting systems.
Data Center Interconnect
High-Density Fiber Management
Telecommunication Networks and CATV networks
LAN/WAN Premises
Standards Compliance of MTP®/MPO Harness Cable
TIA/EIA-568.3-D and ISO/IEC 11801;
IEC-61754 & EIA/TIA-604-5;
NFPA 262 or IEC 60332;
EN 50575;
Our MPO/MTP harness cable complies with GR-1435-CORE, GR-2866-CORE, GR-326-CORE;
Our 100g harness cable is compliant to Directive 2002/95/EC (RoHS) and REACH SvHC.

1 note
·
View note
Text
FIBER OPTICAL CONNECTIVITY
https://www.china-tscom.com/products/fiber-optic-connectivity/
Except traditional connector assembly like LC, SC, MU, FC, ST, E2000, etc., we always cooperate with well-known connectivity suppliers for new connector assembly technology enhancement, for example, CS, SN, MDC connector for new applications.
HomeProductsFiber Optical Connectivity
Standard Patch Cord
Fiber Patch Cord or jumper is a fiber cable that has fiber connectors terminated on one or both ends. General use of these cable assemblies includes the interconnection of fiber cable systems and optics-to-electronic equipment.
As a quality fiber optic patch cord factory, T&S provides types of custom simplex, duplex, single-mode (SM), and multi-mode (MM) fiber patch cords and fiber pigtail assemblies with various types of fiber connectors including ST, FC, SC, LC, MU, MTRJ, E2000 and so on.
Our fiber optic cable patch cord and pigtail range offer choices of any length, connector types, and either PVC or LSZH cable jacket, and all cable assemblies are composed of our top quality ceramic ferrules and fiber connectors housings which ensures stable performance at a high-quality level. Except for standard Fiber Patchcord, we supply other types of Patch cord, including Grade B patch cord, IP68 LC/SC patch cord, LC/SC loopback, outdoor Patchcord, etc. for different applications as well.
Pre-terminated Multifiber Cable
Pre-terminated multi-fiber cables consist of optical fiber cable terminated with various types of connectors, such as the ST, FC, SC, LC, MU, MTRJ, E2000 Connector types. Our polishing craft and expertise ensure excellent optical performance.
All of our multifiber cable assemblies are composed of our top-quality ceramic ferrules and fiber connector housings to ensure stable performance at a high-quality level.
MTP/MPO Cable Assembly
MTP/MPO cable assembly use MTP or MPO multi-fiber connectors. MTP/MPO Fiber Patch Cord greatly save space and are very convenient to use. Based on single ferrule MT technology, the MPO Fiber Patch Cord assemblies provide up to 72 fiber connections in a single point, reducing the physical space and labor requirement, while providing the same bandwidth capacity of a multi-fiber cable with individual fiber connector terminations per cable.
Typically with MT series like MTP/MPO fiber connectors, these MTP/MPO Patch Cord features multi-fiber connection in the same single core fiber optic patch cord. Except for Standard MTP/MPO cable assemblies including MTP/MPO shuffle, hydra, harness and trunk cables, we also provide other types like IP68 MTP/MPO fiber cable, MTP/MPO loopback and so on for different applications.
Fiber Optical Flexplane
Fiber optical flexplanes provide one of the highest density and versatile interconnect systems on the market today. For high fiber-count interconnects in backplanes and cross-connect systems, fiber optical flexplane provides a manageable means of fiber routing from card-to-card or shelf-to-shelf. Designed for versatility, flexplane provides high-density routing on a flexible, flame-resistant substrate. A variety of interconnects, including MTP, MT, MXC, LC, SC and the like can be terminated to connect the optical flex circuits to individual cards in a shelf. Available in any routing scheme, fiber can be routed point-to-point, in a shuffle, or in a logical pattern to meet specific requirements. Both direct and fusion-spliced terminations are available.
Fiber Optical Adapter
The optical fiber adapter connects the connectors at both ends through its internal ceramic sleeve, so as to ensure excellent connection performance between the optical fibers. In order to be fixed on various panels, the shape design can be various types based on the actual application of a variety of structures, such as “with flange/without flange“, simplex/duplex/quad/etc.
Fiber Optical Connector
The optical fiber communication connector is composed of ceramic ferrule and connector kits. different types of connector kits and ferrules are pre-assembled according to different connector types. During patchcord production, optical fiber patchcord or pigtails can be quickly produced with optical cable, and to a certain extent, the production processes of optical fiber cables is less and the efficiency is therefore improved.
Fiber Optical Attenuator
Optical fiber communication attenuator is composed of attenuation optical fiber, attenuator kits, connector kits and cables, Attenuator is used to attenuate input power on optical path to avoid signal distortion at optical receiving end due to excessive input optical power; or used for debugging optical power performance in optical communication system, calibration and correction of optical fiber instrument, and attenuation of optical fiber signal. The products are made of attenuation optical fiber doped with metal ions, and they are able to adjust the optical power to the required level.
Fiber Optical Master Cord
Fiber optical master cord and bus cord are produced by standard ferrule with high-standard connector kits via special production process. According to different application requirements, it can be generally divided into two grades: bus cord and master card. The product has characteristics like low loss, good consistency and good interchangeability, which can minimize the impact of test system on the test results. It is widely used in product testing, instrument calibrations.

0 notes
Text
MPO - MTP ASSEMBLIES - THE GAME CHANGER OF DATA CENTER CABLING
MPO / MTP Fanout & Trunk Cables that can be custom built for any application. All cables come factory terminated and pre-tested, ensuring top performance and ease of installation. Fanout assemblies can be built with any single fiber connector and any major fiber type. These cables are designed to work in conjunction with MPO Fiber Distribution products.
High-Density MPO Fiber Distribution Cassettes offer unsurpassed fiber density and are designed to be used in conjunction with High Density Panels. Each cassette contains a fanout assembly that transitions from a MPO 12 fiber connector to 6 LC duplex pairs. Cassettes are designed to be installed with LC Uniboot assemblies for the highest density available. Panel and cassette combination is capable of supporting 144 fibers in 1RU, 288 fibers in 2RU and 576 fiber in 4RU. MTP / MPO harness cables are available with 8-, 12-, 24-, 36-, 48-, 72-, 96- and 144-fiber options. Read More.
https://www.gbic-shop.de/blog/en/98-mpo-mtp-solutions/278-mpo-mtp-assemblies-the-game-changer-of-data-center-cabling.html
0 notes
Text
MTP/MPO – 24 SC Fiber Optic Harness Breakout/Fanout Cable
MTP to SC SM/MM Fan-out/Breakout Harness cable assembly is mainly used for 10G/40G/100G, The LC fanout cable with 2.0mm/3.0mm branch cable, the SC side could adopts Single SC connector or duplex SC connector. The Harness MTP cable supports polarity support both type A and type B.
0 notes
Text
Breakout Cabling Solution vs. Breakout Patch Panel Solution
As 40/100G fiber network becomes a popular option in data centers, how to connect 40/100G devices with existing 10G devices in a cost-effective manner becomes a primary challenge for most of the data center operators. Breakout cables and breakout patch panels are two main solutions to address this challenge. So, what’s the difference between them, and which is better for your project? Continuing this tutorial, you may find more information about this.
Breakout Cabling Solution
Unlike 10G structures using duplex fiber (usually LC) cabling, the 40/100G or beyond 100G network uses parallel fibers (MPO/MTP) for transmission. Taking 40G network for example, it uses 4 x 10 Gbps parallel transmission mode to achieve the total data rate up to 40 Gbps. According to this principle, using a 40G to 4 x 10G breakout cable can achieve the migration from 10G to 40G network.
What’s Breakout Cable? A breakout cable is a cable with multi-fiber strands. In general, a breakout cable is with one MPO/MTP connector on one end, and with the breakout legs with LC connectors on the other ends which can be divided into multiple duplex cables. As mentioned above, a 40G breakout cable has four individual 10G duplex cables totaling eight strands. Similarly, a the breakout legs of 100G breakout cable are 10 duplex cables, namely 20 fiber strands.
How Breakout Cable Work? The working principle of breakout cable is easy. Still taking example of 40G breakout cable, it can divide a 40G port into four 10G ports. As shown below, the MTP connector end of the breakout cable plugs into a 40G port of a switch and the other four LC duplex ends of the 40G breakout cable plugs into four 10G ports of server. If the switch has up to 32 40G ports, up to 128 10G devices can be connected to it using breakout cables.

Benefits & Challenges Breakout cabling solution offers a quick and easy migrating way for users to connect slower-speed equipment to higher-speed equipment. However, it increases the costs, delays projects and even presents a nightmare scenario for the upgrade and maintenance because of the cable congestion. In addition, labeling is absolutely essential when using so many breakout cables. The profusion of cables makes it difficult to label them clearly and accurately, interfering with your ability to troubleshoot effectively and efficiently.
Breakout Patch Panel Solution
Based on the same working principle with breakout cables, breakout patch panel provides a mature and highly scalable alternative to breakout cables since it allows users to seamlessly and conveniently integrate equipment with different network speeds for today’s and even tomorrow’s connectivity needs.
What’s Breakout Patch Panel? Breakout patch panel is integrated a range of modular, removable fiber assemblies in a rack-mount panels. With a compact and easy maintenance design, it can support a variety of fiber network standards. Moreover, it is easy to mix, match, add, and replace so that it can satisfy all kinds of connectivity needs in data centers.
How Breakout Patch Panel Work? The breakout fiber panels and cassettes are the key to this solution. Just by an easy plug-and-play step, you can easily complete the connectivity between two standard ports, eliminating the complicated cable management segment.

Benefits & Challenges There are more advantages of breakout patch panel solution over the breakout cabling solution. The breakout patch panel solution provides flexibility and scalability for your network upgrade, allowing users to connect diverse network cabling standard seamlessly, without the costly, labor-intensive hassle of replacing channels end-to-end. Designed with standard patch cables, it offers a reliable and readily available option for users. Moreover, with its compact size, it can help save more space and reduce cable congestion.
The biggest challenge of using breakout patch panel solution is how to select the right one to meet your current needs, as well as adapting to and growing with your future needs, because it involves the cost, supported network standard, and the whole network plan concerns.
Conclusion
The above contents show us the details about breakout cabling solution and breakout patch panel solutions. By comparing them, the breakout patch panel solution shows more benefits than the breakout cabling solution, especially for cable management and network upgrade. In fact, with the increasing demands on fast access to larger volumes of data, breakout patch panel seems to be a better choice for network migration. But as mentioned above, users should choose the right one according to their current and future plan to ensure a maximum return on investment. FS.COM offers a full range of breakout cables and breakout patch panels with competitive prices and high quality, such as MTP harness cables, 40GBASE-SR4 breakout patch panel, high-density 144 ports patch panel, and so on. For more information, please contact us over [email protected] or call 1 718 577 1006.
Source: http://www.fs.com/breakout-cabling-solution-vs-breakout-patch-panel-solution-aid-494.html
0 notes
Text
Migrating to 40/100G Networks With MTP Harness Conversion Cable
The market turning to 40G/100G transmission is imperative in today’s gigabit Ethernet applications. MTP cabling assemblies, with their overwhelming advantages, provide a fast, simple and economical upgrade path from 10 Gigabit to 40 or 100 Gigabit applications. As we all know, 40G/100G gigabit Ethernet backbone networks often use 8-fibers per channel, which means most existing equipment doesn’t utilize fibers fully in 12-fiber cabling systems. Today this post will introduce a type of MTP fiber cable—MTP conversion cable which can overcome the problem mentioned above.
Basis of 40G/100G MTP Conversion Cable
12-fiber MTP connectors are popular in the past years. And most backbone networks deploy the 12-fiber cabling systems. But with the quick development of optical transceivers, for 40G/100G gigabit applications, many transceivers that are guiding the industry from 10G to 40G and100G utilize only eight fibers. Then the problem arises. However, MTP conversion cable allows users to convert their existing MTP backbone cables to an MTP type which matches their active equipment. It’s a low-loss alternative to conversion modules because they eliminate one mated MTP pair across the link. There are mainly three types of MTP conversion cable on the market: 1x2, 1x3 and 2x3 MTP conversion cable.
1x2 MTP Conversion Cable
This MTP conversion cable has a 24-fiber MTP connector on one end and two 12-fiber MTP connectors on the other end. It is used to allow existing 10G MTP 12-fiber trunk cables to carry 40G/100G channels. The 40G/100G signal is split equally across two 12-fiber trunks which were previously installed within a traditional MTP modular network.
1x3 MTP Conversion Cable
Like the 1x2 MTP conversion cable, this conversion cable also has a 24-fiber MTP connector on one end. But the other end comprises three 8-fiber MTP connectors, which is different from the former type. This MTP conversion cable allows users to convert their 24-fiber backbone trunks into Base-8 connections so that 40G rates can be achieved easily. A Single Base-24 connection is split out to three Base-8 connections, giving users three 40G ports.
2x3 MTP Conversion Cable
For users who have already installed a 10G MTP based network using 12-fiber and 24-fiber trunk cables and modules, this 2x3 MTP conversion cable can provide the conversion from 12-fiber to 8-fiber connectivity for full-fiber utilization, especially allowing for maximum use of existing fibers when converting to 40G channels. Because the conversion cable has two 12-fiber MTP connectors on one end and three 8-fiber MTP connectors on another end. They are available in either direct or crossed polarity for fast deployment using polarity management method A, and polarity can be reversed on site, offering enhanced flexibility & operability.
Cabling Options with 40G/100G MTP Conversion Cable
The 40G/100G MTP conversion cables eliminate the wasted fibers in current 40 gigabit transmissions and upcoming 100 gigabit transmission. Compared to purchase and install separate conversion cassettes, using MTP conversion cables is a more cost-effective, lower-loss option. Here are three application examples.
Cabling Options for 40G/100G Connectivity With 1x3 MTP Conversion Cable
As shown in the picture below, two 40G/100G switches are connected by 1X3 MTP conversion cables (one 24-fiber MTP connector on one end and three 8-fiber MTP connectors on the other end), 24-fiber MTP trunk cable and MTP adapter panels. With this MTP conversion cable, less fiber cables are required. That brings more conveniences for cable management in data centers.
The cabling solution for 40G/100G conversion with 1x2 MTP conversion cable is similar to the solution of 1x3 MTP conversion cable.
Cabling Options for 40G Connectivity with 2x3 MTP Conversion Cable
In the following applications, connecting the 40G transceivers with a 8-fiber MTP conversion cable rather than a traditional 12-fiber MTP jumper, ensuring the 100% backbone fiber utilization and saving cost.
Summary
The 40G/100G MTP conversion cables provide a cost-effective cabling solution for upgrading to 40G and 100G networks. All the benefits and features of these MTP conversion harness cables are explained in the article. And the three types of 40G/100G MTP conversion cable which are available in OS2, OM3 and OM4 options are provided in FS.COM. If you want to know more details, please contact us via [email protected].
Sources:http://www.chinacablesbuy.com/three-types-40g100g-mtp-conversion-cable-overview.html
0 notes